The Impacts of the Hydrological Regime on the Soil Aggregate Size Distribution and Stability in the Riparian Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
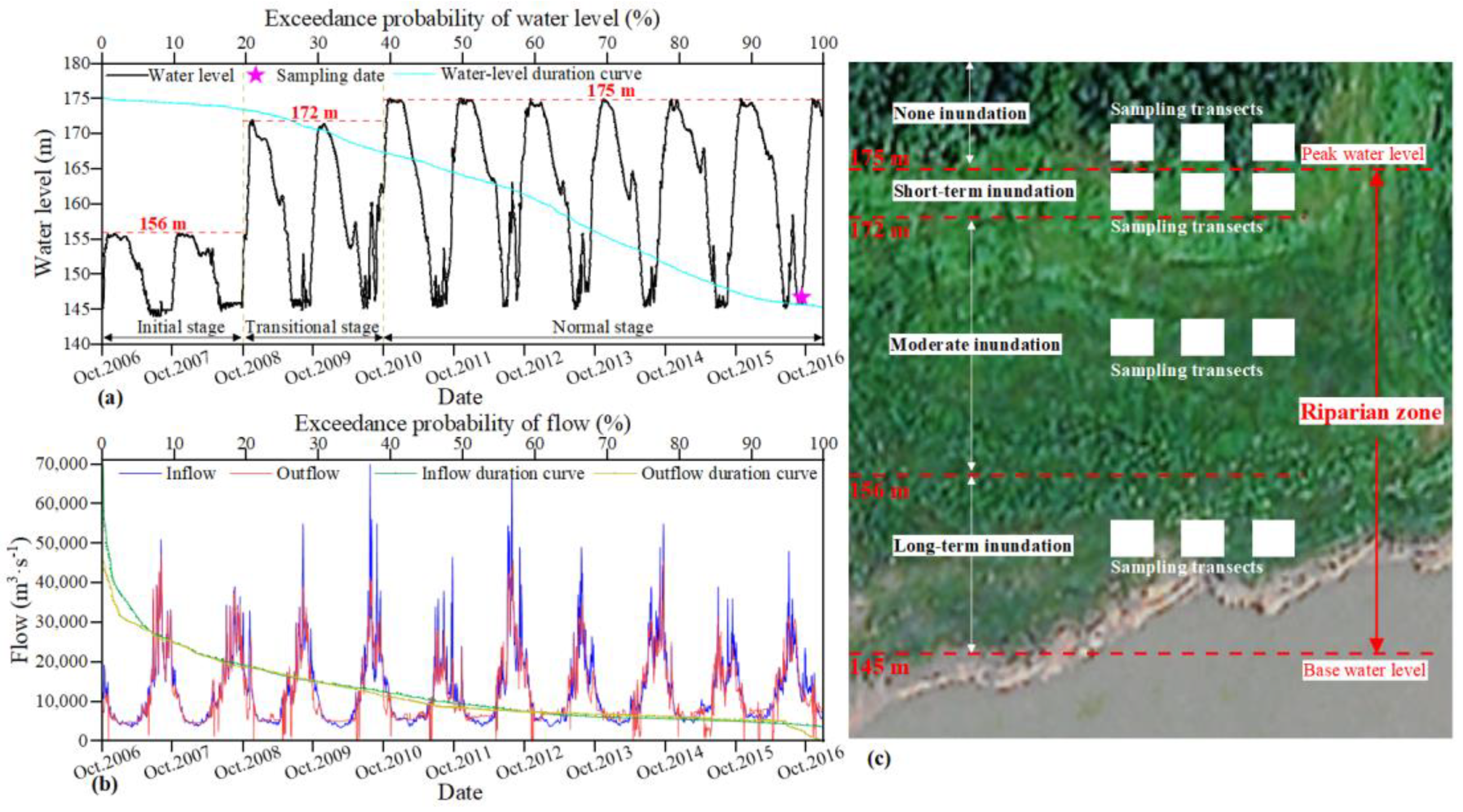
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field Sampling
2.3. Soil Properties Analysis
2.4. Soil Aggregate Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
3.2. Size Distribution of Mechanically Stable Aggregates
3.3. Size Distribution of Water-Stable Aggregates
3.4. Aggregate Stability along the Elevation Gradient
3.5. Determinants of Soil Aggregate Stability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rabot, E.; Wiesmeier, M.; Schlüter, S.; Vogel, H.J. Soil structure as an indicator of soil functions: A review. Geoderma 2018, 314, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkholm, L.J.; Heck, R.J.; Deen, B. Soil pore characteristics assessed from X-ray micro-CT derived images and correlations to soil friability. Geoderma 2012, 181–182, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bissonnais, Y. Aggregate stability and assessment of soil crustability: I. Theory and methodology. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1996, 47, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bissonnais, Y.; Arrouays, D. Aggregate stability and assessment of soil crustability and erodibility: II. Application to humic loamy soils with various organic carbon contents. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1997, 48, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsabimana, G.; Hong, L.; Yuhai, B.; de Dieu Nambajimana, J.; Jinlin, L.; Ntacyabukura, T.; Xiubin, H. Soil aggregate disintegration effects on soil erodibility in the water level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ. Res. 2023, 217, 114928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohošková, M.; Valla, M. Comparison of two methods for aggregate stability measurement—A review. Plant Soil Environ. 2004, 50, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygın, S.D.; Cornelis, W.M.; Erpul, G.; Gabriels, D. Comparison of different aggregate stability approaches for loamy sand soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2012, 54, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seybold, C.; Herrick, J. Aggregate stability kit for soil quality assessments. Catena 2001, 44, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthès, B.; Roose, E. Aggregate stability as an indicator of soil susceptibility to runoff and erosion; validation at several levels. Catena 2002, 47, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wei, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; She, L.; Wang, J.; Cai, C. Effects of soil physicochemical properties on aggregate stability along a weathering gradient. Catena 2017, 156, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, D.; Chenu, C.; Le Bissonnais, Y. Aggregate stability and microbial community dynamics under drying–wetting cycles in a silt loam soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 2053–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utomo, W.; Dexter, A. Changes in soil aggregate water stability induced by wetting and drying cycles in non-saturated soil. J. Soil Sci. 1982, 33, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochman, D.; Dor, M.; Mishael, Y. Diverse effects of wetting and drying cycles on soil aggregation: Implications on pesticide leaching. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Hallett, P.D.; Zhang, B.; Horn, R. Physical response of rigid and non-rigid soils to analogues of biological exudates. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 62, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Guo, Z.C.; Zhang, Z.B.; Zhou, H.; Peng, X.H. Wetting and drying cycles improving aggregation and associated C stabilization differently after straw or biochar incorporated into a Vertisol. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 175, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Collins, A.L.; Wen, A.; He, X.; Bao, Y.; Yan, D.; Long, Y.; Zhang, Y. Particle size differentiation explains flow regulation controls on sediment sorting in the water-level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1114–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Tang, X.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C. The Effects of Timing of Inundation on Soil Physical Quality in the Water-Level Fluctuation Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17, 180043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; He, X.; Wen, A.; Gao, P.; Tang, Q.; Yan, D.; Long, Y. Dynamic changes of soil erosion in a typical disturbance zone of China’s Three Gorges Reservoir. Catena 2018, 169, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Yu, D.; Tang, Q.; He, X.; WEi, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, J. Combined Effects of Hillslope-Concentrated Flows and Riverine Stream Waves on Soil Erosion in the Reservoir Riparian Zone. Water 2021, 13, 3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Bao, Y.; He, X.; Fu, B.; Collins, A.L.; Zhang, X. Flow regulation manipulates contemporary seasonal sedimentary dynamics in the reservoir fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548–549, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Gao, P.; He, X. The water-level fluctuation zone of Three Gorges Reservoir—A unique geomorphological unit. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 150, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, L.F.; Auler, A.C.; Roque, W.L.; Mooney, S.J. X-ray microtomography analysis of soil pore structure dynamics under wetting and drying cycles. Geoderma 2020, 362, 114103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amézketa, E. Soil Aggregate Stability: A Review. J. Sustain. Agric. 1999, 14, 83–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, J.; Adey, M. Changes in microstructure, voids and b-fabric of surface samples of a Vertisol caused by wet/dry cycles. Geoderma 1998, 85, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Horn, R.; Smucker, A. Pore Shrinkage Dependency of Inorganic and Organic Soils on Wetting and Drying Cycles. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.; Ma, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, X.; Wu, S.; Huang, P. Hydrological stress regimes regulate effects of binding agents on soil aggregate stability in the riparian zones. Catena 2021, 196, 104815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.; Ma, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, K.; Yi, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Huang, P. Physicochemical determinants in stabilizing soil aggregates along a hydrological stress gradient on reservoir riparian habitats: Implications to soil restoration. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 143, 105664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsabimana, G.; Bao, Y.; He, X.; Nambajimana, J.d.D.; Wang, M.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Khurram, D. Impacts of Water Level Fluctuations on Soil Aggregate Stability in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsabimana, G.; Bao, Y.; He, X.; Nambajimana, J.d.D.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Uwiringiyimana, E.; Nsengumuremyi, P.; Ntacyabukura, T. Soil aggregate stability response to hydraulic conditions in water level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Catena 2021, 204, 105387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Bao, Y.; Nan, H.; Xiong, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J. Tillage pedogenesis of purple soils in southwestern China. J. Mt. Sci. 2009, 6, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-J.; Tang, Q.; Bao, Y.-H.; He, X.-B.; Tian, F.-X.; Lü, F.-Y.; Wang, M.