Numerical Modeling of Hydrological Mechanisms and Instability for Multi-Layered Slopes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material Properties
3. Mathematical Modeling
3.1. The Numerical Simulation Model
3.2. Simulation Parameter Setting
3.3. Hydraulic Model
3.4. Simulation Cases and Conditions
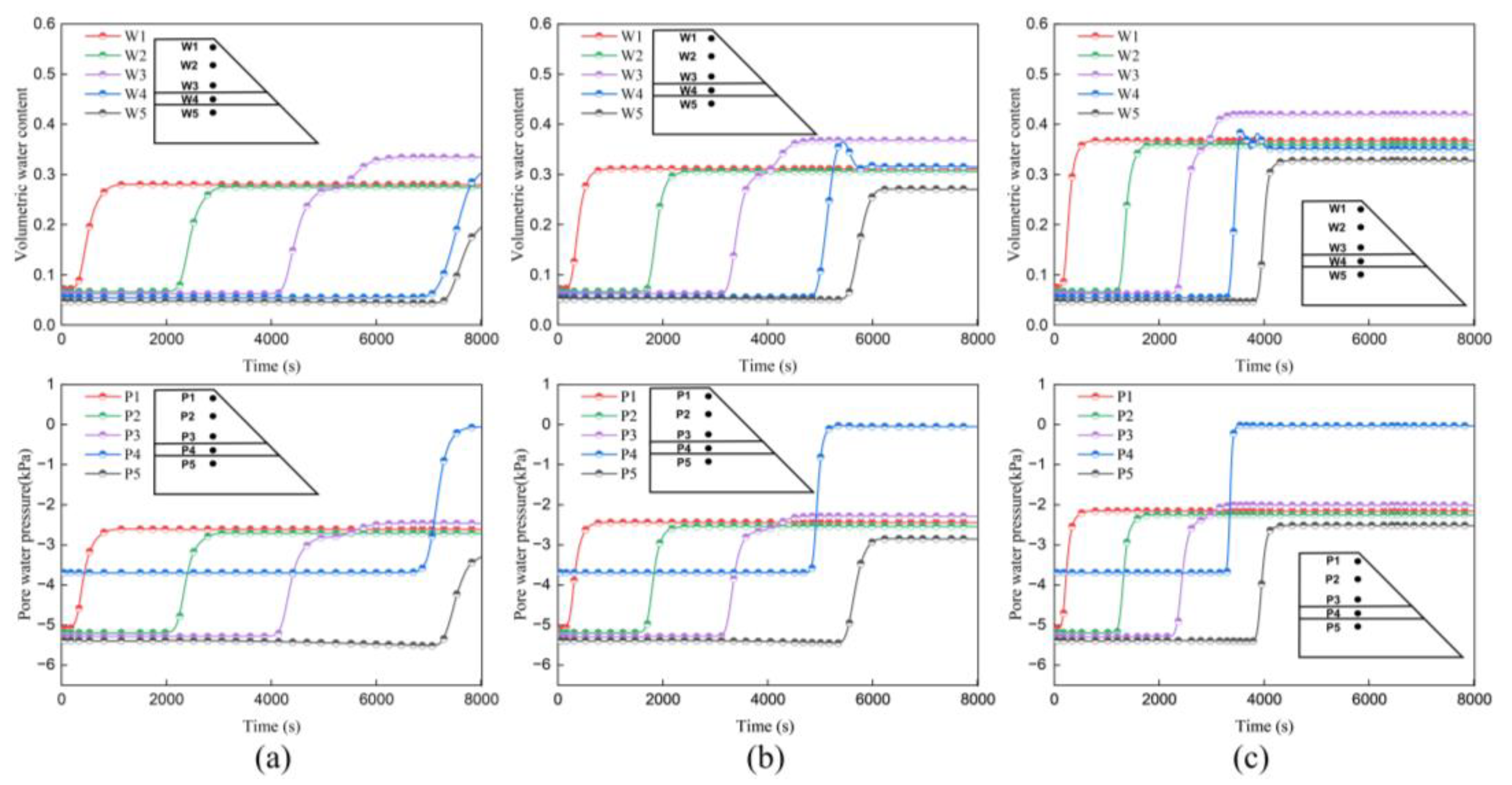
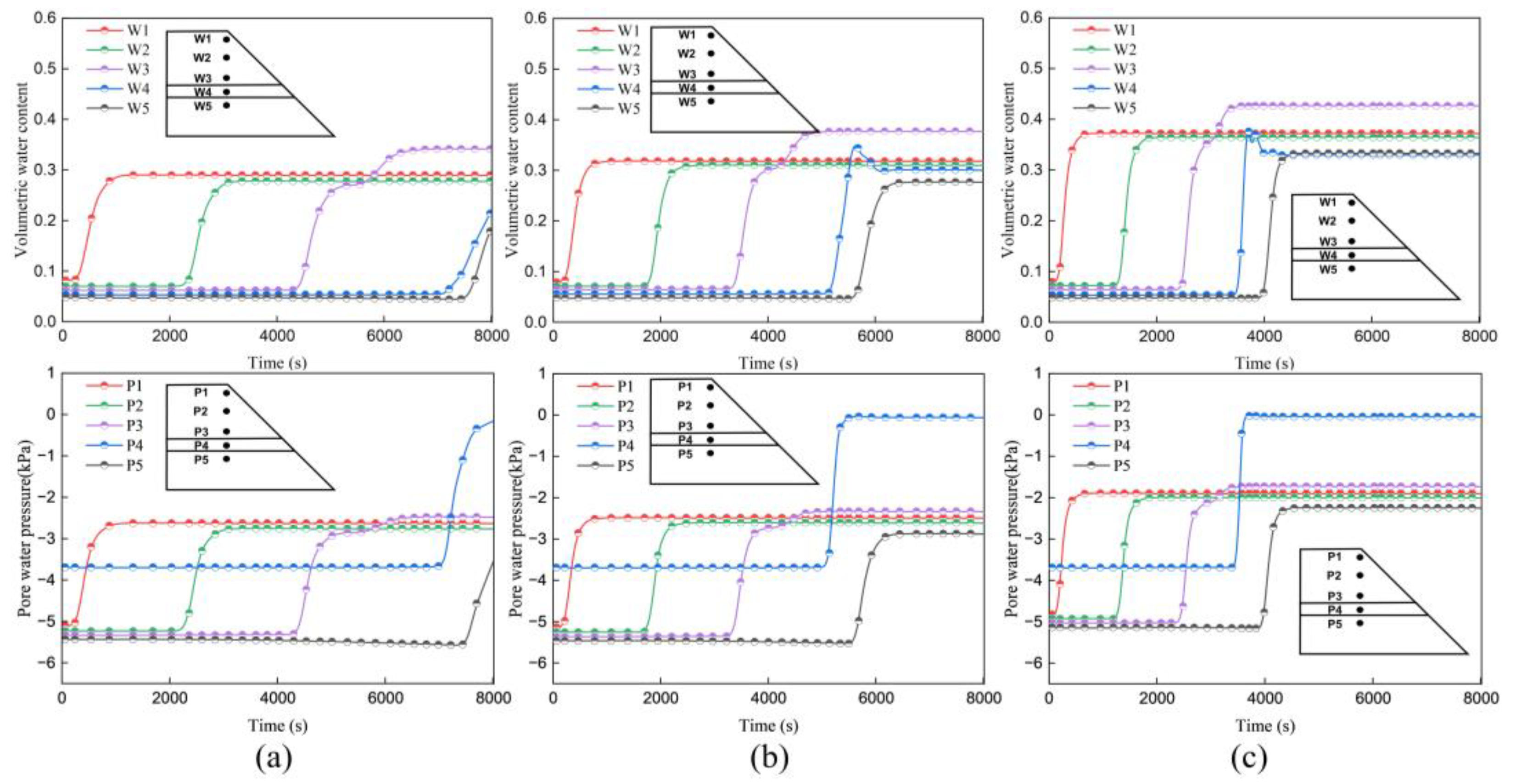
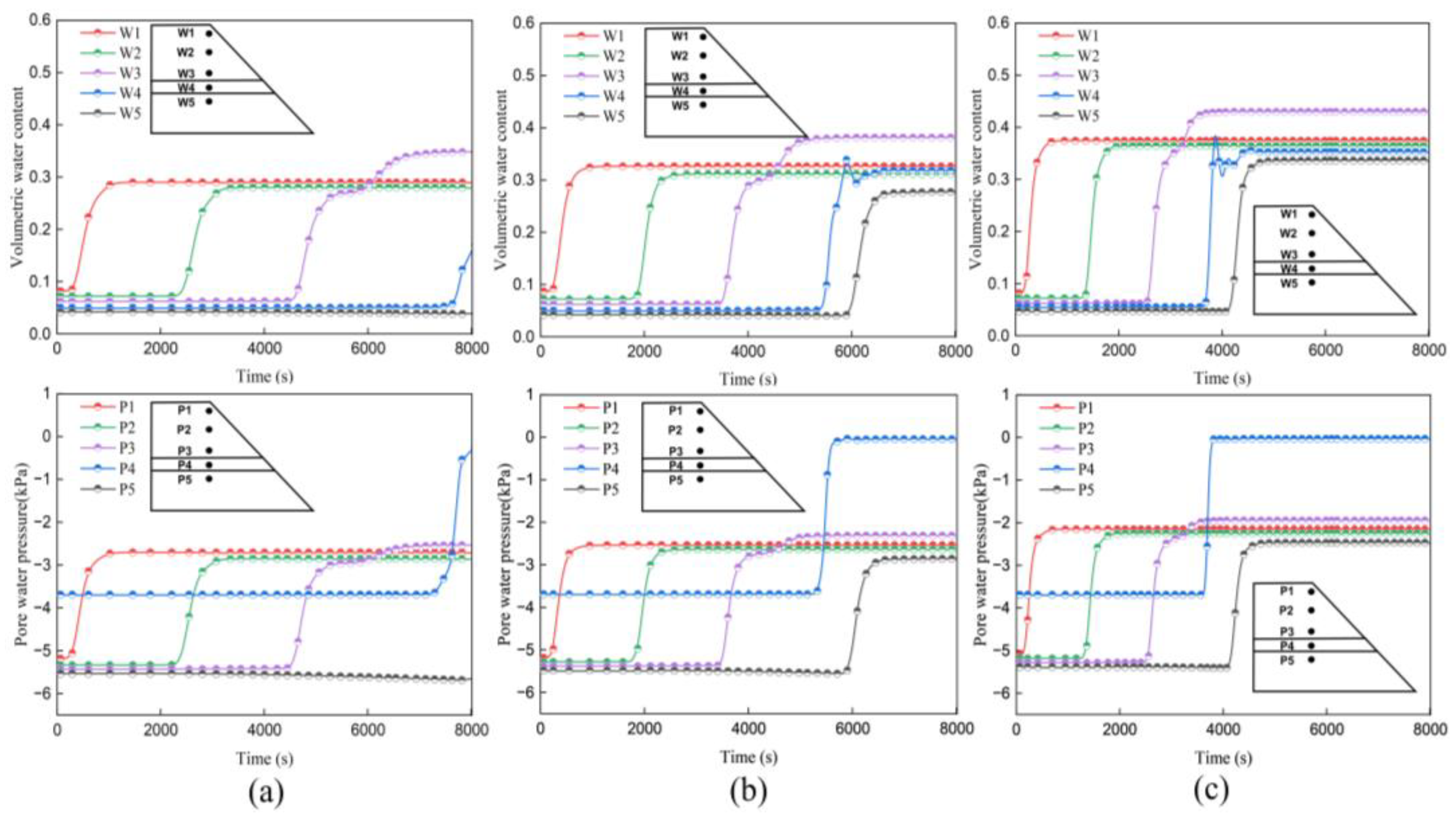
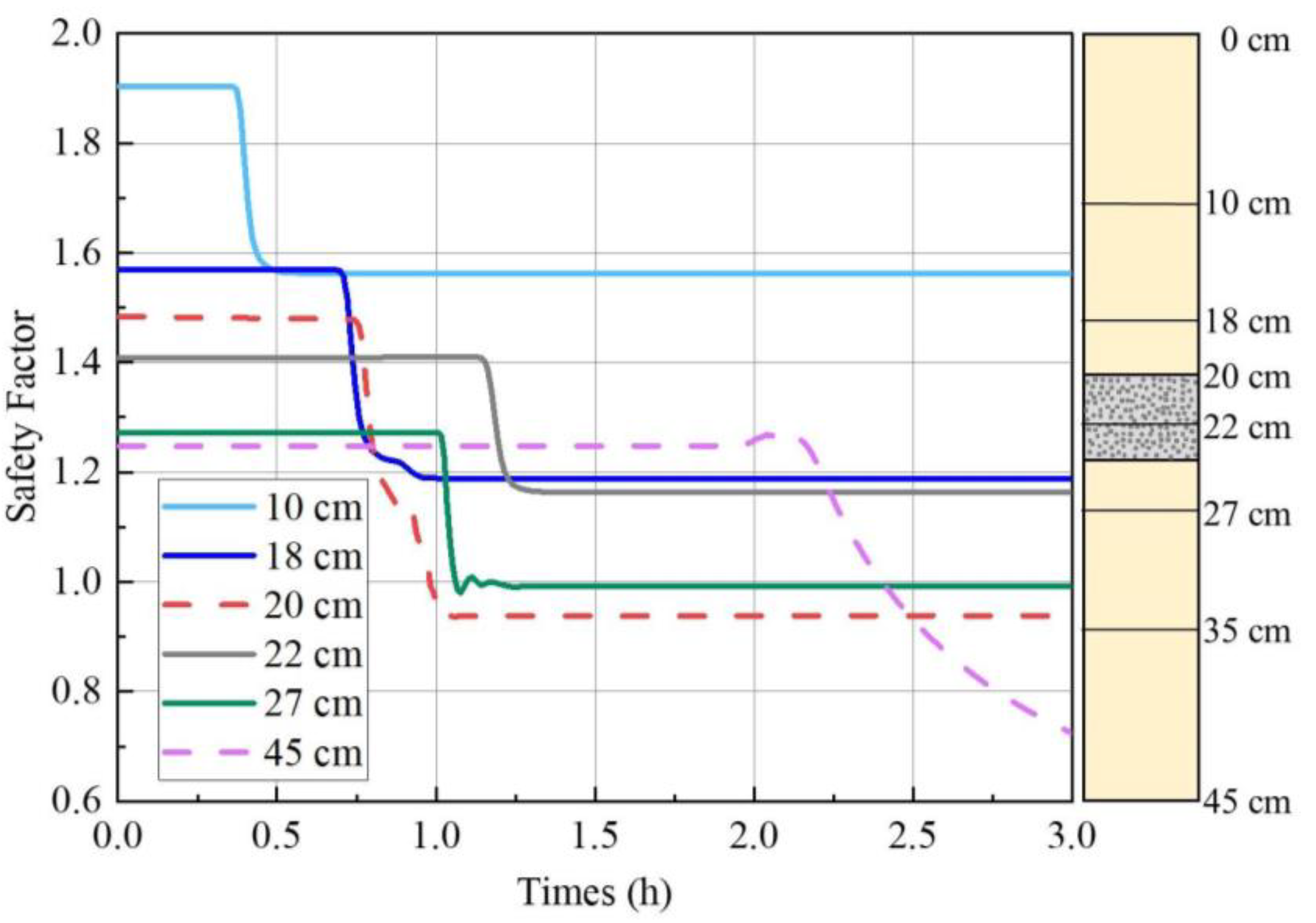
4. Results and Analyses
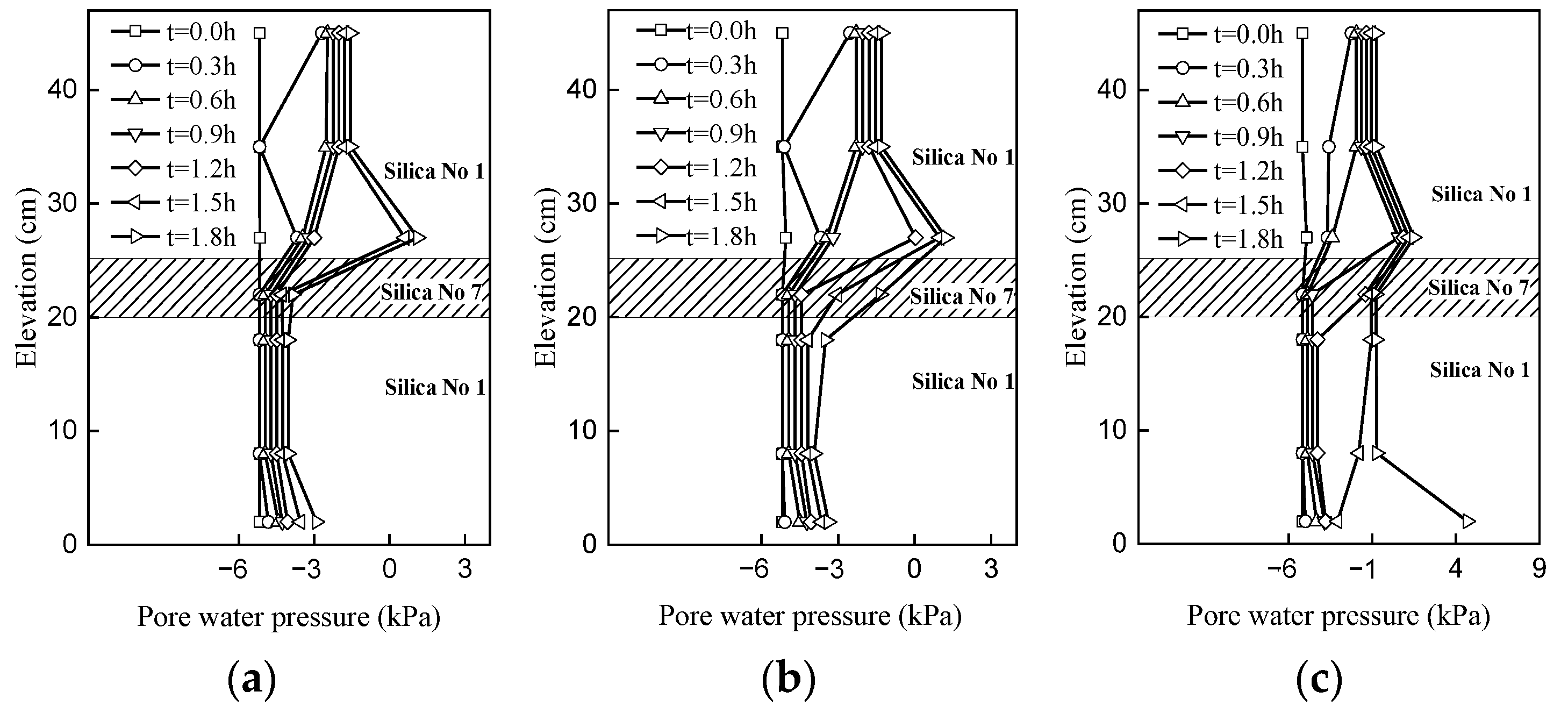
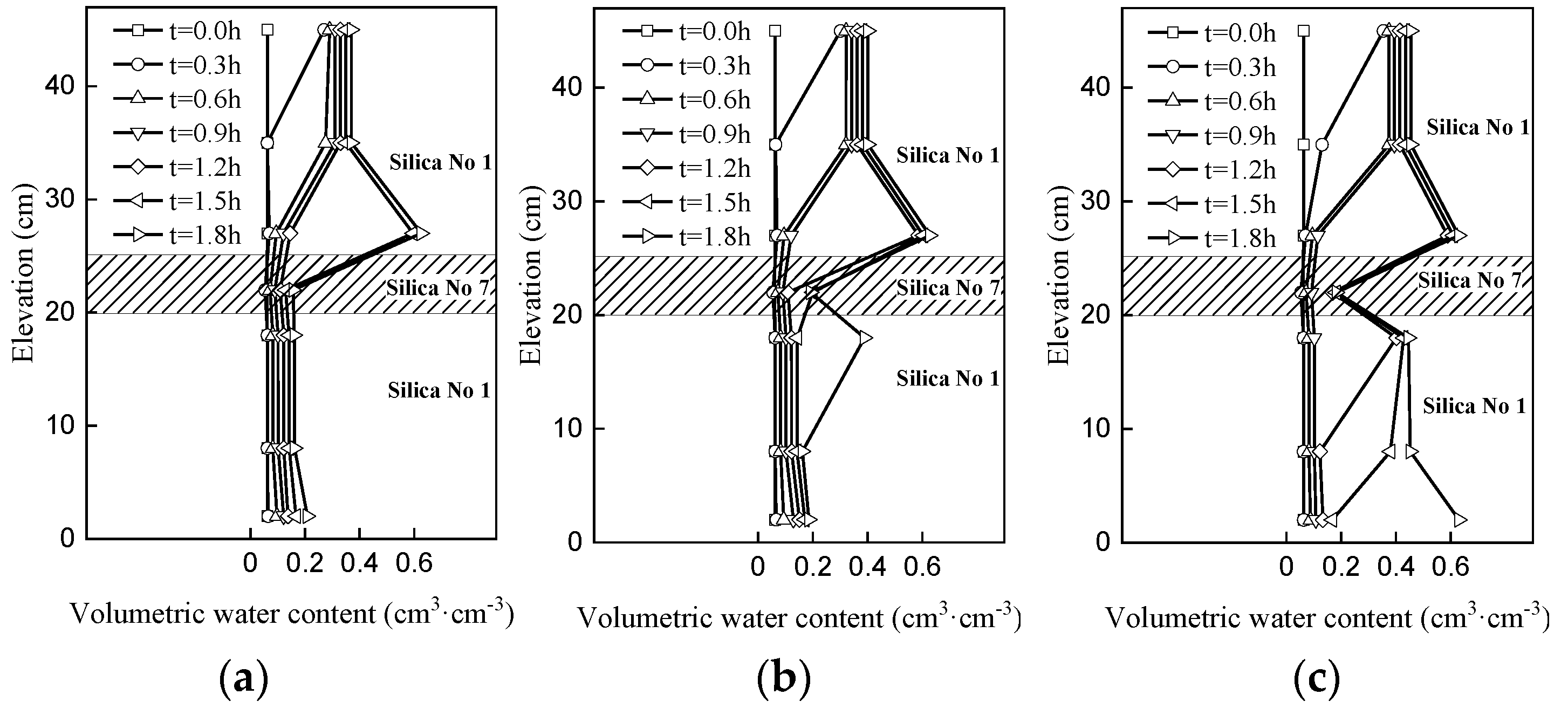
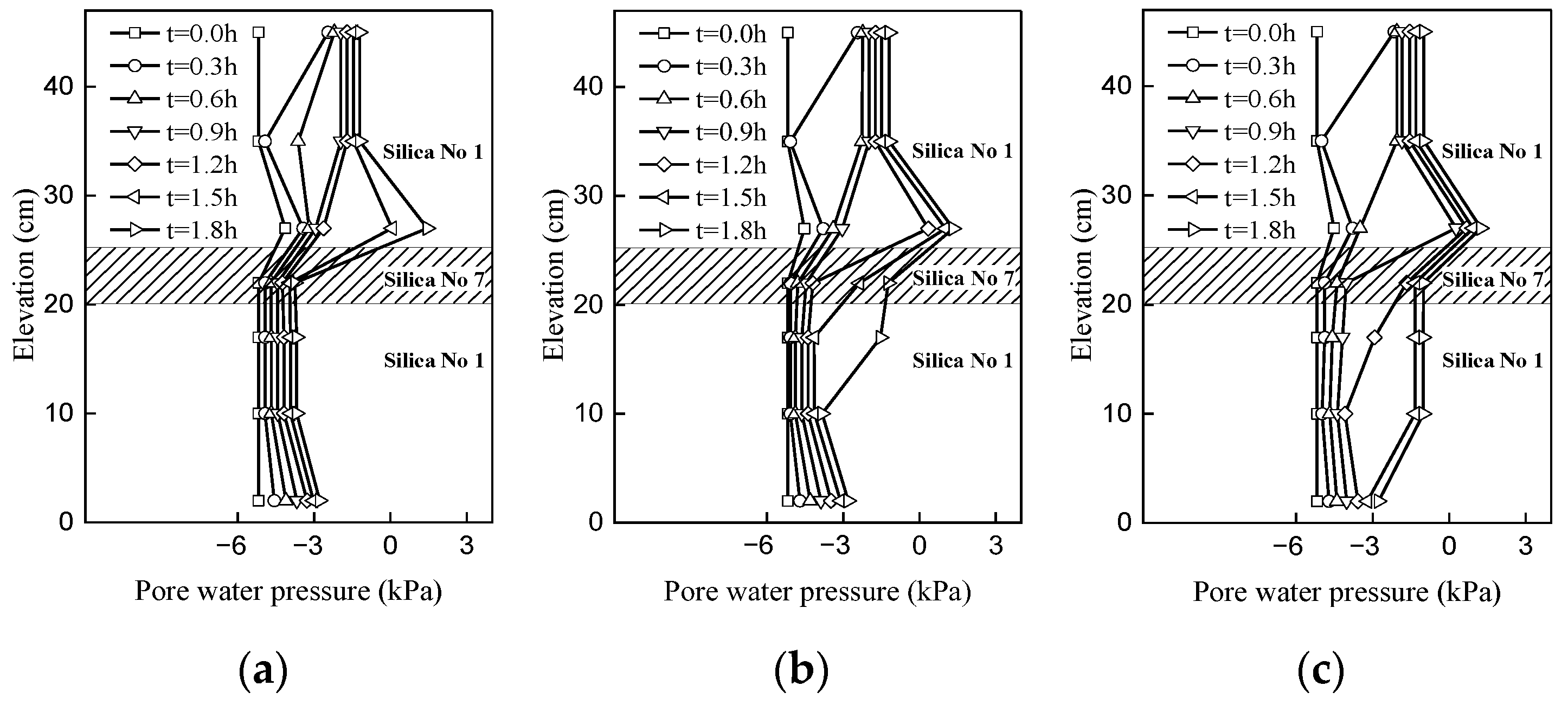
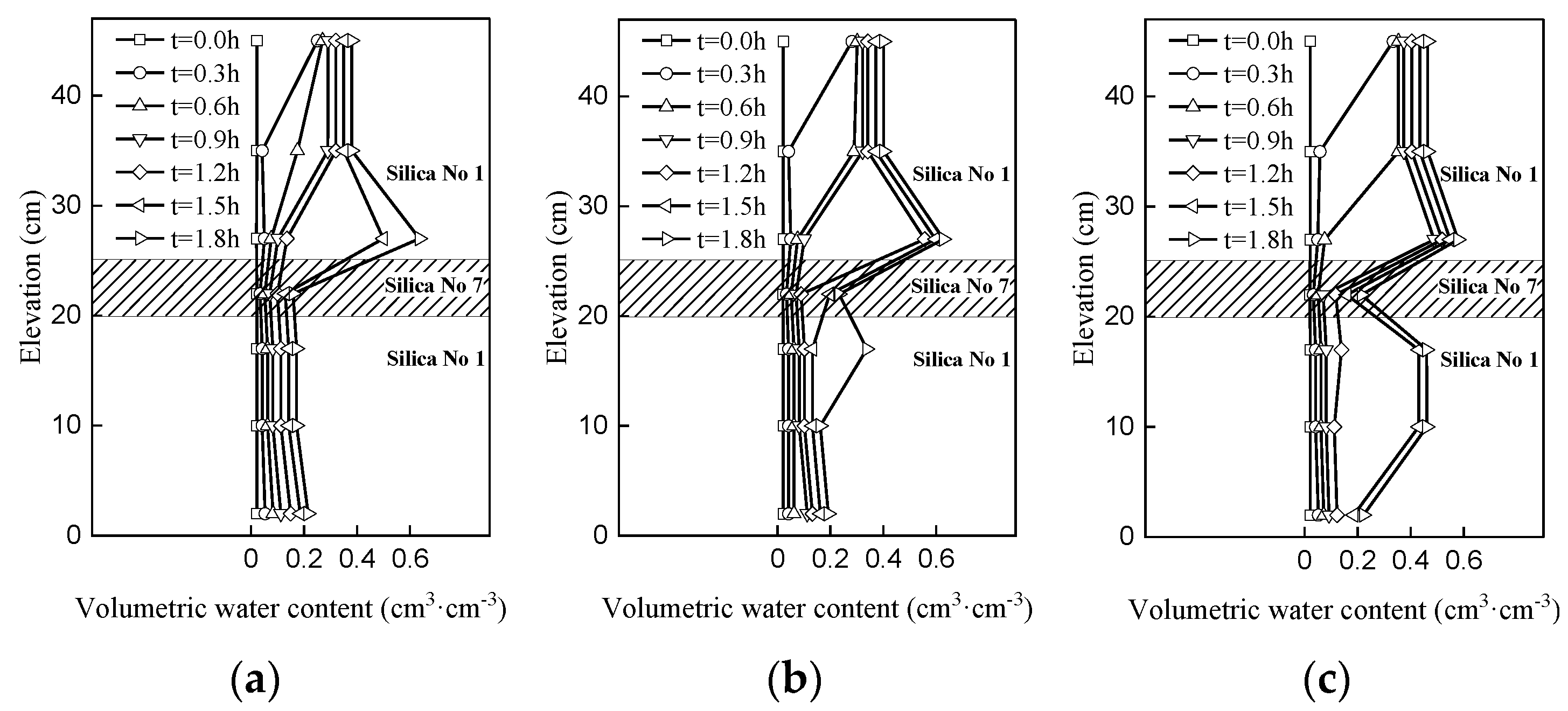
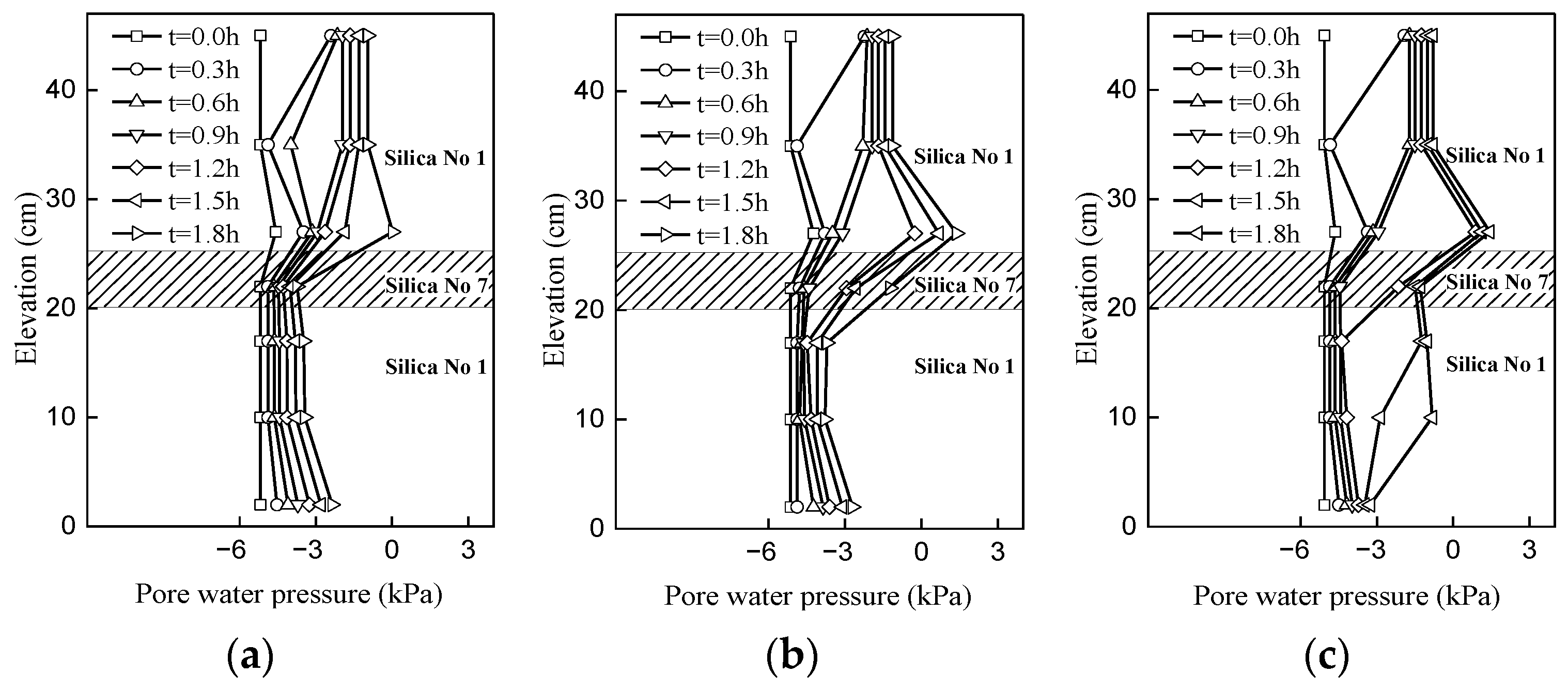
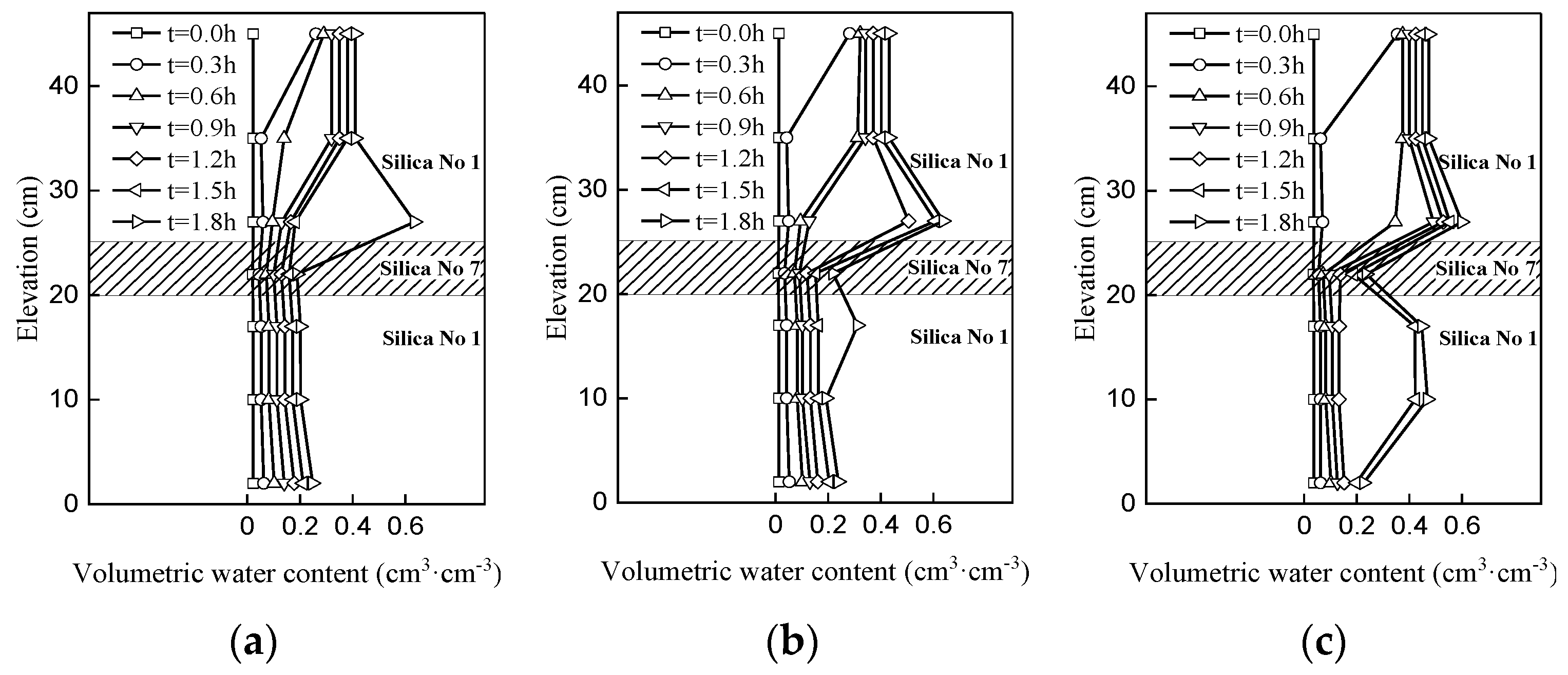
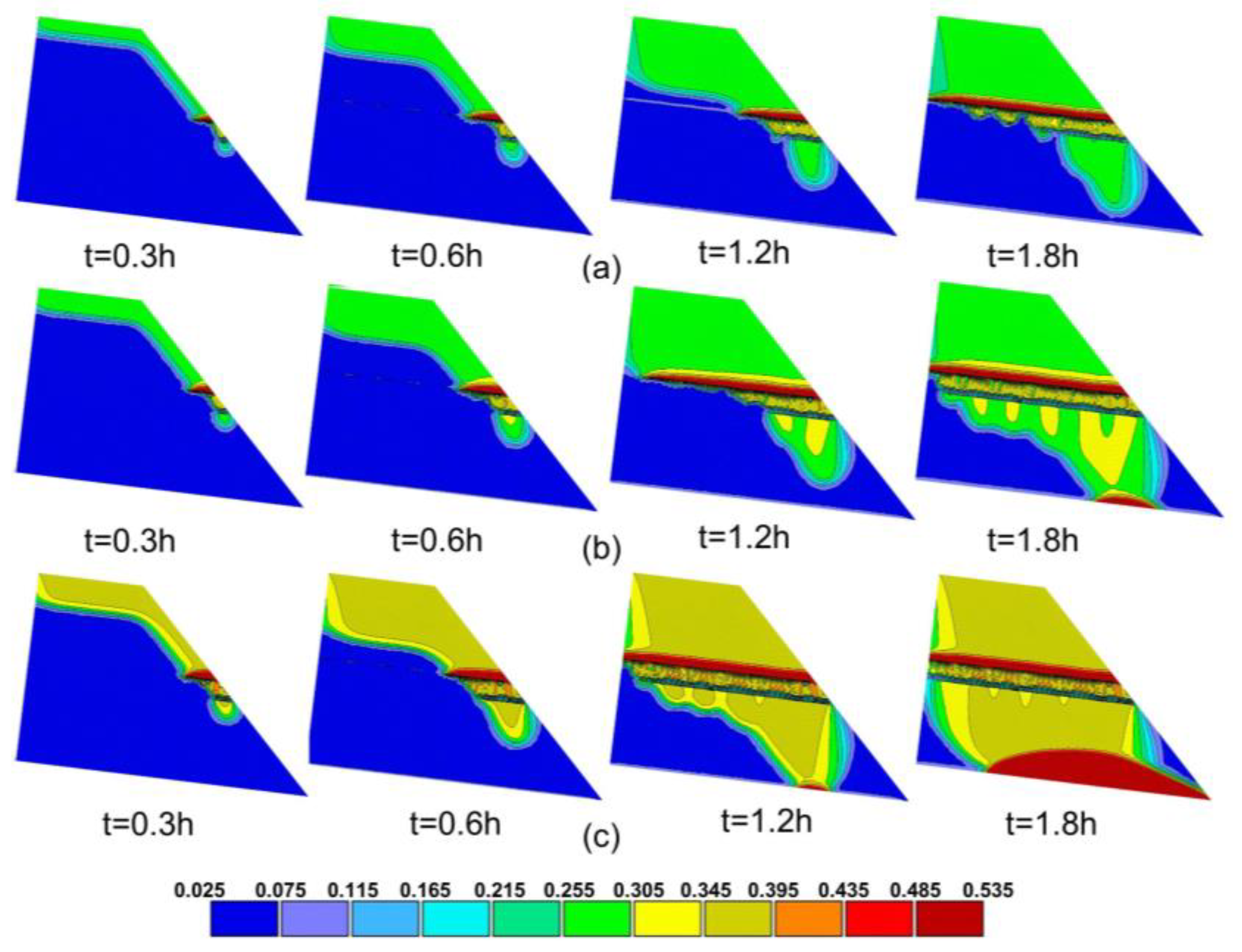
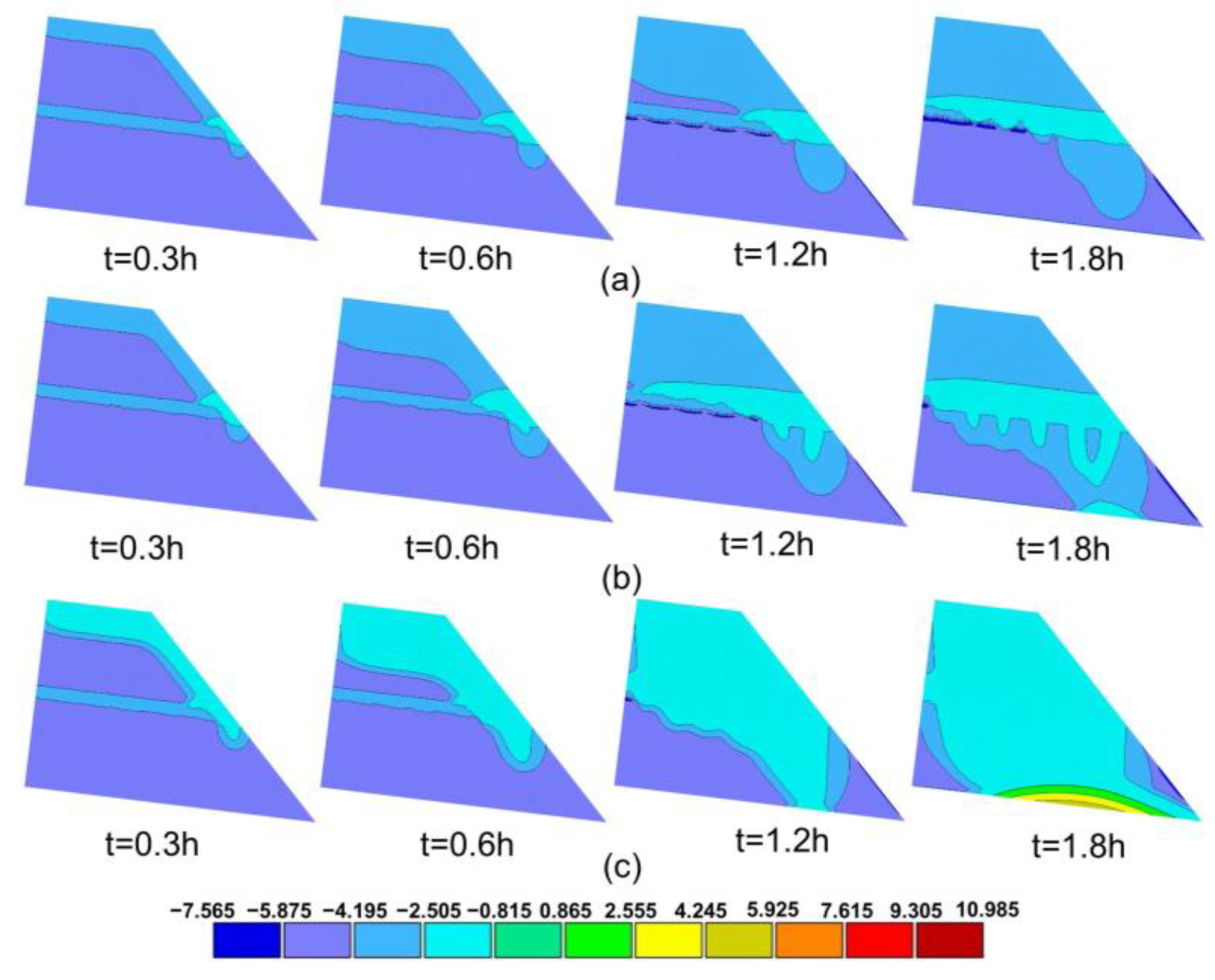
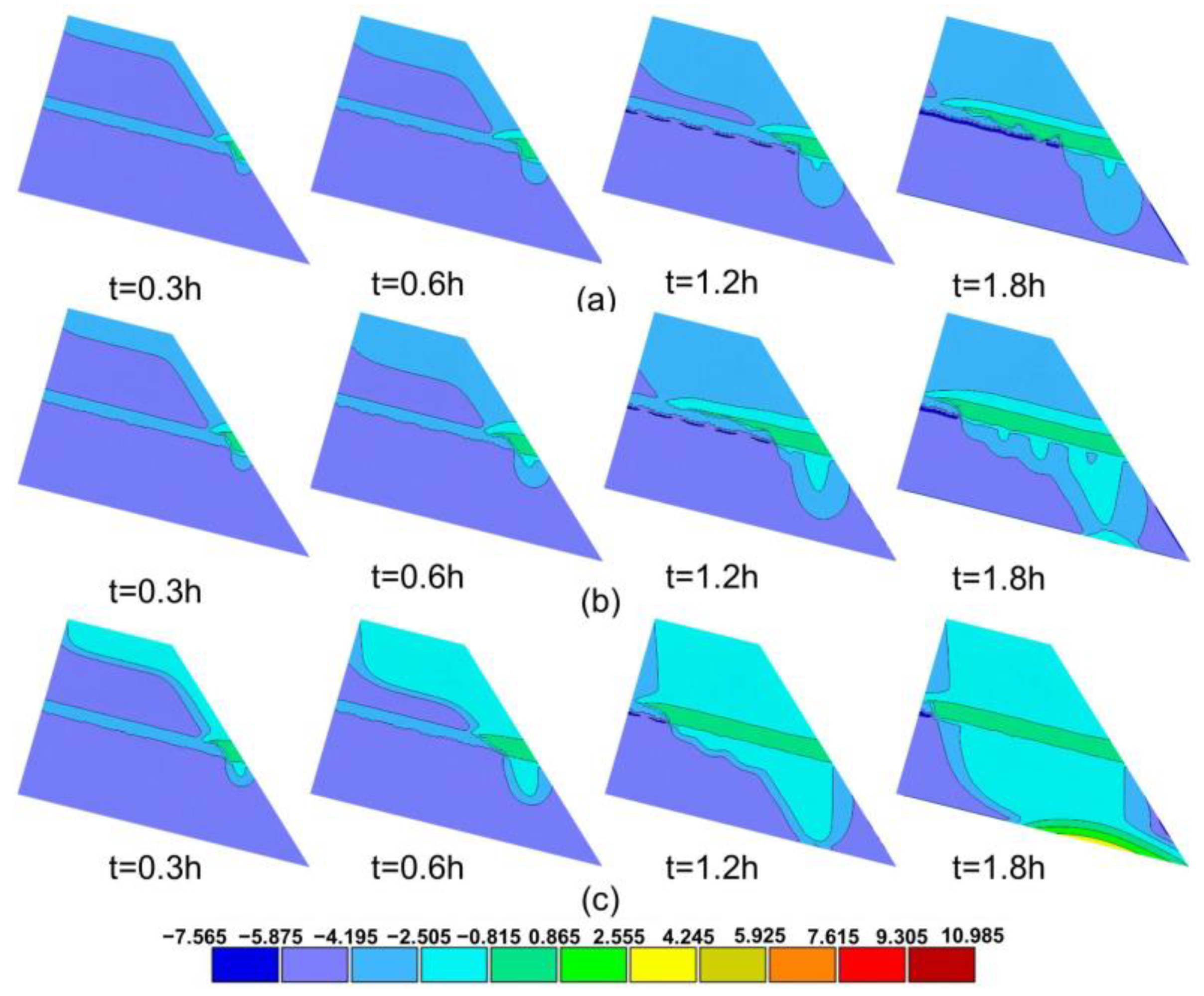
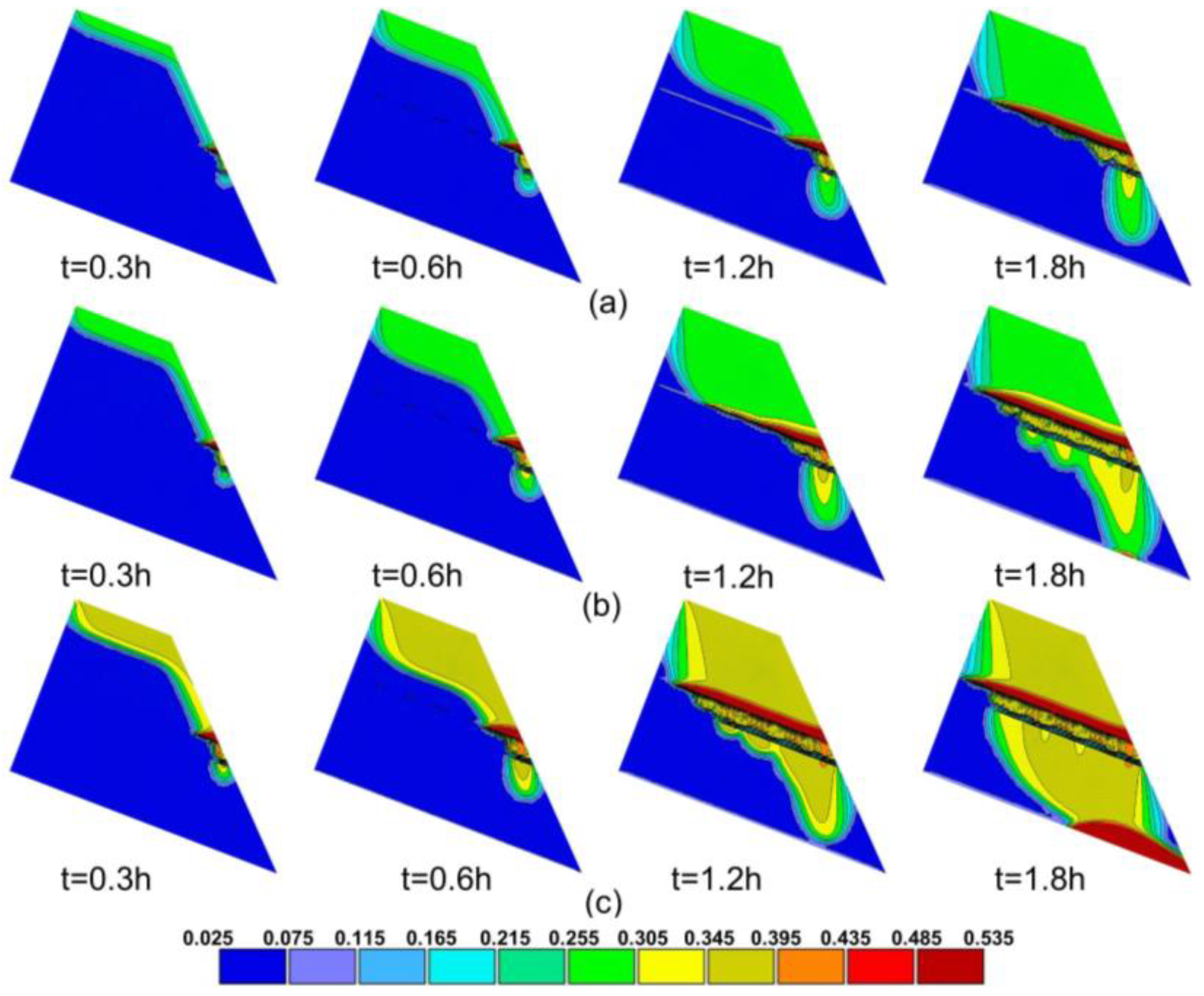
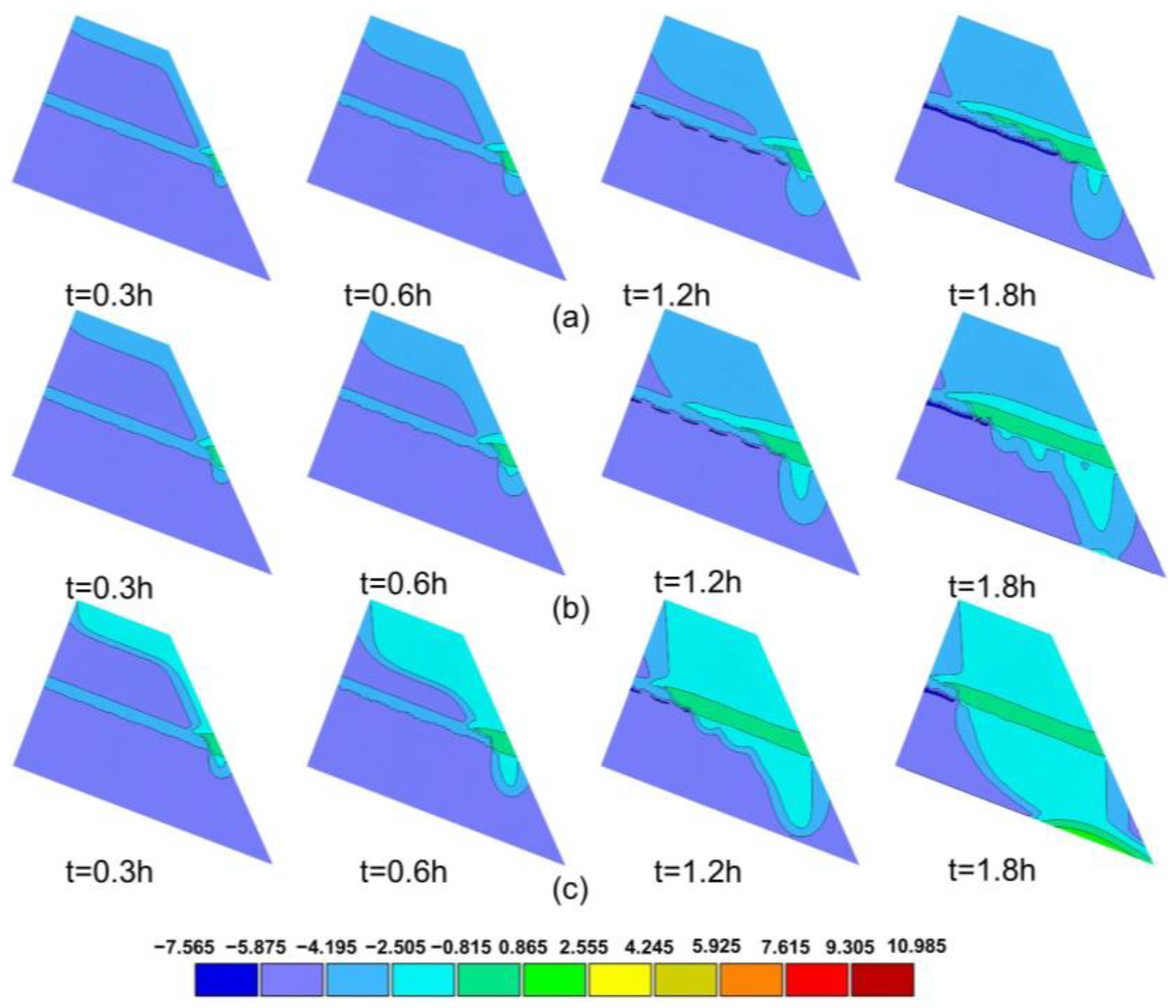
4.1. Profile Characterization of the Hydraulic Mechanisms
4.2. Hydraulic Response in the Slope
4.3. Infiltration Process in Multi-Layered Slope
4.4. Slope Stability Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larsen, M. Rainfall-triggered landslides, anthropogenic hazards, and mitigation strategies. Adv. Geosci. 2008, 14, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, H.; Tan, Q.; Mao, M.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, Y. A generalized early warning criterion for the landslide risk assessment: Deformation probability index (DPI). Acta Geotech. 2024, 19, 2607–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, L.; Picarelli, L. Shallow flowslides triggered by intense rainfalls on natural slopes covered by loose unsaturated pyroclastic soils. Géotechnique 2003, 53, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xue, K.