Decoding Chambal River Shoreline Transformations: A Comprehensive Analysis Using Remote Sensing, GIS, and DSAS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
2.3. Monitoring and Mapping River Shoreline Erosion and Accretion
2.3.1. DSAS Shoreline Analysis
2.3.2. Using Water Indices to Determine the Location of Streambanks
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Distance Change Measurement of Shoreline
3.2. Estimation of River Shoreline Erosion and Accretion Rates
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rentier, E.S.; Cammeraat, L.H. The environmental impacts of river sand mining. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovric, N.; Tosic, R. Assessment of bank erosion, accretion and channel shifting using remote sensing and gis: Case study—Lower course of the bosna river. Quaest. Geogr. 2016, 35, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahon, D.; Sahariah, D.; Debnath, J.; Nath, N.; Meraj, G.; Kumar, P.; Hashimoto, S.; Farooq, M. Assessment of Ecosystem Service Value in Response to LULC Changes Using Geospatial Techniques: A Case Study in the Merbil Wetland of the Brahmaputra Valley, Assam, India. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, R.; Dolui, G.; Das Chatterjee, N. Effect of instream sand mining on hydraulic variables of bedload transport and channel planform: An alluvial stream in South Bengal basin, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Patel, H.K.; Lade, A.D.; Kumar, B. Turbulence structure and bank erosion process in a dredged channel. River Res. Appl. 2023, 39, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negros, R.G.O. Impacts of sand mining. 2019, pp. 1–7. Available online: http://ismenvis.nic.in/Database/Impacts-of-Sand-Mining_3466.aspx (accessed on 18 October 2022).
- Padmalal, D.; Maya, K. Sand Mining; Springer Science: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garde, R.J.; Raju, K.G.R. Mechanics of Sediment Transportation and Alluvial Stream Problems; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, B.; Dunne, T. Gravel transport, gravel harvesting, and channel bed degradation in rivers draining the Southern Olympic Mountains, Washington, USA. Environ. Geol. Water Sci. 1989, 13, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M. Geomorphic and environmental effects of instream gravel mining. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1994, 28, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartfield, P. Headcuts and their effects on freshwater mussels. In Paper Presented at the UMRCC Symposium on Conservation and Management of Freshwater Mussels, Rock Island, Illinois; Upper Mississippi River Conservation Committee: Onalaska, WI, USA, 1993; pp. 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Kondolf, G.M. Hungry water: Effects of dams and gravel mining on river channels. Environ. Manag. 1997, 21, 533–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.P.; Wolman, M.G. Downstream effects of dams on alluvial rivers. US Geol. Surv. Prof. Pap. 1984, 1286, 89. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, G.; Klingeman, P.C.; McLean, D.G. Bedload and size distribution in paved gravel-bed streams. J. Hydraul. Eng. Div. ASCE 1982, 108, 544–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Peter, E.; Müller, R. Formulas for Bed-Load Transport. In Proceedings of the IAHSR 2nd Meeting, Stockholm, Sweden, 7 June 1948. Appendix 2. [Google Scholar]
- Meraj, G.; Romshoo, S.A.; Yousuf, A.R.; Altaf, S.; Altaf, F. Assessing the influence of watershed characteristics on the flood vulnerability of Jhelum basin in Kashmir Himalaya. Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tha, T.; Piman, T.; Bhatpuria, D.; Ruangrassamee, P. Assessment of riverbank erosion hotspots along the mekong river in cambodia using remote sensing and hazard exposure mapping. Water 2022, 14, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knighton, D. Fluvial Forms and Process; Edward Arnold Ltd.: London, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Selby, M.J. Book reviews: Morisawa, m. and hack, j.t. editors, 1985: Tectonic geomorphology. proceedings of the 15th annual binghamton geomorphology symposium. september 1984. boston: Allen and unwin. xiv + 390 pp. £25.00. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2016, 10, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutfin, N.A.; Rowland, J.; Fratkin, M.; Stauffer, S.; Carroll, R.; Brown, W.; Williams, K.H. River bank erosion and lateral accretion linked to hydrograph recession and flood duration in a mountainous snowmelt-dominated system. Authorea Prepr. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoi, D.N.; Dang, T.D.; Pham, L.T.H.; Loi, P.T.; Thuy, N.T.D.; Phung, N.K.; Bay, N.T. Morphological change assessment from intertidal to river-dominated zones using multiple-satellite imagery: A case study of the vietnamesemekong delta. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 34, 101087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmelder, S.; Marra, W.; Markies, H.; De Jong, S.M. Monitoring river morphology & bank erosion using uav imagery—A case study of the river buëch, hautes-alpes, France. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 73, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baki, A.B.M.; Gan, T.Y. Riverbank migration and island dynamics of the braided jamuna river of the ganges-brahmaputra basin using multi-temporal landsat images. Quat. Int. 2012, 263, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, T.; Oguchi, T.; Matsumoto, J.; Grossman, M.J.; Sarker, M.H.; Matin, M.A. Channel braiding and stability of the brahmaputra river, bangladesh, since 1967: Gis and remote sensing analyses. Geomorphology 2007, 85, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolman, M.G. Factors influencing erosion of a cohesive river bank. Am. J. Sci. 1959, 257, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooke, J.M. Magnitude and distribution of rates of river bank erosion. Earth Surf. Process. 1980, 5, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, D.M.; Couperthwaite, J.; Bull, L.J.; Harris, N.M. Bank erosion events and processes in the upper severn basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 1997, 1, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterbottom, S.; Gilvear, D. A gis-based approach to mapping probabilities of river bank erosion: Regulated river tummel, Scotland. Regul. Rivers-Res. Manag. 2000, 16, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, P.; Kumar, R.; Chatterjee, C. Erosion study of a part of majuli river-island using remote sensing data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2003, 31, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakal, L.; Dubey, B.; Sarma, A.K. Estimation of bank erosion in the river brahmaputra near agyathuri by using geographic information system. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2005, 33, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Ta, W.; Jia, X.; Xiao, J.; Yao, Z.; Ta, W.; Jia, X.; Xiao, J. Bank erosion and accretion along the ningxia-inner mongolia reaches of the yellow river from 1958 to 2008. Geomorphology 2011, 127, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Ghosh, K.; De, S.K. A proposed method of bank erosion vulnerability zonation and its application on the river haora, tripura, india. Geomorphology 2014, 224, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ch, M.H.; Ashraf, M.; Hamid, Q.; Sarwar, S.M.; Saqib, Z.A. Geospatial techniques for assessment of bank erosion and accretion in the maralaalexandria reach of the river chenab, Pakistan. Sains Malays. 2017, 46, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, R.; Bilas, R.; Biswas, S.S.; Pal, R. Bank erosion and accretion dynamics explored by gis techniques in lower ramganga river, western uttarpradesh, india. Spat. Inf. Res. 2017, 25, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, N.; Sharma, Y.; Sajjad, H.; Ahmed, R. Estimating bank line migration of the brahmaputra river in the middle brahmaputraoodplains of assam, india using digital shoreline analysis system (dsas). Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, C.; Tiede, J.; Lojek, O.; Visscher, J.; Apel, H.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Quang, C.N.X.; Schlurmann, T. Sand mining in the mekong delta revisited—Current scales of local sediment deficits. Sci. Rep. 2019, 91, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- “Factual and Action Taken Report of Joint Committee Date of Visit: 17th may 2022 Location: National Chambal Sanctuary Stretch”, (2) (2022). Available online: https://greentribunal.gov.in/sites/default/files/news_updates/Factual%20and%20Action%20Taken%20Report%20in%20OA%20No.%20248%20of%202022%20(In%20re%20News%20item%20pulished%20in%20The%20Hindu%20dated%2027.03.2022%20titled%20Digging%20up%20the%20Chambal).pdf (accessed on 29 March 2023).
