A Critical Review of Emerging Technologies for Flash Flood Prediction: Examining Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Internet of Things, Cloud Computing, and Robotics Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- What are the trends and characteristics of studies on smart technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and robotics that have been applied in flash flood early warning predictions?
- (2)
- What are the performance levels of AI/ML algorithms in flash flood susceptibility predictions?
- (3)
- What are the common indicators and influential factors in flash flood susceptibility assessment?
- (4)
- What are the strengths and limitations of current studies that could improve future flash flood early warning and susceptibility predictions?
- (1)
- Focusing exclusively on current evidence of these emerging technological tools applied in flash flood early warning and susceptibility predictions.
- (2)
- Comprehensive coverage of several emerging technologies used in flash flood management: artificial intelligence (AI)/machine learning (ML), the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and robotics.
- (3)
- Covering several artificial intelligence (AI)/machine learning (ML) internet algorithms utilized for flash flood warnings and susceptibility predictions.
- (4)
- Including a detailed review of studies that have applied machine learning for flash flood susceptibility assessment supported by model performance evaluation levels.
- (5)
- Including the temporal trends (from old to most recent papers) of flash flood-related technological studies.
- (6)
- Synthesizing the findings of the studies and suggesting future research priorities and strengths.
2. Methods
3. Results
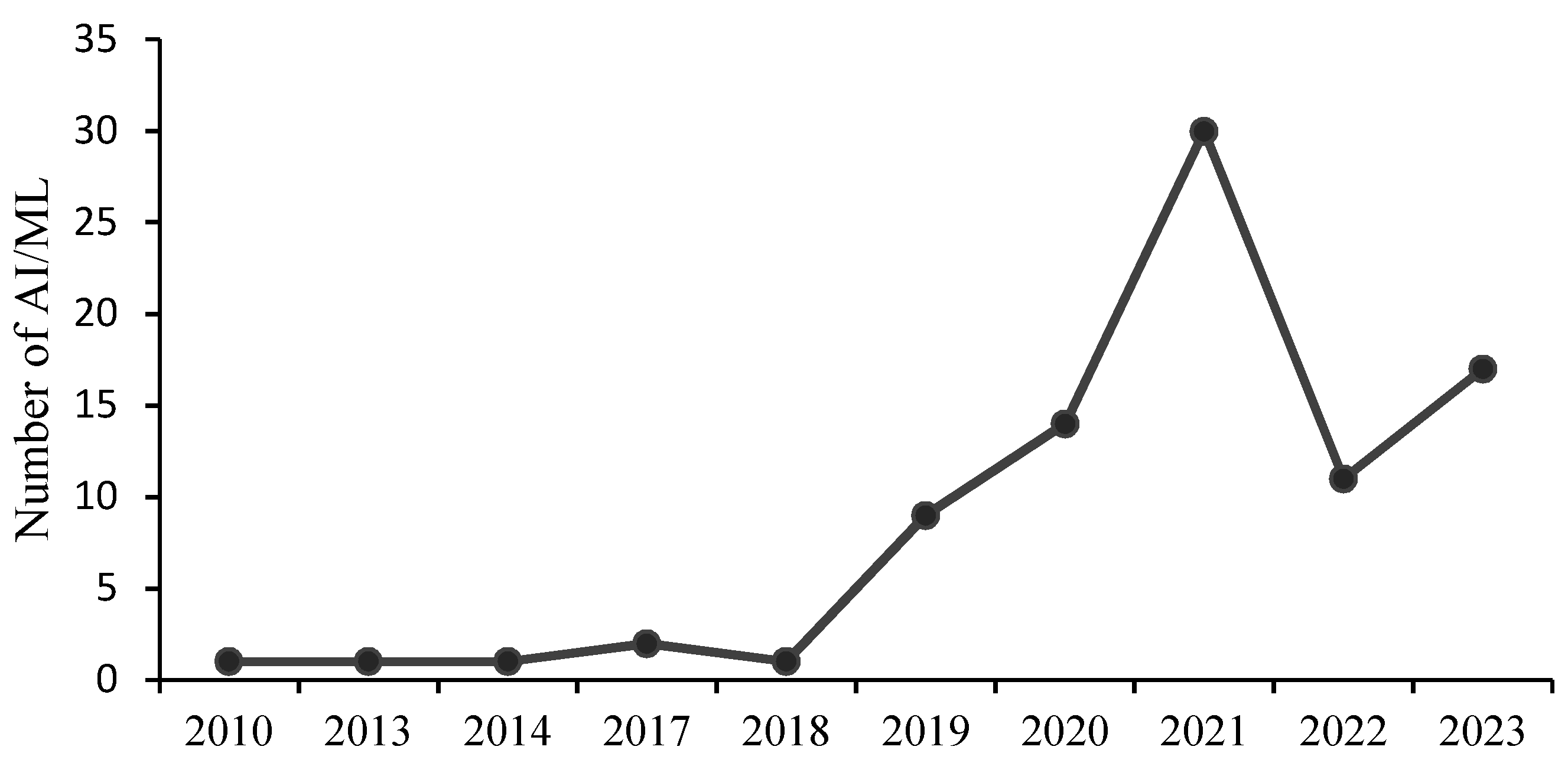
3.1. Bibliographic Analysis of Flash Flood Publications and AI/ML Algorithms
3.1.1. Analysis by Year of Publications and Type of Technology
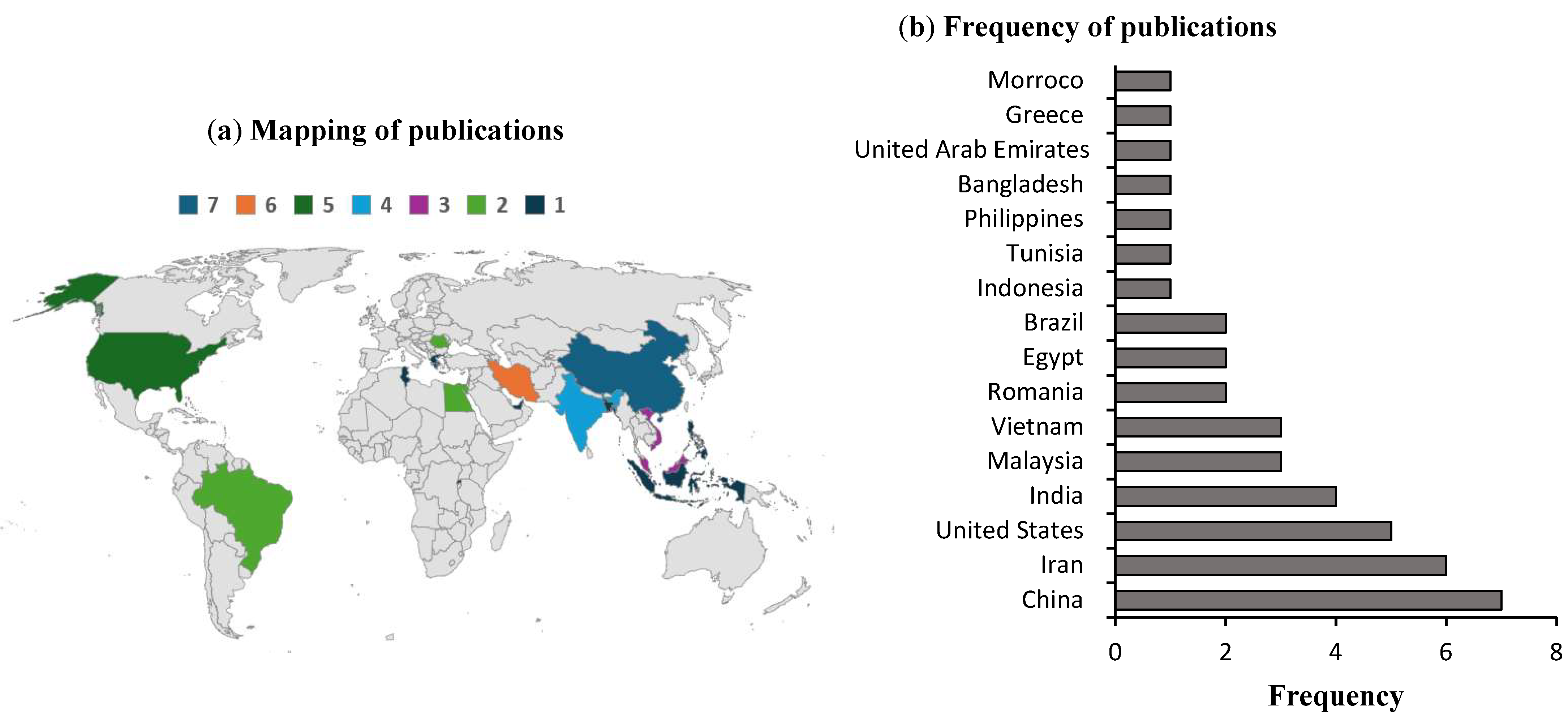
3.1.2. Analysis of Flash Flood Publications by Country
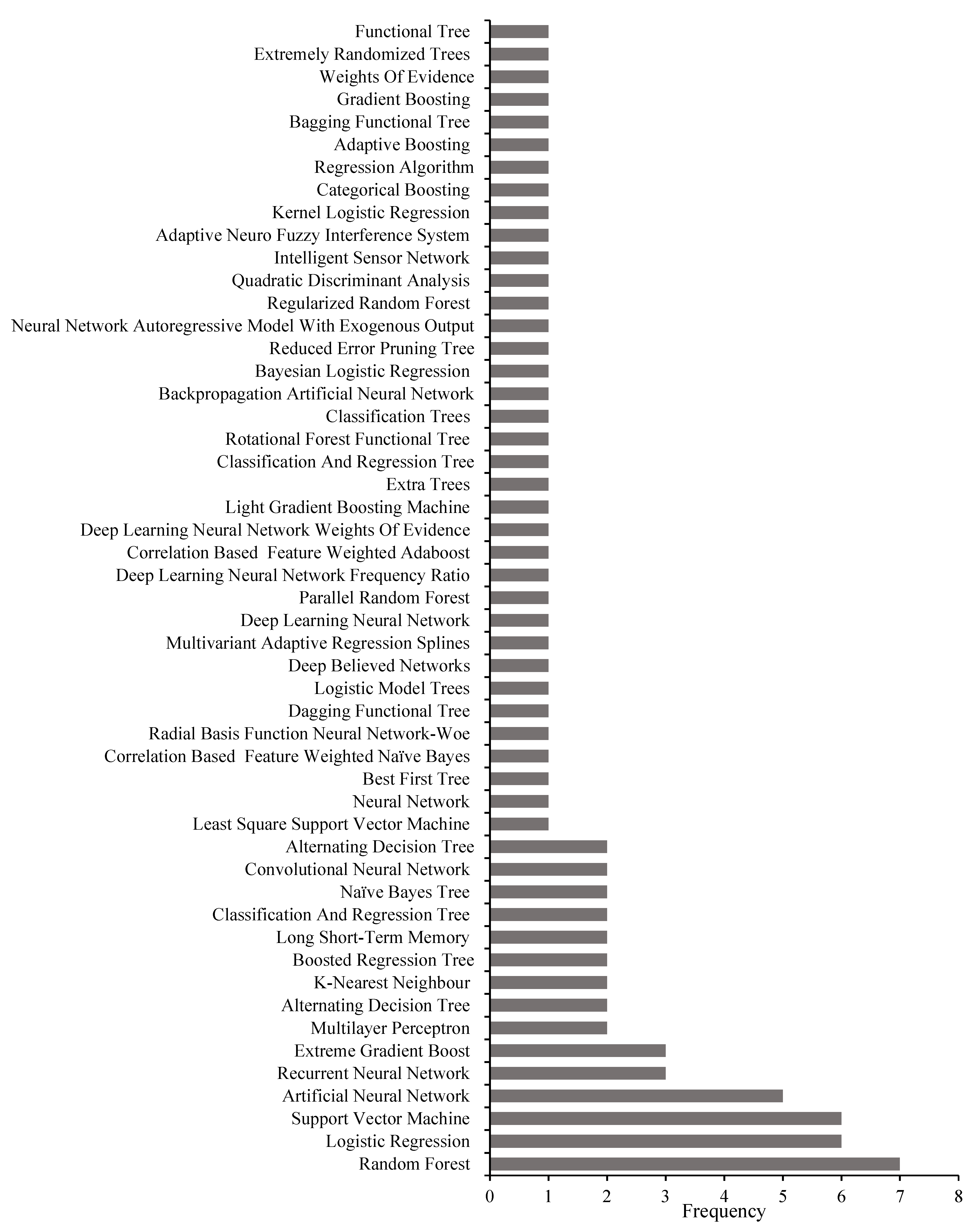
3.1.3. Analysis by Flash Flood AI/ML Algorithm Type
4. Application of Emerging Technologies for Flash Flood Warnings and Susceptibility
4.1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)/Machine Learning (ML)
4.1.1. AI/ML Algorithms Used for Early Warning Predictions
4.1.2. Application of AI/ML Algorithms for Flash Flood Susceptibility Predictions
| Location | AI/ML Method | Performance Levels | Conclusions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) Early Warning Prediction Studies | ||||
| Khosf, Iran | Support vector machine (SVM), artificial neural network (ANN), Nearest neighbor classification (NNC) | Flash flood risk was predicted by the three AI methods. The model performance through the coefficient of determination (r) for the three AI methods was SVM = 0.88, ANN = 0.79, and NNC = 0.89 | An alternate application of computer vision can help improve the prediction of flash floods | [18] |
| Amman, Jordan | Artificial neural networks (ANNs) | The ANN improved flash flood warning forecasting by 93.5% when compared with the conventional forecasting model | High computation cost | [19] |
| Leyte Island, Philippines | Regression algorithm | Able to send flash flood warnings (water level and water speed) via SMS upon reaching the threshold | Warning messages sometimes exceed the memory capacity of the SMS | [22] |
| - | Adaptive neuro fuzzy interference system (ANFIS), meural metwork autoregressive model with exogenous output (NNARX) | It was found that NNARX accurately predicted flash flood water level, velocity, and ocean bottom pressure with >80% accuracy | - | [23] |
| Campos do Jordão, Brazil | Neural network (NN) | There is 100% correctness in the classification of true positives for training and test sets, indicating that the NN is reliably integrated to improve the accuracy of early warning systems | False positives were detected, indicating improvement in the NN | [24] |
| Golestan, Iran | Convolutional neural network (CNN), recurrent neural network (RNN) | The CNN (RMSE = 0.83) performed slightly better than the RNN (RMSE = 0.81) in predicting flash flood events. Both technologies successfully captured spatial heterogeneities of flash flood probabilities in the area | Hyper-parameter tunning could improve the accuracy of these DL networks | [33] |
| Hangzhou, China | Support vector machine (SVM) | The SVM (2.5 milliseconds) accurately forecasted flash flood events compared to traditional numerical models (25 h) | - | [20] |
| Semarang, Indonesia | Artificial neural network (ANN) | The ANN could forecast flash flood events by a 2 h lead time. The application could transmit information to the telemetry system/SMS in 10 min | - | [21] |
| - | Intelligent sensor network (ISN) | The system is fully automated. Reduces false alarms for flash flood events and can diagnose the health data of the affected population to issue alerts | - | [26] |
| China | Long short-term memory (LSTM) | The LSTM approach predicted accurate one-day flash flood warnings with a false alarm rate of 0.09 and two-day warnings with a false alarm rate of 0.21. The LSTM approach gave the best predictions with a critical success index of 0.75 | The lack of a high resolution made predicting flash flood early warnings in complex geographies, such as mountainous areas, difficult | [25] |
| Uttarakhand, India | Gradient boosting (GBT), recurrent neural network (RNN) | The flash prediction accuracy according to the coefficient of the regression value (R2) for the RNN and GBT were 0.98 and 0.92, respectively | Using high-resolution remote sensing data may improve future predictions | [27] |
