China’s Water Footprint on Urban and Rural Food Consumption: A Spatial–Temporal Evolution and Its Driving Factors Analysis from 2000 to 2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
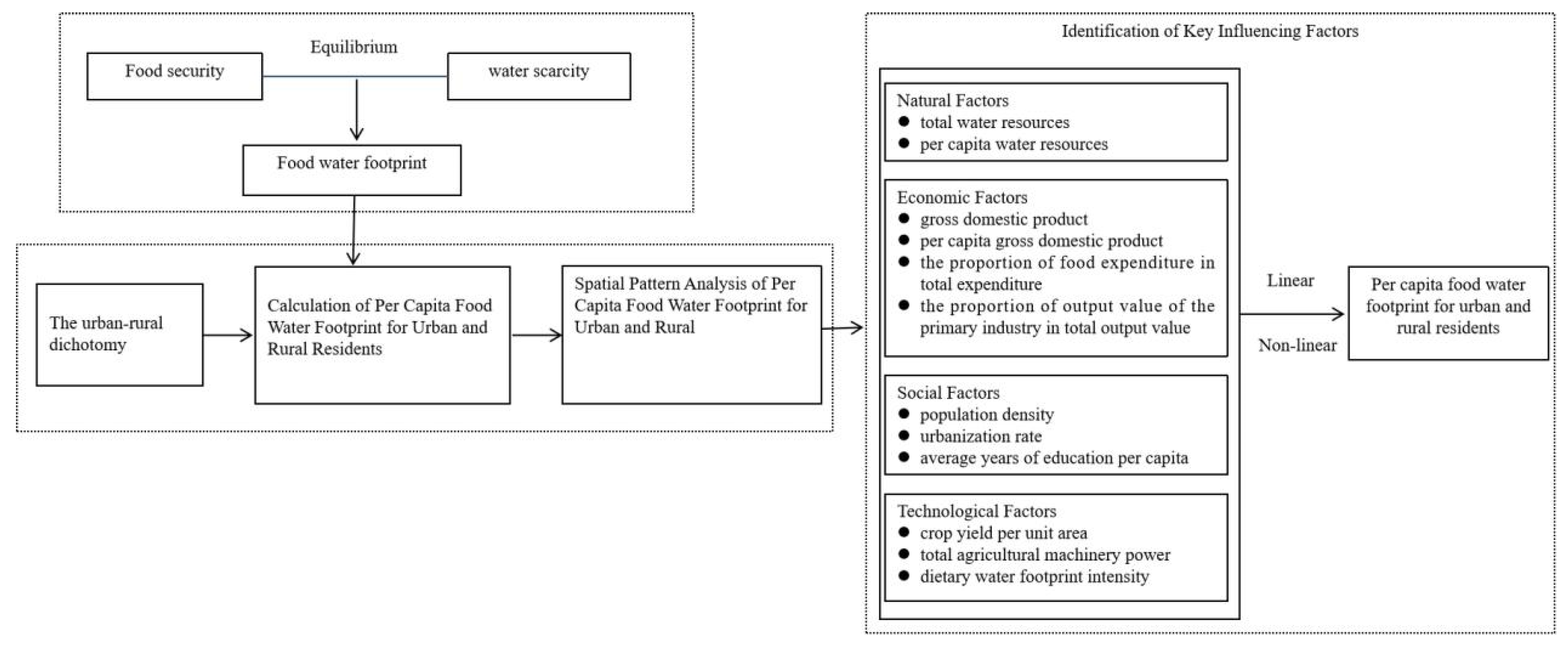
2.1. Analytical Framework
2.2. Research Methodology
2.2.1. Calculation Method for the per Capita Food Water Footprint
