Combined Toxic Effects and Mechanisms of Chloroacetic Acid and N-Nitrosodimethylamine on Submerged Macrophytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Determination of Plant Growth and Chlorophylls
2.4. Enzyme and Total Protein Extraction and Assay
2.5. Microscopic Examination
2.6. Metabolomics Analysis
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Impacts of CAA and NDMA on V. natans Growth and Chlorophylls
3.2. Oxidative Stress Response
3.3. Evaluation of the Combined Toxicity of CAA and NDMA
3.4. Ultrastructural Changes in the Mesophyll Cells of V. natans
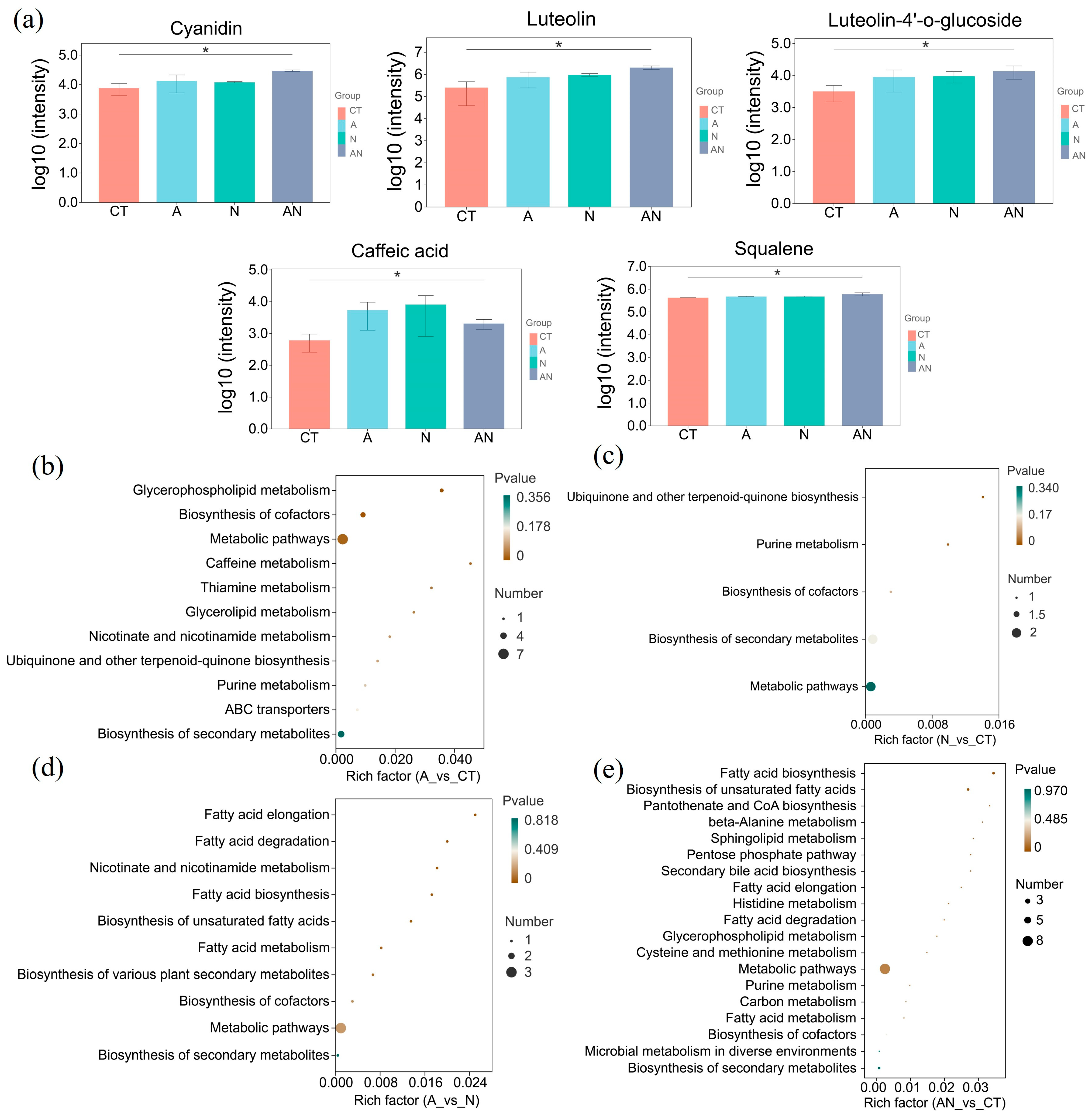
3.5. Metabolic Analysis of V. natans Leaves
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.G.; Song, G.F.; Bi, Y.H.; Gao, W.; He, A.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.W.; Jiang, G.B. Occurrence and distribution of disinfection by products in domestic wastewater effluent, tap water, and surface water during the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4103–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liao, M.F.; He, B.S.; Liu, J.; Hu, X.M.; Yan, D.; Wang, J. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on household disinfectant consumption behaviors and related environmental concerns: A questionnaire-based survey in China. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D. COVID-19 Rarely Spreads through Surfaces. So Why Are We Still Deep Cleaning? Nature 2021, 590, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.H.; Szczuka, A.; Mitch, W.A. Comparison of Toxicity-Weighted Disinfection Byproduct Concentrations in Potable Reuse Waters and Conventional Drinking Waters as a New Approach to Assessing the Quality of Advanced Treatment Train Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3729–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Xiao, F.; Wu, H.; Zou, H. Effects of disinfection by-products in sewage treatment plant effluent on the growth and physiology of Chlorella vulgaris. Huanjing Huaxue-Environ. Chem. 2023, 42, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.H.; Shen, J.; Luan, X.M.; Xiao, R.; Xu, Z.X. Study on secondary risk of water environment under enhanced disinfection of wastewater treatment plant during epidemic prevention and control. Water Wastewater Eng. 2020, 56, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Nabi, G.