Abstract
The simultaneous adsorption of Cu(II) and dyes (MB and MO) on LDH@GO-SH was investigated in single, MB–Cu, and MO–Cu binary systems. The coexistence of dye enhanced the adsorption of Cu(II) by LDH@GO-SH, while the presence of Cu(II) differently affected the adsorption of MB and MO. The adsorption capacity of MO remarkably increased due to the presence of Cu(II). The presence of Cu(II) had a negative effect on MB adsorption for lower MB initial concentration systems (2–10 mg·L−1), while it had a positive effect for higher MB concentration systems (25 mg·L−1 and 50 mg·L−1). The adsorption of Cu(II) in binary systems was satisfactorily fitted by a Langmuir model and pseudo-first-order kinetic model. Surface complex interaction was supposed to be a potential mechanism for the enhancement of Cu(II) adsorption in both MB–Cu and MO–Cu binary systems. The electrostatic interactions between MO and Cu(II) were another reason for the enhancement of Cu(II) adsorption in the MO–Cu binary system. LDH@GO-SH maintained a high adsorption capacity after three adsorption–desorption cycles, indicating that it can be repeatedly used for the treatment of heavy-metal-ion-containing wastewater.
1. Introduction
Heavy metal ions and dyes commonly coexist in wastewater from paper and pulp, textiles, leather, cosmetic, and other industries, and are one of the most significant and dangerous sources of environmental pollution [1,2]. In the printing and dyeing process, metal ions such as copper (II), cadmium (II), and aluminum (III) are usually used as mordant, which causes serious pollution and high water consumption [3]. The coexistence of heavy metal ions and dyes usually leads to great variations in the physical and chemical properties of these contaminants. The variations commonly result in greater toxicity and carcinogenicity, which pose harmful risks to human beings, aquatic life, and the ecological environment [3,4]. Therefore, it is essential to remove these coexistent contaminants in industrial wastewater before discharge into the ecosystem.
Various methods have been successfully applied in the elimination of heavy metal ions and dyes individually [5,6,7,8,9]. However, some of them suffered from drawbacks like high operational costs, secondary pollution, and complicated processes [10,11]. Moreover, the simultaneous treatment process was more complicated than that of a single pollutant system due to the synergistic or antagonistic properties of the coexistent heavy metal ions and dyes [1,12]. Das et al. [13] has attempted the bio-accumulation of heavy metals and a dye by Candida tropicalis simultaneously, but this method required strict control and was only suitable for contaminants at low concentrations. Consequently, the development of an efficient and economical way to remove the above-mentioned coexistent pollutants simultaneously from aqueous solutions is urgently needed.
Adsorption is a simple, efficient, and relatively inexpensive method to eliminate non-biodegradable contaminants (including heavy metal ions and dyes) from wastewater [14,15,16,17]. However, the adsorption capacities of many adsorbents are easily inhibited, especially in mixed contaminant systems, which limits the application of adsorption [18,19]. So, it is vitally important to choose a suitable adsorbent that can maintain a favorable adsorption ability even in mixed contaminant systems. Layered double hydroxides and graphene oxide composite (LDH@GO) has been proven to be a promising adsorbent with good adsorption performance due to its abundant pore structure, high surface area, and multifunctional properties [20,21,22]. It is better to modify the adsorbent to achieve enhanced adsorption performance in complicated conditions. Chemical modification with functional groups like a thiol group has been proved to be an applicable method to enhance adsorption capacities for different kinds of contaminants [23,24,25,26]. In a previous report, thiol-group-modified LDH@GO (LDH@GO-SH) showed evaluated adsorption abilities for heavy metal ions [27].
In this study, LDH@GO-SH was prepared and applied as a functionalized adsorbent for the simultaneous removal of Cu(Ⅱ) ions and dyes. Methylene blue (MB) as a cationic dye and methyl orange (MO) as an anionic dye were chosen to investigate the effect of different kinds of dyes on the adsorption of Cu(Ⅱ). The adsorption behaviors of Cu(Ⅱ) and dyes were investigated in binary systems including MB–Cu and MO–Cu binary systems. The effects of contact time, initial concentration, pH, and ionic strength on Cu(Ⅱ) removal in binary systems were also investigated. Adsorption behavior was studied by the fitting of equilibrium and kinetic models. The interaction mechanism between pollutants and adsorbent was investigated by characterizations of X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) and Fourier-transform infrared spectrometry (FTIR).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Graphite powder was purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Other chemicals were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (Shanghai, China) Co., Ltd. All chemicals were analytical grade and without further purification. All aqueous solutions were prepared with deionized water.
2.2. Fabrication of the Adsorbents
LDH@GO-SH composite was fabricated using co-precipitation and surface functional modification as described in our previous study [27].
In the first stage, 1.0 g of 4-aminothiophene was added to 40 mL of 1 mol·L−1 HCl, with continuous stirring until complete dissolution of 4-aminothiophene was achieved. Subsequently, 50 mL of NaNO2 solution was dropped into the reacting mixture under an ice bath condition. Then, 80 mL of GO suspension was added into the mixture solution. The resulting mixture underwent agitation for a duration of 12 h under an ice bath condition. The mixture underwent thorough washing cycles consisting of acetone, ethanol, and deionized water washes; each was repeated thrice. Finally, the as-prepared GO-SH dispersed in 100 mL deionized water and the GO-SH suspension were completed.
In the second stage, 3.05 g MgCl2·6H2O and 1.21 g AlCl3·9H2O were dissolved in 100 mL deionized water. Another solution containing 1.2 g NaOH and 1.05 g Na2CO3 in 100 mL deionized water was prepared. Both solutions were added to the GO-SH suspension drop-wise at the same time and vigorously stirred at room temperature. During the fabrication procedure, the pH was kept around 10 using diluted NaOH or HCl. The resultant precipitate was continuously stirred for 4 h at room temperature. After that, the mixture was aged in a water bath at 65 °C for another 4 h. The precipitate was centrifuged and washed three times with acetone, ethanol, and deionized water, respectively. Finally, the precipitate was dried overnight at a temperature of 65 °C to obtain LDH@GO-SH.
2.3. Batch Adsorption Experiments
Batch adsorption experiments were carried out in a 150 mL Erlenmeyer flask. In each experiment, 0.02 g of LDH@GO-SH was added into 100 mL of pollutant solutions containing MO and Cu(Ⅱ) or MB and Cu(Ⅱ) at different initial concentrations (0, 2, 5, 10, 25, or 50 mg·L−1). The temperature of the solution was fixed at 25 °C. NaCl (0.01 mol·L−1) was added as the background electrolyte. The initial pH of the solution was adjusted by adding a dilute HCl or NaOH solution. To investigate the effect of different pH values on the adsorption performance of LDH@GO-SH, the adsorption experiments were conducted by varying the pH from two to six. To investigate the influence of solution ionic strength on adsorption performance, the adsorption experiments were conducted by varying the concentrations of NaCl from 0.001 mol·L−1 to 0.1 mol·L−1. To investigate the effect of different temperatures on the adsorption performance of LDH@GO-SH, the adsorption experiments were conducted by varying the temperature from 25 °C to 45 °C. The reusability of LDH@GO-SH was examined using an eluent including 0.1 mol·L−1 Na2EDTA.
2.4. Data Analysis
All the adsorption experiments were repeated in triplicate, and the averages were reported. The equilibrium adsorption capacity qe (mg·g−1) was calculated according to the following formula:
where qe (mg·g−1) is the amount of pollutant (Cu(Ⅱ) ions, MO, or MB) adsorbed at equilibrium time; V is the volume of the solution; m is the weight of the dry LDH@GO-SH composite; and C0 and Ce are the initial and equilibrium concentrations of pollutant (Cu(Ⅱ) ions, MO, or MB), respectively.
An adsorption Enhancement ratio (Er) was applied to investigate the interaction between the coexistent pollutants during the adsorption process in the binary system. The calculation formula is as follows:
where qs,i (mg·g−1) and qb,i (mg·g−1) are the adsorption amount of pollutant i in a single system and binary system, respectively.
The values of Er have three cases:
- (1)
- Er > 0 indicates that the presence of coexistent pollutant j would enhance the adsorption of pollutant i;
- (2)
- Er = 0 indicates that the presence of coexistent pollutant j would not affect the adsorption of pollutant i;
- (3)
- Er < 0 indicates that the presence of coexistent pollutant j would weaken the adsorption of pollutant i.