2.2.2. Model for Analyzing Key Influencing Factors
2.3. Data Source and Variable Description
3. Results
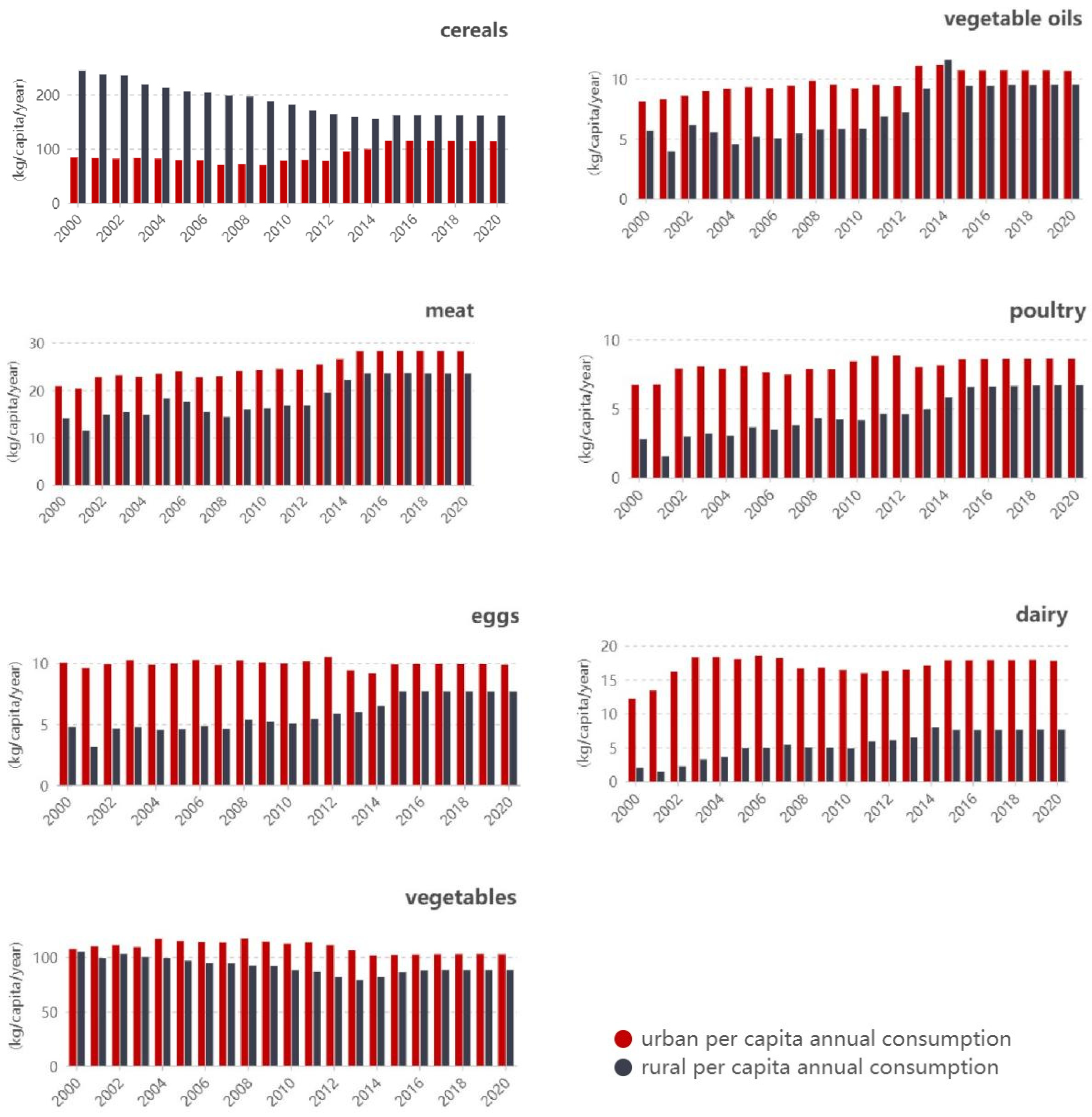