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Bi, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, S.; Zhang, B. Study on the stability and disaster mechanism of layered soil slopes under heavy rain. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoso, A.M.; Phoon, K.-K.; Quek, S.-T. Effects of soil spatial variability on rainfall-induced landslides. Comput. Struct. 2011, 89, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Fu, Y.; Tang, H.; Gao, T.; An, P.; Wu, Q. Landslide model tests with a miniature 2D principal stress (PS) sensor. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, C.; Tang, H.; Wen, T.; Tannant, D.D.; Zhang, B. Input-parameter optimization using a SVR based ensemble model to predict landslide displacements in a reservoir area–A comparative study. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 150, 111107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Miao, M.; Tang, H.; Jia, S.; Dong, A.; An, P.; Zhang, B. Insights into the deformation and failure characteristic of a slope due to excavation through multi-field monitoring: A model test. Acta Geotech. 2023, 18, 1001–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourie, A. Predicting rainfall-induced slope instability. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Geotech. Eng. 1996, 119, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Tang, H.; Li, C.; Su, X.; An, P.; Sun, S. Centrifuge modelling of landslides and landslide hazard mitigation: A review. Geosci. Front. 2023, 14, 101493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polemio, M.; Petrucci, O. Rainfall as a Landslide Triggering Factor an Overview of Recent International Research; Thomas Telford Ltd.: London, UK, 2000; pp. 1219–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Guida, D.; Romanzi, G.; Nocera, N.; Sorbino, G. A preliminary model for the landslides of May 1998 in Campania Region L. Cascini. Geotech. Hard Soil 2000, 3, 1623. [Google Scholar]
- Miyabuchi, Y.; Maeno, F.; Nakada, S. The October 16, 2013 rainfall-induced landslides and associated lahars at Izu Oshima Volcano, Japan. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2015, 302, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-Q.; Zhang, L. Bayesian back analysis of unsaturated hydraulic parameters for rainfall-induced slope failure: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2024, 251, 104714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Lee Barbour, S.; Elshorbagy, A.; Zettl, J.D.; Cheng Si, B. Infiltration and drainage processes in multi-layered coarse soils. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 91, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, E. Effects of layering on triggering mechanisms of rainfall-induced landslides in unsaturated pyroclastic granular soils. Can. Geotech. J. 2019, 56, 1278–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, B. The diversion capacity of capillary barriers. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 2625–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrick, A.; Wierenga, P.; Pan, L. Downward water flow through sloping layers in the vadose zone: Analytical solutions for diversions. J. Hydrol. 