2.5. Model Fitting
Kinetic models including a pseudo-first-order kinetic model and pseudo-second-order kinetic model were employed to fit the experimental data. The determination coefficient (R2) was considered to be a measure of agreement between the experimental data and the proposed models. The mathematical equations of the pseudo-first-order kinetic model and pseudo-second-order kinetic model can be expressed as the following equations [28]:
where qt (mg·g−1) is the amount of pollutant (Cu(Ⅱ) ions, MO, or MB) adsorbed at time t (min); and k1 (min−1) and k2 (g·(mg min) −1) are the rate constants of the pseudo-first-order kinetic model and pseudo-second-order kinetic model, respectively.
Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption isothermal models were used to deal with the adsorption isotherms. The parameters of Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption isothermal adsorption were calculated by the following equations [29]:
where qm (mg·g−1) is the maximum adsorption amount of pollutant (Cu(Ⅱ) ions, MO, or MB); and KL (L·mg−1) and KF (mg1–n·Ln·g−1) are the Langmuir constant and Freundlich constant, respectively.
2.6. Characterization
The concentrations of Cu(Ⅱ) were measured by flame emission spectrometry (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The concentrations of MO and MB were measured using UV-VIS spectrophotometers (Shimadzu, Japan) at 292 nm and 464 nm, respectively. X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) patterns of the samples were recorded by a powder diffractometer (PANalytical B.V., Almelo, Holland), using Cu-Kα as the radiation source. The chemical structure of LDH@GO-SH before and after adsorption was analyzed by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR, Nicolet 6700, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) using KBr pellets over a range of 4000–400 cm−1.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorption Performance
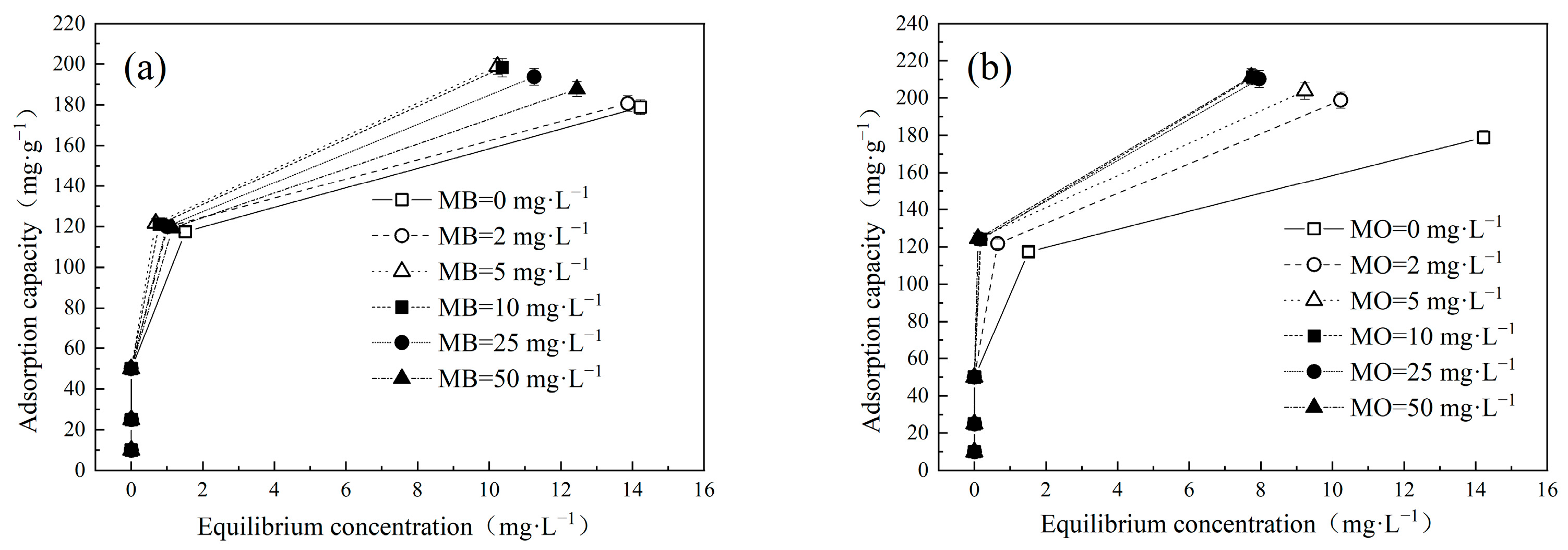
The impact of varying initial pollutant concentrations on adsorption of Cu(Ⅱ) and dyes onto LDH@GO-SH was systematically evaluated using a series of test solutions containing different concentrations of Cu(Ⅱ) (ranging from 0 to 50 mg·L−1) and dyes (ranging from 0 to 50 mg·L−1) in single and binary systems (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Notably, the adsorption capacities of Cu(II) onto LDH@GO-SH exhibited an enhancement in the presence of dyes. At the initial Cu(Ⅱ) concentration of 50 mg·L−1, the adsorption capacities for Cu(Ⅱ) in single, MB–Cu binary, and MO–Cu binary systems (at the initial dye concentration of 50 mg·L−1) were 178.87 mg·g−1, 187.75 mg·g−1, and 211.33 mg·g−1, respectively. Results showed that both MB and MO facilitated the adsorption of Cu(Ⅱ); the effect of MO was more prominent.
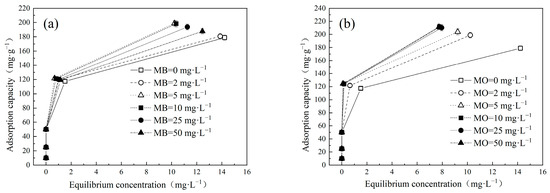
Figure 1.
Effect of different concentrations of (a) MB and (b) MO on Cu(II) adsorption by LDH@GO-SH.
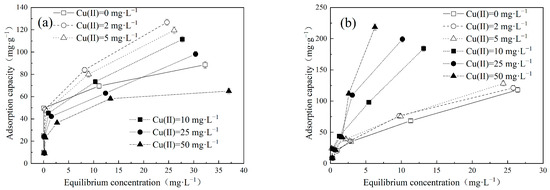
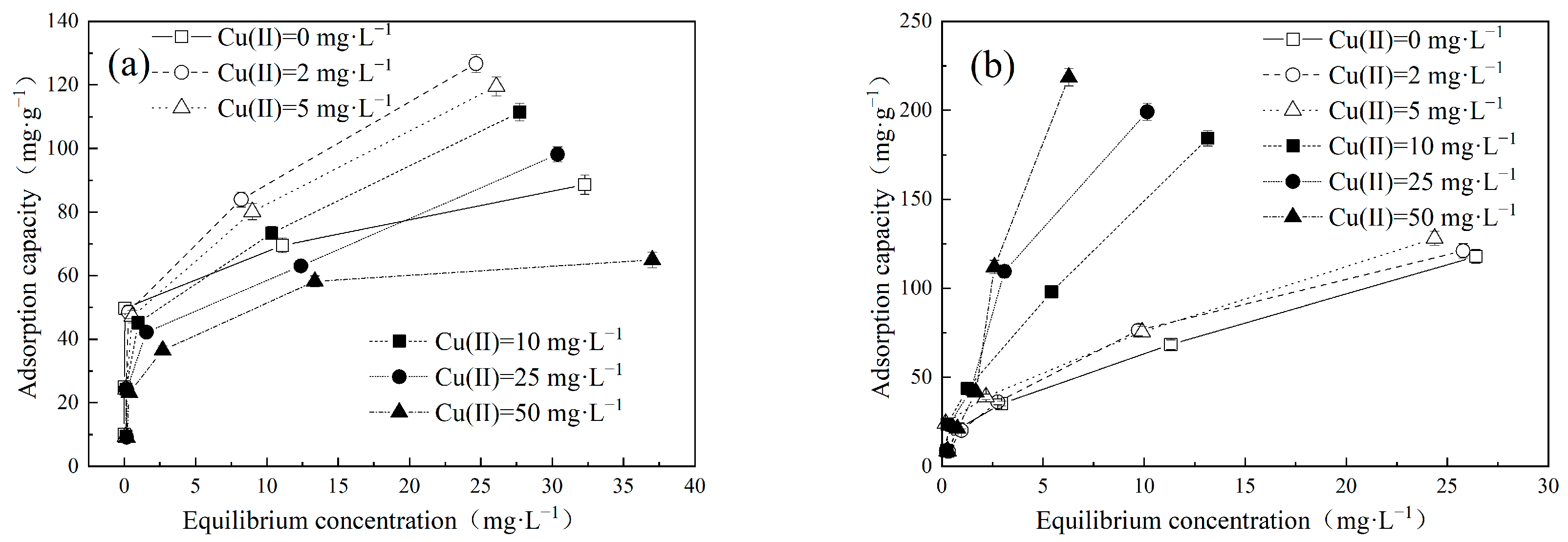
Figure 2.
