The Source, Distribution, and Environmental Effects of Suspended Particulate Matter in the Yangtze River System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data Sources
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Sample Collection
3.3. Sample Filtration
4. Spatiotemporal Distribution of SPM
4.1. Temporal Distribution
4.2. Spatial Distribution
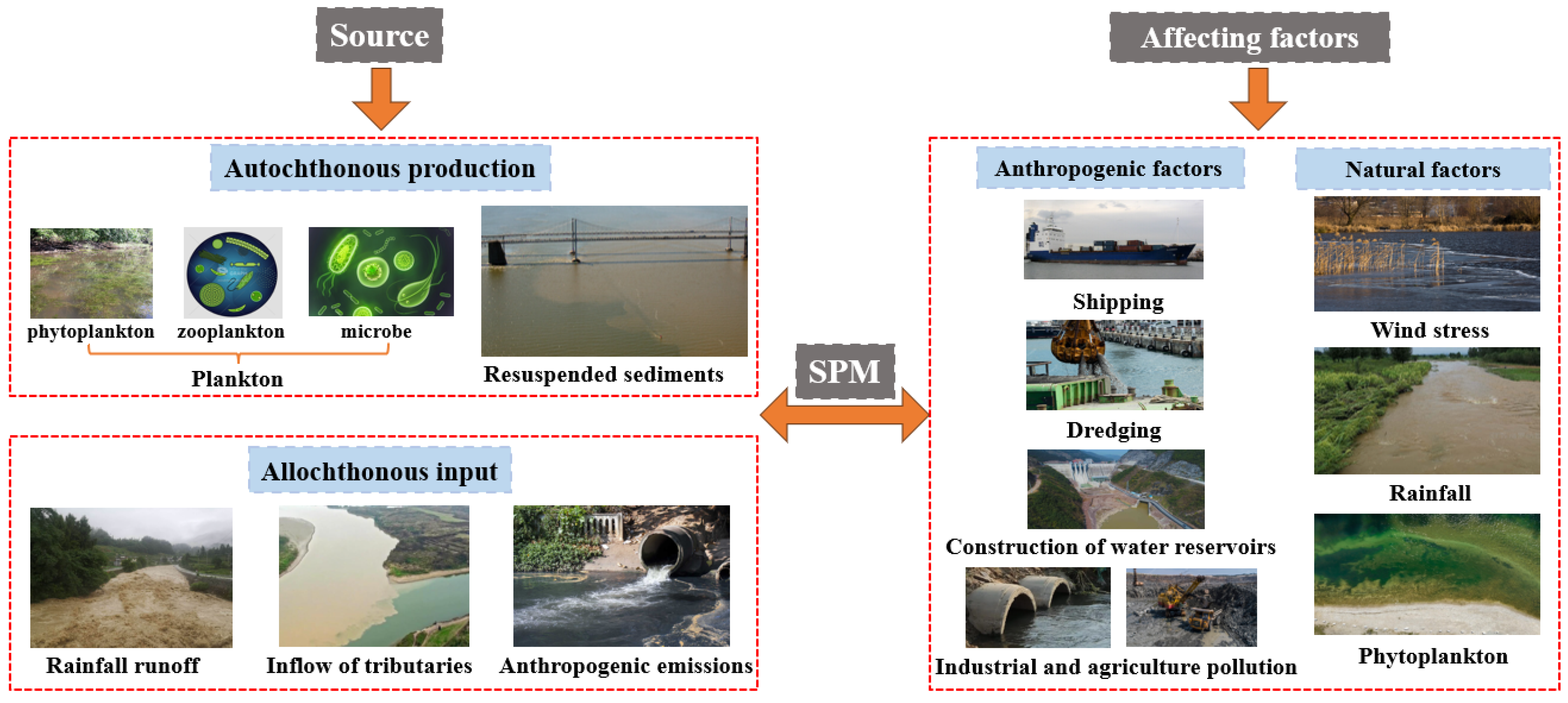
5. The Source of SPM and the Factors That Affect Its Concentration Level
5.1. Sources of SPM
5.1.1. Autochthonous Production
5.1.2. Allochthonous Input
5.2. Affecting Factors
5.2.1. Anthropogenic Factors
Shipping
Dredging
Construction of Water Reservoirs
Industrial and Agricultural Pollution
5.2.2. Natural Factors
Wind Stress
Rainfall
Phytoplankton
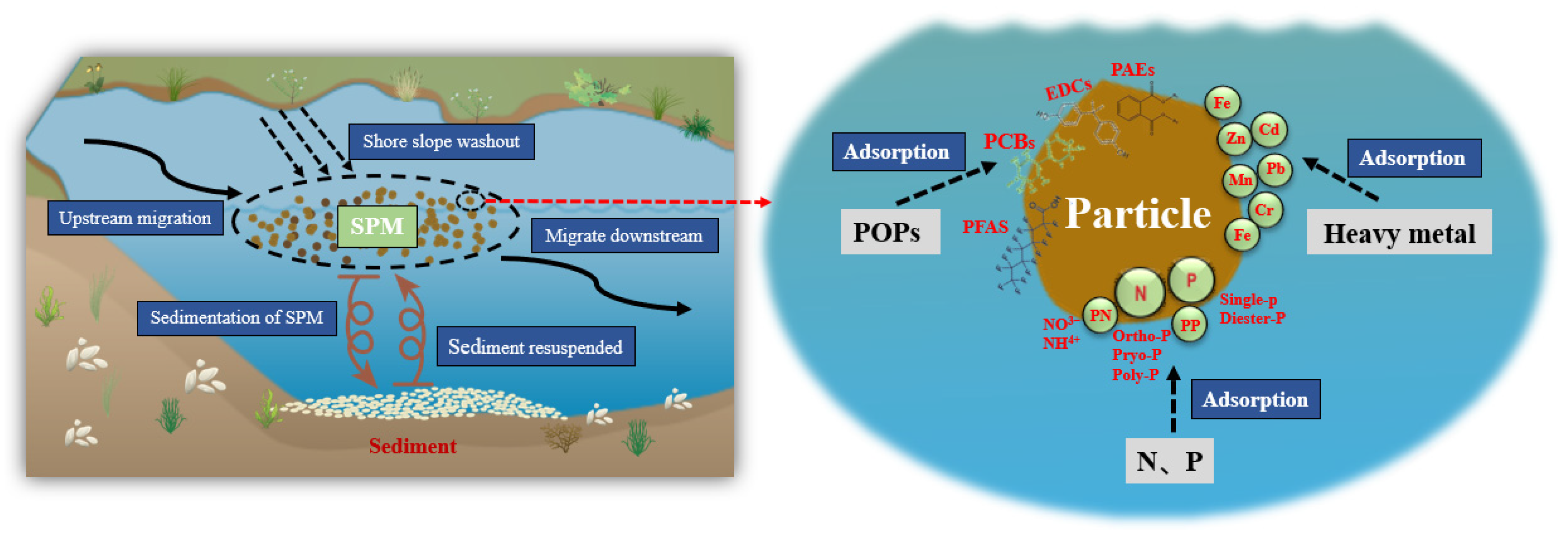
6. The Effects of SPM on Contamination
6.1. The Sorption of N and P on SPM
6.2. The Sorption of Heavy Metals on SPM
6.3. The Sorption of Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) on SPM
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, M.; Zhu, K.; Bi, Y.; Hu, Z. Spatiotemporal patterns of surface-suspended particulate matter in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 23, 3569–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helene, W.; Frank, v.d.K.; Thilo, H. Freshwater suspended particulate matter—Key components and processes in floc formation and dynamics. Water Res. 2022, 220, 118655. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Duan, H.; Shen, M.; Ma, R.; Xue, K.; Liu, D.; Xiao, Q. Using VIIRS/NPP and MODIS/Aqua data to provide a continuous record of suspended particulate matter in a highly turbid inland lake. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 64, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, R.; Jickells, T. The transport of material to the oceans: The atmospheric pathway. In Marine Geochemistry; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; Gao, M. Decline of suspended particulate matter concentrations in Lake Taihu from 1984 to 2020: Observations from Landsat TM and OLI. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 22572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, S.; Yang, S. Influence of Three Gorges Dam and drought on particulate organic carbon flux and its source in the lower Yangtze River. Biogeochemistry 2022, 158, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Ma, R.; Loiselle, S.A.; Duan, H.; Su, W.; Cai, W.; Huang, C.; Yang, J.; Yu, W. Remote sensing of particulate organic carbon dynamics in a eutrophic lake (Taihu Lake, China). Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Li, C.; Ding, H.; Gao, Y. Source and flux of POC in a karstic area in the Changjiang River watershed: Impacts of reservoirs and extreme drought. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 3687–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meybeck, M. Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus transport by world rivers. Am. J. Sci. 1982, 282, 401–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Duan, H.; Yu, S.; Shen, M.; Xue, K. Human-induced eutrophication dominates the bio-optical compositions of suspended particles in shallow lakes: Implications for remote sensing. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Ma, R.; Shen, M.; Li, Y.; Duan, H.; Cao, Z.; Wang, D.; Xiong, J. Variations of suspended particulate concentration and composition in Chinese lakes observed from Sentinel-3A OLCI images. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann-Timm, H. Characteristics, dynamics and importance of aggregates in rivers—An invited review. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2002, 87, 197–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Shan, B.; Sun, B.; Guo, X.; Li, Z. Risk assessment of heavy metals in suspended particulate matter in a typical urban river. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 46649–46664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keßler, S.; Pohlert, T.; Breitung, V.; Wilcsek, K.; Bierl, R. Comparative evaluation of four suspended particulate matter (SPM) sampling devices and their use for monitoring SPM quality. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 27, 5993–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Hua, P.; Zhang, J.; Krebs, P. A decline in the concentration of PAHs in Elbe River suspended sediments in response to a source change. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L.; Mikrenska, M.; Petrov, K.; Foster, I. Suspended particulate matter (SPM) in rivers: Empirical data and models. Ecol. Model. 2004, 183, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Holbach, A.; Wilhelms, A.; Krieg, J.; Qin, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zou, H.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Wu, T.; et al. Identifying spatio-temporal dynamics of trace metals in shallow eutrophic lakes on the basis of a case study in Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wen Huang, W.; Wang, Q. Concentration and partitioning of particulate trace metals in the Changjiang (Yangtze River). Water Air Soil Pollut. 1990, 52, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Shen, Z.; Niu, J.; Cai, Y. Residues of organochlorine pesticides in water and suspended particulate matter from the Yangtze River catchment of Wuhan, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 137, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Fang, H.; Huang, L.; Cui, Z. Particulate organic carbon dynamics with sediment transport in the upper Yangtze River. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Yang, C.; Yin, H. Dynamics of phosphorus composition in suspended particulate matter from a turbid eutrophic shallow lake (Lake Chaohu, China): Implications for phosphorus cycling and management. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yu, J.; Song, Y.; Zhu, G.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of different forms of inorganic nitrogen in three types of rivers around Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 6898–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Yang, T.; Zhou, R.; Zhu, Z.; An, S. Assessment and sources of heavy metals in the suspended particulate matter, sediments and water of a karst lake in Guizhou Province, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 189, 114636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Fan, C.; Xu, F.; Chen, K.; Gu, X. Temporal occurrence and sources of persistent organic pollutants in suspended particulate matter from the most heavily polluted river mouth of Lake Chaohu, China. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, S. Complex responses of suspended particulate matter in eutrophic river and its indicative function in river recovery process. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Pan, D.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Li, T.; Xu, Y.; Gong, C.; Zhang, L. Satellite-derived particulate organic carbon flux in the Changjiang River through different stages of the Three Gorges Dam. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 223, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Deng, B. Seasonal variation of heavy metals in suspended sediments downstream the Three Gorges Dam in the Yangtze River. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Fan, D.; Sun, X.; Sun, X.; Liu, M.; Yang, Z. Characteristics and Origins of Suspended Pyrite in the Mixing Zone of the Yangtze Estuary. J. Ocean Univ. China 2020, 19, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, D.; Xu, H. Qualitative Dynamics of Suspended Particulate Matter in the Changjiang Estuary from Geostationary Ocean Color Images: An Empirical, Regional Modeling Approach. Sensors 2018, 18, 4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M. Seasonal changes of organic matter origins and anammox activity in the Changjiang Estuary deduced from multi-biomarkers in suspended particulates. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 1339–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Qadeer, A.; Liu, M.; Zhu, J.-M.; Huang, Y.-P.; Du, W.-N.; Wei, X.-Y. Occurrence, source, and partition of PAHs, PCBs, and OCPs in the multiphase system of an urban lake, Shanghai. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 106, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Duan, H.; Feng, L.; Ma, R.; Xue, K. Climate- and human-induced changes in suspended particulate matter over Lake Hongze on short and long timescales. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, M.; Lin, C.; Li, Y.; Hao, X.; Wang, A.; He, M.; Liu, X.; Ouyang, W. Distribution, partitioning, and health risk assessment of organophosphate esters in a major tributary of middle Yangtze River using Monte Carlo simulation. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.; Su, W.; Zhang, C.; Deng, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Lv, X.; Lu, C.; Li, S.; Ma, R.; et al. Satellite determining dominant sources of particulate organic carbon across different eutrophic waters. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Z.; Uwiringiyimana, E.; Wei, R.; Du, C.; Cui, M.; Fu, P. Phytoplankton dominates the suspended particulate nitrogen source in the Yangtze River. J. Hydrol. 2022, 615, 128607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, B.; Dong, X.; Ren, Y. Distribution, behavior and budget of Pb in suspended particles in the Changjiang Estuary and adjacent east China sea. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, J.; Guo, M.; Xu, H.; Zhang, S.; Shi, L.; Yao, C. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of alkylphenols, bisphenol A, and tetrabromobisphenol A in surface water, suspended particulate matter, and sediment in Taihu Lake and its tributaries. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 112, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, N.; Kong, X.-Z.; He, W.; He, Q.-S.; Liu, W.-X.; Xu, F.-L. Dustfall-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) over the fifth largest Chinese lake: Residual levels, source apportionment, and correlations with suspended particulate matter (SPM)-bound PAHs in water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 55388–55400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Teng, Y.; Song, L. Iron Isotopic Composition of Suspended Particulate Matter in Hongfeng Lake. Water 2019, 11, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Ji, J.; Wang, D.; Hou, Q.; Yu, T. Dissolved and particulate partitioning of trace elements and their spatial–temporal distribution in the Changjiang River. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 145, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Liu, Q.; Deng, X.; Liu, X.; Fang, S.; Xiong, Y.; Song, J. Organophosphate esters in water, suspended particulate matter (SPM) and sediments of the Minjiang River, China. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 2812–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Du, Y.; Kong, M.; Liu, C. Interactions of riverine suspended particulate matter with phosphorus inactivation agents across sediment-water interface and the implications for eutrophic lake restoration. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 327, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Chen, J.; Yuan, X.; Yang, Z.; Balsam, W.; Ji, J. Seasonal variation in the mineralogy of the suspended particulate matter of the lower Changjiang River at Nanjing, China. Clays Clay Miner. 2010, 58, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhelou, F.; Mansuy-Huault, L.; Lorgeoux, C.; Catteloin, D.; Collin, V.; Bauer, A.; Kanbar, H.J.; Gley, R.; Manceau, L.; Thomas, F.; et al. Suspended particulate matter collection methods influence the quantification of polycyclic aromatic compounds in the river system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 22717–22729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-Y.; He, W.; Liu, W.-X.; Yang, B.; He, Q.-S.; Yang, C.; Xu, F.-L. Impacts of anthropogenic activities on spatial variations of phthalate esters in water and suspended particulate matter from China’s lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, E.; Li, G.; Zhang, L.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Spatial and temporal variations of suspended solid concentrations from 2000 to 2013 in Poyang Lake, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, T.; Yang, F.; Chen, L.; Yan, L. Variability of particle size distribution with respect to inherent optical properties in Poyang Lake, China. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Lyu, H.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Du, C.; Zeng, S.; Wang, H.; et al. Temporal and spatial distribution of Kd(490) and its response to precipitation and wind in lake Hongze based on MODIS data. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Eglinton, T.I.; Zhang, J.; Montlucon, D.B. Spatiotemporal Variation of the Quality, Origin, and Age of Particulate Organic Matter Transported by the Yangtze River (Changjiang). J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2018, 123, 2908–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Bao, H.