Massive Outbreak of Aurelia coerulea in Geoje Bay, Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
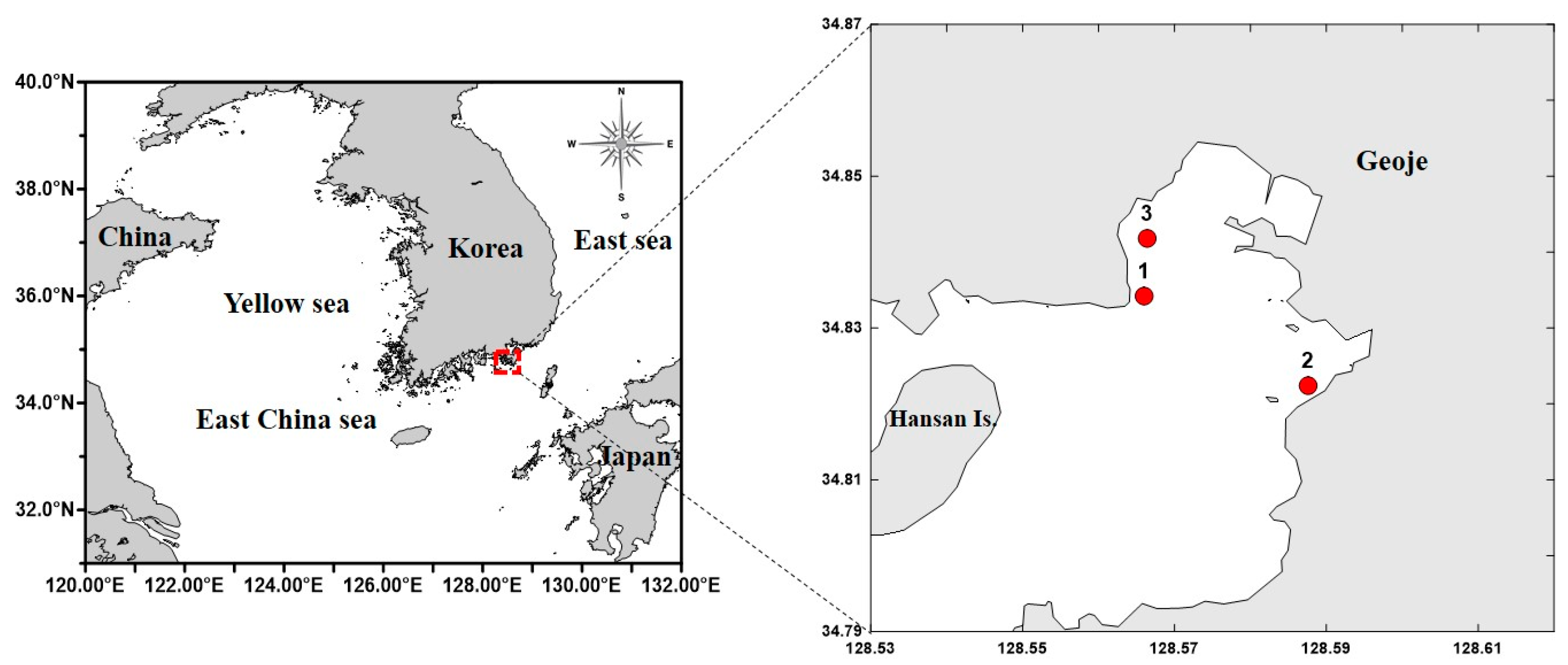
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. Polyp Habitat Survey
2.4. Polyp Formation Experiment
2.5. Molecular Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
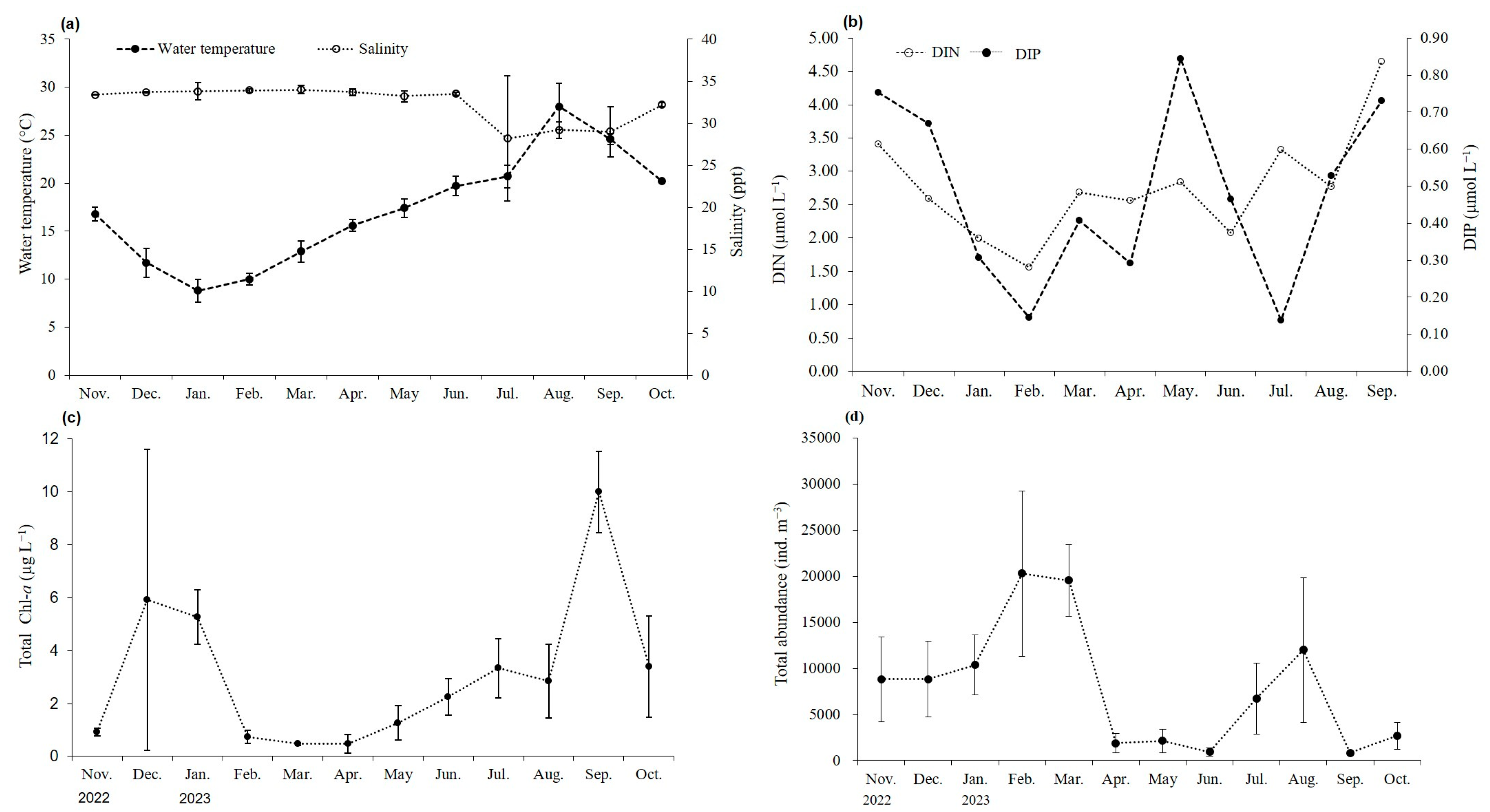
3.1. Habitat Conditions of A. coerulea
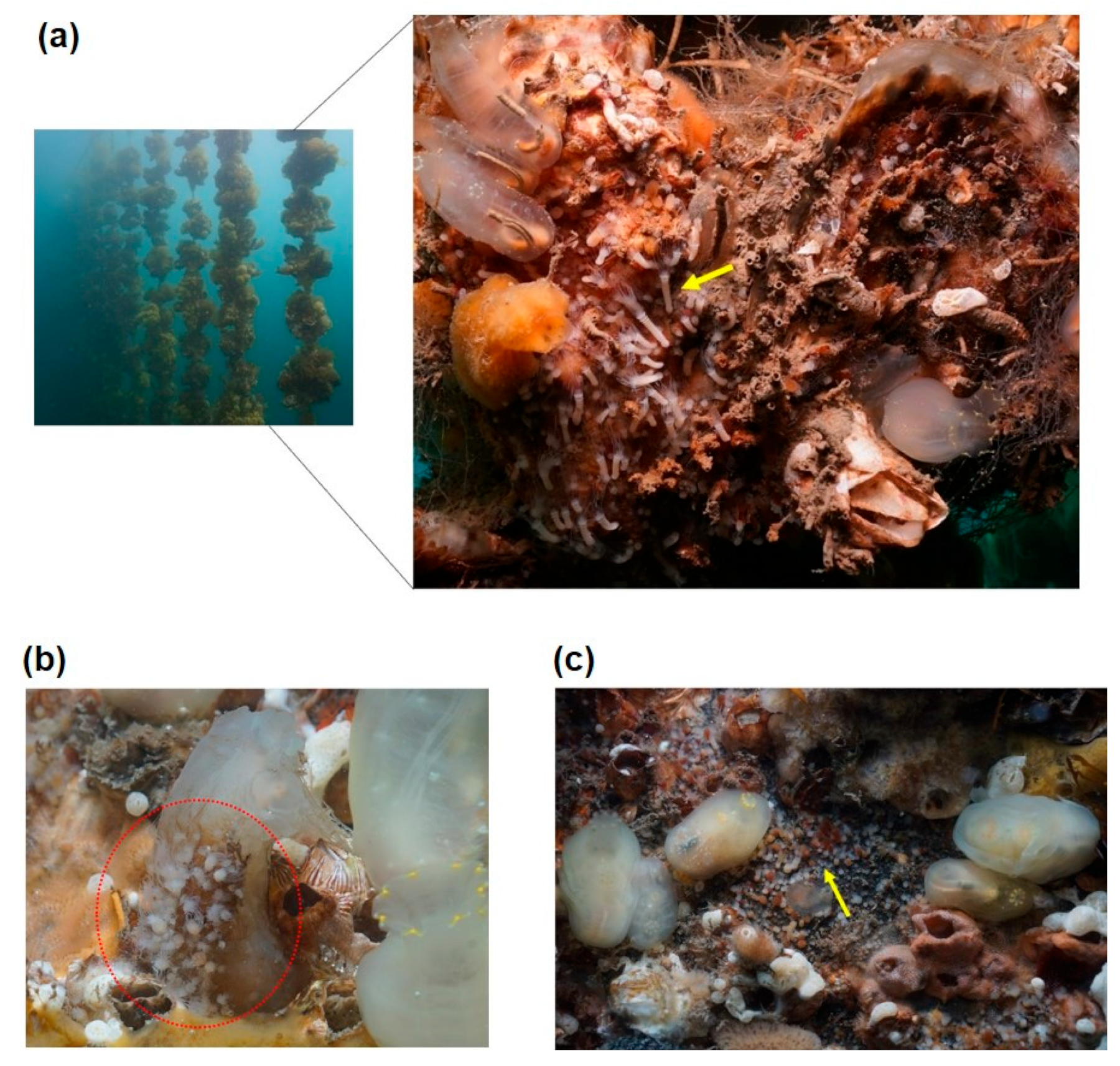
3.2. Habitat of A. coerulea Polyps
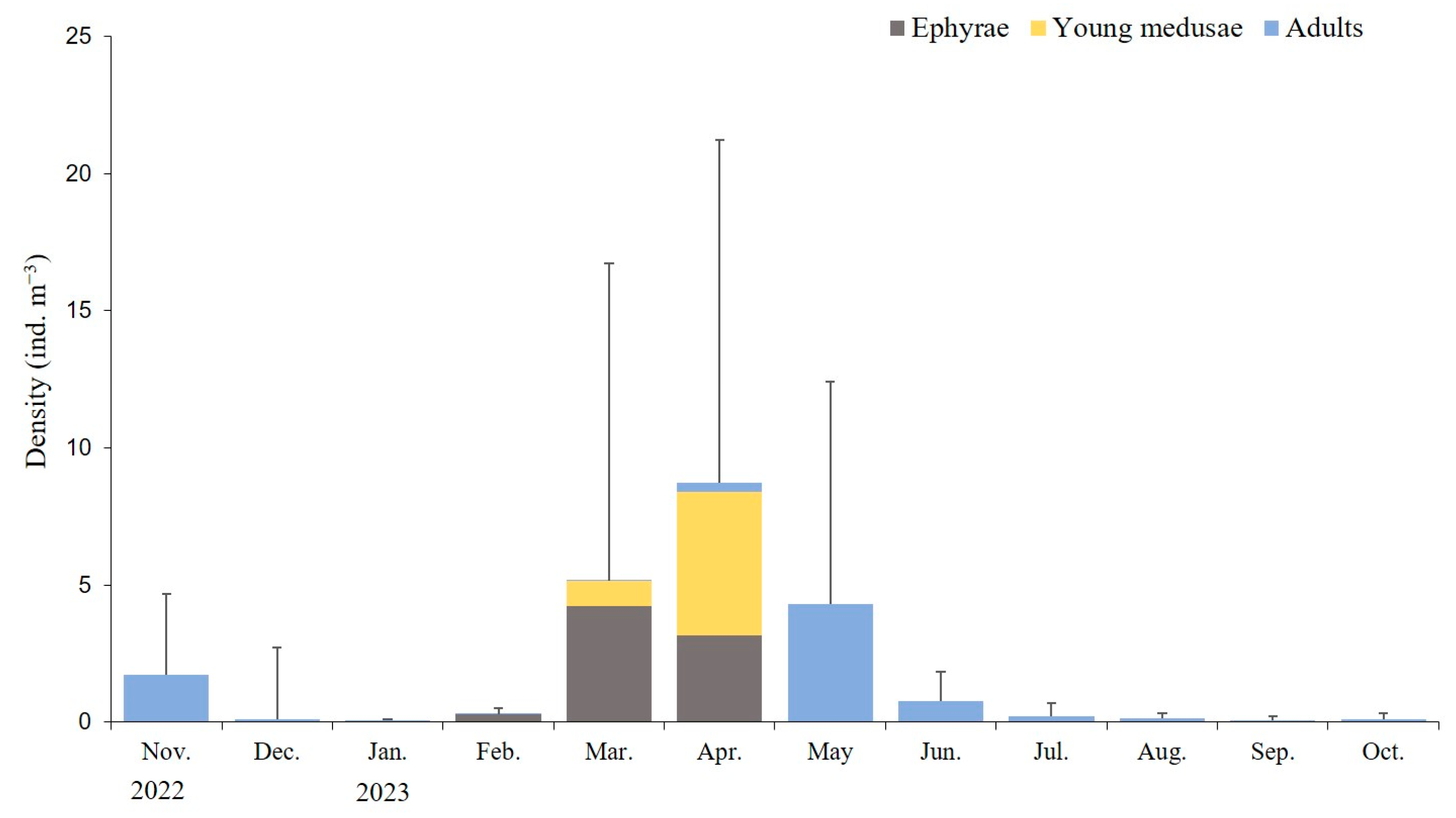
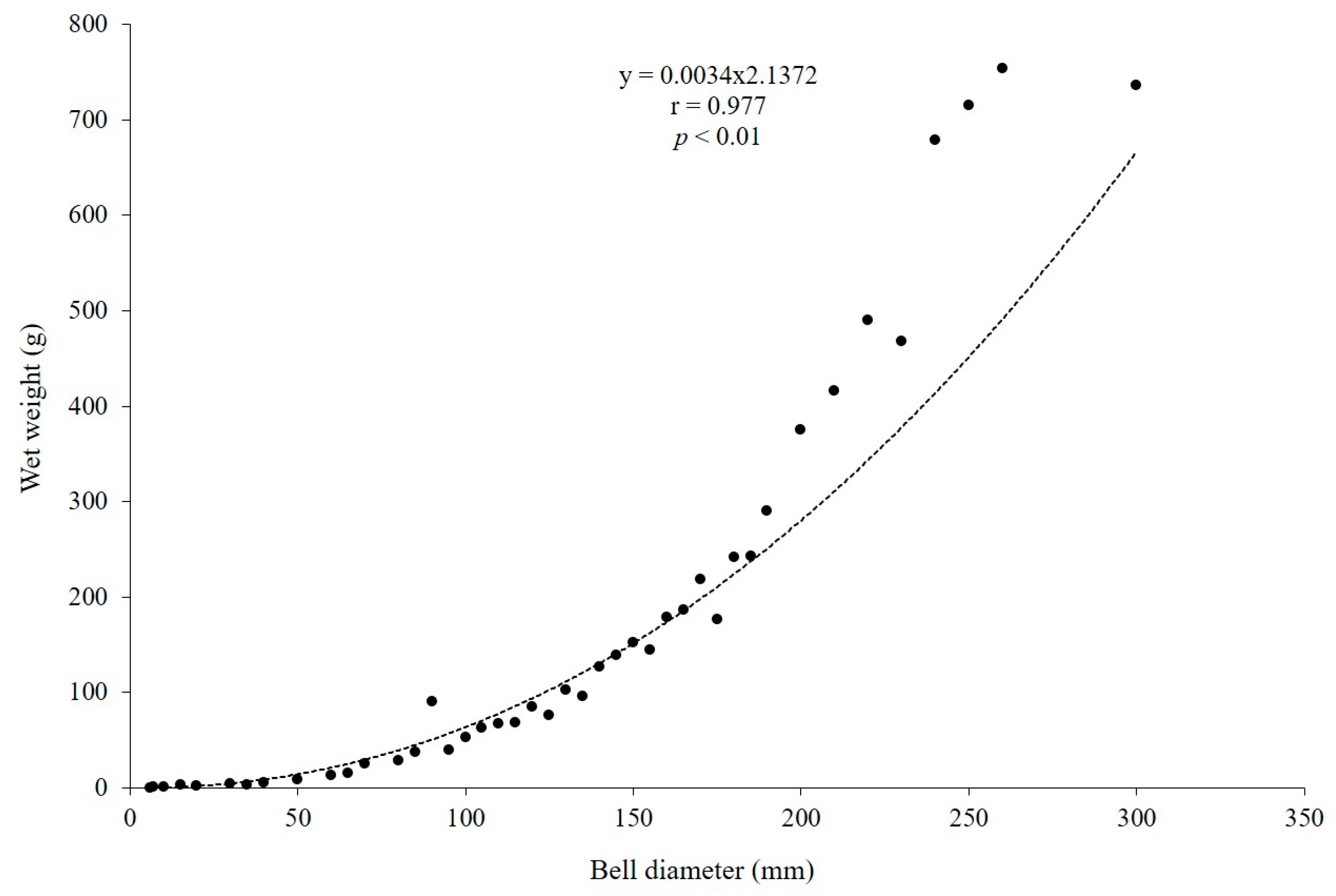
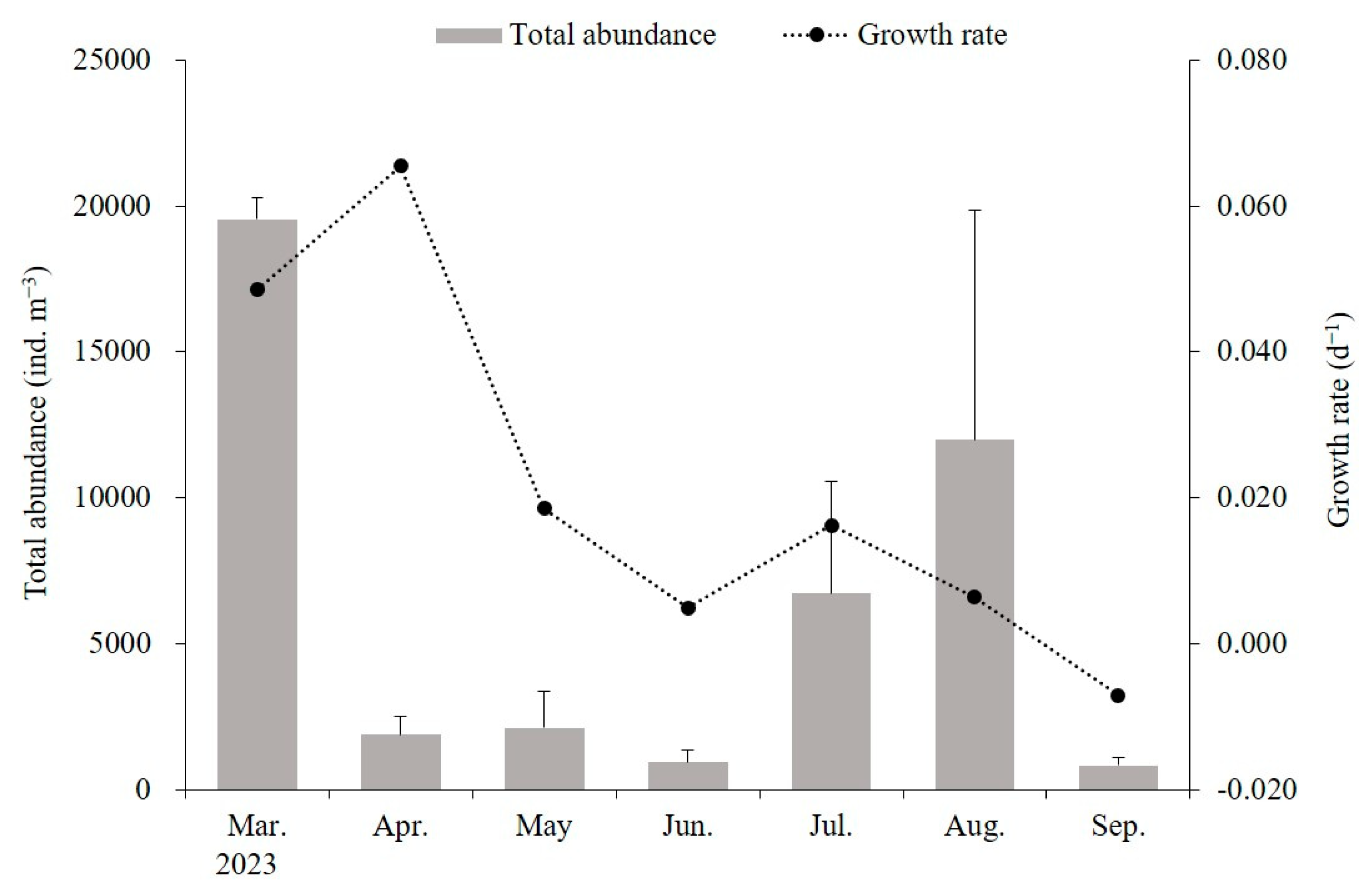
3.3. Population Dynamics and Growth Rates of A. coerulea
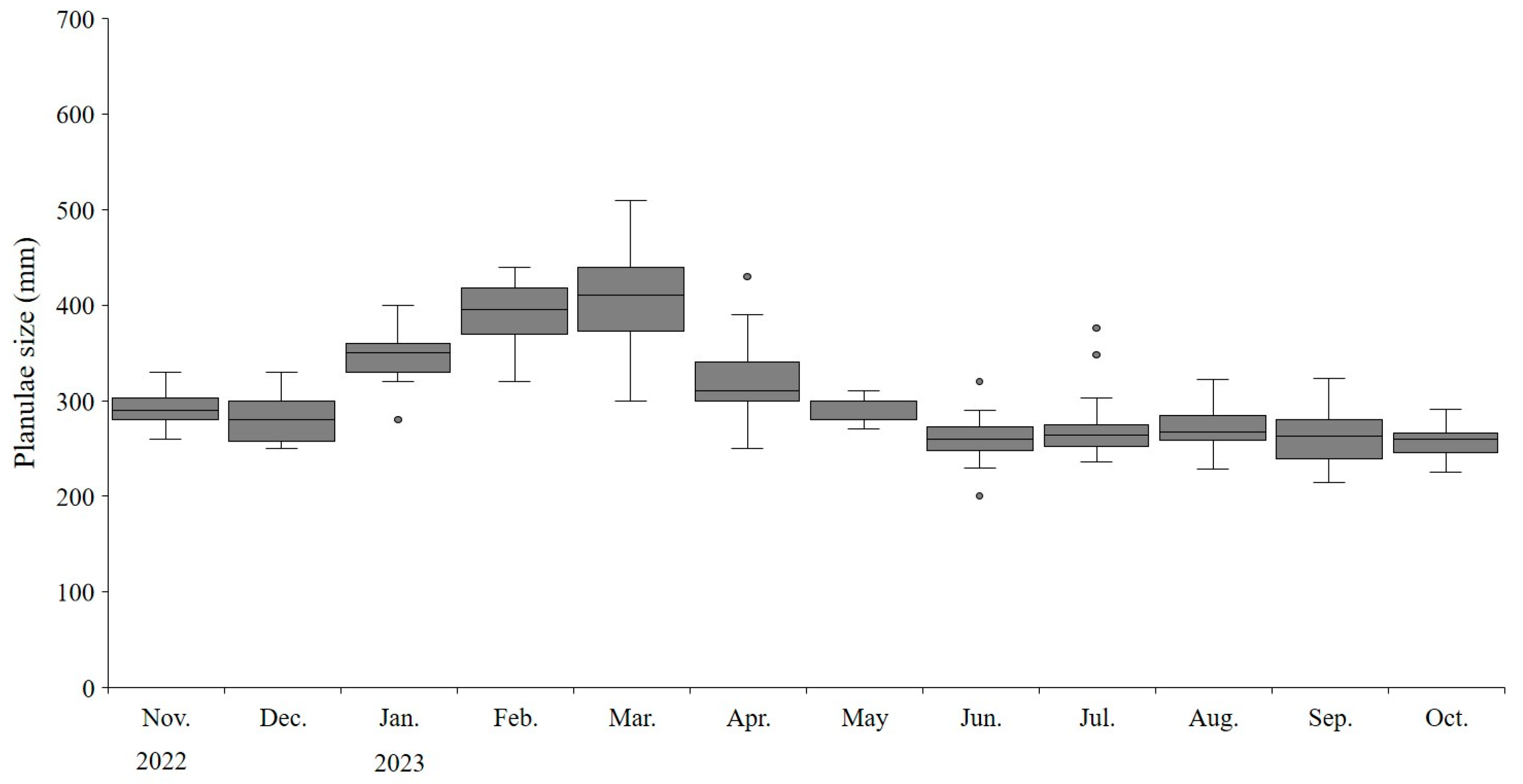
3.4. Characteristics of A. coerulea planulae
4. Discussion
4.1. Habitat Environment of A. coerulea
4.2. A. coerulea Polyp Habitats
4.3. Characteristics of A. coerulea Populations
4.4. Planulae Characteristics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milisenda, G.; Rosa, S.; Fuentes, V.L.; Boero, F.; Guglielmo, L.; Purcell, J.E.; Piraino, S. Jellyfish as Prey: Frequency of Predation and Selective Foraging of Boops boops (Vertebrata, Actinopterygii) on the Mauve Stinger Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Båmstedt, U. Trophodynamics of the Scyphomedusae Aurelia aurita. Predation rate in relation to abundance, size and type of prey organism. J. Plankton Res. 1990, 12, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, N.J. Clearance potential of jellyfish Aurelia aurita and predation impact on zooplankton in a shallow cove. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 124, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, L.J.; Moeslund, O.; Kiørboe, T.; Riisgård, H.U. Clearance rates of jellyfish and their potential predation impact on zooplankton and fish larvae in a neritic ecosystem (Limfjorden, Denmark). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 304, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.H.; Gelcich, S.; Uye, S.I. Living with jellyfish: Management and adaptation strategies. In Jellyfish Blooms; Springer: Dordretch, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.Y.H.; Leong, F.-M.; Rudloe, J. Jellyfish as food. Hydrobiologia 2001, 451, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, J.E.; Uye, S.; Lo, W.-T. Anthropogenic causes of jellyfish blooms and their direct consequences for humans: A review. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 350, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, J.E. Predation on fish eggs and larvae by pelagic cnidarians and ctenophores. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1985, 37, 739–755. [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, J.E.; Arai, M.N. Interactions of pelagic cnidarians and ctenophores with fish: A review. Hydrobiologia 2001, 451, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.J.; Bakun, A.; Hays, G.C.; Gibbons, M.J. The jellyfish joyride: Causes, consequences and management responses to a more gelatinous future. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uye, S.I. Human forcing of the copepod–fish–jellyfish triangular trophic relationship. Hydrobiologia 2011, 666, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, J.E. Environmental effects on asexual reproduction rates of the scyphozoan Aurelia labiata. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 348, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, R.R. Evolution and development of scyphozoan jellyfish. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2018, 93, 1228–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, P.A.; Loureiro, M.L.; Piñol, L.; Sastre, S.; Voltaire, L.; Canepa, A. Analyzing beach recreationists’ preferences for the reduction of jellyfish blooms: Economic results from a stated-choice experiment in Catalonia, Spain. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 0126681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alenka, M.; Kogovšek, T.; Andreja, R.; Catenacci, L. Blooms and population dynamics of moon jellyfish in the northern Adriatic. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2012, 53, 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Scorrano, S.; Aglieri, G.; Boero, F.; Dawson, M.N.; Piraino, S. Unmasking Aurelia species in the Mediterranean Sea: An integrative morphometric and molecular approach. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2017, 180, 243–267. [Google Scholar]
- Lynam, C.P.; Gibbons, M.J.; Axelsen, B.E.; Sparks, C.A.J.; Coetzee, J.; Heywood, B.G.; Brierley, A.S. Jellyfish overtake fish in a heavily fished ecosystem. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, R492–R493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodeur, R.D.; Sugisaki, H.; Hunt, G.L., Jr. Increases in jellyfish biomass in the Bering Sea: Implications for the ecosystem. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 233, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyokawa, M.; Furota, T.; Terazaki, M. Life history and seasonal abundance of Aurelia aurita medusae in Tokyo Bay, Japan. Plankton Biol. Ecol. 2000, 47, 48–58. [Google Scholar]