Effect of different concentrations of Cu(II) on (a) MB and (b) MO adsorption by LDH@GO-SH.
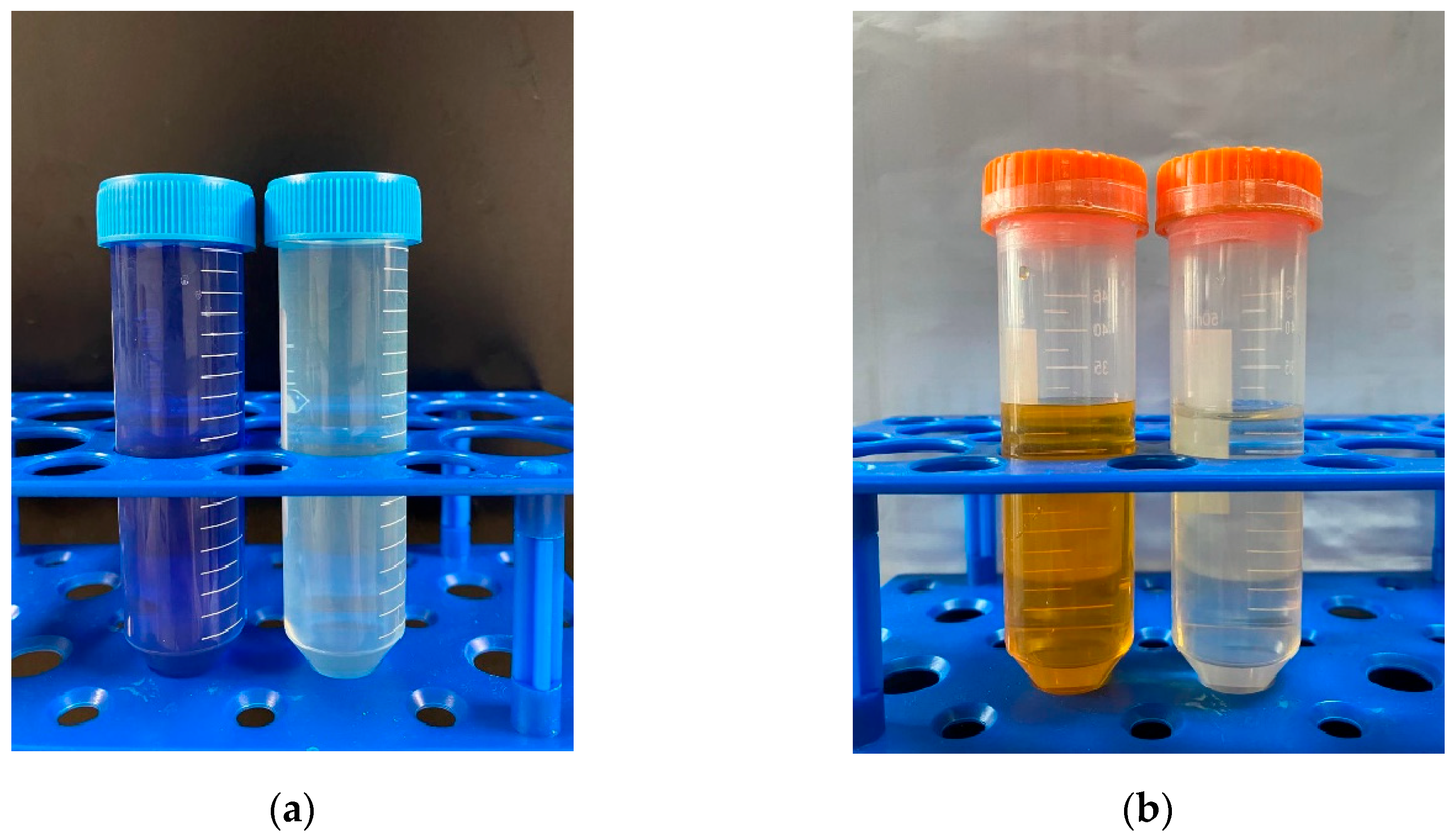
The adsorption performance of MB and MO in a binary system is presented in Figure 2. Interestingly, the presence of Cu(II) exerted distinct effects on the adsorption behaviors of MB and MO. In the MB–Cu binary system, when the concentrations of MB range from 2 mg·L−1 to 10 mg·L−1, the presence of Cu(II) led to a reduction in the adsorption capacity of MB. As the concentration of MB increased to 25 mg·L−1 or 50 mg·L−1, the presence of Cu(II) with a low concentration led to an increase in the adsorption capacity of MB. The enhancement effect weakened with an increase in Cu(II) concentration. However, with a further increase in Cu(II) concentration, the adsorption capacities of MB declined. It can be speculated that both competitive and synergistic effects existed between Cu(II) and MB during the adsorption process. When the competitive effect was stronger than the synergistic effect, the presence of Cu(II) weakened the adsorption of MB, and resulted in a decrease in the adsorption capacities of MB. Conversely, when the synergistic effect prevailed over the competitive effect, the presence of Cu(II) enhanced the adsorption of MB. In the MO–Cu binary system, the presence of Cu(II) significantly facilitated the adsorption capacities of MO on LDH@GO-SH. As MO is an anionic dye, the adsorbed Cu(II) on LDH@GO-SH could provide binding sites for MO, which effectively improved the adsorption capacities of MO. Furthermore, it is noticeable that the color of the mix solution in both the MB–Cu and MO–Cu binary systems became lighter after adsorption, indicating a remarkable adsorption performance of LDH@GO-SH for both MB and MO, as depicted in Figure 3.
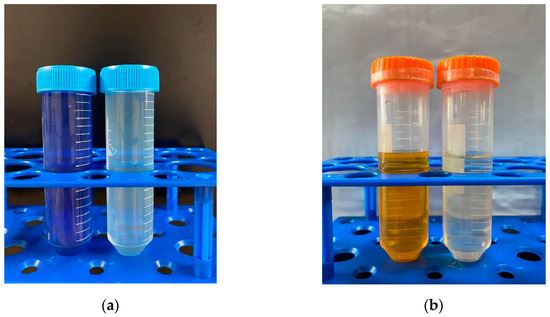
Figure 3.
The color changes of (a) an MB–Cu(Ⅱ) mixed solution and (b) an MO–Cu(Ⅱ) mixed solution before and after adsorption.
