Abstract
In this work, membranes were synthesized by depositing fluoropolymer coatings onto metal meshes using the hot wire chemical vapor deposition (HW CVD) method. By changing the deposition parameters, membranes with different wetting angles were obtained, with water contact angles for different membranes over a range from 130° ± 5° to 170° ± 2° and a constant oil contact angle of about 80° ± 2°. These membranes were used for the separation of an oil–water emulsion in a simple filtration test. The main parameters affecting the separation efficiency and the optimal separation mode were determined. The results reveal the effectiveness of the use of the membranes for the separation of emulsions of water and commercial crude oil, with separation efficiency values that can reach over 99%. The membranes are most efficient when separating emulsions with a water concentration of less than 5%. The pore size of the membrane significantly affects the rate and efficiency of separation. Pore sizes in the range from 40 to 200 µm are investigated. The smaller the pore size of the membranes, the higher the separation efficiency. The work is of great economic and practical importance for improving the efficiency of the membrane separation of oil–water emulsions. It lays the foundation for future research on the use of hydrophobic membranes for the separation of various emulsions of water and oil products (diesel fuel, gasoline, kerosene, etc.).
1. Introduction
The separation of oil and water is an important task for oil production, ecology, wastewater treatment, and other applications [1,2,3]. Existing separation techniques have limitations due to high energy consumption, the formation of secondary pollutants, low separation efficiency, etc. [4]. The use of membranes for the separation of oil–water emulsions was proposed as early as the meddle of the 20th century [5]. Furthermore, attempts were made to modify the membrane surface by imparting hydrophobic or hydrophilic properties [6]. Due to this, the separation efficiency of membranes increased significantly, and the method has begun to compete with others [7]. The rapid development of methods for the manufacture of separating membranes with different wettability started. Three types of materials are usually used as the basis of the membrane: metal meshes [8,9,10,11], textiles [12,13], and polymer meshes [14,15]. The modifier is applied to the base in various ways. The membrane surface modifiers are materials: polymers (fluoropolymer [16,17], polystyrene [18], polydimethylsiloxane [19,20], polybenzoxazine [21], etc.); minerals (diatomite coating [22]; silicon dioxide [23]; graphene oxide [24,25]); and metal oxides [26,27,28], metal hydroxides [29], etc. Modifiers are usually applied to the substrate by using the following methods: dip coating [30], spray coating [31], spin-coating [32], electrodeposition [33], acid–alkaline treatment [34], heat treatment [35], plasma deposition [36], ion beam irradiation [37], chemical etching [38], chemical vapor deposition (CVD) [39], and others [40].
Many materials with different wetting properties are used in the manufacture of membranes, yet there are no strong theories concerning how wetting affects separation efficiency and what wetting range is necessary for effective separation. One parameter of wettability is the water contact angle (WCA). The data presented in various works on the effect of WCA on the separation process are ambiguous and have a wide range of results. For example, Hou and Cao [41] obtained a separation efficiency of 98–99% on fluoropolymer-coated membranes with a WCA of 150° ± 2°, while Dong et al. [42] obtained a stable separation efficiency of 95% on a membrane with a laser-structured copper surface with a WCA of 151° ± 1°. Yin [29] obtained a separation efficiency of over 99% and excellent stability even after 10 uses on a superhydrophobic-copper-hydroxide-coated membrane with a WCA of 154° ± 2°. Undoubtedly, in addition to the WCA, it is also necessary to compare other parameters of the membrane (modifier material, pore size, etc. [4]).
The present work considers the possibility of creating separation membranes by depositing hydrophobic and superhydrophobic fluoropolymer coatings onto the surface of metal meshes by applying the hot wire CVD method. A feature of this method is the possibility of obtaining fluoropolymer coatings with different wetting properties. Depending on the deposition parameters, it is possible to obtain coatings with a contact angle from 120° to 170° [43]. Thus, this approach makes it possible to study the effect of wettability on the efficiency and separation rate within the same material. Fluoropolymers were chosen due to a combination of their unique properties: high hydrophobicity, chemical inertness, heat resistance, etc. The main purpose of the work is to study the influence of the wetting properties of hydrophobic fluoropolymer coatings on metal meshes during the membrane separation process of water–oil emulsions. In addition to the effect of membrane wettability, this work examines the influence of the membrane pore size on the separation process and the stability of the properties of the resulting coatings. Studies make it possible to determine the main parameters of the membrane (WCA, mesh weaving) that affect the rate and efficiency of separation in order to establish the optimal characteristics of separation membranes. The advantage of this work is that commercial crude oil was used in the studies, while many works describe the use of oil simulators. This approach makes it possible to accurately simulate the use of developed membranes in oil and oil refinery industries.
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
AISI 304 stainless steel meshes (Mesh 100, Mesh 180, Mesh 300, and Mesh 400) were purchased from Sunshinelantian Store (Anping, China). The precursor gas was a mixture consisting of hexafluoropropylene oxide (C3F6O) and 1.3% argon produced by LLC “Polymer Kirov-Chepetsk Chemical Plant” (TU standard 95-783-80) (Kirov-Chepetsk, Russia). The used nichrome filament (diameter 0.5 mm) consisted of 77%—Ni; 20%—Cr; and 1.5%—Fe, and the remaining 1.5% included Ti, Al, Si, C, Mn, P, and S (GOST 12766.1-90) produced by ZAO “Sverdlovsk Metallurgical Plant” (Ekaterinburg, Russia). The commercial crude oil (GOST R 51858-2002) was purchased from Rikom LLC (Novosibirsk, Russia).
2.2. Membrane Fabrication
Separation membranes were made by depositing a hydrophobic fluoropolymer coating on variously woven stainless steel meshes with a diameter of 40 mm. The meshes (Mesh 100, Mesh 180, Mesh 300, and Mesh 400) had a flow area of 40, 65, 90, and 200 µm, respectively. The surface of the samples was subjected to preliminary cleaning and processing to remove persistent organic (grease, oil, etc.) and non-organic (metal dust) compounds. Grease, oil, and dust were removed by the preliminary cleaning of meshes in an Ultrasonic Cleaner JP-010S (Skymen Cleaning Equipment Shenzhen Co., Shenzhen, China) with surfactants (sodium lauryl sulfate, 0.1 mol/L) at 90 °C for 30 min. After that, the samples were rinsed with distilled water and then alcohol and dried with a stream of dry argon.
Coatings were deposited using the hot wire chemical vapor deposition (HW CVD) method [43,44,45,46,47,48]. The main idea of the method is to activate the precursor gas flow with a resistively heated catalytic metal filament, that is, an activator. The experimental setup is described in detail in study [43]. This work used a nichrome filament (Ni80/Cr20) as an activator and hexafluoropropylene oxide (C3F6O) as a precursor gas. As a result of activation, radicals formed. These radicals then reach the surface, where they form a coating via polymerization. The structure of the resulting coating depends on the temperature of the activator filament Tf, the precursor gas pressure P, the distance between the activator and the substrate R, the deposition time t, and the temperature of the substrate holder Ts. The influence of these parameters on the structure of the deposited coating is described in detail in [43]. The wettability of membranes depends on the structure of the fluoropolymer coating. According to the Wenzel and Cassie–Baxter law, roughness is important for this [49,50]. During the formation of a fluoropolymer coating, depending on the deposition parameters, nano- and microroughnesses can form. It is their size and shape that determine the wetting properties of the surface in this case.
Three types of fluoropolymer coatings were chosen, which were previously obtained by the authors for other applications [43,44,45]. Depending on morphology, the coatings have different stable wetting properties when WCA = 130°, 150°, and 170°. Thus, each coating is hydrophobic but differs significantly in WCA value from others. The coatings had the same thickness of about 1 μm. The deposition parameters are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Parameters of the coating deposition process in the manufacture of separation membranes.
