Source-Oriented Health Risks and Distribution of BTEXS in Urban Shallow Lake Sediment: Application of the Positive Matrix Factorization Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Laboratory Analysis
2.3. Quality Control and Quality Assurance
2.4. Positive Matrix Factorization
2.5. Source-Oriented Health Risk Assessment
2.6. Monte Carlo Simulation
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
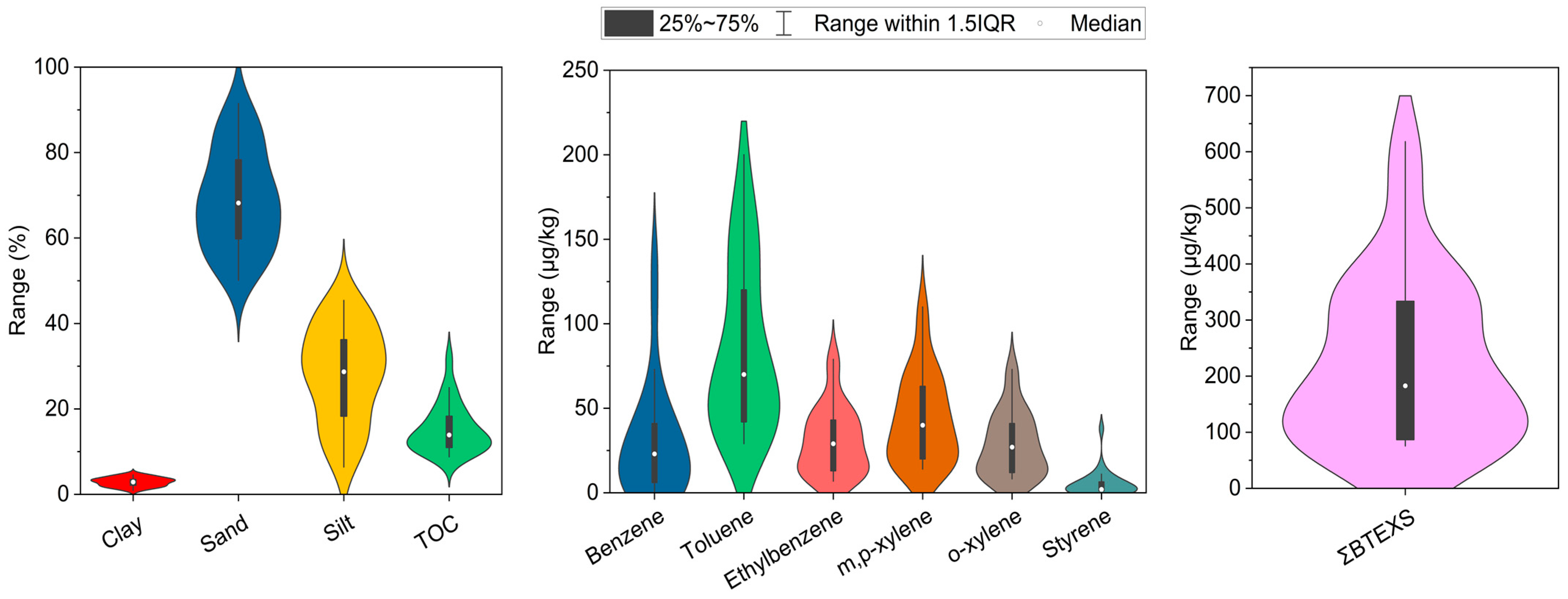
3.1. Occurrence of BTEXS in the Surface Sediments of Bubanj Lake with Concentration Characteristics
3.2. Multivariate Statistics
3.2.1. Pearson Correlation Analysis
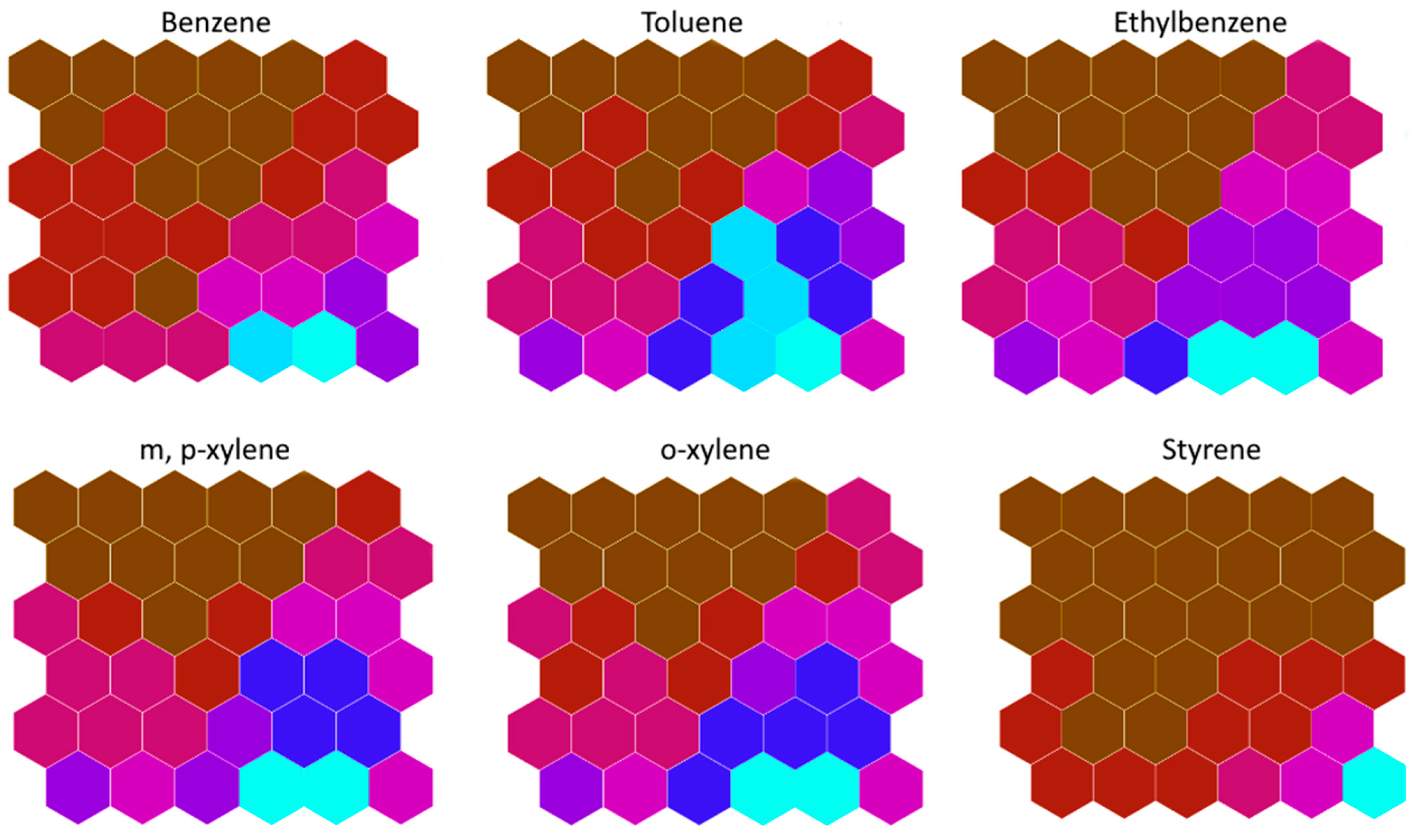
3.2.2. SOMs
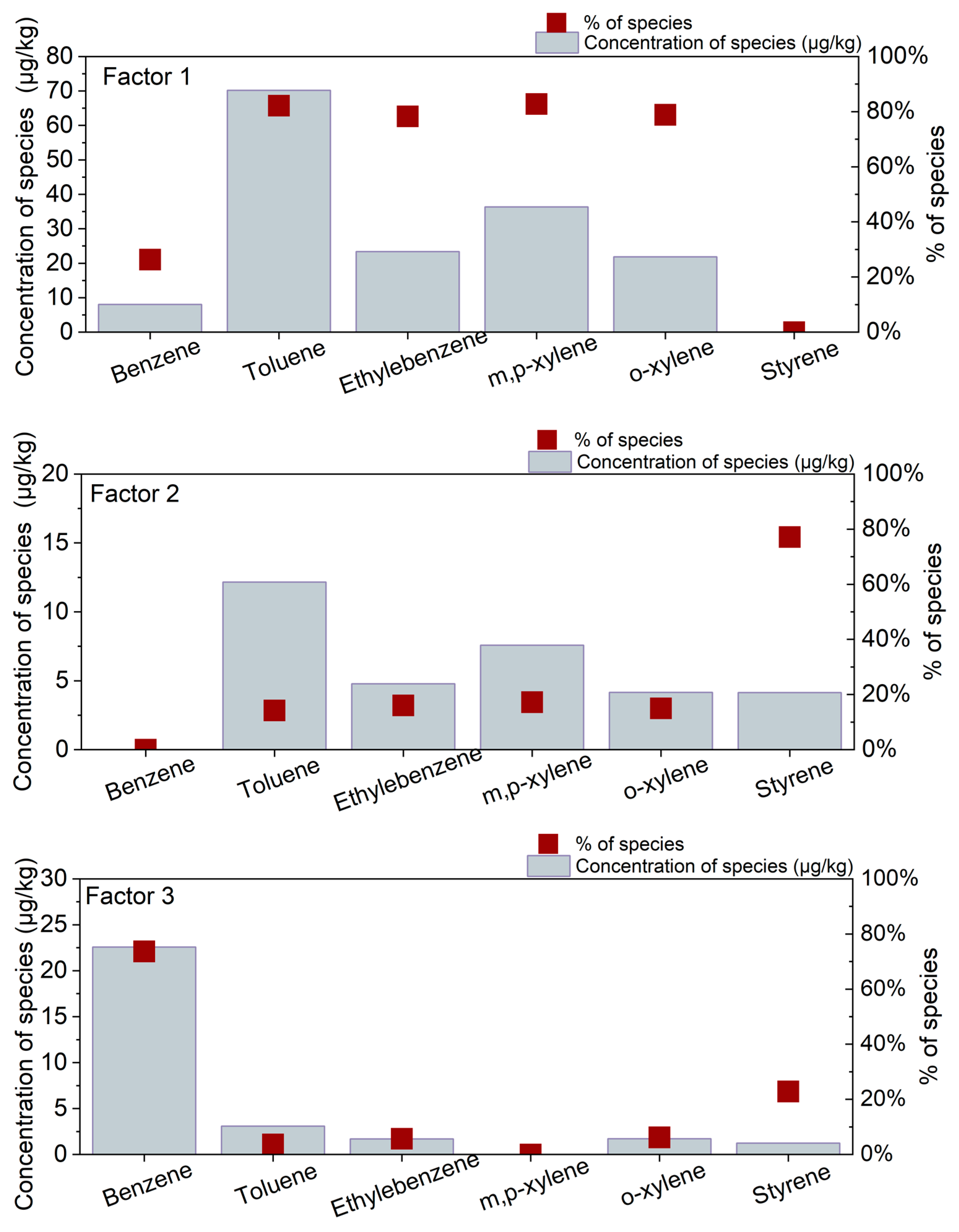
3.3. Pollution Source Apportionment Using the PMF Model
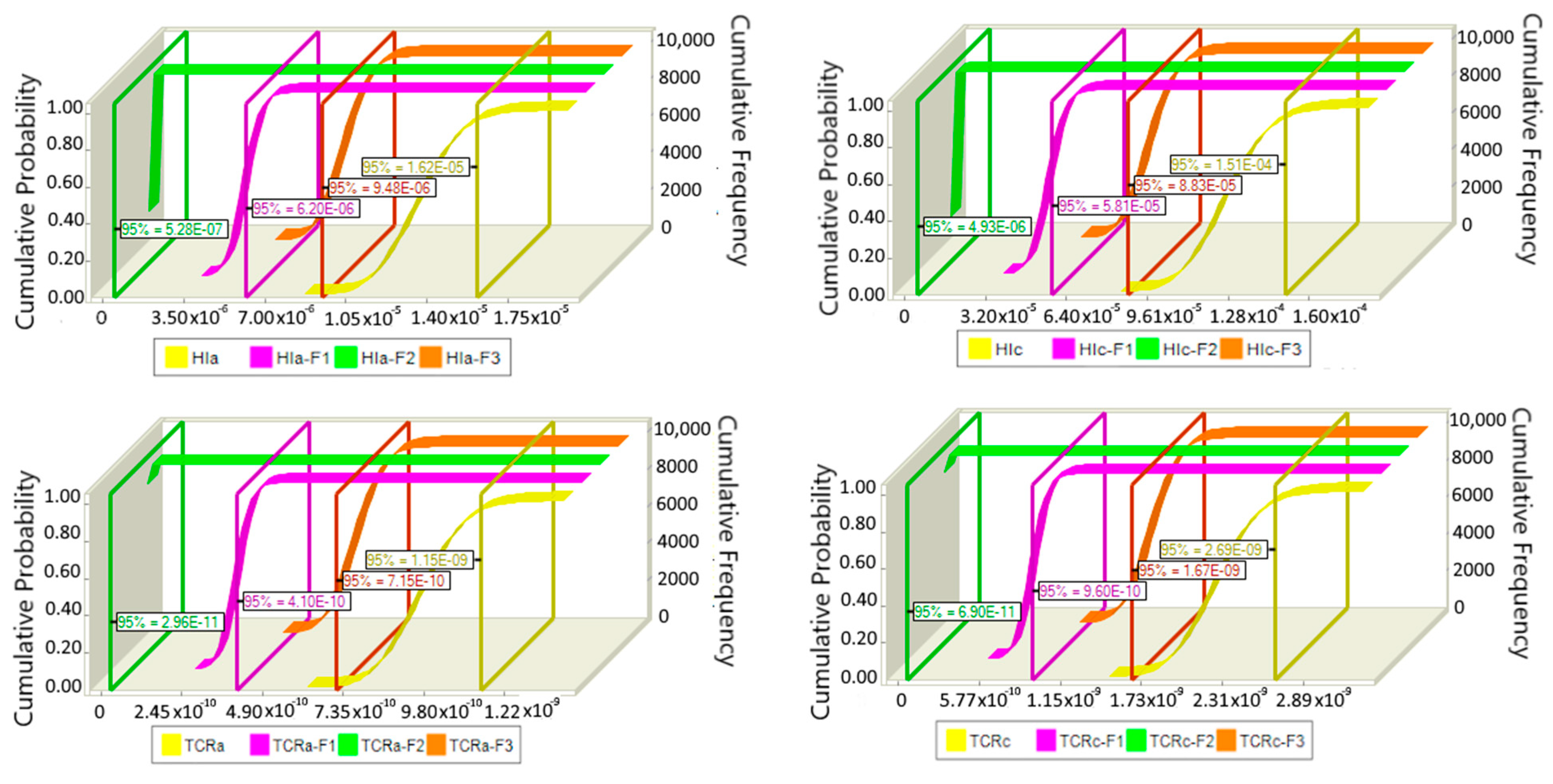
3.4. Health Risks of BTEXS in Sediments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Kahtany, K.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Alharbi, T.; Giacobbe, S.; Nour, H.E. Health Risk Assessment and Contamination of Potentially Toxic Elements in Southwest of the Red Sea Coastal Sediment. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 65, 103103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yu, R.; Chen, J.; Leng, X.; Zhao, D.; Jia, H.; An, S. Ecological Risk of Heavy Metals in Lake Sediments of China: A National-Scale Integrated Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Wang, R.; Zhu, B.; Rudstam, L.G.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xin, W.; Chen, Y. Heavy Metal Gradients from Rural to Urban Lakes in Central China. Ecol. Process 2020, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Andrade, L.C.; Coelho, F.F.; Hassan, S.M.; Morris, L.A.; De Oliveira Camargo, F.A. Sediment Pollution in an Urban Water Supply Lake in Southern Brazil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, M.; Tokatlı, C. Metals and Phosphorus in the Sediments of Streams Emptying into the Çanakkale Strait (Dardanelles): Spatial Distribution, Pollution Status, Risk Assessment and Source Identification. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, J.K.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Noh, H.R.; Lee, Y.-M.; Yu, S.J. Characteristics and Sources of Selected Halocarbon and Hydrocarbon Volatile Organic Compounds in Surface Water of the Han River Basin. Water 2021, 13, 2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Syakir Ishak, M.I.; Bhawani, S.A.; Umar, K. Various Natural and Anthropogenic Factors Responsible for Water Quality Degradation: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoğlu, F.; Islam, M.S.; Tokatli, C. Ecological and Probabilistic Human Health Hazard Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sera Lake Nature Park Sediments (Trabzon, Turkey). Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häder, D.-P.; Banaszak, A.T.; Villafañe, V.E.; Narvarte, M.A.; González, R.A.; Helbling, E.W. Anthropogenic Pollution of Aquatic Ecosystems: Emerging Problems with Global Implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, W.; Dominic Ekpe, O.; Lee, E.-H.; Arafath, S.Y.; Lee, M.; Kim, K.H.; Oh, J.-E. Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Priority Water Pollutants in Surface River Sediments with Emphasis on Industrially Affected Areas. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lin, X.; Yin, S.; Liu, K.; Liu, W. Spatio-Vertical Characterization of the BTEXS Group of VOCs in Chinese Agricultural Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frischmon, C.; Hannigan, M. VOC Source Apportionment: How Monitoring Characteristics Influence Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) Solutions. Atmos. Environ. X 2024, 21, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sentic, M.; Trajkovic, I.; Manojlovic, D.; Stankovic, D.; Nikolic, M.V.; Sojic, N.; Vidic, J. Luminescent Metal–Organic Frameworks for Electrochemiluminescent Detection of Water Pollutants. Materials 2023, 16, 7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, C.J.; Hannigan, J.H.; Bowen, S.E. Effects of Inhaled Combined Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene, and Xylenes (BTEX): Toward an Environmental Exposure Model. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 81, 103518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Guo, Z.; Lu, P.; Song, F.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Rose, N.L.; Wang, F. Positive Matrix Factorization on Source Apportionment for Typical Pollutants in Different Environmental Media: A Review. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Chen, S.; Li, A.; Xu, C.; Jing, G.; Chen, Q.; Hu, Y.; Tang, S.; Lv, M.; Xiao, K. Pollution Source Apportionment of River Tributary Based on PMF Receptor Model and Water Quality Remote Sensing in Xinjian River, China. Water 2022, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghnazar, H.; Johannesson, K.H.; González-Pinzón, R.; Pourakbar, M.; Aghayani, E.; Rajabi, A.; Hashemi, A.A. Groundwater Geochemistry, Quality, and Pollution of the Largest Lake Basin in the Middle East: Comparison of PMF and PCA-MLR Receptor Models and Application of the Source-Oriented HHRA Approach. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, J.; Zhou, C.; Nsabimana, A. Groundwater Pollution Source Identification and Apportionment Using PMF and PCA-APCS-MLR Receptor Models in Tongchuan City, China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 81, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, C.; Yang, W.; Liang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Analysis of the Quality, Source Identification and Apportionment of the Groundwater in a Typical Arid and Semi-Arid Region. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Ilarri, J.; Rodrigo-Clavero, M.-E.; Capilla, J.E.; Romero-Ballesteros, L. Environmental Assessment of Soil and Groundwater Pollution by BTEX Leaching in Valencia Region (Spain). Water 2023, 15, 3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; International Agency for Research on Cancer; World Health Organization: Lyon, France, 2020; Volume 1–123, ISBN 978-92-832-0158-8. [Google Scholar]