| Daqin, China | Long short-term memory (LSTM) | LSTM improved flash flood prediction by reducing flood peak flow and volume error by 3.02–57.4% and 6.3–39.3%, respectively, when coupled with hydrological models (e.g., WRF/WRF–hydro models) | - | [28] |
| (B) Susceptibility Assessment-Based ML Studies | ||||
| Gabes, Tunisia | Artificial neural network (ANN) | The ANN technique could reliably reveal 14% very high flash flood susceptibility/prone areas. The receiver operating characteristics (ROCs) predicted an area under the curve (AUC) value for the ANN of 0.86, indicating the reliability of the ANN risk predictions | The approach could not determine the frequency of occurrence and timing of the flash flood events | [32] |
| Golestan, Iran | The convolutional neural network (CNN) and recurrent neural network (RNN) | The deep learning neural network technique was able to predict heterogeneities in spatial patterns of flash flood risks. The area under the curve (AUC) values for the CNN (0.83) were slightly better than the RNN (0.81). About 40% of the area was considered to have very high susceptibility | There is a need to optimize the CNN and RNN algorithms | [33] |
| Tafresh, Iran | Alternating decision tree (ADT), functional tree (FT), kernel logistic regression (KLR), multilayer perceptron (MLP), quadratic discriminant analysis (QDA) | Flash flood susceptibility predictions were very high in ADT (AUC = 0.97) compared to FT, KLR, MLP, and QDA, whose AUC values were >0.95. More than 80% of the area is highly susceptible to flash floods | Computational, highly efficient data mining methods could be employed to improve future studies | [34] |
| Gorgan, Iran | Bagging functional tree (BFT), dagging functional tree (DFT), and rotational forest functional tree (RFT) | The three AI methods predicted flash flood susceptibility. The AUC values were BFT = 0.95, DFT = 0.93, and RFT = 0.94. About 1.99% and 5.41% of flood susceptibility areas were classified as very high and high, respectively, according to the BFT model | Introducing hybrid models to reduce uncertainties and improve prediction accuracy is important This approach could be used for flash flood vulnerability assessment | [35] |
| Hurghada, Egypt | Light gradient boosting machine (Light GBM) and categorical boosting (Catboost) | AUC values showed that both the Light GBM (0.98) and Catboost (0.97) methods accurately predicted flood-risk zones. The above models predicted 42% and 44% of the areas as very high flash flood-susceptible zones, respectively | - | [36] |
| Central Eastern region, Egypt | Extreme gradient boost (XGBoost) and k-nearest neighbor (KNN) | XGBoost (AUC = 90.2%) exhibited higher prediction accuracy than KNN (AUC = 80.7%) | Applying different optimization techniques can improve model performance | [37] |
| Yunnan, China | Least square support vector machine (LSSVM) and logistic regression (LR) | The prediction accuracy of LSSVM (0.79) was higher than and LR (0.75). A total of 32% of the areas were classified as high flash flood-risk areas. The AUC for LSSVM = 0.8 and LR = 0.78 | These methods are data driven and lack the mechanisms causing the flash flood risk in the area | [38] |
| Yunnan, China | Extreme gradient boost (XGBoost) | Flash flood risk predictions were conducted. The prediction accuracy was 0.84. The high- and highest-risk areas were 40.3% | Long-term flash flood data should be considered in future studies | [39] |
| Longnan County, China | Multilayer perceptron (MLP), logistic regression (LR), support vector machine (SVM, and random forest (RF) | The MLP (AUC = 0.97) and FR (AUC = 0.97) techniques accurately predicted flash flood vulnerability areas compared to the SVM (AUC = 0.96) and LR (AUC = 0.88) | Differences in prediction performance may be due to the differences in the weights of the input variables | [40] |
| Jiangxi, China | Support vector machine (SVM), k-nearest neighbor (KNN), random forest (RF), and logistic Regression (LR) | The prediction accuracy was higher in RF (84.1%) than the SVM (73.1%), KNN (72.8), and LR (70.3%). AUC values were 0.89, 0.78, 0.78, and 0.76, respectively. High-risk zones were 55.1% | Lack of high-resolution spatiotemporal data could affect the reliability of the results | [41] |
| Haraz, Iran | Deep believed network (DBN), logistic regression (LR), naïve Bayes tree (NBT), reduced error pruning tree (REPT), logistic model tree (LMT), Bayesian logistic regression (BLR), alternating decision tree (ADT) | The prediction accuracy according to the AUC was higher in DBN (0.98) than LR (0.88), NBT (0.97), REPT (0.81), LMT (0.93), BLR (0.93), and ADT (0.97) | - | [42] |
| Islands of Rhodes, Greece | Random forest (RF), artificial neural network (ANN) | The flash flood prediction accuracy and the AUC was 84% and 0.87 for RF and 81% and 0.77 for the ANN | - | [43] |
| Northern regions, UAE | Boosted regression tree (BRT), classification and regression tree (CART), and naïve Bayes tree (NBT) | The AUC shows that BRT (0.92) achieved a higher flash flood prediction accuracy than CART (0.90) and NBT (0.79). About 19.3% of the areas were considered very high flood-prone areas | High-resolution remote sensing data could improve future flash flood risk predictions | [44] |
| Tetouan, Morroco | Artificial neural network (ANN), support vector machine (SVM), and random forest (RF) | Flash flood susceptibility was accurately predicted by RF (AUC = 0.99), the ANN (AUC = 0.98), and the SVM (AUC = 0.97) | - | [45] |
| Markazi, Iran | Boosted regression tree (BRT), parallel random forest (PRF), random Forest (RF), regularized random forest (RRF), extremely randomized tree (ERT) | AUC values were higher in ERT (0.82) compared to RRF (0.8), PRF (0.79), RF (0.78), and BRT (0.75). The model found 28.3% of the area to be highly susceptible to flash floods | - | [46] |
