Spatial Variations and Distribution Patterns of Soil Salinity at the Canal Scale in the Hetao Irrigation District
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.1.1. Physical Geography and Climatic Conditions
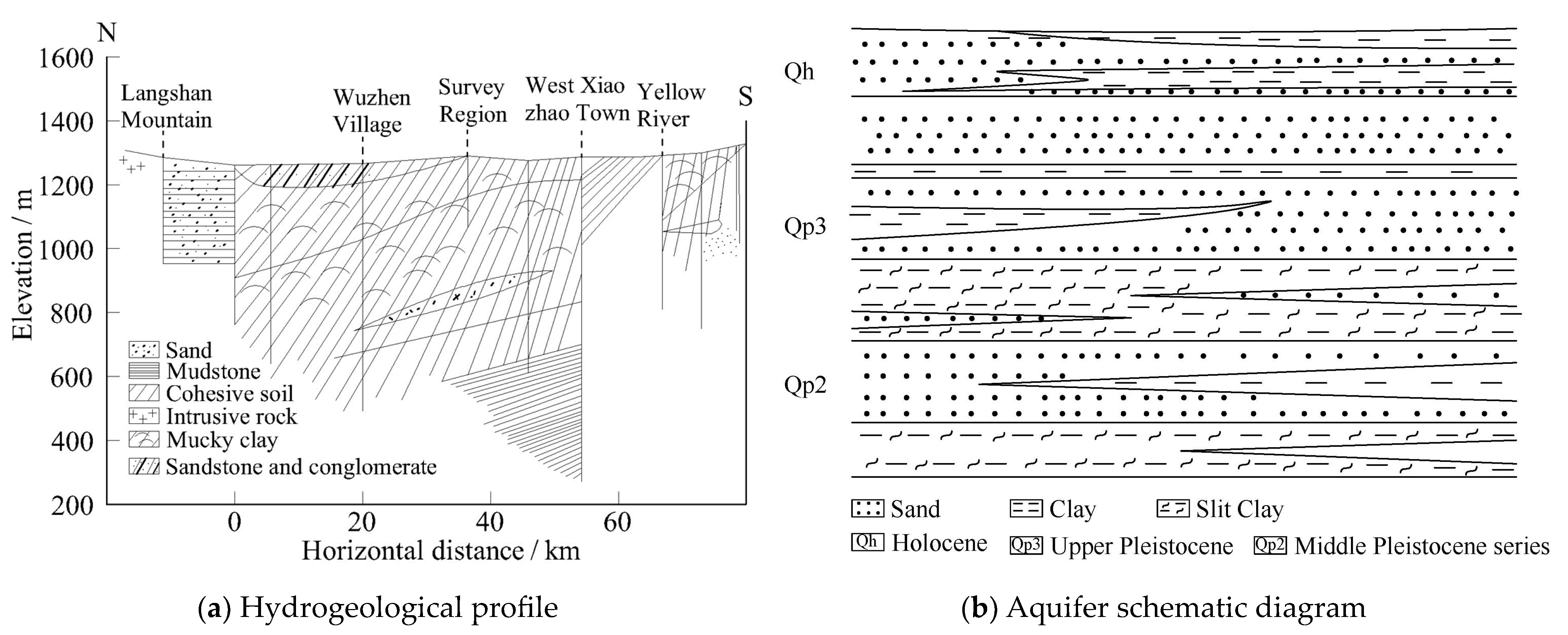
2.1.2. Hydrogeological Framework
2.2. Sampling Point Layout and Data Acquisition
2.2.1. Sampling Point Layout
2.2.2. Data Measurements
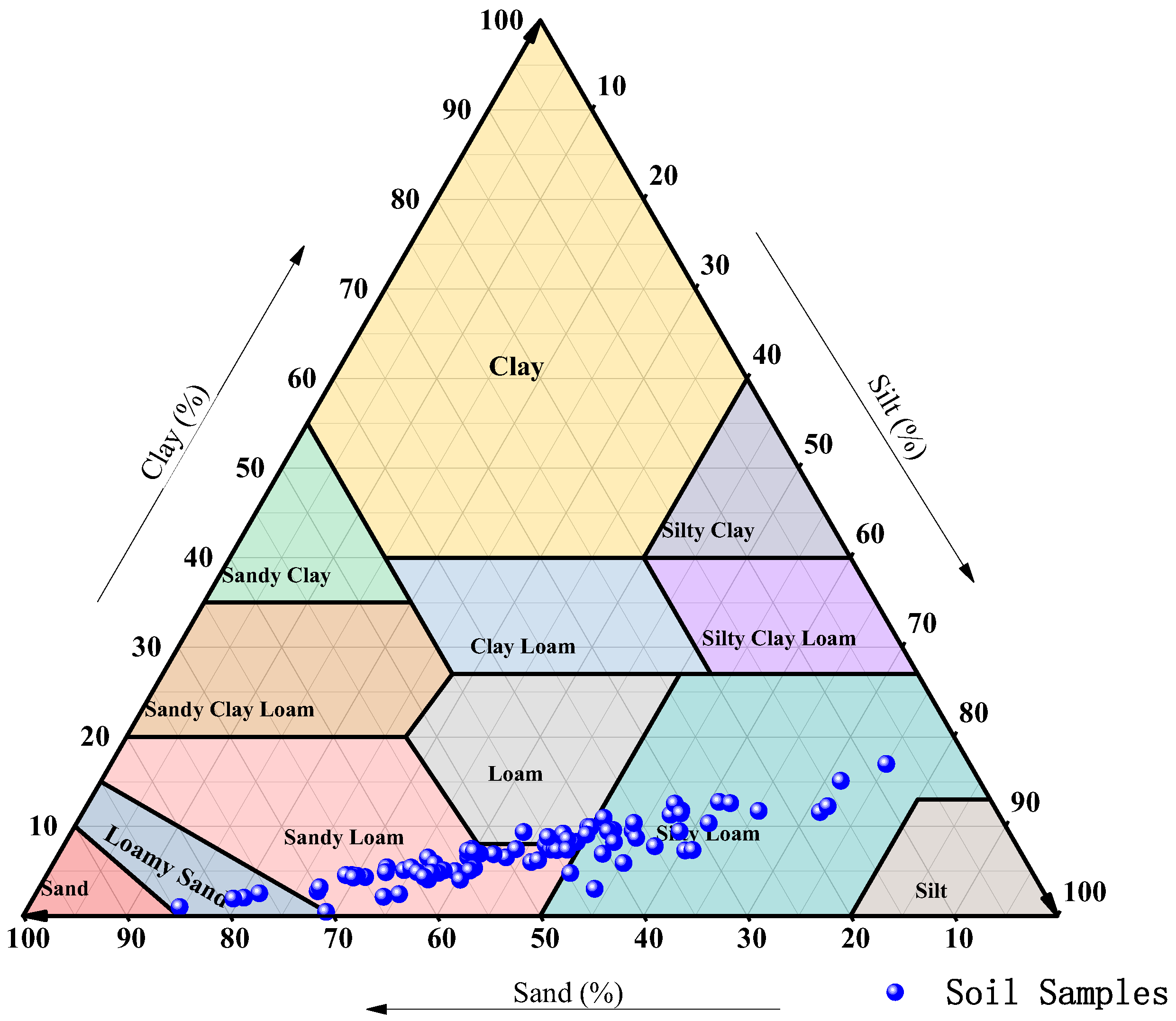
2.2.3. Soil Texture
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. Semi-Variance Function
2.3.2. Ordinary Kriging
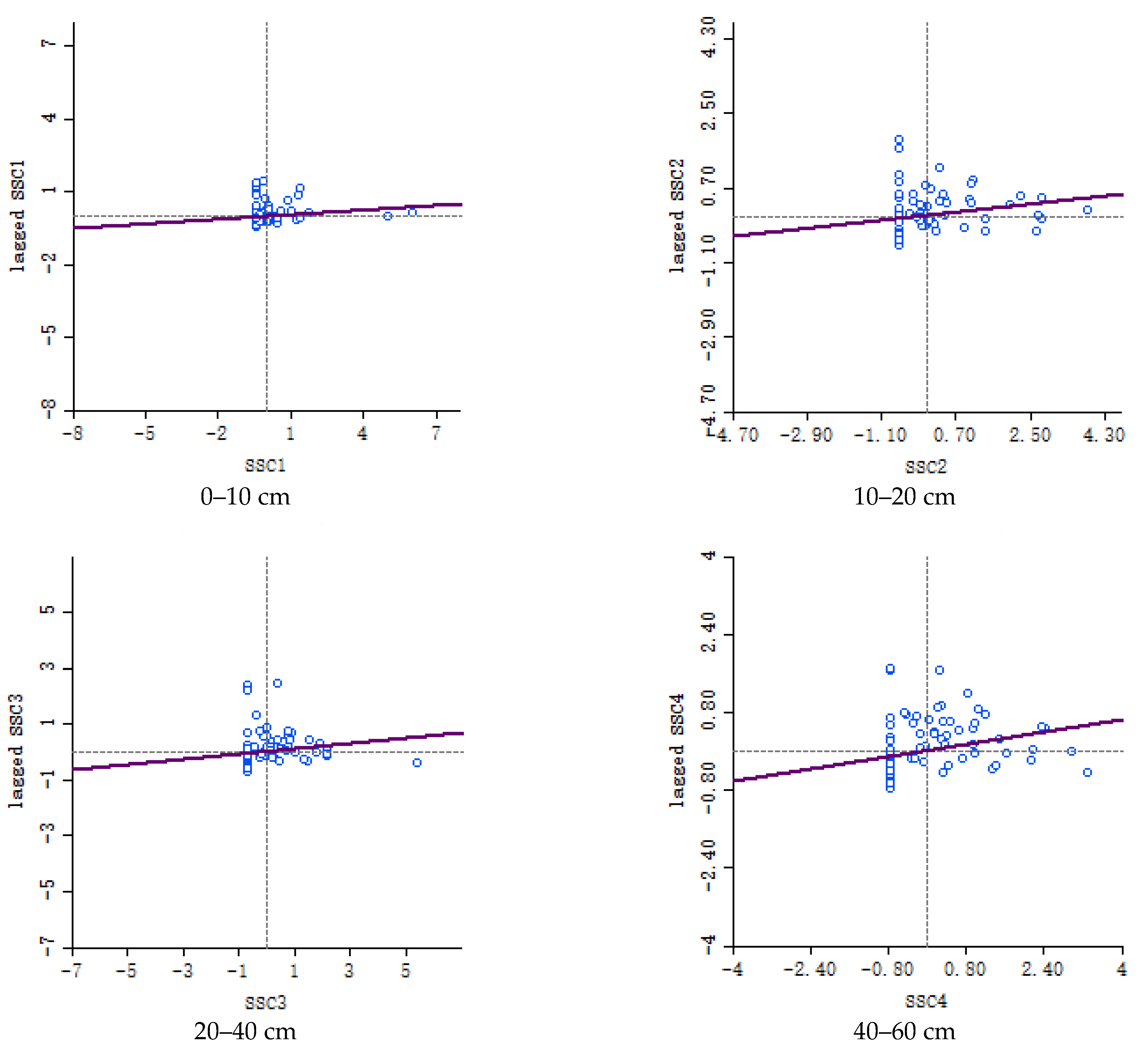
2.3.3. Spatial Autocorrelation Method
2.4. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Analysis of Soil Salinization Characteristics
3.2. Analysis of Spatial Variation Characteristics of Soil Salinization
3.3. Soil Salt Content and Water Content Are Spatially Autocorrelated
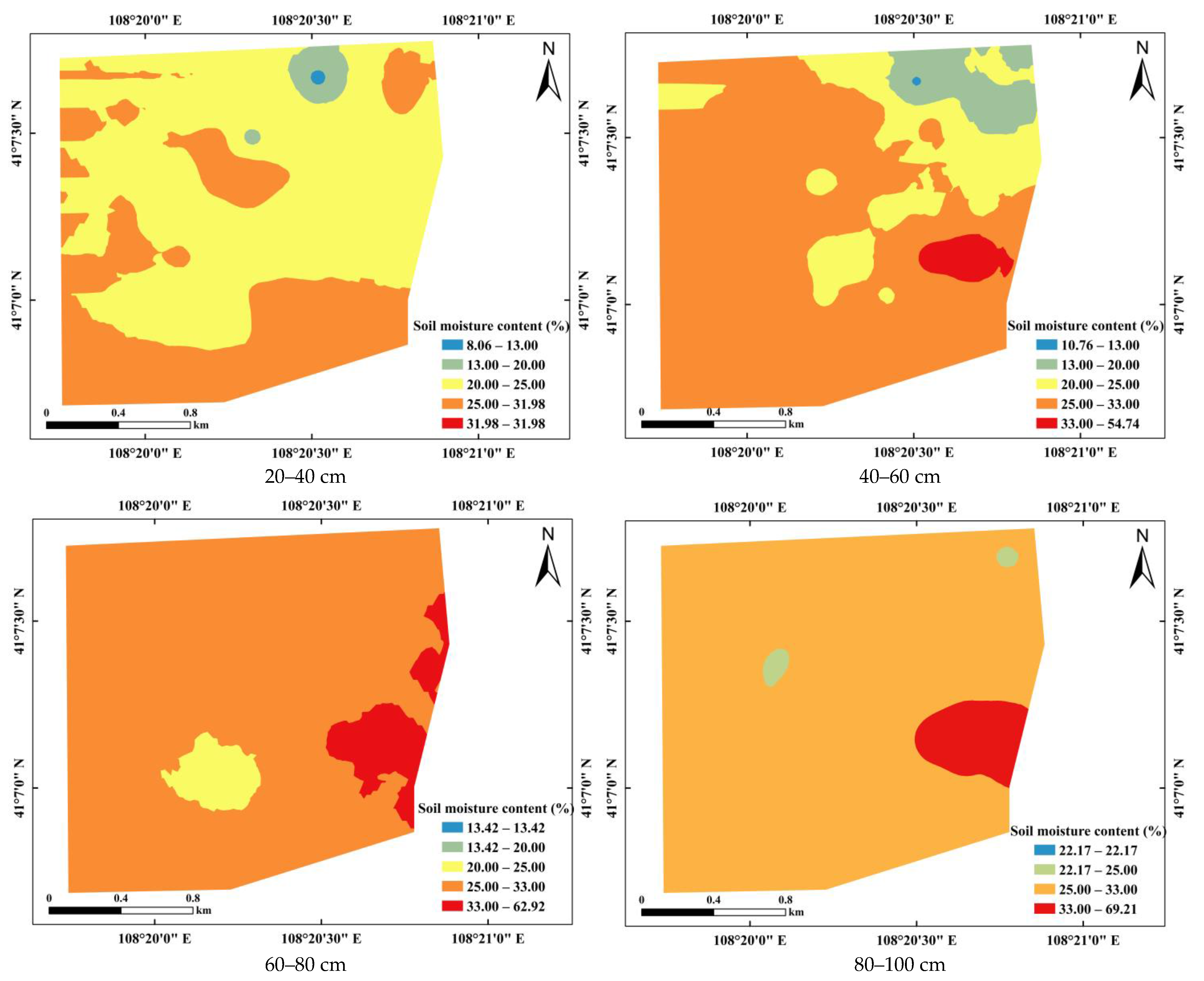
3.4. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Salt and Water Content
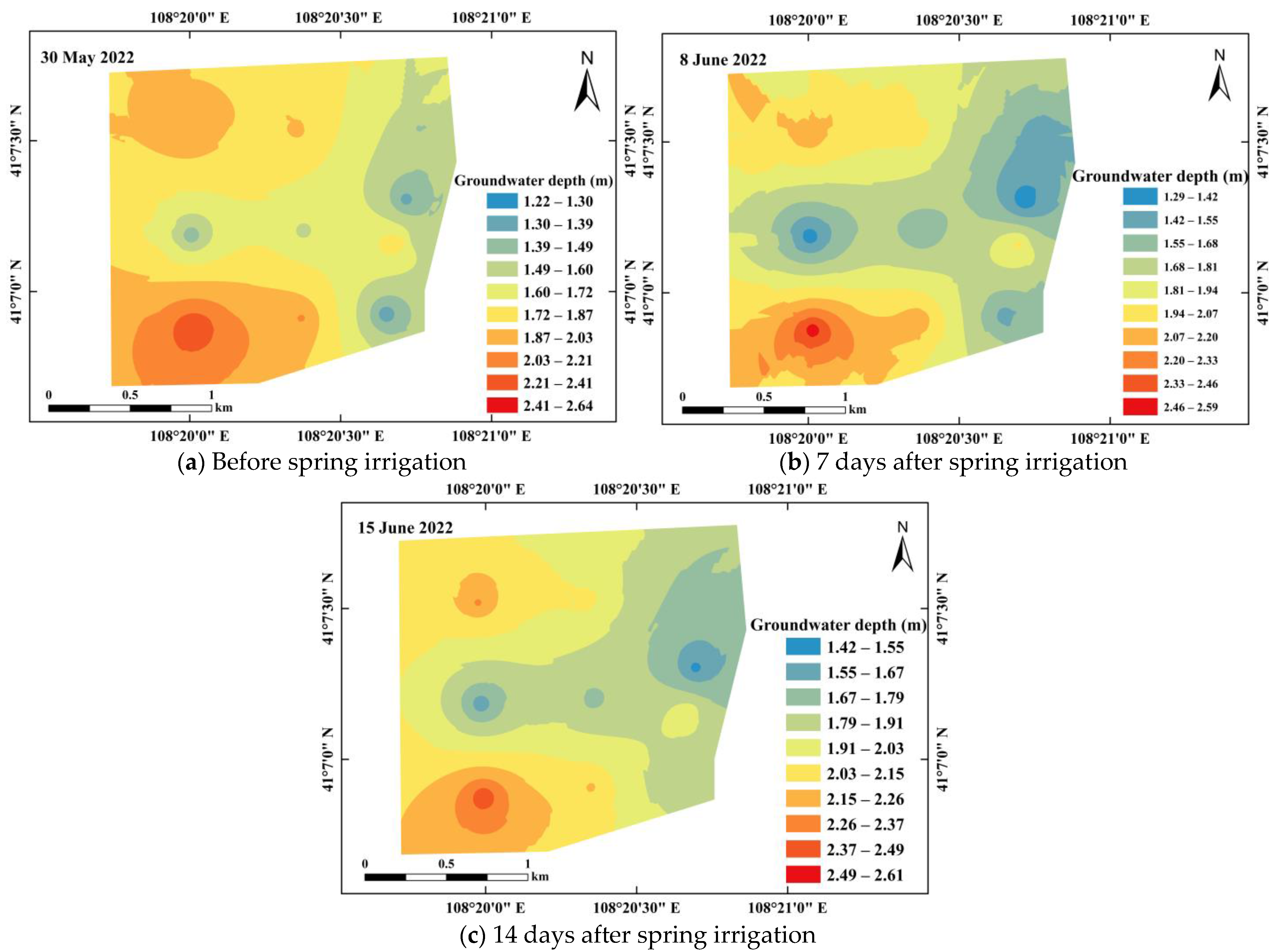
3.5. Effect of Groundwater Depth on Soil Salt Content in Different Layers
4. Discussion
4.1. Variability Mechanism of Soil Water and Salt
4.2. Spatial Correlation of Soil Water and Salt
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AbdelRahman, M.A.; Zakarya, Y.M.; Metwaly, M.M.; Koubouris, G. Deciphering soil spatial variability through geostatistics and interpolation techniques. Sustainability 2020, 13, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosma, C.; Triantafyllidis, V.; Zotos, A.; Pittaras, A.; Kouneli, V.; Karydogianni, S.; Mavroeidis, A.; Kakabouki, I.; Beslemes, D.; Tigka, E.L.; et al. Assessing spatial variability of soil properties in Mediterranean smallholder farming systems. Land 2022, 11, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.; Liu, X.; Ma, L.; Jiao, F.; Wang, Z. Spatial distribution of soil water and salt in a slightly salinized farmland. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouryazdankhah, H.; Shahnazari, A.; Ahmadi, M.Z.; Khaledian, M.; Andersen, M.N. Rice yield estimation based on forecasting the future condition of groundwater salinity in the Caspian coastal strip of Guilan Province, Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Huang, G.; Sun, C.; Pereira, L.S.; Ramos, T.B.; Huang, Q.; Hao, Y. Assessing the effects of water table depth on water use, soil salinity and wheat yield: Searching for a target depth for irrigated areas in the upper Yellow River basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 125, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachshon, U. Cropland soil salinization and associated hydrology: Trends, processes and examples. Water 2018, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar]