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Y.J.; Khan, S.; Wu, Y.F.; Li, D.M. Massive use of disinfectants against COVID-19 poses potential risks to urban wildlife. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.S.; Meng, F.B.; Zhang, D.Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, X.; Huang, X.; Qu, J.H. Spatial variation of dissolved organic nitrogen in Wuhan surface waters: Correlation with the occurrence of disinfection byproducts during the COVID-19 pandemic. Water Res. 2021, 198, 117138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Q.; Zhang, X.R. Comparative toxicity of new halophenolic DBPs in chlorinated saline wastewater effluents against a marine alga: Halophenolic DBPs are generally more toxic than haloaliphatic ones. Water Res. 2014, 65, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.J.; Chen, B.Y.; Jiang, Y.L.; Tao, Y.; Zhu, X.S.; Cai, Z.H. Toxicity of 17 Disinfection By-products to Different Trophic Levels of Aquatic Organisms: Ecological Risks and Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 10534–10541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, A.; Ferreira, C.; Ferreira, I.M.P.L.V.O.; Mansilha, C. Acute and chronic toxicity assessment of haloacetic acids using. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2019, 82, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.G.; Liu, X.Y.; Huang, Z.J.; Hu, S.Y.; Wang, J.J.; Qian, Z.Y.; Feng, J.F.; Xian, Q.M.; Gong, T.T. Occurrence and ecological risk assessment of disinfection byproducts from chlorination of wastewater effluents in East China. Water Res. 2019, 157, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Ni, J.W.; Tian, F.X.; Ji, X.Y.; Hou, M.F.; Li, Y.T.; Yang, L.; Wang, R.X.; Xu, W.W.; Meng, L. Toxicity effects of disinfection byproduct chloroacetic acid to Microcystis aeruginosa: Cytotoxicity and mechanisms. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 129, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breider, F.; Aquillon, C.G.; von Gunten, U. A survey of industrial N-nitrosamine discharges in Switzerland. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plewa, M.J.; Kargalioglu, Y.; Vankerk, D.; Minear, R.A.; Wagner, E.D. Mammalian cell cytotoxicity and genotoxicity analysis of drinking water disinfection by-products. Env. Mol. Mutagen. 2002, 40, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, M.; Longrée, P.; Dorusch, F.; Ort, C.; Hollender, J. Occurrence and removal of N-nitrosamines in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4381–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.H.; Shabani, F.; Munoz, J.; Aflaki, R.; Hammond, S.D.; Mitch, W.A. Comparing industrial and domestic discharges as sources of N-nitrosamines and their chloramine or ozone-reactive precursors. Environ. Sci.-Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.L.; McCraven, S.; Garcia, J.; Gasca, M.; Johnson, T.A.; Motzer, W.E. Field evidence of biodegradation of N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) in groundwater with incidental and active recycled water recharge. Water Res. 2009, 43, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.F.; Ren, S.Y.; Zhang, H.F.; Yu, J.W.; An, W.; Hu, J.Y.; Yang, M. Occurrence of nine nitrosamines and secondary amines in source water and drinking water: Potential of secondary amines as nitrosamine precursors. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4930–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.J.; Wan, Y.; Yuan, G.X.; Meng, L.P.; Dong, Z.M.; Hu, J.Y. Occurrence and source of nitrosamines and secondary amines in groundwater and its adjacent Jialu River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3236–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.G.; Wang, W.L.; Zhou, J.L.; Yi, X.L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.N.; Liu, Z.T. Screening