- Debnath, J.; Sahariah, D.; Saikia, A.; Meraj, G.; Nath, N.; Lahon, D.; Annayat, W.; Kumar, P.; Chand, K.; Singh, S.K.; et al. Shifting Sands: Assessing Bankline Shift Using an Automated Approach in the Jia Bharali River, India. Land 2023, 12, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereli, M.A.; Tercan, E. Assessment of shoreline changes using historical satellite images and geospatial analysis along the lake salda in turkey. Earth Sci. Inform. 2020, 13, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalized difference water index (ndwi) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, T.D.; Lee, D.H.; Yang, I.T.; Lee, J.K. Identification of water bodies in a landsat 8 oli image using a j48 decision tree. Sensors 2016, 16, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, L.; Sivagnanam, N.; Usha, T.; Chokkalingam, L.; Sundar, S.; Gowrappan, M.; Roy, P.D. Shoreline changes over last five decades and predictions for 2030 and 2040: A case study from cuddalore, southeast coast of India. Earth Sci. Inform. 2021, 14, 1315–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.K.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Jana, N.C.; Mukhopadhyay, R. Sand quarrying activities in an alluvial reach of Damodar River, Eastern India: Towards a geomorphic assessment. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2016, 14, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackney, C.R.; Darby, S.E.; Parsons, D.R.; Leyland, J.; Best, J.L.; Aalto, R.; Nicholas, A.P.; Houseago, R.C. River bank instability from unsustainable sand mining in the lower Mekong River. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, J.; Sahariah, D.; Lahon, D.; Nath, N.; Chand, K.; Meraj, G.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, S.; Kanga, S.; Farooq, M. Assessing the impacts of current and future changes of the planforms of River Brahmaputra on its land use-land cover. Geosci. Front. 