Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Groundwater Quality in Phreatic and Confined Aquifers of the Hebei Plain, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
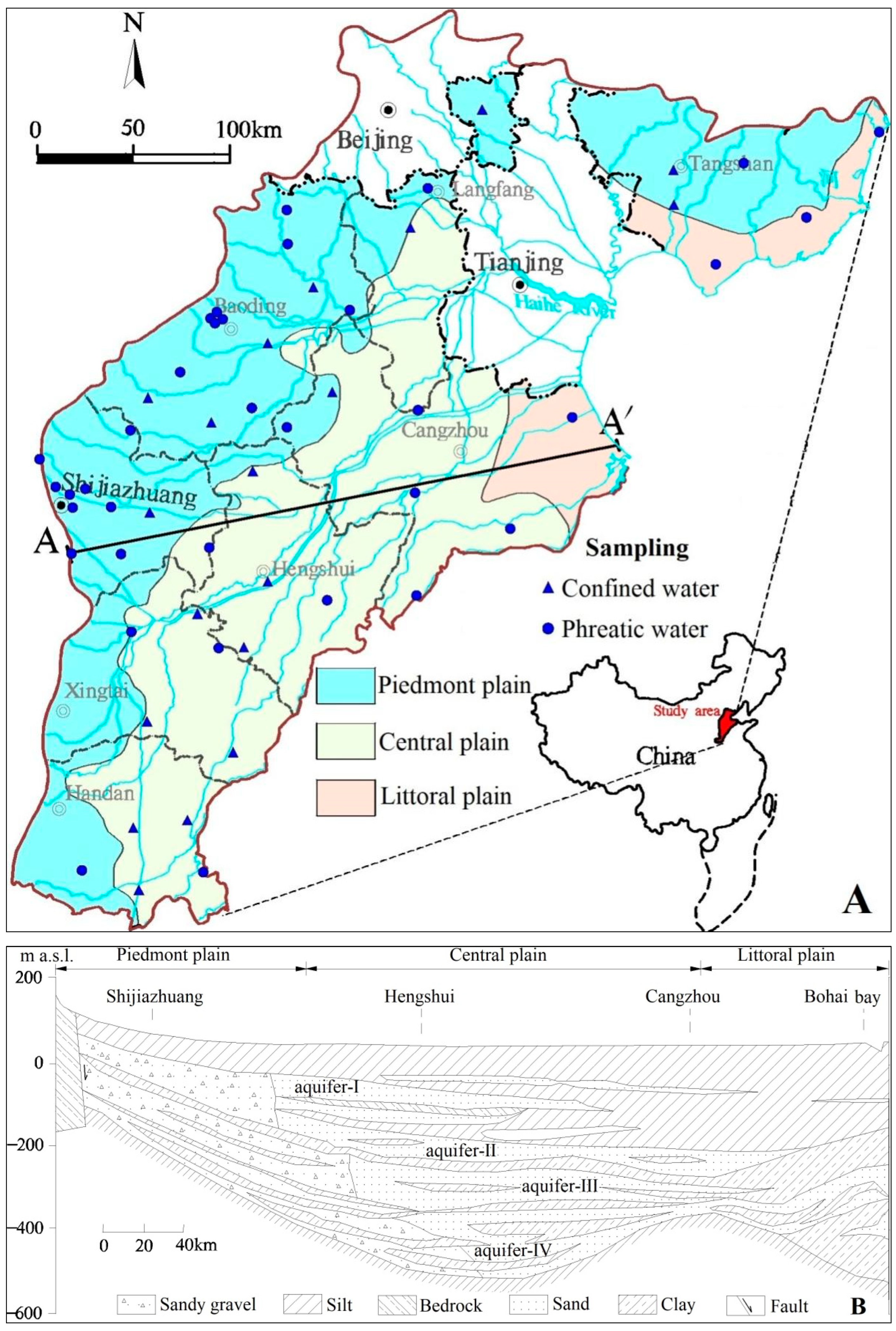
2. Study Area
2.1. Geographical Conditions
2.2. Geological and Hydrogeological Conditions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Groundwater Sampling
3.2. Analytical Techniques
3.3. Fuzzy Synthetic Evaluation (FSE) Method
3.4. Principal Components Analysis (PCA)
4. Results and Discussion
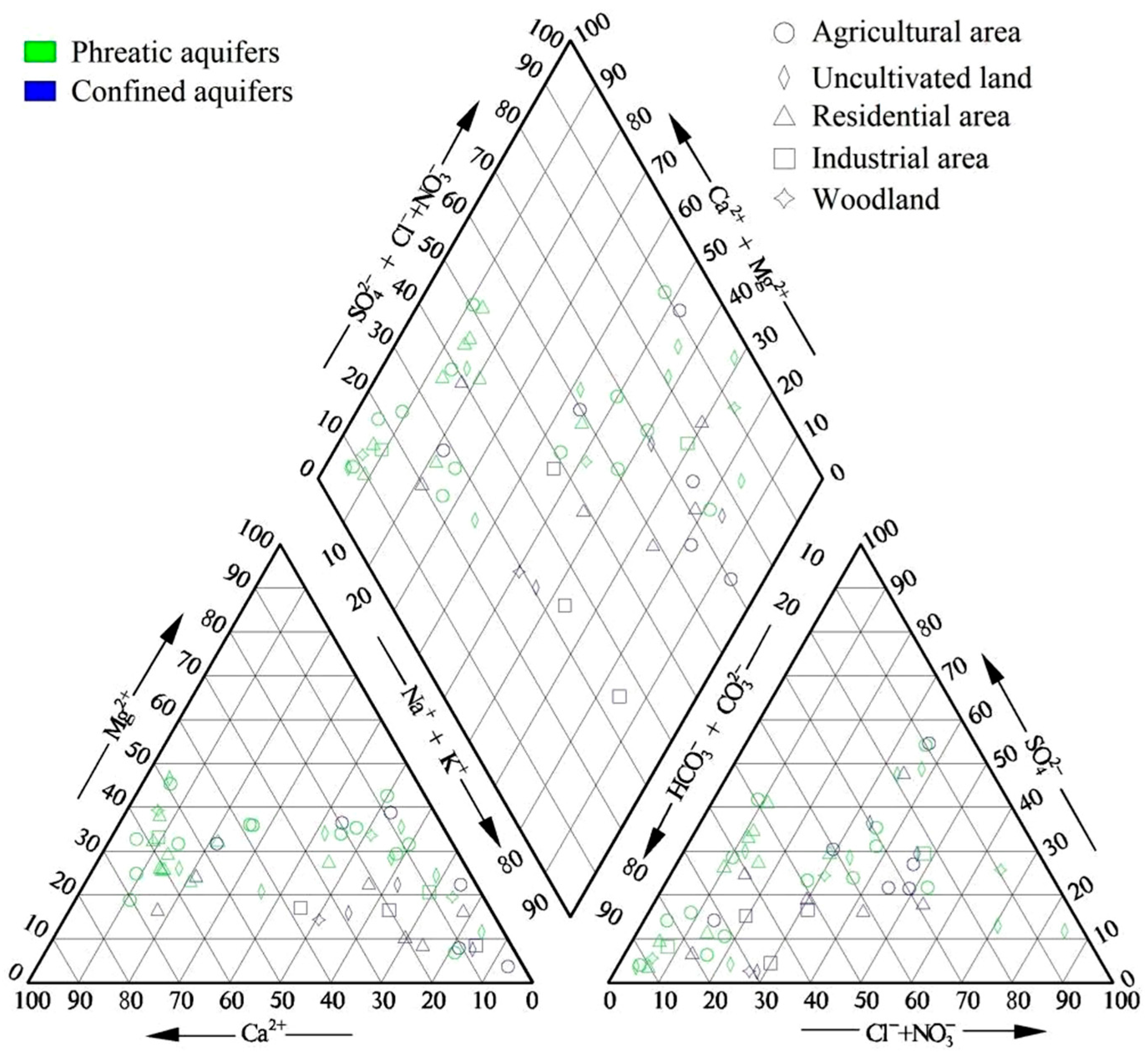
4.1. Characteristics of Groundwater Chemistry
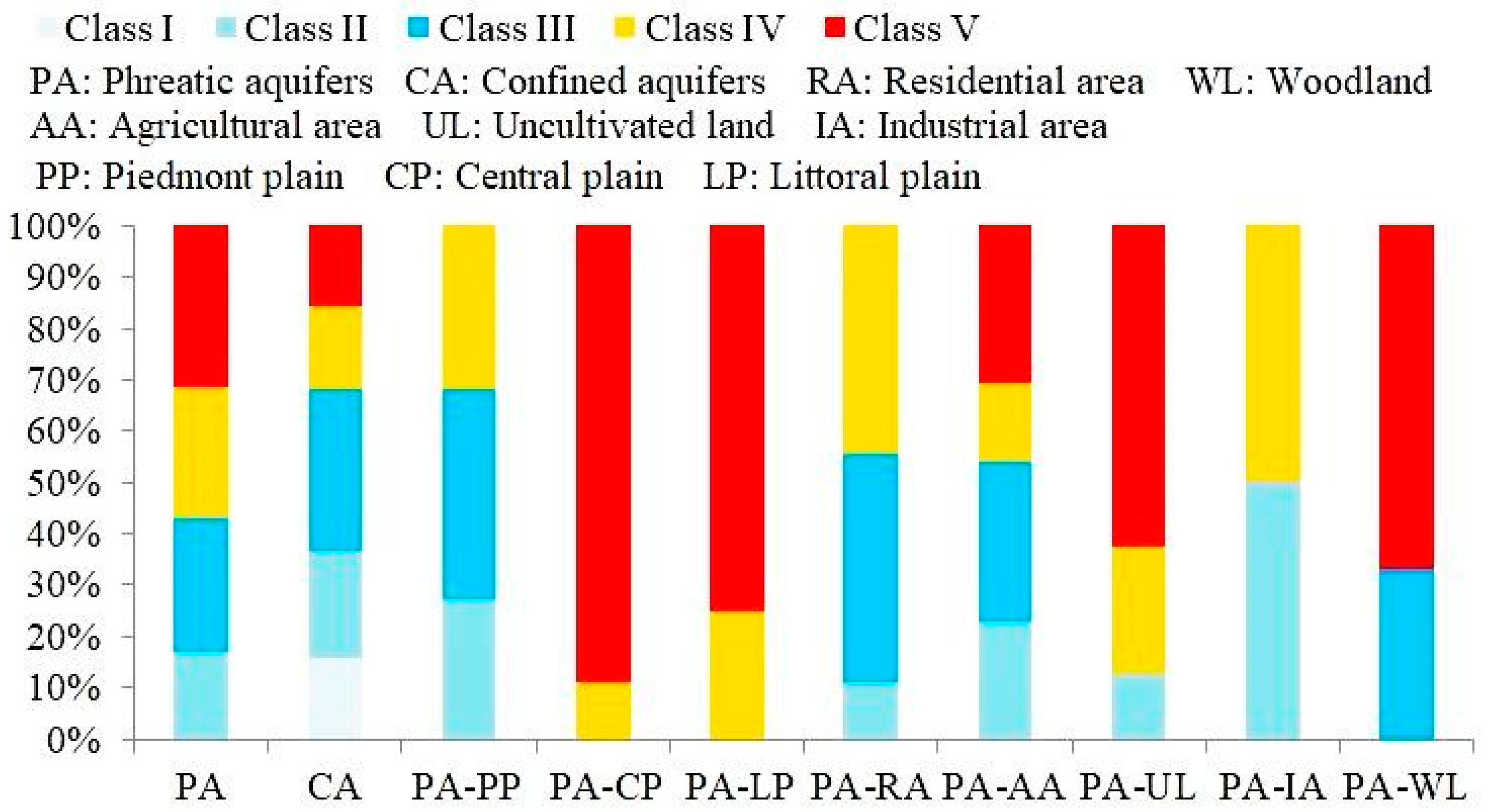
4.2. Distribution of Groundwater Quality
4.3. Factors Controlling Groundwater Quality
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, X.; Jin, M.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Wang, B. Groundwater Recharge at Five Representative Sites in the Hebei Plain, China. Groundwater 2011, 49, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, H.; Hu, L.; Yang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Lian, X.; Ma, X.; Jiang, Y.; Xi, B. Groundwater nitrate pollution risk assessment of the groundwater source field based on the integrated numerical simulations in the unsaturated zone and saturated aquifer. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J. Distributions and origins of nitrate, nitrite, and ammonium in various aquifers in an urbanized coastal area, south China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayari, J.; Barbieri, M.; Agnan, Y.; Sellami, A.; Braham, A.; Dhaha, F.; Charef, A. Trace element contamination in the mine-affected stream sediments of Oued Rarai in north-western Tunisia: A river basin scale assessment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 4027–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Pei, L.; Li, L.; Liu, C. Natural background levels in groundwater in the Pearl River Delta after the rapid expansion of urbanization: A new pre-selection method. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 151890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayari, J.; Barbieri, M.; Barhoumi, A.; Boschetti, T.; Braham, A.; Dhaha, F.; Charef, A. Trace metal element pollution in media from the abandoned Pb and Zn mine of Lakhouat, Northern Tunisia. J. Geochem. Explor. 2023, 247, 107180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, P.; Liu, R.; Huang, G.; Li, D. Evaluating natural background levels of heavy metals in shallow groundwater of the Pearl River Delta via removal of contaminated groundwaters: Comparison of three preselection related methods. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 335, 122382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Huang, G.; Pei, L.; Gan, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, M.; Han, D.; Song, J. Distributions, origins, and health-risk assessment of nitrate in groundwater in typical alluvial-pluvial fans, North China Plain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 17031–17048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Cui, X.; Yue, C.; Guo, C.; Zhen, S.; Wang, W.; Huang, G.