of high phytotoxicity priority pollutants and their ecological risk assessment in China’s surface waters. Chemosphere 2015, 128, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.A.; Wu, Z.H. Growth and antioxidant response in Ceratophyllum demersum L. under sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), phenol and joint stress. Ecotox Environ. Safe 2018, 163, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.M.; Gao, Y.; Hu, Z.X.; Jiang, X.; Yang, L.Y. The Growth of and Its Epiphytic Biofilm in Simulated Nutrient-Rich Flowing Water. Water 2022, 14, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K.; Wellburn, A.R. Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1983, 11, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Luo, X.; Huang, S.; Zheng, Z. Combined toxic effects of enrofloxacin and microplastics on submerged plants and epiphytic biofilms in high nitrogen and phosphorus waters. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Y.; Liu, B.; Ma, H.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; Moenga, S.; Riely, B.; Fayyaz, A.; Wang, M.; Li, H. The methionine biosynthesis regulator AaMetR contributes to oxidative stress tolerance and virulence in Alternaria alternata. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 219, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Li, Q.; Luo, X.; Fu, J.; Zhang, J.B. Responses of the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans to a water depth gradient. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhu, L.Z. Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Investigation of Metabolic Perturbations in Oryza sativa L. Triggered by Three Pesticides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6115–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Oyang, X.; Xie, X.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Xi, J.; Guo, Y.; Tian, X.; Liu, B.; Li, J.; et al. Phytotoxicity induced by perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate via metabolomics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, W.S. A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Econ. Entomol. 