Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Evolution of Karst Groundwater in Heilongdong Spring Basin, Northern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
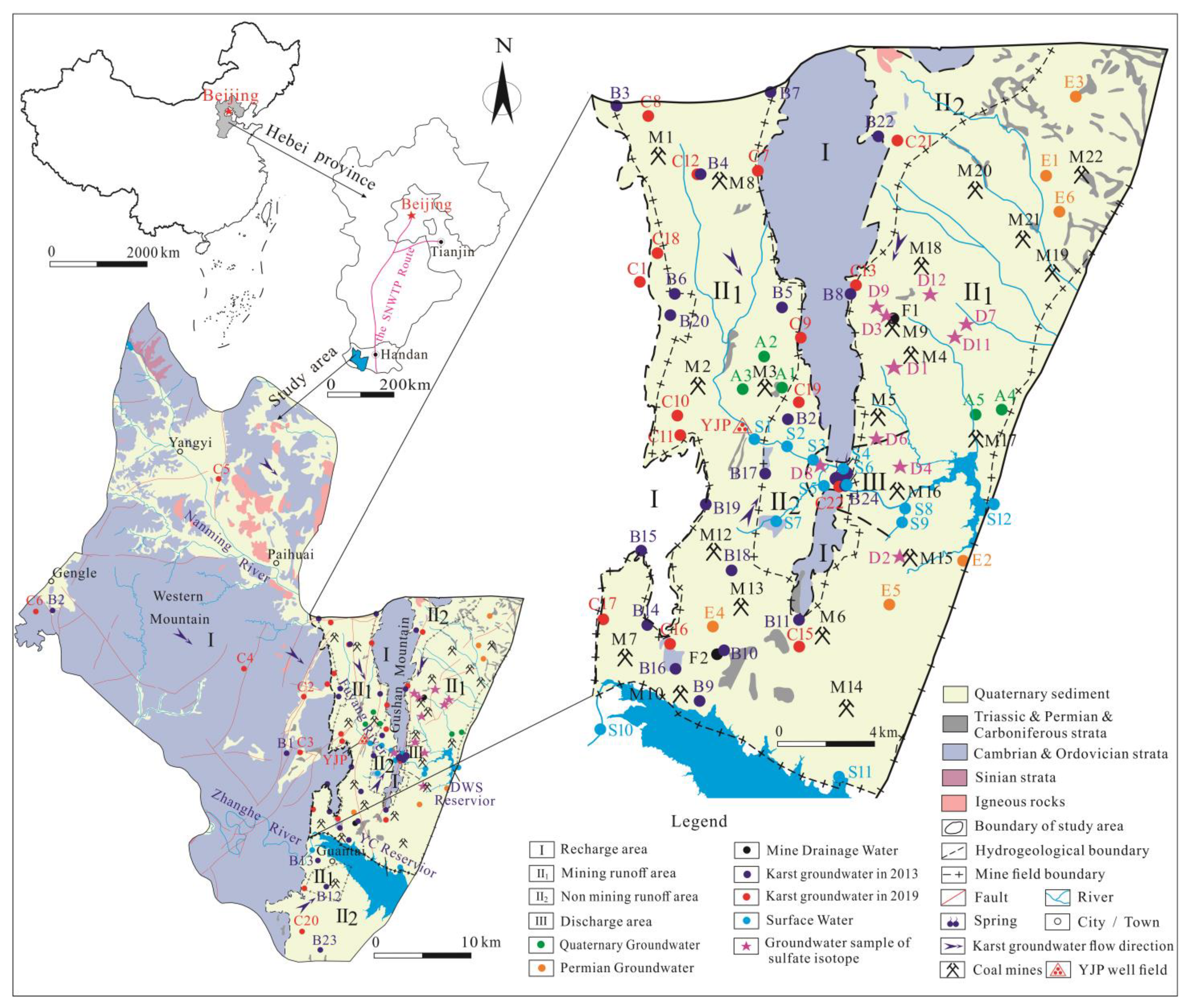
2.1. General Setting
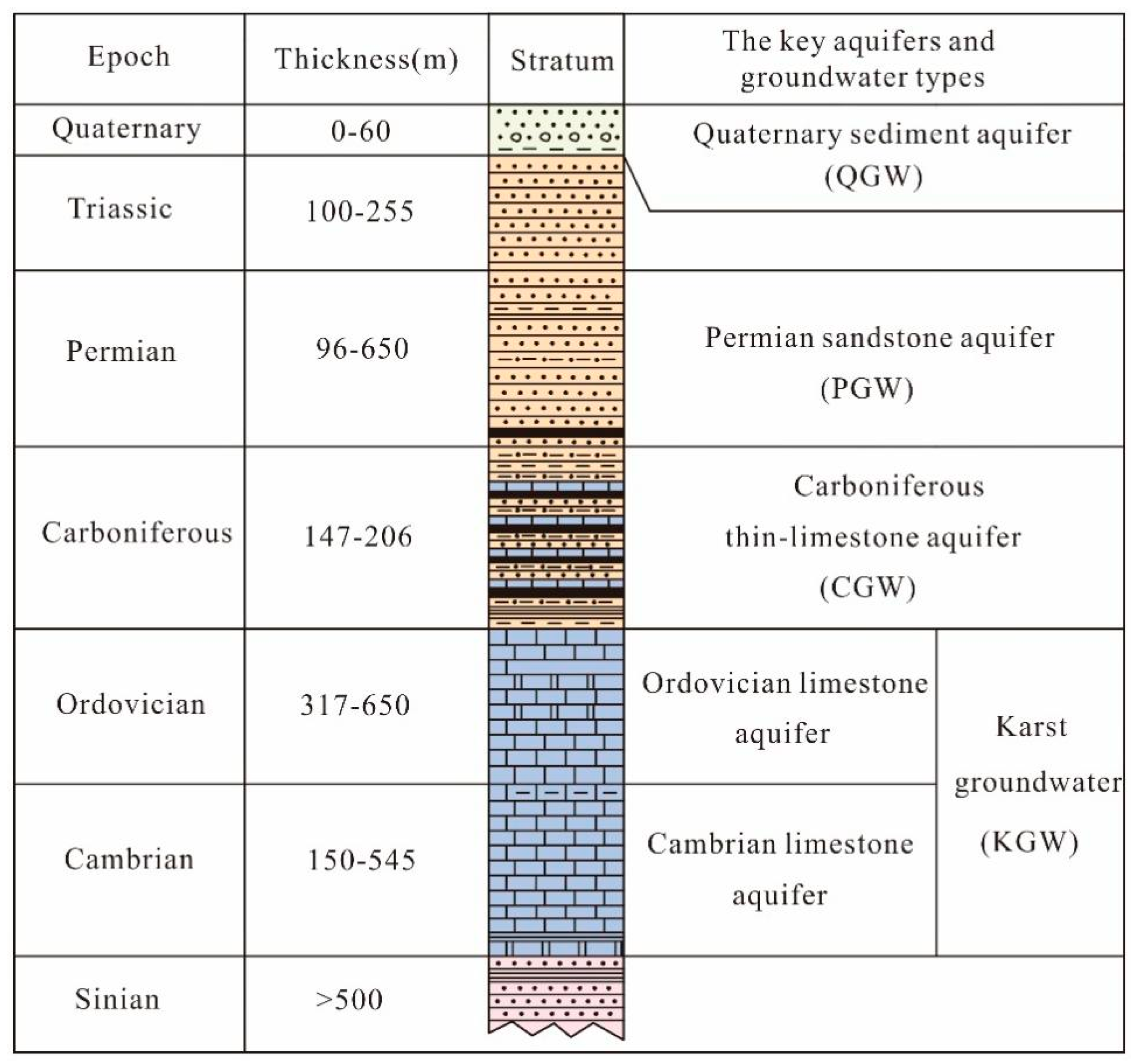
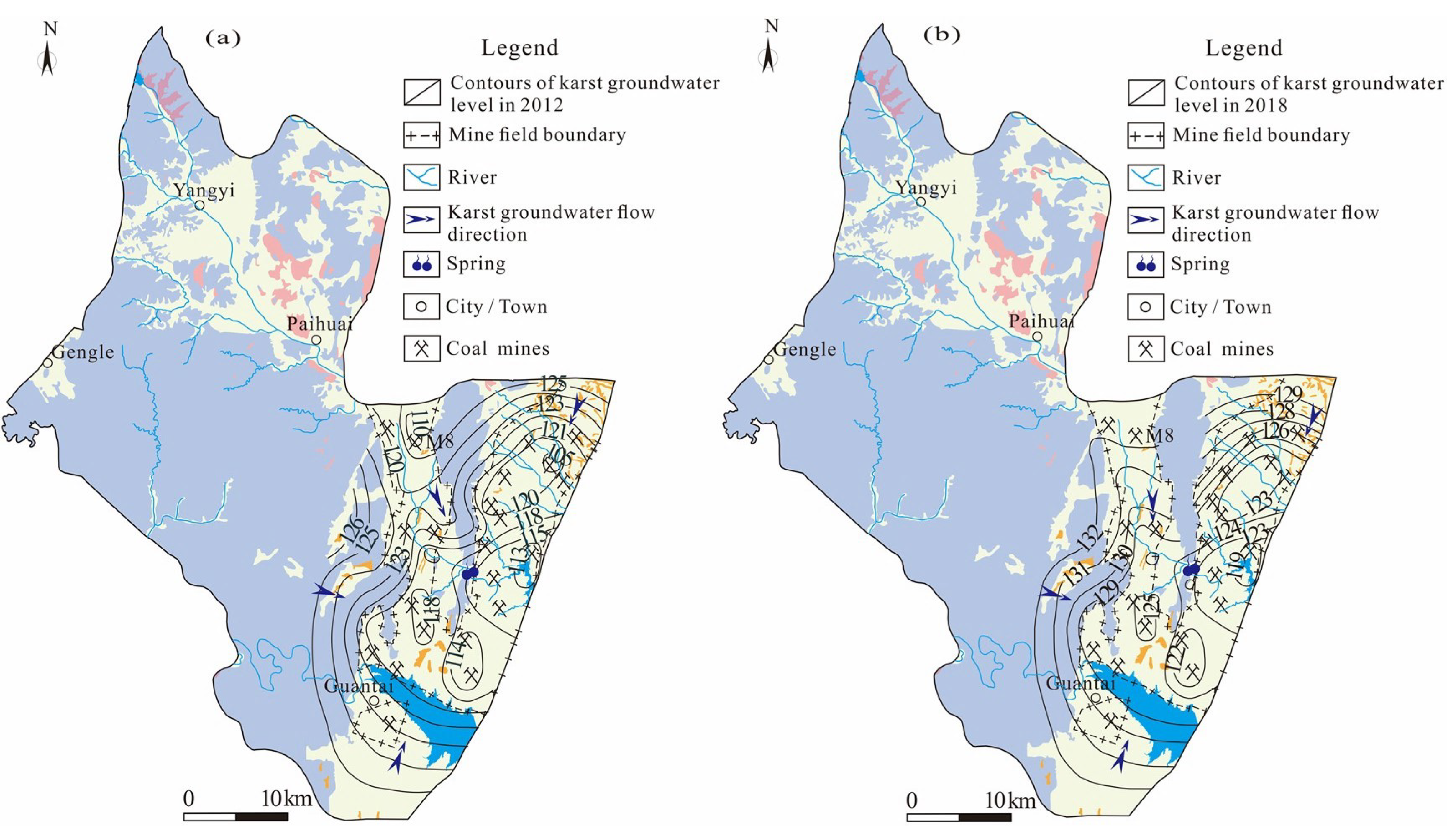
2.2. Geological and Hydrogeological Setting
2.3. Coal Mining
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Collection and Analysis
3.2. Analytical Methods
4. Results
4.1. Statistics of Hydrochemical Compositions
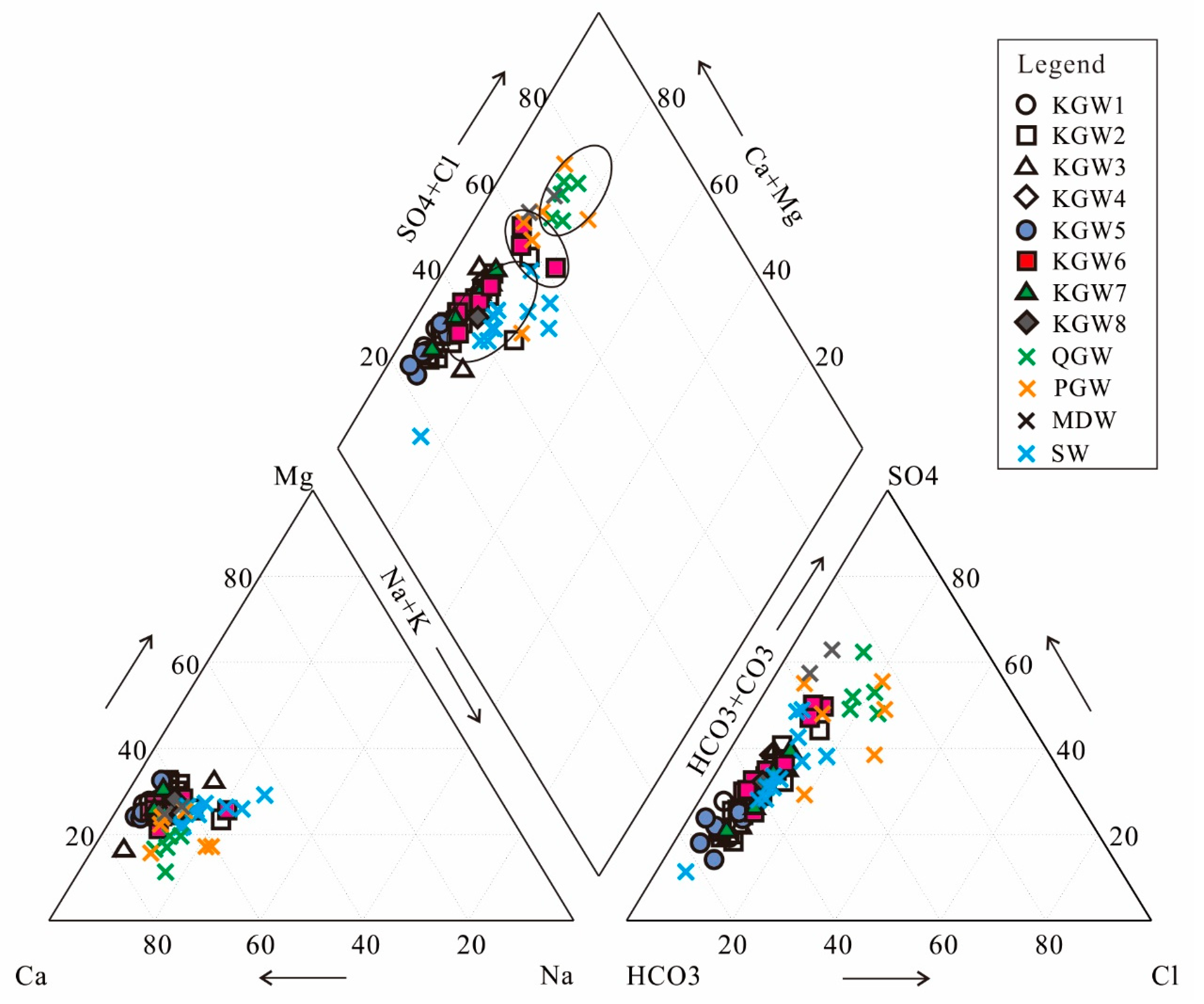
4.2. Hydrochemical Types
5. Discussion
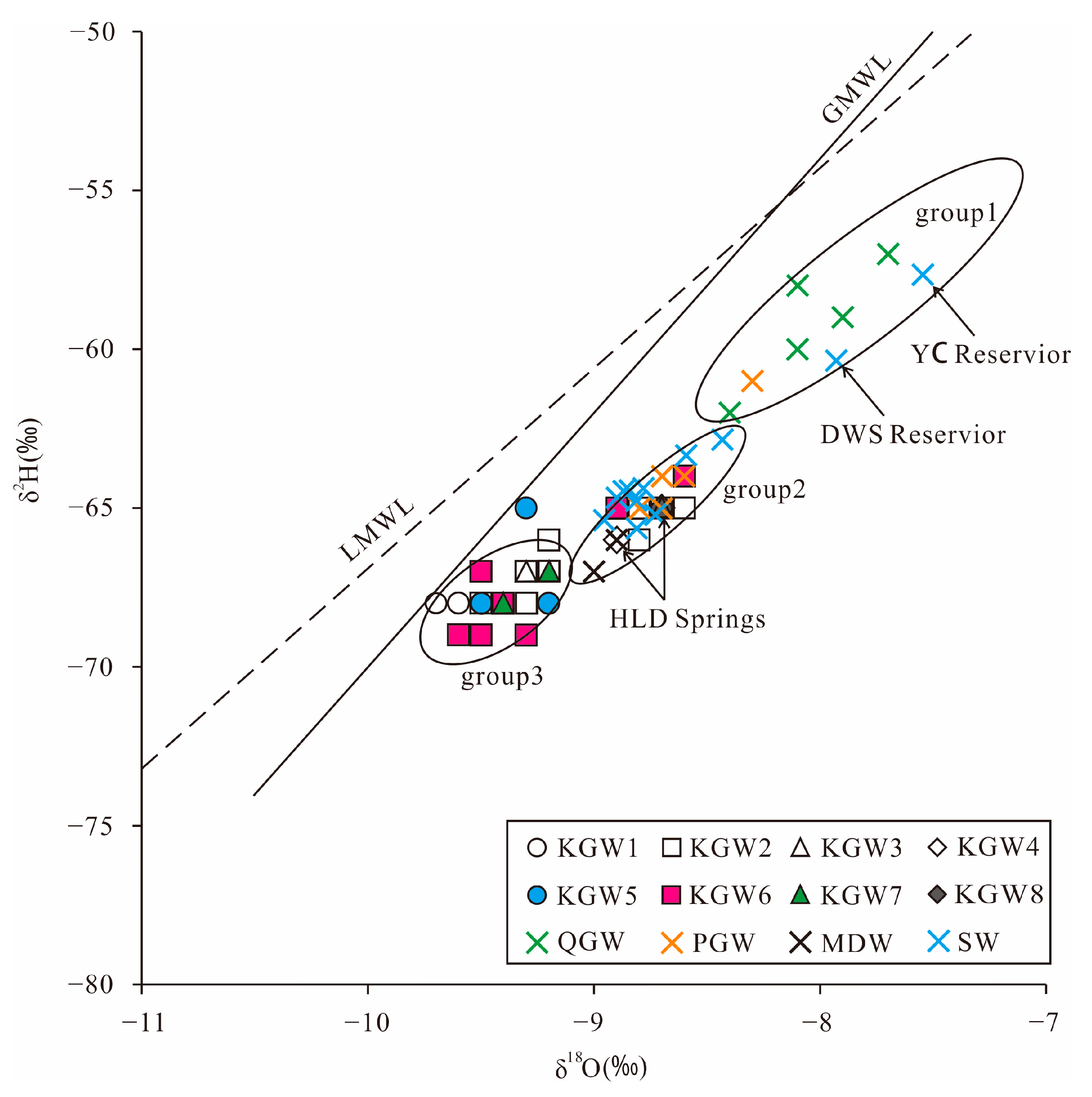
5.1. Groundwater Isotopic Composition and Sources
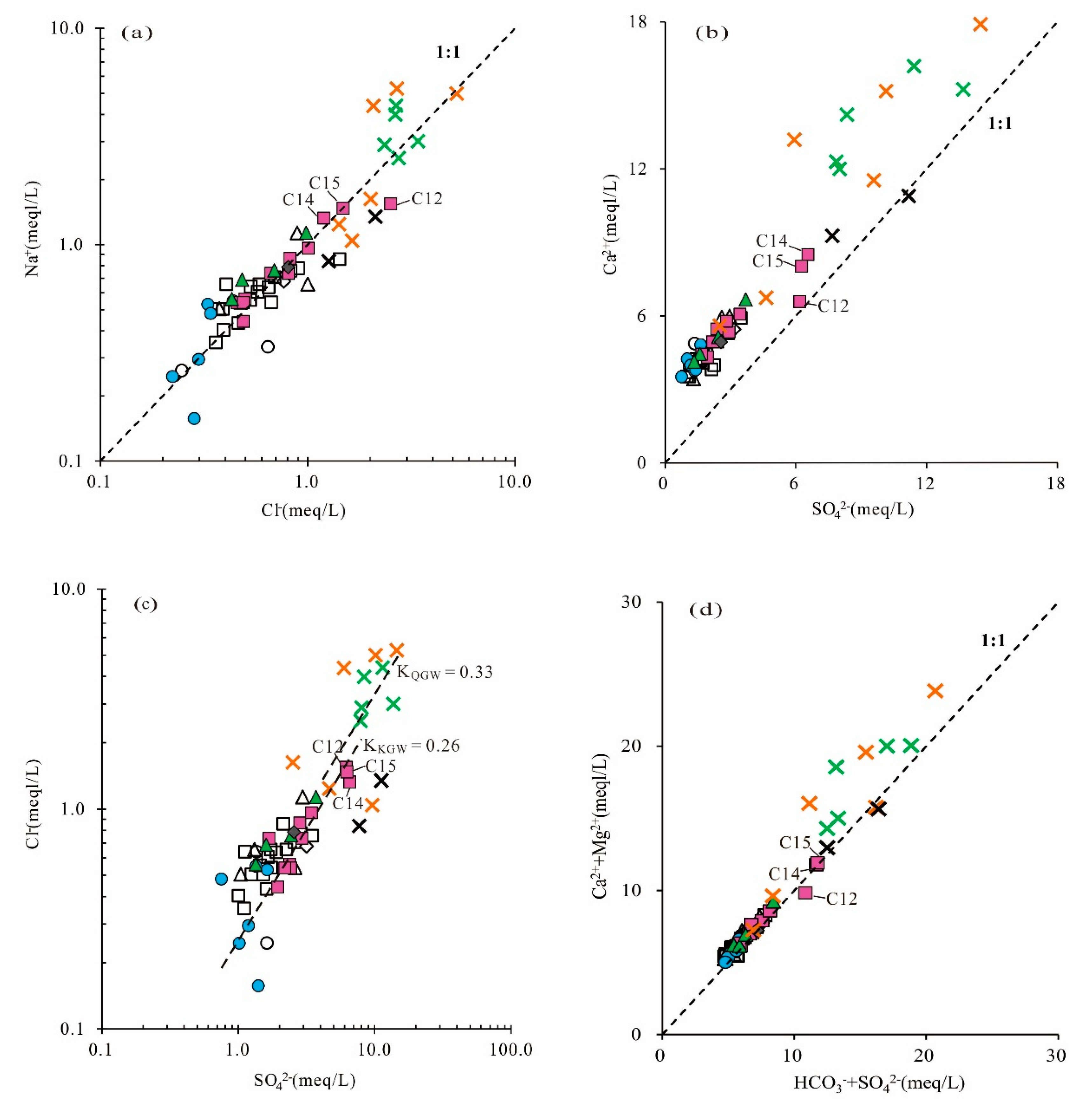
5.2. Rock Weathering and Evaporation
5.3. Correlation of Hydrochemical Composition
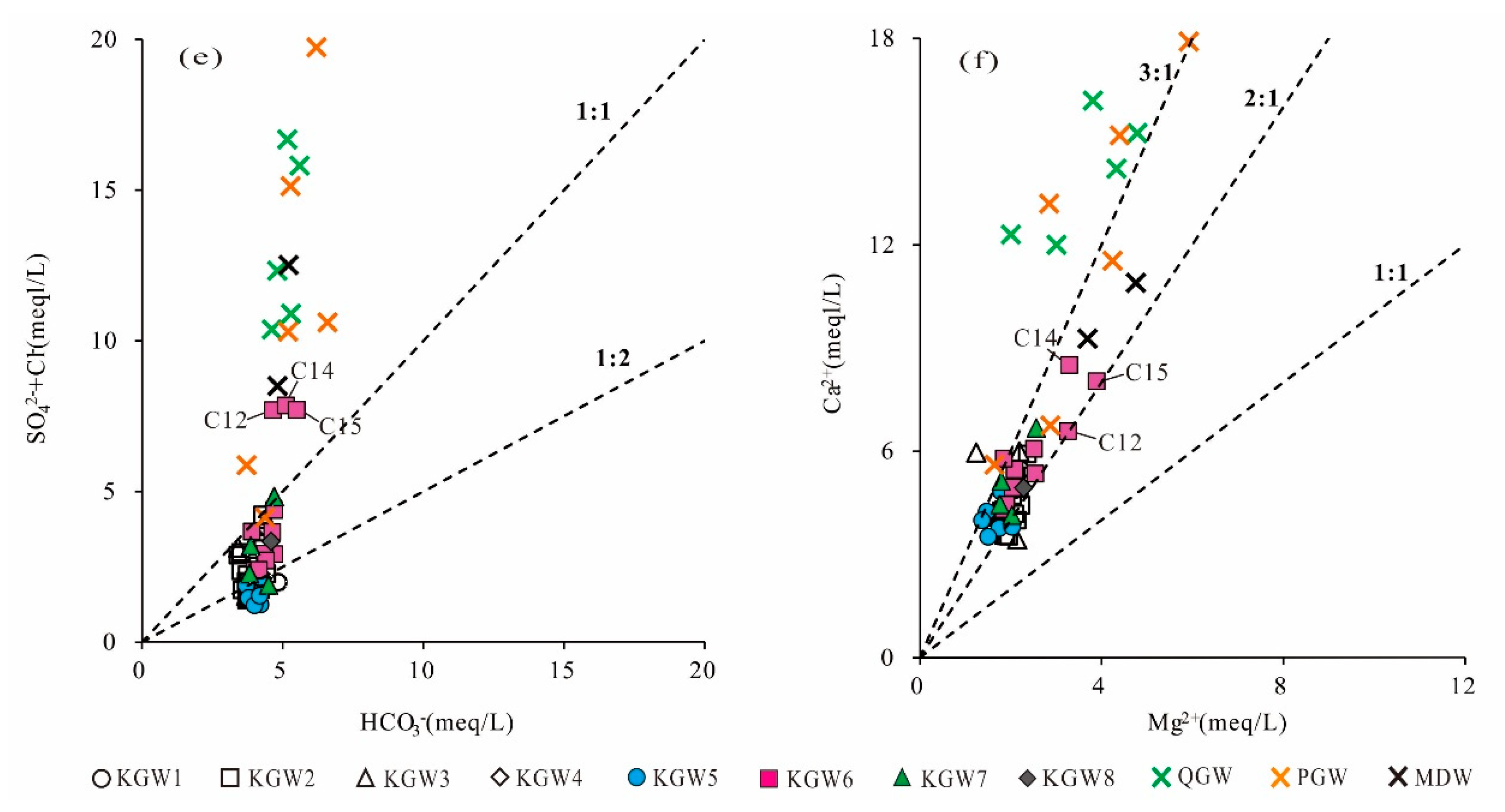
5.4. Water–Rock Interaction
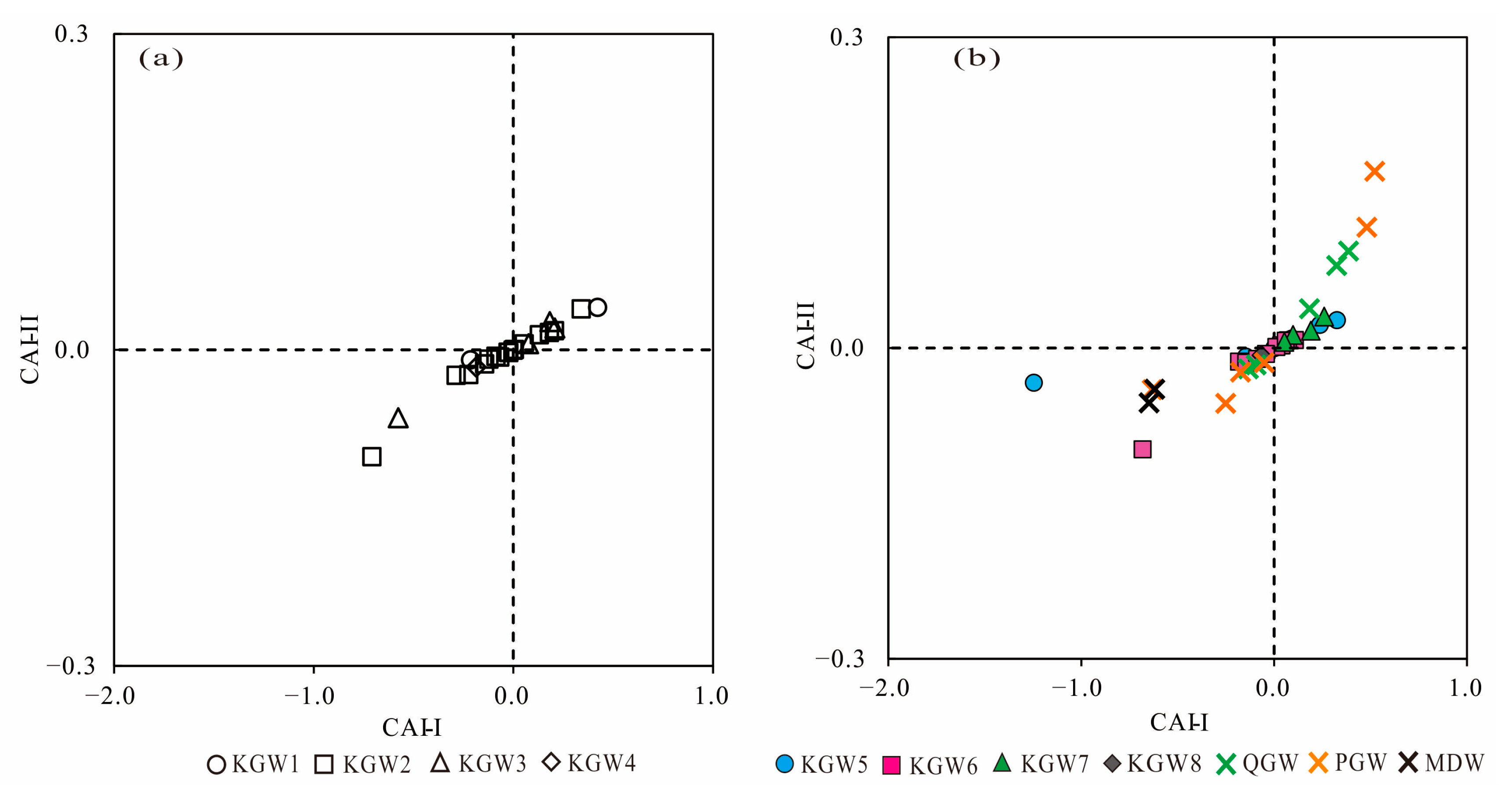
5.5. Ion Exchange Processes
5.6. Saturation Indices
5.7. Analyses of the Sources of SO42− in Groundwater
5.8. Anthropogenic Factors Affecting the Groundwater Quality
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- In the past six years (2013–2019), due to the influence of coal mining and other factors, the average concentrations of TDS, Na+, Cl−, SO42− and other major ions had been increasing in the mining runoff areas, and even exceeded the concentrations in the discharge area. Especially, the concentration of SO42− in the karst groundwater changed the most. A sulfur isotope analysis showed that SO42− concentrations in the karst groundwater were potentially derived from the combination of gypsum dissolution and sulfide oxidation by meteoric water.
- (2)
- With the closure of some coal mines, the karst groundwater level in the runoff area began to recover. The SI values of calcite and dolomite in karst groundwater varied greatly during 2013–2019, which reflected the changing runoff conditions in the area, and the karst groundwater transferred gradually from an oversaturated state to saturated state.
- (3)
- Agricultural production and domestic sewage except for mining activities also had a negative impact on the quality of regional groundwater, which caused the increase in the content of NO3− and Cl− in the Quaternary sediment groundwater, Permian bedrock groundwater and a small amount of karst groundwater. It also meant that some samples (C12, C14, C15) from the coal mine runoff area (II1) had a relatively close hydraulic connection with shallow groundwater.
- (4)
- Given the increasingly serious environmental and geological problems in the HSB, future research work should enhance the hydraulic connection between karst aquifers and coal seams or other aquifers, reduce the pollution of karst groundwater by coal mining and agricultural activities and strengthen the continuous monitoring of groundwater level and hydrochemical abnormal areas, which is important for the management of karst groundwater resources in North China.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HSB | Heilongdong Spring Basin |