2.3. Membrane Characterization
The morphology of the resulting fluoropolymer coatings on the surface of a metal mesh was studied using a JEOL JSM6700F scanning electron microscope (Tokyo, Japan). The morphology of the obtained samples was studied at a magnification of ×140 (general view of the membrane network), ×20,000, and ×50,000 (morphology of the fluoropolymer coating). Imaging parameters were selected individually depending on the electrical properties of the sample, namely, the accelerating voltage was 5–15 keV, and the operating focal length was 3.0–15.1 mm.
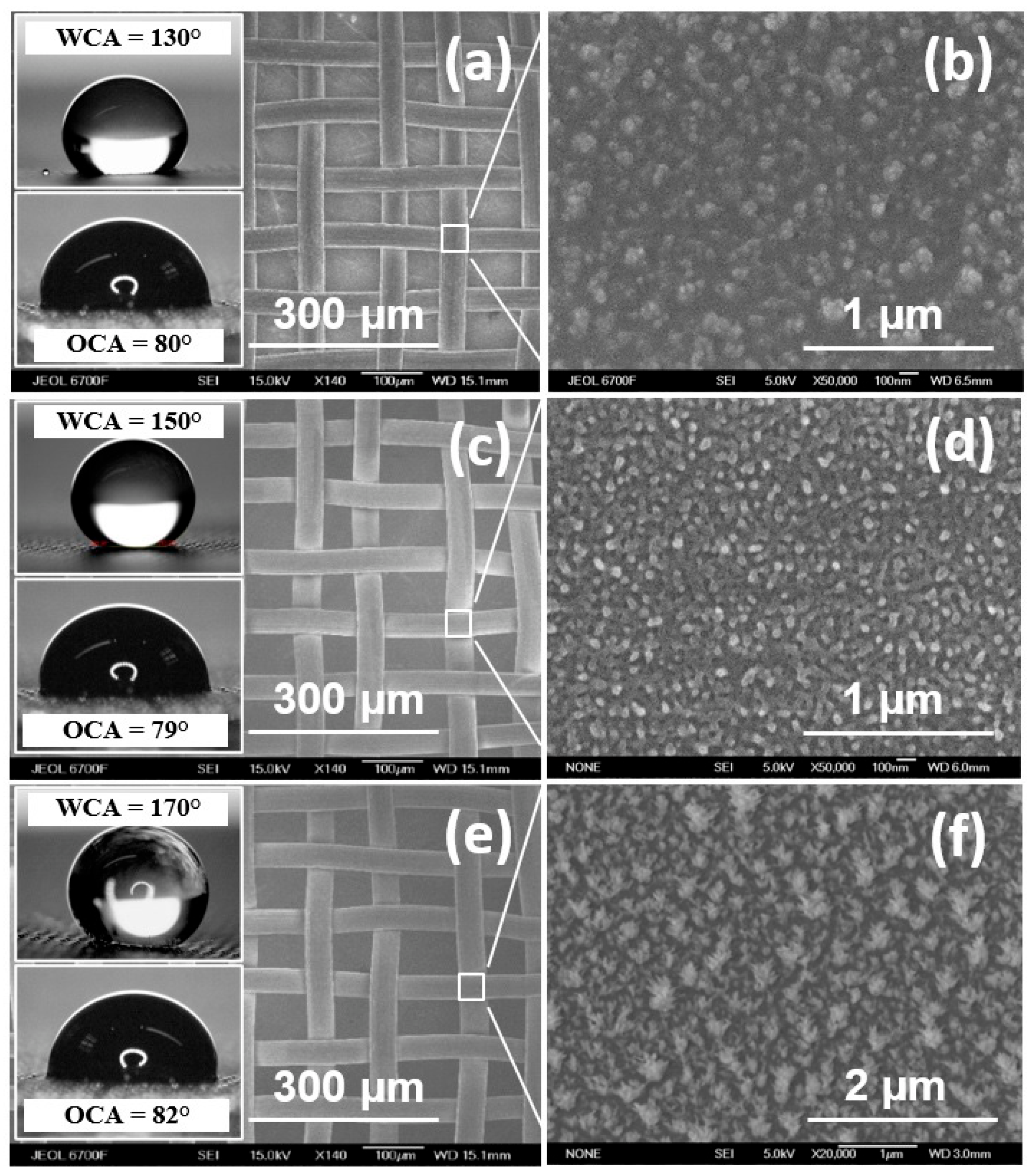
Figure 1 shows micrographs of a metal mesh after the deposition of hydrophobic fluoropolymer coatings and their water- and oil-wetting properties. The morphology of the fluoropolymer coating is different for each type of coating. However, the morphology is homogeneous over the entire mesh surface for each type of coating.
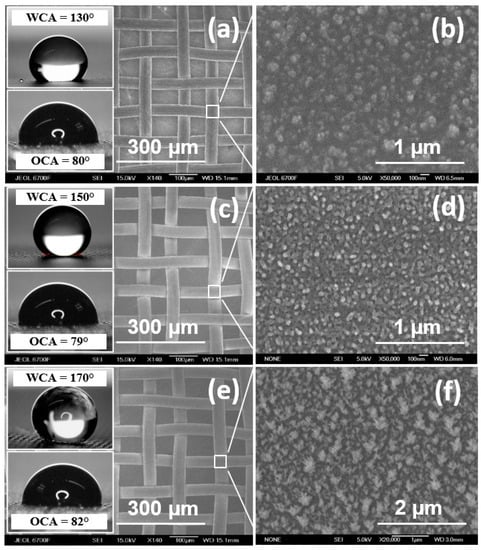
Figure 1.
Micrograph of the surface of membranes with various fluoropolymer coatings: (a,b) Type 1, (c,d) Type 2, and (e,f) Type 3. Insets include WCA values and photographs of water and oil droplets on the membrane surface.
The wetting properties of the resulting membranes were determined by measuring the water contact angle (WCA) or oil contact angle (OCA) using a DSA-E100 drop-shape analyzer (KRUSS, Hamburg, Germany). A drop of a characteristic volume of 3 µL was placed on the membrane surface. The image of the drop was captured using the shadow technique. The program recognizes the contour, and then the geometric model of the contour is selected. The baseline (contact line) was set in the program to more accurately determine the contact angle. The measured angle between the tangent to the drop contour and the baseline is the contact angle. Two methods were used to analyze the drop’s contour: the Young–Laplace method and the conic section method. Both methods evaluate the full contour of a lying drop. To accurately determine the wettability of the membranes, measurements were carried out in five different places, three times for each. The OCA of the obtained coatings was found to be similar at ~80° ± 2°, while the WCA was found to depend strongly on the morphology of the coating, varying in the range from ~130° ± 5° to 170° ± 2°.
2.4. Emulsion Preparation
The emulsion for experiments was prepared by mixing commercial crude oil and distilled water in various proportions. The use of commercial crude oil made it possible to accurately simulate the use of membranes in real conditions because oil contains a large number of various low- and high-molecular fractions, salts, and other impurities. All these components can interact with the membrane surface in different ways. For experiments, emulsions were prepared with different volume concentrations of water and oil. The mixture was stirred with a Braun MQ-5237 BK kitchen blender (Bucharest, Romania) for two minutes. The initial water content in commercial oil is less than 0.5% (GOST R 51858-2002), and it is neglected. The concentration was determined from:
where φw is the concentration of water in the emulsion, Vw is the volume of water mixed into the oil, and ΣVe is the total volume of the prepared emulsion. In the experiments, the values of concentration φw were as follows: 5%, 10%, 25%, 50%, and 90%. For each separation cycle, an emulsion was prepared in a volume of ΣVe = 50 mL.