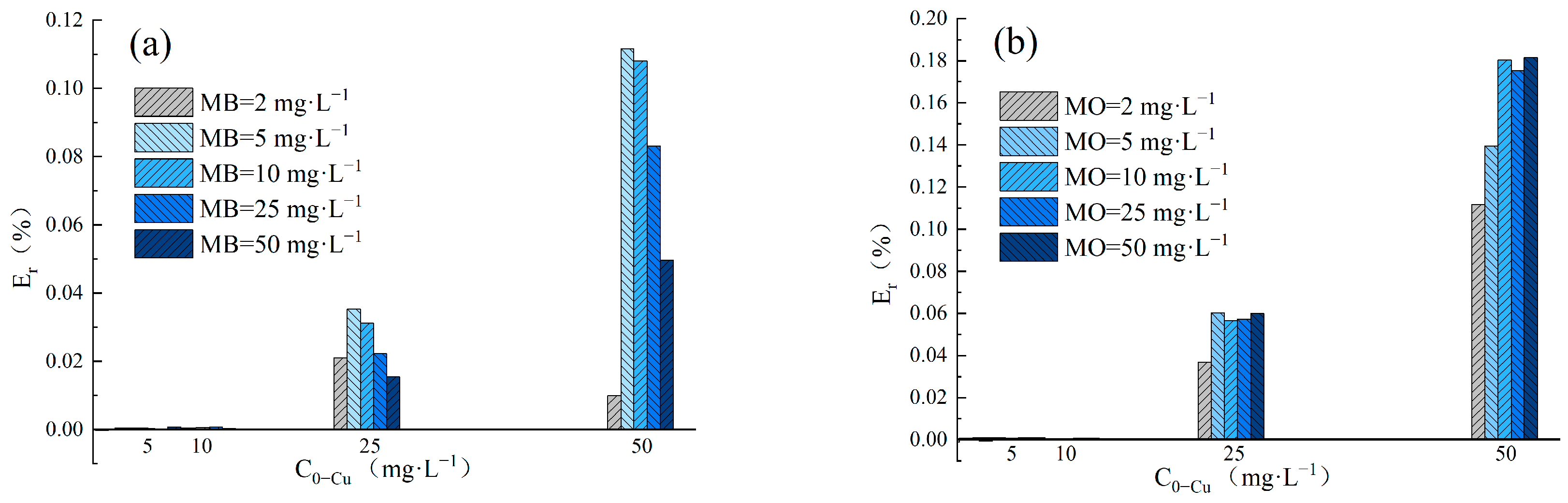
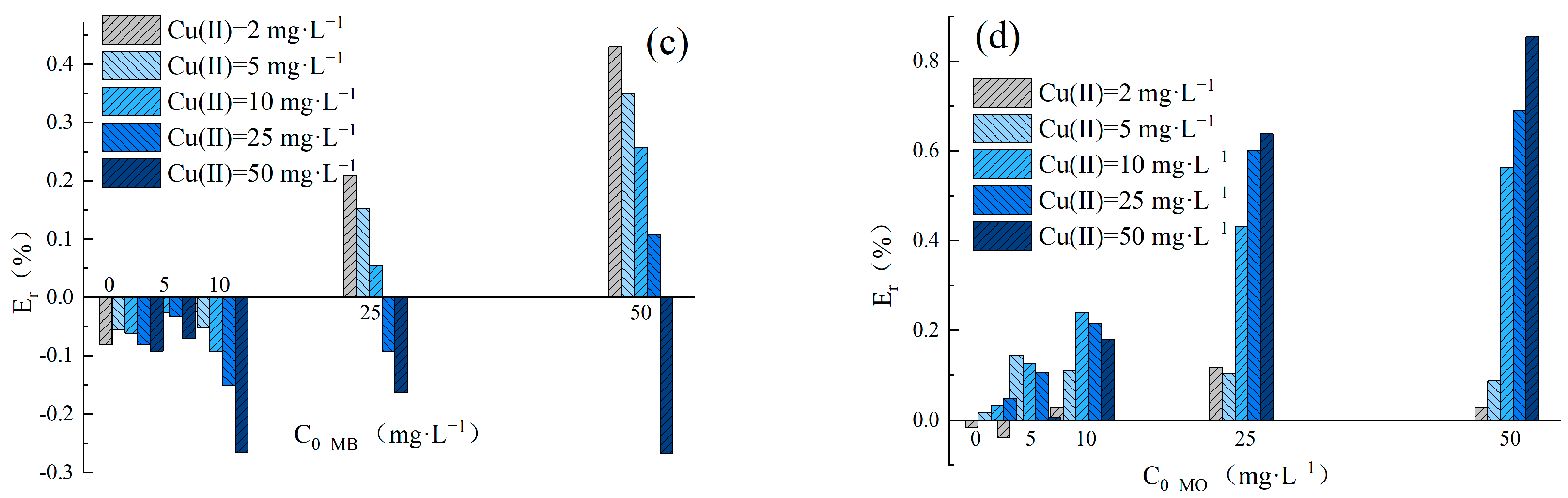
The adsorption Enhancement ratio (Er) was utilized to determine the impact of Cu(II) and dyes in binary systems on the removal performance of LDH@GO-SH. The Er values obtained in MB–Cu and MO–Cu binary systems are presented in Figure 4. The results showed that Er values were nearly zero for Cu(II) adsorption in binary systems at an initial Cu(II) concentration lower than 10 mg·L−1. LDH@GO-SH has a significant adsorption ability, thus the presence of dyes had a negligible impact on Cu(II) adsorption by LDH@GO-SH at low pollutant concentrations. As the concentration of Cu(II) increased to 25 mg·L−1 or 50 mg·L−1, Er-Cu values were greater than zero, signifying that the presence of MB or MO promoted the adsorption of Cu(II) on LDH@GO-SH. As the concentration of MB increased, Er-Cu values first increased but subsequently declined. This trend could be attributed to coexistent MB and Cu(II) in the mixed solution having both competitive and synergistic effects. As the concentration of MB increased, the competition effect between MB and Cu(II) intensified, and the promotion of MB on Cu(II) adsorption was finally weakened. In MO–Cu binary system, Er-Cu values were generally positive for Cu(II) adsorption at the initial Cu(II) concentrations of 25 mg·L−1 and 50 mg·L−1, reflecting efficient synergistic adsorption properties for Cu(II) and MO. Similar trends have been observed by Chen Ling et al. [3] for the synergic adsorption of acid black 1 and copper (II) with hyper-crosslinked resin.
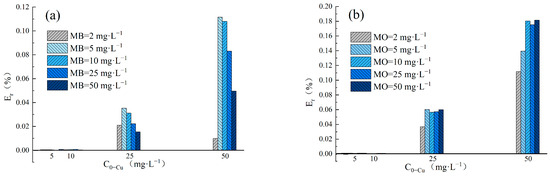
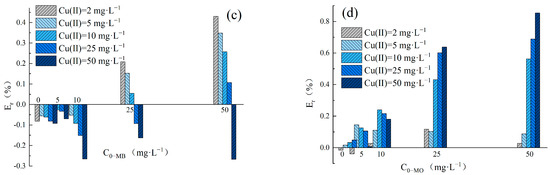
Figure 4.
(a) The Er-Cu values for adsorption amounts in the MB–Cu(II) binary system; (b) the Er-Cu values for adsorption amounts in the MO-Cu(II) binary system; (c) the Er-MB values for adsorption amounts in the MB-Cu(II) binary system; and (d) the Er-MO values for adsorption amounts in the MO-Cu(II) binary system.
The values of Er-MB and Er-MO obtained in MB–Cu and MO–Cu binary systems are presented in Figure 4c,d, respectively. In the MB–Cu binary system, Er-MB values were negative when the concentration of MB was in the range of 2–10 mg·L−1, indicating that the adsorption of MB was weakened in the presence of Cu(II). As the concentration of MB increased to 25 mg·L−1 or 50 mg·L−1, a decreasing trend was observed in the Er-MB values with an increased Cu(II) concentration. When the concentration of Cu(II) was at a lower level, Er-MB > 0; the synergistic effect between Cu(II) and MB was dominant. However, as the concentration of Cu(II) increased, the synergistic effect weakened; the competition effect gradually played a major role. Noticeably, Er-MO values were positive for MO adsorption in the MO–Cu binary system, revealing that the coexistence of Cu(II) effectively strengthened the adsorption of MO onto LDH@GO-SH. Furthermore, MO adsorption was significantly enhanced in the presence of Cu(II), especially at higher concentrations of Cu(II). In the MO–Cu binary system, when the concentrations of Cu(II) and MO were both 50 mg·L−1, the adsorption capacity of MO was 218.61 mg·g−1, which was about twice as much as the adsorption capacity of MO in the single system (117.92 mg·g−1). The significant enhancement in MO adsorption could be attributed to the fact that anionic dye MO adsorbed on the surface of LDH@GO-SH was conducive to electrostatic interactions with Cu(II), thus enhancing the adsorption capacity of MO onto LDH@GO-SH.
3.2. Isotherm Studies
As depicted in Figure 1, the adsorption trends for Cu(II) in MB–Cu and MO–Cu binary systems were basically consistent with the trend observed in the single system. The adsorption capacity of Cu(II) by LDH@GO-SH was closely related to the initial concentration of Cu(II). When the initial concentration of Cu(II) increased, the adsorption capacity increased rapidly at first, then slowly increased, and finally approached equilibrium. The equilibrium solution pH after adsorption was about six. Langmuir and Freundlich models were employed to describe the adsorption of Cu(II) on LDH@GO-SH, and the calculated relevant parameters are presented in Table 1. The Langmuir model was more suitable to describe the adsorption behavior of Cu(II) than the Freundlich model in single and binary systems, which was confirmed by the higher determination coefficients (R2 > 0.99). Moreover, the maximum adsorption capacities (qm) of Cu(II) calculated using the Langmuir model were also similar to the experimental values (qe). The well-fitting of the Langmuir model indicated that the adsorption behaviors of Cu(II) were based on a monolayer chemical adsorption mechanism in single and binary systems [18]. Compared with the single system, the adsorption capacities of Cu(II) in the binary systems were gradually enhanced with an increase in dye concentration. Thus, the functional groups on MB or MO played an important role in the collaborative adsorption process.

