Spatiotemporal Variations in Snow Cover on the Tibetan Plateau from 2003 to 2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Snow Product Processing
2.3.2. Linear Regression
3. Results
3.1. Temporal and Spatial Variations in Snow Cover Duration
3.1.1. Overall Trends in Snow Cover Duration (SCD)
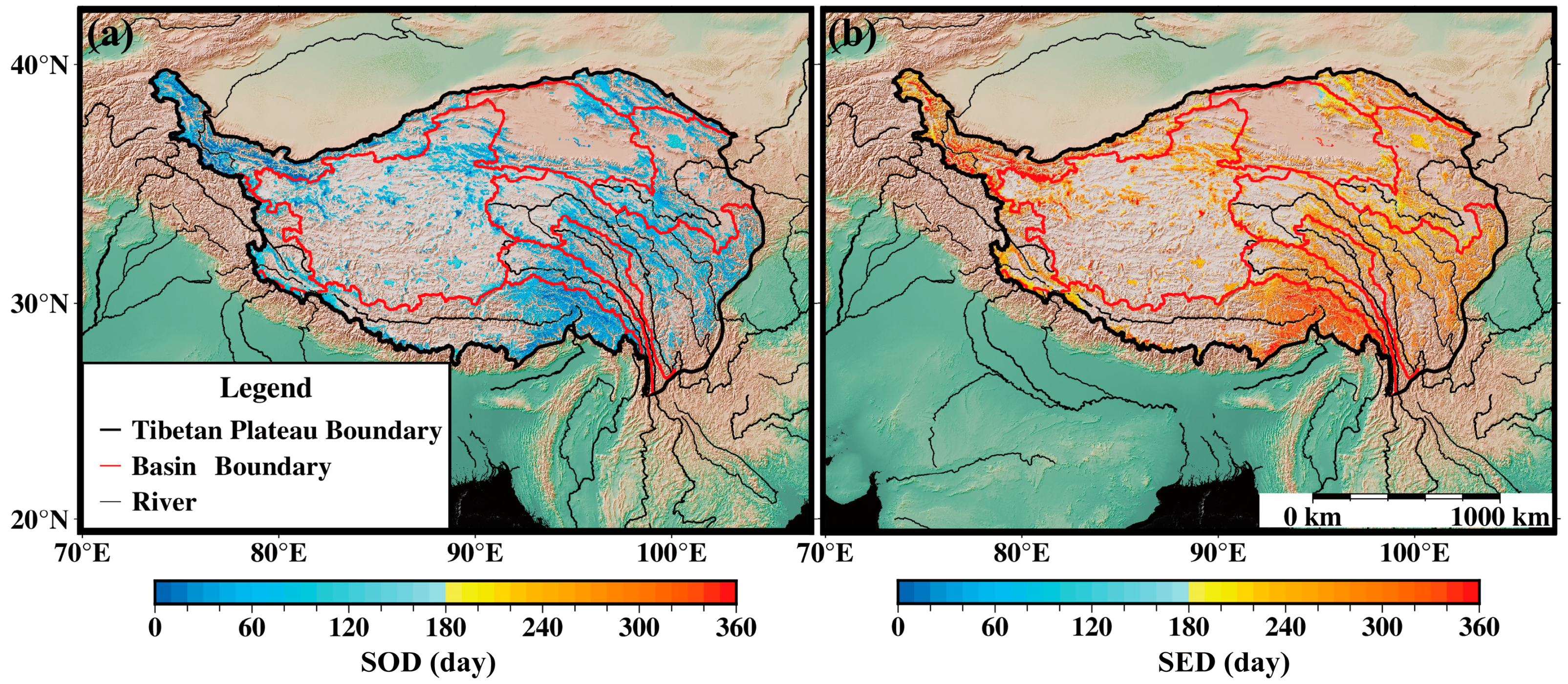