1997, 192, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubertin, M.; Cifuentes, E.; Apithy, S.; Bussière, B.; Molson, J.; Chapuis, R.P. Analyses of water diversion along inclined covers with capillary barrier effects. Can. Geotech. J. 2009, 46, 1146–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, T.L.; Li, H.; Jia, G.; Chen, Y.; Fredlund, D. Physical and numerical study of lateral diversion by three-layer inclined capillary barrier covers under humid climatic conditions. Can. Geotech. J. 2014, 51, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancarella, D.; Doglioni, A.; Simeone, V. On Capillary Barrier Effects And Debris Slide Triggering In Unsaturated Layered Covers. Eng. Geol. 2012, 147–148, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xiong, H. Influence of layer transition zone on rainfall-induced instability of multilayered slope. Lithosphere 2021, 2021, 2277284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junfeng, T. Physical Model Experiments on Water Infiltration and Failure Modes in Multi-Layered Slopes under Heavy Rainfall. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.E. Infiltration analysis to evaluate the surficial stability of two-layered slopes considering rainfall characteristics. Eng. Geol. 2009, 105, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mburu, J.W.; Li, A.-J.; Lin, H.-D.; Lu, C.-W. Investigations of unsaturated slopes subjected to rainfall infiltration using numerical approaches—A parametric study and comparative review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stormont, J.C.; Anderson, C.E. Capillary Barrier Effect from Underlying Coarser Soil Layer. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 1999, 125, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, S.-É.; Cabral, A. Design of inclined covers with capillary barrier effect. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2006, 24, 689–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mayahi, A.K.; Al-Ismaily, S.S.; Breitenstein, D.; Al-Busaidi, H.S.; Al-Maktoumi, A.K.; Lehmann, P.; Or, D.; Kacimov, A.R.; Fahrni, S.; Al-Shukaili, A.H. Soil water distribution and dynamics across prescribed capillary barriers under evaporating surfaces. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 226, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stormont, J.C.; Morris, C.E. Method to estimate water storage capacity of capillary barriers. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 1998, 124, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M.J.; Azevedo, M.M.; Zornberg, J.G.; Palmeira, E.M. Capillary barriers incorporating non-woven geotextiles. Environ. Geotech. 2017, 5, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussière, B.; Aubertin, M.; Chapuis, R.P. A laboratory set up to evaluate the hydraulic behavior of inclined capillary barriers. In Physical Modelling in Geotechnics; Routledge: London, UK, 2022; pp. 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Aubertin, M.; Cifuentes, E.; Martin, V.; Apithy, S.; Bussière, B.; Molson, J.; Chapuis, R.P.; Maqsoud, A. An investigation of factors that influence the water diversion capacity of inclined covers with capillary barrier effects. In Unsaturated Soils 2006; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 2006; pp. 613–624. [Google Scholar]
- Hübner, R.; Günther, T.; Heller, K.; Noell, U.; Kleber, A. Impacts of a capillary barrier on infiltration and subsurface stormflow in layered slope deposits monitored with 3-D ERT and hydrometric measurements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 5181–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.E.; Stormont, J.C. Evaluation of numerical simulations of capillary barrier field tests. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 1998, 16, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capparelli, G.; Damiano, E.; Greco, R.; Olivares, L.; Spolverino, G. Physical modeling investigation of rainfall infiltration in steep layered volcanoclastic slopes. J. Hydrol. 2020, 580, 124199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredlund, D.G.; Rahardjo, H. Soil Mechanics for Unsaturated Soils; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Fredlund, D.G.; Xing, A.; Fredlund, M.; Barbour, S. The relationship of the unsaturated soil shear strength to the soil-water characteristic curve. Can. Geotech. J. 1996, 33, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Liu, J.; Ng, C.W.; Chen, Z.K. Influence of slope angle on water flow in a three-layer capillary barrier soil cover under heavy rainfall. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2019, 83, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chai, J.; Cao, J.; Qin, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X. Effects of seepage on a three-layered slope and its stability analysis under rainfall conditions. Nat. Hazards 2020, 102, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junfeng, T.; Taro, U.; Shangning, T.; Dong, H.; Jiren, X. Water movement and deformation in unsaturated multi-layered slope under heavy rainfall. GEOMATE J. 2020, 19, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Uchimura, T.; Tao, S.; Toda, T. Water movement in unsaturated multi-layered slope under heavy rainfall conditions in wetting and dry process. Jpn. Geotech. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2020, 8, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mualem, Y. A new model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Lu, N. Slope stability analysis under unsaturated conditions: Case studies of rainfall-induced failure of cut slopes. Eng. Geol. 2015, 184, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Cai, H.; Shao, W.; Huang, D.; Uchimura, T.; Lei, X.; Tian, H.; Qiao, J. Clarifying the hydrological mechanisms and thresholds for rainfall-induced landslide: In situ monitoring of big data to unsaturated slope stability analysis. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 2139–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, R.L.; Godt, J.W.; Savage, W.Z. Estimating the timing and location of shallow rainfall-induced landslides using a model for transient, unsaturated infiltration. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2010, 115, F03013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Godt, J.W. Hillslope Hydrology and Stability; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
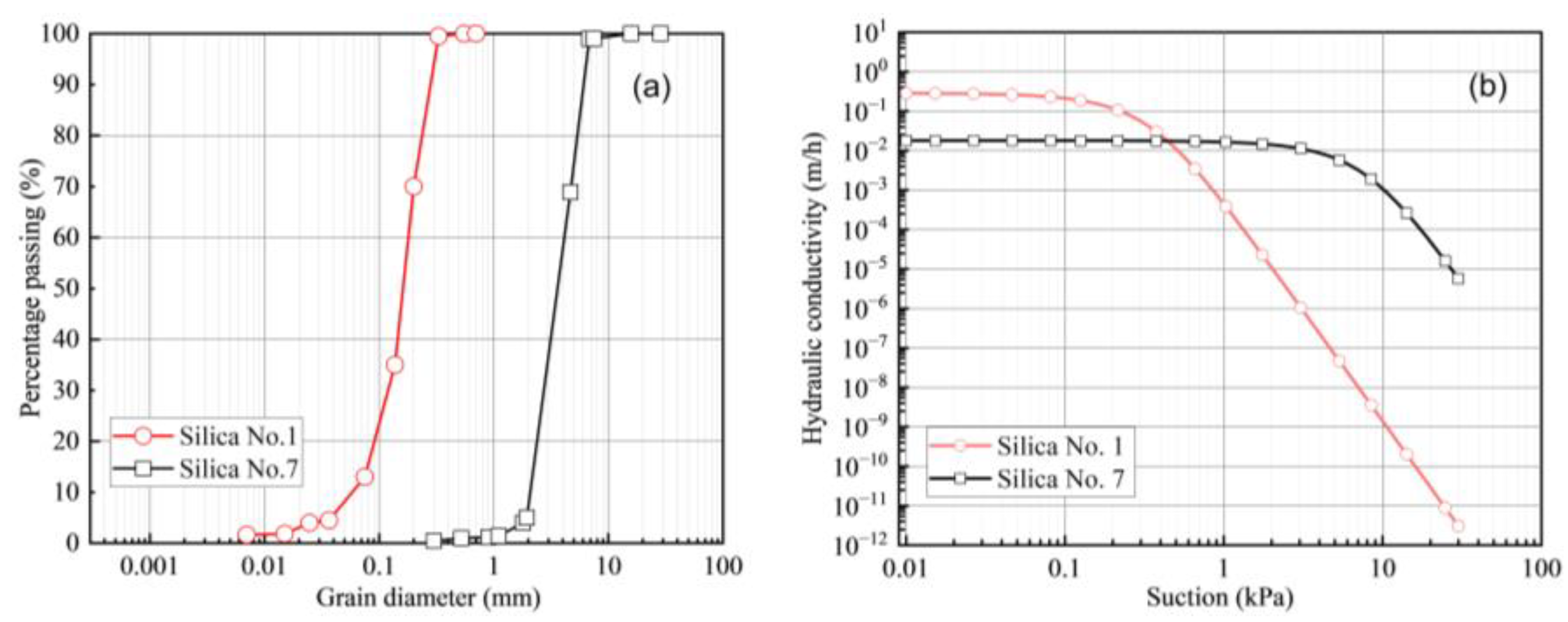


| Description | Silica No. 7 | Silica No. 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Specific gravity Gs | 2.63 | 2.62 |
| Gravel content (>4.75 mm; %) | 0 | 97.13 |
| Sand content (%) | 87.31 | 2.86 |
| Fine content (<0.075 mm; %) | 11.64 | 0 |
| D50 (mm) | 0.152 | 3.52 |
| (kPa) | 6.26 | 0.8 |
| 37.79° | 41° |
| Materials | Name | θr [−] | θs [−] | α [1/cm] | n [−] | [cm/h] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | S1 | 0.001 | 0.44 | 32.2 | 1.42 | 100 |
| 2 | S7 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 0.41 | 4.06 | 39 |