Table 1.
Isotherm parameters for the adsorption of Cu(II) by LDH@GO-SH in MB–Cu and MO–Cu binary systems.
3.3. Kinetic Studies
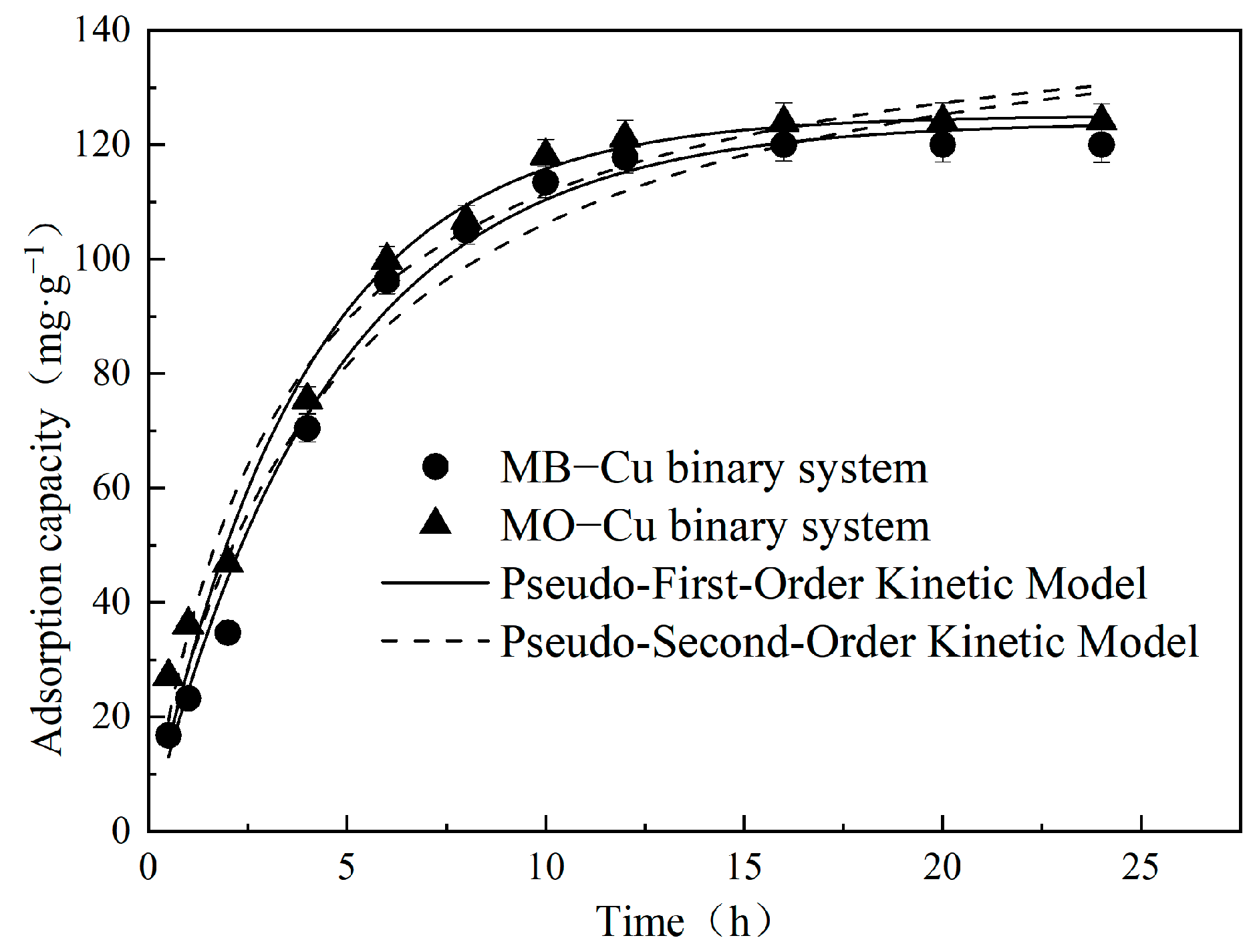
The influence of contact time on Cu(II) adsorption in both MB–Cu and MO–Cu binary systems was studied under conditions where the initial concentration of pollutant (Cu(II), MB, or MO) was 25 mg·L−1; the temperature was 25 °C; and pH = 5. The results are depicted in Figure 5. The adsorption capacities of Cu(II) increased sharply during the first 5 h, and finally achieved equilibrium at approximately 12 h in both MB–Cu and MO–Cu binary systems. Adsorption kinetic data were analyzed using a pseudo-first-order kinetic model and pseudo-second-order kinetic model, and the resulting kinetic parameters are summarized in Table 2. The adsorption kinetics of Cu(II) in both MB–Cu and MO–Cu binary systems could be well-described by the pseudo-first-order kinetic model, and were confirmed by the high determination coefficients (R2 > 0.98), and the experimental equilibrium adsorption capacities (qe,exp) of Cu(II) were similar to the calculated equilibrium adsorption capacities (qe,cal). The existence of different dyes (MB and MO) did not significantly affect the adsorption capacities of Cu(II) by LDH@GO-SH, which was evidenced by the similar adsorption kinetics curves observed from MB–Cu and MO–Cu binary systems. Kinetic results also showed a similar qe,cal of 123.98 for the MB–Cu system and 125.12 mg·g−1 for the MO–Cu binary system.
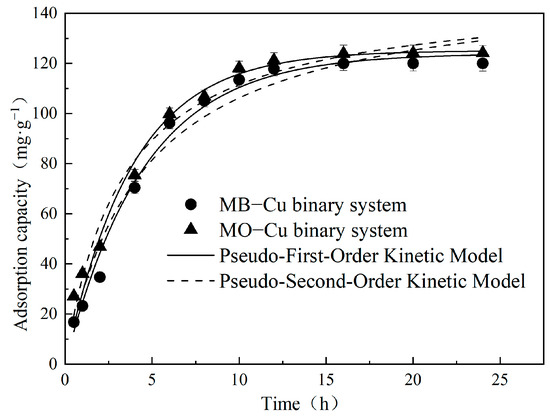
Figure 5.
Adsorption kinetics for the adsorption of Cu(II) by LDH@GO-SH.

Table 2.
Kinetic parameters for the adsorption of Cu(II) by LDH@GO-SH.
