An Integrated Principal Component and Hierarchical Cluster Analysis Approach for Groundwater Quality Assessment in Jazan, Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
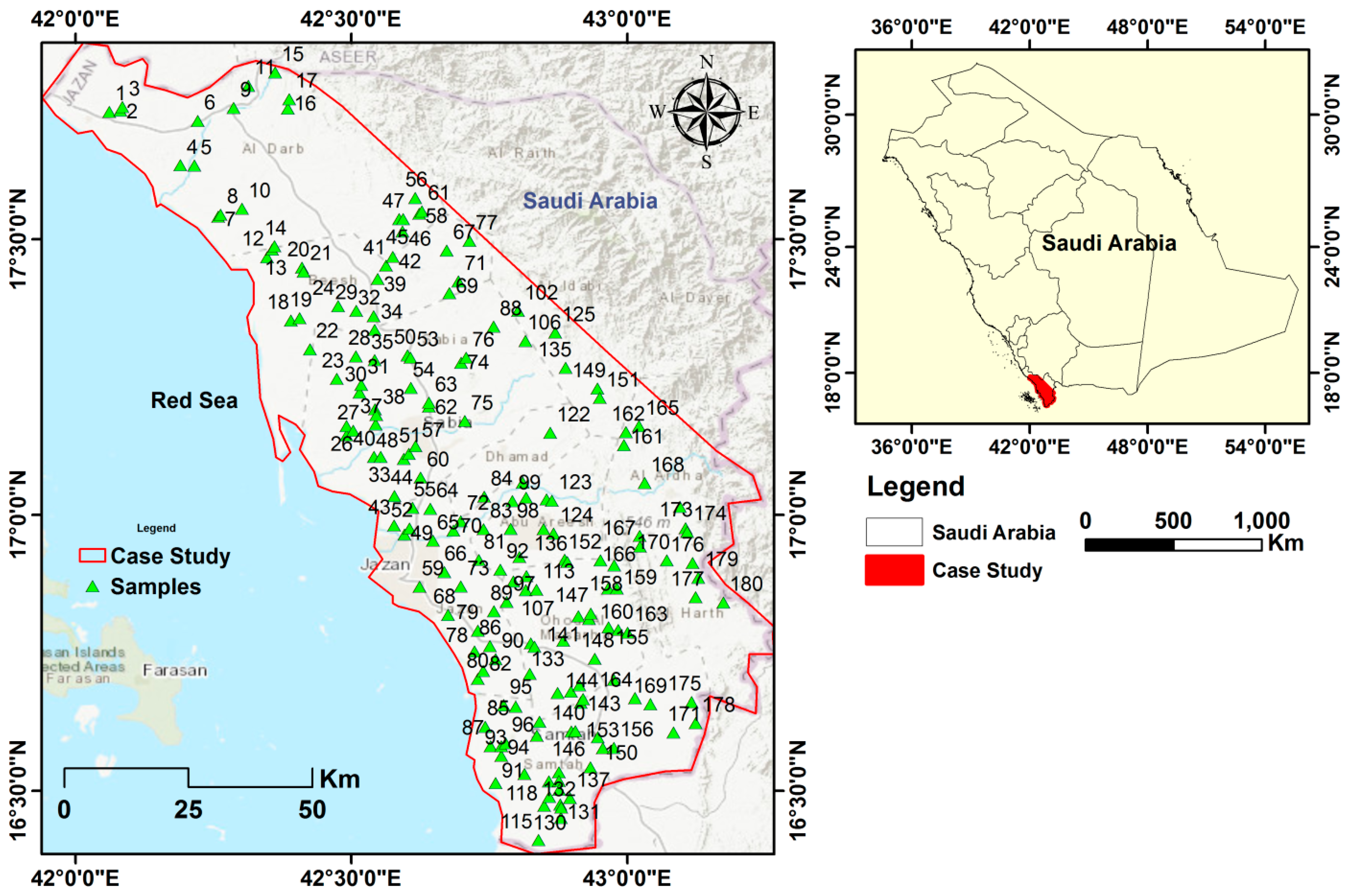
2.1. Study Area Describtion
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ionic Dominance
3.2. Irrigation Water Quality Assessment
3.3. Ion Exchange Processes
3.3.1. Chloro-Alkaline Indices CAI-1 and CAI-II
3.3.2. Hydrochemical Ratios and Chemical Water Type
3.3.3. Mechanisms of Controlling Groundwater Chemistry
3.4. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3.4.1. Correlation Coefficients
3.4.2. Factor Analysis
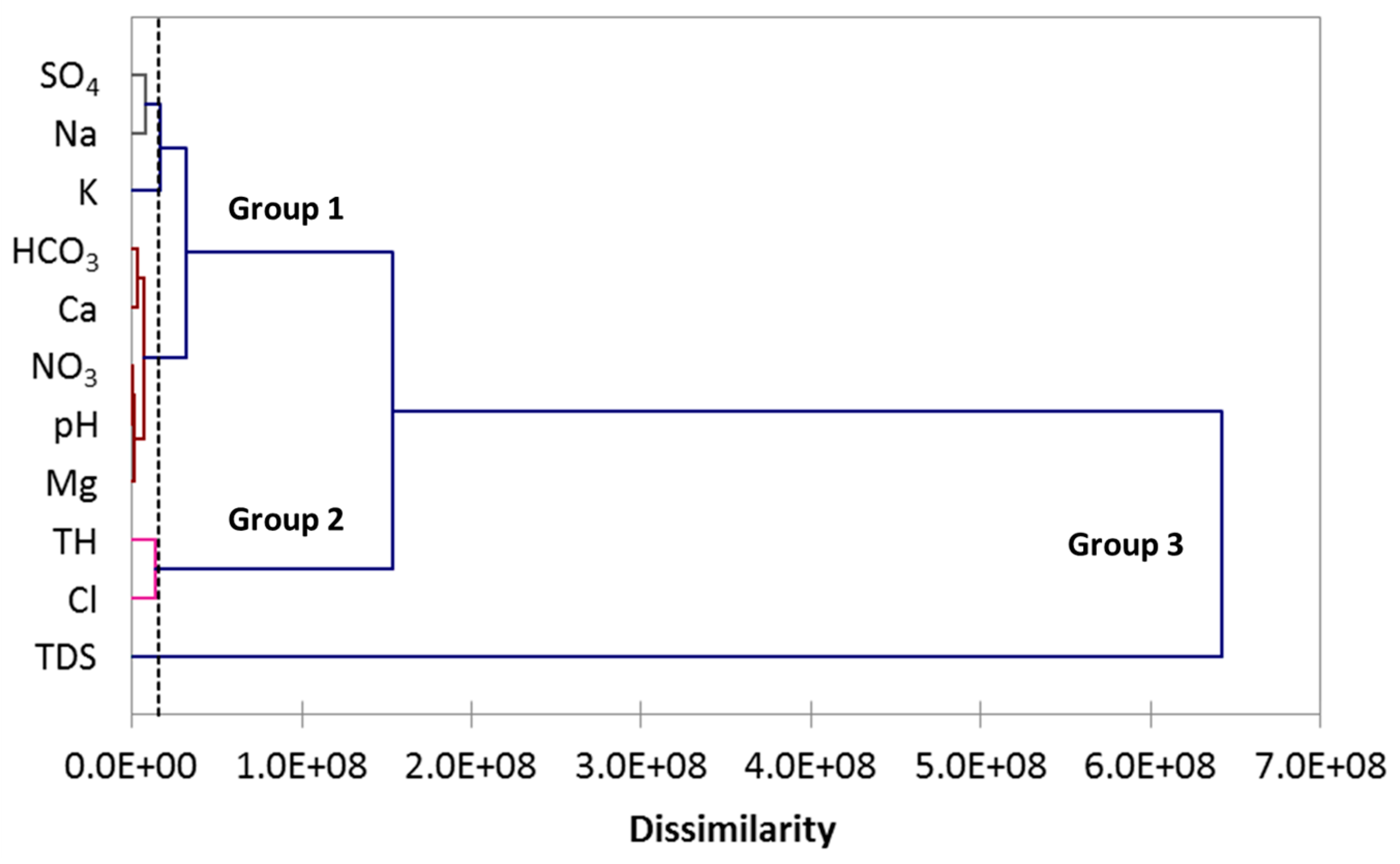
3.5. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA)
4. Conclusion and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alkolibi, F.M. Possible effects of global warming on agriculture and water resources in Saudi Arabia: Impacts and responses. Clim. Chang. 2002, 54, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K. A novel approach on water resource management with Multi-Criteria Optimization and Intelligent Water Demand Forecasting in Saudi Arabia. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazel, H.K.; Abdo, S.M.; Althaqafi, A.; Eldosari, S.H.; Zhu, B.-K.; Safaa, H.M. View of Saudi Arabia Strategy for Water Resources Management at Bishah, Aseer Southern Region Water Assessment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Al-Zahrani, M. Characterizing water resources and trends of sector wise water consumptions in Saudi Arabia. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2015, 27, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEWA (Ministry of Environment Water & Agriculture). Anural Report. 2021. Available online: https://www.mewa.gov.sa/ar/Pages/default.aspx (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Alzubieri, A.G.; Bantan, R.A.; Abdalla, R.; Antoni, S.; Al-Dubai, T.A.; Majeed, J. Application of GIS and remote sensing to monitor the impact of development activities on the coastal zone of Jazan City on the Red Sea, Saudi Arabia. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2018, XLII-3/W4, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.M.; Pradhan, B.; Sabtan, A.A.; El-Harbi, H.M. Coupling of remote sensing data aided with field investigations for geological hazards assessment in Jazan area, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 65, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanaty, N.; Mansour, K.; Fathi, H. Satellite-based assessment of the anthropogenic impacts on environmental sustainability in Jazan region, Red Sea. Egypt. J. Remote. Sens. Space Sci. 2023, 26, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SODP (Saudi Open Data Portal). Available online: https://od.data.gov.sa/en/home (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Abdalla, F. Ionic Ratios as Tracers to Assess Impacts of Seawater Intrusion into a Coastal Aquifer, Jazan, Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SWPC (Ministry of Environment Water & Agriculture). Seven Year Statement for KSA’s Water. Available online: https://idadesal.