- ATSDR Substance Listing. Toxic Substance Portal. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/TSP/substances/SubstanceAZ.aspx (accessed on 12 July 2024).
- USEPA. User’s Guide: Human Health Risk Assessment; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2008.
- Chen, K.; Liu, Q.; Yang, T.; Ju, Q.; Hou, X.; Gao, W.; Jiang, S. Groundwater Pollution Source Identification and Health Risk Assessment in the North Anhui Plain, Eastern China: Insights from Positive Matrix Factorization and Monte Carlo Simulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 895, 165186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Cao, H.; Du, P.; Ren, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, H. Source-Oriented Probabilistic Health Risk Assessment of Soil Potentially Toxic Elements in a Typical Mining City. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesković, J.; Deršek-Timotić, I.; Lučić, M.; Miletić, A.; Đolić, M.; Ražić, S.; Onjia, A. Entropy-Weighted Water Quality Index, Hydrogeochemistry, and Monte Carlo Simulation of Source-Specific Health Risks of Groundwater in the Morava River Plain (Serbia). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 201, 116277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miletić, A.; Vesković, J.; Lučić, M.; Onjia, A. Monte Carlo Simulation of Source-Specific Risks of Soil at an Abandoned Lead-Acid Battery Recycling Site. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2024, 38, 3313–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesković, J.; Bulatović, S.; Miletić, A.; Tadić, T.; Marković, B.; Nastasović, A.; Onjia, A. Source-Specific Probabilistic Health Risk Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Groundwater of a Copper Mining and Smelter Area. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2024, 38, 1597–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, M.; Gavrilović, D. Municipalities and Regions of the Republic of Serbia; Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia: Belgrade, Serbia, 2023; ISBN 2217-7981.
- Stajic, J.M.; Milenkovic, B.; Pucarevic, M.; Stojic, N.; Vasiljevic, I.; Nikezic, D. Exposure of School Children to Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, Heavy Metals and Radionuclides in the Urban Soil of Kragujevac City, Central Serbia. Chemosphere 2016, 146, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab Amiri, M.; Gocić, M. Innovative Trend Analysis of Annual Precipitation in Serbia during 1946–2019. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranković, B.; Simić, S.; Bogdanović, D. Phytoplankton as Indicator of Water Quality of Lakes Bubanj and Šumarice during Autumn. Kragujev. J. Sci. 2006, 28, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, W.; Shi, W.; Cui, Y.; Chen, L.; Shao, J. Source Apportionment and Migration Characteristics of Heavy Metal(Loid)s in Soil and Groundwater of Contaminated Site. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 338, 122584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Hurtado, A.; Eguilior, S.; Llamas Borrajo, J.F. Acute and Chronic Risk Assessment of BTEX in the Return Water of Hydraulic Fracturing Operations in Marcellus Shale. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miletić, A.; Lučić, M.; Onjia, A. Exposure Factors in Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal(Loid)s in Soil and Sediment. Metals 2023, 13, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RAIS. The Risk Assessment Information System: Toxicity Values and Physical Parameters. Available online: https://rais.ornl.gov/cgi-bin/tools/TOX_search?select=chemtox (accessed on 14 July 2024).