| Basca Chiojdului, Romania | Deep learning neural network frequency ratio (DLNN-FR), deep learning neural network weights of evidence (DLNN-WOE), alternating decision tree (ADT-FR), and alternating decision tree (ADT-WOE) | The prediction accuracy based on AUC values was higher in DLNN-WOE (0.92) than in DLNN-FR (0.90), ADT-WOE (0.89), and ADT-FR (0.87). Nearly 59.4% of the areas were classified as having a very high flash flood susceptibility | - | [47] |
| Zabala, Romania | Weights of evidence (WOEs), logistic regression (LR), classification and regression tree (CART), and radial basis function neural network–WOE (RBFN-WOE) | LR predictions were the most accurate (AUC = 0.92), whereas all the remaining models performed equally well, with an AUC > 0.85. A total of 55% of the areas fall within the high–very high susceptible zones | - | [48] |
| Southeast region, United States | Random forest (RF) | The RF approach accurately predicted damaged regions due to flash floods with 81% accuracy. The AUC = 0.87 | Additional watershed predictor variables could improve future predictions | [49] |
| Alabama, United States | Random forest (RF), extreme gradient boost (XGBoost), adaptive boosting (Adaboost), extra tree (ET) | About 9.35% of the area was classified as high risk. The overall prediction precision was RF = 0.975, XGBoost = 0.976, Adaboost = 0.974, and ET = 0.975. Also, AUC values were RF = 0.845, XGBoost = 0.842, Adaboost = 0.790, and ET = 0.834 | - | [50] |
| Hanoi, Vietnam | Deep learning neural network (DL), correlation-based feature weighted naïve Bayes (CFWNB), and correlation based feature weighted Adaboost (CFWNB-AB) | DL (AUC = 0.97) better predicted hilly terrain flash flood susceptibility than CFWNB and CFWNB-AB, which both had an AUC > 0.8. About 38.1% of the areas were classified as very highly susceptible zones | There was a lack of time series rainfall data for the analysis, and new ensemble ML models could enhance model performance in the future | [51] |
| Bac Ha, Bao Yen, Vietnam | Support vector machine (SVM), backpropagation artificial neural network (BPANN), classification tree (CTree) | Performance for flash flood susceptivity according to the AUC value was 0.96. A total of 10% of the areas were described as very high and high risk according to the MARS-PSO model | - | [52] |
| Tran Yen, Vietnam | Support vector machine (SVM), classification and regression tree (CART), logistic regression (LR), best first tree (BFTree) | The performance of these AI methods according to AUC values are SVM = 0.93, CART = 0.81, LR = 0.90, and BFTree = 0.88. The susceptibility areas were classified as very high (5%) and high (5%) | - | [53] |
4.1.3. Flash Flood Susceptibility Indicators and Influential Factors
| Location | Susceptibility Variables | Influential Factors | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tunisia | Elevation slope, drainage density, land use, soil type, lithology, rainfall | Land use, such as increasing urbanization, affects drainage systems | [32] |
| Iran | The topographic wetness index, altitude, plan curvature, proximity to roads, slope aspect, elevation, slope, land use, lithology, rainfall | Low elevation and gentle slopes have a strong association with flood events | [33] |
| Iran | Elevation, soil type, distance from rivers, slope aspect, slope, land use, lithology, rainfall | Land use features (residential areas, orchards) strongly influence flood occurrence | [34] |
| Iran | The topographic wetness index, the topography position index, the terrain ruggedness index, the convergence index, drainage density, the NDVI, soil type, distance to streams, altitude, plan curvature, land use, elevation, slope, land use, lithology, rainfall | Elevation, distance to streams, and greenery (NDVI) have a stronger impact on floods | [35] |
| Egypt | The topographic wetness index, flow accumulation, the sediment transport index, the NDVI, vertical flow distance, aspect, altitude, plan curvature, land use, elevation, slope, land use, lithology, rainfall | Land use, such as coastal areas, is prone to floods | [36] |
| Egypt | The topographic wetness index, distance from stream, stream density, plan curvature, elevation, slope aspect, slope, lithology | Elevation, slope, and stream density are the most influential floods to flood events | [37] |
| China | The topographic wetness index, rainfall, digital elevation model, slope, river density, vegetation coverage, curve number, soil moisture, population, gross domestic product, flash flood prevention efforts | Flat terrain, low elevation, mountainous streams, and population are risk factors for flood susceptibility | [39] |
| China | Elevation, slope, aspect, lithology, the NDVI, plan curvature, profile curvature, the topographic wetness index, surface radiation, gully density, rainfall, highway density, population density, the MNDWI | Elevation, gully density, and population density are the main contributors to floods | [40] |
| China | Slope, elevation, shape factor, concentration gradient, the topographic wetness index, the NDVI, distance to rivers, rainfall, peak discharge per unit area, and time of concentration | River distribution is associated with flood occurrence | [41] |
| Iran | Slope angle, elevation, curvature, rainfall, the topographic wetness index, distance to rivers, the NDVI, land use, river density, lithology, the sediment power index | Distance to rivers and river density are the major contributors to flood occurrence | [42] |
| Greece | Slope angle, elevation, aspect, curvature, land use, soil type, plan curvature, profile curvature, rainfall, the topographic wetness index, distance to rivers, the sediment transport index, sediment power index, lithology | Lithology, land use, slope, elevation, and the topographic wetness index were the main predictors of floods | [43] |
