Development-Ecological Protection Conflicts and Coordination at West Taijinel Salt Lake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of the West Taijinel Area
2.1. Geographical and Climatic Characteristics
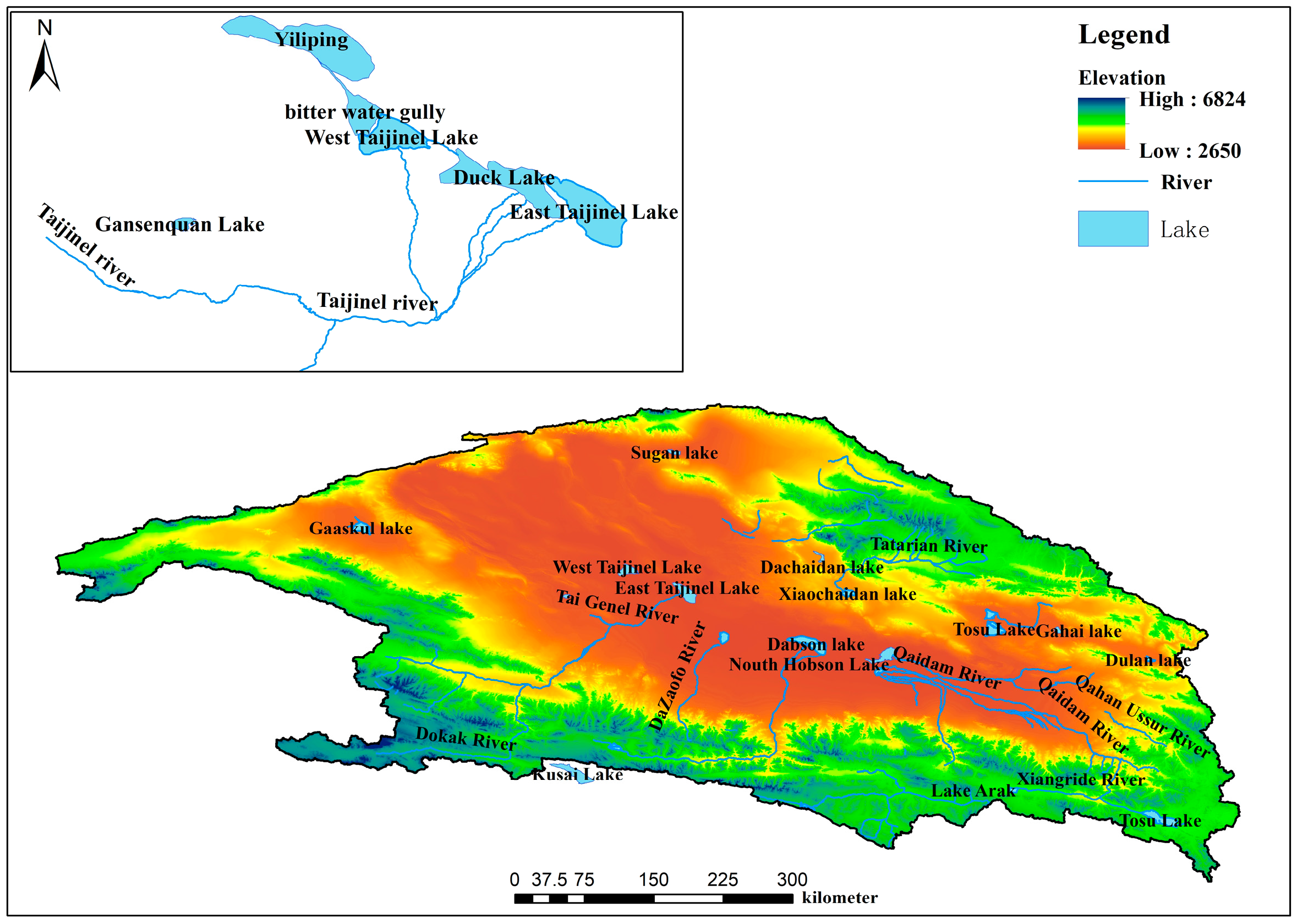
2.2. The Hydrological Systems around West Taijinel Lake
