Experimental Study of Wave Overtopping Flow Behavior on Composite Breakwater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
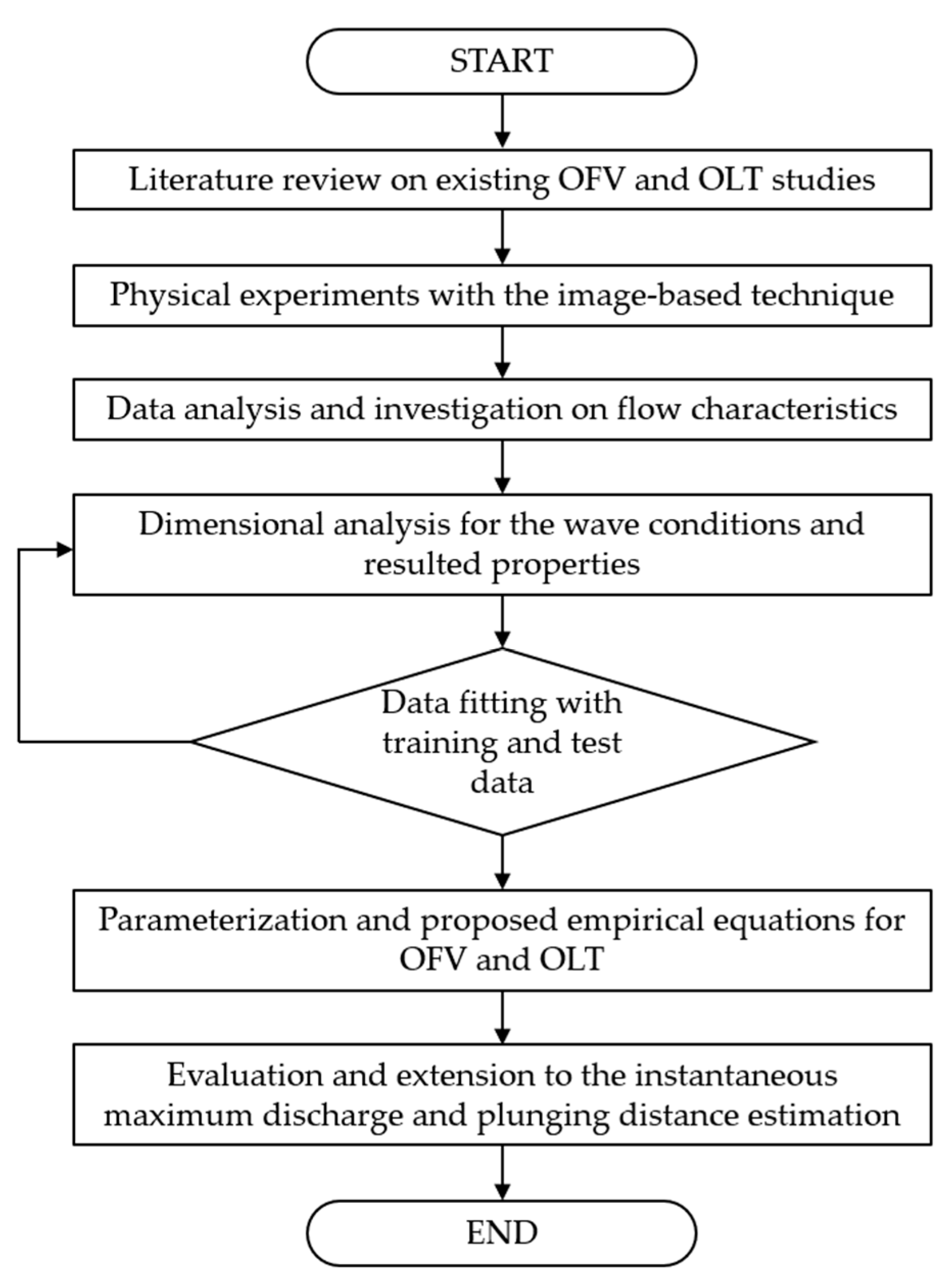
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Review

2.2. New Wave Overtopping Estimator
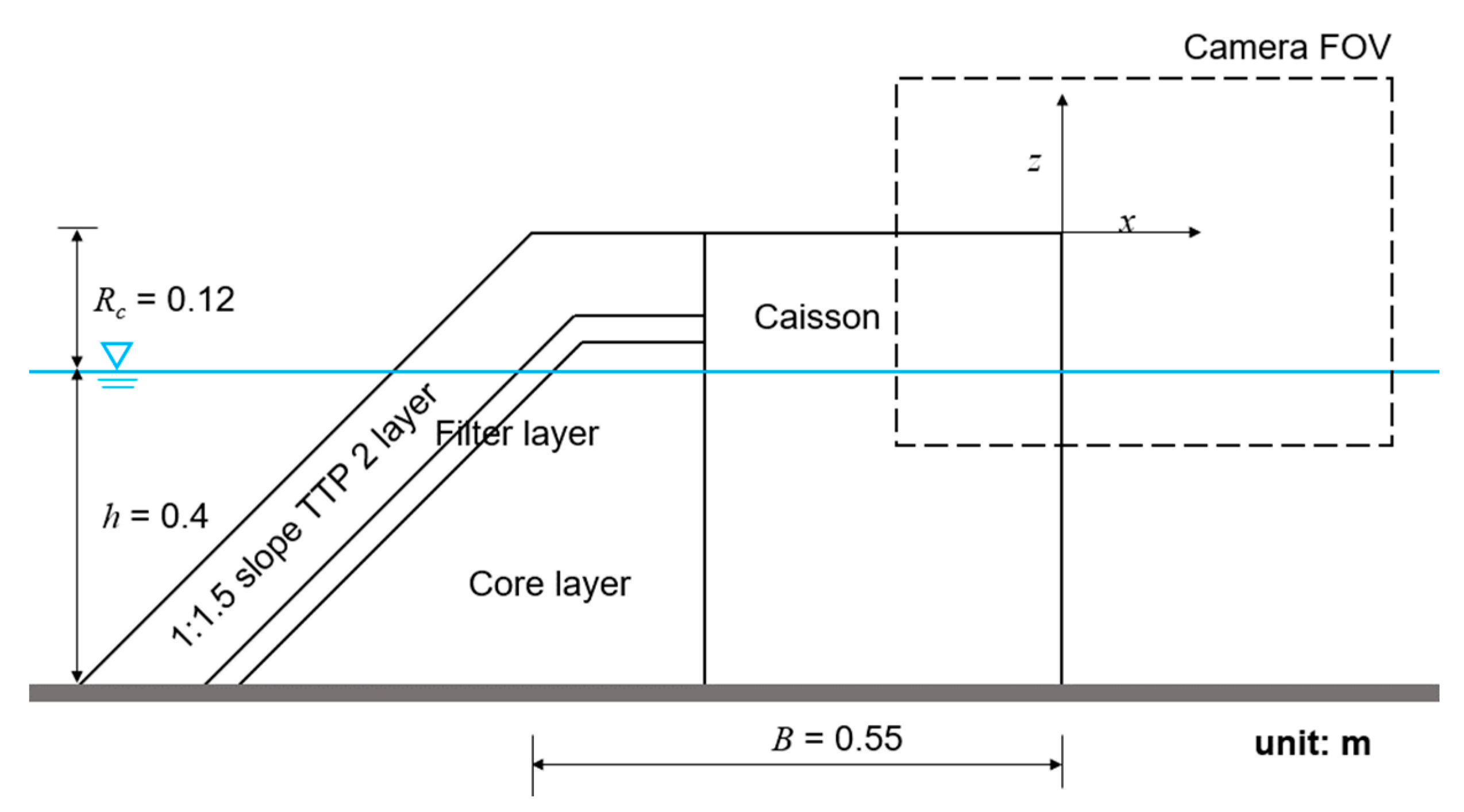
2.3. Setup of the Experiments
2.4. Measurement Instruments
2.5. Test Conditions
3. Results
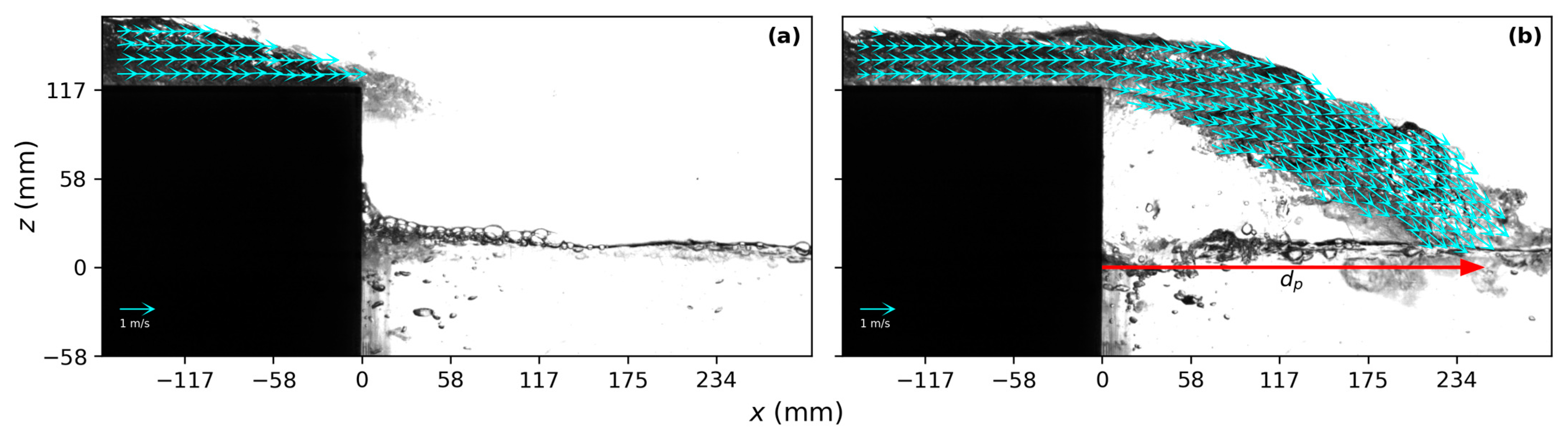