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; Kattner, G. Temporal variability of particulate organic carbon in the lower Changjiang (Yangtze River) in the post-Three Gorges Dam period: Links to anthropogenic and climate impacts. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2015, 120, 2194–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Zheng, B.; Qin, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Cao, W.; Chi, M. Impact of upstream river inputs and reservoir operation on phosphorus fractions in water-particulate phases in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Jian, X.; Shang, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Fu, H. Underestimated heavy metal pollution of the Minjiang River, SE China: Evidence from spatial and seasonal monitoring of suspended-load sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 142586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Tian, L.; Jiang, X.; Wu, H.; Yu, S. Human activities changed organic carbon transport in Chinese rivers during 2004–2018. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Fu, R.; Liu, Y.; Suo, C. Spatiotemporal variations of water quality and their driving forces in the Yangtze River Basin, China, from 2008 to 2020 based on multi-statistical analyses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 69388–69401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, L.; Ma, H.; Ji, J. Concentration and distribution characteristic of main toxic metals in suspended particle material in Nanjing reach, Changjiang River. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 173, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Gao, L. Dynamics of dissolved and particulate organic matter in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary and the adjacent East China Sea shelf. J. Mar. Syst. 2019, 198, 103188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Liu, C.-Q.; Wang, Z.-L.; Zhu, X.; Teng, Y.; Liang, L.; Tang, S.; Li, J. Iron isotope fractionation during biogeochemical cycle: Information from suspended particulate matter (SPM) in Aha Lake and its tributaries, Guizhou, China. Chem. Geol. 2011, 280, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G. Understanding the long-term trend of particulate phosphorus in a cyanobacteria-dominated lake using MODIS-Aqua observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, M.P. Linking the Dissolved and Particulate Domain of Organic Carbon in Inland Waters. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2021, 126, e2021JG006266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Li, W. Differences in the composition, source, and stability of suspended particulate matter and sediment organic matter in Hulun Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 27163–27174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiwei, L.; Xin, Y.; Keqiang, S.; Baohua, Z.; Guang, G. Unraveling the sources and fluorescence compositions of dissolved and particulate organic matter (DOM and POM) in Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 26, 4027–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; He, Y.; Dai, L.; He, Q.; Ai, H.; Yang, G.; Liu, M.; Jiang, W.; Li, H. Interactions between suspended particulate matter and algal cells contributed to the reconstruction of phytoplankton communities in turbulent waters. Water Res. 2019, 149, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Z.; Tan, X.; Ali, I.; Wu, X.; Cao, J.; Xu, Y.; Shi, L.; Gao, W.; Ruan, Y.; Chen, C. Comparison of organic matter (OM) pools in water, suspended particulate matter, and sediments in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China: Implication for dissolved OM tracking, assessment, and management. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Wei, Z.; Xiaoge, X.; Zongpu, X.; Lin, C. Vertical composition types of sediment and composition at sediment-water interface in Lake Taihu. Lake Sci. 2022, 34, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zehui, Z.; Zhong, P.; Cheng, Y.; Liao, M.; Jiao, Y. Longitudinal variation characteristics of stable isotope ratios of suspended particulate organic matter in the headwaters of the Qingjiang River, China. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2021, 422, 7 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, X.; Xia, P.; Yang, G.