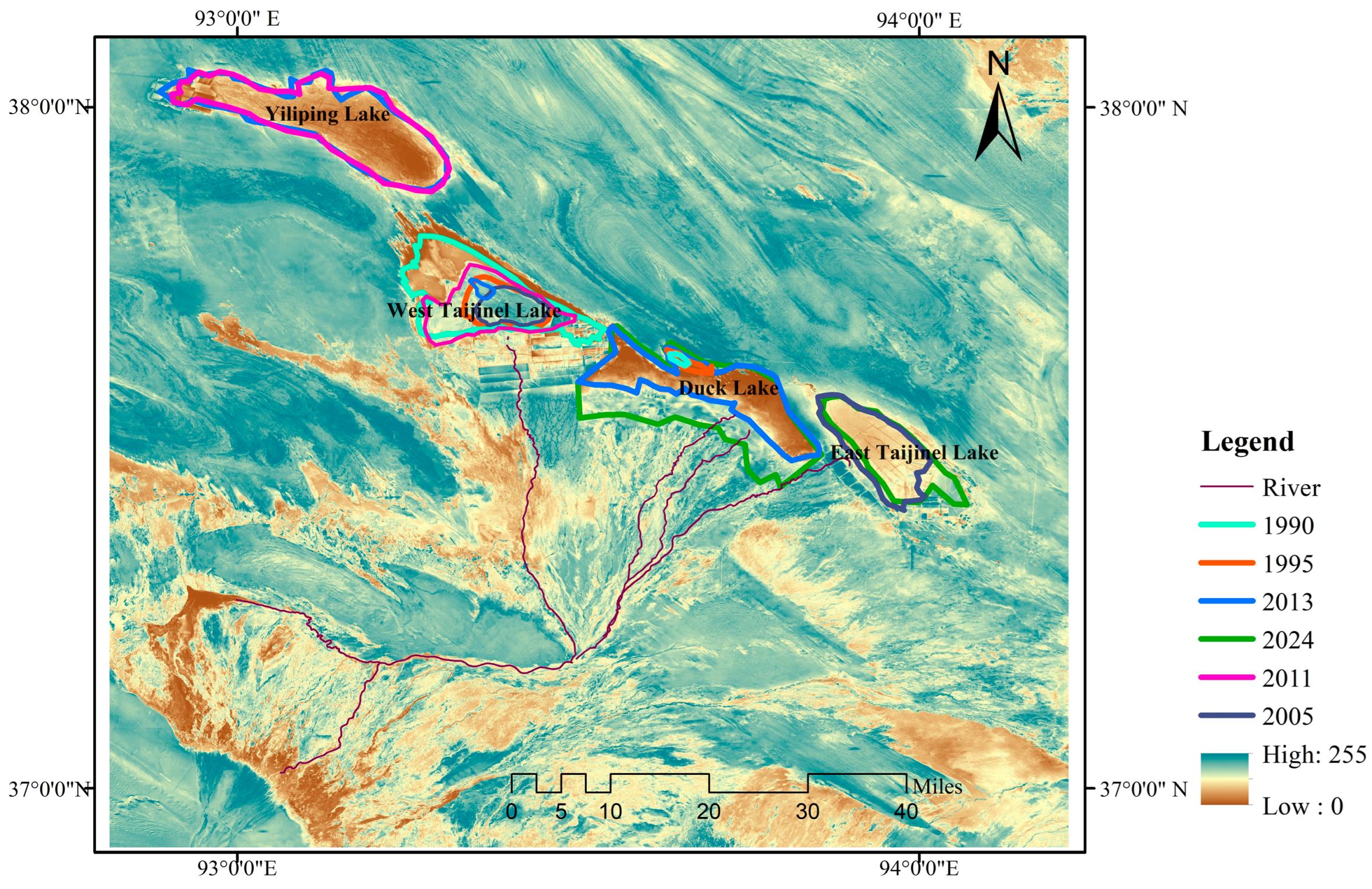
2.3. Ecosystems before and after Development
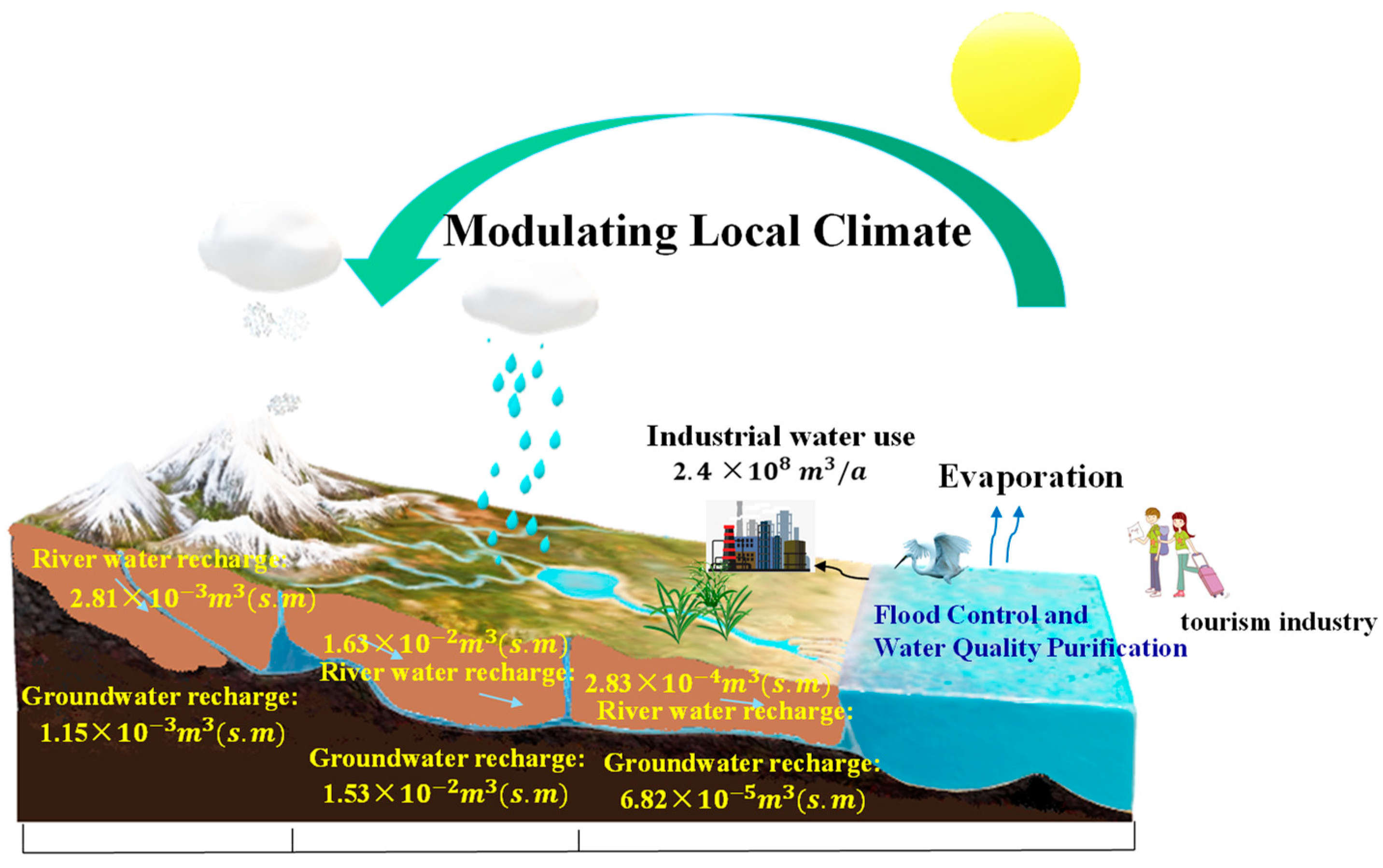
2.4. Brine Replenishment Processes
3. Conflict between Development and Ecological Protection of West Taijinel Lake