| UAE | Slope, altitude, land use, plan curvature, relief, distance to streams, stream density, lithology | Land use, such as mountainous areas and wider plains, has an elevated risk of floods | [44] |
| Morrocco | Elevation, aspect, slope, land use, the stream power index, plan curvature, profile curvature, the topographic power index, the topographic wetness index | Not given | [45] |
| Iran | Altitude, slope, aspect, plan curvature, profile curvature, distance to rivers, distance from roads, land use, lithology, soil type, rainfall, the topographic power index, the topographic wetness index | Altitude, rainfall, and distance to the river are the main predictors of flood occurrence | [46] |
| Romania | Slope, the topographic power index, the topographic wetness index, land use, profile curvature, lithology, the aspect, convergence index, the sediment power index, hydrological soil group | Slope angle and land use are the predictors of flood occurrence | [47] |
| Romania | Slope, rainfall, land use, hydrological soil group, lithology, plan curvature, profile curvature, the convergence index, aspect, the topographic wetness index, the modified Fournier index | Not given | [48] |
| United States | Population, home value, household composition and disability, intensity, slope, duration, latitude, longitude, onset time, month | Not given | [49] |
| United States | Elevation, slope, aspect, plan curvature, profile curvature, drainage density, distance to streams, curve number, rainfall, the NDVI, the sediment transport index, the topographic roughness index, the topographic wetness index, the stream power index | Curve number, the NDVI, slope, and drainage are the main factors influencing flood occurrence | [50] |
| Vietnam | Elevation, elevation difference, slope, aspect, curvature, the topographic wetness index, the sediment power index, drainage density, land use, geomorphology, structural zone, lithology, weathering crust, rainfall | Hilly areas are at an elevated risk of floods | [51] |
| Vietnam | Elevation, slope, curvature, toposhade, the topographic wetness index, the stream power index, stream density, the NDVI, soil type, lithology, and rainfall | Not given | [52] |
| Vietnam | Slope, aspect, curvature, elevation, the topographic wetness index, land use, river density, soil type, lithology, rainfall | Slope, land use, curvature, the and topographic wetness index are the most influential factors of flood occurrence | [53] |
4.2. Internet of Things (IoT)
| Location | Activity | Composition | The Study Outcome | Challenges | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Early Warning Alert | Water Senser Flows, Rain Gauge Senser, Long-Range Radio (LoRa), Subscriber Identity Module (SIM), Warning System, Monitoring System, App | Communities living within mountain areas were able to receive continuous flash flood early warning notifications via short message service (SMS) through long-range (LoRa) systems due to internet issues in mountainous areas | Fluctuations in steeper slopes and water levels make it challenging for the IoT system to read and provide outputs | [57] |
| São Carlos, Brazil | Fault Tolerance Predictions | SENDI (System for dEtecting and Forecasting Natural Disasters Based on the IoT), ns-3 Simulator | The overall accuracy of flash flood alerts of the system exceeded 65%, with 80% for red and 61% for yellow alerts. A high degree of accuracy was achieved, even under unfavorable conditions | The performance of the technology needs to be tested under system failure and ensure readings from several nodes | [58] |
| Maryland, United States | Flood Prediction | Gen1 On-Prem IoT: 3G Network Protocol, Flood Level Sensor. Linus, Apache, MySQL, Hypertext Preprocessor (PHP), Just Another Virtual Processor (JAVA), Email Trigger | The system had high reliability and availability. However, it showed low performance. It successfully deployed information despite internet problems | There were challenges in supporting multiple users | [59] |
| Johor Bahru, Malaysia | Early Warning Alert | Arduino Microcontroller, Raspberry Pi, Database Server, Web Server, Smartphone | The system enabled users to receive real-time flash flood status (whether it will occur or not) and alerts | - | [60] |
| Kigali, Rwanda | Early Warning Alert | Distance Measurement Ultrasonic Sensor, Rain Sensor, Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT), Arduino Microcontroller, ThingsSpeak, WiFi | The system was able to effectively transmit flash flood alert messages (containing flash flood alert type and the state of the flash flood) to users | Future studies could integrate cameras and drones to improve monitoring | [61] |
| India | Early Warning Alert | IoT Sensors, Drainage Data, Flood Data | The system offered real-time information to users. The process was able to continue until the flash flood came under control | The current system can be coupled with ML in the future | [62] |
| Uttarakhand, India | Early Warning Alert | Arduino Microcontroller, Mobile Phone, IoT Cloud, Water Flow Sensor, Distance Measurement Ultrasonic Sensor | The system was able to effectively transmit real-time flash flood alert messages | The current system can be integrated with remote sensing and geographical information systems to improve its performance | [27] |
| Uttarakhand, India | Early Warning Alert | Arduino Microcontroller, Mobile phone, Android App, Google Cloud, Water Flow Sensor, Distance Measurement Ultrasonic Sensor | Users were able to effectively receive real-time flash flood alert messages through mobile applications and updated alerts every 5 min | The current system can be integrated with remote sensing and geographical information systems | [63] |
| Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia | Early Warning Alert | TensorFlow, Raspberry Pi, Telegram Channel, Camera, SDDMobileNetV1 | The system successfully provided flash flood alerts on flash flood levels and normal levels via the Telegram Channel | - | [64] |
| Melaka, Malaysia | Flood Prediction, Early Warning Alert | Raspberry Pi, Synology Network Access Storage, Modem, Web Server, Android Mobile Phone, Web Browser (e.g., Google Chrome) | The system effectively predicts (e.g., lighting locations, rainfall levels, and locations of flash floods) and generates flash flood alert messages to the residents through mobile phone applications | - | [65] |
4.3. Cloud Computing
| Location | Activity | Composition | The Study Outcome | Challenges | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maryland, United States | Early Warning Alert | Cloud, 3G, Central Processing Unit (CPU), Water Level Ultrasonic Sensors, Solar Panels, Application Programming Interphase (API) | The system could transmit flash flood status, including images, through social media platforms, such as Twitter | Data loss issues and poor cloud connectivity. Integration of computer vision could help in the future | [59] |
| Texas, United States | Flash Flood Prediction | Research Distributed Hydrological Model (RDHM), Cloud, GeoJSON, GIS, and Google Maps | The RDHM in the cloud computer system could show flash flood status online to local emergency response managers and issue alerts through mobile apps | - | [70] |
| Bangladesh | Early Warning Alert | Cloud Servers (e.g., CloudSim), Gradient Servers Communications, Water Level, Ultrasonic Sensors | The system was able to issue flash flood early warnings by mimicking water levels of river banks during rainfall | The system was unable to read water levels due to sediments. A lack of cloud centers across the country was a major concern | [71] |
4.4. Robotics
4.5. Other Innovative Flash Flood Warning Technologies (Storm Cell Identification, Video-Based Surveillance, Interactive Voice Response, Digital Image Analysis)
| Location | Technology | Performance Levels | Challenges | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catalonia, Spain | Storm Cell Identification and Tracking Algorithm (SCIT) | Improved the current flash flood forecasting systems by including different precipitation thresholds. Was able to identify topography as a triggering factor | It can be enhanced by including the role of the ocean (e.g., melting of ice particles in the rain) | [79] |
| Manado, Indonesia | Video-Based Surveillance System (VSS) | The system can provide surveillance on water levels and has the potential to activate social media networks for public consumption | - | [80] |
| Sunamganj, Bangladesh | SMS, Interactive Voice Response (IVR), Cell Broadcasting Service (CBS) | SMS and IVR were suitable for the dissemination of flash flood forecasting due to ease of understanding and accessibility | The system can be enhanced by incorporating mixing push- and pull-based telecommunication services | [81] |
| Indonesia | Digital Image Analysis | Data on water levels were successfully integrated with a computer server and shared via Android phones for public consumption | The application was interrupted by an internet disconnection issue, especially during data transfer | [82] |
| Laos, Thailand | International River Cooperative (iRIC) Software | The iRIC showed satisfactory performance in estimating flash flood disasters for both gauged and ungauged basins | Requires an accurate digital elevation model (DEM) to ensure successful forecasting | [83] |
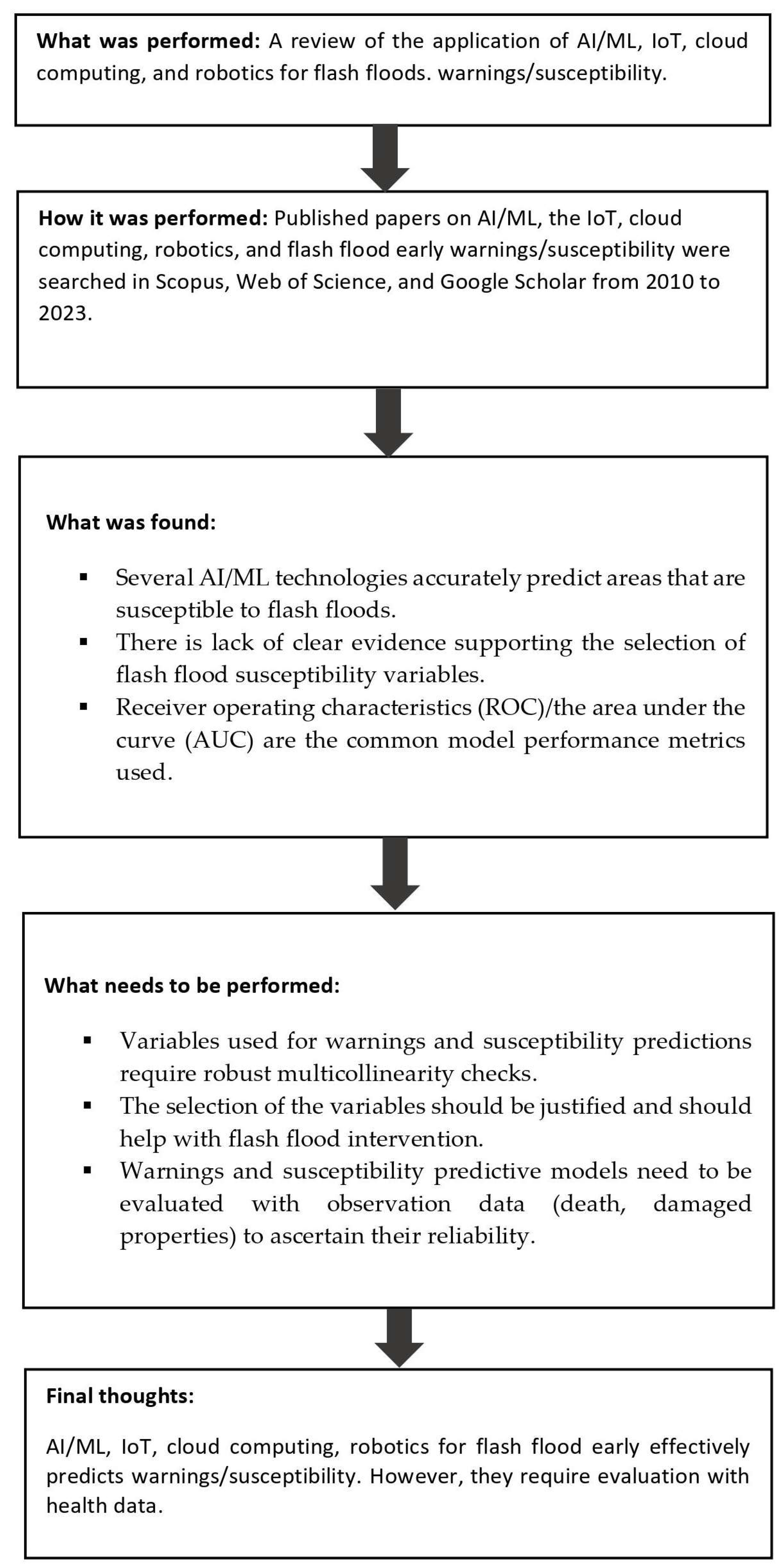
5. Discussion
6. Summary of the Main Findings, Limitations, and Future Perspectives
- (I)
- Current technologies, especially AI/ML, the IoT, and cloud computing, can successfully issue flash flood early warnings in real time. However, this approach has challenges with false alarms, internet connectivity issues, and data loss problems. Therefore, future research should include aerial robotics and computer vision to improve their performance.
- (II)
- The current AI/ML methods require optimization techniques to improve their current prediction performance.
- (III)
- Random forest and the support vector machine were the most accurate AI/ML methods. However, these algorithms could be integrated with other technologies, such as computer vision, to help enhance their capabilities.
- (IV)
- The current AI/ML utilizes a wide range of topographical, geological, and hydrological variables. Future studies should include sociodemographic, health, and housing data variables to help generate more realistic flood susceptibility maps.
- (V)
- There are inconsistencies and limited information regarding the rationale for selecting the susceptibility variables, and there is potential multicollinearity among the variables.
- (VI)
- The current flash flood susceptibility prediction models have not been evaluated with health data (flash flood-related death cases) to test their reliability in predicting vulnerable flood-prone areas.
- (VII)
- Future AL/ML-based flash flood prediction studies should project susceptibility maps or early warnings under different climate change scenarios.
- (VIII)
- Quantifying flash flood-associated deaths, morbidity, and healthcare costs among susceptible communities could improve future research.
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WEF. What Is a Flash Flood? A Civil Engineer Explains. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2022/08/what-is-a-flash-flood-a-civil-engineer-explains/ (accessed on 20 November 2023).
