Effect of Hydraulic Loading Rate on Treatment Performance of a Pilot Wetland Roof Treating Greywater from a Household
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
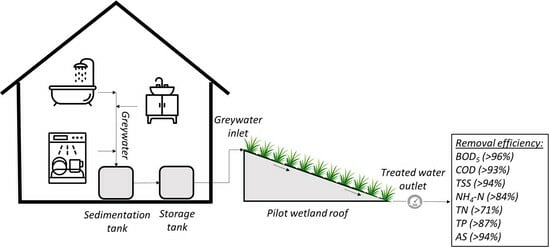
2.1. Experimental Set-Up: Pilot-Scale Plant
2.2. Sampling and Water Quality Analysis
2.3. Evapotranspiration
2.4. Estimation of Plant Vitality
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Overall Treatment Performance of the PWR System
3.1.1. Measurement of pH, Eh, DO, and EC
3.1.2. BOD5 and COD
3.1.3. NH4-N, NO3-N and TN
3.1.4. TP, TSS, and E. coli
3.1.5. AS
3.2. Effect of HLR on GW Treatment
3.3. EVT during Hot Summer Days
3.4. Plant Vitality
4. Potential Application of the PWR System
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dadashpoor, H.; Azizi, P.; Moghadasi, M. Land use change, urbanization, and change in landscape pattern in a metropolitan area. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNESCO. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2017. Wastewater: The Untapped Resource; The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, A.; Liang, H.; Li, G.; Szivak, I.; Traber, J.; Pronk, W. A low energy gravity-driven membrane bioreactor system for grey water treatment: Permeability and removal performance of organics. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 542, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noutsopoulos, C.; Andreadakis, A.; Kouris, N.; Charchousi, D.; Mendrinou, P.; Galani, A.; Mantziaras, I.; Koumaki, E. Greywater characterization and loadings—Physicochemical treatment to promote onsite reuse. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 216, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuppaladadiyam, A.K.; Merayo, N.; Prinsen, P.; Luque, R.; Blanco, A.; Zhao, M. A review on greywater reuse: Quality, risks, barriers and global scenarios. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 77–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsulaili, A.D.; Hamoda, M.F. Quantification and characterization of greywater from schools. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 1973–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, R.K.; Sivongxay, A. Reuse of laundry greywater as affected by its interaction with saturated soil. J. Hydrol. 2009, 366, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascoli, R., Jr.; Passoni, C.M.; Santos, F.M.; Bernardes, F.S.; Magalhães Filho, F.J.C.; Paulo, P.L. Assessment of Surfactant Removal Capacity and Microbial Community Diversity in a Greywater-Treating Constructed Wetland. Resources 2023, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramprasad, C.; Philip, L. Contributions of various processes to the removal of surfactants and personal care products in constructed wetland. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, I.; Somasundaran, P. Handbook for Cleaning/Decontamination of Surfaces; Johansson, I., Somasundaran, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; ISBN 9780080555539. [Google Scholar]
- Boano, F.; Caruso, A.; Costamagna, E.; Ridolfi, L.; Fiore, S.; Demichelis, F.; Galvão, A.; Pisoeiro, J.; Rizzo, A.; Masi, F. A review of nature-based solutions for greywater treatment: Applications, hydraulic design, and environmental benefits. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteng-Peprah, M.; Acheampong, M.A.; DeVries, N.K. Greywater characteristics, treatment systems, reuse strategies and user perception—A review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedler, E.; Hadari, M. Economic feasibility of on-site greywater reuse in multi-storey buildings. Desalination 2006, 190, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Mo, W.; Dilkina, B.; Gardner, K.; Stang, S.; Huang, J.-C.; Foreman, M.C. Decentralized water collection systems for households and communities: Household preferences in Atlanta and Boston. Water Res. 2019, 167, 115134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remy, C.A.; Jekel, M. Sustainable wastewater management: Life cycle assessment of conventional and source-separating urban sanitation systems. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, T.A.; Udert, K.M.; Lienert, J. Source Separation and Decentralization for Wastewater Management, Knowledge Unlatched (KU); IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 9781780401072. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, R.; Fidélis, T.; Roebeling, P.C.; Teles, F. The Institutionalization of Nature-Based Solutions—A Discourse Analysis of Emergent Literature. Resources 2020, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.; Shmueli, O.; Ronen, Z.; Raveh, E. Recycled vertical flow constructed wetland (RVFCW)—A novel method of recycling greywater for irrigation in small communities and households. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winward, G.P.; Avery, L.M.; Frazer-Williams, R.; Pidou, M.; Jeffrey, P.; Stephenson, T.; Jefferson, B. A study of the microbial quality of grey water and an evaluation of treatment technologies for reuse. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 32, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalawneh, A.; Chang, T.-K.; Alshawabkeh, H. Greywater treatment by granular filtration system using volcanic tuff and gravel media. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Miino, M.C.; Gomez, F.H.; Torretta, V.; Rada, E.C.; Sorlini, S. Horizontal Flow Constructed Wetland for Greywater Treatment and Reuse: An Experimental Case. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelgas-Orbecido, A.; Funamizu, N. Membrane System for Gray Water. In Resource-Oriented Agro-Sanitation Systems; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2019; pp. 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, K.Z.; Al Saadi, S.; Al Rawahi, M.; Knappe, J.; van Afferden, M.; Moeller, L.; Bernhard, K.; Müller, R.A. A multi-functional nature-based solution (NBS) for greywater treatment and reuse at the same plot. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 191, 106952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramprasad, C.; Smith, C.S.; Memon, F.A.; Philip, L. Removal of chemical and microbial contaminants from greywater using a novel constructed wetland: GROW. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 106, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.F.; Barron, N.J.; Zinger, Y.; Hatt, B.; Prodanovic, V.; Deletic, A. Pollutant removal performance of field scale dual-mode biofilters for stormwater, greywater, and groundwater treatment. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 163, 106192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, Y.M.; Patki, V.K.; Jahagirdar, S.; Karale, R.; Angathekar, V. Greywater treatment by vegetated vermifilter: A low cost material for rural sanitation in India. Mater Today-Proc. 2021, 45, 6946–6950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zraunig, A.; Estelrich, M.; Gattringer, H.; Kisser, J.; Langergraber, G.; Radtke, M.; Rodriguez-Roda, I.; Buttiglieri, G. Long term decentralized greywater treatment for water reuse purposes in a tourist facility by vertical ecosystem. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 138, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, N.D.; De Mattia, C.; Gandini, M.A.; Maucieri, C.; Stevanato, P.; Squartini, A.; Borin, M. Green walls to treat kitchen greywater in urban areas: Performance from a pilot-scale experiment. Sci Total Environ. 2021, 757, 144189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, S.; Al-Ghamdi, S.G.; Mackey, H.R. Greywater treatment by ornamental plants and media for an integrated green wall system. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 145, 104792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, S.; Schmauck, S.; Zehnsdorf, A. Biodiversity Impact of Green Roofs and Constructed Wetlands as Progressive Eco-Technologies in Urban Areas. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nivala, J.; Zehnsdorf, A.; van Afferden, M.; Müller, R.A. Green Infrastructure for Increased Resource Efficiency in Urban Water Management. In Urban Transformations—Sustainable Urban Development through Resource Efficiency, Quality of Life and Resilience; Kabisch, S., Koch, F., Gawel, E., Haase, A., Knapp, S., Krellenberg, K., Nivala, J., Zehnsdorf, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 133–143. [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg, M. Sumpfpflanzendächer als Variante der Dachbegrünung. In Regewasserbewirtschaftung. GWF Praxiswissen (Marsh Plant Roofs as a Variant of Roof Greening, Gwf—The Gas and Water, Supply Practice); Ziegler, C., Ed.; Deutscher Industrieverlag: Munich, Germany, 2011; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Zehnsdorf, A.; Blumberg, M.; Müller, R.A. Helophyte mats (wetland roofs) with high evapotranspiration rates as a tool for decentralised rainwater management—Process stability improved by simultaneous greywater treatment. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2019, 19, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jácome, J.A.; Molina, J.; Suárez, J.; Mosqueira, G.; Torres, D. Performance of constructed wetland applied for domestic wastewater treatment: Case study at Boimorto (Galicia, Spain). Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapater-Pereyra, M.; Van Dien, F.; Van Bruggen, J.J.A.; Lens, P.N.L. Material selection for a constructed wetroof receiving pre-treated high strength domestic wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 2264–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehnsdorf, A.; Willebrand, K.C.U.; Trabitzsch, R.; Knechtel, S.; Blumberg, M.; Müller, R.A. Wetland Roofs as an Attractive Option for Decentralized Water Management and Air Conditioning Enhancement in Growing Cities—A Review. Water 2019, 11, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.-D.; Bui, X.-T.; Lin, C.; Nguyen, V.-T.; Hoang, T.-K.; Nguyen, H.-H.; Nguyen, P.-D.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. A mini-review on shallow-bed constructed wetlands: A promising innovative green roof. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2019, 12, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapater-Pereyra, M.; Lavrinc, S.; Van Dien, F.; Van Bruggen, J.J.A.; Lens, P.N.L. Constructed wetroofs: A novel approach for the treatment and reuse of domestic wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, U.; Kim, E.; Bang, J.H.; Son, D.J.; Waldmann, B.; Lee, E.J. Wetlands are an effective green roof system. Build. Environ. 2013, 66, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehnsdorf, A.; Stock, N.; Richter, J.; Blumberg, M.; Müller, R.A. Grauwasserreinigung mit einer Sumpfpflanzenmatte unter Praxisbedingungen. Chem. Ing. Technol. 2016, 88, 1138–1144. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN ISO 11732; Water Quality—Determination of Ammonium Nitrogen—Method by Flow Analysis (CFA and FIA) and Spectrometric Detection. ISO: London, UK, 2005.
- EN ISO 10304-1; Water Quality—Determination of Dissolved Anions by Liquid Chromatography of Ions—Part 1: Determination of Bromide, Chloride, Fluoride, Nitrate, Nitrite, Phosphate and Sulfate. ISO: London, UK, 2007.
- EN ISO 15681-1; Water Quality—Determination of Orthophosphate and Total Phosphorus Contents by Flow Analysis (FIA and CFA)—Part 1: Method by Flow Injection Analysis (FIA). ISO: London, UK, 2003.
- ISO 9308-2; Water Quality—Enumeration of Escherichia coli and Coliform Bacteria—Part 2: Most Probable Number Method. ISO: London, UK, 2012.
- Jurado, E.; Fernández-Serrano, M.; Nunez-Olea, J.; Luzon, G.; Lechuga, M. Simplified spectrophotometric method using methylene blue for determining anionic surfactants: Applications to the study of primary biodegradation in aerobic screening tests. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DWA-A 221; Principles for the Use of Small Sewage Treatment Plants; DWA Set of Rules. The German Association for Water, Wastewater and Waste (DWA): Hennef, Germany, 2019; ISBN 978-3-88721-911-6.
- European Union. Regulation (EU) 2020/741 of the European Parliament and of the council 25 May 2020 on Minimum Requirements for Water Reuse. Off. J. Eur. Union 2020, OJ L 177, 32–55. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32020R0741&from=EN (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Magalhães Filho, F.J.C.; Sobrinho, T.A.; Steffen, J.L.; Arias, C.A.; Paulo, P.L. Hydraulic and hydrological aspects of an evapotranspiration–constructed wetland combined system for household greywater treatment. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2018, 53, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standard DWA-A 262E; Principles for Dimensioning, Construction and Operation of Wastewater Treatment Plants with Planted and Unplanted Filters for Treatment of Domestic and Municipal Wastewater. The German Association for Water, Wastewater and Waste (DWA): Hennef, Germany, 2017; (Translated from German and Published in English).