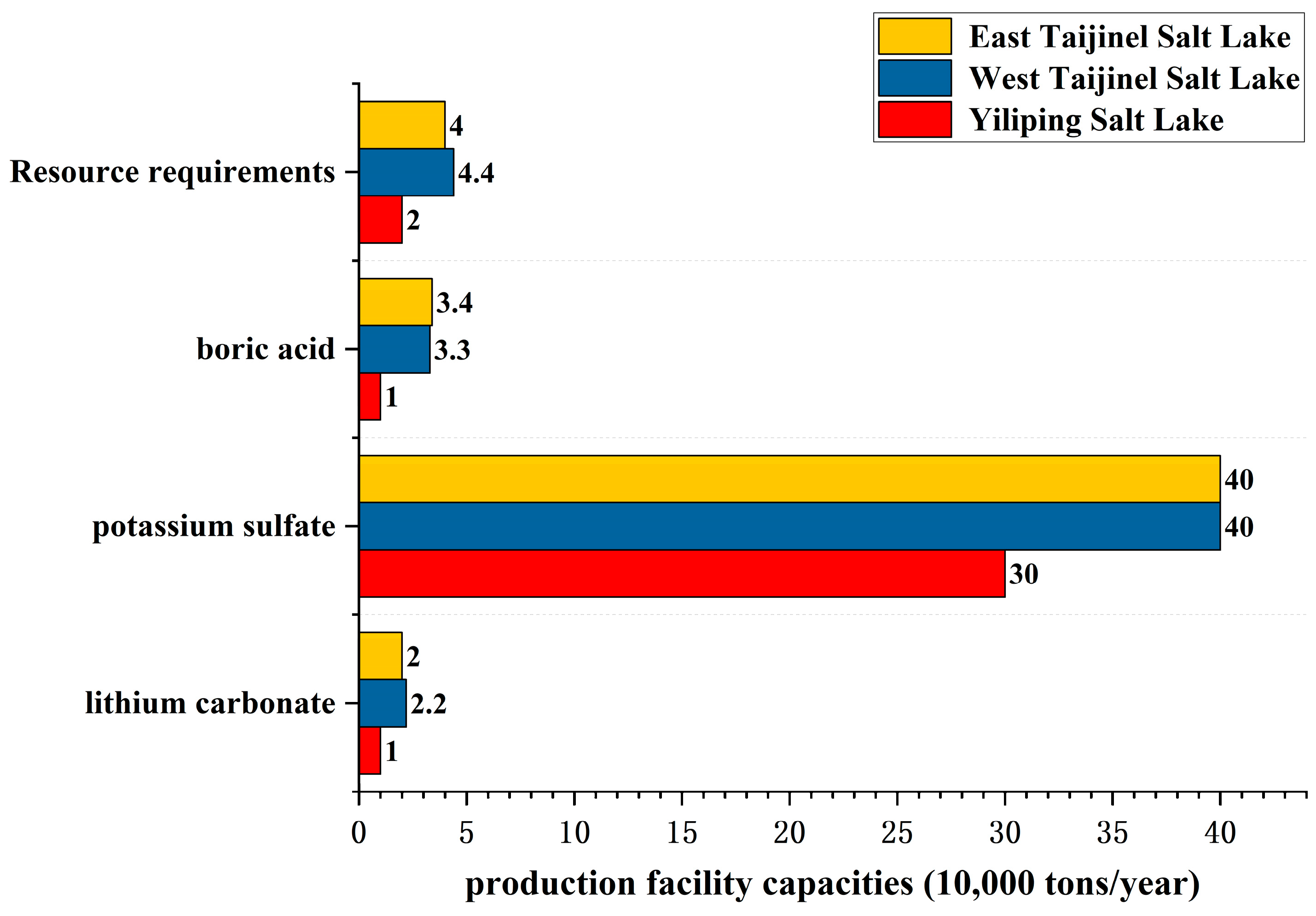
3.1. The Significance of Developing Salt Lake Resources
3.2. The Importance of Ecological Conservation
- Manage lake shorelines to preserve their natural shape;
- Permit and supervise water extraction for projects;
- Remove flood control dikes to restore ecological water flow and the water surface of West Taijinaier Lake;
- Ensure and require the correction of illegal encroachments on river and lake shorelines.
3.3. Conflict of Position between the Salt Lake as a Mineral and Mineral Development Area and the Protection of the Natural Lake State