3.1. Flow Pattern of the Overtopping Flow
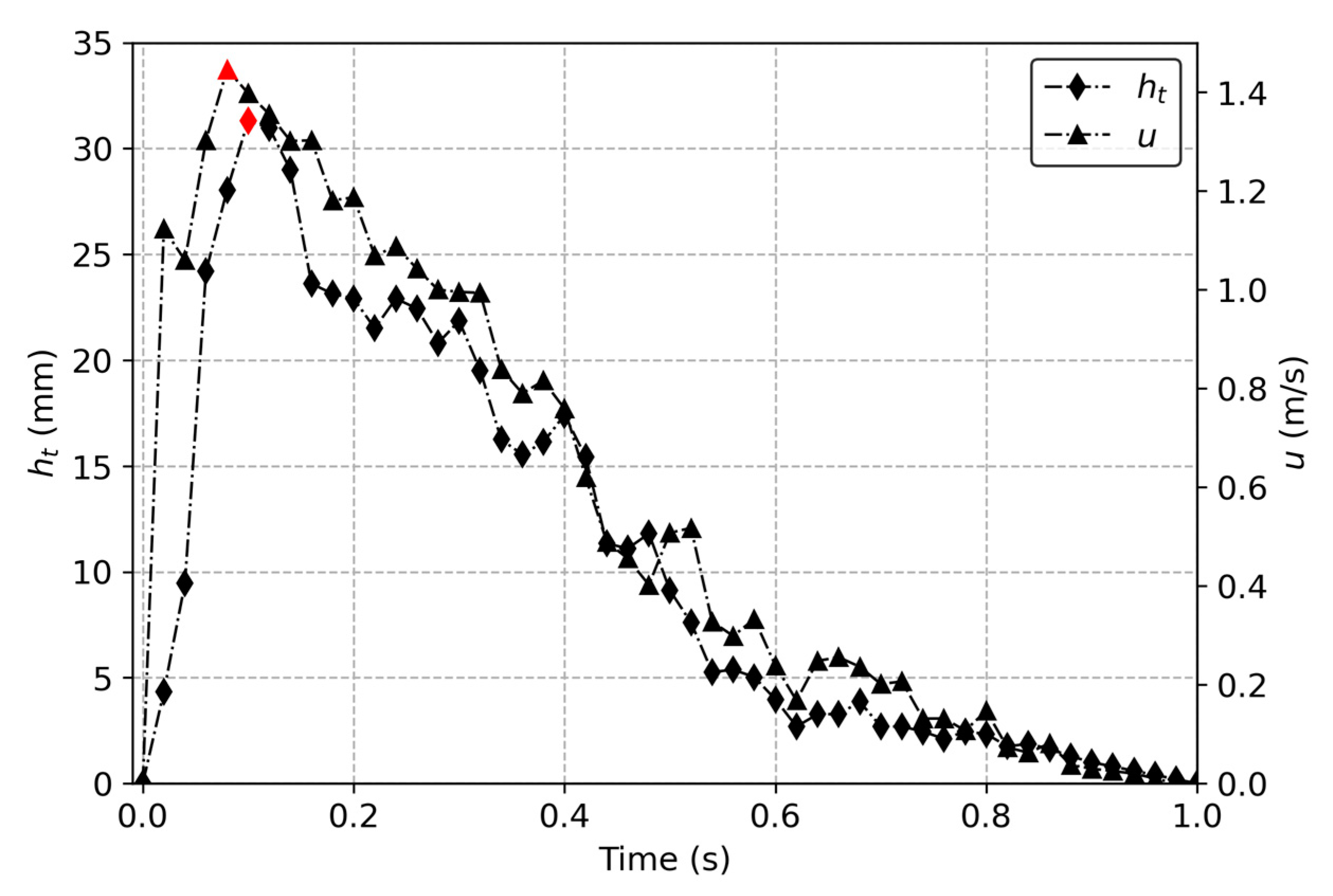
3.2. Overtopping Flow Velocity
3.3. Overtopping Layer Thickness
3.4. Maximum Instantaneous Overtopping Discharge
3.5. Plunging Distance
4. Discussion
- Define the following irregular wave parameters for the design structure: the significant wave height (), the averaged wave period (), and the relative crest freeboard parameter ().
- Calculate the wave steepness () and the relative crest freeboard parameter ().
- Compute the empirical parameters, , , and , for Equation (14) and calculate the empirical parameters, , , and , for Equation (15).
- Estimate the expected maximum OFV using Equation (14) and the maximum OLT using Equation (15).
- Plot the OFV and OLT for a given range of wave steepness values and relative crest freeboard.