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Su, C.; et al. Report on the Investigation and Evaluation of the Basic Environmental Conditions of Groundwater Around the State Control Assessment Points in Hebei Province; The Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences: Shijiazhuang, China, 2022. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xing, L.; Guo, H.; Zhan, Y. Groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and processes along flow paths in the North China Plain. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 70–71, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, J. Natural background levels of chemical components in groundwater of Hutuo River catchment area, North China Plain. Environ. Forensics 2017, 18, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Sun, J.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, X. Controls on the spatial distribution of iodine in groundwater in the Hebei Plain, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 16702–16709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, D.; Lv, S.; Ding, J.; Yan, M.; Han, G. Spatial evolution analysis of groundwater chemistry, quality, and fuoride health risk in southern Hebei Plain, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 61032–61051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zou, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhen, P. Factors controlling groundwater chemical evolution with the impact of reduced exploitation. Catena 2022, 214, 106261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Wei, Q.; Dong, H.; Ma, T.; Liu, X.; Li, D.; Dong, J. Geochemical evidence for annual variability of fluoride levels in deep groundwater on land subsidence plain in Cangzhou, Hebei Province, China. Geochemistry 2023, 125985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Hou, C.; Shao, J.; Cui, Y. Evolution of groundwater major components in the Hebei Plain: Evidences from 30-year monitoring data. J. Earth Sci. 2014, 25, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, F. Impact of anthropogenic and natural processes on the evolution of groundwater chemistry in a rapidly urbanized coastal area, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marandi, A.; Shand, P. Groundwater chemistry and the Gibbs Diagram. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 97, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Huang, G.; Sun, J.; Jing, J.; Zhang, Y. A new evaluation method for groundwater quality applied in Guangzhou region, China: Using fuzzy method combining toxicity index. Water Environ. Res. 2016, 88, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, C.; Kurt, M.A.; Alpaslan, M.; Akbulut, C. Assessment of the impact of anthropogenic activities on the groundwater hydrology and chemistry in Tarsus coastal plain (Mersin, SE Turkey) using fuzzy clustering, multivariate statistics and GIS techniques. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414–415, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Shi, L.; Zeng, J.; Yang, J.; Zha, Y.; Yao, Y.; Cao, G. Estimation of actual irrigation amount and its impact on groundwater depletion: A case study in the Hebei Plain, China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 543, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Zheng, C.; Scanlon, B.R.; Liu, J.; Li, W. Use of flow modeling to assess sustainability of groundwater resources in the North China Plain. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Qi, J.; Xu, J.; Xu, J.; Ye, H.; Nan, Y. Paleoclimatic interpretation of the past 30 ka from isotopic studies of the deep confined aquifer of the North China Plain. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 997–1009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, H.; Sun, L.; Fischer, G.; Tian, Z.; Liang, Z. Optimizing regional cropping systems with a dynamic adaptation strategy for water sustainable agriculture in the Hebei Plain. Agric. Syst. 2019, 173, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shi, D.; Shen, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Xue, Y. Evolution and development of groundwater environment in North China Plain under human activities. Acta Geosci. Sin. 1997, 18, 337–344. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Nie, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, J.; Nan, Y. Isotopes and sustainability of ground water resources, North China Plain. Ground Water 2005, 43, 485–493. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Fei, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, Z.; Wang, Y. Investigation and Assessment of Sustainable Utilization of Groundwater Resources in the North China Plain; Geology Press: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 28–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- General administration of quality supervision inspection and quarantine of the people’s republic of China (GAQSIQPRC). In Standard for Groundwater Quality; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Zhang, F.; Huang, G.; Hou, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q. Groundwater quality in the Pearl River Delta after the rapid expansion of industrialization and urbanization: Distributions, main impact indicators, and driving forces. J. Hydrol. 2019, 577, 124004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Chen, Z.; Liu, F.; Sun, J.; Wang, J. Impact of human activity and natural processes on groundwater arsenic in an urbanized area (South China) using multivariate statistical techniques. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 13043–13054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z. Groundwater is important for the geochemical cycling of phosphorus in rapidly urbanized areas: A case study in the Pearl River Delta. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Hou, Q.; Han, D.; Liu, R.; Song, J. Large scale occurrence of aluminium-rich shallow groundwater in the Pearl River Delta after the rapid urbanization: Co-effects of anthropogenic and geogenic factors. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2023, 254, 104130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, E.; Wang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Ma, T.; Zhang, D.; Zhan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Fei, Y.; Wang, S. Iodine in groundwater of the North China Plain: Spatial patterns and hydrogeochemical processes of enrichment. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 135, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhang, M.; Liu, C.; Li, L.; Chen, Z. Heavy metal(loid)s and organic contaminants in groundwater in the Pearl River Delta that has undergone three decades of urbanization and industrialization: Distributions, sources, and driving forces. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, S.; Qin, L.; Li, X. Investigating sources, driving forces and potential health risks of nitrate and fluoride in groundwater of a typical alluvial fan plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhong, Z. Hydrogeochemical modeling of groundwater chemical environmental evolution in Hebei Plain. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 1997, 40, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravenscroft, P.; McArthur, J.M. Mechanism of regional enrichment of groundwater by boron: The examples of Bangladesh and Michigan, USA. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 1413–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y. Elevated manganese concentrations in shallow groundwater of various aquifers in a rapidly urbanized delta, south China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, M.; Jing, J.; Li, L. A regional scale investigation on factors controlling the groundwater chemistry of various aquifers in a rapidly urbanized area: A case study of the Pearl River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, W.M.; Cook, J.M.; Darling, W.G.; Kinniburgh, D.G.; Miles, D.L.; Bath, A.H.; Morgan-Jones, M.; Andrews, J.N. Baseline geochemical conditions in the Chalk aquifer, Berkshire, U.K.: A basis for groundwater quality management. Appl. Geochem. 1987, 2, 251–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahib, L.Y.; Marandi, A.; Schüth, C. Strontium isotopes as an indicator for groundwater salinity sources in the Kirkuk region, Iraq. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barica, J. Salinization of groundwater in arid zones. Water Res. 1972, 6, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwade, D.V.; Nandakumar, M.V.; Kesari, M.P.; Mondal, N.C.; Singh, V.S.; Singh, B. Evaluation of sea water ingress into an Indian atoll. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Song, J.; Han, D.; Liu, R.; Liu, C.; Hou, Q. Assessing natural background levels of geogenic contaminants in groundwater of an urbanized delta through removal of groundwaters impacted by anthropogenic inputs: New insights into driving factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mather, J.D.; Porteous, N.C. The geochemistry of boron and its isotopes in groundwaters from marine and non-marine sandstone aquifers. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Qian, K.; Xie, X.; Xue, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Fluoride and iodine enrichment in groundwater of North China Plain: Evidences from speciation analysis and geochemical modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Li, L.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Z. Spatial distribution and origin of shallow groundwater iodide in a rapidly urbanized delta: A case study of the Pearl River Delta. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, P.; Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Li, L. Geochemical factors controlling natural background levels of phosphate in various groundwater units in a large-scale urbanized area. J. Hydrol. 2022, 608, 127594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Han, D.; Song, J.; Li, L.; Pei, L. A sharp contrasting occurrence of iron-rich groundwater in the Pearl River Delta during the past dozen years (2006-2018): The genesis and mitigation effect. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rye, R.O.; Back, W.; Hanshaw, B.B.; Rightmire, C.T.; Pearson, F.J., Jr. The origin and isotopic composition of dissolved sulfide in groundwater from carbonate aquifers in Florida and Texas. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1981, 45, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hem, J.D. Chemistry and occurrence of cadmium and zinc in surface water and groundwater. Water Resour. Res. 1972, 8, 661–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Items | Class I | Class II | Class III | Class IV | Class V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.5–8.5 | 6.5–8.5 | 6.5–8.5 | 5.5–6.5 and 8.5–9.0 | <5.5 and >9.0 |
| TH (mg/L) | ≤150 | ≤300 | ≤450 | ≤650 | >650 |
| TDS (mg/L) | ≤300 | ≤500 | ≤1000 | ≤2000 | >2000 |
| COD (mg/L) | ≤1 | ≤2 | ≤3 | ≤10 | >10 |
| Cl− (mg/L) | ≤50 | ≤150 | ≤250 | ≤350 | >350 |
| NO3− (as N, mg/L) | ≤2 | ≤5 | ≤20 | ≤30 | >30 |
| SO42− (mg/L) | ≤50 | ≤150 | ≤250 | ≤350 | >350 |
| F− (mg/L) | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤2 | >2 |
| NO2− (as N, mg/L) | ≤0.01 | ≤0.1 | ≤1 | ≤4.8 | >4.8 |
| I− (µg/L) | ≤40 | ≤40 | ≤80 | ≤500 | >500 |
| S2− (mg/L) | ≤0.005 | ≤0.01 | ≤0.02 | ≤0.1 | >0.1 |
| NH4+ (as N, mg/L) | ≤0.02 | ≤0.1 | ≤0.5 | ≤1.5 | >1.5 |
| Na+ (mg/L) | ≤100 | ≤150 | ≤200 | ≤400 | >400 |
| B (mg/L) | ≤0.02 | ≤0.1 | ≤0.5 | ≤2 | >2 |
| Al (mg/L) | ≤0.01 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.2 | ≤0.5 | >0.5 |
| Fe (mg/L) | ≤0.1 | ≤0.2 | ≤0.3 | ≤2 | >2 |
| Mn (mg/L) | ≤0.05 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.1 | ≤1.5 | >1.5 |
| Ba (mg/L) | ≤0.01 | ≤0.1 | ≤0.7 | ≤4 | >4 |
| Zn (mg/L) | ≤0.05 | ≤0.5 | ≤1 | ≤5 | >5 |
| Pb (µg/L) | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤10 | ≤100 | >100 |
| As (µg/L) | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤10 | ≤50 | >50 |
| Se (µg/L) | ≤10 | ≤10 | ≤10 | ≤100 | >100 |
| Ni (µg/L) | ≤2 | ≤2 | ≤20 | ≤100 | >100 |
| Cd (µg/L) | ≤0.1 | ≤1 | ≤5 | ≤10 | >10 |
| Cr(VI) (µg/L) | ≤5 | ≤10 | ≤50 | ≤100 | >100 |
| Hg (µg/L) | ≤0.1 | ≤0.1 | ≤1 | ≤2 | >2 |
| Suitability | Drinking, Irrigation | Drinking, Irrigation | Drinking, Irrigation | Irrigation | Not suitable |
| Items | Phreatic Aquifers | Confined Aquifers | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min. | Med. | Max. | Min. | Med. | Max. | |
| pH | 6.75 | 7.49 | 8.22 | 7.17 | 8.21 | 8.82 |
| COD | 0.31 | 0.81 | 14.11 | 0.3 | 0.63 | 1.39 |
| TH | 69.2 | 469.5 | 6415 | 41.5 | 136.9 | 3808 |
| TDS | 256 | 686 | 23,550 | 185 | 463 | 9570 |
| CO32− | <DL | <DL | 5.9 | <DL | 5.9 | 29.7 |
| HCO3− | 108.7 | 388.8 | 1009 | 73.1 | 228.9 | 845.7 |