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H. Sources and features of particulate organic matter in tropical small mountainous rivers (SW China) under the effects of anthropogenic activities. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Wu, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Huang, C.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Z.; Du, C.; Mu, M.; Xu, J.; et al. Remote sensing monitoring of the suspended particle size in Hongze Lake based on GF-1 data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 40, 3179–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Du, Y.; Yin, H.; Fan, C.; Chen, K.; Zhong, J.; Gu, X. Exchanges of nitrogen and phosphorus across the sediment-water interface influenced by the external suspended particulate matter and the residual matter after dredging. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Chen, L. High Temporal Resolution Monitoring of Suspended Matter Changes from GOCI Measurements in Lake Taihu. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Navarro, G.; Ruiz, J. Multi-platform assessment of turbidity plumes during dredging operations in a major estuarine system. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 68, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Shen, F.; He, Q.; Cao, F.; Zhao, H.; Li, M. Changes in suspended sediments in the Yangtze River Estuary from 1984 to 2020: Responses to basin and estuarine engineering constructions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Gao, L.; Feng, M.; Qin, L.; Shi, J.; Cheng, D. Polychlorinated diphenyl ethers (PCDEs) in surface sediments, suspended particulate matter (SPM) and surface water of Chaohu Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Du, C.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Lyu, H.; Mu, M.; Miao, S.; et al. An approach for retrieval of horizontal and vertical distribution of total suspended matter concentration from GOCI data over Lake Hongze. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, F.G.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, B. Lake Topography and Wind Waves Determining Seasonal-Spatial Dynamics of Total Suspended Matter in Turbid Lake Taihu, China: Assessment Using Long-Term High-Resolution MERIS Data. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Q.; Xiao-Guang, X.; Kuan, S.; Li-Min, Z.; Yang, Z.; Hui, L.; Xin-Ting, W.; Guo-Xiang, W.; Han, M. In situ resuspension rate monitoring method in the littoral zone with multi-ecotypes of a shallow wind-disturbed lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 7476–7485. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C. Estimation on dynamic release of phosphorus from wind-induced suspended particulate matter in Lake Taihu. Sci. China Ser. D 2004, 47, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Qin, B. Monitoring the river plume induced by heavy rainfall events in large, shallow, Lake Taihu using MODIS 250m imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 173, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Sun, J.; Zhou, Y.; Gu, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J. Variations of different dissolved and particulate phosphorus classes during an algae bloom in a eutrophic lake by 31P NMR spectroscopy. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Li, S.; Han, X.; Chen, Q.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Q. Characterization and source identification of nitrogen in a riverine system of monsoon-climate region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chen, K.; Wang, Z.; Fan, C.; Gu, X.; Huang, W. Nitrogen exchange across the sediment-water interface after dredging: The influence of contaminated riverine suspended particulate matter. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yao, H.; Wu, B.; Wang, B.; Chen, J. Limited capacity of suspended particulate matter in the Yangtze river estuary and hangzhou bay to carry phosphorus into coastal seas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 258, 107417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Chao, J.; Zhuang, W.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.; Hou, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L.; Gao, G.; Wang, Y. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Particulate Phosphorus and Their Correlation with Environmental Factors in a Shallow Eutrophic Chinese Lake (Lake Taihu). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labry, C.; Youenou, A.; Delmas, D.; Michelon, P. Addressing the measurement of particulate organic and inorganic phosphorus in estuarine and coastal waters. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 60, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Fan, C.; Shen, Q.; Shao, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Q. Effects of riverine suspended particulate matter on post-dredging metal re-contamination across the sediment–water interface. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 2329–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Liu, C.-Q.; Zhu, X.; Ngwenya, B.T.; Wang, Z.; Song, L.; Li, J. Zinc Isotope Characteristics in the Biogeochemical Cycle as Revealed by Analysis of Suspended Particulate Matter (SPM) in Aha Lake and Hongfeng Lake, Guizhou, China. J. Earth Sci. 2019, 31, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, G.; Zhang, Q. Effects of agricultural abandonment on soil aggregation, soil organic carbon storage and stabilization: Results from observation in a small karst catchment, Southwest China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 288, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Dong, J.; Fan, Z.; Yan, H.; Mao, F. Key role of suspended particulate matter in assessing fate and risk of endocrine disrupting compounds in a complex river-lake system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Mao, W.; Shen, Y.; Feng, W.; Mao, G.; Zhao, T.; Yang, L.; Yang, L.; Meng, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Distribution, source, and environmental risk assessment of phthalate esters (PAEs) in water, suspended particulate matter, and sediment of a typical Yangtze River Delta City, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 24609–24619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Song, K.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; He, W.; Xu, F. Suspended particulate matter (SPM)-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in lakes and reservoirs across a large geographical scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 142863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Zhang, X.; Li, R.; Tu, W.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Mai, B. Spatiotemporal distribution, partitioning behavior and flux of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in surface water and sediment from Poyang Lake, China. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, S.L.; Xu, W.; Cui, W.Y.; Zhang, J. Occurrence of Chlorophenol Compounds in Aquatic Environments of China and Effect of Suspended Particles on Toxicity of These Chemicals to Aquatic Organisms: A Review. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 7901–7913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-z.; Meng, W.; Zhang, Y. Occurrence and Partitioning of Phenolic Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs) Between Surface Water and Suspended Particulate Matter in the North Tai Lake Basin, Eastern China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 92, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wang, Q.; He, W.; Xu, F. The occurrence, composition and partitioning of phthalate esters (PAEs) in the water-suspended particulate matter (SPM) system of Lake Chaohu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Sampling Machine | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Picture | Features | References |
| Niskin sampler (General Oceanics Inc., Miami, FL, USA) |  | It features a “smooth flow” structure of the sampling tube, and there are no cone valves or ball valves at either end of the sampling tube to obstruct the flow of water through the sampling tube. | [27] |
| Binnensammler floating collector (BS) |  | Two vertical fins at the bottom and rear ensure a stable position parallel to the flow direction, and the funnel-shaped interior of the BS acts as a sedimentation disc as the SPM-water mixture moves from horizontal flow mode to circulating flow mode. | [14] |
| Self-constructed Phillips sampler (PS) |  | PS is characterized by reducing the flow rate by expanding the diameter from 4 mm (inlet) to 100 mm (central cavity). | |
| Continuous-flow centrifuge (CFC) |  | CFC is characterized by the fact that sampling sites are limited to flat sidewalks by the river, SPM is collected on the surface of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)-coated CFC bowl, and wet sediment samples can be taken directly from the CFC bowl. | |