2.5. Emulsion Separation Arrangement and Mechanism
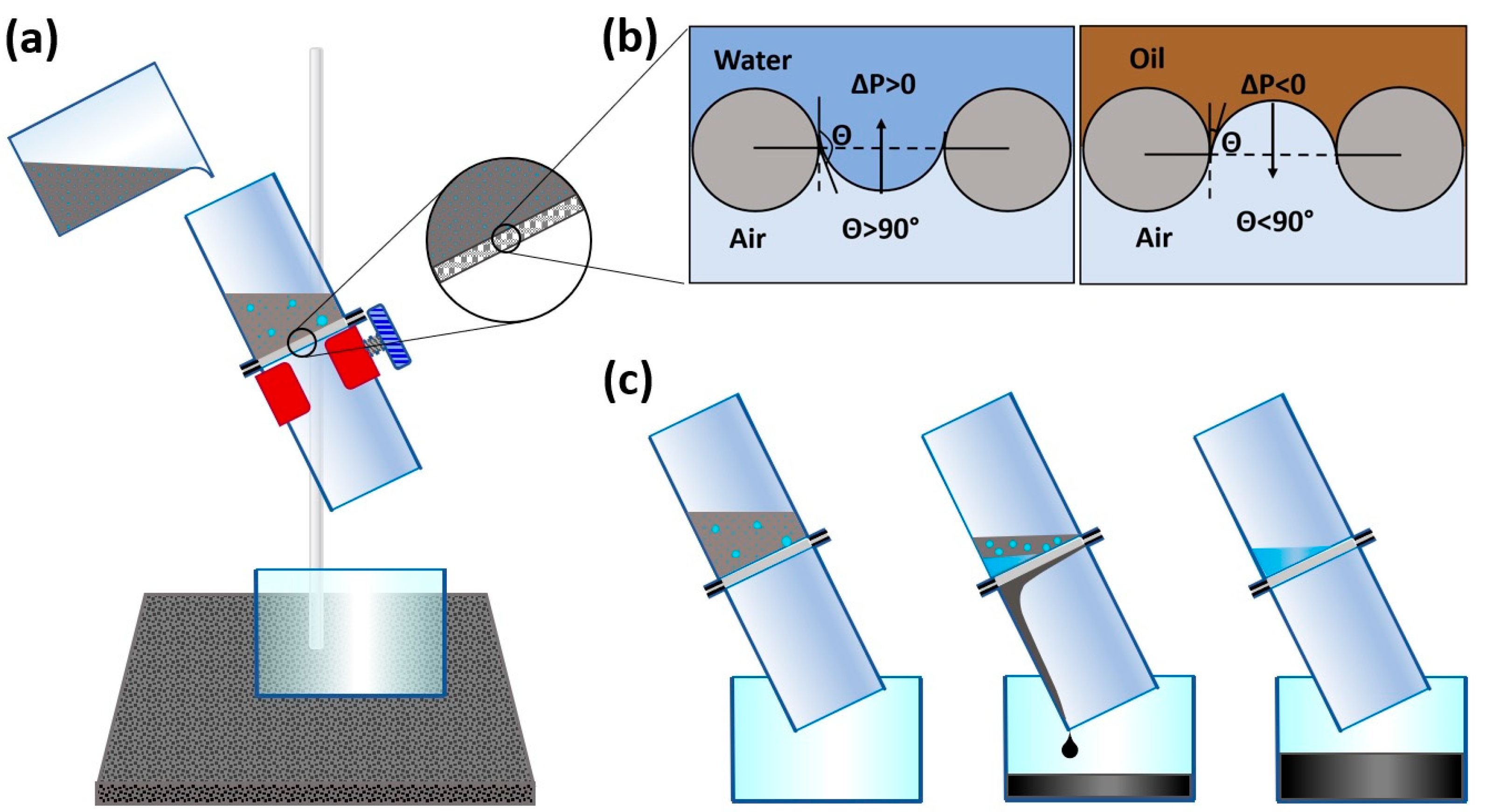
The experimental arrangement used for the separation tests is shown in Figure 2a. A membrane filter is fixed on a laboratory stand. This filter consists of two tightly connected glass tubes, between which the obtained membranes were installed. The membrane’s diameter was 33 mm.

Figure 2.
(a) Experimental stand for separation. (b) Schematic showing the oil–water separation mechanism on the superhydrophobic mesh. (c) Schematic of the separation process.
Figure 2b shows a scheme of the separation mechanism. It is assumed that the separation on the membrane is caused by the fact that the capillary pressure of oil and water in the pores is different.
The pressure can be calculated by using the Young–Laplace Equation (2) [51]:
where σ is the surface tension of the liquid–air interface, R is the meniscus radius, D is the center of the cross-section of adjacent, parallel stainless-steel wires, l is the mesh thickness, A is the cross-sectional area of the pore, and θA is the wetting angle of the liquid at the surface. It follows from this equation that in the absence of external pressure on the emulsion, WCA θA > 90°, water will not be able to spontaneously penetrate the pores because there is a pressure drop when ΔP > 0, which prevents it. However, for oil, the value is θA < 90°, so the pressure drop becomes ΔP < 0, and the oil will spontaneously penetrate the pores; that is, it will pass through the membrane. The process of the separation of water–oil emulsion will take place.
For the obtained membranes with various fluoropolymer coatings, OCA remains almost unchanged, while the WCA changes significantly. According to the equation, with an increase in hydrophobic properties, the pressure drop and separation efficiency should increase. That is, the higher the WCA value, the better and faster the separation of water and oil.
Figure 2c schematically shows the principle of the operation of the membrane filter; namely, the prepared emulsion is poured into the receiving container of the membrane filter, and the stopwatch is simultaneously started. Since the coating is hydrophobic, during the separation process, water remains above the surface of the membrane, while oil flows into the container under the filter. After separation, the volume of water is measured, recorded, and removed from the filter. The separation cycles continue as long as the water is released during the separation process. A new membrane was used each time to separate the new emulsion.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Wettability on Separation Efficiency and Rate
The separation efficiency was determined from:
where η is the separation efficiency, Vs is the volume of separated water from the emulsion, and Vw is the volume of water mixed into the emulsion. On average, the experiments were carried out 3–5 times. Considering the statistics, the error bars are indicated in the figures. The points on the figures and the results in the tables correspond to the average value of the results obtained.