- Saeed, T.; Sun, G. A review on nitrogen and organics removal mechanisms in subsurface flow constructed wetlands: Dependency on environmental parameters, operating conditions and supporting media. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 112, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.; Wiel-Shafran, A.; Bondarenko, N.; Ronen, Z. Reliability of small scale greywater treatment systems and the impact of its effluent on soil properties. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2008, 65, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randerson, P.F.; Moran, C.; Andrzej, B. Oxygen transfer capacity of willow (Salix viminalis L.). Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 2306–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colliver, B.B.; Stephenson, T. Production of nitrogen oxide and dinitrogen oxide by autotrophic nitrifiers. Biotechnol. Adv. 2000, 18, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyjoo, Y.; Pareek, V.K.; Ang, M. A review of greywater characteristics and treatment processes. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1403–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Carvalho, P.N.; Muller, J.A.; Manoj, V.R.; Dong, R. Sanitation in constructed wetlands: A review on the removal of human pathogens and fecal indicators. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arden, S.; Ma, X. Constructed wetlands for greywater recycle and reuse: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolde, E. Greywater reuse systems for toilet flushing in multi-storey buildings–over ten years experience in Berlin. Urban Water 2000, 1, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaillou, K.; Gérente, C.; Andrès, Y.; Wolbert, D. Bathroom greywater characterization and potential treatments for reuse. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 215, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Leal, L.; Temmink, H.; Zeeman, G.; Buisman, C.J.N. Characterization and anaerobic biodegradability of grey water. Desalination 2011, 270, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wichmann, K.; Otterpohl, R. Review of the technological approaches for grey water treatment and reuses. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3439–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbar, Y. New Standards for Treated Wastewater Reuse in Israel. In Wastewater Reuse—Risk Assessment, Decision-Making and Environmental Security; Zaidi, M.K., Ed.; NATO Science for Peace and Security Series; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Badmus, S.O.; Amusa, H.K.; Oyehan, T.A.; Saleh, T.A. Environmental risks and toxicity of surfactants: Overview of analysis, assessment, and remediation techniques. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 62085–62104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrispim, M.C.; Nolasco, M.A. Greywater treatment using a moving bed biofilm reactor at a university campus in Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, J.L.; Levine, L.H.; Yorio, N.C.; Adams, J.L.; Hummerick, M.E. Response of greywater recycling systems based on hydroponic plant growth to three classes of surfactants. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1952–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, H.C.; Platzer, M.; Winker, E.; von Muench, E. Technology Review of Constructed Wetlands—Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands for Greywater and Domestic Wastewater Treatment; Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH: Eschborn, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Thon, A.; Kircher, W.; Thon, I. Constructed Wetlands on Roofs as a Module of Sanitary Environmental Engineering to Improve Urban Climate and Benefit of the On Site Thermal Effects. Miestu Zeldynu Formavimas 2010, 1, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig, M.L. Green roofs: New ecosystems to defend species diversity. Isr. J. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 62, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailor, D.; Elley, T.B.; Gibson, M. Exploring the building energy impacts of green roof design decisions—A modeling study of buildings in four distinct climates. J. Build. Phys. 2011, 35, 372–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driesen, E.; Van den Ende, W.; De Proft, M.; Saeys, W. Influence of Environmental Factors Light, CO2, Temperature, and Relative Humidity on Stomatal Opening and Development: A Review. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, M. Wetland Roofs—A Multifunctional Green Roof Type—Basics and Perspectives from Engineering Practice. In Proceedings of the Closed Cycles and the Circular Society Conference, Wädenswil, Switzerland, 2–4 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Semeraro, T.; Scarano, A.; Buccolieri, R.; Santino, A.; Aarrevaara, E. Planning of Urban Green Spaces: An Ecological Perspective on Human Benefits. Land 2021, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Parameters | Unit | Treatment Performance | Discharge Guidelines according to DWA-A 221 [46] d | Reclaimed Water Quality Requirements for Agricultural Irrigation according to the EU [47] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflow (Mean ± SD) | Outflow (Mean ± SD) | Reduction (%) | N a | ||||
| BOD5 | mg L–1 | 285 ± 169 | 9.0 ± 11 | 96 | 88 | 40 | 10 e/25 f/25 g/25 h |
| COD | mg L–1 | 744 ± 653 | 42 ± 31 | 92 | 103 | 150 | n.p. |
| TSS | mg L–1 | 344 ± 687 | 6.0 ± 6.5 | 93 | 99 | n.p. | 10 e/35 f/35 g/35 h |
| NH4-N | mg L–1 | 16 ± 7 | 2.4 ± 2.7 | 83 | 103 | n.p. | n.p. |
| NO3-N | mg L–1 | 0.4 ± 0.7 | 5.3 ± 4.7 | - | 103 | n.p. | n.p. |
| TN | mg L–1 | 34 ± 16 | 11 ± 7 | 66 | 104 | n.p. | n.p. |
| TP | mg L–1 | 2.5 ± 2.6 | 0.24 ± 0.33 | 85 | 103 | n.p. | n.p. |
| AS | mg L–1 | 7.9 ± 4.4 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 93 | 51 b | n.p. | n.p. |
| E. coli | MPN 100 mL–1 | 2.8 × 106 ± 4.1 × 106 | 4.4 × 104 ± 1.9 × 105 | 1.81 c | 100 | n.p. | 10 e/100 f/1000 g/10,000 h |
| pH | - | 7.0 ± 0.4 | 7.7 ± 0.2 | - | 102 | n.p. | n.p. |
| DO | mg L–1 | 0.8 ± 0.7 | 10.4 ± 3.2 | - | 102 | n.p. | n.p. |
| Eh | mV | −246 ± 50 | 147 ± 43 | - | 102 | n.p. | n.p. |
| EC | µS cm–1 | 1054 ± 276 | 1034 ± 239 | - | 102 | n.p. | n.p. |
| Parameters | Mass Loading and Removal Rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loading Rate (g m–2 d–1) | Removal Rate (g m–2 d–1) | Efficiency (%) | N a | |
| BOD5 | 12.8 ± 12 | 11.8 ± 12 | 96 | 92 |
| COD | 36 ± 41 | 33.4 ± 39 | 93 | 105 |
| TSS | 15.2 ± 30 | 14.9 ± 30 | 94 | 99 |
| NH4-N | 0.73 ± 0.55 | 0.59 ± 0.47 | 84 | 103 |
| NO3-N | 0.02 ± 0.03 | - | - | 103 |
| TN | 1.53 ± 1.3 | 1.10 ± 1.05 | 71 | 102 |
| TP | 0.11 ± 0.16 | 0.10 ± 0.15 | 87 | 103 |
| AS | 0.45 ± 0.39 | 0.43 ± 0.38 | 94 | 51 b |
| E. coli | 1.48 × 109 c | 2.02 × 107 d | 1.86 e | 97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahman, K.Z.; Chen, X.; Blumberg, M.; Bernhard, K.; Müller, R.A.; Mackenzie, K.; Trabitzsch, R.; Moeller, L. Effect of Hydraulic Loading Rate on Treatment Performance of a Pilot Wetland Roof Treating Greywater from a Household. Water 2023, 15, 3375. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193375
Rahman KZ, Chen X, Blumberg M, Bernhard K, Müller RA, Mackenzie K, Trabitzsch R, Moeller L. Effect of Hydraulic Loading Rate on Treatment Performance of a Pilot Wetland Roof Treating Greywater from a Household. Water. 2023; 15(19):3375. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193375
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Khaja Zillur, Xiaoyan Chen, Michael Blumberg, Katy Bernhard, Roland A. Müller, Katrin Mackenzie, Ralf Trabitzsch, and Lucie Moeller. 2023. "Effect of Hydraulic Loading Rate on Treatment Performance of a Pilot Wetland Roof Treating Greywater from a Household" Water 15, no. 19: 3375. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193375
APA StyleRahman, K. Z., Chen, X., Blumberg, M., Bernhard, K., Müller, R. A., Mackenzie, K., Trabitzsch, R., & Moeller, L. (2023). Effect of Hydraulic Loading Rate on Treatment Performance of a Pilot Wetland Roof Treating Greywater from a Household. Water, 15(19), 3375. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193375