1925, 18, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatidou, G.; Thomaidis, N.S. Evaluation of single and joint toxic effects of two antifouling biocides, their main metabolites and copper using phytoplankton bioassays. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 85, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.G.; Li, E.H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.L.; Song, L.R. Combined toxic effects and mechanisms of microsystin-LR and copper on Vallisneria Natans (Lour.) Hara seedlings. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 328, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.C.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; Ji, R.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, J.G.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Guo, H.Y. Physiological and biochemical changes imposed by CeO2 nanoparticles on wheat: A life cycle field study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11884–11893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, F.; Jia, Y.L.; Yang, C.P.; Li, T.L.; Wu, Z.X.; Liu, J.; Song, L.R. Multiple physiological response analyses aid the understanding of sensitivity variation between Microcystis aeruginosa and Chlorella sp. under paraquat exposures. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, V.; Shahzad, B.; Ramakrishnan, M.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Bali, A.S.; Handa, N.; Kapoor, D.; Yadav, P.; Khanna, K.; et al. Photosynthetic response of plants under different abiotic stresses: A review. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 39, 509–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 909–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Ma, X.X.; Wang, Y.R.; Saleem, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.M. Ecotoxicity of herbicide carfentrazone-ethyl towards earthworm in soil. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 2022, 253, 109250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Huang, D.Y.; Deng, H.; Zhang, J.B. Responses of submerged plant Vallisneria natans growth and leaf biofilms to water contaminated with microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Zhong, G.D.; Zhou, J.N.; Liu, Y.L.; Pang, Y.J.; Cai, H.; Wu, Z.H. Separate and combined effects of glyphosate and copper on growth and antioxidative enzymes in Salvinia natans (L.) All. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torok, A.; Gulyas, Z.; Szalai, G.; Kocsy, G.; Majdik, C. Phytoremediation capacity of aquatic plants is associated with the degree of phytochelatin polymerization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Chen, X.K.; Kong, C.M.; Gao, D.D.; Liu, W.J.; Liao, H.P.; Junaid, M.; Wang, J. Single and combined toxicity of polystyrene nanoplastics and PCB-52 to the aquatic duckweed Spirodela polyrhiza. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 166482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.Z.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.X.; Yu, Y.J.Z.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Xiao, Y.X.; Wen, Y.L.; Wang, Q.C.; Lei, N.F.; et al. Joint toxicity mechanisms of perfluorooctanoic acid and sulfadiazine on submerged macrophytes and periphytic biofilms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 131910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, T.; Templeton, M.R.; Kamal, N.H.M.; Graham, N.; Kanda, R. Nitrogenous disinfection byproducts in English drinking water supply systems: Occurrence, bromine substitution and correlation analysis. Water Res. 2015, 85, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Liu, C.L.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Y.T.; Hu, H.T.; Jahan, N.; Lv, Y.; Qian, Q.; Guo, L.B. A 3-bp deletion of WLS5 gene leads to weak growth and early leaf senescence in rice. Rice 2019, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalmann, M.; Santelia, D. Starch as a determinant of plant fitness under abiotic stress. New Phytol. 