- Rajasekhar, B.; Nambi, I.M.; Govindarajan, S.K. Human Health Risk Assessment for Exposure to BTEXN in an Urban Aquifer Using Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods: A Case Study of Chennai City, India. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Teng, Y.; Guo, G.; Li, F.; Zhang, C. Risk Assessment of BTEX in the Groundwater of Songyuan Region of Songhua River in China. Water Supply 2016, 16, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devic, G.; Pergal, M.; Pergal, M. Ecological and Health Risk Assessment of Nitrates and Heavy Metals in the Groundwater of the Alluvial Area of the Danube River near Kostolac Basin, Serbia. Water 2024, 16, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavković-Beškoski, L.; Ignjatović, L.; Ćujić, M.; Vesković, J.; Trivunac, K.; Stojaković, J.; Perić-Grujić, A.; Onjia, A. Ecological and Health Risks Attributed to Rare Earth Elements in Coal Fly Ash. Toxics 2024, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA EPA. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 5.0 Fundamentals and User Guide; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Asejeje, G.I.; Ipeaiyeda, A.R.; Onianwa, P.C. Occurrence of BTEX from Petroleum Hydrocarbons in Surface Water, Sediment, and Biota from Ubeji Creek of Delta State, Nigeria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 15361–15379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Yuan, Z.; Yu, Z.; Xue-song, F. BTEX in the Environment: An Update on Sources, Fate, Distribution, Pretreatment, Analysis, and Removal Techniques. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, T.; Clapp, R.; Harrison, R.; Shusterman, D. Solvent-based Paint and Varnish Removers: A Focused Toxicologic Review of Existing and Alternative Constituents. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2020, 40, 1325–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinsanya, B.; Ayanda, I.O.; Onwuka, B.; Saliu, J.K. Bioaccumulation of BTEX and PAHs in Heterotis Niloticus (Actinopterygii) from the Epe Lagoon, Lagos, Nigeria. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünlü, S.; Alpar, B. Evaluation of Sediment Contamination by Monoaromatic Hydrocarbons in the Coastal Lagoons of Gulf of Saros, NE Aegean Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 118, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etiope, G.; Panieri, G.; Fattorini, D.; Regoli, F.; Vannoli, P.; Italiano, F.; Locritani, M.; Carmisciano, C. A Thermogenic Hydrocarbon Seep in Shallow Adriatic Sea (Italy): Gas Origin, Sediment Contamination and Benthic Foraminifera. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 57, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, E.; Alimohammadi, M.; Lyons, J.; Davis, E.; Walker, T.R.; Lake, C.B. Characterization and Spatial Distribution of Organic-Contaminated Sediment Derived from Historical Industrial Effluents. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onyena, A.P.; Nkwoji, J.A.; Chukwu, L.O.; Walker, T.R.; Sam, K. Risk Assessment of Sediment PAH, BTEX, and Emerging Contaminants in Chanomi Creek Niger Delta, Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okogbue, C.O.; Oyesanya, O.U.; Anyiam, O.A.; Omonona, V.O. Assessment of Pollution from Produced Water Discharges in Seawater and Sediments in Offshore, Niger Delta. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünlü, V.S.; Alpar, B. Spatial Distribution and Sources of BTEX and TPH Contamination in Freshwater Sediments from Lake Iznik, NW Turkey. Int. J. Environ. Geoinform. 