| Cl− | 9 | 82.3 | 13,830 | 2.5 | 61.6 | 2066 |
| NO3−-N | <DL | 3.2 | 23.9 | <DL | 0.4 | 16.9 |
| SO42− | 7 | 147.1 | 2736 | 6.1 | 70.3 | 3964 |
| K+ | 0.4 | 1.9 | 51 | 0.4 | 1.4 | 3.2 |
| Na+ | 5.9 | 62.5 | 6465 | 24 | 111.4 | 1940 |
| Ca2+ | 18.3 | 98.3 | 570.8 | 7.5 | 24.4 | 281.8 |
| Mg2+ | 6.3 | 41.7 | 1219 | 5.4 | 13.6 | 759 |
| I− | <DL | <DL | 0.906 | <DL | <DL | 0.665 |
| NO2−-N | <DL | <DL | 0.223 | <DL | <DL | 0.081 |
| NH4+-N | <DL | <DL | 1.02 | <DL | <DL | 0.37 |
| S2− | <DL | <DL | 0.19 | <DL | 0.005 | 0.217 |
| F− | 0.16 | 0.47 | 2.57 | 0.15 | 0.6 | 2.11 |
| B | <DL | 0.06 | 1.31 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.95 |
| Mn | <DL | 0.03 | 3.89 | <DL | 0.02 | 0.77 |
| Al | <DL | 0.07 | 0.54 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.15 |
| Fe | <DL | 0.06 | 78.31 | <DL | 0.07 | 2.94 |
| Ba | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.41 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.19 |
| Zn | <DL | <DL | 36.11 | <DL | 0.01 | 2.26 |
| Ni | <DL | 0.001 | 0.007 | <DL | <DL | 0.006 |
| Cd | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL |
| Pb | <DL | <DL | 0.001 | <DL | <DL | 0.003 |
| Se | <DL | <DL | 0.016 | <DL | <DL | 0.002 |
| Hg | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL |
| As | <DL | <DL | 0.009 | <DL | <DL | 0.008 |
| Cr(VI) | <DL | <DL | 0.006 | <DL | <DL | 0.008 |
| Items | Piedmont Plain | Central Plain | Littoral Plain | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min. | Med. | Mean | Max. | Min. | Med. | Mean | Max. | Min. | Med. | Mean | Max. | |
| pH | 7.03 | 7.53 | 7.52 | 8.22 | 6.75 | 7.34 | 7.38 | 7.88 | 7.22 | 7.45 | 7.53 | 7.99 |
| COD | 0.31 | 0.58 | 0.70 | 1.52 | 0.69 | 1.48 | 1.61 | 2.82 | 1.57 | 2.20 | 5.02 | 14.11 |
| TH | 69 | 391 | 386 | 662 | 356 | 980 | 1211 | 2619 | 297 | 920 | 2138 | 6415 |
| TDS | 256 | 555 | 575 | 1118 | 1394 | 2356 | 3109 | 7110 | 511 | 4646 | 8338 | 23,550 |
| HCO3− | 109 | 311 | 339 | 610 | 296 | 754 | 710 | 1009 | 293 | 485 | 442 | 507 |
| Cl− | 9 | 58 | 61 | 160 | 135 | 464 | 545 | 1551 | 51 | 2143 | 4542 | 13,830 |
| NO3−-N | <DL | 7.1 | 8.0 | 19.7 | <DL | 0.4 | 2.9 | 23.9 | <DL | 0.8 | 1.2 | 3.2 |
| SO42− | 7 | 66 | 94 | 249 | 302 | 477 | 995 | 2736 | 21 | 634 | 629 | 1229 |
| K+ | 0.4 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 3.0 | 0.7 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 3.1 | 6.2 | 19.5 | 24.1 | 51.0 |
| Na+ | 6 | 32 | 48 | 200 | 323 | 530 | 648 | 1565 | 76 | 1358 | 2314 | 6465 |
| Ca2+ | 18 | 91 | 98 | 207 | 41 | 103 | 135 | 326 | 32 | 114 | 208 | 571 |
| Mg2+ | 6 | 34 | 36 | 80 | 57 | 143 | 215 | 523 | 25 | 166 | 394 | 1219 |
| I− | <DL | <DL | 0.02 | 0.34 | 0.04 | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.45 | <DL | 0.11 | 0.28 | 0.91 |
| NO2−-N | <DL | <DL | 0.01 | 0.22 | <DL | <DL | 0.02 | 0.11 | <DL | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.15 |
| NH4+-N | <DL | <DL | 0.01 | 0.14 | <DL | 0.06 | 0.19 | 1.02 | <DL | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.37 |
| S2− | <DL | <DL | <DL | 0.010 | <DL | <DL | 0.042 | 0.190 | <DL | 0.008 | 0.014 | 0.040 |