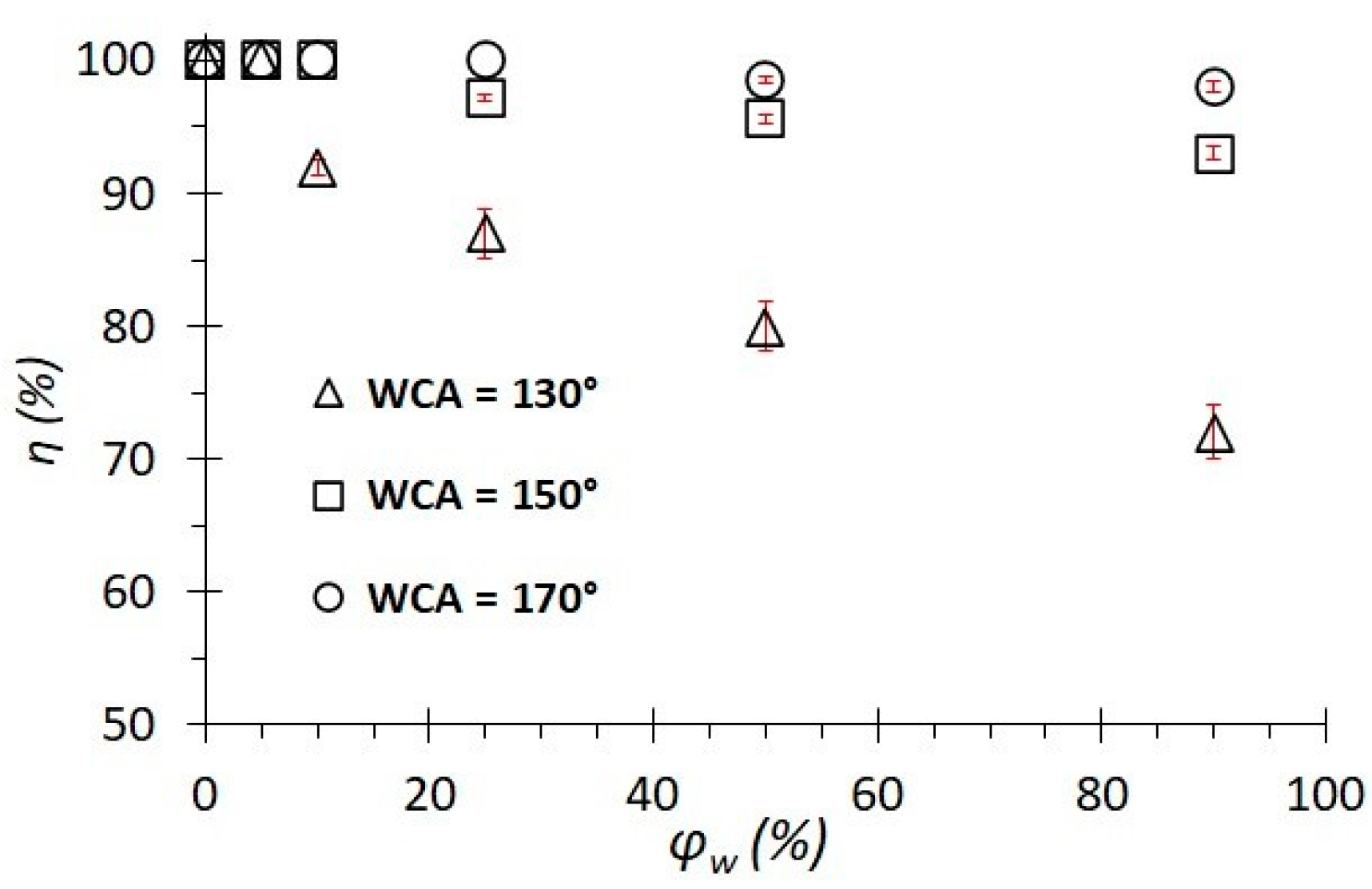
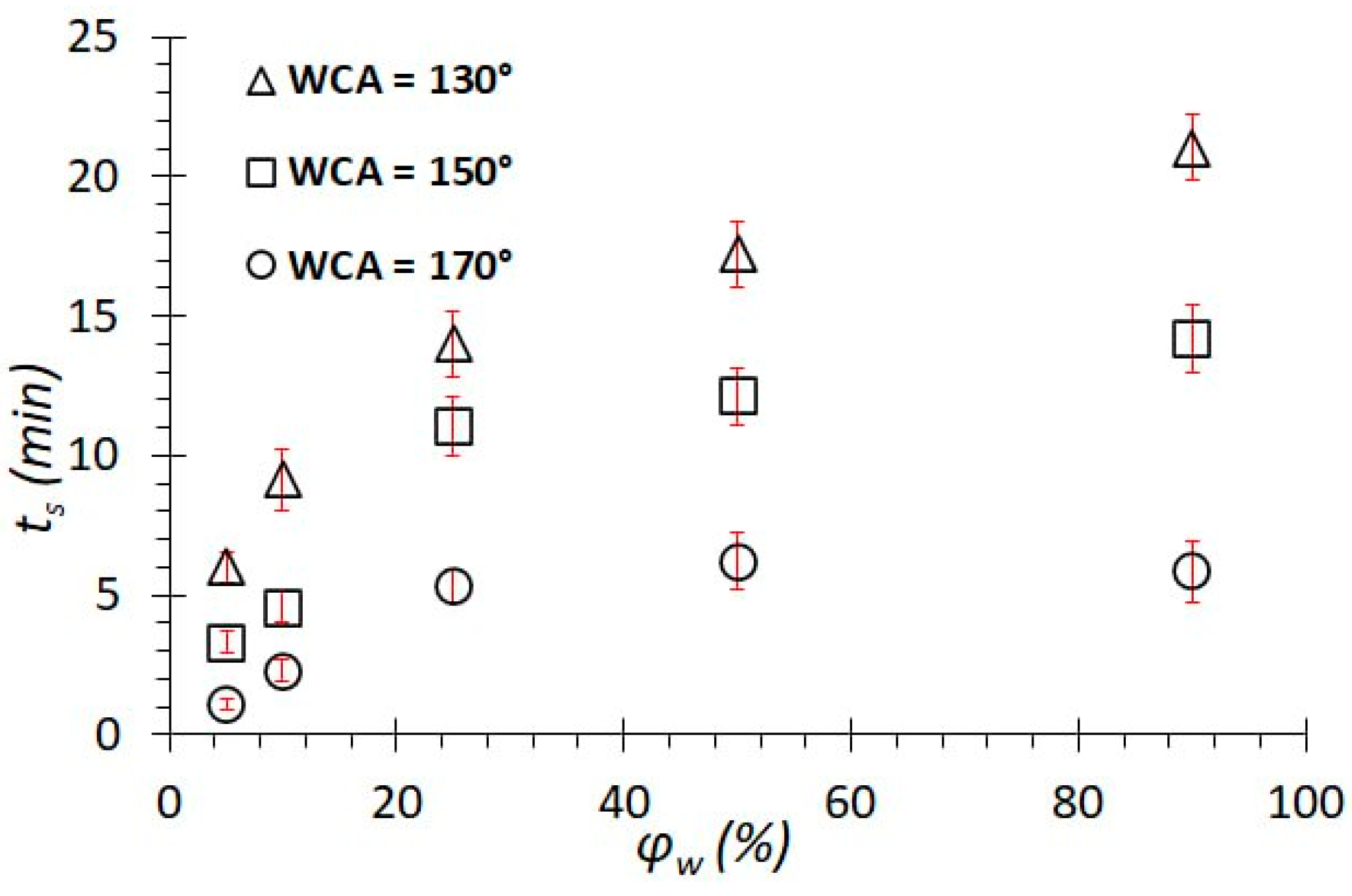
Figure 3 shows the results of the separation of emulsions with different water concentrations on membranes with different wettability. The separation of crude oil showed an efficiency close to 100%. The separation of distilled water showed an efficiency equal to η = 0%; that is, the entire volume of water remained on the membrane’s surface. Next, the separation of emulsions with different concentrations from 5% to 90% was carried out. The separation process is carried out in several cycles n, on average, 5–6. The graphs show the results of all separation cycles. The maximum separation efficiency of emulsions is achieved for membranes with a WCA = 170° and is about 99%. For superhydrophobic membranes, these values remain in a wide range of water concentrations in the emulsion. For membranes with hydrophobic coatings (WCA = 130°–150°) at low water concentrations (φw = 5%), the separation efficiency is also high and is about 98–99%. As the water concentration φw increases from 5 to 90% in the emulsion, the value of the separation efficiency decreases monotonically from η = 98% to 93% for membranes with a WCA = 150°. Similarly, for membranes with a WCA = 130°, the efficiency decreases to 75%. Thus, the wetting properties of the membrane significantly affect the separation efficiency. That is, superhydrophobic membranes can be used to separate emulsions with high water concentrations, while hydrophobic membranes are effective with emulsions with low water concentrations (φw = 5–25%).
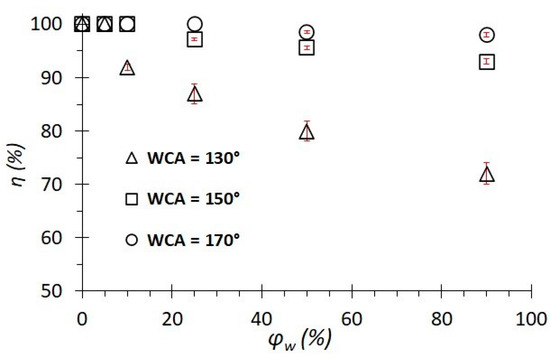
Figure 3.
Dependence of the separation efficiency on the water concentration in the emulsion for coatings with different wetting contact angles.
