Comprehensive Study on Hydrogeological Conditions and Suitability Evaluation of In Situ Leaching for Sandstone-Hosted Uranium Deposit in Erlian Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
2.1. Physical Geography
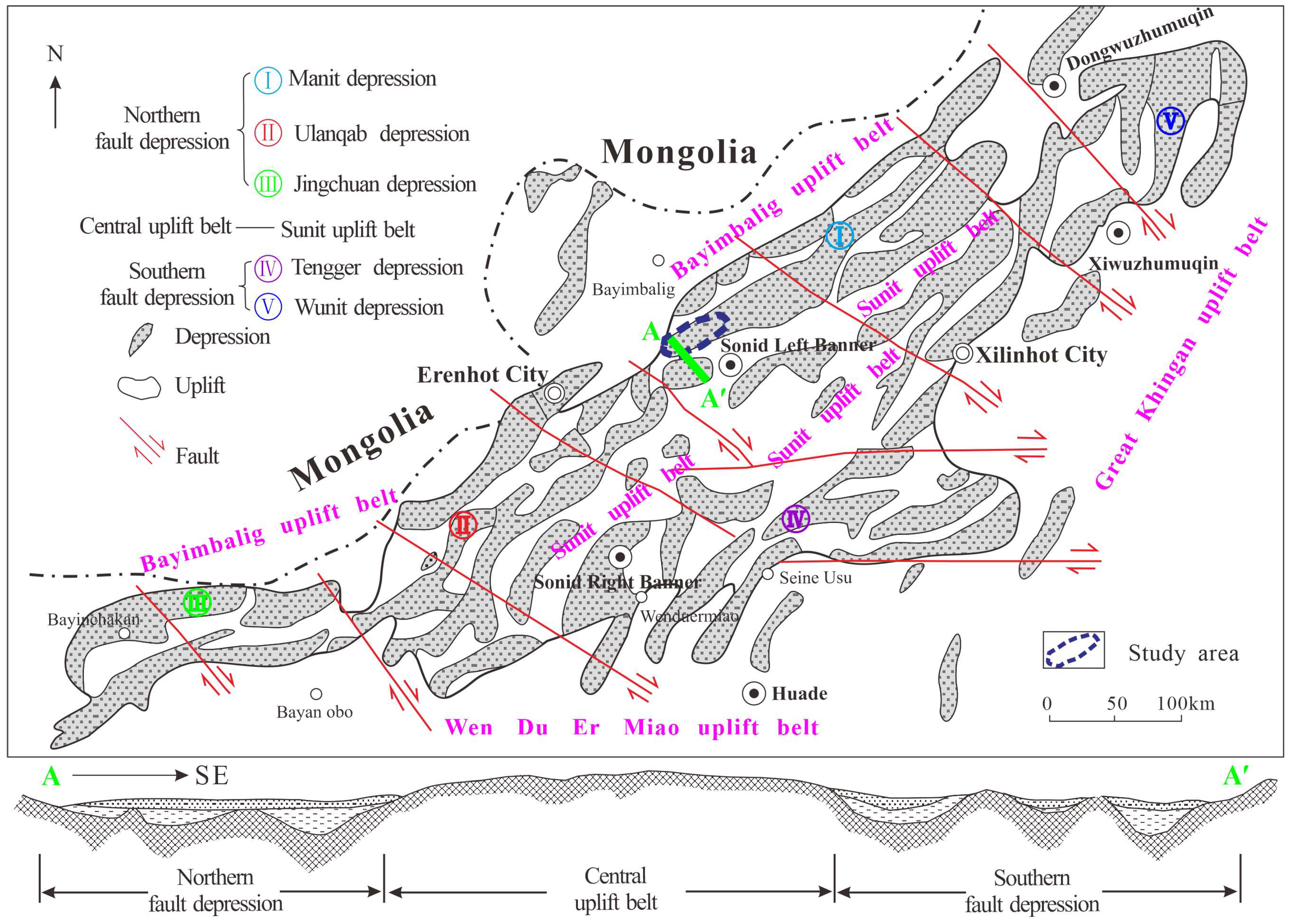
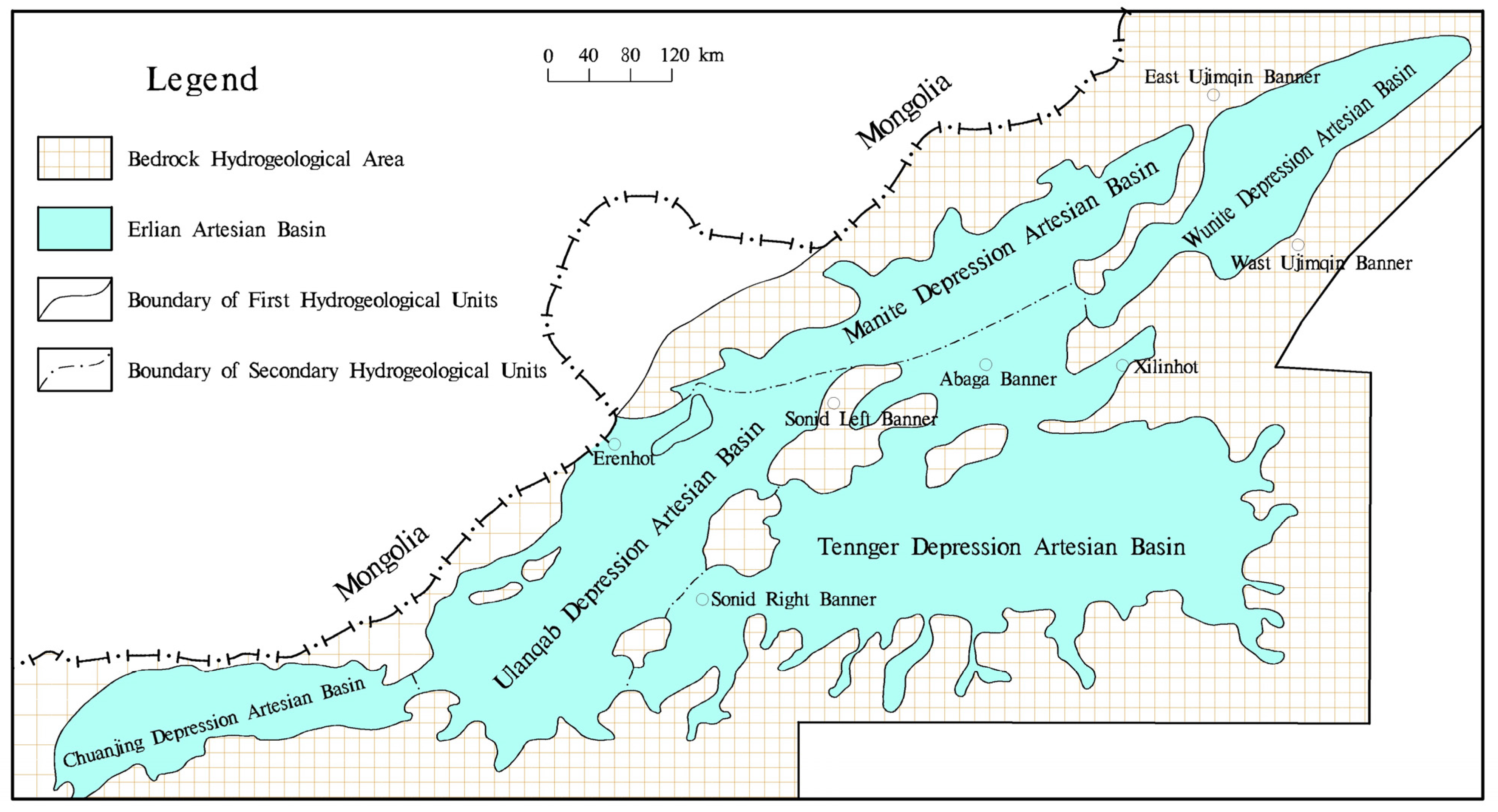
2.2. Regional Geological Structure
2.3. Regional Stratigraphy
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
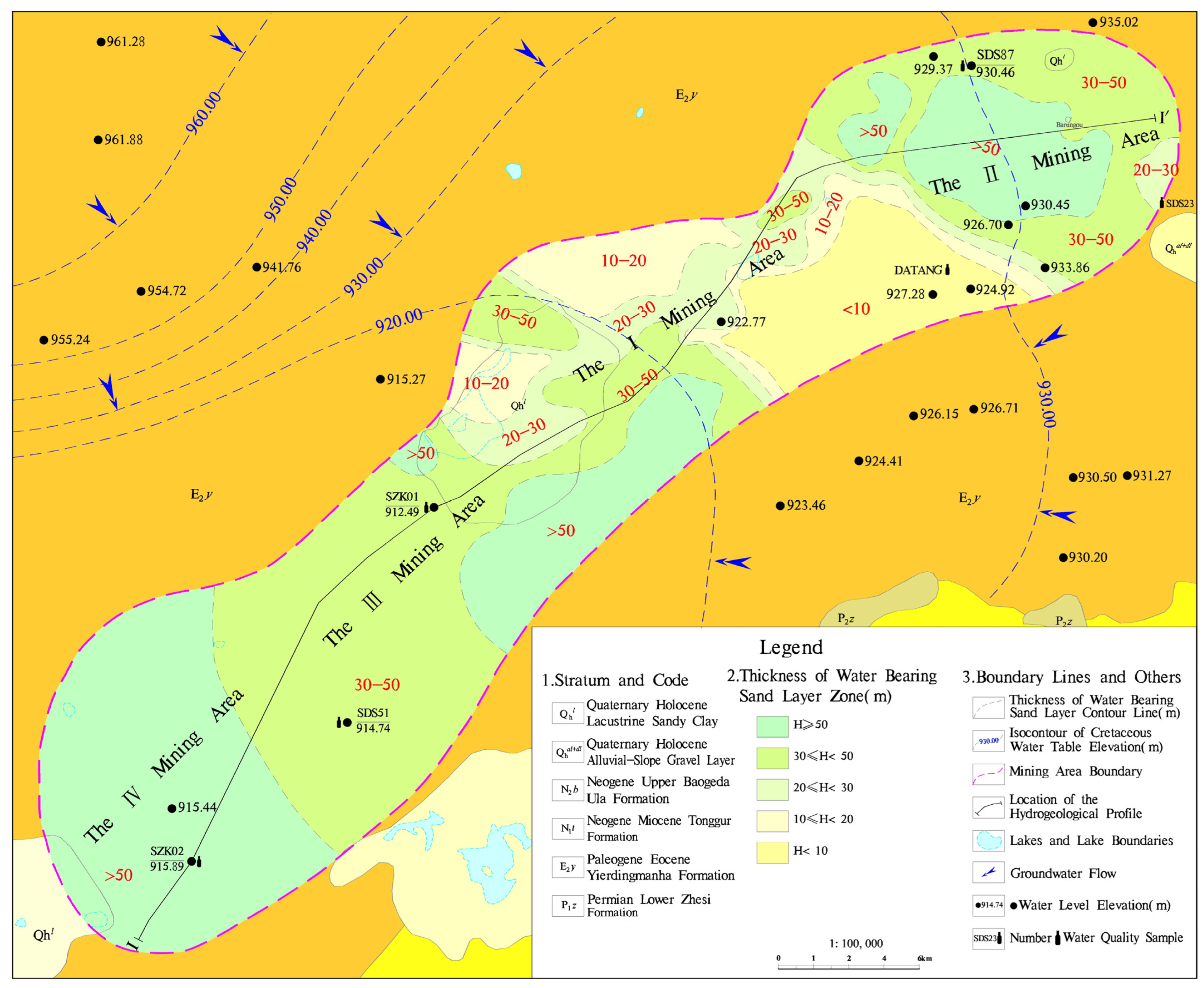
4.1. Hydrogeological Characteristics of Uranium Ore Beds in the Luhai Mining Area
4.1.1. Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Groundwater
4.1.2. Hydrogeological Study of Uranium Deposit
- (1)
- Hydrogeological Characteristics of U-hosting Aquifer in Orebody II
- (2)
- Hydrogeological Characteristics of U-hosting Aquifer in Orebody I
- (3)
- Hydrogeological Characteristics of U-hosting Aquifer in Orebodies III-IV
4.1.3. Genetic Analysis of Sandstone-Type Uranium Deposits in the Luhai Area
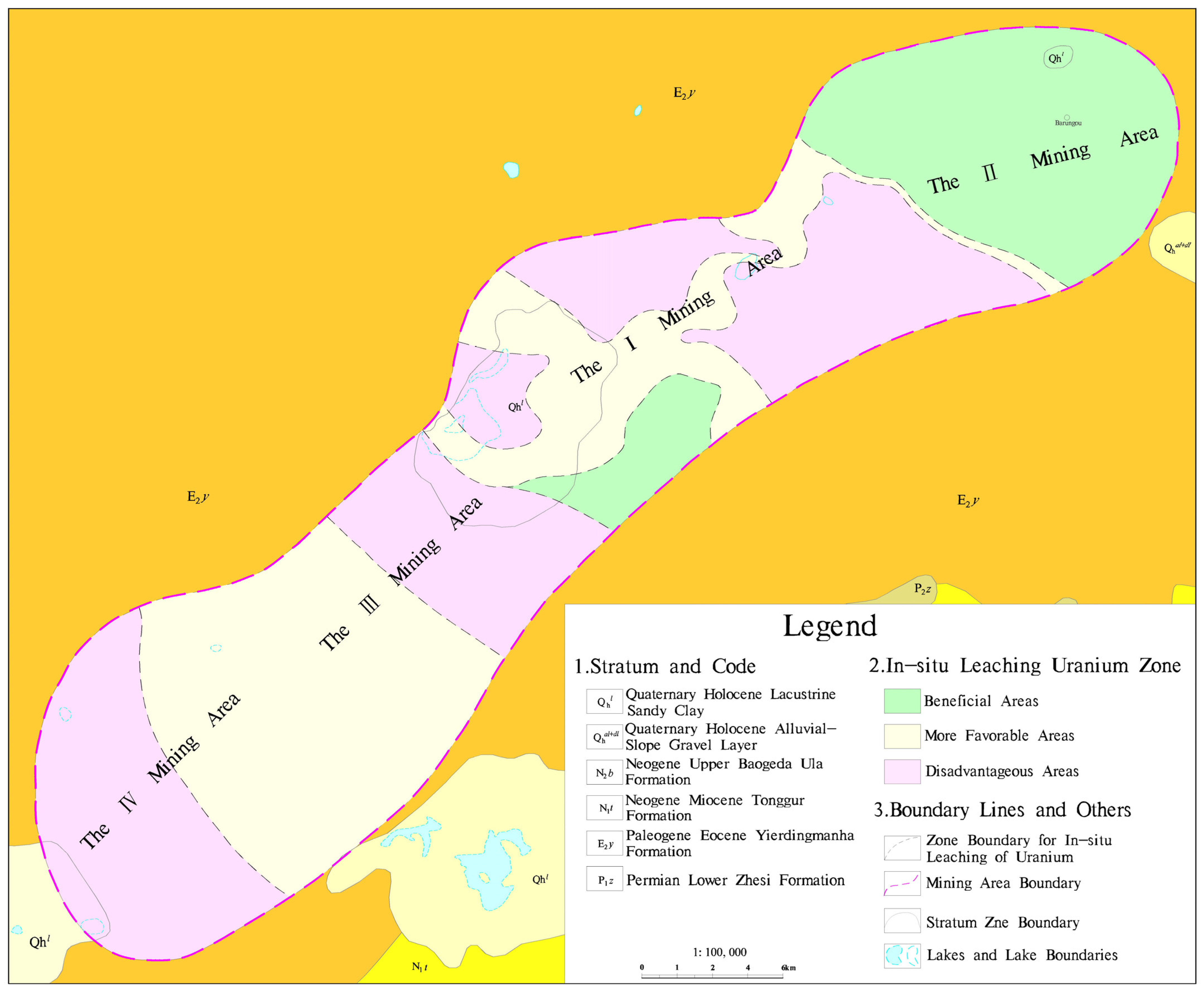
4.2. Evaluation of Suitability for Leaching and Mining of Sandstone-Type Uranium Ore
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cobb, J. World Nuclear Performance Report 2017. VGB PowerTech 2017, 12, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Tsouris, C. Uranium extraction: Fuel from seawater. Nat. Energy 2017, 4, 17022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cui, W.; Zhang, C.; Liang, R.; Qiu, J. Regenerable, anti-biofouling covalent organic frameworks for monitoring and extraction of uranium from seawater. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Gao, J.; Wang, D.; Yuan, Y.; Wen, J.; Yan, B.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X. Sunlight Polymerization of Poly(amidoxime) Hydrogel Membrane for Enhanced Uranium Extraction from Seawater. Adv. Sci. 2019, 13, 1900085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yu, Q.; Cao, M.; Feng, L.; Feng, S.; Liu, T.; Feng, T.; Yan, B.; Wang, Z.; Guo, N. Selective extraction of uranium from seawater with biofouling-resistant polymeric peptide. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 8, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Liu, J.; Yu, J.; Chen, R.; Liu, P.; Wang, J. Simple one-step synthesis of woven amidoximated natural material bamboo strips for uranium extraction from seawater. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lan, Y.; Jia, J.; Geng, Y.; Dai, X.; Yan, L.; Hu, T.; Chen, J.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Ye, G. Multi-scale computer-aided design and photo-controlled macromolecular synthesis boosting uranium harvesting from seawater. Nat. Commun. 2022, 1, 3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zeng, W.; Wang, J.; Ma, L.; Yang, J. Analysis of supply and demand situation of uranium resourcesin the world and China. N. China Geol. 2021, 44, 25–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cumberland, S.; Douglas, G.; Grice, K.; Moreau, J. Uranium mobility in organic matter-rich sediments: A review of geological and geochemical processes. Earth Sci. Rev. 2016, 1, 160–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Feng, X.; Li, J.; Guo, H.; Miao, P.; Jin, R.; Tang, C.; Zhao, H.; Wang, G.; et al. Uranium occurrence state in the Tarangaole area of the Ordos Basin, China: Implications for enrichment and mineralization. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 115, 103034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, E. Economic geology: Uranium-ore giants. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 2, 96–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuney, M. The extreme diversity of uranium deposits. Miner. Deposita 2009, 1, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuney, M. Evolution of Uranium Fractionation Processes through Time: Driving the Secular Variation of Uranium Deposit Types. Econ. Geol. 2010, 3, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, S.; Birch, W.; Maas, R.; Phillips, D.; Plimer, I. Lake Boga Granite, northwestern Victoria: Mineralogy, geochemistry and geochronology. J. Geol. Soc. Aust. 2008, 55, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargar, J.; Williams, K.; Campbell, K.; Long, P.; Stubbs, J.; Suvorova, E.; Lezama-Pacheco, J.; Alessi, D.; Stylo, M.; Webb, S. Uranium redox transition pathways in acetate-amended sediments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 12, 4506–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Wang, G. Relationship between the hydrogeochemical environment and sandstone-type uranium mineralization in the Ili basin, China. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Ao, C.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, B.; Miao, P.; Si, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Yu, R.; Chen, Y. Occurrence and mechanism of uranium enrichment with a unique eolian sedimental environment in the Pengyang uranium deposit, Ordos Basin. Ore geol. Rev. 2022, 141, 104641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Su, X.; Tan, Y.; Li, S.; Su, Y.; Li, J.; Deng, P.; Xu, L.; Pan, Z. Development Strategy of Nuclear Energy Mineral Resources. Strateg. Study CAE 2019, 1, 113–118. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Yu, R.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Teng, X.; Wang, S.; Si, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, T. Paleo-environmental constraints on uranium mineralization in the Ordos Basin: Evidence from the color zoning of U-bearing rock series. Ore Geol. Rev. J. Compr. Stud. Ore Genes. Ore Explor. 2019, 104, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Sun, Z.; Nie, F.; Li, C.; Zhen, Y.; Zhou, Z. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of the sandstone-hosted uranium mineralization in northern Ordos Basin, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 126, 103769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Wu, L.; Rong, H.; Zhang, F.; Yue, L. Architecture of a sandstone uranium reservoir and the spatial distribution of its internal carbonaceous debris: A case