- Aeman, H.; Shu, H.; Abbas, S.; Aisha, H.; Usman, M. Sinking delta: Quantifying the impacts of saltwater intrusion in the Indus Delta of Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, S.; Li, P.; Zheng, X.; Liu, T.; Walther, M. Saltwater intrusion induced micro-scale mineral precipitation and evolution in porous media. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 129968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Yang, S.; Li, R.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Yan, J.; Miao, Q.; Li, Z. Soil water and salt movement and soil salinization control in Hetao Irrigation District: Current state and future prospect. J. Irrig. Drain 2020, 39, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Loescher, W.; Chan, Z.; Grumet, R. Options for developing salt-tolerant crops. HortScience 2011, 46, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, Q.; Lu, Q. Salt-water balance and dry drainage desalting in Hetao Irrigating Area, Inner Mongolia. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2006, 26, 460. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Shi, H.; Yan, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J. Relation between groundwater depth and soil water and salt after water saving reform in salinization irrigation district. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 28, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elaty, I.; Zelenakova, M. Saltwater intrusion management in shallow and deep coastal aquifers for high aridity regions. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 40, 101026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, H.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wang, W. Dynamic and transformational relationship between soil water and groundwater in typical areas of Hetao Irrigation District. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 352–362. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; He, Y.; Fang, H. Spatial variability of soil properties in the field based on GPS and GIS. Nongye Gongcheng Xuebao (Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng.) 2003, 19, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, R.; Yang, J.; Liu, G. Spatial variability of soil salinity and moisture and their estimations by co kriging method—A case study in characteristic field of Yellow River delta. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2006, 20, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Qianji, H.; Shaoyuan, F.; Zhou, G. Intra-annual spatiotemporal variation in salt content in the plough layer in Hetao Irrigation District. J. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 39, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, A.; Jiang, P.; Sheng, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. Spatial variability of surface soil salinity in Manas River basin. Acta Pedofil. Sin 2014, 51, 410–414. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Lu, C.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Saidy, E.; Liu, B.; Shu, L. Spatio-temporal variability of hydraulic conductivity in the floodplain riverbank of a hyporheic zone. CATENA 2023, 228, 107172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Z. Multifractal study on spatial variability of soil water and salt and its scale effect. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, X.; Yang, P.; Lv, Y. Analysis on spatial variability of soil properties based on multifractal theory. J. Basic Sci. Eng 2011, 19, 712–720. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, P.; Walter, M.; Miller, J.; Epanchin-Niell, R.; Gedan, K.; Yawatkar, V.; Nguyen, E.; Tully, K.L. The spread and cost of saltwater intrusion in the US Mid-Atlantic. Nat. Sustain. 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Wu, D.; Yan, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, K. Spatial temporal Variation of Soil Salinity after Water Saving Transformation in Salinized Irrigation District. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 318–331. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L. Analysis of Distribution Patterns and Spatial Variability of Soil Salinity Affecting Factors in Topsoil Layer ofSalinized Soil in Jinghe Oasis. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2018, 34, 64–73. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Lü, Y.; Fu, B.; Wei, W. A framework on landscape pattern analysis and scale change by using pattern recognition approach. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 663–670. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Pan, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, F.; Shi, X. Study on spatial distribution of soil quality and quantitative evaluation of soil fertility quality under middle spatial scale. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2003, 34, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shi, H.; Wei, Z. Scale effect of spatial variability of soil water-salt. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2004, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, D.; Xu, X.; Huang, G. Irrigation water use in typical irrigation and drainage system of Hetao Irrigation District. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng 2019, 35, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseva, S. Data transformations between soil texture schemes. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1997, 48, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ma, L.; Smanov, Z.; Samarkhanov, K.; Abuduwaili, J. Clarifying Soil Texture and Salinity Using Local Spatial Statistics (Getis-Ord Gi* and Moran’s I) in Kazakh–Uzbekistan Border Area, Central Asia. Agronomy 2022, 12, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yi, Y.; Ling, G.; Wang, S. Utilization of geostatistics in soil spatial variability. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2005, 36, 265–268. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, T.C.; Ferraz, G.A.; Carvalho, L.C.; Silva, F.M.; Alves, M.C.; Marin, D.B. Spatial variability of soil physical properties in longitudinal profiles. An. Acad. Bras. Ciências 2022, 94, e20200411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, R.; Yang, J.; Liu, G.; Zou, P. Spatial variability of soil salinity in characteristic field of the Yellow River Delta. Trans. CSAE 2006, 22, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Zhu, H. Analysis of spatial variation of soil moisture-salinity-nutrient in Ebinur Lake wetlands, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, G. Spatial prediction of cultivated land soil nutrients in typical region of yellow river delta. J. Nat. Resour. 2018, 33, 489–503. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, G.; Mao, W.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J. Geostatistical Analysis of Spatial Variability of Soil Water and Salt in Hetao Irrigation District. J. Irrig. Drain. 2022, 41, 101–109. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guan, X.