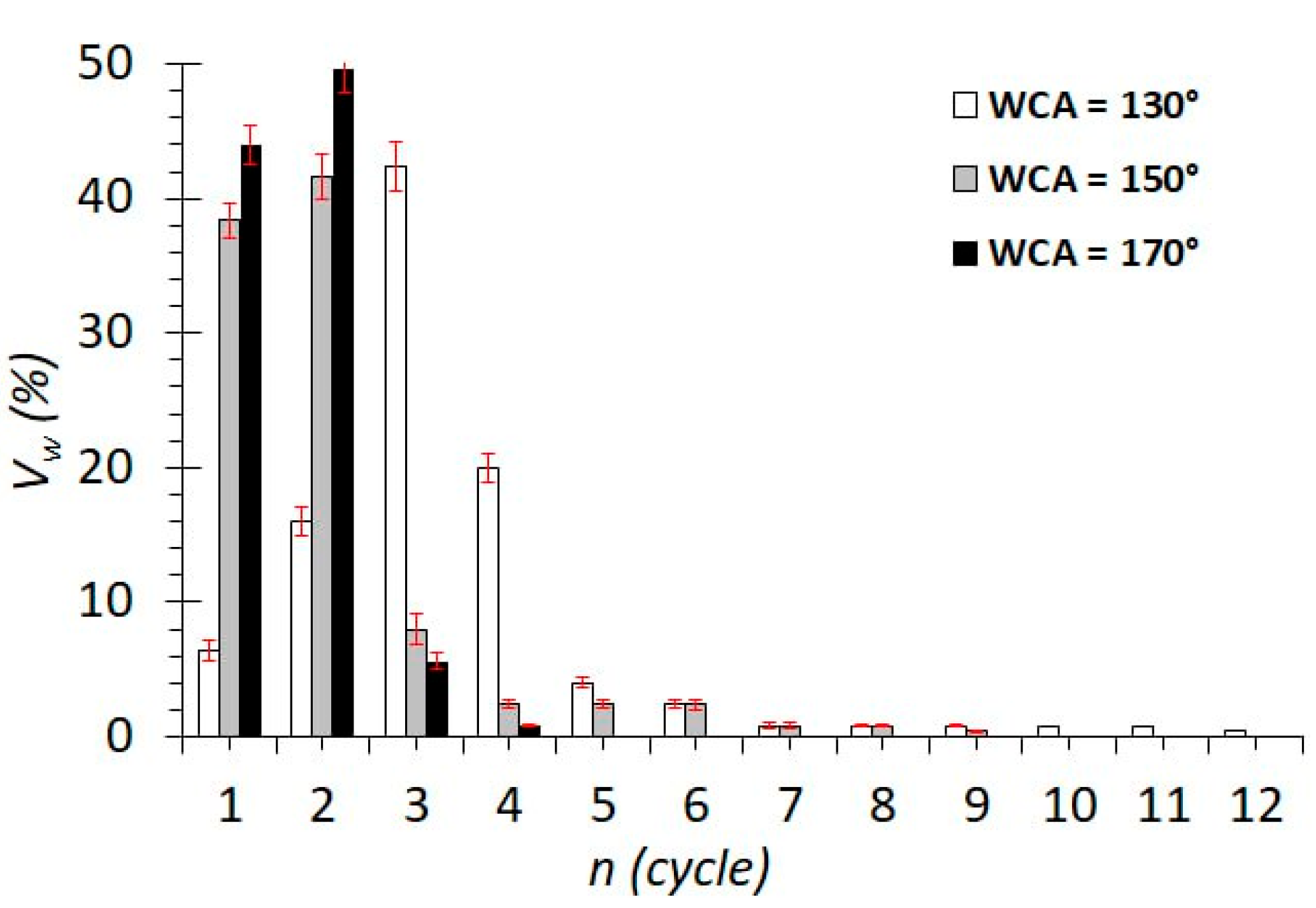
Figure 4 shows data on the volumes of water released in each cycle during the separation of an emulsion with a water concentration φw = 25%. It can be noted that the main volume of water is released during separation in the first 5–6 cycles. For membranes with WCAs between 150° and 170°, the maximum volume of water is released in the first two separation cycles, and for membranes with a WCA of 130°, the maximum volume of water is in the second, third, and fourth cycles. There is a clear dependence of the separation efficiency on the WCA of the membrane. The higher the WCA of the membrane, the faster the release of water from the emulsion.
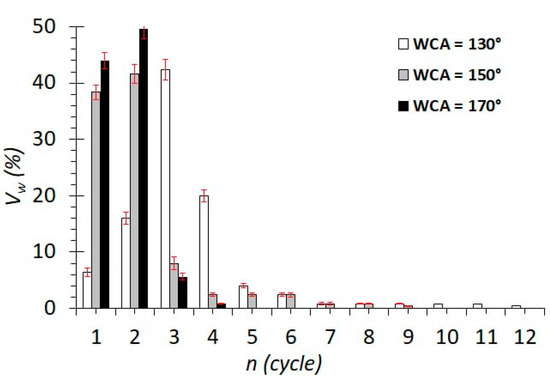
Figure 4.
Dependence of the volume of released water on the cycle number for different wetting contact angles.
In this case, the separation time increases with increasing water concentrations (Figure 5). Firstly, when a mixture of oil and water flows through the membrane filter, oil freely penetrates through the membrane with a hydrophobic coating, while water is repelled from the mesh due to a large negative capillary effect and remains on the surface, blocking the pores and thereby increasing the separation time. Secondly, the higher the concentration of water in the emulsion, the higher its viscosity, which prevents the flow of “fresh” portions of the emulsion to the membrane’s pores.
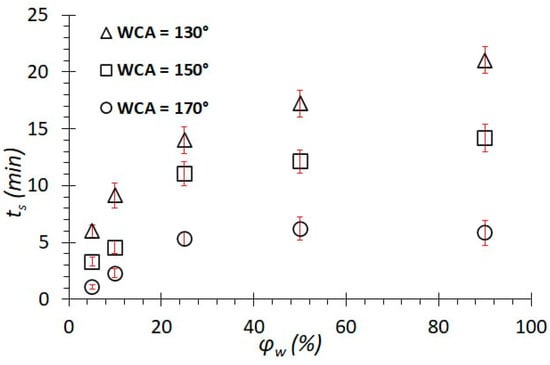
Figure 5.
Dependence of the separation time on the concentration of water in the emulsion for coatings with different wetting contact angles.
The total separation time on meshes with a WCA of 170° is higher than on meshes with a WCA between 150° and 130°. This is due to the fact that capillary pressure increases with an increasing contact angle; therefore, water is more efficiently and quickly separated from oil and remains on the surface, slowing down the flow of oil.
3.2. Influence of Mesh Pore Size on Separation Efficiency
To study the dependence of the separation efficiency of an oil–water emulsion on the pore size of hydrophobic membranes, stainless steel metal meshes with various weaves were used. Pore sizes were 40, 65, 90, and 200 microns. Fluoropolymer coatings with a wetting contact angle of 130° (Type 1) were deposited on the surfaces of the meshes. In the experiments, an emulsion with a water concentration of φw = 25% was used.