| Hydrocyclone (HC) |  | HC is characterized by the fact that water enters the cylinder at a high flow rate and is forced to form a downward vortex, which, due to the action of centrifugal force, the particles are pressed against the wall, where they are deposited, and then collected in a tank. | |
| Rosette sampler |  | Rosette multichannel water sample collector with a maximum sampling depth of 1500 m is suitable for nearshore and river water collection. | [28] |
| Hydro’s integrated water sampler |  | It is used for columnar integral sampling of the water body, and the sampling depth can be freely set. Columnar water samples of different depths can be obtained. | [29] |
| Van Dorn sampler |  | It is divided into horizontal and vertical samplers. Horizontal samplers collect water samples of specific water formations, especially on the demarcation layer or sediment surface. Vertical samplers are used in weakly corroded water bodies and are suitable for plankton and floating sediment collection. | [1] |
| Sediment trap |  | Multichannel sedimentation traps are designed primarily for the automated collection of sediments from lakes, continental shelves, and aquatic environments with relatively vertical particle flows. | [24] |
| Water pump |  | The water pump rotates through the impeller at high speed. The liquid rotates with the blades and, under the action of centrifugal force, flows out from the nozzle. The submersible pump is unsuitable for VOCs sampling, and its disturbance is significant. | [30] |
| Manual sampler | |||
| Name | Picture | Features | References |
| Plexiglass water sampler |  | It collects water samples within 0~30 m depth of rivers, lakes, reservoirs, and oceans. The top two semi-circle upper caps can be easily opened and closed, and the bottom is equipped with round holes and floating plates to ensure that when the bottle body sinks underwater, the water flow can freely enter and exit the body. | [31] |
| Polyethylene water sampler |  | When the components to be measured of the collected sample are divided into the main parts of glass, it is best to use a polyethylene water sample collector. | [32] |
| Stainless steel water sampler |  | It is suitable for water sample collection for analyzing organic matter, microorganisms (bacteria), and other indicators and for collecting corrosive samples containing acid and alkali. | [33] |
| Filter Filtration | ||
|---|---|---|
| Name | Size | References |
| Whatman GF/F glass ultrafiber filter (Whatman, UK) | 0.7 μm pore size, 47 mm diameter | [34] |
| 0.45 μm pore size, 47 mm diameter | [35] | |
| 0.7 μm pore size, 25 mm diameter | [36] | |
| 0.45 μm pore size, 50 mm diameter | [37] | |
| 0.45 μm pore size | [38] | |
| Cellulose acetate filter (Sartorius, Germany) | 0.45 μm pore size, 47 mm diameter | [27] |
| Microporous HA membrane filter Millipore HA (MilliporeSigma, Burlington, MA, USA) | 0.45 μm pore size,47 mm diameter | [39] |
| Fiber filters | 0.7 μm pore size | [29] |
| Normal filter | 0.45 μm pore size | [40] |
| 0.20 μm pore size | ||
| Quartz filter | 0.45 mm | [41] |
| Membrane filtration | ||
| Name | Size | References |
| PTFE membrane | 0.45 μm | [42] |
| Millipore membrane | 0.45 μm | [43] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, J.; Yang, J.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, S. The Source, Distribution, and Environmental Effects of Suspended Particulate Matter in the Yangtze River System. Water 2023, 15, 3429. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193429
Fan J, Yang J, Cheng F, Zhang S. The Source, Distribution, and Environmental Effects of Suspended Particulate Matter in the Yangtze River System. Water. 2023; 15(19):3429. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193429
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Jianxin, Jiaxin Yang, Fulong Cheng, and Shikuo Zhang. 2023. "The Source, Distribution, and Environmental Effects of Suspended Particulate Matter in the Yangtze River System" Water 15, no. 19: 3429. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193429
APA StyleFan, J., Yang, J., Cheng, F., & Zhang, S. (2023). The Source, Distribution, and Environmental Effects of Suspended Particulate Matter in the Yangtze River System. Water, 15(19), 3429. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193429