- Yang, Z.; Huang, W.; McKenzie, J.E.; Xu, R.; Yu, P.; Ye, T.; Wen, B.; Gasparrini, A.; Armstrong, B.; Tong, S.; et al. Mortality risks associated with floods in 761 communities worldwide: Time series study. BMJ 2023, 383, e075081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafizur Rahman, M.; Alam Shobuj, I.; Tanvir Hossain, M.; Tasnim, F. Impact of Disaster on mental health of women: A case study on 2022 flash flood in Bangladesh. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2023, 96, 103935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basahi, J.M.; Masoud, M.H.Z.; Rajmohan, N. Effect of flash flood on trace metal pollution in the groundwater—Wadi Baysh Basin, western Saudi Arabia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 147, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, T.R.; Er, A.C.; Muhamad, N.; Pereira, J.J. The socioeconomic impact of climate-related hazards: Flash flood impact assessment in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Nat. Hazards 2021, 109, 1509–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gourbesville, P.; Liu, C. Flash Floods: Forecasting, Monitoring and Mitigation Strategies. Water 2023, 15, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudashiru, R.B.; Sabtu, N.; Abustan, I.; Balogun, W. Flood hazard mapping methods: A review. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Chowdhury, P. Local-scale Flash Flood Susceptibility Assessment in Northeastern Bangladesh using Machine Learning Algorithms. Environ. Chall. 2024, 14, 100833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloke, H.L.; Pappenberger, F. Ensemble flood forecasting: A review. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agonafir, C.; Lakhankar, T.; Khanbilvardi, R.; Krakauer, N.; Radell, D.; Devineni, N. A review of recent advances in urban flood research. Water Secur. 2023, 19, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, D.K.; Gernowo, R.; Nirwansyah, A.W. Flood prediction with time series data mining: Systematic review. Nat. Hazards Res. 2024, 4, 194–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, U.; Perez, P.; Li, W.; Barthelemy, J. How computer vision can facilitate flood management: A systematic review. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 53, 102030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zounemat-Kermani, M.; Batelaan, O.; Fadaee, M.; Hinkelmann, R. Ensemble machine learning paradigms in hydrology: A review. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnasiri, P.; Adeniyi, O.; Thurairajah, N. Data-driven approaches to built environment flood resilience: A scientometric and critical review. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2023, 57, 102085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, C.H.; Lee, C.H.; Ban, Y.U. Analysis of the impact and moderating effect of high-density development on urban flooding. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munawar, H.S.; Hammad, A.W.A.; Waller, S.T. A review on flood management technologies related to image processing and machine learning. Autom. Constr. 2021, 132, 103916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavic, M.S.; Lanzafame, R.J. Artificial Intelligence and Scientific Publication. Jsls 2024, 28, e2024.00006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakhaei, M.; Nakhaei, P.; Gheibi, M.; Chahkandi, B.; Wacławek, S.; Behzadian, K.; Chen, A.S.; Campos, L.C. Enhancing community resilience in arid regions: A smart framework for flash flood risk assessment. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 153, 110457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasali, F.; Tawalbeh, R.; Ghanem, Z.; Mohammad, F.; Alghazzawi, M. A Sustainable Early Warning System Using Rolling Forecasts Based on ANN and Golden Ratio Optimization Methods to Accurately Predict Real-Time Water Levels and Flash Flood. Sensors 2021, 21, 4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yin, H.; Yu, G.; Chen, F.; Jin, J.; Yan, J. Urban flash flood forecast using support vector machine and numerical simulation. J. Hydroinform. 2018, 20, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windarto, J. Flood Early Warning System Develop at Garang River Semarang using Information Technology base on SMS and Web. Int. J. Geomat. Geosci. 2010, 1, 14–28. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, J.T.d.; Salistre, G.M.; Byun, Y.-C.; Gerardo, B.D. Flash Flood Prediction Model based on Multiple Regression Analysis for Decision Support System. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science, San Francisco, CA, USA, 23–25 October 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, T.A.; Alam, M.; Shahid, Z.; Suud, M.M. Prior Investigation for Flash Floods and Hurricanes, Concise Capsulization of Hydrological Technologies and Instrumentation: A survey. In Proceedings of the IEEE 3rd International Conference on Engineering Technologies and Social Sciences (ICETSS), Bangkok, Thailand, 7–8 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, G.R.T.d.; Scofield, G.B. Feasibility study on operational use of neural networks in a flash flood early warning system. Rbrh 2021, 26, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, R.; Yang, M.; Tu, T.; Ma, M.; Hong, Y.; Wang, X. Large-scale flash flood warning in China using deep learning. J. Hydrol. 2022, 604, 127222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancona, M.; Corradi, N.; Dellacasa, A.; Delzanno, G.; Dugelay, J.L.; Federici, B.; Gourbesville, P.; Guerrini, G.; La Camera, A.; Rosso, P.; et al. On the Design of an Intelligent Sensor Network for Flash Flood Monitoring, Diagnosis and Management in Urban Areas Position Paper. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 32, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, C.; Barthwal, A.; Acharya, D. FLOODALERT: An internet of things based real-time flash flood tracking and prediction system. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 43701–43727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y. A WRF/WRF-Hydro Coupled Forecasting System with Real-Time Precipitation–Runoff Updating Based on 3Dvar Data Assimilation and Deep Learning. Water 2023, 15, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, K.H.; O’Malley, A.J.; Mauri, L. Receiver-Operating Characteristic Analysis for Evaluating Diagnostic Tests and Predictive Models. Circulation 2007, 115, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towfiqul Islam, A.R.M.; Talukdar, S.; Mahato, S.; Kundu, S.; Eibek, K.U.; Pham, Q.B.; Kuriqi, A.; Linh, N.T.T. Flood susceptibility modelling using advanced ensemble machine learning models. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, K.; Pham, B.T.; Chapi, K.; Shirzadi, A.; Shahabi, H.; Revhaug, I.; Prakash, I.; Tien Bui, D. A comparative assessment of decision trees algorithms for flash flood susceptibility modeling at Haraz watershed, northern Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahri, N.; Yousfi, R.; Bouamrane, A.; Abida, H.; Pham, Q.B.; Derdous, O. Comparison of analytic network process and artificial neural network models for flash flood susceptibility assessment. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2022, 193, 127222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, M.; Jaafari, A.; Shirzadi, A.; Shahabi, H.; Rahmati, O.; Omidvar, E.; Lee, S.; Bui, D.T. Deep learning neural networks for spatially explicit prediction of flash flood probability. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janizadeh, S.; Avand, M.; Jaafari, A.; Phong, T.V.; Bayat, M.; Ahmadisharaf, E.; Prakash, I.; Pham, B.T.; Lee, S. Prediction Success of Machine Learning Methods for Flash Flood Susceptibility Mapping in the Tafresh Watershed, Iran. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabameri, A.; Saha, S.; Chen, W.; Roy, J.; Pradhan, B.; Bui, D.T. Flash flood susceptibility modelling using functional tree and hybrid ensemble techniques. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 125007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, M.; Boulmaiz, T.; Guermoui, M.; Abdrabo, K.I.; Kantoush, S.A.; Sumi, T.; Boutaghane, H.; Nohara, D.; Mabrouk, E. Examining LightGBM and CatBoost models for wadi flash flood susceptibility prediction. Geocarto Int. 2021, 37, 7462–7487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Magd, S.A.A.; Pradhan, B.; Alamri, A. Machine learning algorithm for flash flood prediction mapping in Wadi El-Laqeita and surroundings, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wang, H.; Jia, P.; Tang, G.; Wang, D.; Ma, Z.; Yan, H. Application of the GPM-IMERG Products in Flash Flood Warning: A Case Study in Yunnan, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zhao, G.; He, B.; Li, Q.; Dong, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z. XGBoost-based method for flash flood risk assessment. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, K.; Zeng, S.; Hong, A. Modeling rules of regional flash flood susceptibility prediction using different machine learning models. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1117004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, T. Flash flood susceptibility mapping based on catchments using an improved Blending machine learning approach. Hydrol. Res. 2023, 54, 557–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabi, H.; Shirzadi, A.; Ronoud, S.; Asadi, S.; Pham, B.T.; Mansouripour, F.; Geertsema, M.; Clague, J.J.; Bui, D.T. Flash flood susceptibility mapping using a novel deep learning model based on deep belief network, back propagation and genetic algorithm. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilia, I.; Tsangaratos, P.; Tzampoglou, P.; Chen, W.; Hong, H. Flash flood susceptibility mapping using stacking ensemble machine learning models. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 15010–15036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmahdy, S.; Ali, T.; Mohamed, M. Flash Flood Susceptibility Modeling and Magnitude Index Using Machine Learning and Geohydrological Models: A Modified Hybrid Approach. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, E.M.; Maanan, M.; Rhinane, H. Performance of Machine Learning Algorithms for Mapping and Forecasting of Flash Flood Susceptibility in Tetouan, Morocco. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 46, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Band, S.S.; Janizadeh, S.; Chandra Pal, S.; Saha, A.; Chakrabortty, R.; Melesse, A.M.; Mosavi, A. Flash Flood Susceptibility Modeling Using New Approaches of Hybrid and Ensemble Tree-Based Machine Learning Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costache, R.; Arabameri, A.; Blaschke, T.; Pham, Q.B.; Pham, B.T.; Pandey, M.; Arora, A.; Linh, N.T.T.; Costache, I. Flash-Flood Potential Mapping Using Deep Learning, Alternating Decision Trees and Data Provided by Remote Sensing Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costache, R.; Pham, Q.B.; Arabameri, A.; Diaconu, D.C.; Costache, I.; Crăciun, A.; Ciobotaru, N.; Pandey, M.; Arora, A.; Ali, S.A.; et al. Flash-flood propagation susceptibility estimation using weights of evidence and their novel ensembles with multicriteria decision making and machine learning. Geocarto Int. 2021, 37, 8361–8393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, A.; Ahmadalipour, A.; Abbaszadeh, P.; Moradkhani, H. Leveraging machine learning for predicting flash flood damage in the Southeast US. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 024011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmekcioğlu, Ö.; Koc, K.; Özger, M.; Işık, Z. Exploring the additional value of class imbalance distributions on interpretable flash flood susceptibility prediction in the Black Warrior River basin, Alabama, United States. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi Thanh Ngo, H.; Duc Dam, N.; Thi Bui, Q.-A.; Al-Ansari, N.; Costache, R.; Ha, H.; Duy Bui, Q.; Hung Mai, S.; Prakash, I.; Thai Pham, B. Prediction of Flash Flood Susceptibility of Hilly Terrain Using Deep Neural Network: A Case Study of Vietnam. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2023, 135, 2219–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, D.T.; Ngo, P.-T.T.; Pham, T.D.; Jaafari, A.; Minh, N.Q.; Hoa, P.V.; Samui, P. A novel hybrid approach based on a swarm intelligence optimized extreme learning machine for flash flood susceptibility mapping. Catena 2019, 179, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, P.-T.T.; Pham, T.D.; Nhu, V.-H.; Le, T.T.; Tran, D.A.; Phan, D.C.; Hoa, P.V.; Amaro-Mellado, J.L.; Bui, D.T. A novel hybrid quantum-PSO and credal decision tree ensemble for tropical cyclone induced flash flood susceptibility mapping with geospatial data. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 125682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaduvula, K.; Kranthi kumar, K.; Markapudi, B.R.; Rathna Jyothi, C. Design and Implementation of IoT based flood alert monitoring system using microcontroller 8051. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 80, 2840–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, O.; Zeadally, S. Toward efficient smartification of the Internet of Things (IoT) services. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 92, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binti Zahir, S.; Ehkan, P.; Sabapathy, T.; Jusoh, M.; Nasrun Osman, M.; Najib Yasin, M.; Abdul Wahab, Y.; Hambali, N.A.M.; Ali, N.; Bakhit, A.S.; et al. Smart IoT Flood Monitoring System. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1339, 012043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, W.-T.; Devi, I.V.; Hsiao, S.-J. Early warning of impending flash flood based on AIoT. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2022, 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furquim, G.; Filho, G.P.R.; Jalali, R.; Pessin, G.; Pazzi, R.W.; Ueyama, J. How to Improve Fault Tolerance in Disaster Predictions: A Case Study about Flash Floods Using IoT, ML and Real Data. Sensors 2018, 18, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basnyat, B.; Singh, N.; Roy, N.; Gangopadhyay, A. Design and Deployment of a Flash Flood Monitoring IoT: Challenges and Opportunities. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing (SMARTCOMP), Bologna, Italy, 14–17 September 2020; pp. 422–427. [Google Scholar]
- Wai, A.; Rohani, M.F.a.b. Flash Flood Management System Using IoT Technology. In UTM Computing Proceedings Innovation in Computing Technology and Applications; 2017; Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Flash-Flood-Management-System-Using-IoT-Technology-Wai/cd256a75dbf6df74ad55281e3ba6138f81c1dfa6 (accessed on 14 July 2024).
- Florentine, M.; Enan, N.; Louis, S. Flood Monitoring System in Rwanda Using Internet of Things. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Manag. 2023, 5, 956–965. Available online: https://ijaem.net/issue_dcp/Flood%20Monitoring%20System%20in%20Rwanda%20Using%20Internet%20of%20Things.pdf (accessed on 14 July 2024).
- Goyal, H.R.; Ghanshala, K.K.; Sharma, S. Flash flood risk management modeling in indian cities using IoT based reinforcement learning. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 10533–10538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, C.; Barthwal, A.; Acharya, D. FLOODWALL: A Real-Time Flash Flood Monitoring and Forecasting System Using IoT. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.A.; Ariffin, M.A.M.; Kasiran, Z. IoT-Based Flash Flood Detection and Alert Using TensorFlow. In Proceedings of the 2021 11th IEEE International Conference on Control System, Computing and Engineering (ICCSCE), Penang, Malaysia, 27–28 August 2021; pp. 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Nahar, H.; Bahaman, N.; Shah, W.M.; Abdul-Aziz, A.; Khalid, A.M.; Hassan, A.; Ahmad, M.R. Real-time Monitoring IoT-based System for Early Flash Flood Notification in Melaka. Multidiscip. Appl. Res. Innov. 2022, 4, 29–36. Available online: https://publisher.uthm.edu.my/periodicals/index.php/mari/article/view/9695 (accessed on 14 July 2024).
- Han, Y.; Mozumder, P. Risk-based flood adaptation assessment for large-scale buildings in coastal cities using cloud computing. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 76, 103415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, S.; Bhatia, S.; Al Harrasi, A.; Shah, Y.A.; Anwer, M.K.; Philip, A.K.; Shah, S.F.A.; Khan, A.; Ahsan Halim, S. Unraveling the role of cloud computing in health care system and biomedical sciences. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujjwal, K.C.; Saurabh, G.; James, H.; Jagannath, A.; Nicholas, F.-S. Cloud Computing in natural hazard modeling systems: Current research trends and future directions. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 38, 101188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, H.R.; Sharma, S. Flood Management System Using Cloud Computing and Internet-of-Things. In Proceedings of the 2023 5th Biennial International Conference on Nascent Technologies in Engineering (ICNTE), Navi Mumbai, India, 20–21 January 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lyons, E.; Seo, D.-J.; Kim, S.; Habibi, H.; Papadimitriou, G.; Tanaka, R.; Deelman, E.; Zink, M.; Mandal, A. Predicting Flash Floods in the Dallas-Fort Worth Metroplex Using Workflows and Cloud Computing. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 17th International Conference on eScience (eScience), Innsbruck, Austria, 20–23 September 2021; pp. 259–261. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, N.; Azad, A.K.; Habib, M.R.K.A.; Shahid, S.G.S. ShonaBondhu: A Cloud Based System to Handle Flash Flood. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Networking Systems and Security (NSysS), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 7–9 January 2016; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wilk-Jakubowski, G.; Harabin, R.; Ivanov, S. Robotics in crisis management: A review. Technol. Soc. 2022, 68, 101935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M. Robotics Applications in Natural Hazards. Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 43, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afridi, A.; Minallah, N.; Sami, I.; Allah, M.; Ali, Z.; Ullah, S. Flood Rescue Operations Using Artificially Intelligent UAVs. In Proceedings of the 2019 15th International Conference on Emerging Technologies (ICET), Peshawar, Pakistan, 2–3 December 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Asami, K.; Svinin, M. Toward Cooperative Multi-robot Control for Detecting and Tracking an Expanding Flood Area. In Proceedings of the 2019 12th International Conference on Developments in eSystems Engineering (DeSE), Kazan, Russia, 7–10 October 2019; pp. 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Pouransari, A.; Pouransari, H.; Inallou, M.M. Intelligent rescuer robot for detecting victims accurately in natural disasters. In Proceedings of the 2015 2nd International Conference on Knowledge-Based Engineering and Innovation (KBEI), Tehran, Iran, 5–6 November 2015; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Li, B.; Jiang, Y.; Wen, C.-Y. A Camera-Based Target Detection and Positioning UAV System for Search and Rescue (SAR) Purposes. Sensors 2016, 16, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedoro, S.J.B.; Angay, Q.E.L.; Rosado, A.C.; Salvaña, K.H.Z. Sumalongson: An Autonomous Arduino-based Flash Flood Early Warning Robot and Water Quality Indicator. Gold. Tara Res. J. 2018, 1. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/39825207/Sumalongson_An_Autonomous_Arduino_based_Flash_Flood_Early_Warning_Robot_and_Water_Quality_Indicator (accessed on 14 July 2024).