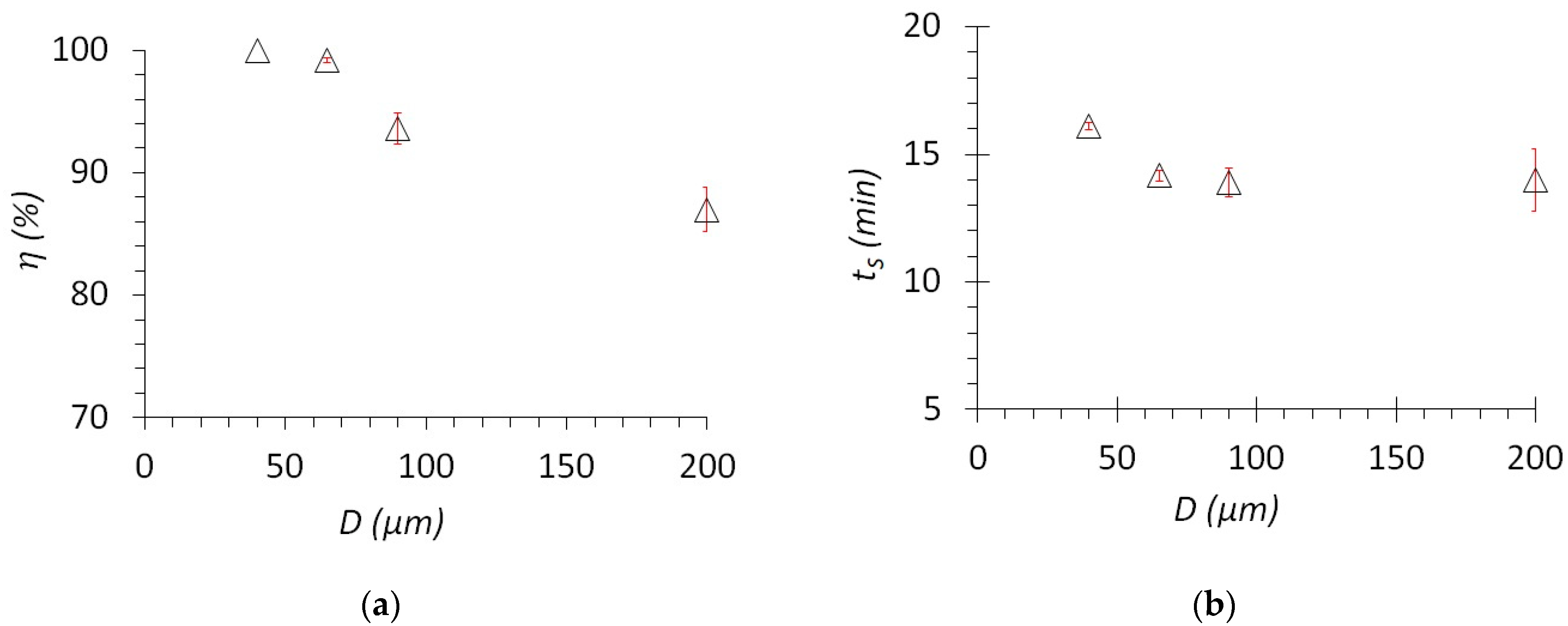
Figure 6a shows the dependence of the separation efficiency of the oil–water emulsion on the pore size of the membranes D. It can be noted that with a decrease in the pore size, the separation efficiency increases. Specifically, a membrane with a pore size of 200 µm separates with an efficiency of 87% and when using a pore size of 40 µm an efficiency increases to 99%. This is due to the fact that a membrane with small pores can retain water drops (micelles) with a smaller diameter on the surface, while water drops can penetrate through larger pores of the membrane, thereby reducing the separation efficiency. However, as the membrane’s pore size decreases, the separation time increases (Figure 6b). The time increases from 11 to 16 min for membranes with a pore size of 200 µm and 40 µm, respectively. This can be easily explained by an increase in hydrodynamic resistance caused by a decrease in the flow area of the membrane pores.
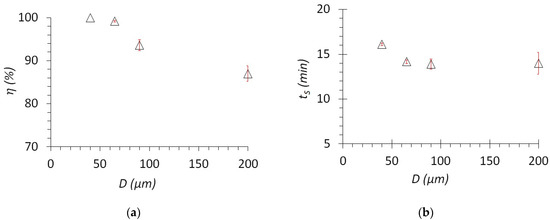
Figure 6.
(a) Dependence of separation efficiency on the pore size of a metal mesh and (b) dependence of separation time on the pore size of a metal mesh.
Apparently, the reason for the discrepancy between WCA and separation efficiency with respect to different authors is precisely the different pore sizes in the membranes.
3.3. Evaluation of Separation Efficiency on Membranes
The conducted studies have shown that it is necessary to introduce a parameter that would take into account all the above measurements and would make it possible to determine the overall efficiency of the separation process. This parameter is the coefficient of separation efficiency (CSE), which is determined by the following formula:
where η is the separation efficiency, ts is the separation time, and n is the number of separation cycles. The higher the CSE value, the higher the overall separation efficiency.
Using this formula, the coefficients for each membrane were determined. The results are presented in Table 2. Analyzing the data obtained, it can be noted that it is most effective to use membranes with a superhydrophobic coating for small concentrations of water in an oil emulsion.

Table 2.
Efficiency coefficient for the separation of emulsions with different water concentrations for different contact angles of a hydrophobic membrane.
Separation coefficients for membranes with different pore sizes were determined in a similar way (Table 3). In this case, superhydrophobic membranes with a pore size of 40 µm are more effective. However, the influence of the membrane pore size on efficiency is not as significant as the influence of the wetting properties of the membrane.

Table 3.
Efficiency coefficient for the separation of emulsions with a water concentration of 25% for different pore sizes of a hydrophobic membrane.
The results show that the highest efficiency is achieved when separating membranes with a superhydrophobic coating (WCA = 170°) and a minimum pore size (40 µm).
3.4. Resource Tests
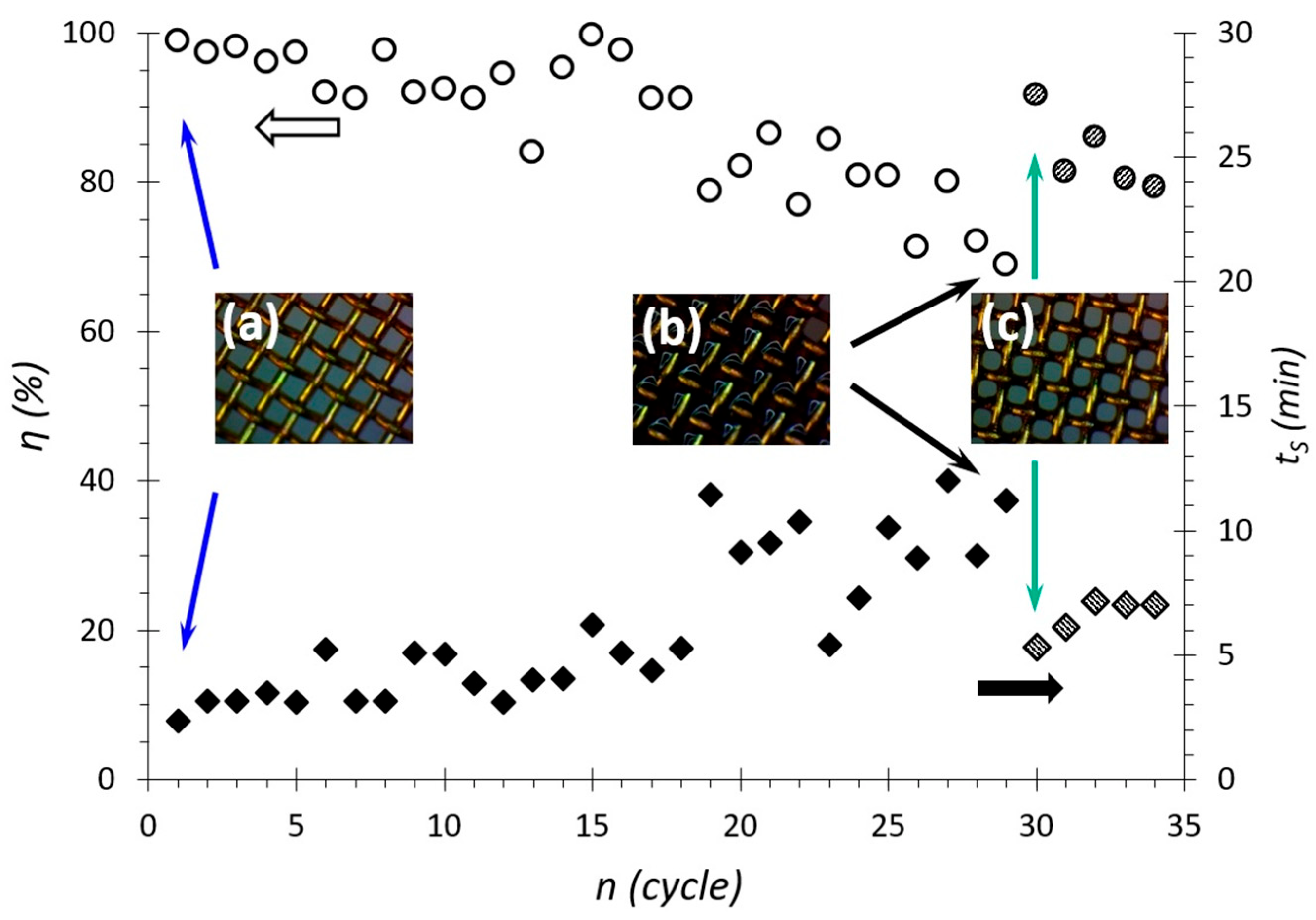
Resource tests were performed using the membranes obtained as described earlier in this paper. The fluoropolymer coating with a WCA = 130° had the highest wear resistance of the coatings in the study [46]. Therefore, these coatings were selected for resource testing. On a membrane with a pore size of 200 µm and a WCA = 130°, 30 successive cycles of separation of the emulsion with a water concentration φw = 25% were carried out. After each cycle, the efficiency and separation time were recorded. The results are shown in Figure 7. The results showed a decrease in separation efficiency after about six cycles. At the same time, for 18–20 cycles, the membrane separates the emulsion with a slight decrease in efficiency, and then, by the 30th cycle, there is a significant decrease in separation efficiency up to 70%. A similar pattern is observed with separation time. Namely, the separation time is almost unchanged up to the 6th cycle and is about 11 min, but by the 30th cycle, it increases to 40 min. The examination of the membrane with an optical microscope showed that with each new cycle, a “deposit” is formed on the membrane surface (Figure 7b). This “deposit” blocks the flow area of the pores, reducing the flow rate of the emulsion and the wetting properties of the membrane. Therefore, the efficiency decreases, and the separation time increases. It is likely that this “deposit” comprises high molecular weight hydrocarbons (paraffin, resin, etc.) contained in crude oil since it can be removed from the membrane surface by washing it for 5 min in diesel fuel. Using a microscope, small remnants of the “deposit” can be observed on the walls of the membrane pores (Figure 7b). However, this simple method of cleaning the membrane surface proved to be effective. After washing, the separation efficiency once again increased to ~92%, and the separation time decreased to 15 min.