study of the Zhiluo Formation, eastern Ordos Basin, northern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2020, 191, 104219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Campbell, K.; Kelly, S.; Roebbert, Y.; Weyer, S.; Bernier-Latmani, R.; Borch, T. Biogenic non-crystalline U(IV) revealed as major component in uranium ore deposits. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Yang, J.; Ward, C.; Hower, J.; Liu, H.; Garrison, T. Geochemical and mineralogical evidence for a coal-hosted uranium deposit in the Yili Basin, Xinjiang, northwestern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 70, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.; Kukkadapu, R.; Qafoku, N.; Peacock, A.; Lesher, E.; Williams, K.; Bargar, J.; Wilkins, M.; Figueroa, L.; Ranville, J. Geochemical, mineralogical and microbiological characteristics of sediment from a naturally reduced zone in a uranium-contaminated aquifer. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.; Rodriguez, D.; Honeyman, B. Upscaling Sorption/Desorption Processes in Reactive Transport Models to Describe Metal/Radionuclide Transport: A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7996–8007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Rong, H.; Huang, K.; Peng, H.; Wan, J. Hydrogeochemistry Characteristics and Uranium Metallogenic Conditions of the Groundwater in Yili Basin. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2019, 1, 7–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Rong, H.; Huang, K.; Wang, Z.; Wan, J. Relationship between uranium mineralization and hydrologic condition in Yili Basin. Bullet Geol. Sci. Technol. 2020, 5, 139–147. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Ao, C.; Meng, L.; Teng, X.; Wei, X.; Wang, D.; Feng, P.; Yu, H. Analysis of neogeneuranium reservoir development and uranium mineralization hydrogeological conditions in southwest Qaidam basin. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2022, 22, 931–938. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hou, B.; Keeling, J.; Li, Z. Paleovalley-related uranium deposits in Australia and China: A review of geological and exploration models and methods. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 88, 201–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shi, Z.; Zachara, J. Kinetics of Uranium(VI) Desorption from Contaminated Sediments: Effect of Geochemical Conditions and Model Evaluation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6560–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Xiu, W.; Guo, H.; Lian, G.; Yang, B.; Zhang, T.; Bi, E.; Shi, Z. Multi-Isotope Based Identification and Quantification of Oxygen Consuming Processes in Uranium Hosting Aquifers with CO2 + O2 In Situ Leaching. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 3, e2022WR033980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Liu, Z.; Yao, Y.; Du, Z. Petrology, mineralogy, and ore leaching of sandstone-hosted uranium deposits in the Ordos Basin, North China. Ore Geol. Rev. J. Compr. Stud. Ore Genes. Ore Explor. 2020, 127, 103768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yan, G.; Ma, Y.; Scheuermann, A. Measurement of In-Situ Flow Rate in Borehole by Heat Pulse Flowmeter: Field-Case Study and Reflection. Geosciences 2023, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Fan, H.; He, F.; Liu, H.; Jia, L.; Yi, L.; Yang, M. Features of hydrogeochemistry and uranium metallogenesis in Binxian County area on the southern margin of Ordos Basin. Geol. Bull. China 2017, 36, 503–510. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Man, A.; Chen, X.; Xiong, Y.; Shao, J.; Wang, L.; Sun, P. Relationship Between Hydrogeology and Sandstone Uranium Mineralization in Sedimentary Basin: A Case Study of Sandstone Uranium Survey in the Kailu Depression of the Songliao Basin. Geotecton. Et Metallog. 2021, 6, 1174–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S.; Basu, A.; Christensen, J.; Reimus, P.; Heikoop, J.; Simmons, A.; Woldegabriel, G.; Maher, K.; Weaver, K.; Clay, J. Isotopic Evidence for Reductive Immobilization of Uranium Across a Roll-Front Mineral Deposit. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6189–6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Jin, R.; Cuney, M.; Petrov, V.; Miao, P. The strata constraint on large scale sandstone-type uranium mineralization in Meso-Cenozoic basins, northern China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2024, 98, 1953–1976. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, Y.; Baars, O.; Guo, D.; Whitham, J.; Srivastava, S.; Dong, H. Mineral-bound trace metals as cofactors for anaerobic biological nitrogen fixation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 7206–7216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Permeability of Ore-Bearing Aquifer | Bearing Capacity of Ore-Bearing Aquifer | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Classification of deposit | K (m/d) | Classification of deposit | Groundwater depth (m) |
| High permeability | K ≥ 10 | High confined water | H ≥ 100 |
| Relatively high permeability | 1 < K ≤ 10 | Relatively high confined water | 20 < H ≤ 100 |
| General permeability | 0.1 < K ≤ 1 | Low confined water | H ≤ 20 |
| Limited permeability | K ≤ 0.1 | Non- confined water | Missing bulkhead |
| Inflow rate of water in the ore-bearing aquifer | Groundwater table in the ore-bearing aquifer | ||
| Classification of deposit | Inflow rate of water (L/s·m) | Classification of deposit | Groundwater Table (m) |
| Huge water yield | Q ≥ 0.10 | Large depth of groundwater level | h ≥ 150 |
| Large water yield | 0.05 < Q ≤ 0.10 | Medium depth of groundwater level | 50 < h ≤ 150 |
| Small water yield | 0.01 < Q ≤ 0.05 | Little depth of groundwater level | h ≤ 50 |
| Little water yield | Q ≤ 0.01 | ||
| Number | Depth of Well (m) | Well Discharge (m3/d) | Specific Discharge of a Well (L/S·m) | Drawdown (m) | Hydraulic Conductivity (m/d) | Transmissivity (m2/d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDS05 | 76 | 809.28 | 2.019 | 4.64 | 4.15 | 178.71 |