3.1.2. Variations in Onset Date and End Date of Snow Cover
3.1.3. Altitude Distribution Characteristics of SCD, SOD, and SED Changes
3.2. Snow Cover Variations in Sub-Basins of the Tibetan Plateau
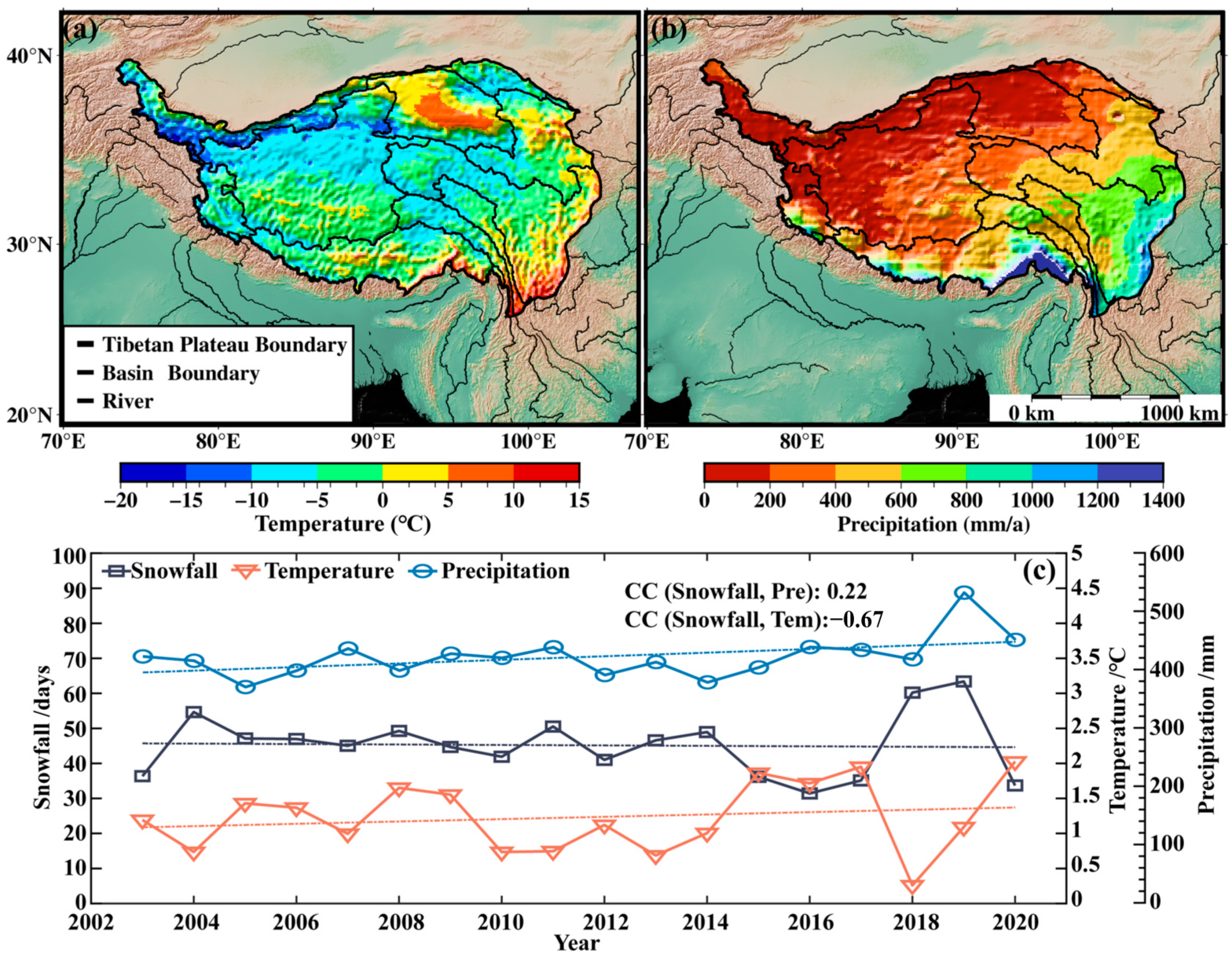
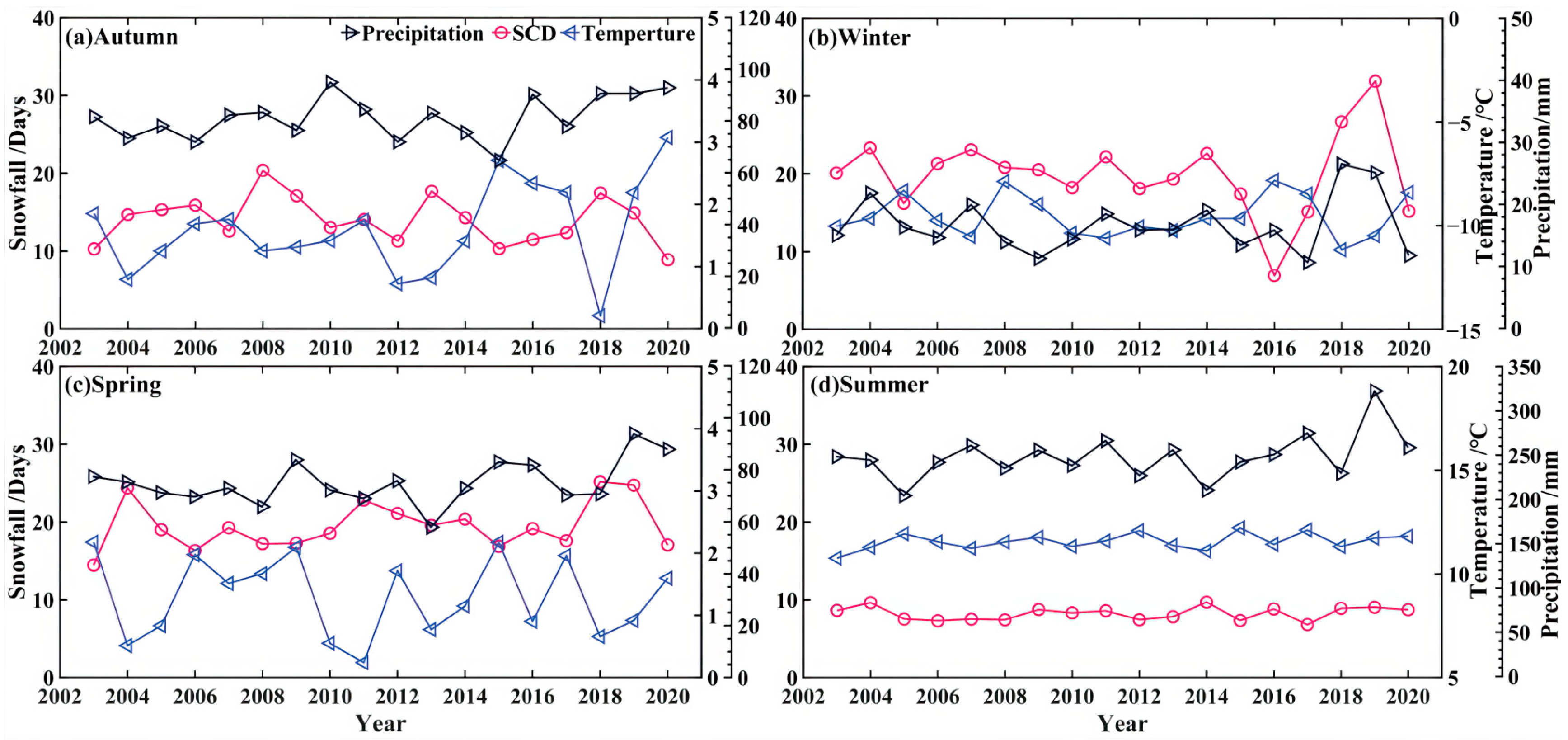
3.3. The Response of Snow Cover Variability to Climate Change
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The average annual SCD on the Tibetan Plateau is 45.2 days, showing a slight downward trend. SCD is longer in spring (19.5 days) and winter (20.0 days), but shorter in summer. The snow cover presents significant spatial heterogeneity over the Tibetan Plateau, with SCD exceeding 180 days in the southern and northwestern regions, but 0 days in the central plateau.