- Utilize the range of the OFV and OLT for an early investigation of wave overtopping parameters based on the given wave and structure conditions.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| coefficient in Equation (17) | |
| coefficient in Equation (14) | |
| crest width | |
| coefficient in Equation (17) | |
| coefficient in Equation (14) | |
| wave celerity | |
| coefficient in Equation (8) | |
| coefficient in Equation (3) | |
| coefficient in Equation (2) | |
| coefficient in Equation (6) | |
| coefficient in Equation (9) | |
| plunging distance | |
| acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s2) | |
| regular wave height | |
| still water depth at structure’s toe | |
| significant wave height from spectral analysis | |
| significant wave height defined as highest one-third of wave heights () | |
| average of highest 1/x th of wave heights | |
| root mean square wave height | |
| flow thickness | |
| wave overtopping layer thickness | |
| wave run-up layer thickness | |
| coefficient in Equation (7) | |
| wave length | |
| foreshore slope | |
| exponential coefficient in Equation (17) | |
| exponential coefficient in Equation (14) | |
| instantaneous maximum wave overtopping discharge | |
| coefficient of determination | |
| crest freeboard | |
| wave run-up height | |
| regular wave period | |
| spectral peak wave period | |
| significant wave period () | |
| spectral wave period | |
| averaged wave period | |
| flow velocity | |
| wave overtopping flow velocity | |
| wave run-up velocity | |
| location on structure crest, measured horizontally from structure seaward edge | |
| location on seaward slope, measured vertically from still water level | |
| angle between structure slope and horizontal | |
| influence factor for a berm | |
| influence factor for oblique wave attack | |
| influence factor for the permeability and roughness of or on the slope | |
| Iribarren’s number | |
| ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter (3.14) |
Appendix A
| Author | Equations | Note |
|---|---|---|
| EurOtop [5] | Fictitious wave run-up height: with a maximum of where is given by Wave run-up velocity at seaward edge: OFV along the structure crest: | Originally developed for impermeable structure Seadike; however, it is applicable for rough and permeable slope structure. The roughness factor and empirical coefficient need to be calibrated for different types of armor units and slope angles, as shown in [17,31]. |
| Mares-Nassare et al. [20] | The equation was derived for rubble mound breakwater with three different armors: 1-layer Cubipod, 2-layer cube and 2-layer rock. The value of coefficient, , for each armor unit is available in Table 3. | |
| Present Study | The equation was derived based on composite breakwater with 2-layer tetrapod armor unit and permeable core. The value of each coefficient is 0.98, 0.14, and 1.41. |
| Authors | Equations | Note |
|---|---|---|