| SDS21-1 | 120 | 98.40 | 0.077 | 14.7 | 0.25 | 7.50 |
| SDS87 | 90 | 682.80 | 2.833 | 2.79 | 5.64 | 225.75 |
| SDS90 | 110 | 867.36 | 1.227 | 8.18 | 2.24 | 108.17 |
| Number | Depth of Well (m) | Well Discharge (m3/d) | Specific Discharge of a Well (L/S·m) | Drawdown (m) | Hydraulic Conductivity (m/d) | Transmissivity (m2/d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDS14 | 59 | 443.28 | 5.765 | 0.89 | 11.01 | 418.2 |
| Number | Depth of well (m) | Location | Aquifer Thickness (m) | Well Discharge (m3/d) | Specific Discharge of a Well (L/S·m) | Drawdown (m) | Hydraulic Conductivity (m/d) | Transmissivity m2/d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SZK01 | 126 | Orebody III | 78.35 | 1054.08 | 1.379 | 8.85 | 1.75 | 137.06 |
| 780.24 | 1.552 | 5.82 | 1.86 | 146.01 | ||||
| 485.52 | 2.073 | 2.71 | 2.25 | 176.01 | ||||
| SZK02 | 158 | Orebody IV | 27.45 | 52.70 | 0.009 | 67.54 | 0.035 | 0.91 |
| Number | Orebody II | Orebody I | Orebody III | Orebody IV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classification Index | |||||
| Permeability | Relatively Strong | Medium | Relatively Strong | Medium | |
| Confined | Strong | Strong | Strong | Strong | |
| Water yield | Large | Relatively Small | Large | Relatively Small | |
| Underground water level | Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium | |
| Hydrogeological complexity | Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Evaluation Parameter | Evaluation Grade of Hydrogeological Conditions of Ground Immersion | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Most Advantageous | Advantageous | Generally Favorable | Unfavorable | |
| Water yield (m3/d) | 1200–240 | 240–120 | 120–24 | ≥1200 or <24 |
| Hydraulic conductivity (m/d) | 10–1 | 1–0.5 | 0.5–0.1 | ≥10 or <0.1 |
| Hydrogeological structure | Stable watertight top and bottom anchor | Poor stable watertight top and bottom anchor | Missing watertight top and bottom anchor | |