- (2)
- The snow cover is significantly different in the various plateaus’ inner basins, although they are geographically adjacent. The Tarim River Basin records the highest average annual SCD (83 days), while the adjoining area of the Inner Basin shows less snow cover (32 days). The Yellow River Basin has the lowest (31 days), especially in winter (15 days).
- (3)
- The Tibetan Plateau is experiencing surface air warming and moistening, with the annual mean temperature rising at a rate of 0.17 ± 0.54 °C/10a and the annual mean precipitation increasing at a rate of 3.09 ± 3.81 mm/a. Temperature has a greater impact on snow cover changes (CC = −0.67) compared to precipitation. However, precipitation has a greater influence on SCD (CC = 0.70) than temperature in winter.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, R.D.; Mote, P.W. The Response of Northern Hemisphere Snow Cover to a Changing Climate. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 2124–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Nelson, F.E.; Shiklomanov, N.I.; Guo, D.; Wan, G. Permafrost degradation and its environmental effects on the Tibetan Plateau: A review of recent research. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2010, 103, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Pang, G.; Wan, G.; Liu, Z. The Tibetan Plateau cryosphere: Observations and model simulations for current status and recent changes. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 190, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, W.; Kumar, A.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, R. Relationship between anomalies of Eurasian snow and southern China rainfall in winter. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wu, B.; Rong, X. Decadal variability in springtime snow over Eurasia: Relation with circulation and possible influence on springtime rainfall over China. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Deng, J.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Q.; Hao, X.; Liang, T. Spatiotemporal dynamics of snow cover based on multi-source remote sensing data in China. Cryosphere 2016, 10, 2453–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Jin, H.; Kang, E.; Che, T.; Jin, R.; Wu, L.; Nan, Z.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y. Cryospheric change in China. Glob. Planet. Change 2008, 62, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Zhou, B.; Xiao, C. Progress in studies of cryospheric changes and their impacts on climate of china. J. Meteorol. Res. 2014, 28, 732–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Xue, Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, F.; Thompson, L.; Cui, P.; Koike, T.; Lau, W.K.-M.; Lettenmaier, D.; Mosbrugger, V.; et al. Recent Third Pole’s Rapid Warming Accompanies Cryospheric Melt and Water Cycle Intensification and Interactions between Monsoon and Environment: Multidisciplinary Approach with Observations, Modeling, and Analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Asia’s water balance. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J. Trouble in tibet. Nature 2016, 529, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Ye, B.; Zhou, D.; Wu, B.; Foken, T.; Qin, J.; Zhou, Z. Response of hydrological cycle to recent climate changes in the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Change 2011, 109, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhu, X.; Li, N.; Pan, Y. Gap-Filling of a MODIS Normalized Difference Snow Index Product Based on the Similar Pixel Selecting Algorithm: A Case Study on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jing, Y.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. The recent developments in cloud removal approaches of MODIS snow cover product. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 2401–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.T.; Wu, R.G. Interannual and decadal variations of snow cover over Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and their relationships to summer monsoon rainfall in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 17, 18–30. [Google Scholar]