2023, 14, 101557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, J.; Sahariah, D.; Lahon, D.; Nath, N.; Chand, K.; Meraj, G.; Farooq, M.; Kumar, P.; Kanga, S.; Singh, S.K. Geospatial modeling to assess the past and future land use-land cover changes in the Brahmaputra Valley, NE India, for sustainable land resource management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taigor, S.R.; Rao, R.J. Habitat features of Aquatic animals in the National Chambal Sanctuary, Madhya Pradesh, India. Asian J. Exp. Biol. Sci. 2010, 1, 409–414. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, R.K. Markers for global climate change and its impact on social, biological and ecological systems: A review. Am. J. Clim. Change. 2020, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somaweera, R.; Nifong, J.; Rosenblatt, A.; Brien, M.L.; Combrink, X.; Elsey, R.M.; Grigg, G.; Magnusson, W.E.; Mazzotti, F.J.; Pearcy, A.; et al. The ecological importance of crocodylians: Towards evidence-based justification for their conservation. Biol. Reviews. 2020, 95, 936–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilbanks, T.J.; Fernandez, S. Climate Change and Infrastructure, Urban Systems, and Vulnerabilities: Technical Report for the US Department of Energy in Support of the National Climate Assessment; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, N. Detecting coastline change with all available landsat data over 1986–2015: A case study for the state of Texas, USA. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayaz, M.; Meraj, G.; Khader, S.A.; Farooq, M.; Kanga, S.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Sahu, N. Management of Landslides in a Rural–Urban Transition Zone Using Machine Learning Algorithms—A Case Study of a National Highway (NH-44), India, in the Rugged Himalayan Terrains. Land 2022, 11, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, A.; Meraj, G.; Kanga, S.; Farooq, M.; Singh, S.K.; Sahu, N.; Kumar, P. Vulnerability and Risk Assessment to Climate Change in Sagar Island, India. Water 2022, 14, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinhans, M.G.; Cohen, K.M.; Hoekstra, J.; IJmker, J.M. Evolution of a bifurcation in a meandering river with adjustable channel widths, Rhine delta apex, The Netherlands. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2011, 36, 2011–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Musso, N.M.; Capolongo, D.; Caldara, M.; Surian, N.; Pennetta, L. Channel changes and controlling factors over the past 150 years in the Basento river (southern Italy). Water 2020, 12, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, X.; Wu, M.; Liu, Z. Spatiotemporal evolution trajectory of channel morphology and controlling factors of Yongding River, Beijing, China. Water 2021, 13, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafle, L.; Xu, W.J.; Zeng, S.Y.; Nagel, T. A numerical investigation of slope stability influenced by the combined effects of reservoir water level fluctuations and precipitation: A case study of the Bianjiazhai landslide in China. Eng. Geol. 2022, 297, 106508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaboyedoff, M.; Michoud, C.; Derron, M.H.; Voumard, J.; Leibundgut, G.; Sudmeier-Rieux, K.; Nadim, F.; Leroi, E. Human-induced landslides: Toward the analysis of anthropogenic changes of the slope environment. In Landslides and Engineered Slopes. Experience, Theory and Practice; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 217–232. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Yong, R.; EzEldin, M.A. Stability analysis of stratified rock slopes with spatially variable strength parameters: The case of Qianjiangping landslide. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2017, 76, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Dong, Y.; Sun, P. Impact of reservoir impoundment-caused groundwater level changes on regional slope stability: A case study in the Loess Plateau of Western China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGranahan, G.; Balk, D.; Anderson, B. The rising tide: Assessing the risks of climate change and human settlements in low elevation coastal zones. Environ. Urban. 