| EurOtop [5] | Fictitious wave run-up height: with a maximum of where is given by Wave run-up layer thickness at seaward edge: OLT along the structure crest: | The same fictitious wave run-up height equation can be used in OLT estimation as well. It is also recommended to calibrate the roughness factor and empirical coefficient for different type of armor unit and slope angle. Example of the application can also be found in [17,31]. |
| Mares-Nassare et al. [20] | The equation was derived for rubble mound breakwater with three different armors: 1-layer Cubipod, 2-layer cube, and 2-layer rock. The value of coefficient, , for each armor units are available in Table 2. | |
| Present Study | The equation was derived based on composite breakwater with 2-layers tetrapod armor unit and permeable core. The value of each coefficient is 0.24, 0.15, and 0.52. |
Appendix B
| Author | Training Dataset | Test Dataset | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| This study (Equation (14)) | 0.955 | 0.001 | 0.920 | 0.010 |
| Adibhusana et al. [31] | 0.735 | 0.026 | 0.714 | 0.005 |
| Mares-Nassare et al. [20]: 2-Layer rock 2-Layer cube 1-Layer Cubipod | 0.000 0.000 0.000 | 0.704 0.728 0.762 | 0.000 0.000 0.000 | 0.698 0.727 0.761 |
| EurOtop [5] | 0.701 | 0.077 | 0.695 | 0.100 |
| Author | Training Dataset | Test Dataset | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| This study (Equation (15)) | 0.815 | 0.051 | 0.701 | 0.095 |
| Adibhusana et al. [31] | 0.390 | 0.027 | 0.237 | 0.083 |
| Mares-Nassare et al. [20]: 2-Layer rock 2-Layer cube 1-Layer Cubipod | 0.000 0.000 0.000 | 1.897 1.218 1.025 | 0.000 0.000 0.000 | 2.147 1.449 1.242 |
| EurOtop [5] | 0.340 | 0.014 | 0.282 | 0.094 |
| Coefficient | Original | Modified | Difference (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Value | Value | |||||||
| Training | Test | Training | Test | Training | Test | ||||
| 1.330 | 0.001 | 0.010 | 1.396 | 0.095 | 0.087 | 5 | 9,400 | 970 | |
| 0.136 | 0.001 | 0.010 | 0.143 | 0.050 | 0.042 | 5 | 4,900 | 520 | |
| 1.416 | 0.001 | 0.010 | 1.487 | 0.043 | 0.057 | 5 | 4,400 | 470 | |
| Coefficient | Original | Modified | Difference (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Value | Value | |||||||
| Training | Test | Training | Test | Training | Test | ||||
| 0.305 | 0.051 | 0.095 | 0.321 | 0.246 | 0.308 | 5 | 382 | 224 | |
| 0.174 | 0.051 | 0.095 | 0.182 | 0.181 | 0.239 | 5 | 255 | 152 | |
| 0.545 | 0.051 | 0.095 | 0.572 | 0.092 | 0.064 | 5 | 280 | 167 | |
References
- Bae, H.U.; Yun, K.M.; Yoon, J.Y.; Lim, N.H. Human Stability with Respect to Overtopping Flow on the Breakwater. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2016, 11, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Ma, X.; Dong, G.; Chen, H.; Liu, Q.; Zang, J. Investigation on the Effects of Bragg Reflection on Harbor Oscillations. Coast. Eng. 2021, 170, 103977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Shi, H.; Zang, J.; Liu, Y. Mechanism Analysis on the Mitigation of Harbor Resonance by Periodic Undulating Topography. Ocean Eng. 2023, 281, 114923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-H.; Heo, K.-Y.; Son, J.-H.; Jo, Y.-H.; Choi, J.-Y.; Kwon, J.