- Xuejin, T.; Zhenni, W.; Xingmin, M.; Peng, G.; Guangju, Z.; Wenyi, S.; Chaojun, G. Spatiotemporal changes in snow cover over China during 1960–2013. Atmos. Res. 2019, 218, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Kang, S.; Ren, G.; Fraedrich, K.; Pepin, N.; Yan, Y.; Ma, L. Observed changes in snow depth and number of snow days in the eastern and central Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Res. 2011, 46, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, W. Interdecadal variation of spring snow depth over the Tibetan Plateau and its influence on summer rainfall over East China in the recent 30 years. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 3654–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Tang, Z.; Hu, G.; Wang, J.; Sang, G.; Li, J. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Snowline Altitude and Their Responses to Climate Change in the Tienshan Mountains, Central Asia, during 2001–2019. Sustainability 2021, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Liang, J.; Li, C.; Wang, X. Extraction and assessment of snowline altitude over the Tibetan plateau using MODIS fractional snow cover data (2001 to 2013). J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Wang, X.; Deng, G.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Sang, G. Spatiotemporal variation of snowline altitude at the end of melting season across High Mountain Asia, using MODIS snow cover product. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 2629–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, Z.; Deng, G.; Hu, G.; You, Y.; Zhao, Y. Landsat Satellites Observed Dynamics of Snowline Altitude at the End of the Melting Season, Himalayas, 1991–2022. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Che, T.; Ding, Y.; Hao, X. Evaluation of snow cover and snow depth on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau derived from passive microwave remote sensing. Cryosphere 2017, 11, 1933–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.; Bookhagen, B. Changes in seasonal snow water equivalent distribution in High Mountain Asia (1987 to 2009). Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, H.; Gonsamo, A.; Liu, Z. No evidence of widespread decline of snow cover on the Tibetan Plateau over 2000–2015. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, R.; Zhao, P.; Yao, S.; Jia, X. Formation of Snow Cover Anomalies Over the Tibetan Plateau in Cold Seasons. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2019, 124, 4873–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Jiang, Z. Spatiotemporal Variation of Snow Cover in Tianshan Mountains, Central Asia, Based on Cloud-Free MODIS Fractional Snow Cover Product, 2001–2015. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.; Xu, L.; Salomonson, V.V. MODIS/Terra observed seasonal variations of snow cover over the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Deng, J.; Xie, H.; Liang, T. Spatio-Temporal Change of Snow Cover and Its Response to Climate over the Tibetan Plateau Based on an Improved Daily Cloud-Free Snow Cover Product. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 169–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Su, F.; Yang, D.; Tong, K.; Meng, F.; Kan, B. Spatiotemporal variation of snow cover over the Tibetan Plateau based on MODIS snow product, 2001–2014. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 708–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Chen, X.; Zhong, R.; Wu, P.; Ju, Q.; Zeng, J.; Yao, T. Extraction of snow melting duration and its spatiotemporal variations in the Tibetan Plateau based on MODIS product. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 70, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes-Da-Silva, E.; Magnusson, W.E.; Sinervo, B.; Caetano, G.H.; Miles, D.B.; Colli, G.R.; Diele-Viegas, L.M.; Fenker, J.; Santos, J.C.; Werneck, F.P. Extinction risks forced by climatic change and intraspecific variation in the thermal physiology of a tropical lizard. J. Therm. Biol. 2018, 73, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, T.N.; Santos, M.S.; Magalhães, M. Climate change and economic growth: A heterogeneous panel data approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 22725–22735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.G.; Huang, R.H.; Chen, W.; Dong, W.J. Spatial Distributions and Interdecadal Variations of the Snow at the TIbetan Plateau Weather Stations. Sci. Atmos. Sin. 2002, 26, 496–508. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, B.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Xu, W.; Wu, J.; Zheng, Z. HMRFS-TP: Long-term daily gap-free snow cover products over the Tibetan Plateau from 2002 to 2021 based on hidden Markov random field model. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 4445–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Deng, G.; Hu, G.; Zhang, H.; Pan, H.; Sang, G. Satellite observed spatiotemporal variability of snow cover and snow phenology over high mountain Asia from 2002 to 2021. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jpl, N. NASADEM Merged DEM Global 1 arc Second V001; NASA EOSDIS Land Processes DAAC: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2020.