- Park, N.; Yeom, J.; Jeong, R.; Lee, W. Novel attempt at discrimination of a bullet-shaped siphonophore (Family Diphyidae) using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-ToF MS). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.H. Population dynamics of Aurelia aurita (Scyphozoa) from an isolated brackish lake, with particular reference to sexual reproduction. J. Plankton Res. 1996, 18, 987–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Båmstedt, U. Food regulation of growth and maturation in a natural population of Aurelia aurita (L.). J. Plankton Res. 1998, 20, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongze, X.; Qian, L.; Mei, Z.; Yu, Z.; Tiezhu, M.I.; Zhigang, Y.U. Effects of Temperature and Salinity on the Asexual Reproduction of Aurelia coerulea Polyps. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2020, 38, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Purcell, J.E. Effects of temperature, salinity, and predators on mortality of and colonization by the invasive hydrozoan Moerisia lyonsi. Mar. Biol. 2005, 147, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, J.E. Climate effects on formation of jellyfish and ctenophore blooms: A review. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2005, 85, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, S. Effects of climate warming on strobilation and ephyra production of North Sea scyphozoan jellyfish. Hydrobiologia 2012, 690, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.H. Reproduction and life history strategies of the common jellyfish, Aurelia aurita, in relation to its ambient environment. Hydrobiologia 2001, 451, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Lai, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, M. Combined effects of temperature and salinity on the growth and pulsation of moon jellyfish (Aurelia coerulea) ephyrae. Am. J. Life Sci. 2020, 8, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcox, S.; Moltschaniwskyj, N.A.; Crawford, C.M. Population dynamics of natural colonies of Aurelia sp. scyphistomae in Tasmania, Australia. Mar. Biol. 2008, 154, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambill, M.; Peck, M.A. Respiration rates of the polyps of four jellyfish species: Potential thermal triggers and limits. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2014, 459, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawley, J.W.; Gamero-Mora, E.; Maronna, M.M.; Chiaverano, L.M.; Stampar, S.N.; Hopcroft, R.R.; Collins, A.G.; Morandini, A.C. The importance of molecular characters when morphological variability hinders diagnosability: Systematics of the moon jellyfish genus Aurelia (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa). PeerJ 2021, 9, e11954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.-H.; Kawahara, M.; Uye, S. Seasonal variations in the trophic relationship between the scyphomedusa Aurelia aurita s. l. and mesozooplankton in a eutrophic brackish-water lake, Japan. Plankton Benthos Res. 2009, 4, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.T.; Chen, I.L. Population succession and feeding of Scyphomedusae, Aurelia aurita, in a eutrophic tropical lagoon in Taiwan. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 76, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, H.; Iwao, K.; Kakinuma, Y. Life history and environment of Aurelia aurita. South Pac. Study. 1997, 17, 273–285. [Google Scholar]
- Kogovšek, T.; Molineiro, J.C.; Lučić, D.; Onofri, I.; Gangai, B.; Miloslavić, M.; Bonnet, D.; Malej, A. Interannual size changes of adult Aurelia sp. 5 medusae stage in the Marine Protected Area of Mljet Island South Adriatic. Acta Adriat. 2012, 53, 233–242. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, Y.H. The Characteristics on the Spatio-temporal Distributions of Phytoplankton Communities in Deukryang Bay, Southwestern Korea. Korean Soc. Environ. Biol. 1999, 17, 481–492. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, M.H.; Song, T.Y.; Kim, E.S.; Choi, J.K. The characteristics on the spatial and temporal distribution of phytoplankton in the western Jinhae bay, Korea. J. Korean Soc. Oceanogr. 2007, 12, 305–314. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; Baek, S.H. Changes in marine environmental factors and phytoplankton community composition observed via short-term investigation in a harbor in the eastern part of the south sea of Korea. J. Korean Soc. Mar. Environ. Saf. 2017, 23, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiyama, T. Microzooplankton as a food source for the scyphozoan Aurelia coerulea: Growth and feeding responses of the polyp stage in field assemblages. Plankton Benthos Res. 2023, 18, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiyama, T. Planktonic ciliates as food for the scyphozoan Aurelia coerulea: Feeding and growth responses of ephyra and metephyra stages. J. Oceanogr. 