| Group | Experiment | Sediment Type | No. of Layers | Inclination (°) | Rainfall Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group I | Case 1 | Silica No. 7, Silica No. 1 | 3 | 7 | 30 mm/h |
| Case 2 | Silica No. 7, Silica No. 1 | 3 | 15 | 30 mm/h | |
| Case 3 | Silica No. 7, Silica No. 1 | 3 | 21 | 30 mm/h | |
| Group II | Case 4 | Silica No. 7, Silica No. 1 | 3 | 7 | 45 mm/h |
| Case 5 | Silica No. 7, Silica No. 1 | 3 | 15 | 45 mm/h | |
| Case 6 | Silica No. 7, Silica No. 1 | 3 | 21 | 45 mm/h | |
| Group III | Case 7 | Silica No. 7, Silica No. 1 | 3 | 7 | 75 mm/h |
| Case 8 | Silica No. 7, Silica No. 1 | 3 | 15 | 75 mm/h | |
| Case 9 | Silica No. 7, Silica No. 1 | 3 | 21 | 75 mm/h |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, X.; Mi, J. Numerical Modeling of Hydrological Mechanisms and Instability for Multi-Layered Slopes. Water 2024, 16, 2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172422
Tang J, Ma Z, Zhou D, Zhang S, Zhang F, Zhou X, Mi J. Numerical Modeling of Hydrological Mechanisms and Instability for Multi-Layered Slopes. Water. 2024; 16(17):2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172422
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Junfeng, Zhuxiang Ma, Dezhou Zhou, Shiyu Zhang, Fengmin Zhang, Xingyu Zhou, and Jinping Mi. 2024. "Numerical Modeling of Hydrological Mechanisms and Instability for Multi-Layered Slopes" Water 16, no. 17: 2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172422
APA StyleTang, J., Ma, Z., Zhou, D., Zhang, S., Zhang, F., Zhou, X., & Mi, J. (2024). Numerical Modeling of Hydrological Mechanisms and Instability for Multi-Layered Slopes. Water, 16(17), 2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172422