-I. Characteristics of Swell-like Waves in the East Coast of Korea Using Atmospheric and Wave Hindcast Data. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meer, J.W.; Allsop, N.W.H.; Bruce, T.; De Rouck, J.; Kortenhaus, A.; Pullen, T.; Schüttrumpf, H.; Troch, P.; Zanuttigh, B. EurOtop-Manual on Wave Overtopping of Sea Defences and Related Structures: An Overtopping Manual Largely Based on European Research, but for Worldwide Application; TU Delft: Delft, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, L.; de Gerloni, M.; van der Meer, J.W. Wave Overtopping on Vertical And Composite Breakwaters. In Coastal Engineering; Edge, B.L., Ed.; American Society of Civil Engineers: Kobe, Japan, 1994; pp. 1030–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, D.; Yuan, J.; Chen, H.; Zhao, K.; Liu, P.L.-F. Wave Overtopping Flow Striking a Human Body on the Crest of an Impermeable Sloped Seawall. Part I: Physical Modeling. Coast. Eng. 2021, 167, 103891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Chen, H.; Yuan, J. Inline Force on Human Body Due to Non-Impulsive Wave Overtopping at a Vertical Seawall. Ocean Eng. 2021, 219, 108300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abt, S.R.; Wittier, R.J.; Taylor, A.; Love, D.J. Human Stability in a High Flood Hazard Zone. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1989, 25, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endoh, K.; Takahasi, S. Numerically Modeling Personnel Danger on a Promenade Breakwater Due to Overtopping Waves. In Coastal Engineering 1994; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 1995; pp. 1016–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Jonkman, S.N.; Penning-Rowsell, E. Human Instability in Flood Flows. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2008, 44, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, C.; Bruce, T. Wave Overtopping Hazard to Pedestrians: Video Evidence from Real Accidents. In Coasts, Marine Structures and Breakwaters 2017; ICE Publishing: London, UK, 2018; pp. 501–512. [Google Scholar]
- Schüttrumpf, H.; Oumeraci, H. Layer Thicknesses and Velocities of Wave Overtopping Flow at Seadikes. Coast. Eng. 2005, 52, 473–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüttrumpf, H.; van Gent, M.R.A. Wave Overtopping at Seadikes. In Coastal Structures 2003; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2003; pp. 431–443. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Meer, J.W.; Hardeman, B.; Steendam, G.J.; Schuttrumpf, H.; Verheij, H. Flow Depths and Velocities at Crest and Landward Slope of a Dike, in Theory and with The Wave Overtopping Simulator. Coast. Eng. Proc. 2011, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gent, M.R.A.; Wolters, G.; Capel, A. Wave Overtopping Discharges at Rubble Mound Breakwaters Including Effects of a Crest Wall and a Berm. Coast. Eng. 2022, 176, 104151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mares-Nasarre, P.; Argente, G.; Gómez-Martín, M.E.; Medina, J.R. Overtopping Layer Thickness and Overtopping Flow Velocity on Mound Breakwaters. Coast. Eng. 2019, 154, 