2018, 5, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, M.; Rostami Aghdam Shendi, M.; Ghaffari, H.R.; Ebrahimi Aval, H.; Ahmadi, E.; Taban, E.; Gholizadeh, A.; Yazdani Aval, M.; Mohammadi, A.; Azari, A. Investigation of Outdoor BTEX: Concentration, Variations, Sources, Spatial Distribution, and Risk Assessment. Chemosphere 2016, 163, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbueri, J.C.; Ukah, B.U.; Ubido, O.E.; Unigwe, C.O. A Chemometric Approach to Source Apportionment, Ecological and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Industrial Soils from Southwestern Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 3399–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajaj, A.; J’Bari, S.; Ononogbo, A.; Buonocore, F.; Bear, J.C.; Mayes, A.G.; Morgan, H. An Insight into the Growing Concerns of Styrene Monomer and Poly(Styrene) Fragment Migration into Food and Drink Simulants from Poly(Styrene) Packaging. Foods 2021, 10, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Kim, S.-K.; Hyun, J.-H. Environmental Distribution of Styrene Oligomers (SOs) Coupled with Their Source Characteristics: Tracing the Origin of SOs in the Environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuranchie, F.A.; Angnunavuri, P.N.; Attiogbe, F.; Nerquaye-Tetteh, E.N. Occupational Exposure of Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene and Xylene (BTEX) to Pump Attendants in Ghana: Implications for Policy Guidance. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2019, 5, 1603418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ho, K.-F.; Yim, S.H.L. Source Apportionment of Hourly-Resolved Ambient Volatile Organic Compounds: Influence of Temporal Resolution. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesković, J.; Onjia, A. Environmental Implications of the Soil-to-Groundwater Migration of Heavy Metals in Mining Area Hotspots. Metals 2024, 14, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yue, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Source-Specific Probabilistic Contamination Risk and Health Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals in a Typical Ancient Mining Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, G.; Ghosh, S.; Banerjee, S.; Bhattacharyya, P. Appraisal of Potential Metal Risk in Calcareous Agricultural Soils: An Insight into Human and Environmental Health Employing Multimodal Tactics. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2024, 235, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Pan, Y.; Welsch, E.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Xu, S.; Peng, H.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Shi, H.; et al. Prioritization of Control Factors for Heavy Metals in Groundwater Based on a Source-Oriented Health Risk Assessment Model. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 267, 115642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Exposure Parameter | Units | Children | Adults | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingestion rate (IngR) | mg/day | 200 | 100 | Triangular |
| Exposure frequency (EF) | day(s)/year | 350 | 350 | Triangular |
| Exposure duration (ED) | year(s) | 6 | 24 | Point |
| Body weight (BW) | kg | 15 | 70 | Lognormal |
| Average non-carcinogenic time (ATnc) | day(s) | 2190 | 8760 | Point |
| Average carcinogenic time (ATc) | day(s) | 25,550 | 25,550 | Point |
| Skin surface area (SA) | cm2 | 2800 | 5700 | Point |
| Adherence factor (AF) | mg/cm2/day | 0.2 | 0.07 | Lognormal |
| Dermal absorption factor (ABS) | unitless | 0.001 | 0.001 | Point |
| Conversion factor (CF) | kg/mg | 10−6 | 10−6 | Point |
| Pollutant | RfDing (mg/kg/Day) | RfDderm (mg/kg/Day) | CSFing (mg/kg/Day)−1 | CSFderm (mg/kg/Day)−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzene | 0.004 | 0.00388 | 0.055 | 0.0567 |
| Toluene | 0.08 | 0.064 | – | – |
| Ethylbenzene | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.011 | 0.0138 |
| m,p-xylene | 0.2 | 0.16 | – | – |
| o-xylene | 0.2 | 0.16 | – | – |
| Styrene | 0.2 | – | – | – |
| Area, Country | Benz | Tol | eB | mpX | oX | Styr | ΣBTEXS | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ubeji Creek, Nigeria | 1600 | 980 | 1060 | 1140 | 790 | n.a. | 5570 | [42] |