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.; Joyce, R.; Xie, P.; Yoo, S.H. NASA global precipitation measurement (GPM) integrated multi-satellite retrievals for GPM (IMERG). Algorithm Theor. Basis Doc. (ATBD) Version 2015, 4, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Dutra, E.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Albergel, C.; Arduini, G.; Balsamo, G.; Boussetta, S.; Choulga, M.; Harrigan, S.; Hersbach, H.; et al. ERA5-Land: A state-of-the-art global reanalysis dataset for land applications. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 4349–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Wu, T.; Shen, L.; Pepin, N.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Kang, S.; AghaKouchak, A. Review of snow cover variation over the Tibetan Plateau and its influence on the broad climate system. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 201, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Song, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Ren, C.; Li, Y. Changes in global air temperature from 1981 to 2019. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 2660–2672. [Google Scholar]
- Notarnicola, C. Hotspots of snow cover changes in global mountain regions over 2000–2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 243, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Dong, H.; Dai, Y.; Mou, N.; Wei, W. Contrasting changes of snow cover between different regions of the Tibetan Plateau during the latest 21 years. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Data Type | Data | Period | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Snow products | HMRFS-TP: long-term daily gap-free snow cover products over the Tibetan Plateau | 2002–2021 | 500 m | 1 d | https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/en/data/ (accessed on 10 January 2024) |
| Daily cloud-free MODIS NDSI and snow phenology dataset over High-Mountain Asia (2000–2021) | 2002–2020 | 500 m | 1 a | https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/en/data/ (accessed on 10 January 2024) | |
| DEM | NASADEM Merged DEM Global 1 arc second V001 | 2000 | 30 m | – | https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 3 January 2024) |
| Meteorological data | GPM IMERG Final Precipitation L3 1 month 0.1 degree × 0.1 degree V07 (GPM_3IMERGM) | 2000–2023 | 0.10° × 0.10° | Monthly | https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/datasets/ (accessed on 2 January 2024) |
| ERA5-Land monthly averaged data from 1950 to present | 1980–2022 | 0.10° × 0.10° | Monthly | https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 2 January 2024) |
| Source | Dataset | Period | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| This study | HMRFS-TP: long-term daily gap-free snow cover products over the Tibetan Plateau and Daily cloud-free MODIS NDSI and snow phenology dataset over High Mountain Asia (2000–2021) | 2003–2020 | Trend (SCD): −0.06 days/a; Location (High SC): Southeast and Northwest of TP; CC (SCD, Pre): 0.70 (Winter); CC (SCD, Tem): −0.74 (Annual); |
| Pu et al. (2007) [28] | MODIS snow cover data | 2000–2006 | Trend (SCF): −0.34%/a; Location (High SC): South and Northwest of TP |
| You et al. (2011) [17] | In situ data of snow depth and days | 1961–2005 | Trend (SCD) in Winter: 0.40 days/10a (1961–1990), −1.59 days/10a (1991–2005); |
| Wang et al. (2015) [29] | Daily cloud-free snow-cover products based on MODIS and AMSR-E data | 2003–2010 | Trend (SCD): Slightly Decrease (Qualitative) |
| Li et al. (2018) [30] | MODIS snow cover data | 2001–2014 | Trend (SCF): −0.08%/a; CC (SC, Pre): −0.35; CC (SC, Tem): 0.05; Location (High SCD): South and Northwest of TP; |
| Jin et al. (2022) [31] | Long time-series data of snow cover area on Qinghai–Tibet Plateau dataset | 2003–2014 | CC (SCR, Pre): −0.07; CC (SCR, Tem): −0.52; Location (High SC): Southeast of TP |
| Yang et al. (2023) [43] | Multi-source data fusion snow cover dataset | 2000–2021 | Trend (SCD): −1.5 days/a (Southeast of TP); Trend (SCD): 2.1 days/a (Northwest of TP); Location (High SC): Northwest of TP |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pu, C.; Zhou, S.; Sun, P.; Luo, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, Z. Spatiotemporal Variations in Snow Cover on the Tibetan Plateau from 2003 to 2020. Water 2024, 16, 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101364
Pu C, Zhou S, Sun P, Luo Y, Li S, Sun Z. Spatiotemporal Variations in Snow Cover on the Tibetan Plateau from 2003 to 2020. Water. 2024; 16(10):1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101364
Chicago/Turabian StylePu, Chaoxu, Shuaibo Zhou, Peijun Sun, Yunchuan Luo, Siyi Li, and Zhangli Sun. 2024. "Spatiotemporal Variations in Snow Cover on the Tibetan Plateau from 2003 to 2020" Water 16, no. 10: 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101364
APA StylePu, C., Zhou, S., Sun, P., Luo, Y., Li, S., & Sun, Z. (2024). Spatiotemporal Variations in Snow Cover on the Tibetan Plateau from 2003 to 2020. Water, 16(10), 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101364