3.3.1. Flood Control Measures May Conflict with Ecological Protection Efforts
3.3.2. An Abstraction License Be Sought for Flood Resources?
4. Mitigation Options
4.1. Defining the Functional Position of the Salt Lake Resource Development Zone
4.2. The Principles and Flexibility of Wetland Conservation
4.2.1. Flood Barrier Management
4.2.2. Flood Resources and Management
5. Conclusions and Future Perspective
5.1. Clarify the Positioning of Production Areas in Planned and Authorized Salt Lakes to Avoid Unreasonable Requirements for Maintaining the Lake Surface
5.2. Revision of the Regulations on the Development and Protection of Salt Lake in Qinghai Province
5.3. Implement a Three-Tier Integrated Approach to Develop a Comprehensive Ecological Data Platform
5.4. Coordinated Management
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MacDonald, G.K.; Noel, P.E.; Chmura, P.G.L. The legacy of agricultural reclamation on channel and pool networks of bay of fundy Salt Marshes. Estuaries Coasts 2010, 33, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrin, V.L.; Pratolongo, P.D.; Villalobos, A.E.D.; Botté, S.E.; Marcovecchio, J.E. Biomass, decomposition and nutrient cycling in a SW Atlantic Sarcocornia perennis marsh. J. Sea Res. 2015, 97, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desroches, M.B.; Lavoie, M.; Lavoie, C. Establishing the value of a salt marsh as a potential benchmark: Vegetation surveys and paleoecological analyses as assessment tools. Botany 2013, 91, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.J.; Allen, C.B.; Kelleway, J. Saltmarsh of the Parramatta River-Sydney Harbour: Determination of cover and species composition including comparison of API and pedestrian survey. Cunninghamia A J. Plant Ecol. East. Aust. 2011, 12, 29–43. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Gao, R.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xing, X.; Bai, Z.; Jia, L.; Yu, X. Diversity and evaluation of phytoplankton in salt marsh wetland of Ordos Plateau. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2009, 23, 143–148. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Liu, A.; Tie, N.; Gao, R.; Zhang, Q. Study on ecological environment characteristics of desert salina wetland in Inner Mongolia. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2013, 40, 158–162. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L. Study on Plant Eco-Stoichiometry of Salt Marsh Zone in Salt Lake of Qaidam Basin. Master’s Thesis, University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dale, P.; Eslami-Andargoli, L.; Knight, J. The impact of encroachment of mangroves into saltmarshes on saltwater mosquito habitats. J. Vector Ecol. 2013, 38, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Q. Study on the Lowest Ecological Water Level of Inner Mongolia Desert Salt Marsh Wetland. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2013, 40, 150–152+166. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, G. Haixi Strives to Build a World-Class Salt Lake Industrial Base. Available online: http://www.cdmrb.com.cn/pc/202108/26/c73426.html (accessed on 4 November 2021).
- Zhang, Q. Xi Jinping Emphasizes the Importance of Respecting, Adapting to, and Protecting Nature, and Advocates for the Robust Establishment of a National Ecological Security Barrier. Available online: http://www.xinhuanet.com/politics/201608/24/c_1119448608.htm?from=groupmessage&isappinstalled=0 (accessed on 13 January 2024).
- Hu, Y.; Su, H.; Zhu, Z.; Qi, T.; Pang, Q. Environmentally benign techniques of lithium extraction from salt lakes: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, L.; Li, W. The extraction rules investigation of mental(Li, Na, K, Mg, Ca) ion in salt lake brine by TBP-FeCl3 extraction system. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 763, 138249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Cai, Z.; Zhou, Z. Novel ionic liquid as co-extractant for selective extraction of lithium ions from salt lake brines with high Mg/Li ratio. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 277, 119471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, L.; Li, W. Lithium extraction from salt lake brine with high mass ratio of Mg/Li using TBP-DIBK extraction system. Separations 2022, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, L.; Li, W. Study of lithium extraction mechanism by TBP extraction system. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2022, 791, 139371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, W.D. Environmental threats to salt lakes and the likely status of inland saline ecosystems in 2025. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S. Study on ecological environment protection in Qinghai Lake region. J. Poyang Lake 2010, 4, 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Wu, C.; Lai, Z.; Guo, S.; Cong, L. A Chronological Study on the Sedi-mentation of the West Taijinel Lake in the Qaidam Basin. Rid Land Geogr. 2019, 42, 876–884. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H. Water Resource Reasonable Exploitation and Environmental Protection in Qaidam-Basin; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.B.; Zhou, G.Y.; Yang, L.C.; Liu, H.; Song, W. The biomass allocation patterns of desert shrub vegetation in the Qaidam Basin. J. Desert Res. 2014, 34, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.Q.; Gao, C.L.; Cheng, A.Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.S.; He, X.H. Geomorphic, hydroclimatic and hydrothermal controls on the formation of lithium brine deposits in the Qaidam Basin, northern Tibetan Plateau, China. Ore. Geol. Rev. 2013, 50, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, J. Study on the dynamic changes of brine in West Taijina. Ground Water 2014, 5, 102–103. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Wu, Y. Analysis on development and utilization of water resources in Nalingguole River of Qaidam Basin. Groundwater 2014, 36, 166–167. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Pan, M. Flood control contingency scheme for tail area of Nalenggele River. Yellow River 2018, 40, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H.; Li, H.M.; Wen, T.T.; Shen, H.; Han, Z.; Zhu, B. Risk Zoning of Summer Rainstorm Disaster and Its Influence in Qaidam Basin. Arid. Zone Res. 2021, 38, 757–763. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, N. Changes of lake area in Qaidam basin and the influence factors. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2014, 28, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.C.; Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Duan, S. Analysis of Long-Term Changes Intemperature and Precipitation and Their Relationships with Water Resources in the Qaidam Basin in China. Resour. Sci. 2011, 33, 408–415. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhuge, Y.; Shi, Y.; Du, Q.; Zhang, X.; Nie, R. Identification of natural eco-hydrological characteristics of lakes in the Qaidam Basin. Water Resour. Prot. 2023, 39, 225–233. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Ni, W.; Li, T.; Zhou, B.; Qu, Y.; Yuan, K. Influences of anthropogenic factors on lakes area in the Golmud Basin, China, from 1980 to 2015. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Liu, X.; Dong, Y. Research on the genesis of semi-submerged yardan land form in the duck lake area of qaidam basin. Geol. Rev. 2018, 64, 1505–1518. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.; Han, J.B.; Liu, J.B. Variation Characteristics of LiCl Deposit under Condition of Mining in East Taijnar Salt Lake, Qaidam Basin. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 2020, 25, 17–22, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. Analysis of dynamic changes in the underground brine water level characteristics in the west Taijinel salt lake mining area. Ground Water 2018, 40, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.W.; Huang, J.T.; Fang, T.; Song, G.; Sun, F.Q. Relationship of Uunderground Water Level and Climate in Northwest China’s Inland Basins under the Global Climate Change: Taking the Golmud River Catchment as an Example. China Geol. 2021, 4, 402–409. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.H.; Xu, D.D.; Jia, W.H.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhang, J. Responses of Phreatophyte Transpiration to Falling Water Table in Hyper-Arid and Arid Regions, Northwest China. China Geol. 2021, 4, 410–420. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Jiao, J.J.; Luo, X.; Zuo, J.; Lu, M.; Liu, Y.; Liang, W.; Kuang, X. Control factors on nutrient cycling in the lake water and groundwater of the Badain Jaran Desert, China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Su, X.; Dai, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhu, P.; Huang, Y. Multi-tracer investigation of river and groundwater interactions: A case study in Nalenggele River basin, northwest China. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Zheng, M.P. Metallogenic models of potassium ore deposits in China and demonstration of deep exploration technology. Earth Sci. Front. 2021, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff, J.L.; Israde-Alcántara, I.; Garduño-Monroy, V.H.; Shanks Iii, W.C. The springs of Lake Pátzcuaro: Chemistry, salt-balance, and implications for the water balance of the lake. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 1827–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Tong, H.; Ren, X.; Shi, H. Analysis of salt lake resource security capacity in Qinghai qaidam basin and countermeasure research. China Min. Mag. 2023, 32, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.; Xie, A.; Zan, C. Development status and countermeasure research of brine resources in the east and west Taijinel salt lakes and the yiliping salt lake. Ind. Miner. Process. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Tang, J.; Guo, J.; Dai, Y.; Li, G.; Yan, B. Integrated system of comprehensive utilizing the concentrated brine of Yuncheng salt-lake basing on salt-forming diagram. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Ma, H.Z.; Gao, D.L.; Wang, T.; Yang, Z.H.; Zhang, M.G. Dynamic changes of K, Li and B in hydrochemistry in brine of the mining area of taijinair salt lake during the initial period of mining. J. Lake Sci. 2007, 19, 727–734. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.X.; Li, L.G.; Chen, Y.J.; Qin, J.Z.; Liu, H. Grade variation in the past mining years and it’s forecast in the next 10 years of potassium, boron, lithium and magnesium in west Taijinel salt lake brine. J. Salt Lake Res. 2021, 29, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M.; Hou, X. Comprehensive utilization and sustainable development strategy of Qinghai salt lake resources. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2017, 35, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Li, P.; Xiao, L.; Wang, B.; Xu, Y.; Pan, J. Identification of Key Areas for Ecological Restoration and Division of Restoration Zones in Qinghai Province. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 38, 252–265. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Chen, Y. Thoughts on Ecological Construction of Qaidam Basin. For. Grassl. Policy Res. 2021, 1, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, W.; Long, D.; Hong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Xiao, P.; Duan, H.; Han, Z.; Gu, X. A lake data set for the Tibetan Plateau from the 1960s, 2005, and 2014. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Ni, W.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Yuan, K.; Zhou, B. Evaluation of the eco-geo-environment in the Qaidam Basin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, L. Investigation and assessment of ecological water resources in the salt marsh area of a salt lake: A case study of West Taijinar Lake in the Qaidam Basin, China. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnault, C.J.G. Sustainable development and integrated management of water resources. In Overexploitation and Contamination of Shared Groundwater Resources; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 309–324. [Google Scholar]