| Epe Lagoon, Nigeria | 0 | 10,070 | 7450 | 7720 | 6140 | n.a. | 31,380 | [45] |
| Chanomi Creek, Nigeria | 3.525 | 5.523 | 6.714 | 5.364 * | 5.646 ** | n.a. | 26.773 | [49] |
| Lake Iznik, Turkey | 2.8 | 25.9 | 6.0 | 57.9 | 13.5 | n.a. | 106.1 | [51] |
| Offshore sediments, Nigeria | n.r. | n.a. | 2.0 | [50] | ||||
| Gulf of Saros, Turkey | 0.7 | 23.4 | 4.1 | 31.9 | 1.5 | n.a. | 61.6 | [46] |
| Adriatic Sea, Italy | 20.3 | 5.44 | 1.18 | <0.5 *** | n.a. | 26.9 | [47] | |
| Industrial areas, South Korea | 0.388 | 90.0 | 1.44 | 1.84 | 0.898 | 0.0559 | 94.6 | [10] |
| Pictou County, Canada | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | <DL | n.a. | – | [48] |
| Bubanj Lake, Serbia | 34.7 | 85.8 | 30.6 | 43.8 | 28.5 | 5.4 | 225 | Current study |
| Clay | Sand | Silt | TOC | Benz | Tol | eB | mpX | oX | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | −0.464 * | ||||||||
| Silt | 0.391 | −0.997 * | |||||||
| TOC | −0.327 | 0.431 * | −0.418 * | ||||||
| Benz | −0.339 | −0.197 | 0.236 | 0.092 | |||||
| Tol | −0.113 | −0.351 | 0.375 | 0.254 | 0.844 * | ||||
| eB | −0.191 | −0.302 | 0.332 | 0.199 | 0.895 * | 0.968 * | |||
| mpX | −0.192 | −0.3 | 0.329 | 0.238 | 0.887 * | 0.980 * | 0.992 * | ||
| oX | −0.184 | −0.337 | 0.367 | 0.231 | 0.879 * | 0.974 * | 0.985 * | 0.993 * | |
| Styr | −0.419 | −0.054 | 0.095 | 0.041 | 0.648 * | 0.505 * | 0.541 * | 0.552 * | 0.527 * |
| Health Risk Index | Pollutant | Adults | Children | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Max | Min | Mean | Max | Min | ||
| HI | Benzene | 1.05 × 10−5 | 4.81 × 10−5 | 1.72 × 10−7 | 9.81 × 10−5 | 4.49 × 10−4 | 1.60 × 10−6 |
| Toluene | 1.48 × 10−6 | 3.44 × 10−6 | 4.99 × 10−7 | 1.38 × 10−5 | 3.21 × 10−5 | 4.65 × 10−6 | |
| Ethylbenzene | 8.39 × 10−7 | 2.17 × 10−6 | 1.87 × 10−7 | 7.83 × 10−6 | 2.02 × 10−5 | 1.74 × 10−6 | |
| m,p-xylene | 3.02 × 10−7 | 7.57 × 10−7 | 9.64 × 10−8 | 2.81 × 10−6 | 7.06 × 10−6 | 8.98 × 10−7 | |
| o-xylene | 1.96 × 10−7 | 5.02 × 10−7 | 5.64 × 10−8 | 1.83 × 10−6 | 4.68 × 10−6 | 5.26 × 10−7 | |
| Styrene | 3.68 × 10−8 | 2.60 × 10−7 | 3.42 × 10−9 | 3.43 × 10−7 | 2.43 × 10−6 | 3.20 × 10−8 | |
| Total | 1.34 × 10−5 | 5.51 × 10−5 | 1.29 × 10−6 | 1.25 × 10−4 | 5.14 × 10−4 | 1.20 × 10−5 | |
| TCR | Benzene | 7.94 × 10−10 | 3.63 × 10−9 | 1.30 × 10−11 | 1.85 × 10−9 | 8.46 × 10−9 | 3.02 × 10−11 |
| Ethylbenzene | 1.59 × 10−10 | 4.10 × 10−10 | 3.53 × 10−11 | 3.70 × 10−10 | 9.56 × 10−10 | 8.23 × 10−11 | |
| Total | 9.52 × 10−10 | 4.04 × 10−9 | 8.05 × 10−11 | 2.22 × 10−9 | 9.42 × 10−9 | 1.87 × 10−10 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trajković, I.; Sentić, M.; Vesković, J.; Lučić, M.; Miletić, A.; Onjia, A. Source-Oriented Health Risks and Distribution of BTEXS in Urban Shallow Lake Sediment: Application of the Positive Matrix Factorization Model. Water 2024, 16, 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162302
Trajković I, Sentić M, Vesković J, Lučić M, Miletić A, Onjia A. Source-Oriented Health Risks and Distribution of BTEXS in Urban Shallow Lake Sediment: Application of the Positive Matrix Factorization Model. Water. 2024; 16(16):2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162302
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrajković, Ivana, Milica Sentić, Jelena Vesković, Milica Lučić, Andrijana Miletić, and Antonije Onjia. 2024. "Source-Oriented Health Risks and Distribution of BTEXS in Urban Shallow Lake Sediment: Application of the Positive Matrix Factorization Model" Water 16, no. 16: 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162302
APA StyleTrajković, I., Sentić, M., Vesković, J., Lučić, M., Miletić, A., & Onjia, A. (2024). Source-Oriented Health Risks and Distribution of BTEXS in Urban Shallow Lake Sediment: Application of the Positive Matrix Factorization Model. Water, 16(16), 2302. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16162302