3.4. Effects of Solution pH and Ionic Strength
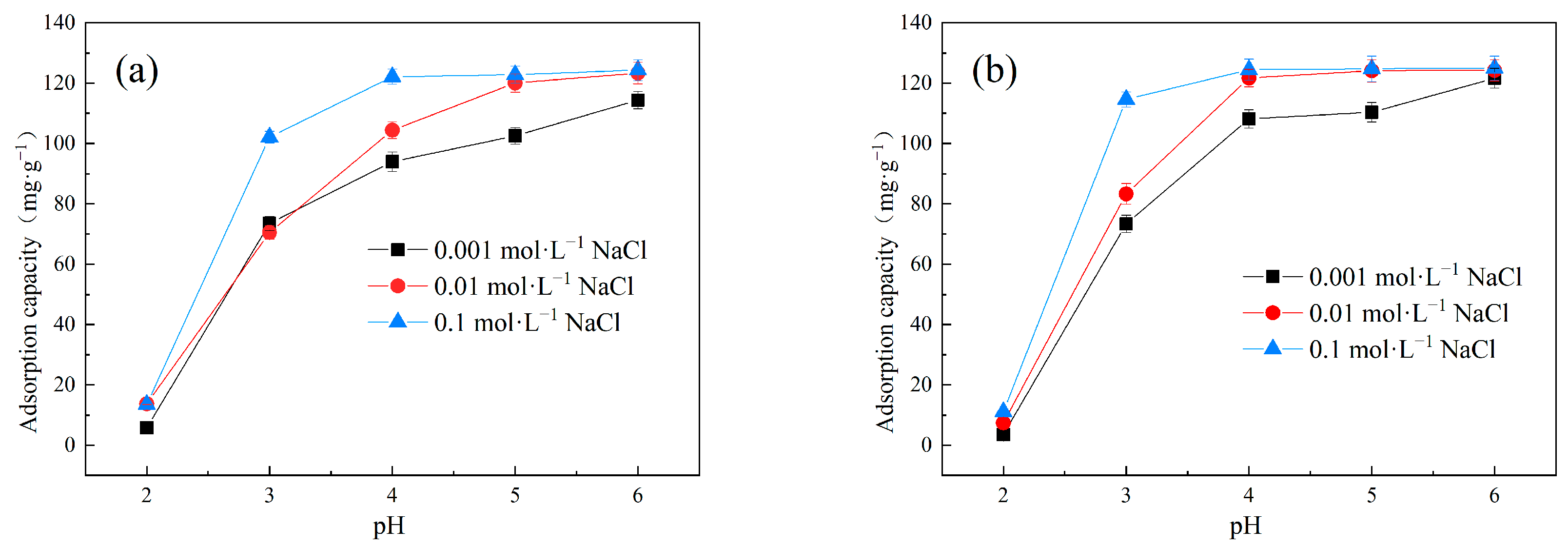
Figure 6 exhibits the effect of pH and ionic strength on the adsorption performance of Cu(II) onto LDH@GO-SH in binary systems. It is notable that an increase in solution pH significantly facilitated Cu(II) adsorption; the adsorption capacities increased sharply when the solution pH increased from two to four, and followed a slight increase with further increasing of the pH to six. Similar findings were obtained in Cu(II) adsorption on banana stalk biochar [30] and functionalized straw [18]. The pH of a solution is a crucial factor influencing adsorption performance. Theoretically, pH can affect the surface charge of the adsorbent and the existing forms of pollutants in the solution [31]. At high pH levels, the thiol groups on LDH@GO-SH tended to deprotonate, and the surface of LDH@GO-SH was negatively charged. The negatively charged surface of LDH@GO-SH was beneficial for improving the adsorption capacities of Cu(II) due to the electrostatic attractive force. Consequently, the effect of pH on Cu(II) adsorption by LDH@GO-SH can be attributed to the electrostatic interaction mechanism between the negatively charged LDH@GO-SH surface and positively charged Cu(II).
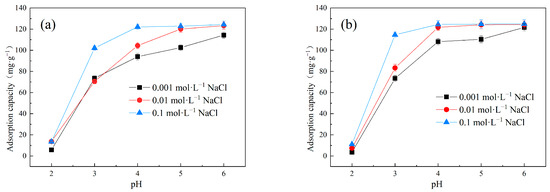
Figure 6.
The effect of pH and ionic strength on the adsorption capacities of Cu(II) by LDH@GO-SH in (a) MB–Cu and (b) MO–Cu binary systems.
Foreign salt additives (ionic strength) usually abundantly exist in actual dyeing industry wastewater and other industrial wastewater, which may have a significant impact on adsorption [32]. The influence of ionic strength on the adsorption performance of Cu(II) by LDH@GO-SH was investigated, and the results are displayed in Figure 6. With an increase in NaCl concentration, the adsorption capacities of LDH@GO-SH for Cu(Ⅱ) slightly enhanced in both MB–Cu and MO–Cu binary systems. This result could be attributed to a salt-out effect, which weakened the water solubility of dyes at higher ionic strength and enhanced the adsorption of dyes on LDH@GO-SH [3], and then, through the synergistic effect between dyes and Cu(II), facilitated Cu(II) adsorption on LDH@GO-SH.
3.5. Effect of Temperature
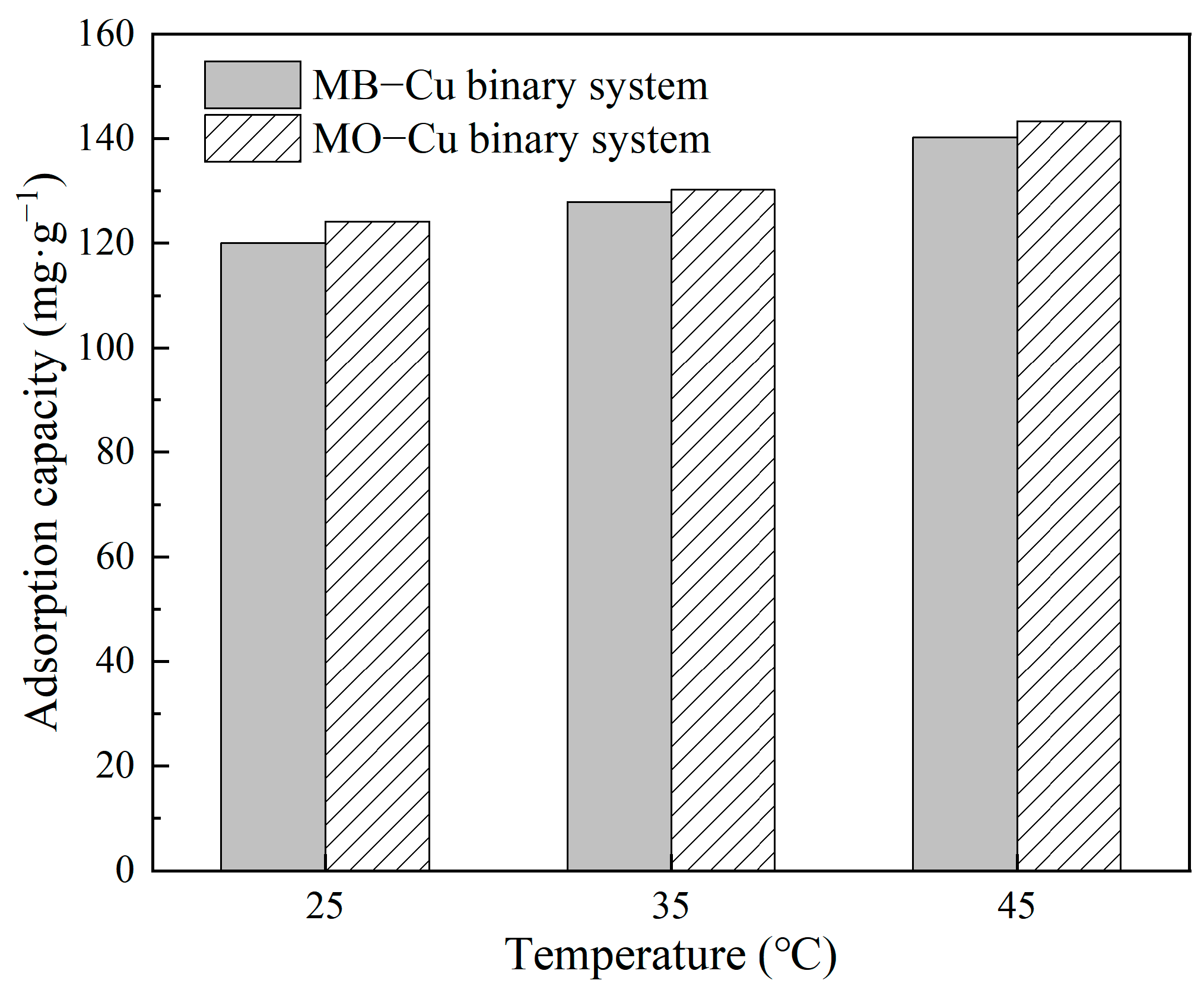
The effect of temperature on Cu(II) adsorption in both MB–Cu and MO–Cu binary systems is illustrated in Figure 7. The results showed that temperature slightly improved the adsorption of Cu(II) in binary systems. When the temperature increased from 25 °C to 45 °C, the adsorption capacities of Cu(II) increased from 120.04 mg·g−1 to 140.21 mg·g−1 for the MB–Cu binary system, and increased from 124.17 mg·g−1 to 143.27 mg·g−1 for the MO–Cu binary system. This concluded that a higher temperature is favorable to the adsorption processes of Cu(II) on LDH@GO-SH.
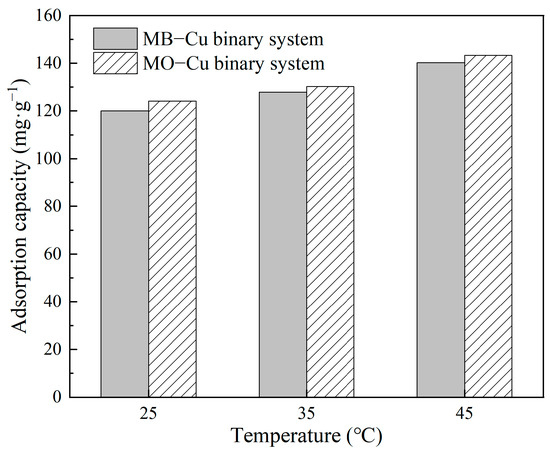
Figure 7.