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/SWPC-7-Year-planning-Statement-2020-%E2%80%93-2026-Eng.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Mogren, S. Saltwater Intrusion in Jizan coastal zone, southwest Saudi Arabia, inferred from geoelectric resistivity survey. Int. J. Geosci. 2015, 6, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bassam, A.M.; Hussein, M.T. Combined Geo-Electrical and Hydro-Chemical Methods to Detect Salt- Water Intrusion. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2008, 19, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, M.H.; Basahi, J.M.; Rajmohan, N. Impact of flash flood recharge on groundwater quality and its suitability in the Wadi Baysh Basin, Western Saudi Arabia: An integrated approach. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, M.; Rajmohan, N.; Basahi, J.; Schneider, M.; Niyazi, B.; Alqarawy, A. Integrated Hydrogeochemical Groundwater Flow Path Modelling in an Arid Environment. Water 2022, 14, 3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hamid, A.; Hazem, T.; Hafiz, M.A.; Wenlong, W.; Qiaomin, L. Detection of environmental degradation in Jazan region on the Red Sea, KSA, Using mathematical treatments of remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 2, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaifi, H.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Qaysi, S.; Kahal, A.; Almadani, S.; Alshehri, F.; Zaidi, F.K. Evaluation of heavy metal contamination and groundwater quality along the Red Sea coast, southern Saudi Arabia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnashiri, H.M. Assessment of physicochemical parameters and heavy metal concentration in the effuents of sewage treatment plants in Jazan Region, Saudi Arabia. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2021, 33, 101600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, M.H.; Rajmohan, N.; Basahi, J.M.; Niyazi, B.A. Application of water quality indices and health risk models in the arid coastal aquifer, Southern Saudi Arabia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 70493–70507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D.V.; World Health Organization; UNESCO; United Nations Environment Programme. Water Quality Assessments: A Guide to the Use of Biota, Sediments and Water in Environmental Monitoring, 2nd ed.; Deborah, C., Ed.; E & FN Spon: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/41850 (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- El-Rawy, M.; Fathi, H.; Abdelrady, A.; Negm, A.M. Environmental Impacts of Treated Wastewater Contaminates on Groundwater Quality in the Nile River Valley, Egypt. In Sustainability of Groundwater in the Nile Valley, Egypt; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 91–120. [Google Scholar]