2007, 19, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adger, W.N.; Hughes, T.P.; Folke, C.; Carpenter, S.R.; Rockstrom, J. Social-ecological resilience to coastal disasters. Science 2005, 309, 1036–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Masud, M.M.; Gain, A.K.; Azad, A.K. Tidal river management for sustainable agriculture in the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta: Implication for land use policy. Land Use Policy 2020, 92, 104443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraj, G. Assessing the Impacts of Climate Change on Ecosystem Service Provisioning in Kashmir Valley India. Ph.D. Thesis, Suresh Gyan Vihar University, Jaipur, India, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Meraj, G.; Singh, S.K.; Kanga, S.; Islam, M.N. Modeling on comparison of ecosystem services concepts, tools, methods and their ecological-economic implications: A review. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 8, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraj, G.; Farooq, M.; Singh, S.K.; Islam, M.N.; Kanga, S. Modeling the sediment retention and ecosystem provisioning services in the Kashmir valley, India, Western Himalayas. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 3859–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
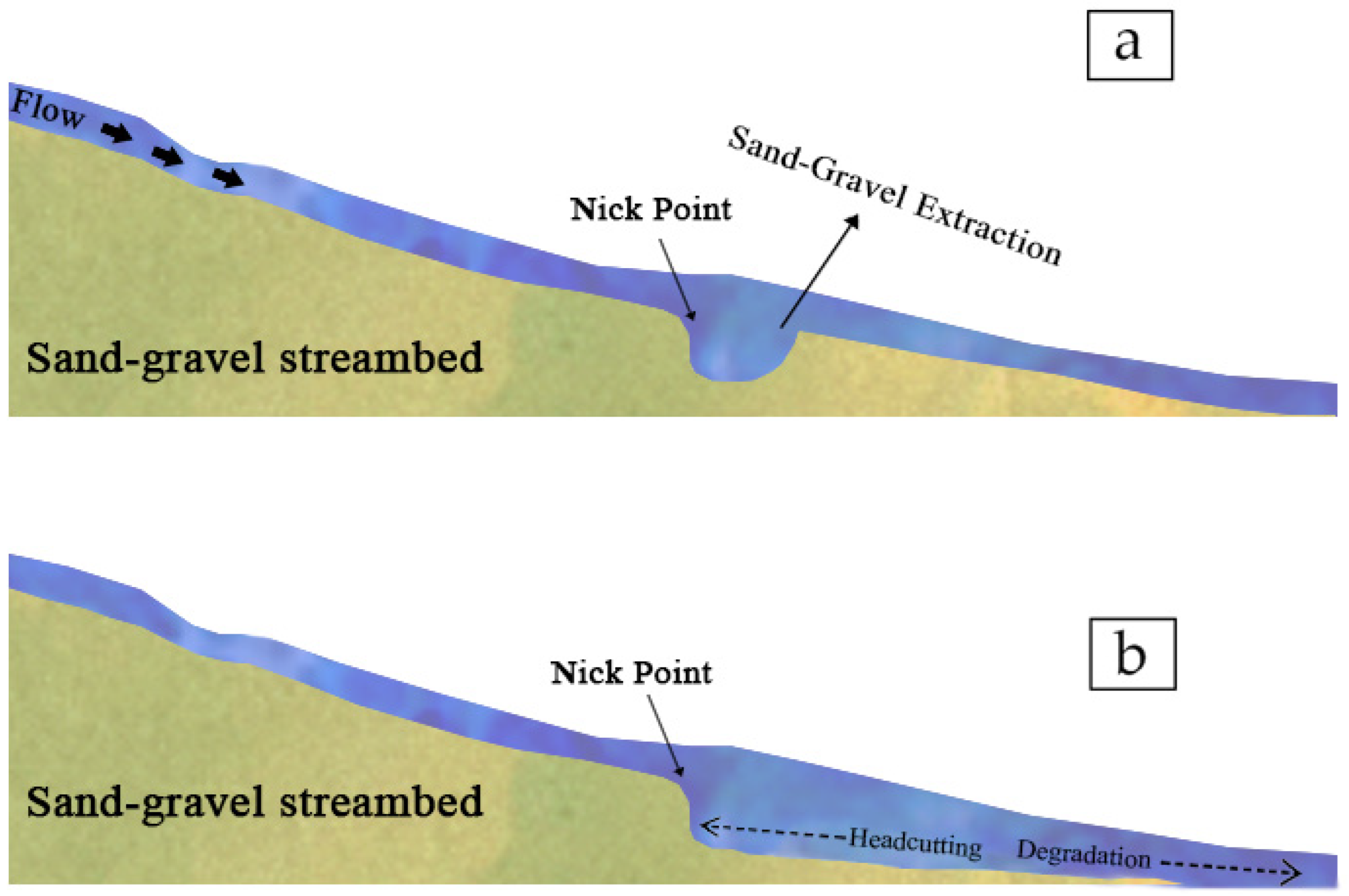

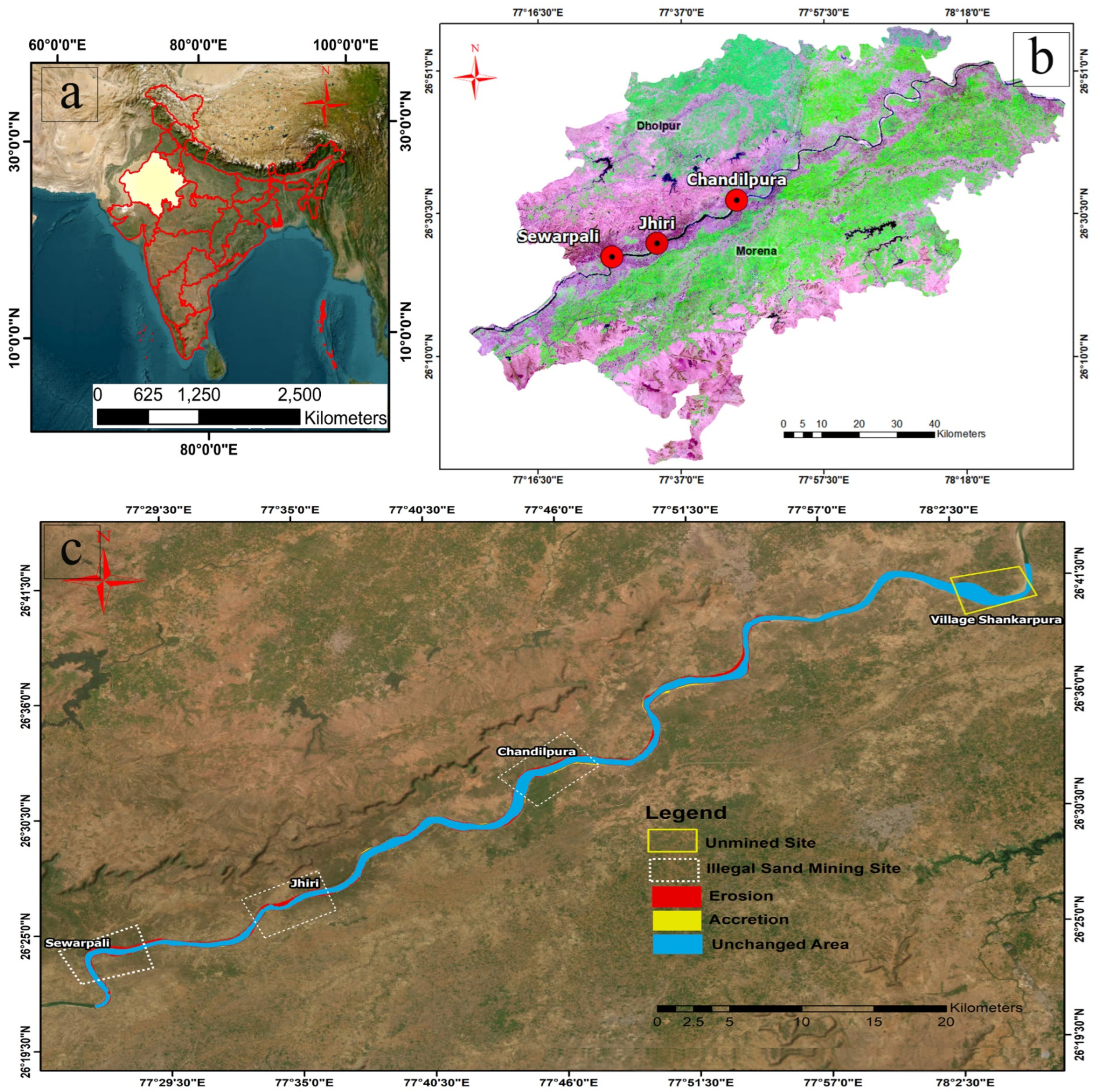


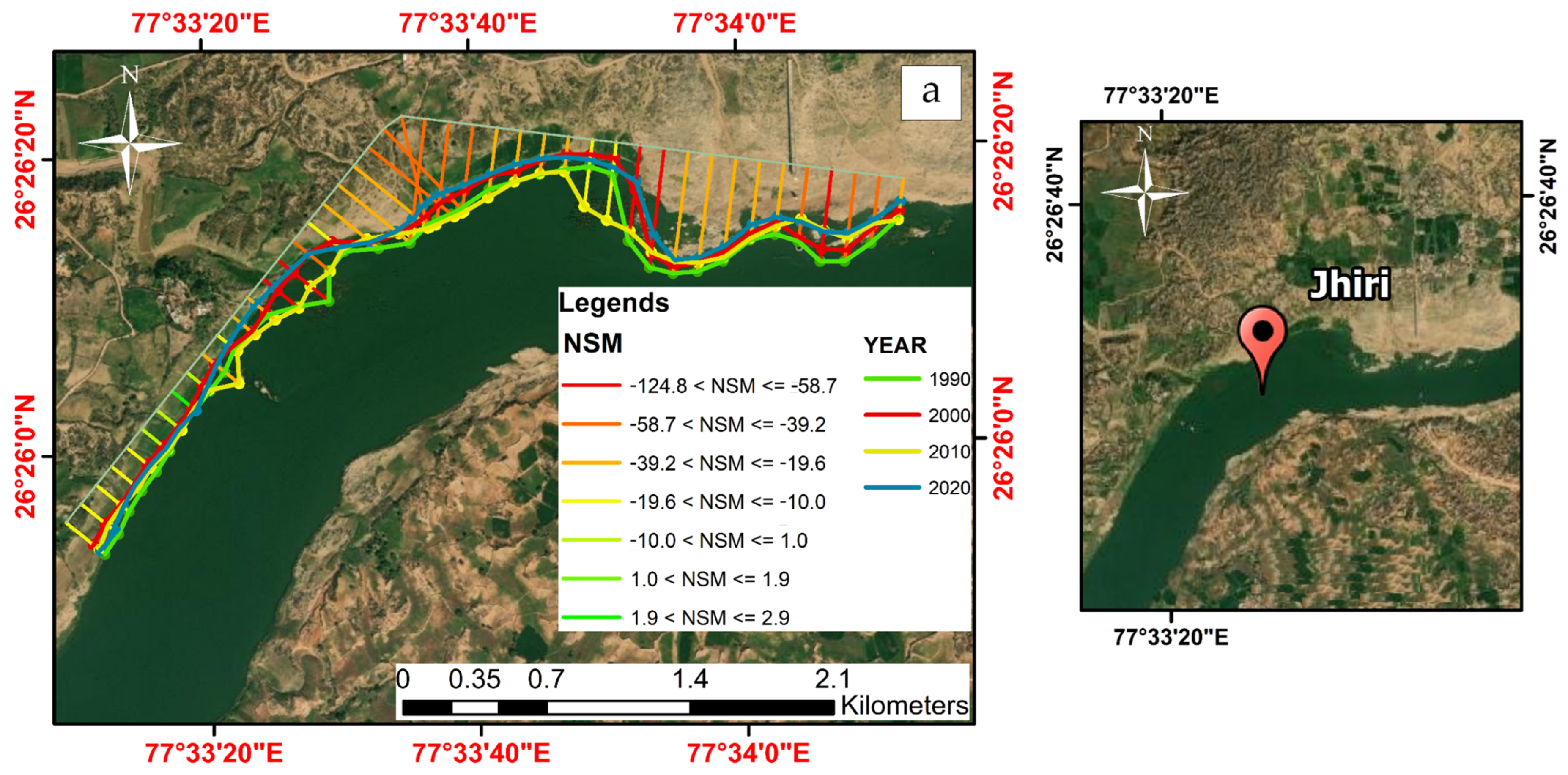







| S. No. | Data | Year of Acquisition | Resolution (Pixel Size) (m) | UTM Zone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Landsat 5 TM | 1990 | 30 | 43R |
| 2 | Landsat 7 ETM+ | 2000 | 30 | 43R |
| 3 | Landsat 7 ETM+ | 2010 | 30 | 43R |
| 4 | Sentinel-2A/MSI | 2020 | 10–20 | 43R |
| 5 | NGT Report for non-mining areas | |||