The effect of temperature on the adsorption capacities of Cu(II) by LDH@GO-SH in MB–Cu and MO–Cu binary systems.
3.6. Reusability
The reusability of an adsorbent is an important factor to evaluate its practical application potential. The reusability of LDH@GO-SH was examined by a series of desorption and regeneration experiments. A solution of 0.1 mol·L−1 Na2EDTA was chosen as an eluant, and three consecutive adsorption–desorption experiments were conducted. The adsorption capacities of LDH@GO-SH for Cu(II) were maintained over 88% after three consecutive adsorption–desorption cycles in both MB–Cu and MO–Cu binary systems. The results showed that LDH@GO-SH has good reusability and high practical application potential in removing heavy metal ions.
3.7. Adsorption Mechanisms
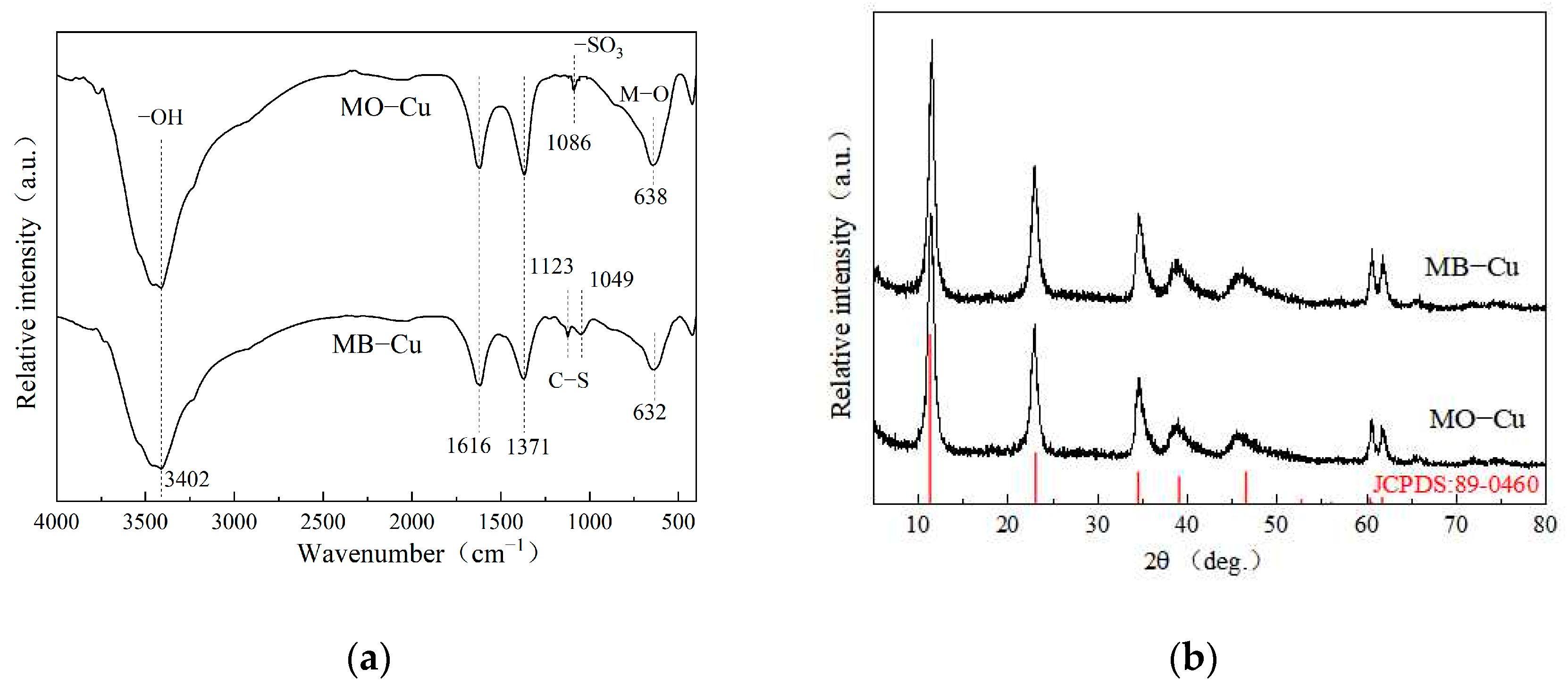
The characterizations of the as-prepared LDH@GO-SH before adsorption were displayed in our previous study [27]. The N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms of the LDH@GO-SH are presented in Figure S1. The specific surface area, pore size, and pore volume of LDH@GO-SH were 59.44 m2·g−1, 10.70 nm, and 0.139 cm3·g−1, respectively. The XRD pattern demonstrated that the synthesized LDH@GO-SH was composed of a hexagonal LDHs phase, and no diffraction peaks of impurities were found. In the FTIR spectra, the thiol groups in LDH@GO-SH failed to be identified because their specific peaks may be overlapped with other stronger ones.
The FTIR spectra of LDH@GO-SH after adsorption are shown in Figure 8a. Compared with the FTIR before adsorption, the intensity of adsorption peaks at ~3450 cm−1 and ~1630 cm−1 decreased obviously, indicating that functional groups like hydroxyl groups are involved in the adsorption process [33,34]. Peaks occurred at 1123 cm−1 and 1049 cm−1 and are indicative of the stretching vibration of the C–S bond of MB, which directly confirmed the plentiful loading of MB on LDH@GO-SH. Evidence of the presence of -SO3 groups of MO at 1086 cm−1 is presented in Figure 8a. These results revealed that LDH@GO-SH had significant adsorption abilities for MB and MO. Moreover, the adsorbed MB or MO provided new groups on LDH@GO-SH, which might provide additional adsorption sites for Cu(II). The XRD spectra of LDH@GO-SH after adsorption in binary systems are shown in Figure 8b. After adsorption, LDH@GO-SH maintained its original crystal structure and no new diffraction peak appeared, indicating the material structure did not change during the adsorption process.
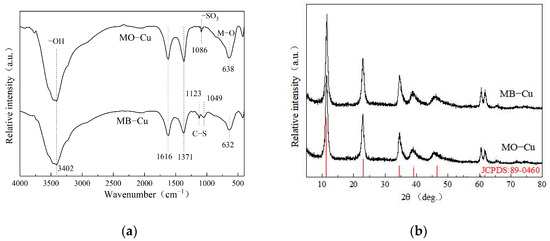
Figure 8.
(a) FTIR and (b) XRD spectra of LDH@GO-SH after adsorption in binary systems.
Based on the above discussions, surface complex interaction between Cu(II) in liquid phase and adsorbed dyes in solid phase was a potential mechanism for the enhancement effect in the adsorption process, especially in high Cu(II) concentrated systems. Furthermore, the electrostatic attraction between an anionic dye (MO) and positively charged Cu(II) ions also played a key role in the enhanced adsorption of Cu(II) in the MO–Cu binary system.