| HLD | Heilongdong |
| YC | Yuecheng (place name) |
| DWS | Dongwushi (place name) |
| Z | Sinian |
| ∈ | Cambrian |
| O | Ordovician |
| C | Carboniferous |
| P | Permian |
| T | Triassic |
| Q | Quaternary sediments |
| KGW | Karst groundwater in the Cambrian and Ordovician limestone aquifers |
| SNWTP | South-to-North Water Transfer Project |
| YJP | Yangjiaopu (place name) |
| QGW | Groundwater in the Quaternary sediment aquifer |
| PGW | Groundwater in the Permian sandstone aquifer |
| CGW | Carboniferous thin-layer limestone groundwater (CGW) |
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
| ICP-OES | Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometer |
| CBE | Charge Balance Error |
| VSMOW | Vienna Standard Mean Ocean Water |
| TCEA | Thermal conversion elemental analyzer |
| V-CDT | Vienna Canyon Diablo Troilite |
| MDW | Mine drainage water |
| SW | Surface water |
| KGW1 | Karst groundwater in recharge area in 2013 |
| KGW2 | Karst groundwater in mining runoff area in 2013 |
| KGW3 | Karst groundwater in no mining runoff area in 2013 |
| KGW4 | Karst groundwater in discharge area in 2013 |
| KGW5 | Karst groundwater in recharge area in 2019 |
| KGW6 | Karst groundwater in mining runoff area in 2019 |
| KGW7 | Karst groundwater in no mining runoff area in 2019 |
| KGW8 | Karst groundwater in discharge area in 2019 |
| LMWL | The local meteoric water line |
| GMWL | The global meteoric water line |
| SI | Saturation indices |
| WHO | The World Health Organization |
References
- Gomez, M.; Perdiguero, J.; Sanz, A. Socioeconomic Factors Affecting Water Access in Rural Areas of Low and Middle Income Countries. Water 2019, 11, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.D.; Adams, E.A.; Neville, G.; Wada, Y.; Sherbinin, A.D.; Bernhardt, E.M.; Adamo, S.B. Urban growth and water access in sub-Saharan Africa: Progress, challenges, and emerging research directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiocchini, U.; Castaldi, F.; Barbieri, M.; Eulilli, V. A stratigraphic and geophysical approach to studying the deep-circulating groundwater and thermal springs, and their recharge areas, in Cimini Mountains-Viterbo area, central Italy. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 1319–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrard, N.; Foster, T.; Willetts, J. Groundwater as a Source of Drinking Water in Southeast Asia and the Pacific: A Multi-Country Review of Current Reliance and Resource Concern. Water 2019, 11, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.; Barberio, M.D.; Banzato, F.; Billi, A.; Boschetti, T.; Franchini, S.; Gori, F.; Petitta, M. Climate change and its effect on groundwater quality. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Z.; Gao, Y.; Green, S.M.; Wen, X.F.; Yang, J.; Xiong, B.L.; Quine, T.A.; He, N.P. Chemical Characteristics of Flow Driven by Rainfall and Associated Impacts on Shallow Groundwater Quality in a Karst Watershed, Southwest China. Environ. Prog. 2021, 8, 615–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.S.; Shi, L.M.; Song, X.F.; Yeh, T.C.; Zhen, P.N. Coupling hydrochemistry and stable isotopes to identify the major factors affecting groundwater geochemical evolution in the Heilongdong Spring Basin, North China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 205, 106352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanović, Z. Global distribution and use of water from karst aquifers. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2018, 466, 217–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Zhang, C.C.; Hou, X.W. Characteristics of groundwater circulation and evolution in Jindong large coal base driven by coal mining: An example of Xin’an spring area. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 3015–3026. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Li, X.H.; Wei, A.H. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and gradual changes of groundwater in the Baiquan karst spring region, northern China. Carbonates Evaporites 2022, 37, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.C.; Li, X.Q.; Ma, J.F.; Wang, Z.X.; Hou, X.W. Stable isotope and hydrochemical evolution of shallow groundwater in mining area of the Changzhi Basin, northern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.P.; Gao, X.B.; Zhao, C.H.; Tang, C.L.; Shen, H.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Wang, Y.X. Review: Characterization, evolution, and environmental issues of karst water systems in Northern China. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1371–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.J.; Song, J.X.; Yang, W.K.; Zheng, Y.J.; Li, C.Y.; Kuang, D. Distribution of carbonate rocks and variation analysis of karst water resources in China. Carbonates Evaporites 2020, 35, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.B.; Qin, X.Q.; Yang, Q.Y.; Liu, P.Y.; Zhang, J.S. Identification of dissolved sulfate sources and the role of sulfuric acid in carbonate weathering using δ13CDIC and δ34S in karst area, northern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 51. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.Q.; Guo, L.; Guo, Y.Y.; Luo, H.L.; Liang, Y.P. Research on the effects of coal mining on the karst hydrogeological environment in Jiaozuo mining area, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 434. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Hoth, N.; Drebenstedt, C.; Sun, Y.J.; Xu, Z.M. Hydro-geochemical paths of multi-layer groundwater system in coal mining regions—Using multivariate statistics and geochemical modeling approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.Z.; Peng, Y.X.; Zhao, W.D.; Ma, L.; He, X.R.; Lu, Y.H. Hydrochemical processes and evolution of karst groundwater in the northeastern Huaibei Plain, China. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1721–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.C.; Li, X.Q.; Ma, J.F.; Liu, L.X.; Gao, M.; Bai, Z.X. A hydrochemistry and multi-isotopic study of groundwater origin and hydrochemical evolution in the middle reaches of the Kuye River basin. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 98, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesari, T.; Roy, A.; Mohokar, H.; Pant, D.; Sinha, U.K. Characterization of mechanisms and processes controlling groundwater recharge and its quality in drought-prone region of central India (Buldhana, Maharashtra) using isotope hydrochemical and end-member mixing modeling. Nat. Resour. Res. 2020, 29, 1951–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Wang, G.C.; Shi, Z.M.; Xu, Q.Y.; Guo, Y.Y.; Ma, L.; Sheng, Y.Z. Using stable isotopes (δD, δ18O, δ34S and 87Sr/86Sr) to identify sources of water in abandoned mines in the Fengfeng coal mining district, northern China. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Lyu, Z.C.; Wang, G.C.; Ma, L.; Xu, Q.Y.; Huang, X.J.; Gao, S.Z. Hydrogeochemical simulation of groundwater in Eastern Fengfeng mining area. Coal Geol. Explor. 2016, 44, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, C.M.; Sun, W.; He, P.Y.; Li, C. The impact of nearly 30 years mining activities on the hydrochemistry characteristic of karst groundwater in Fengfeng coal mining area. China Min. Mag. 2015, 24, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, C.M.; Huang, Y.; He, P.Y.; Sun, W. Isotope Drift Characteristics in Ordovician Limestone Karst Water Caused by Coal Mining in Northern China. Mine Water Environ. 2019, 38, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhen, P.N.; Wang, S. Groundwater quality assessment and health risks from nitrate contamination in the Heilongdong Spring Basin, a typical headwater basin of the North China Plain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 17655–17670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Research on Groundwater Circulation and Hydrochemical Formation Mechanism in the Heilongdong Spring Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, Hebei University of Engineering, Handan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Guan, Y.Q.; Sun, Y.Z.; Zhang, H.S.; Bian, K. Water inrush type division and water inrush mode in Fengfeng Mining Area. Saf. Health Coal Mines 2021, 52, 186–194. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.X.; Li, X.Q.; Hou, X.W. Hydrogeochemistry of River Water in the Upper Reaches of the Datong River Basin, China: Implications of Anthropogenic Inputs and Chemical Weathering. Acta Geol. Sin.-Engl. Ed. 2021, 95, 962–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.C.; Li, C.S.; Sun, B.; Geng, F.Q.; Gao, S.; Lv, M.H.; Ma, X.Y.; Li, H.; Xing, L.T. Groundwater hydrogeochemical formation and evolution in a karst aquifer system affected by anthropogenic impacts. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 2609–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Ren, H.X.; Wu, Y.Z.; Cao, F.L.; Jia, F.J.; Qu, P.C. The evolution of hydrogeochemical characteristics of a typical piedmont karst groundwater system in a coal-mining area, Northern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeller, H. Qualitative Evaluation of Groundwater Resources. In Methods and Techniques of Groundwater Investigations and Development; Unesco: Paris, France, 1965; pp. 54–83. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatramanan, S.; Chung, S.Y.; Ramkumar, T.; Gnanachandrasamy, G.; Vasudevan, S.; Lee, S.Y. Application of GIS and hydrogeochemistry of groundwater pollution status of Nagapattinam district of Tamil Nadu, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 4429–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. User’s Guide to PHREEQC (Version 2) a Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-Reaction, One-Dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations: U.S Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 99-4259. 1999. Available online: https://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/wri994259 (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- Wu, J.H.; Li, P.Y.; Qian, H. Hydrochemical characterization of drinking groundwater with special reference to fluoride in an arid area of China and the control of aquifer leakage on its concentrations. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 8575–8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.P.; Huang, G.X. Groundwater Level Mapping Using Multiple-Point Geo-statistics. Water 2016, 8, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.J. Study on Karst Water Cycle Evolution Law in Heilongdong Spring Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Hebei University of Engineering, Handan, China, 20 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Krouse, H.R.; Mayer, B. Sulphur and Oxygen Isotopes in Sulphate. In Environmental Tracers in Subsurface Hydrology; Cook, P.G., Herczeg, A.L., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 195–231. [Google Scholar]