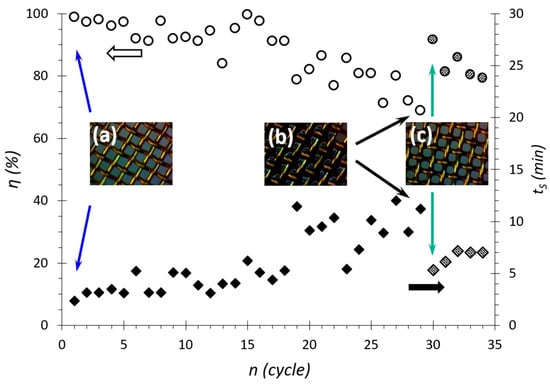
Figure 7.
Dependences of efficiency and separation time on the number of separation cycles. In the inserts, the surface of (a) clean, (b) used, and (c) washed membranes. The arrows indicate the points where clean (blue arrows), used (black arrows) and washed (green arrows) were used.
The obtained results showed comparable or better separation efficiency in comparison with the results presented in [25,27,28].
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The HW CVD method can be applied to the fabrication of highly efficient hydrophobic separation membranes by depositing fluoropolymer coatings onto the surfaces of metal meshes. Depending on the deposition parameters, it is possible to obtain membranes with different surface-wetting properties; specifically, in this work, the WCA ranges from 130 to 170°, while the OCA remains constant and is about 80° ± 2°.
- (2)
- Studies have shown the effectiveness of the use of the obtained membranes for the separation of emulsions of water and commercial crude oil, with separation efficiency values that can reach over 99%. The membrane-wetting properties affect the rate and efficiency of separation. The higher the WCA value of the membrane surface, the more efficient the separation. It has been established that emulsions with a lower water concentration (5%) are most effectively separated.
- (3)
- The pore size of the membrane significantly affects the rate and efficiency of separation. The smaller the pore size of the membranes, the higher the separation efficiency, but the lower its rate.
- (4)
- The use of the proposed coefficient of separation efficiency made it possible to determine the optimal parameters for the use of membranes for separating emulsions. The highest efficiency is achieved when separating membranes with a superhydrophobic coating (WCA = 170°) and a minimum pore size (40 µm).
- (5)
- The experiments were performed to explore whether hydrophobic coated membranes produced by the HW CVD method can be used for several separation cycles. The used membranes can be easily washed and reused without significant reduction in separation efficiency.
- (6)
- The work is of great economic and practical importance for improving the efficiency of the membrane separation of oil–water emulsions. It lays the foundation for future research on the use of hydrophobic membranes for the separation of various emulsions of water and oil products (diesel fuel, gasoline, kerosene, etc.).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S.; methodology, A.S.; validation, A.S.; investigation, A.M. and A.B.; resources, A.S. and A.B.; data curation, A.M. and A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M. and A.S.; writing—review and editing, A.S., A.M., A.P. and C.N.M.; visualization, A.M.; supervision, C.N.M.; project administration, A.P.; funding acquisition, C.N.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was executed from the state contract with IT SB RAS, project number 121031800218–5. The deposition of unique fluoropolymer coatings for this work was funded by the Russian Science Foundation, project number 18-79-10119. The experimental equipment was provided by the Government of the Russian Federation, under Megagrant project number 075-15-2022-1043.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge shared research facilities VTAN at NSU.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Joye, S.B. Deepwater Horizon, 5 Years On. Science 2015, 349, 592–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrope, M. Oil Spill: Deep Wounds. Nature 2011, 472, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaulding, M.L. State of the Art Review and Future Directions in Oil Spill Modeling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobolčiak, P.; Popelka, A.; Tanvir, A.; Al-Maadeed, M.A.; Adham, S.; Krupa, I. Some Theoretical Aspects of Tertiary Treatment of Water/Oil Emulsions by Adsorption and Coalescence Mechanisms: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.; Friedrich, E.; Schwarz, H.H.; Bartsch, D.; Hicke, H.G.; Neustadt, W.; Morgenstern, S.; Sawatzki, P.; Tietze, R. Membrane filtration for oil-water emulsion separation. Chem. Tech. 1979, 31, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Srijaroonrat, P.; Julien, E.; Aurelle, Y. Unstable Secondary Oil/Water Emulsion Treatment Using Ultrafiltration: Fouling Control by Backflushing. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 159, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, M.N.; Mishu, M.R.; Stylios, G.K.; Hasan, S.W.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zarra, T.; Belgiorno, V.; Naddeo, V. Sustainable Treatment of Food Industry Wastewater Using Membrane Technology: A Short Review. Water 2021, 13, 3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Li, W.; Ye, H.; Zhu, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, H. Environmentally Benign Development of Superhydrophilic and Underwater Superoleophobic Mesh for Effective Oil/Water Separation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 377, 124892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudu, B.K.; Kumar, A. Robust and Durable Superhydrophobic Steel and Copper Meshes for Separation of Oil-Water Emulsions. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 133, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pan, Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; Liu, X. Facile Fabrication of Durable Superhydrophobic Mesh via Candle Soot for Oil-Water Separation. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 136, 105253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Liang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, H. Improving the Corrosion Resistance of Aluminum Alloy by Creating a Superhydrophobic Surface Structure through a Two-Step Process of Etching Followed by Polymer Modification. Polymers 2022, 14, 4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Si, Y.; Raza, A.; Yang, L.; Mao, X.; Ding, B.; Yu, J. An in Situ Polymerization Approach for the Synthesis of Superhydrophobic and Superoleophilic Nanofibrous Membranes for Oil–Water Separation. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y. Oil-Water Separation Capability of Superhydrophobic Fabrics Fabricated via Combining Polydopamine Adhesion with Lotus-Leaf-like Structure. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, e42614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Rodrigue, D. A Review on Porous Polymeric Membrane Preparation. Part II: Production Techniques with Polyethylene, Polydimethylsiloxane, Polypropylene, Polyimide, and Polytetrafluoroethylene. Polymers 2019, 11, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Liu, F.; Xue, L. Under Seawater Superoleophobic PVDF Membrane Inspired by Polydopamine for Efficient Oil/Seawater Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 476, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Mai, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. A Super-Hydrophobic and Super-Oleophilic Coating Mesh Film for the Separation of Oil and Water. Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 2046–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Seeger, S. Polyester Materials with Superwetting Silicone Nanofilaments for Oil/Water Separation and Selective Oil Absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 4699–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, W.; Han, Y. A Composite Polymer Film with Both Superhydrophobicity and Superoleophilicity. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halake, K.; Bae, S.; Lee, J.; Cho, Y.; Jo, H.; Heo, J.; Park, K.; Kim, H.; Ju, H.; Kim, Y.; et al. Strategies for Fabrication of Hydrophobic Porous Materials Based on Polydimethylsiloxane for Oil-Water Separation. Macromol. Res. 2019, 27, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Xie, F.; Meng, J. Preparation of Superhydrophobic Porous Coating Film with the Matrix Covered with Polydimethylsiloxane for Oil/Water Separation. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 125, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldona, E.B.; De Leon, A.C.C.; Thomas, P.G.; Naylor, D.F.; Pajarito, B.B.; Advincula, R.C. Superhydrophobic Rubber-Modified Polybenzoxazine/SiO 2 Nanocomposite Coating with Anticorrosion, Anti-Ice, and Superoleophilicity Properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 1485–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cui, M.; Tian, H.; Wu, Y.; Zha, F.; Feng, H.; Tang, X. Facile Fabrication of Anti-Corrosive Superhydrophobic Diatomite Coatings for Removal Oil from Harsh Environments. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 189, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.-H.; Ji, P.-T.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y.-R.; Jia, S.-T. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic and Superoleophilic Textiles for Oil–Water Separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 284, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, K.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Fan, Q.; Xue, H. Highly Efficient and Robust Oil/Water Separation Materials Based on Wire Mesh Coated by Reduced Graphene Oxide. Langmuir 2017, 33, 9590–9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullahi, B.O.; Ahmed, E.; Al Abdulgader, H.; Alghunaimi, F.; Saleh, T.A. Facile Fabrication of Hydrophobic Alkylamine Intercalated Graphene Oxide as Absorbent for Highly Effective Oil-Water Separation. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 325, 115057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Zheng, S.; Wong, C.-P.; Liu, S.; Peng, Q. Massively Engineering the Wettability of Titanium by Tuning Nanostructures and Roughness via Laser Ablation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 30382–30388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, U.; Dastageer, M.A.; Gondal, M.A. Facile Fabrication of Super-Wettable Mesh Membrane Using Locally-Synthesized Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Application in Efficient Gravity Driven Oil/Water Separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 660, 130793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, A.; Al Abdulgader, H.; Alsaeed, D.; Drmosh, Q.A.; Baroud, T.N.; Saleh, T.A. Hydrophobic Tungsten Oxide-Based Mesh Modified with Hexadecanoic Branches for Efficient Oil/Water Separation. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 102931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Mu, P.; Zhu, G.; Li, J. Facile Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Copper Hydroxide Coated Mesh for Effective Separation of Water-in-Oil Emulsions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 230, 115856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wen, X.; Cheng, J.; Yang, Z. Sticky Superhydrophobic Filter Paper Developed by Dip-Coating of Fluorinated Waterborne Epoxy Emulsion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 8739–8746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yan, L.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Zha, F.; Lei, Z. A Facile One-Step Spray-Coating Process for the Fabrication of a Superhydrophobic Attapulgite Coated Mesh for Use in Oil/Water Separation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 53802–53808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Peng, S.; Deng, W.; Yang, X.; Miao, K.; Wen, N.; Miao, X.; Deng, W. Robust and Thermal-Healing Superhydrophobic Surfaces by Spin-Coating of Polydimethylsiloxane. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 508, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jiang, D.; Wei, Z.; Chen, J.; Jing, J. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Nano-Aluminum Films on Stainless Steel Meshes by Electrophoretic Deposition for Oil-Water Separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wang, F.; Zhao, B.; Ning, Y.; Lai, Y.; Wang, L. Acid/Base Treatment of Monolithic Activated Carbon for Coating Silver with Tunable Morphology. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2017, 32, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Yu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, R. Fabrication of Super-Hydrophobic and Super-Oleophilic Boehmite Membranes from Anodic Alumina Oxide Film via a Two-Phase Thermal Approach. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salapare, H.S.; Suarez, B.A.T.; Cosiñero, H.S.O.; Bacaoco, M.Y.; Ramos, H.J. Irradiation of Poly(Tetrafluoroethylene) Surfaces by CF4 Plasma to Achieve Robust Superhydrophobic and Enhanced Oleophilic Properties for Biological Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 46, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Lee, D.-H. Effect of Irradiation on the Surface Morphology of Nanostructured Superhydrophobic Surfaces Fabricated by Ion Beam Irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 477, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Baig, N. Efficient Chemical Etching Procedure for the Generation of Superhydrophobic Surfaces for Separation of Oil from Water. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 133, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padaki, M.; Isloor, A.M.; Nagaraja, K.K.; Nagaraja, H.S.; Pattabi, M. Conversion of Microfiltration Membrane into Nanofiltration Membrane by Vapour Phase Deposition of Aluminium for Desalination Application. Desalination 2011, 274, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liravi, M.; Pakzad, H.; Moosavi, A.; Nouri-Borujerdi, A. A Comprehensive Review on Recent Advances in Superhydrophobic Surfaces and Their Applications for Drag Reduction. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 140, 105537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Cao, C. Superhydrophobic Cotton Fabric Membrane Prepared by Fluoropolymers and Modified Nano-SiO 2 Used for Oil/Water Separation. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 31675–31687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Sun, X.; Kong, D.; Chu, D.; Hu, Y.; Duan, J.-A. Spatial Light Modulated Femtosecond Laser Ablated Durable Superhydrophobic Copper Mesh for Oil-Water Separation and Self-Cleaning. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 402, 126254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safonov, A.I.; Sulyaeva, V.S.; Gatapova, E.Y.; Starinskiy, S.V.; Timoshenko, N.I.; Kabov, O.A. Deposition Features and Wettability Behavior of Fluoropolymer Coatings from Hexafluoropropylene Oxide Activated by NiCr Wire. Thin Solid Films 2018, 653, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safonov, A.I.; Bogoslovtseva, A.L.; Sulyaeva, V.S.; Kiseleva, M.S.; Zhidkov, I.S.; Starinskiy, S.V. Effect of Annealing on the Structure and Properties of Thin Fluoropolymer Coatings Prepared by HW CVD. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 62, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starinskiy, S.V.; Bulgakov, A.V.; Gatapova, E.Y.; Shukhov, Y.G.; Sulyaeva, V.S.; Timoshenko, N.I.; Safonov, A.I. Transition from Superhydrophilic to Superhydrophobic of Silicon Wafer by a Combination of Laser Treatment and Fluoropolymer Deposition. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 255307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.P.; Lau, K.K.S.; Chan, K.; Mao, Y.; Gupta, M.; Shannan O’Shaughnessy, W.; Gleason, K.K. Initiated Chemical Vapor Deposition (ICVD) of Polymeric Nanocoatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 9400–9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuoka, H.; Yoshida, M.; Sugita, K.; Ohdaira, K.; Murata, H.; Matsumura, H. Fabrication of PTFE Thin Films by Dual Catalytic Chemical Vapor Deposition Method. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safonov, A.; Sulyaeva, V.; Timoshenko, N.; Gatapova, E.; Kabov, O.; Kirichenko, E.; Semenov, A. Deposition and Investigation of Hydrophobic Coatings. MATEC Web Conf. 2015, 37, 01047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boinovich, L.B.; Emelyanenko, A.M. Hydrophobic Materials and Coatings: Principles of Design, Properties and Applications. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2008, 77, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drelich, J.; Chibowski, E.; Meng, D.D.; Terpilowski, K. Hydrophilic and Superhydrophilic Surfaces and Materials. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 9804–9828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Gu, W.; Fu, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S. Preparation of Superhydrophobic/Oleophilic Copper Mesh for Oil-Water Separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 412, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).