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z.; Lv, Y.; Fu, X. Spatio-temporal variability of soil salinity and its relationship with the depth to groundwater in salinization irrigation district. Acta Ecol. Sin 2012, 32, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Shi, H.; Miao, Q.; Tian, F.; Yu, D.; Zhou, L.; Liang, Z. Temporal and spatial variability analysis of soil water and salt and the influence of groundwater depth on salt in saline irrigation area. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 33, 246–253. [Google Scholar]
- Bin, L.; Haibin, S.; Debao, T. Soil salinity profile characteristics and its spatial distribution before and after water saving. Arid Zone Res. 2015, 32, 663–673. [Google Scholar]
- Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Vázquez, E.V.; Miranda, J.G.V. Assessing soil particle-size distribution on experimental plots with similar texture under different management systems using multifractal parameters. Geoderma 2010, 160, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Z. Investigating the hydrodynamic and biogeochemical evolutions of the hyporheic zone due to large-scale reservoir impoundment. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoncini, M.; Sapkota, T.B.; Barberi, P.; Antichi, D.; Risaliti, R. Long-term effect of tillage, nitrogen fertilization and cover crops on soil organic carbon and total nitrogen content. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 114, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ge, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Feng, S. Study on relationship between soil salinization and groundwater table depth based on indicator Kriging. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Liu, C.; Cai, T.; Zhang, S. 3D spatial distribution characteristics of soil organic matter and total nitrogen in farmland. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2015, 46, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Friedel, M.J. Estimation and scaling of hydrostratigraphic units: Application of unsupervised machine learning and multivariate statistical techniques to hydrogeophysical data. Hydrogeol. J. 2016, 24, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, S.; Wang, X. Regional 3-D soil salt spatial variability based on electromagnetic induction technology. Nongye Jixie Xuebao = Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2013, 44, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Laslett, G.; McBratney, A.; Pahl, P.J.; Hutchinson, M. Comparison