2017, 214, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, G.H.; Singhal, R.; Kachroo, A.; Kachroo, P. Fatty Acid- and Lipid-Mediated Signaling in Plant Defense. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2017, 55, 505–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhou, C.; Fan, J.; Shanklin, J.; Xu, C. Mechanisms and functions of membrane lipid remodeling in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 107, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Liu, W.; Shi, R.; Zeb, A.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Zheng, Z.; Tang, J. Effects of polyethylene and polylactic acid microplastics on plant growth and bacterial community in the soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Luo, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, L.; Feng, S.; Yuan, M.; Ding, C. Polyphenols from Blumea laciniata Extended the Lifespan and Enhanced Resistance to Stress in Caenorhabditis elegans via the Insulin Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.N.; Shang, N.Y.; Kang, Y.Y.; Sheng, N.; Lan, J.Q.; Tang, J.S.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.L.; Peng, Y. Caffeic acid alleviates cerebral ischemic injury in rats by resisting ferroptosis via Nrf2 signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 45, 248–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, C.M.; Wagner, D.C.; Ofoegbu, P.C.; Kirwa, N.J.; Clubb, P.; Coates, K.; Zenobio, J.E.; Adeleye, A.S. Toxicity assessment of perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) on a spontaneous plant, velvetleaf (Abutilon theophrasti), via metabolomics. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
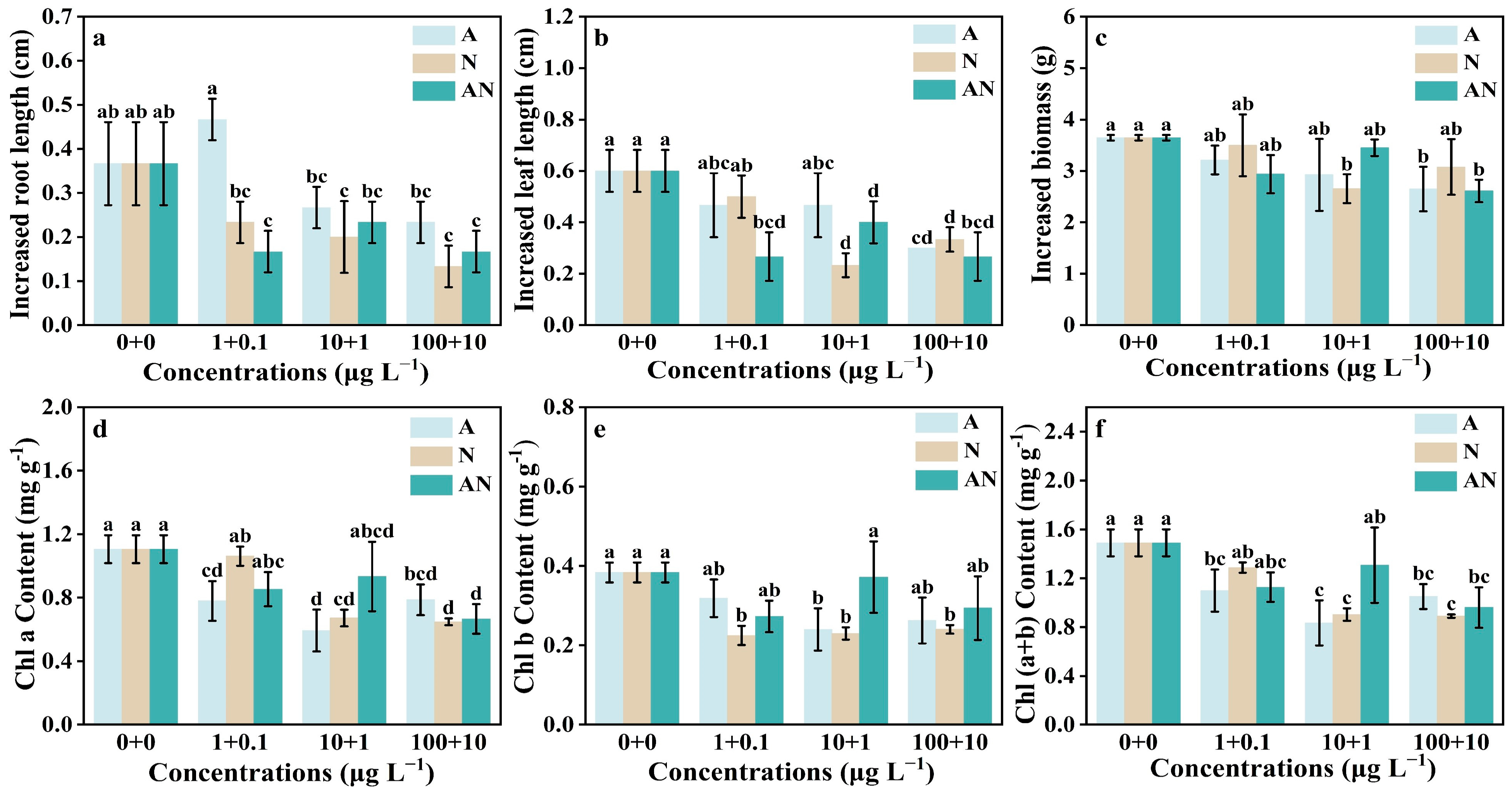
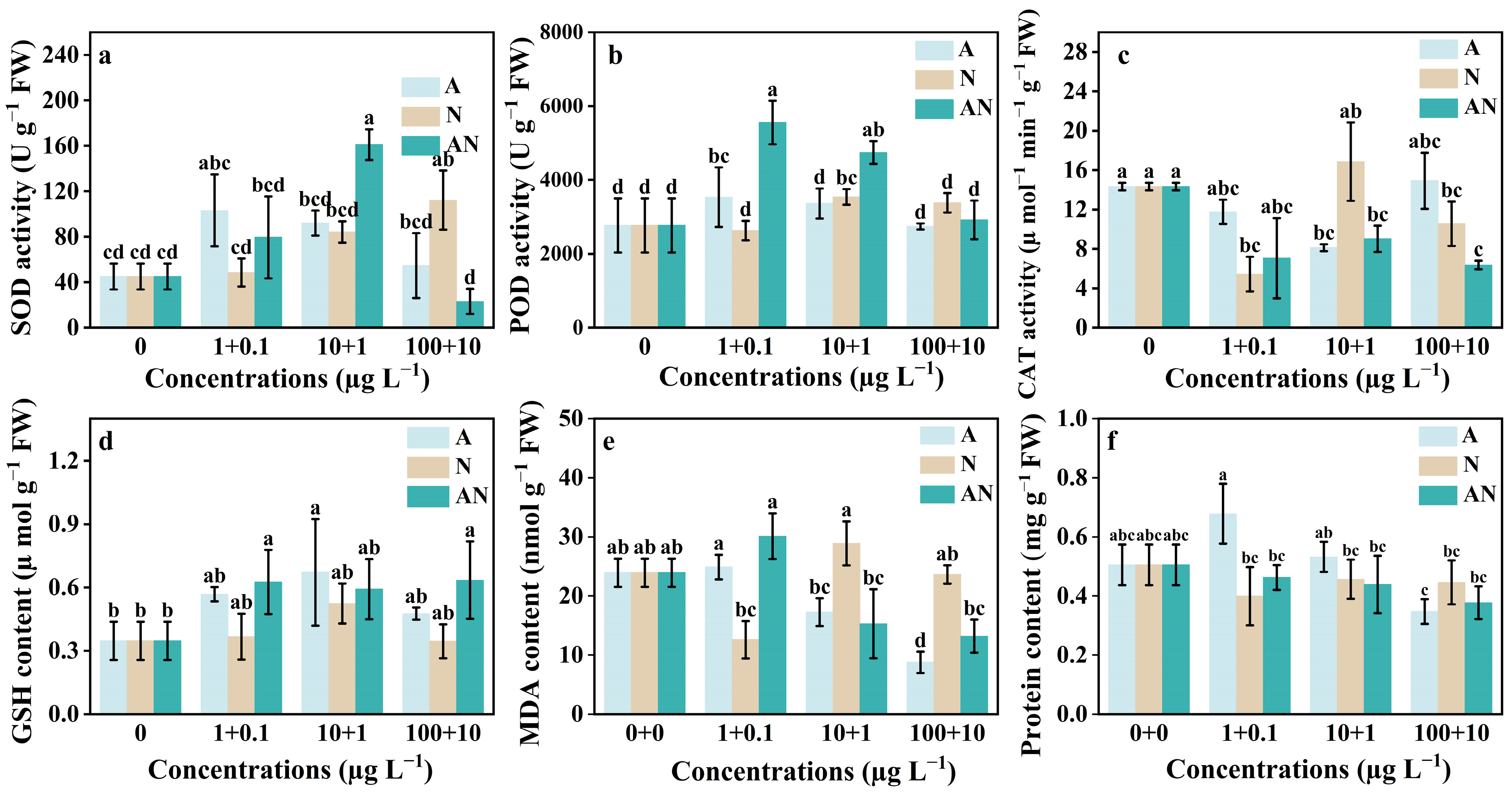
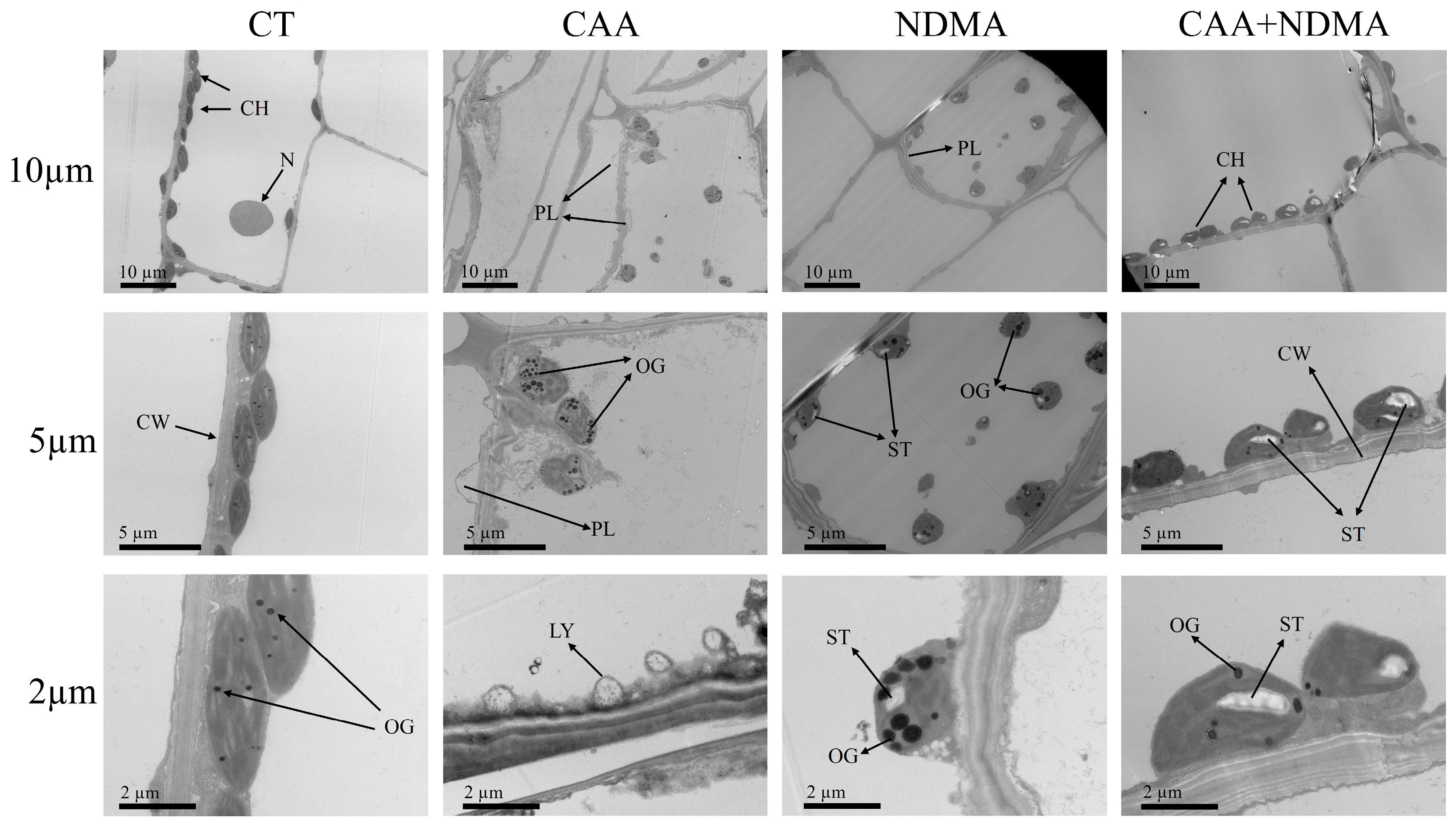
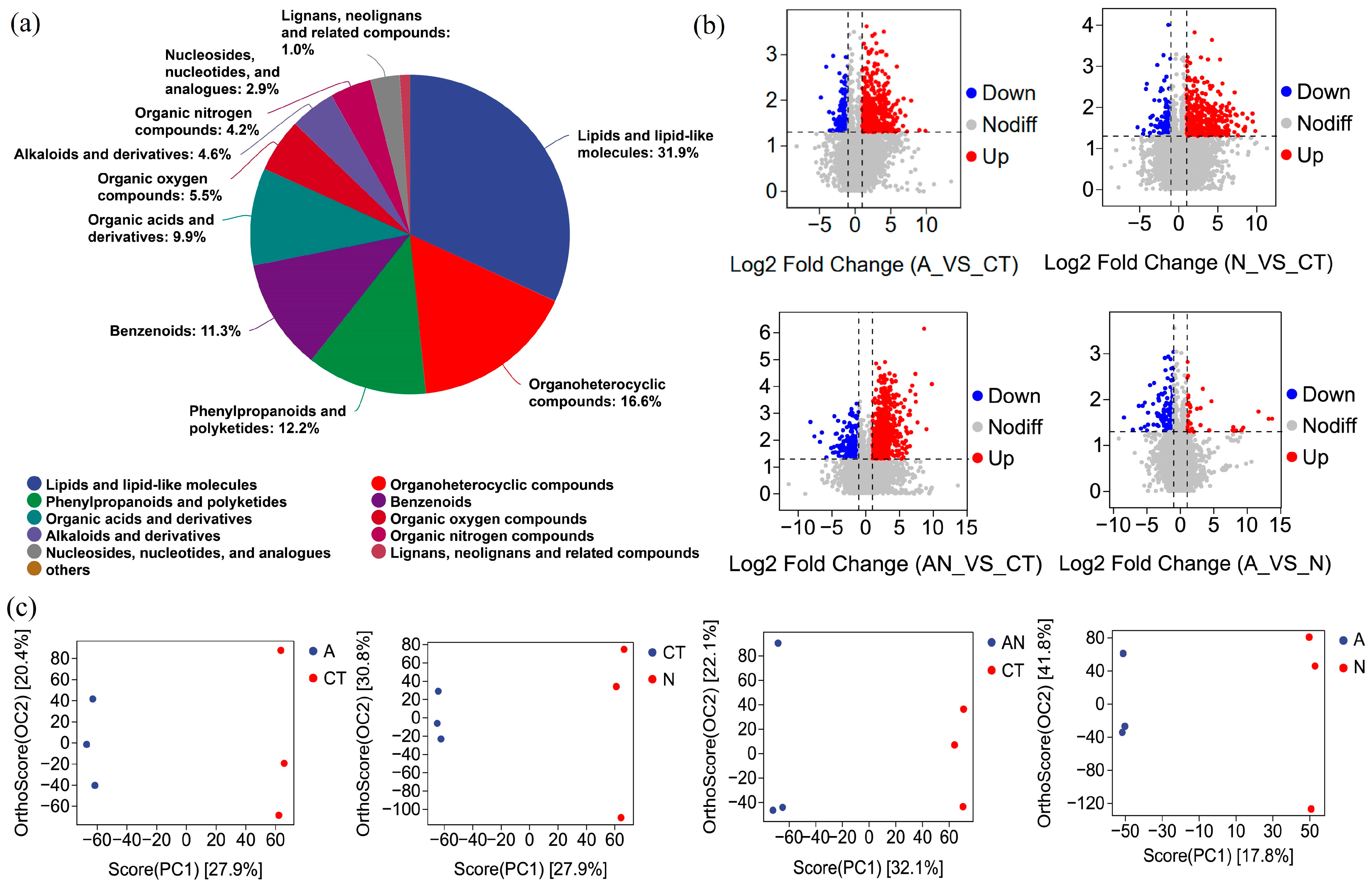
| Indicators | CAA (μg L−1) | A | NDMA (μg L−1) | B | AN (μg L−1) | Observed Inhibition (%) | Cexp (%) | RI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.00 | 26.26 | 0.10 | 13.60 | 1.00 + 0.10 | 24.36 | 36.29 | 0.67 | |