4. Conclusions
In summary, LDH@GO-SH was prepared as an efficient adsorbent for the simultaneous elimination of Cu(II) and dyes including MB and MO. LDH@GO-SH showed excellent adsorption characteristics owing to the modified thiol groups on the surface of LDH@GO-SH. The enhanced adsorption performance of LDH@GO-SH for Cu(II) was achieved in the presence of dyes. At the initial pollutant concentration of 50 mg·L−1, the adsorption capacities for Cu(Ⅱ) in MB–Cu binary and MO–Cu binary systems were 187.75 and 211.33 mg·g−1, respectively. The existence of Cu(II) had distinct impacts on the adsorption of MB and MO. In the presence of Cu(II), the adsorption capacity of MO increased significantly, but the adsorption performance of MB weakened under low concentrations of MB (2 mg·L−1–10 mg·L−1). It is suspected that both a synergistic effect and competition effect existed between MB and Cu(II) but only a synergistic effect existed between MO and Cu(II). The adsorption isotherms and kinetics in binary systems were studied in detail. The adsorption processes of Cu(II) in binary systems could be well-described by Langmuir isotherms. The pseudo-second-order kinetic model gave a more satisfactory fit of the experimental data than the pseudo-first-order kinetic model. The adsorption of Cu(II) on LDH@GO-SH was strongly dependent on pH but weakly dependent on ionic strength. The adsorption capacities of Cu(II) on LDH@GO-SH slightly improved with increasing temperature. LDH@GO-SH exhibited good reusability; the adsorption capacities of Cu(II) were maintained over 88% after three adsorption–desorption cycles. The potential mechanism for the enhancement effect of Cu(II) in binary systems was attributed to the surface complex interaction between Cu(II) in liquid phase and adsorbed dyes in solid phase. Moreover, the electrostatic interaction between an anionic dye (MO) and Cu(II) also contributed to the enhancement of Cu(II) adsorption in the MO–Cu binary system. LDH@GO-SH showed excellent adsorption performance in binary systems, hinting that LDH@GO-SH can be applied as an efficient adsorbent for the simultaneous elimination of heavy metal ions and dyes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16141968/s1, Figure S1: (a) Isotherm curve of N2 adsorption–desorption and (b) pore size distribution of LDH@GO-SH.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.L. and H.L.; methodology, W.L. and H.L.; software, W.L.; validation, W.L. and X.Y.; investigation, W.L.; resources, H.L.; data curation, W.L.; writing—original draft preparation, W.L.; writing—review and editing, X.Y. and Y.L.; visualization, W.L.; supervision, X.Y.; project administration, Y.L.; funding acquisition, W.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Key Project of Chongqing Technology Innovation and Application Development (CSTB2023TIAD-KPX0091).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Wei Liao and Xiaowen Yu were employed by the company Chongqing CEPREI Industrial Technology Research Institute Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Huang, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Niu, D.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z. Citric acid-crosslinked β-cyclodextrin for simultaneous removal of bisphenol A, methylene blue and copper: The roles of cavity and surface functional groups. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 82, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Oatley, D.L.; Williams, P.M.; Wright, C.J. Characterisation and application of a novel positively charged nanofiltration membrane for the treatment of textile industry wastewaters. Water Res. 2012, 46, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Liu, F.-Q.; Long, C.; Chen, T.-P.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Li, A.-M. Synergic removal and sequential recovery of acid black 1 and copper (II) with hyper-crosslinked resin and inside mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Gómez, R.; Rivera-Ramírez, D.A.; Hernández-Montoya, V.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Durán-Valle, C.J.; Montes-Morán, M.A. Synergic adsorption in the simultaneous removal of acid blue 25 and heavy metals from water using a Ca(PO3)2-modified carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 199–200, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.-J.; Jiang, S.-K.; Chao, X.-Y.; Zhang, C.-X.; Shi, Q.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Liu, M.-L.; Sun, S.-P. Removing miscellaneous heavy metals by all-in-one ion exchange-nanofiltration membrane. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.; Solaiman; Roy, C.K.; Firoz, S.H.; Foyez, T.; Imran, A.B. Role of Ionic Moieties in Hydrogel Networks to Remove Heavy Metal Ions from Water. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, W.; Pan, F.; Sun, P.; Fu, J. An overview of nanomaterials applied for removing dyes from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 15882–15904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Tong, J.; Shao, X.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Han, Y.; Yang, X.; Ding, F.; Zhang, J.; et al. Alkaline ball-milled peanut-hull biosorbent effectively removes aqueous organic dyes. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Yang, K.; Zhu, E.; Li, X.; Sun, M.; Xiao, L.; Hari, Q.; Tang, S. Peracetic Acid Activated with Electro-Fe2+ Process for Dye Removal in Water. Coatings 2022, 12, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, A.; Azari, A.; Rezakazemi, M.; Ansarpour, M. Removal of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewaters: A Review. ChemBioEng Rev. 2017, 4, 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, N.A.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D.U. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. Npj Clean Water 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajiboye, T.O.; Oyewo, O.A.; Onwudiwe, D.C. Simultaneous removal of organics and heavy metals from industrial wastewater: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Charumathi, D.; Das, N. Bioaccumulation of the synthetic dye Basic Violet 3 and heavy metals in single and binary systems by Candida tropicalis grown in a sugarcane bagasse extract medium: Modelling optimal conditions using response surface methodology (RSM) and inhibition kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.D.; Danh, H.T.; Silva-Martinez, S. Single and Binary Adsorption Systems of Rhodamine B and Methylene Blue onto Alkali-Activated Vietnamese Diatomite. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2021, 2021, 1014354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Kang, W.; Huang, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Hu, J.; Li, Y. Cadmium(II) Capture Using Amino Functionalized Hydrogel with Double Network Interpenetrating Structure: Adsorption Behavior Study. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2022, 39, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, R.; Pelalak, R.; Pishnamazi, M.; Marjani, A.; Shirazian, S. A water-stable functionalized NiCo-LDH/MOF nanocomposite: Green synthesis, characterization, and its environmental application for heavy metals adsorption. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Bai, Z.; Jiang, H.; Prinsen, P.; Luque, R.; Zhao, S.; Xuan, J. Selective heavy metal removal and water purification by microfluidically-generated chitosan microspheres: Characteristics, modeling and application. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Lu, J.; Yu, G.; Möslang, M.; Zhou, Y. Superior adsorption capacity of functionalised straw adsorbent for dyes and heavy-metal ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 121040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cheng, G.; Chen, K.; Lu, J.; Lei, J.; Pu, S. Adsorptive removal of bisphenol A, chloroxylenol, and carbamazepine from water using a novel β-cyclodextrin polymer. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya, V.N.; Rajkumar, M.; Mobika, J.; Sibi, S.P.L. Adsorption of As (V) ions from aqueous solution by carboxymethyl cellulose incorporated layered double hydroxide/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites: Isotherm and kinetic studies. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 26, 102268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.; Raheem, A. Graphene oxide/Mg-Zn-Al layered double hydroxide for efficient removal of doxycycline from water: Taguchi approach for optimization. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 354, 118899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Jana, A.; Das, D.; Biswas, S.; Sheshadri, H.; Rao, M.S.; De, S. Surfactant assisted APTES functionalization of graphene oxide intercalated layered double hydroxide (LDH) for uranium adsorption from alkaline leach liquor. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 390, 136058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryam Hafezian, S.; Biparva, P.; Bekhradnia, A.; Naser Azizi, S. Amine and thiol functionalization of SBA-15 nanoparticles for highly efficient adsorption of sulforaphane. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zounia, M.; Hakimi, M.; Yazdi, M.R.S.; Zare, H.; Amiri, A. The effect of thiol ligands on the adsorption behavior of silver ions on functionalized nanomagnetic graphene oxides. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2024, 144, 110943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Induvesa, P.; Ratanatawanate, C.; Wongrueng, A.; Punyapalakul, P. Adsorption of iodinated trihalomethanes onto thiol functionalized ZIF-8s: Active adsorption sites, adsorptive mechanisms, and dehalogenation by-products. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezarjaribi, M.; Bakeri, G.; Sillanpää, M.; Chaichi, M.J.; Akbari, S.; Rahimpour, A. Novel adsorptive PVC nanofibrous/thiol-functionalized TNT composite UF membranes for effective dynamic removal of heavy metal ions. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 284, 111996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Bao, D.; Li, H.-q.; Yang, P. Cu(II) and Cd(II) removal from aqueous solution with LDH@GO-NH2 and LDH@GO-SH: Kinetics and probable mechanism. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 65848–65861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.-J.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Chao, H.-P. Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Water Res. 2017, 120, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Liao, B.; Lin, L.; Qiu, W.; Song, Z. Adsorption of Cu(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by ferromanganese binary oxide–biochar composites. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Li, Q.; Huang, M.; Li, A.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Kang, C.; Mo, W. Removal of Zn(II), Mn(II) and Cu(II) by adsorption onto banana stalk biochar: Adsorption process and mechanisms. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 2962–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Adsorption of cadmium and lead ions by phosphoric acid-modified biochar generated from chicken feather: Selective adsorption and influence of dissolved organic matter. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 292, 121948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.-H.; Zhang, X.-R.; Zeng, G.-M.; Gong, J.-L.; Niu, Q.-Y.; Liang, J. Simultaneous removal of Cd(II) and ionic dyes from aqueous solution using magnetic graphene oxide nanocomposite as an adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 226, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Jiang, L.; Wang, D.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, S. Intercalation of thiacalix[4]arene anion via calcined/restored reaction into LDH and efficient heavy metal capture. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 220, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Sui, J.; Li, J.; Tang, Y.; Cai, W. Efficient removal of heavy metal ions by thiol-functionalized superparamagnetic carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 210, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).