-F.; Anjum, R. Effects of seasonal water-level fluctuation on soil pore structure in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 2192–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, R. A direct method of aggregate analysis of soils and a study of the physical natural of erosion losses. J. Am. Soc. Agron. 1936, 28, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemper, W.; Rosenau, R. Aggregate Stability and Size Distribution. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1: Physical and Mineralogical Methods; Klute, A., Ed.; ASA and SSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 425–442. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Tang, C.; Liao, K.; Liu, Y. Factors contributing to aggregate stability at different particle sizes in ultisols from Southern China. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 19, 1342–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bavel, C. Mean weight-diameter of soil aggregates as a statistical index of aggregation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1950, 14, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurak, A. Effect of gaseous phase on water-stable synthetic aggregates. Soil Sci. 1950, 69, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, S.; Wheatcraft, S. Fractal scaling of soil particle-size distribution: Analysis and limitation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Horn, R. Mechanisms of aggregate stabilization in Ultisols from subtropical China. Geoderma 2001, 99, 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, J.; Tabacchi, E.; Dufour, S.; Corenblit, D.; Peiry, J.L. Hydrogeomorphic processes affecting riparian habitat within alluvial channel-floodplain river systems: A review for the temperate zone. River Res. Appl. 2005, 21, 719–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhu, K.; Li, W.; Liu, Z.; Huang, P. Soil types differentiated their responses of aggregate stability to hydrological stresses at the riparian zones of the Three Gorges Reservoir. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, C. Impact of drying-wetting cycles on the soil aggregate stability of Alfisols in southwestern China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 73, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Butler, O.M.; Chen, C.; Liu, W.; Du, M.; Zhang, Q. Shifts in characteristics of the plant-soil system associated with flooding and revegetation in the riparian zone of Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Geoderma 2020, 361, 114015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Zhang, K.; Deng, Q.; Zhang, Q. Plant communities in relation to flooding and soil characteristics in the water level fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut Res. Int. 2013, 20, 1794–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; Shao, Y. Response of dominant plant species to periodic flooding in the riparian zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir (TGR), China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronick, C.J.; Lal, R. Soil structure and management: A review. Geoderma 2005, 124, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A history of research on the link between (micro)aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; He, X.; Bao, Y.; Tang, Q.; Gao, J.; Yan, D.; Wang, M.; Li, Y. Estimation of soil reinforcement by the roots of four post-dam prevailing grass species in the riparian zone of Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2016, 13, 508–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Yan, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Sun, H. Assessing the contributions of sesquioxides and soil organic matter to aggregation in an Ultisol under long-term fertilization. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 146, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdall, J.M.; Oades, J.M. Organic matter and water-stable aggregates in soils. J. Soil Sci. 1982, 33, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Hu, J.; Bao, Y.; Wang, F.; He, X. Soil nutrients in relation to vertical roots distribution in the riparian zone of Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 1498–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sampling Transects | Inundation Year (Year) | Inundation Month | Inundation Day (Day) | Inundation Height (m) | Soil Type | Vegetation Cover (%) | Slop Gradient (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Entisol | 72 | 3–5 |