| Chl (a + b) | 10.00 | 44.08 | 1.00 | 39.40 | 10.00 + 1.00 | 12.30 | 66.11 | 0.19 |
| 100.00 | 29.52 | 10.00 | 40.29 | 100.00 + 10.00 | 35.49 | 57.92 | 0.61 | |
| 1.00 | −128.96 | 0.10 | −7.70 | 1.00 + 0.10 | −76.37 | −146.59 | 0.52 | |
| SOD | 10.00 | −104.19 | 1.00 | −87.03 | 10.00 + 1.00 | −257.41 | −281.90 | 0.91 |
| 100.00 | −21.41 | 10.00 | −149.06 | 100.00 + 10.00 | 48.72 | −202.39 | −0.24 | |
| 1.00 | −102.41 | 0.10 | −30.94 | 1.00 + 0.10 | −123.17 | −165.03 | 0.75 | |
| GSH | 10.00 | −139.38 | 1.00 | −86.83 | 10.00 + 1.00 | −111.02 | −347.23 | 0.32 |
| 100.00 | −69.66 | 10.00 | −23.18 | 100.00 + 10.00 | −126.18 | −108.98 | 1.16 | |
| 1.00 | −4.01 | 0.10 | 47.39 | 1.00 + 0.10 | −25.89 | 45.28 | −0.57 | |
| MDA | 10.00 | 27.86 | 1.00 | −20.75 | 10.00 + 1.00 | 36.03 | 12.89 | 2.80 |
| 100.00 | 63.41 | 10.00 | 1.27 | 100.00 + 10.00 | 44.87 | 63.87 | 0.70 | |
| 1.00 | −34.19 | 0.10 | 20.95 | 1.00 + 0.10 | 8.48 | −6.08 | −1.39 | |
| Protein | 10.00 | −5.33 | 1.00 | 9.66 | 10.00 + 1.00 | 13.13 | 4.84 | 2.71 |
| 100.00 | 31.29 | 10.00 | 11.78 | 100.00 + 10.00 | 25.42 | 39.38 | 0.65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, K.; Huang, H.; Huang, X.; Lao, A.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, H. Combined Toxic Effects and Mechanisms of Chloroacetic Acid and N-Nitrosodimethylamine on Submerged Macrophytes. Water 2024, 16, 2689. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182689
Huang K, Huang H, Huang X, Lao A, Zheng Z, Wu H. Combined Toxic Effects and Mechanisms of Chloroacetic Acid and N-Nitrosodimethylamine on Submerged Macrophytes. Water. 2024; 16(18):2689. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182689
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Kaili, Haiqing Huang, Xuhui Huang, An Lao, Zheng Zheng, and Hanqi Wu. 2024. "Combined Toxic Effects and Mechanisms of Chloroacetic Acid and N-Nitrosodimethylamine on Submerged Macrophytes" Water 16, no. 18: 2689. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182689