- Bahrami, M.; Zarei, A.R.; Rostami, F. Temporal and spatial assessment of groundwater contamination with nitrate by nitrate pollution index (NPI) and GIS (case study: Fasarud Plain, southern Iran). Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 3119–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.X.; Liu, C.Y.; Sun, J.C.; Zhang, M.; Jing, J.H.; Li, L.P. A regional scale investigation on factors controlling the groundwater chemistry of various aquifers in a rapidly urbanized area: A case study of the Pearl River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 398–403. [Google Scholar]




| K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− | NO3− | TDS | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KGW Total (n = 24) | ||||||||||
| Min | 0.92 | 6.03 | 68.79 | 14.95 | 8.75 | 47.94 | 207.5 | 12.8 | 313.4 | 7.55 |
| Max | 2.94 | 32.72 | 120.1 | 31.7 | 49.18 | 207.3 | 294.9 | 57.6 | 599.6 | 8.52 |
| Mean | 1.37 | 14.61 | 91.01 | 23.46 | 22.77 | 95.34 | 241.91 | 21.63 | 405.95 | 8.05 |
| Std | 0.44 | 7.16 | 16.85 | 3.73 | 8.45 | 41.82 | 23 | 8.74 | 76.24 | 0.39 |
| KGW1(n = 2) | ||||||||||
| Min | 1.3 | 6.03 | 82.73 | 19.96 | 8.75 | 64.96 | 237.8 | 12.8 | 336.9 | 7.55 |
| Max | 1.45 | 7.77 | 97.67 | 24.95 | 22.76 | 77.45 | 294.9 | 29.36 | 404.9 | 7.66 |
| Mean | 1.38 | 6.9 | 90.2 | 22.46 | 15.76 | 71.21 | 266.35 | 21.08 | 370.9 | 7.61 |
| Std | 0.11 | 1.23 | 10.56 | 3.53 | 9.91 | 8.83 | 40.38 | 11.71 | 48.08 | 0.08 |
| KGW2 (n = 17) | ||||||||||
| Min | 0.92 | 8.28 | 70.76 | 19.29 | 12.56 | 47.94 | 207.5 | 13.48 | 317.1 | 7.57 |
| Max | 2.94 | 32.72 | 120.1 | 31.7 | 49.18 | 207.3 | 270.2 | 27.52 | 599.6 | 8.52 |
| Mean | 1.39 | 15.07 | 88.94 | 23.83 | 22.95 | 94.97 | 238.53 | 19.95 | 402.38 | 8.15 |
| Std | 0.51 | 7.46 | 15.04 | 3.35 | 8.3 | 43.06 | 20.1 | 3.8 | 76.57 | 0.38 |
| KGW3 (n = 4) | ||||||||||
| Min | 0.99 | 8.62 | 68.79 | 14.95 | 17.95 | 49.88 | 209 | 17.8 | 313.4 | 7.64 |
| Max | 1.44 | 23.02 | 120 | 26.31 | 40.27 | 141.9 | 269 | 57.6 | 522.2 | 8.49 |
| Mean | 1.2 | 15.76 | 95.66 | 21.43 | 25.2 | 94.91 | 238.2 | 29.84 | 416.4 | 7.97 |
| Std | 0.24 | 7.05 | 27.75 | 5.53 | 10.3 | 45.3 | 26.28 | 18.79 | 94.07 | 0.36 |
| KGW4 (n = 1) | 1.52 | 17.59 | 109.2 | 27.31 | 24.05 | 151.6 | 265.4 | 18.48 | 494.9 | 7.61 |
| K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− | NO3− | TDS | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KGW Total (n = 22) | ||||||||||
| Min | 0.92 | 5.12 | 70.44 | 16.44 | 5.59 | 35.94 | 225.8 | 1.25 | 301.5 | 7.3 |
| Max | 3.7 | 57.75 | 170.2 | 46.69 | 54.97 | 313.8 | 335 | 64.62 | 798.5 | 7.74 |
| Mean | 1.62 | 16.42 | 103.7 | 26.02 | 25.72 | 125.72 | 265.27 | 22.98 | 466.96 | 7.52 |
| Std | 0.68 | 11.82 | 26.49 | 7.57 | 13.24 | 80.91 | 27.59 | 11.44 | 145.54 | 0.13 |
| KGW5 (n = 6) | ||||||||||
| Min | 0.92 | 5.12 | 70.44 | 16.44 | 5.59 | 35.94 | 225.8 | 18.35 | 301.5 | 7.45 |
| Max | 2.76 | 10.03 | 96.61 | 24.39 | 19.56 | 78.03 | 256.9 | 31.42 | 394.6 | 7.74 |
| Mean | 1.69 | 7.32 | 80.61 | 19.84 | 13.39 | 58.43 | 244.92 | 22.19 | 336.68 | 7.63 |
| Std | 0.78 | 1.64 | 9.24 | 2.97 | 5.88 | 14.83 | 13.63 | 4.79 | 31.71 | 0.1 |
| KGW6 (n = 11) | ||||||||||