- Taşan, M.; Demir, Y.; Taşan, S. Groundwater quality assessment using principal component analysis and hierarchical cluster analysis in Alaçam, Turkey. Water Supply 2022, 22, 3431–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Osta, M.; Masoud, M.; Alqarawy, A.; Elsayed, S.; Gad, M. Groundwater Suitability for Drinking and Irrigation Using Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Modeling in Makkah Al-Mukarramah Province, Saudi Arabia. Water 2022, 14, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna Kumar, S.; Logeshkumaran, A.; Magesh, N.S.; Godson, P.S.; Chandrasekar, N. Hydro-geochemistry and application of water quality index (WQI) for groundwater quality assessment, Anna Nagar, part of Chennai City, Tamil Nadu, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2015, 5, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, T.; Bhardwaj, R.; Arora, S. Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes using hydrochemical studies in Malwa region, southwestern part of Punjab, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3301–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzal, Y.; Ahmed, I.; Al-Arifi, N.S.; Ghrefat, H.; Batayneh, A.; Abuamarah, B.A.; Zaidi, F.K. A combined hydrochemical-statistical analysis of Saq aquifer, northwestern part of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Geosci. J. 2015, 19, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, T.K.; Opoku, F.; Acquaah, S.O.; Akoto, O. Groundwater quality assessment using statistical approach and Water Quality Index in Ejisu-Juaben Municipality, Ghana. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldaw, E.; Huang, T.; Mohamed, A.K.; Mahama, Y. Classification of groundwater suitability for irrigation purposes using a comprehensive approach based on the AHP and GIS techniques in North Kurdufan Province, Sudan. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rawy, M.; Ismail, E.; Abdalla, O. Assessment of groundwater quality using GIS, hydrogeochemistry, and factor statistical analysis in Qena Governorate, Egypt. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 162, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, S.; Hussein, H.; Moghanm, F.S.; Khedher, K.M.; Eid, E.M.; Gad, M. Application of Irrigation Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Statistical Techniques for Surface Water Quality Assessments in the Northern Nile Delta, Egypt. Water 2020, 12, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Scholz, M.; Ali, M.; Gad, M.; Elsayed, S.; Khadr, M.; Hussein, H.; Ibrahim, H.H.; Eid, M.H.; et al. Evaluation and Prediction of Groundwater Quality for Irrigation Using an Integrated Water Quality Indices, Machine Learning Models and GIS Approaches: A Representative Case Study. Water 2023, 15, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.; Eldeeb, H.; El-Rawy, M. Assessment of surface and groundwater interaction using field measurements: A case study of Dairut City, Assuit, Egypt. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2020, 15, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- El-Rawy, M.; Abdalla, F.; Negm, A.M. Groundwater Characterization and Quality Assessment in Nubian Sandstone Aquifer, Kharga Oasis, Egypt. In Groundwater in Egypt’s Deserts; Negm, A., Elkhouly, A., Eds.; Springer Water; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.; Gaagai, A.; Eid, M.H.; Szűcs, P.; Hussein, H.; Elsherbiny, O.; Elsayed, S.; Khalifa, M.M.; Moghanm, F.S.; Moustapha, M.E.; et al. Groundwater Quality and Health Risk Assessment Using Indexing Approaches, Multivariate Statistical Analysis, Artificial Neural Networks, and GIS Techniques in El Kharga Oasis, Egypt. Water 2023, 15, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yustika, R.D.; Ariani, R. Water quality in Cidurian watershed, Indonesia. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 306, 04009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, M.H.; Elbagory, M.; Tamma, A.A.; Gad, M.; Elsayed, S.; Hussein, H.; Moghanm, F.S.; Omara, A.E.-D.; Kovács, A.; Péter, S. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality for Irrigation in Deep Aquifers Using Multiple Graphical and Indexing Approaches Supported with Machine Learning Models and GIS Techniques, Souf Valley, Algeria. Water 2023, 15, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, F.; Haque, M.M.; Tareq, S.M. Recent status of water quality in Bangladesh: A systematic review, meta-analysis and health risk assessment. Environ. Chall. 2022, 6, 100416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, M.; El Osta, M.; Alqarawy, A.; Elsayed, S.; Gad, M. Evaluation of groundwater quality for agricultural under different conditions using water quality indices, partial least squares regression models, and GIS approaches. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaagai, A.; Aouissi, H.A.; Bencedira, S.; Hinge, G.; Athamena, A.; Haddam, S.; Gad, M.; Elsherbiny, O.; Elsayed, S.; Eid, M.H.; et al. Application of Water Quality Indices, Machine Learning Approaches, and GIS to Identify Groundwater Quality for Irrigation Purposes: A Case Study of Sahara Aquifer, Doucen Plain, Algeria. Water 2023, 15, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basyoni, M.H.; Aref, M.A. Composition and origin of the sabkha brines, and their environmental impact on infrastructure in Jizan area, Red Sea Coast, Saudi Arabia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, F.; Al-Turki, A.; Al Amri, A. Evaluation of groundwater resources in the Southern Tihama plain, Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 3299–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakami, A.; Ghrefat, H.; Elwaheidi, M.; Galmed, M.; Yahya, M.A. Assessment of the corrosivity of the Southern Red Sea coastal sabkha soil: An integrated mineralogical, geochemical, and GIS approach. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th ed.; American Public Health Association Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Raghunath, H.M. Groundwater; Wiley Eastern Ltd.: Delhi, India, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Karanth, K.R. Groundwater Assessment, Development and Management; Tata McGraw Hill: New Delhi, India, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Doneen, L.D. Water Quality for Agriculture; Department of Irrigation, University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 1964; p. 48. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, W.P. Alkali Soils—Their Formation Properties and Reclamation; Reinhold Pub.: New York, NY, USA, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Schoeller, H. Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In Methods and Techniques of Groundwater Investigations and Development; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1965; p. 5483. [Google Scholar]
- Amadi, A.N.; Nwankwoala, H.O.; Olasehinde, P.I.; Okoye, N.O.; Okunlola, I.A.; Alkali, Y.B. Investigation of aquifer quality in Bonny Island, Eastern Niger Delta, Nigeria using geophysical and geochemical techniques. J. Emerg. Trends Eng. Appl. 2012, 3, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajmohan, N.; Elango, L. Identification and evolution of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment in an area of the Palar and Cheyyar River Basins, Southern India. Environ. Geol. 2014, 46, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Equation | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium percentage (Na%) | [44] | |
| Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR) | [45] | |
| Potential salinity (PS) | [46] | |
| Kelley’s ratio | [47] | |
| Magnesium hazard | [44] | |
| Permeability index | [46] | |
| Chloroalkaline Index (CAI) | [48] |
| Minimum | Maximum | Average | Std. Deviation | Variance | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na% | 1.9 | 97.1 | 56.06 | 16.21 | 262.83 | −0.35 | 0.49 |
| SAR | 0.01 | 41.7 | 8.25 | 6.50 | 42.29 | 2.15 | 7.04 |
| PI% | 5.5 | 79.9 | 58.98 | 17.36 | 301.28 | −0.10 | −0.28 |
| PS | 0.95 | 117.0 | 19.89 | 20.47 | 419.14 | 2.43 | 7.34 |
| MH% | 4.0 | 56.9 | 24.36 | 9.61 | 92.26 | 1.05 | 1.17 |
| KR | 0.01 | 19.19 | 1.49 | 1.75 | 3.06 | 6.46 | 59.06 |
| CAI (I) | −42.97 | 104.23 | 14.24 | 19.69 | 387.79 | 2.25 | 7.43 |
| CAI (II) | −1.68 | 101.37 | 14.70 | 18.22 | 332.06 | 2.73 | 9.06 |
| Gibbs ratio1 | 0.07 | 0.98 | 0.69 | 0.20 | 0.04 | −0.59 | −0.42 |
| Gibbs ratio2 | 0.02 | 0.98 | 0.62 | 0.16 | 0.03 | −0.73 | 1.30 |
| r(Na + K)/rCl | 0.03 | 43.27 | 1.78 | 3.42 | 11.71 | 10.22 | 121.17 |
| rCa/rMg | 0.74 | 47.69 | 3.99 | 4.00 | 16.01 | 8.03 | 81.42 |
| rSO4/rCl | 0.06 | 19.50 | 1.00 | 1.69 | 2.85 | 7.82 | 80.57 |
| Water Quality Indices | Water Type | Range | No. of Samples | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC (μS/cm) | <250 | Excellent | 1 | 0.56 |
| 250–750 | Good | 17 | 9.44 | |
| 750–2250 | Permissible | 77 | 42.78 | |
| 2250–5000 | Doubtful | 63 | 35.00 | |
| >5000 | Unsuitable | 22 | 12.22 | |
| The sodium percentage (Na%) | <20 | Excellent | 3 | 1.67 |
| 20–40 | Good | 24 | 13.33 | |
| 40–60 | Permissible | 78 | 43.33 | |
| 60–80 | Doubtful | 65 | 36.11 | |
| >80 | Unsuitable | 10 | 5.56 | |
| Sodium adsorption ratio (SAR) | <10 | Excellent | 131 | 72.78 |
| 10–18 | Good | 34 | 18.89 | |
| 18–26 | Doubtful | 11 | 6.11 | |
| >26 | Unsuitable | 4 | 2.22 | |