- del Moral, A.; Llasat, M.d.C.; Rigo, T. Connecting flash flood events with radar-derived convective storm characteristics on the northwestern Mediterranean coast: Knowing the present for better future scenarios adaptation. Atmos. Res. 2020, 238, 104863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosey, H.I.R.; Pandara, D.P.; Bobanto, M.D.; Sangian, H.S. A simple low-cost video-based surveillance system for a flash flood warning system. In Proceedings of the IORA-ICOR2018, Manado, Indonesia, 20–21 September 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Cumiskey, L.; Jerry Velasquez, D.; Werner, M.; Meijer, K.; Fakhruddin, S.H.M.; Hassan, A. Improving the social performance of flash flood early warnings using mobile services. Int. J. Disaster Resil. Built Environ. 2015, 6, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priantama, R.; Nugraha, N.; Darmawan, E. The Innovation Development of Early Flash Flood Warning System Based on Digital Image Processing through Android Smartphone. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1477, 032015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanit, W.; Weesakul, U. Application of Iric Software for Flash Flood Disaster Prediction in Laos and Thailand. In Proceedings of the 22nd IAHR-APD Congress, Sapporo, Japan, 14–17 September 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Debnath, J.; Sahariah, D.; Nath, N.; Saikia, A.; Lahon, D.; Islam, M.N.; Hashimoto, S.; Meraj, G.; Kumar, P.; Singh, S.K.; et al. Modelling on assessment of flood risk susceptibility at the Jia Bharali River basin in Eastern Himalayas by integrating multicollinearity tests and geospatial techniques. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2024, 10, 2393–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terti, G.; Ruin, I.; Anquetin, S.; Gourley, J.J. A Situation-Based Analysis of Flash Flood Fatalities in the United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkman, S.N.; Curran, A.; Bouwer, L.M. Floods have become less deadly: An analysis of global flood fatalities 1975–2022. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 6327–6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Tang, G.; Shi, P. An Improved Transfer Learning Model for Cyanobacterial Bloom Concentration Prediction. Water 2022, 14, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, F.; Di Nunno, F.; Modoni, G. Hybrid Machine Learning Models for Soil Saturated Conductivity Prediction. Water 2022, 14, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Mitra, R.; Das, J.; Mandal, D.K. Urban flash flood prediction modelling using probabilistic and statistical approaches. Results Earth Sci. 2024, 2, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, S.; Chen, M.; Gourley, J.J.; Liu, C.; Prein, A.F.; Hong, Y. The conterminous United States are projected to become more prone to flash floods in a high-end emissions scenario. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Lin, Q.; Luo, R. Projection of changes in flash flood occurrence under climate change at tourist attractions. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 126039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Ningsheng, C.; Mahmud, G.I.; Islam, M.M.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Ahmad, H.; Habumugisha, J.M.; Washakh, R.M.A.; Alam, M.; Liu, E.; et al. Flooding and its relationship with land cover change, population growth, and road density. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugianto, S.; Deli, A.; Miswar, E.; Rusdi, M.; Irham, M. The Effect of Land Use and Land Cover Changes on Flood Occurrence in Teunom Watershed, Aceh Jaya. Land 2022, 11, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.; Black, J.; Jones, M.; Wilson, L.; Salvador-Carulla, L.; Astell-Burt, T.; Black, D. Flooding and Mental Health: A Systematic Mapping Review. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
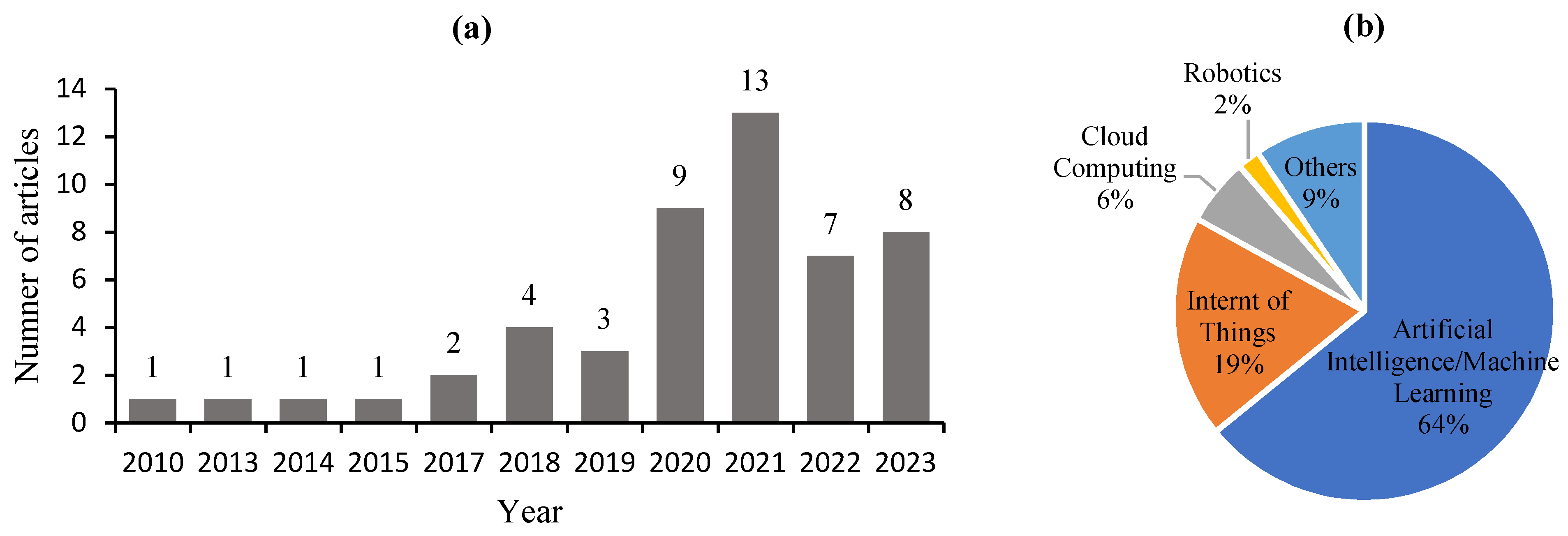
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Rawas, G.; Nikoo, M.R.; Al-Wardy, M.; Etri, T. A Critical Review of Emerging Technologies for Flash Flood Prediction: Examining Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Internet of Things, Cloud Computing, and Robotics Techniques. Water 2024, 16, 2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16142069
Al-Rawas G, Nikoo MR, Al-Wardy M, Etri T. A Critical Review of Emerging Technologies for Flash Flood Prediction: Examining Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Internet of Things, Cloud Computing, and Robotics Techniques. Water. 2024; 16(14):2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16142069
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Rawas, Ghazi, Mohammad Reza Nikoo, Malik Al-Wardy, and Talal Etri. 2024. "A Critical Review of Emerging Technologies for Flash Flood Prediction: Examining Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Internet of Things, Cloud Computing, and Robotics Techniques" Water 16, no. 14: 2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16142069
APA StyleAl-Rawas, G., Nikoo, M. R., Al-Wardy, M., & Etri, T. (2024). A Critical Review of Emerging Technologies for Flash Flood Prediction: Examining Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Internet of Things, Cloud Computing, and Robotics Techniques. Water, 16(14), 2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16142069