- Jiani, D. Status Quo, Problems and countermeasures of water resources in Qaidam Basin. Sci. Technol. 2013, 17, 263. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, M.; Wu, H.; Li, Y. Analysis on wetland definition and classification of the wetland conservation law of the People’s Republic of China. Wetl. Sci. 2022, 20, 404–412. [Google Scholar]
- RSIS. Ramsar Sites Information Service. 2020. Available online: https://rsis.ramsar.org/ris-search/?f%5B0%5D5wetlandTypes_en_ss%3AInland%%2020wetlands (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Unregulated expansion of Salt Lake Resource Development in the Qaidam Basin, Qinghai Province, Intensifies the Ecological and Environmental Burden. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/zysthjbhdc/dcjl/202312/t20231201_1057812.shtml (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Central Ecological and Environmental Protection Inspectorate: Qinghai Salt Lake Group and other Enterprises Have Been Illegally Taking Water for a Long Time. Available online: http://www.jwview.com/jingwei/html/05-09/317323.shtml (accessed on 9 May 2020).
- Williams, W.D. Lake Corangamite, Australia, a permanent saline lake: Conservation and management issues. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 1995, 1, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, V.G.; Mormile, M.R. A case for the protection of saline and hypersaline environments: A microbiological perspective. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tourian, M.J.; Elmi, O.; Chen, Q.; Devaraju, B.; Roohi, S.; Sneeuw, N. A spaceborne multisensor approach to monitor the desiccation of Lake Urmia in Iran. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Das, S.K.K.; Goyal, S.A.K. Conservation Planning of Sambhar Lake, Rajasthan Using Satellite Remote Sensing and GIS. M.tech Thesis, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam, India, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Shadkam, S.; Ludwig, F.; van Vliet, M.T.; Pastor, A.; Kabat, P. Preserving the world second largest hypersaline lake under future irrigation and climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 559, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Meng, W.; Shu, J.; Li, X.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Y. Ecological Civilization Construction for the Saline Industry in Qaidam Basin. Strateg. Study CAE 2017, 19, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ecological Protection Content | Reference to Regulations | Current Status of Management | Major Conflicts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lake shoreline management | “Guidelines for the Implementation of the River and Lake Length System”, “Regulations on Water Resources Management in Haixi Mongol and Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture” | Strengthening shoreline management and preserving natural lake shorelines | The natural landscape has been permanently changed due to development and cannot be fully restored to its original state while meeting ecological preservation standards. |
| Floodwall management | “Guidelines for the Implementation of the River and Lake Length System” | Removing floodwalls and restoring natural lake waters | After removing the flood wall, the flood season may impact the quality of resources in the mining area, affecting enterprise development. |
| Natural watercourses management | “Guidelines for the Implementation of the River and Lake Length System” | Illegal occupation of natural watercourses | The Bitterroot has been managed as an internal production area and cannot be returned to its natural state. |
| Flood resource management | “Regulations on Water Resources Management in Haixi Mongol and Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture” | Application for water-abstraction permit | After evaporation, floodwater resources used by enterprises become brackish water with a high salt concentration, which falls outside the realm of water resource management. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zha, X.; Jia, S. Development-Ecological Protection Conflicts and Coordination at West Taijinel Salt Lake. Water 2024, 16, 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152139
Zha X, Jia S. Development-Ecological Protection Conflicts and Coordination at West Taijinel Salt Lake. Water. 2024; 16(15):2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152139
Chicago/Turabian StyleZha, Xizhuoma, and Shaofeng Jia. 2024. "Development-Ecological Protection Conflicts and Coordination at West Taijinel Salt Lake" Water 16, no. 15: 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152139
APA StyleZha, X., & Jia, S. (2024). Development-Ecological Protection Conflicts and Coordination at West Taijinel Salt Lake. Water, 16(15), 2139. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152139