| SI | 6 | October–January | 3–97 | 0–3 | Entisol | 70 | 3–5 |
| MI | 8 | September–April | 97–249 | 3–19 | Entisol | 67 | 4–7 |
| LI | 10 | September–May | 249–365 | 19–30 | Entisol | 63 | 5–9 |
| Sampling Transects | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) | BD (g·cm−3) | Total Porosity (%) | pH | SOC (g·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 8.17 ± 0.81 c | 88.18 ± 0.44 a | 3.65 ± 0.43 a | 1.26 ± 0.21 b | 52.31 ± 8.08 a | 8.19 ± 0.05 b | 12.59 ± 1.51 a |
| SI | 10.32 ± 0.63 c | 86.52 ± 0.45 a | 3.16 ± 0.19 a | 1.42 ± 0.12 a | 46.23 ± 4.65 b | 8.59 ± 0.06 a | 10.56 ± 1.22 b |
| MI | 16.65 ± 2.90 b | 80.15 ± 2.86 b | 3.20 ± 0.25 a | 1.49 ± 0.15 a | 43.65 ± 5.49 b | 8.55 ± 0.24 a | 8.36 ± 1.06 c |
| LI | 23.39 ± 5.56 a | 74.21 ± 4.93 c | 2.40 ± 0.72 b | 1.56 ± 0.13 a | 41.00 ± 4.95 b | 8.59 ± 0.05 a | 4.16 ± 0.99 d |
| Sampling Transects | Mass Percentage of Aggregates at Different Sizes (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >5 mm | 5–2 mm | 2–1 mm | 1–0.5 mm | 0.5–0.25 mm | <0.25 mm | |
| CK | 79.15 ± 3.47 a | 13.28 ± 2.24 b | 4.31 ± 0.82 b | 1.30 ± 0.27 b | 0.74 ± 0.13 b | 1.22 ± 0.01 b |
| SI | 70.73 ± 1.30 b | 15.23 ± 1.76 ab | 6.81 ± 0.15 a | 2.74 ± 0.13 a | 2.49 ± 0.35 ab | 2.00 ± 0.14 b |
| MI | 69.87 ± 2.03 b | 14.61 ± 0.68 ab | 6.89 ± 0.51 a | 2.73 ± 0.27 a | 2.85 ± 0.45 a | 3.05 ± 0.57 ab |
| LI | 64.25 ± 1.24 b | 17.90 ± 0.54 a | 8.26 ± 0.44 a | 2.82 ± 0.21 a | 2.02 ± 0.29 ab | 4.75 ± 0.09 a |
| Sampling Transects | Mass Percentage of Aggregates at Different Sizes (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >5 mm | 5–2 mm | 2–1 mm | 1–0.5 mm | 0.5–0.25 mm | <0.25 mm | |
| CK | 77.35 ± 1.51 a | 8.00 ± 0.68 b | 3.03 ± 0.30 b | 2.58 ± 0.33 c | 1.80 ± 0.08 b | 7.25 ± 0.33 b |
| SI | 68.35 ± 2.11 a | 11.73 ± 0.53 b | 4.28 ± 0.35 b | 4.40 ± 0.48 c | 3.30 ± 0.36 ab | 7.95 ± 0.70 b |
| MI | 64.29 ± 1.29 b | 10.79 ± 0.51 b | 5.10 ± 0.28 b | 4.97 ± 0.32 b | 3.40 ± 0.20 b | 11.45 ± 0.62 b |
| LI | 21.91 ± 2.95 c | 13.98 ± 1.10 a | 11.58 ± 1.05 a | 13.78 ± 0.84 a | 11.94 ± 1.43 a | 26.83 ± 2.92 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Chen, T.; Bao, Y.; Tang, Q.; Li, Y.; He, X. The Impacts of the Hydrological Regime on the Soil Aggregate Size Distribution and Stability in the Riparian Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Water 2023, 15, 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091791
Zhang S, Chen T, Bao Y, Tang Q, Li Y, He X. The Impacts of the Hydrological Regime on the Soil Aggregate Size Distribution and Stability in the Riparian Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Water. 2023; 15(9):1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091791
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shujuan, Tianyi Chen, Yuhai Bao, Qiang Tang, Yongtao Li, and Xiubin He. 2023. "The Impacts of the Hydrological Regime on the Soil Aggregate Size Distribution and Stability in the Riparian Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China" Water 15, no. 9: 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091791
APA StyleZhang, S., Chen, T., Bao, Y., Tang, Q., Li, Y., & He, X. (2023). The Impacts of the Hydrological Regime on the Soil Aggregate Size Distribution and Stability in the Riparian Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Water, 15(9), 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091791