| F− | 0.16 | 0.35 | 0.45 | 1.92 | 0.39 | 0.87 | 1.13 | 2.57 | 0.47 | 0.83 | 0.86 | 1.30 |
| B | <DL | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.16 | 0.48 | 0.59 | 1.31 | 0.06 | 0.76 | 0.60 | 0.82 |
| Mn | <DL | <DL | 0.07 | 1.11 | 0.12 | 0.27 | 0.49 | 1.43 | 0.34 | 0.42 | 1.27 | 3.89 |
| Al | <DL | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.54 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.15 |
| Fe | <DL | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.61 | 0.04 | 0.76 | 10.11 | 78.31 | <DL | 0.64 | 0.65 | 1.33 |
| Ba | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.41 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.25 |
| Zn | <DL | <DL | 0.01 | 0.09 | <DL | 0.01 | 4.02 | 36.11 | <DL | <DL | 0.01 | 0.03 |
| Ni | <DL | <DL | 0.001 | 0.004 | <DL | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 | <DL | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.007 |
| Cd | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL |
| Pb | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | 0.001 | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL |
| Se | <DL | <DL | 0.001 | 0.005 | <DL | <DL | 0.002 | 0.016 | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL |
| Hg | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL |
| As | <DL | <DL | <DL | 0.005 | <DL | <DL | 0.002 | 0.009 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 |
| Cr(VI) | <DL | <DL | 0.001 | 0.006 | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL |
| Items | Allowable Limits | Phreatic Aquifers | Confined Aquifers | Piedmont Plain | Central and Littoral Plains |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TH | <450 mg/L | 54.3% | 5.3% | 40.9% | 76.9% |
| Mn | <0.1 mg/L | 45.7% | 15.8% | 13.6% | 100% |
| TDS | <1000 mg/L | 40.0% | 15.8% | 9.1% | 92.3% |
| Na+ | <200 mg/L | 37.1% | 21.1% | 4.5% | 92.3% |
| Fe | <0.3 mg/L | 34.3% | 15.8% | 13.6% | 69.2% |
| Cl− | <250 mg/L | 31.4% | 15.8% | 0 | 84.6% |
| I− | <0.08 mg/L | 31.4% | 15.8% | 4.5% | 76.9% |
| SO42− | <250 mg/L | 31.4% | 5.3% | 0 | 84.6% |
| B | <0.5 mg/L | 20.0% | 5.3% | 0 | 53.8% |
| F− | <1 mg/L | 17.1% | 26.3% | 4.5% | 38.5% |
| S2− | <0.02 mg/L | 14.3% | 31.6% | 0 | 38.5% |
| Al | <0.2 mg/L | 5.7% | 0 | 0 | 15.4% |
| Zn | <1 mg/L | 2.9% | 5.3% | 0 | 7.7% |
| COD | <3 mg/L | 2.9% | 0 | 0 | 7.7% |
| NO3−-N | <20 mg/L | 2.9% | 0 | 0 | 7.7% |
| NH4+-N | <0.5 mg/L | 2.9% | 0 | 0 | 7.7% |
| Se | <0.01 mg/L | 2.9% | 0 | 0 | 7.7% |
| pH | 6.5–8.5 | 0 | 5.3% | 0 | 0 |
| NO2−-N | <1 mg/L | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ba | <0.7 mg/L | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ni | <0.02 mg/L | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cd | <0.005 mg/L | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pb | <0.01 mg/L | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hg | <0.001 mg/L | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| As | <0.01 mg/L | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cr(VI) | <0.05 mg/L | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Items | Phreatic Aquifers | Items | Confined Aquifers | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | ||
| Cl− | 0.976 | 0.063 | −0.045 | −0.064 | −0.079 | TDS | 0.991 | 0.015 | 0.083 |