| Thickness of ore-bearing aquifer (m) | 20–30 | 30–50, 10–20 | 50–100 | <10 or ≥100 |
| Rock granularity | Coarse sand | Medium sand | Fine sand | Silty sand |
| Clay content (%) | <10 | 10–20 | 20–30 | ≥30 |
| Sorting | Good | Preferably | Medium | Poor |
| Cementation degree | Loose | Relatively loose | Relatively compact | Compact |
| Underground water level (m) | <50 | 50–100 | 100–150 | ≥150 |
| Head (m) | ≥100 | ≥50 | ≥20 | <20 |
| Ratio of hydraulic conductivity between ore-bearing and non-ore-bearing layers | ≥1 | 1–0.75 | 0.75–0.5 | <0.5 |
| Ratio of thickness of ore-bearing aquifer to ore layer | 1–5 | 5–10 | ≥10 | |
| TDS (g/L) | <1 | 1–3 | 3–5 | ≥5 |
| Carbonate content (%) | <1 | 1–2 | 2–3 | ≥3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, L.; Ning, H.; Jiang, W.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, W.; Tang, C. Comprehensive Study on Hydrogeological Conditions and Suitability Evaluation of In Situ Leaching for Sandstone-Hosted Uranium Deposit in Erlian Basin. Water 2024, 16, 2785. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192785
Meng L, Ning H, Jiang W, Sheng Y, Wang W, Tang C. Comprehensive Study on Hydrogeological Conditions and Suitability Evaluation of In Situ Leaching for Sandstone-Hosted Uranium Deposit in Erlian Basin. Water. 2024; 16(19):2785. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192785
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Lishan, Hang Ning, Wanjun Jiang, Yizhi Sheng, Wei Wang, and Chao Tang. 2024. "Comprehensive Study on Hydrogeological Conditions and Suitability Evaluation of In Situ Leaching for Sandstone-Hosted Uranium Deposit in Erlian Basin" Water 16, no. 19: 2785. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192785
APA StyleMeng, L., Ning, H., Jiang, W., Sheng, Y., Wang, W., & Tang, C. (2024). Comprehensive Study on Hydrogeological Conditions and Suitability Evaluation of In Situ Leaching for Sandstone-Hosted Uranium Deposit in Erlian Basin. Water, 16(19), 2785. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192785