| Permeability Index (PI) | >75 | Good | 38 | 21.11 |
| 75–25 | Moderate | 139 | 77.22 | |
| <25 | Poor | 3 | 1.67 | |
| Potential salinity (PS) | <3 | Excellent to good | 14 | 7.78 |
| 3–5 | Good to injurious | 16 | 8.89 | |
| >5 | Injurious to unsatisfactory | 150 | 83.33 | |
| Magnesium hazard (MH) | >50% | Unsuitable | 3 | 1.67 |
| <50% | Suitable | 177 | 98.33 | |
| Kelley’s ratio (KR) | >1 | Unsuitable | 99 | 55.00 |
| <1 | Good | 81 | 45.00 |
| Variables | pH | K+ | Na+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | SO42− | Cl− | HCO3− | NO3− | TDS | TH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | ||||||||||
| K+ | −0.239 | 1 | |||||||||
| Na+ | −0.107 | 0.456 | 1 | ||||||||
| Mg2+ | −0.251 | 0.274 | 0.424 | 1 | |||||||
| Ca2+ | −0.283 | 0.279 | 0.505 | 0.795 | 1 | ||||||
| SO42− | −0.221 | 0.577 | 0.590 | 0.441 | 0.580 | 1 | |||||
| Cl− | −0.167 | 0.286 | 0.809 | 0.786 | 0.805 | 0.412 | 1 | ||||
| HCO3− | −0.276 | 0.241 | 0.078 | 0.128 | 0.042 | 0.079 | 0.004 | 1 | |||
| NO3− | −0.043 | 0.489 | 0.166 | 0.193 | 0.248 | 0.479 | 0.089 | 0.131 | 1 | ||
| TDS | −0.228 | 0.426 | 0.850 | 0.804 | 0.852 | 0.650 | 0.957 | 0.094 | 0.230 | 1 | |
| TH | −0.283 | 0.292 | 0.494 | 0.937 | 0.957 | 0.545 | 0.841 | 0.085 | 0.235 | 0.876 | 1 |
| F1 | F2 | F3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0.103 | 0.058 | 0.487 |
| K+ | 0.272 | 0.441 | 0.021 |
| Na+ | 0.574 | 0.000 | 0.071 |
| Mg2+ | 0.719 | 0.054 | 0.034 |
| Ca2+ | 0.801 | 0.040 | 0.006 |
| SO42− | 0.515 | 0.155 | 0.061 |
| Cl− | 0.802 | 0.114 | 0.002 |
| HCO3− | 0.022 | 0.222 | 0.382 |
| NO3− | 0.124 | 0.428 | 0.092 |
| TDS | 0.950 | 0.018 | 0.004 |
| TH | 0.850 | 0.051 | 0.018 |
| Eigenvalue | 5.731 | 1.581 | 1.178 |
| Variability (%) | 52.097 | 14.374 | 10.708 |
| Cumulative% | 52.097 | 66.472 | 77.180 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Rawy, M.; Fathi, H.; Abdalla, F.; Alshehri, F.; Eldeeb, H. An Integrated Principal Component and Hierarchical Cluster Analysis Approach for Groundwater Quality Assessment in Jazan, Saudi Arabia. Water 2023, 15, 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081466
El-Rawy M, Fathi H, Abdalla F, Alshehri F, Eldeeb H. An Integrated Principal Component and Hierarchical Cluster Analysis Approach for Groundwater Quality Assessment in Jazan, Saudi Arabia. Water. 2023; 15(8):1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081466
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Rawy, Mustafa, Heba Fathi, Fathy Abdalla, Fahad Alshehri, and Hazem Eldeeb. 2023. "An Integrated Principal Component and Hierarchical Cluster Analysis Approach for Groundwater Quality Assessment in Jazan, Saudi Arabia" Water 15, no. 8: 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081466
APA StyleEl-Rawy, M., Fathi, H., Abdalla, F., Alshehri, F., & Eldeeb, H. (2023). An Integrated Principal Component and Hierarchical Cluster Analysis Approach for Groundwater Quality Assessment in Jazan, Saudi Arabia. Water, 15(8), 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081466