| COD | 0.976 | 0.065 | 0.000 | 0.025 | 0.024 | Cl− | 0.991 | 0.058 | 0.033 |
| Na+ | 0.969 | 0.215 | −0.018 | −0.004 | −0.016 | Na+ | 0.986 | 0.072 | 0.008 |
| TDS | 0.964 | 0.242 | 0.001 | 0.065 | 0.009 | Mg2+ | 0.985 | −0.018 | 0.139 |
| Mn | 0.932 | 0.183 | −0.111 | 0.089 | 0.069 | TH | 0.982 | −0.054 | 0.158 |
| TH | 0.931 | 0.262 | 0.012 | 0.217 | 0.053 | SO42− | 0.981 | −0.010 | 0.131 |
| Mg2+ | 0.924 | 0.312 | −0.006 | 0.161 | 0.047 | Mn | 0.969 | −0.056 | 0.100 |
| K+ | 0.889 | −0.124 | −0.058 | −0.198 | 0.052 | B | 0.950 | 0.223 | −0.131 |
| Ca2+ | 0.857 | 0.048 | 0.090 | 0.416 | 0.071 | HCO3− | 0.945 | −0.105 | −0.055 |
| I− | 0.161 | 0.826 | −0.221 | −0.020 | 0.029 | Fe | 0.943 | 0.225 | 0.142 |
| HCO3− | 0.100 | 0.806 | 0.123 | 0.224 | 0.073 | I− | 0.915 | 0.249 | −0.086 |
| B | 0.479 | 0.759 | 0.184 | −0.063 | 0.215 | Ca2+ | 0.914 | −0.210 | 0.239 |
| SO42− | 0.424 | 0.680 | 0.180 | 0.297 | 0.199 | COD | 0.686 | 0.298 | −0.328 |
| F− | 0.041 | 0.574 | −0.082 | −0.557 | 0.144 | Zn | 0.024 | 0.925 | −0.033 |
| Se | −0.034 | 0.066 | 0.955 | 0.031 | −0.008 | S2− | 0.611 | 0.771 | −0.091 |
| Zn | 0.022 | 0.184 | 0.935 | −0.075 | 0.109 | pH | −0.501 | 0.648 | −0.253 |
| NO3− | −0.098 | −0.323 | 0.706 | 0.173 | −0.276 | K+ | 0.220 | 0.074 | 0.832 |
| pH | −0.191 | −0.281 | −0.052 | −0.800 | −0.066 | F− | 0.089 | 0.289 | −0.805 |
| Fe | 0.078 | 0.106 | −0.101 | 0.617 | 0.499 | Eigenvalue | 12.3 | 2.3 | 1.7 |
| NH4+ | 0.032 | 0.025 | −0.056 | 0.072 | 0.853 | Explained variance (%) | 68.2 | 12.7 | 9.5 |
| S2− | −0.009 | 0.349 | 0.256 | 0.221 | 0.487 | Cumulative % of variance | 68.2 | 80.9 | 90.4 |
| Al | 0.000 | 0.260 | −0.155 | −0.354 | 0.435 | ||||
| Eigenvalue | 8.4 | 3.5 | 2.6 | 2.0 | 1.6 | ||||
| Explained variance (%) | 38.1 | 15.7 | 11.6 | 9.1 | 7.4 | ||||
| Cumulative % of variance | 38.1 | 53.8 | 65.4 | 74.5 | 81.9 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, Y.; Hou, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhen, S.; Yue, C.; Cui, X.; Guo, C. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Groundwater Quality in Phreatic and Confined Aquifers of the Hebei Plain, China. Water 2023, 15, 3071. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173071
Qian Y, Hou Q, Wang C, Zhen S, Yue C, Cui X, Guo C. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Groundwater Quality in Phreatic and Confined Aquifers of the Hebei Plain, China. Water. 2023; 15(17):3071. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173071
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Yong, Qinxuan Hou, Chunxiao Wang, Shijun Zhen, Chen Yue, Xiangxiang Cui, and Chunyan Guo. 2023. "Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Groundwater Quality in Phreatic and Confined Aquifers of the Hebei Plain, China" Water 15, no. 17: 3071. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173071
APA StyleQian, Y., Hou, Q., Wang, C., Zhen, S., Yue, C., Cui, X., & Guo, C. (2023). Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Groundwater Quality in Phreatic and Confined Aquifers of the Hebei Plain, China. Water, 15(17), 3071. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15173071