| Min | 1.15 | 10.45 | 86.58 | 22.16 | 15.72 | 80.51 | 238 | 1.25 | 386.6 | 7.3 |
| Max | 3.7 | 57.75 | 170.2 | 46.69 | 54.97 | 313.8 | 335 | 64.62 | 798.5 | 7.64 |
| Mean | 1.76 | 21.75 | 117.33 | 29.83 | 31.45 | 168.84 | 277.8 | 22.61 | 545.08 | 7.46 |
| Std | 0.73 | 14.14 | 27.37 | 8.37 | 14.08 | 89.33 | 28.62 | 15.91 | 155.45 | 0.08 |
| KGW7 (n = 4) | ||||||||||
| Min | 0.95 | 9.9 | 82.78 | 21.21 | 19.91 | 64.17 | 233.1 | 19.92 | 378.3 | 7.38 |
| Max | 1.57 | 22.61 | 133.6 | 30.82 | 40.27 | 177.5 | 286.8 | 29.18 | 582.9 | 7.73 |
| Mean | 1.2 | 14.87 | 102.06 | 24.5 | 27.9 | 108.83 | 257.65 | 25.98 | 446.98 | 7.54 |
| Std | 0.26 | 5.77 | 22.63 | 4.45 | 8.75 | 51.03 | 27.11 | 4.17 | 95.82 | 0.17 |
| KGW8 (n = 1) | 1.36 | 18.5 | 98.8 | 27.42 | 27.94 | 122.8 | 280.1 | 19.72 | 469.2 | 7.35 |
| QGW (n = 5) | ||||||||||
| Min | 0.26 | 53.95 | 240 | 24.08 | 89.28 | 377.5 | 282 | 34.82 | 1031 | 7.21 |
| Max | 2.23 | 78.22 | 323.9 | 57.5 | 156.1 | 656.7 | 341.7 | 190.1 | 1465 | 7.4 |
| Mean | 1.05 | 63.49 | 279.84 | 43.1 | 119.34 | 473.4 | 311.2 | 100.52 | 1253.8 | 7.31 |
| Std | 0.82 | 8.95 | 36.49 | 13.26 | 28.26 | 124.14 | 23.78 | 60.45 | 189.21 | 0.07 |
| PGW (n = 6) | ||||||||||
| Min | 0.95 | 32.53 | 112.2 | 19.76 | 37.02 | 120.5 | 227.3 | 12.09 | 563.4 | 7.21 |
| Max | 2.56 | 120.4 | 358.2 | 71.07 | 186.9 | 694.9 | 402.7 | 198 | 1647 | 7.62 |
| Mean | 1.52 | 57.74 | 233.95 | 43.89 | 109.79 | 378.15 | 319.13 | 86.69 | 1095.4 | 7.4 |
| Std | 0.63 | 32.3 | 95.72 | 18.07 | 70.6 | 208.87 | 65.82 | 68.53 | 437.38 | 0.14 |
| MDW (n = 2) | ||||||||||
| Min | 3.76 | 29.06 | 185.5 | 44.34 | 29.8 | 368 | 294.1 | 10.08 | 846.6 | 7.3 |
| Max | 4.03 | 48.75 | 218 | 57.12 | 47.85 | 536.4 | 317.9 | 17.4 | 1096 | 7.55 |
| Mean | 3.9 | 38.91 | 201.75 | 50.73 | 38.83 | 452.2 | 306 | 13.74 | 971.3 | 7.43 |
| Std | 0.19 | 13.92 | 22.98 | 9.04 | 12.76 | 119.08 | 16.83 | 5.18 | 176.35 | 0.18 |
| SW * (n = 12) | ||||||||||
| Min | 0.98 | 7.13 | 30.75 | 6.33 | 9.82 | 28.85 | 198.07 | 5.81 | 223.65 | 8 |
| Max | 6.44 | 64.57 | 155.38 | 40.59 | 58.91 | 312.84 | 349.53 | 22.31 | 784.56 | 8.6 |
| Mean | 3.96 | 31.12 | 94.94 | 26.16 | 32.83 | 151.15 | 268.36 | 17.46 | 491.8 | 8.2 |
| Std | 1.55 | 15.55 | 33.19 | 9.53 | 11.77 | 88.71 | 47.41 | 5.27 | 168.52 | 0.2 |
| QGW (n = 5) | PGW (n = 6) | KGW (n = 19) | MDW (n = 2) | SW (n = 12) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | |
| δ2H (‰) | −62.0 | −57.0 | −59.2 | −65.0 | −64.0 | −64.3 | −69.0 | −64.0 | −67.3 | −67.0 | −66.0 | −66.5 | −65.4 | −57.6 | −63.6 |
| δ18O (‰) | −8.4 | −7.7 | −8.0 | −8.8 | −8.5 | −8.7 | −9.6 | −8.6 | −9.3 | −9.1 | −8.9 | −9.0 | −8.9 | −7.5 | −8.6 |
| K | Na | Ca | Mg | Cl | SO4 | HCO3 | NO3 | TDS | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | 1.000 | 0.118 | 0.106 | 0.413 ** | −0.020 | 0.274 * | 0.244 | −0.222 | 0.161 | −0.176 |