103561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.A.; Thornton, C.I.; Van der Meer, J.W.; Scholl, B.N. Improvements in Describing Wave Overtopping Processes. Coast. Eng. Proc. 2012, 1, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mares-Nasarre, P.; Gómez-Martín, M.E.; Medina, J.R. Influence of Mild Bottom Slopes on the Overtopping Flow over Mound Breakwaters under Depth-Limited Breaking Wave Conditions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mares-Nasarre, P.; Molines, J.; Gómez-Martín, M.E.; Medina, J.R. Explicit Neural Network-Derived Formula for Overtopping Flow on Mound Breakwaters in Depth-Limited Breaking Wave Conditions. Coast. Eng. 2021, 164, 103810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørgaard, J.Q.H.; Lykke Andersen, T.; Burcharth, H.F. Distribution of Individual Wave Overtopping Volumes in Shallow Water Wave Conditions. Coast. Eng. 2014, 83, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosman, G.; van der Meer, J.; Hoffmans, G.; Schüttrumpf, H.; Verhagen, H.J. Individual Overtopping Events at Dikes. Coast. Eng. 2009, 5, 2944–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gent, M.R.A. Wave Overtopping Events at Dikes. In Coastal Engineering 2002; World Scientific: Singapore, 2002; pp. 2203–2215. ISBN 978-981-238-238-2. [Google Scholar]
- Koosheh, A.; Etemad-Shahidi, A.; Cartwright, N.; Tomlinson, R.; van Gent, M.R.A. Individual Wave Overtopping at Coastal Structures: A Critical Review and the Existing Challenges. Appl. Ocean Res. 2021, 106, 102476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.; Chang, K.-A.; Lim, H.-J. Use of Bubble Image Velocimetry for Measurement of Plunging Wave Impinging on Structure and Associated Greenwater. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrozo-Acuña, A.; de Alegría-Arzaburu, A.R.; Torres-Freyermuth, A.; Mendoza, E.; Silva, R. Laboratory Investigation of Pressure Gradients Induced by Plunging Breakers. Coast. Eng. 2011, 58, 722–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Chang, K.; Huang, Z.; Na, B. Experimental Study on Plunging Breaking Waves in Deep Water. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 2007–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.; Chang, K.-A.; Mercier, R. Runup and Green Water Velocities Due to Breaking Wave Impinging and Overtopping. Exp. Fluids 2007, 43, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raby, A.; Jayaratne, R.; Bredmose, H.; Bullock, G. Individual Violent Wave-Overtopping Events: Behaviour and Estimation. J. Hydraul. Res. 2020, 58, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibhusana, M.N.; Lee, J.-I.; Ryu, Y. Wave Overtopping Plunging on the Rear Side of Composite Breakwater. J. Coast. Res. 2021, 114, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibhusana, M.N.; Lee, J.-I.; Kim, Y.-T.; Ryu, Y. Study of Overtopping Flow Velocity and Overtopping Layer Thickness on Composite Breakwater under Regular Wave. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, T.; van der Meer, J.W.; Franco, L.; Pearson, J.M. Overtopping Performance of Different Armour Units for Rubble Mound Breakwaters. Coast. Eng. 2009, 56, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüttrumpf, H.; Möller, J.; Oumeraci, H. Overtopping Flow Parameters on The Inner Slope of Seadikes. In Coastal Engineering 2002; World Scientific Publishing Company: Singapore, 2002; pp. 2116–2127. [Google Scholar]