of several spatial prediction methods for soil pH. J. Soil Sci. 1987, 38, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, E.; Gallichand, J.; Marcotte, D. Theoretical and experimental performance of spatial interpolation methods for soil salinity analysis. Trans. ASAE 1994, 37, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Yang, J.; Han, J. Comparative study of simulations of spatial variability of soil salinity in coastal polders. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2012, 49, 275–281. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, M.; Webster, R. A tutorial guide to geostatistics: Computing and modelling variograms and kriging. Catena 2014, 113, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Fu, B.; Ma, K.; Chen, L. Spatial variability of soil nutrients based on geostatistics combined with GIS—A case study in Zunghua City of Hebei Province. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2000, 11, 557–563. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Shi, H.; Li, X.; Zheng, Q.; Guo, J.; Wang, W. Analysis of water and salt transportation and balance during cultivated land, waste land and lake system in Hetao Irrigation Area. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2019, 50, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y. Optimum allocation of salt discharge areas in land consolidation for irrigation districts by SahysMod. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 256, 107060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Feng, Q.; Yang, H. Soil salinity distribution and its relationship with soil particle size in the lower reaches of Heihe River, Northwestern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J. Migration characteristics of soil water and salt and their interaction under different groundwater levels. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; Yang, F.; Cen, R.; Liu, J.; Chen, H. Effects of straw biochar application on soil temperature, available nitrogen and growth of corn. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Gao, J.; Cen, R.; Yang, F.; He, Z.; Wu, J.; Miao, Q.; Liao, H. Effects of polyacrylamide-based super absorbent polymer and corn straw biochar on the arid and semi-arid salinized soil. Agriculture 2020, 10, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Wang, T.; Yang, F.; Cen, R.; Liao, H.; Qu, Z. Effects of biochar on soil evaporation and moisture content and the associated mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2023, 35, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inam, A.; Adamowski, J.; Prasher, S.; Albano, R. Parameter estimation and uncertainty analysis of the Spatial Agro Hydro Salinity Model (SAHYSMOD) in the semi-arid climate of Rechna Doab, Pakistan. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 94, 186–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inam, A.; Adamowski, J.; Prasher, S.; Halbe, J.; Malard, J.; Albano, R. Coupling of a distributed stakeholder-built system dynamics socio-economic model with SAHYSMOD for sustainable soil salinity management–Part 1: Model development. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 596–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Depth/cm | Minimum | Maximum | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Variance | Skewness | Kurtosis | Coefficient of Variation/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil salt content (g/kg) | 0–10 | 0.51 | 50.52 | 4.64 | 8.11 | 65.77 | 4.41 | 21.96 | 1.75 |
| 10–20 | 0.52 | 17.68 | 2.90 | 2.94 | 8.67 | 2.89 | 11.57 | 1.01 | |
| 20–40 | 0.51 | 11.21 | 2.58 | 2.21 | 4.89 | 2.19 | 5.22 | 0.86 | |
| 40–60 | 0.55 | 11.47 | 2.95 | 2.26 | 5.09 | 1.68 | 3.19 | 0.77 | |
| 60–80 | 0.59 | 22.69 | 3.63 | 4.12 | 16.95 | 3.05 | 11.13 | 1.13 | |
| 80–100 | 0.66 | 26.35 | 3.59 | 4.03 | 16.20 | 3.89 | 19.93 | 1.12 | |
| Soil moisture content (%) | 0–10 | 13.71 | 44.65 | 21.12 | 4.84 | 23.43 | 2.68 | 10.72 | 0.23 |
| 10–20 | 15.60 | 38.54 | 22.94 | 3.68 | 13.56 | 1.56 | 5.79 | 0.16 | |
| 20–40 | 8.06 | 31.98 | 24.19 | 3.64 | 13.28 | −1.61 | 6.76 | 0.15 | |
| 40–60 | 10.76 | 54.74 | 26.48 | 5.79 | 33.47 | 1.88 | 12.58 | 0.21 | |
| 60–80 | 13.42 | 62.92 | 28.48 | 6.77 | 45.89 | 3.25 | 14.75 | 0.23 | |
| 80–100 | 22.17 | 69.21 | 20.01 | 7.10 | 50.37 | 4.24 | 21.34 | 0.35 |
| Index | Depth/cm | Model | Nugget (C0) | Sill (C0 + C) | Partial Sill C0/(C0 + C) | RSS | R2 | Range/km |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil salt content | 0–10 | Exponential | 0.019 | 1.763 | 0.011 | 0.102 | 0.927 | 0.031 |
| 10–20 | Exponential | 0.032 | 0.826 | 0.039 | 0.069 | 0.826 | 0.018 | |
| 20–40 | Exponential | 0.086 | 0.639 | 0.135 | 0.072 | 0.721 | 0.015 | |
| 40–60 | Exponential | 0.133 | 0.596 | 0.223 | 0.089 | 0.546 | 0.011 | |
| 60–80 | Exponential | 0.001 | 0.752 | 0.001 | 0.127 | 0.419 | 0.004 | |
| 80–100 | Exponential | 0.113 | 0.675 | 0.167 | 0.012 | 0.663 | 0.005 | |