| Na | 0.118 | 1.000 | 0.866 ** | 0.762 ** | 0.876** | 0.849 ** | 0.626 ** | 0.716 ** | 0.907 ** | −0.434 ** |
| Ca | 0.106 | 0.866 ** | 1.000 | 0.861 ** | 0.923** | 0.954 ** | 0.788 ** | 0.676 ** | 0.992 ** | −0.524 ** |
| Mg | 0.413 ** | 0.762 ** | 0.861 ** | 1.000 | 0.742** | 0.932 ** | 0.819 ** | 0.395 ** | 0.896 ** | −0.429 ** |
| Cl | −0.020 | 0.876 ** | 0.923 ** | 0.742 ** | 1.000 | 0.817 ** | 0.646 ** | 0.773 ** | 0.920 ** | −0.452 ** |
| SO4 | 0.274 * | 0.849 ** | 0.954 ** | 0.932 ** | 0.817** | 1.000 | 0.793 ** | 0.494 ** | 0.970 ** | −0.504 ** |
| HCO3 | 0.244 | 0.626 ** | 0.788 ** | 0.819 ** | 0.646** | 0.793 ** | 1.000 | 0.290 * | 0.786 ** | −0.525 ** |
| NO3 | −0.222 | 0.716 ** | 0.676 ** | 0.395 ** | 0.773** | 0.494 ** | 0.290 * | 1.000 | 0.668 ** | −0.368 ** |
| TDS | 0.161 | 0.907 ** | 0.992 ** | 0.896 ** | 0.920** | 0.970 ** | 0.786 ** | 0.668 ** | 1.000 | −0.519 ** |
| pH | −0.176 | −0.434 ** | −0.524 ** | −0.429 ** | −0.452** | −0.504 ** | −0.525 ** | −0.368 ** | −0.519 ** | 1.000 |
| SO42− (mg/L) | Cl− (mg/L) | δ34S (‰, CDT) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | Min | Max | Mean | |
| PGW | 120.5 | 694.9 | 481.4 | 57.8 | 186.9 | 140.7 | 2.7 | 5.7 | 4.7 |
| CGW | 513.5 | 2591.1 | 1262.0 | 30.9 | 59.2 | 43.6 | −10.6 | −1.0 | −5.8 |
| KGW in the recharge area | 56.6 | 67.0 | 62.7 | 5.6 | 19.6 | 11.9 | 3.0 | 14.1 | 7.1 |
| KGW in the runoff area | 93.1 | 408.9 | 159.5 | 15.7 | 70.4 | 30.8 | 2.1 | 13.0 | 6.2 |
| KGW in the discharge area | 97.4 | 122.8 | 110.1 | 15.8 | 27.9 | 21.9 | 6.3 | 8.2 | 7.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, M.; Li, X.; Qian, J.; Wang, Z.; Hou, X.; Fu, C.; Ma, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, J. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Evolution of Karst Groundwater in Heilongdong Spring Basin, Northern China. Water 2023, 15, 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040726
Gao M, Li X, Qian J, Wang Z, Hou X, Fu C, Ma J, Zhang C, Li J. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Evolution of Karst Groundwater in Heilongdong Spring Basin, Northern China. Water. 2023; 15(4):726. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040726
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Ming, Xiangquan Li, Jiazhong Qian, Zhenxing Wang, Xinwei Hou, Changchang Fu, Jianfei Ma, Chunchao Zhang, and Jinqiu Li. 2023. "Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Evolution of Karst Groundwater in Heilongdong Spring Basin, Northern China" Water 15, no. 4: 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040726
APA StyleGao, M., Li, X., Qian, J., Wang, Z., Hou, X., Fu, C., Ma, J., Zhang, C., & Li, J. (2023). Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Evolution of Karst Groundwater in Heilongdong Spring Basin, Northern China. Water, 15(4), 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040726