2018, 74, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiyama, T. Planktonic ciliates as food for the scyphozoan Aurelia aurita (sl): Effects on asexual reproduction of the polyp stage. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2013, 445, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiyama, T. Planktonic ciliates as a food source for the scyphozoan Aurelia aurita (sl): Feeding activity and assimilation of the polyp stage. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2011, 407, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.L.; Graham, W.M. Long-term change in the abundances of northern Gulf of Mexico Scyphomedusae Chrysaora sp. and Aurelia spp. with links to climate variability. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Sun, S. Population dynamics of Aurelia sp.1 ephyrae and medusae in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Hydrobiologia 2015, 754, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Pitt, K.A.; Lucas, C.H.; Purcell, J.E.; Uye, S.I.; Robinson, K.; Brotz, L.; Decker, M.B.; Sutherland, K.R.; Malej, A.; et al. Is global ocean sprawl a cause of jellyfish blooms? Front. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 11, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.M.; Dean, R.J.; Michael, J.K. Use of eDNA to determine source location of deadly jellyfish (Cubozoa) in an open coastal system. Coasts 2024, 4, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyokawa, M.; Aoki, K.; Yamada, S.; Yasuda, A.; Murata, Y.; Kikuchi, T. Distribution of ephyrae and polyps of jellyfish aurelia aurita (Linnaeus 1758) sensu lato in Mikawa Bay, Japan. J. Oceanogr. 2011, 67, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOF. Annual Report for the Restoration and Improvement of Marine Habitats in Korea, 39–49. Available online: http://www.mof.go.kr (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Pitt, K. Life history and settlement preferences of the edible jellyfish Catostylus mosaicus (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae). Mar. Biol. 2000, 136, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, H.; Terazaki, M.; Kakinuma, Y. On the polyps of the common jellyfish Aurelia aurita in Kagoshima Bay. J. Oceanogr. 2002, 58, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, S.; Jarms, G. Substrate choice and settlement preferences of planula larvae of five Scyphozoa (Cnidaria) from German Bight, North Sea. Mar. Biol. 2007, 151, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.T.; Purcell, J.E.; Hung, J.J.; Su, H.M.; Hsu, P.K. Enhancement of jellyfish (Aurelia aurita) populations by extensive aquaculture rafts in a coastal lagoon in Taiwan. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Katsukoshi, K. Seasonal and vertical distribution of Aurelia aurita polyps on a pylon in the inner most part of Tokyo Bay. J. Oceanogr. 2010, 66, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condon, R.H.; Lukas, C.H.; Pitt, K.A.; Uye, S.I. Jellyfish blooms and ecological interactions. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 510, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO-Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Fisheries and Aquaculture Department Website. 2007. Available online: http://www.fao.org (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Hoover, R.A.; Purcell, J.E. Substrate preferences of scyphozoan Aurelia labiata polyps Namong common dock-building materials. Hydrobiologia 2009, 616, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Fisheries Science. Report on the Jellyfish Monitoring and Mitigation in 2020, Busan, Republic of Korea, National Institute of Fisheries Science Printing Office. 2020. Available online: http://nifs.go.kr/main.do (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- Yasuda, T. Ecological studies on the jellyfish, Aurelia aurita in Urazoko Bay, Fukui Prefecture—IV. Monthly change in the bell-length composition and breeding season. Bull. JPN Soc. Sci. Fish. 1971, 37, 364–370, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, M.; Ishii, H.; Fujinaga, A. Life history strategy of Aurelia aurita (Cnidaria, Scyphomedusae) and its impact on the zooplankton community of Tokyo Bay. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1995, 52, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, Z.B.; Özdemir, S.; Özsandıkçı, U.; Büyükdeveci, F.; Baykal, B. The seasonally determination of disc diameter-weight relationship of moon jellyfish Aurelia aurita in the Black Sea Coasts of Turkey. Turk. J. Marit. Mar. Sci. 2019, 5, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, G. The common jellyfish Aurelia aurita: Standing stock, excretion and nutrient regeneration in the Kiel Bight, western Baltic 1982~1984. Mar. Biol. 1989, 100, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, L.F.; Riisgård, H.U. Population dynamics, growth and predation impact of the common jellyfish Aurelia aurita and two hydromedusae, Sarsia tubulosa, and Aequorea vitrina in Limfjorden (Denmark). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 346, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamner, W.M.; Jenssen, R.M. Growth, degrowth, and irreversible cell differentiation in Aurelia aurita. Am. Zool. 1974, 14, 833–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, N.J.; Frandsen, K.; Riisgard, H.H.U. Population dynamics, growth and energetics of jellyfish Aurelia aurita in a shallow fjord. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 105, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Båmstedt, U.; Wild, B.; Martinussen, M.B. Significance of food type for growth of ephyrae Aurelia aurita (Scyphozoa). Mar. Biol. 2001, 139, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uye, S.; Shimauchi, H. Population biomass, feeding, respiration and growth rates, and carbon budget of the scyphomedusa Aurelia aurita in the Inland Sea of Japan. J. Plankton Res. 2005, 27, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, E. Distribution and abundance of moon jellyfish (Aurelia aurita) and its zooplankton food in the Black Sea. Mar. Biol. 2001, 138, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröndahl, F. Interactions between polyps of Aurelia aurita and planktonic larvae of scyphozoans: An experimental study. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1988, 45, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, H. Population dynamics of Aurelia aurita medusae in Kiel Bight, Germany (FRG). Mar. Biol. 1980, 60, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakinuma, Y. An Experimental Study of the Life Cycle and Organ Differentiation of Aurelia aurita Lamarck. Bull. Mar. Bio. Stn. Asamushi. 1975, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, G.; Weisse, T. Metabolism measurements of Aurelia aurita planulae larvae, and calculation of maximal survival period of the free swimming stage. Helgol. Meeresunters 1985, 39, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, T. Ecological studies on the jellyfish, Aurelia aurita in Urazoko Bay, Fukui Prefecture—XI. An observation on ephyrae formation. Publ. Seto. Mar. Bio. Lab. 1975, 22, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatje, S.; Hall, S. The effect of temperature on the evolution of per offspring investment in a globally distributed family of marine invertebrates (Crustacea: Decapoda: Lithodidae). Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, G. Larvae production of the common jellyfish Aurelia aurita in the western Baltic. Kiel. Meersforsch. Sonderh. 1988, 6, 295–300. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, C.H.; Graham, W.M.; Widmer, C. Jellyfish life histories: Role of polyps in forming and maintaining scyphomedusa populations. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2012, 63, 133–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.S.; Suzuki, K.W.; Kumakura, E.; Sato, K.; Oe, Y.; Sato, T.; Sawada, H.; Masuda, R.; Nogata, Y. Seasonal alternation of the ontogenetic development of the moon jellyfish Aurelia coerulea in Maizuru Bay, Japan. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, K.; Yamada, S.; Toyokawa, M.; Yasuda, A.; Kikuchi, T. Horizontal distribution and growth of jellyfish, Aurelia aurita (Linnaeus 1758) sensu lato, in Mikawa Bay, Japan. Coast. Mar. Sci. 2012, 35, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, R.; Albouy-Boyer, S.; Delpy, F.; Carre, C.; Le Floc’h, E.; Roques, C.; Molinero, J.C.; Bonnet, D. Pelagic population dynamics of Aurelia sp. in French Mediterranean lagoons. J. Plankton Res. 2015, 37, 1019–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benovic, A.; Lucic, D.; Onofri, V.; Pehardia, M.; Caric, M.; Jasprica, N.; Bobanovic-Colic, S. Ecological characteristics of the Mljet Islands seawater lakes (South Adriatic Sea) with special reference to their resident populations of medusae. Sci. Mar. 2000, 64, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernroth, L.; Gröndahl, F. On the biology of Aurelia aurita (L.) 1. Release and growth of Aurelia aurita (L.) ephyrae in the Gullmar Fjord, western Sweden, 1982–1983. Ophelia 1983, 22, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.H.; Williams, J.A. Population dynamics of the scyphomedusa Aurelia aurita in Southampton Water. J. Plankton Res. 1994, 16, 879–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.Y.; Youn, S.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, W. Massive Outbreak of Aurelia coerulea in Geoje Bay, Korea. Water 2024, 16, 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192846
Kim KY, Youn SH, Choi SY, Park W. Massive Outbreak of Aurelia coerulea in Geoje Bay, Korea. Water. 2024; 16(19):2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192846
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kyoung Yeon, Seok Hyun Youn, Seo Yeol Choi, and Wongyu Park. 2024. "Massive Outbreak of Aurelia coerulea in Geoje Bay, Korea" Water 16, no. 19: 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192846
APA StyleKim, K. Y., Youn, S. H., Choi, S. Y., & Park, W. (2024). Massive Outbreak of Aurelia coerulea in Geoje Bay, Korea. Water, 16(19), 2846. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192846