| Soil moisture content | 0–10 | Exponential | 0.0002 | 0.047 | 0.004 | 0.0003 | 0.799 | 0.012 |
| 10–20 | Exponential | 0.001 | 0.029 | 0.031 | 0.0001 | 0.764 | 0.015 | |
| 20–40 | Exponential | 0.010 | 14.940 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.619 | 0.009 | |
| 40–60 | Exponential | 0.001 | 0.636 | 0.002 | 0.291 | 0.856 | 0.034 | |
| 60–80 | Exponential | 0.0001 | 0.043 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.679 | 0.008 | |
| 80–100 | Exponential | 0.0001 | 0.036 | 0.003 | 0.0003 | 0.731 | 0.008 |
| Depth/cm | Moran’I | Z | P | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Salt Content (g/kg) | Soil Moisture Content (%) | Soil Salt Content (g/kg) | Soil Moisture Content (%) | Soil Salt Content (g/kg) | Soil Moisture Content (%) | |
| 0~10 | 0.16 | 0.46 | 1.61 | 5.61 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| 10~20 | 0.11 | 0.46 | 1.58 | 5.64 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| 20~40 | 0.09 | 0.46 | 1.55 | 5.58 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| 40~60 | 0.16 | 0.48 | 2.14 | 5.85 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| 60~80 | 0.19 | 0.43 | 2.62 | 5.21 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| 80~100 | 0.10 | 0.45 | 1.84 | 5.51 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Z.; Miao, Q.; Shi, H.; Feng, W.; Hou, C.; Yu, C.; Mu, Y. Spatial Variations and Distribution Patterns of Soil Salinity at the Canal Scale in the Hetao Irrigation District. Water 2023, 15, 3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193342
Hu Z, Miao Q, Shi H, Feng W, Hou C, Yu C, Mu Y. Spatial Variations and Distribution Patterns of Soil Salinity at the Canal Scale in the Hetao Irrigation District. Water. 2023; 15(19):3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193342
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Zhiyuan, Qingfeng Miao, Haibin Shi, Weiying Feng, Cong Hou, Cuicui Yu, and Yunfang Mu. 2023. "Spatial Variations and Distribution Patterns of Soil Salinity at the Canal Scale in the Hetao Irrigation District" Water 15, no. 19: 3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193342
APA StyleHu, Z., Miao, Q., Shi, H., Feng, W., Hou, C., Yu, C., & Mu, Y. (2023). Spatial Variations and Distribution Patterns of Soil Salinity at the Canal Scale in the Hetao Irrigation District. Water, 15(19), 3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193342