| Sand Mining Sites | No. of Transects | Transect Spacing (m) | Minimum (m) | Maximum (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jhiri | 44 | 50 | 10.86 | 130.27 |
| Sewarpali | 40 | 50 | 22.45 | 67.68 |
| Chandilpura | 41 | 50 | 15.42 | 96.68 |
| Sand Mining Sites | No. of Transects | Transect Spacing (m) | Percentage of All Transects (Negative Distance) | Percentage of All Transects (Positive Distance) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jhiri | 44 | 50 | 97.73% | 2.27% |
| Sewarpali | 40 | 50 | 97.44% | 2.56% |
| Chandilpura | 41 | 50 | 64.1% | 2.56% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, S.; Meraj, G.; Kumar, P.; Singh, S.K.; Kanga, S.; Johnson, B.A.; Prajapat, D.K.; Debnath, J.; Sahariah, D. Decoding Chambal River Shoreline Transformations: A Comprehensive Analysis Using Remote Sensing, GIS, and DSAS. Water 2023, 15, 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091793
Singh S, Meraj G, Kumar P, Singh SK, Kanga S, Johnson BA, Prajapat DK, Debnath J, Sahariah D. Decoding Chambal River Shoreline Transformations: A Comprehensive Analysis Using Remote Sensing, GIS, and DSAS. Water. 2023; 15(9):1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091793
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Saurabh, Gowhar Meraj, Pankaj Kumar, Suraj Kumar Singh, Shruti Kanga, Brian Alan Johnson, Deepak Kumar Prajapat, Jatan Debnath, and Dhrubajyoti Sahariah. 2023. "Decoding Chambal River Shoreline Transformations: A Comprehensive Analysis Using Remote Sensing, GIS, and DSAS" Water 15, no. 9: 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091793
APA StyleSingh, S., Meraj, G., Kumar, P., Singh, S. K., Kanga, S., Johnson, B. A., Prajapat, D. K., Debnath, J., & Sahariah, D. (2023). Decoding Chambal River Shoreline Transformations: A Comprehensive Analysis Using Remote Sensing, GIS, and DSAS. Water, 15(9), 1793. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15091793