- Molines, J.; Medina, J.R. Calibration of Overtopping Roughness Factors for Concrete Armor Units in Non-Breaking Conditions Using the CLASH Database. Coast. Eng. 2015, 96, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, Y. Random Seas and Design of Maritime Structures; World Scientific Publishing Company: Singapore, 2010; Volume 33, ISBN 9813101024. [Google Scholar]
- Kudale, M.D.; Kobayashi, N. Hydraulic Stability Analysis of Leeside Slopes of Overtopped Breakwaters. In Coastal Engineering 1996; American Society of Civil Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 1721–1734. [Google Scholar]

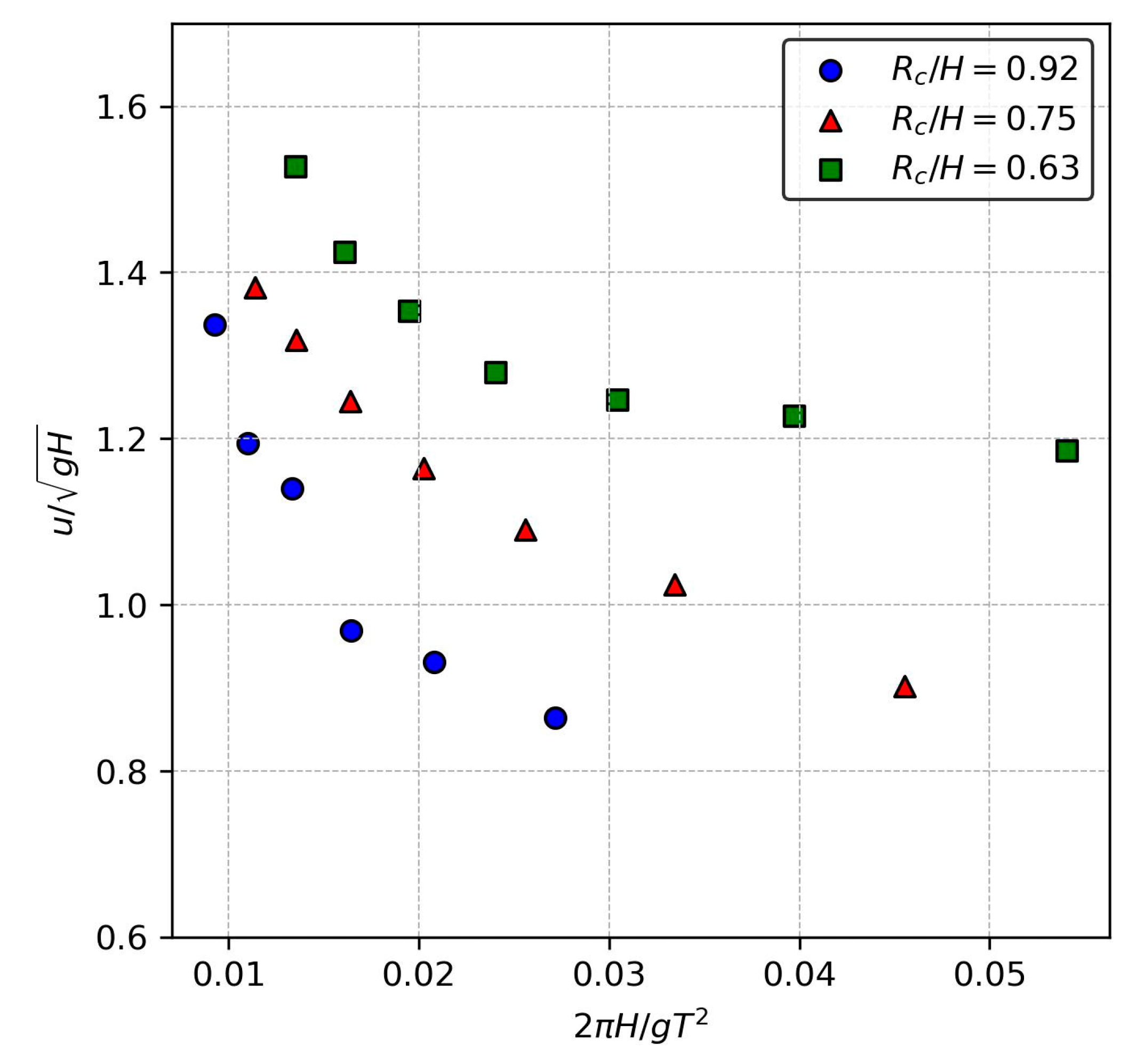


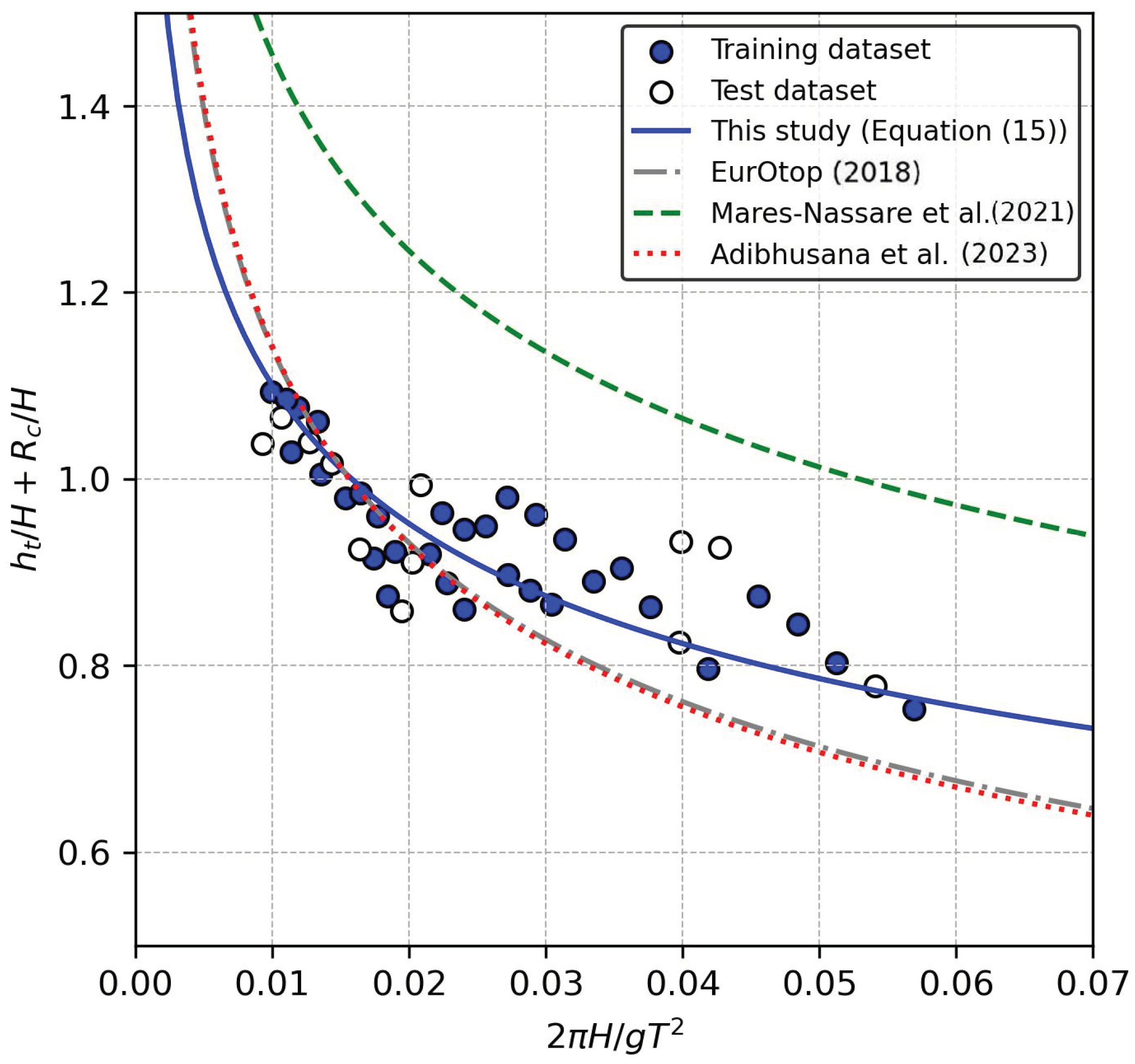
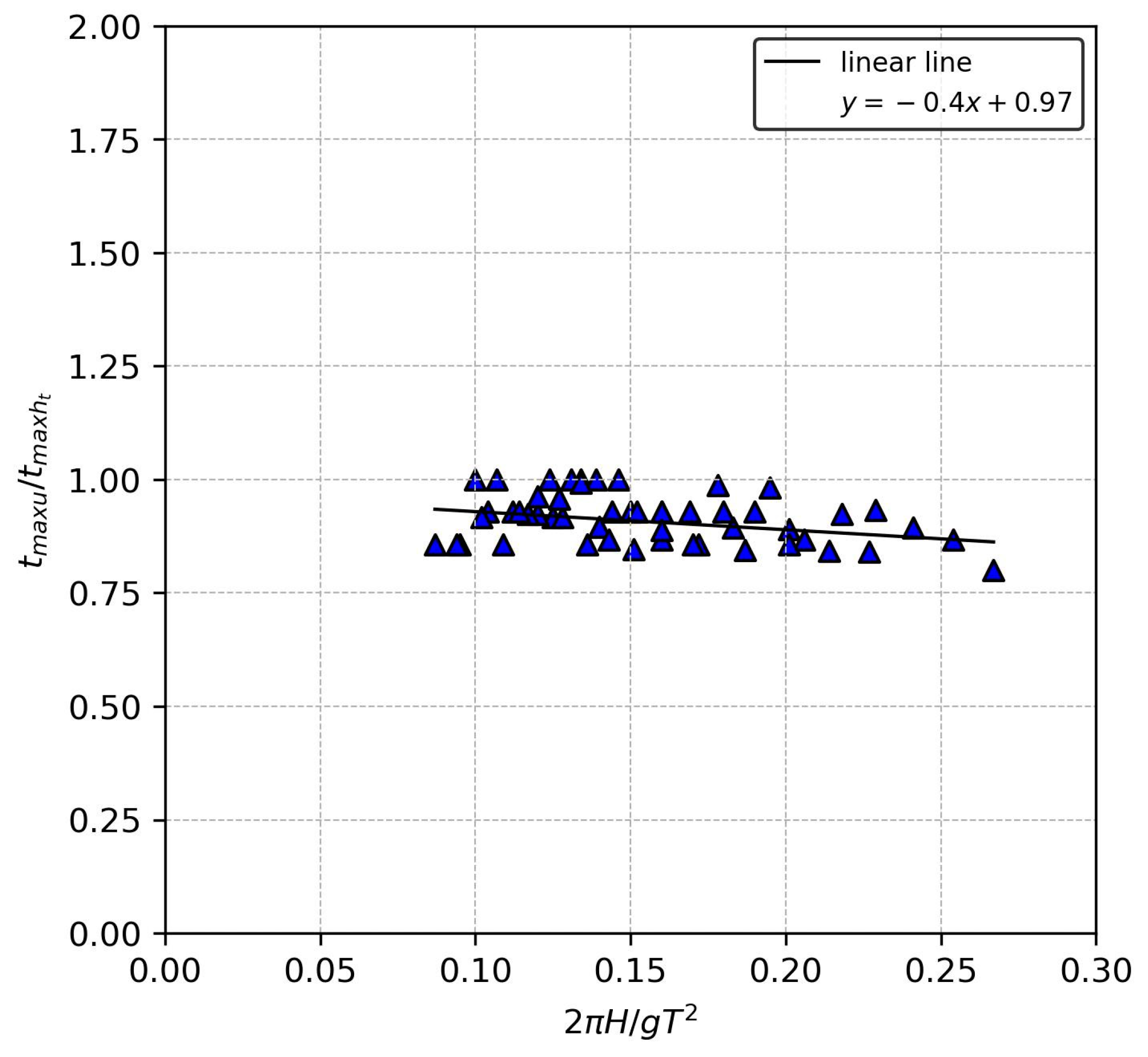


| Authors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| van Gent [23] | 0.7–2.2 | 1/4 | 1.30 | 0.15 | 0.40 |
| Schüttrumpf et al. [33] | 0.0–4.4 | 1/3, 1/4, 1/6 | 1.37 | 0.33 | 0.89 |
| van der Meer et al. [15] | 0.7–2.9 | 1/3 | 0.35cot | 0.19 | 0.13 |
| EurOtop [5] | - | - | 1.4, 1.5 | 0.20, 0.30 | – |
| Mares-Nasarre et al. [17] | 0.34–1.75 | 2/3 | – | 0.52 | 0.89 |
| Adibhusana et al. [31] | 0.6–1 | 1/1.5 | 1.21 | 0.21 | – |
| Armor Layer | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cubipod-1L | 0 | 4 | 1/3 | 0.095 | 0.03 |
| Cube-2L | 0 | 2 | 0.3 | 0.085 | 0.02 |
| Rock-2L | 1/3 | 10 | 0.45 | 0.080 | 0.03 |
| Armor Layer | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cubipod-1L | 2 | 20 | 2 | 0.20 | 1 |
| Cube-2L | 4 | 30 | 2 | 0.20 | 1 |
| Rock-2L | 2 | 30 | 2 | 0.20 | 0.5 |
| Description | Parameter | Ranges |
|---|---|---|
| Wave period | 1.5–3.0 s | |
| Wave height | 0.12–0.20 m | |
| Relative water depth | 0.028–0.114 | |
| Wave steepness | 0.008–0.057 | |
| Iribarren’s number | 2.795–7.216 | |
| Relative crest freeboard | 0.6–1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adibhusana, M.N.; Lee, J.-I.; Ryu, Y. Experimental Study of Wave Overtopping Flow Behavior on Composite Breakwater. Water 2023, 15, 4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15244239
Adibhusana MN, Lee J-I, Ryu Y. Experimental Study of Wave Overtopping Flow Behavior on Composite Breakwater. Water. 2023; 15(24):4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15244239
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdibhusana, Made Narayana, Jong-In Lee, and Yonguk Ryu. 2023. "Experimental Study of Wave Overtopping Flow Behavior on Composite Breakwater" Water 15, no. 24: 4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15244239
APA StyleAdibhusana, M. N., Lee, J.-I., & Ryu, Y. (2023). Experimental Study of Wave Overtopping Flow Behavior on Composite Breakwater. Water, 15(24), 4239. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15244239