3.1. Urban and Rural Residents’ per Capita Food Consumption
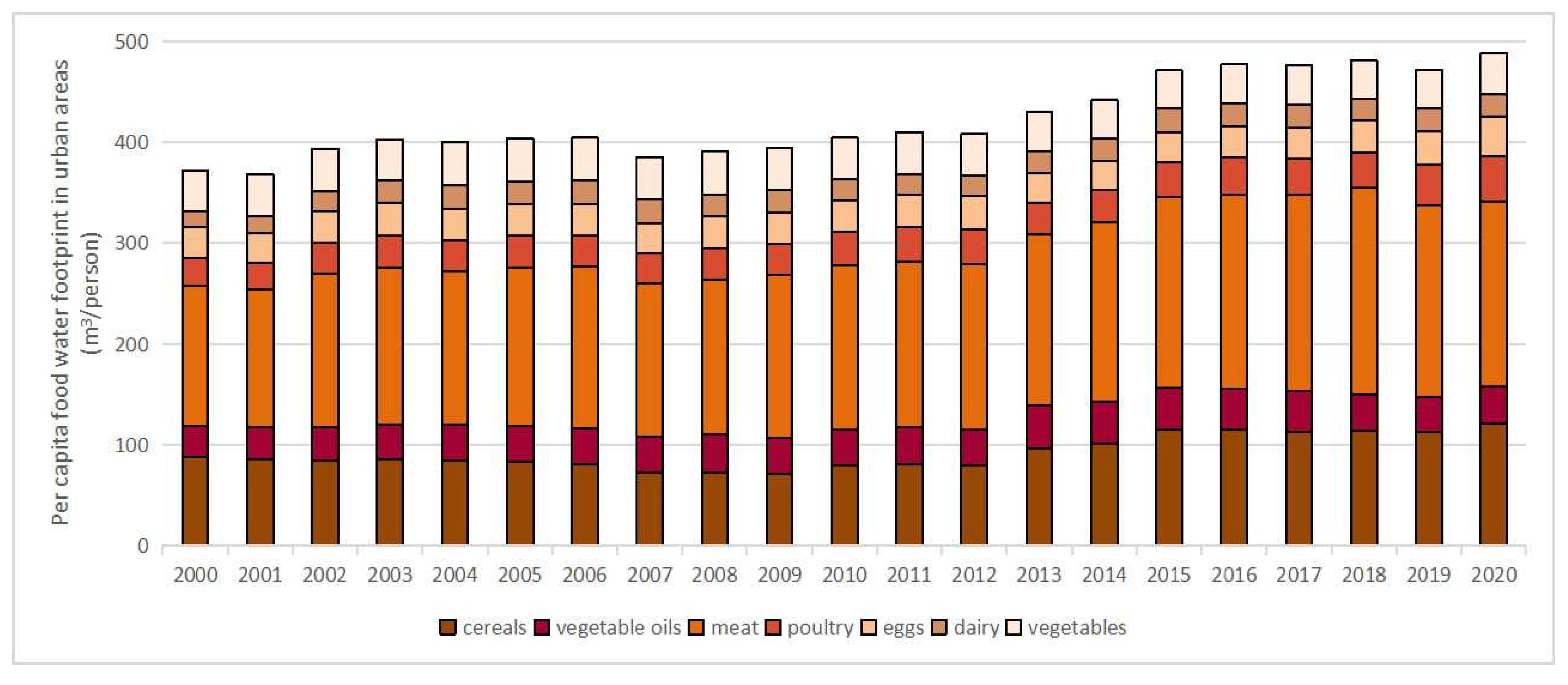
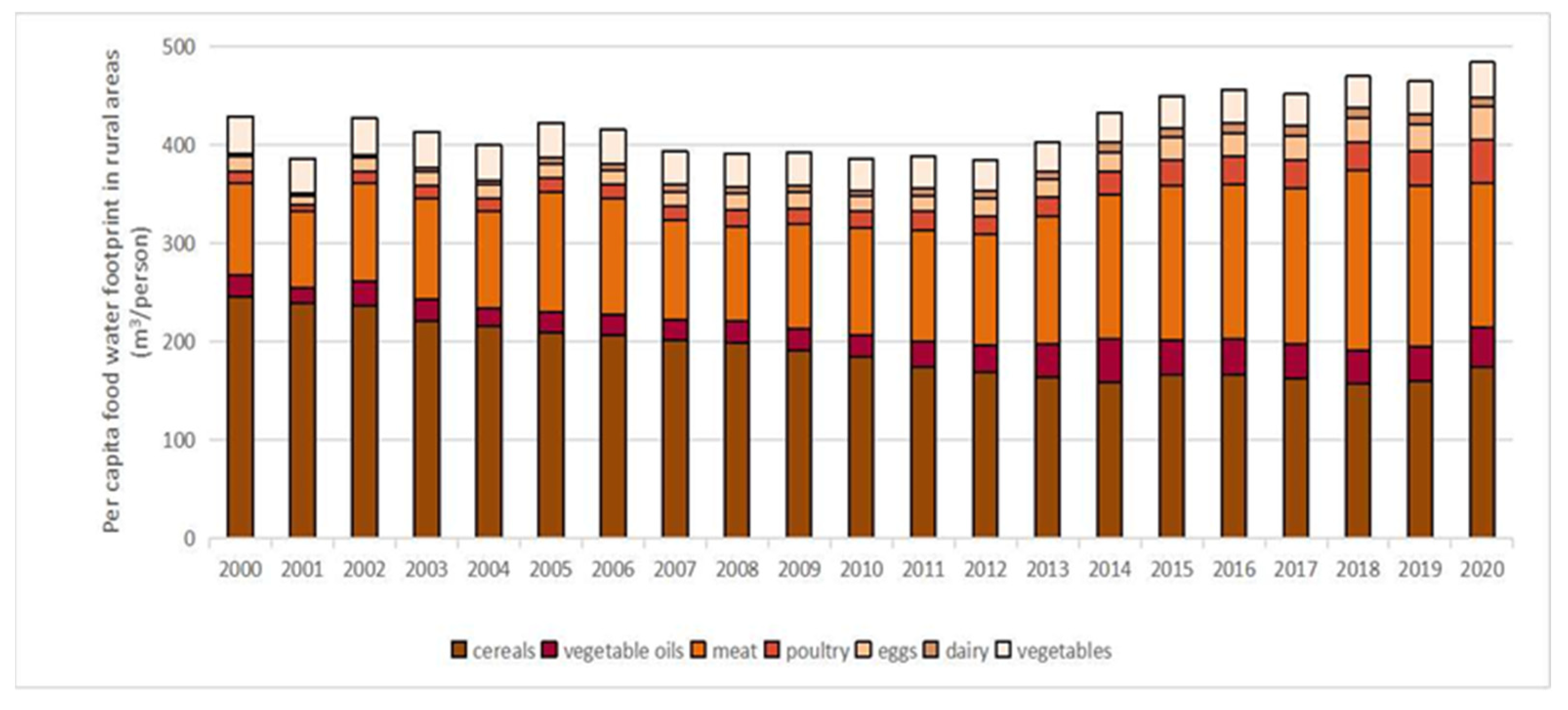
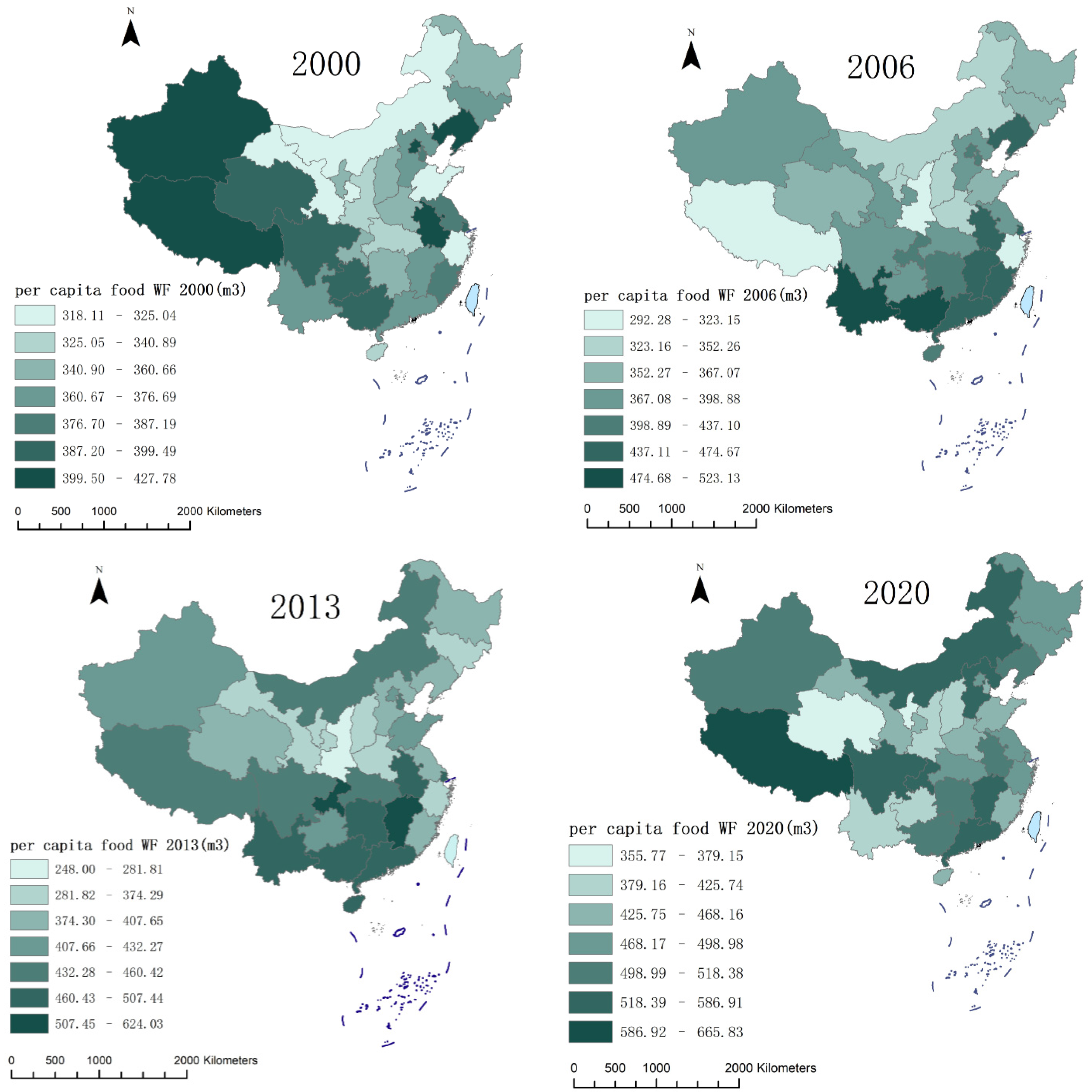
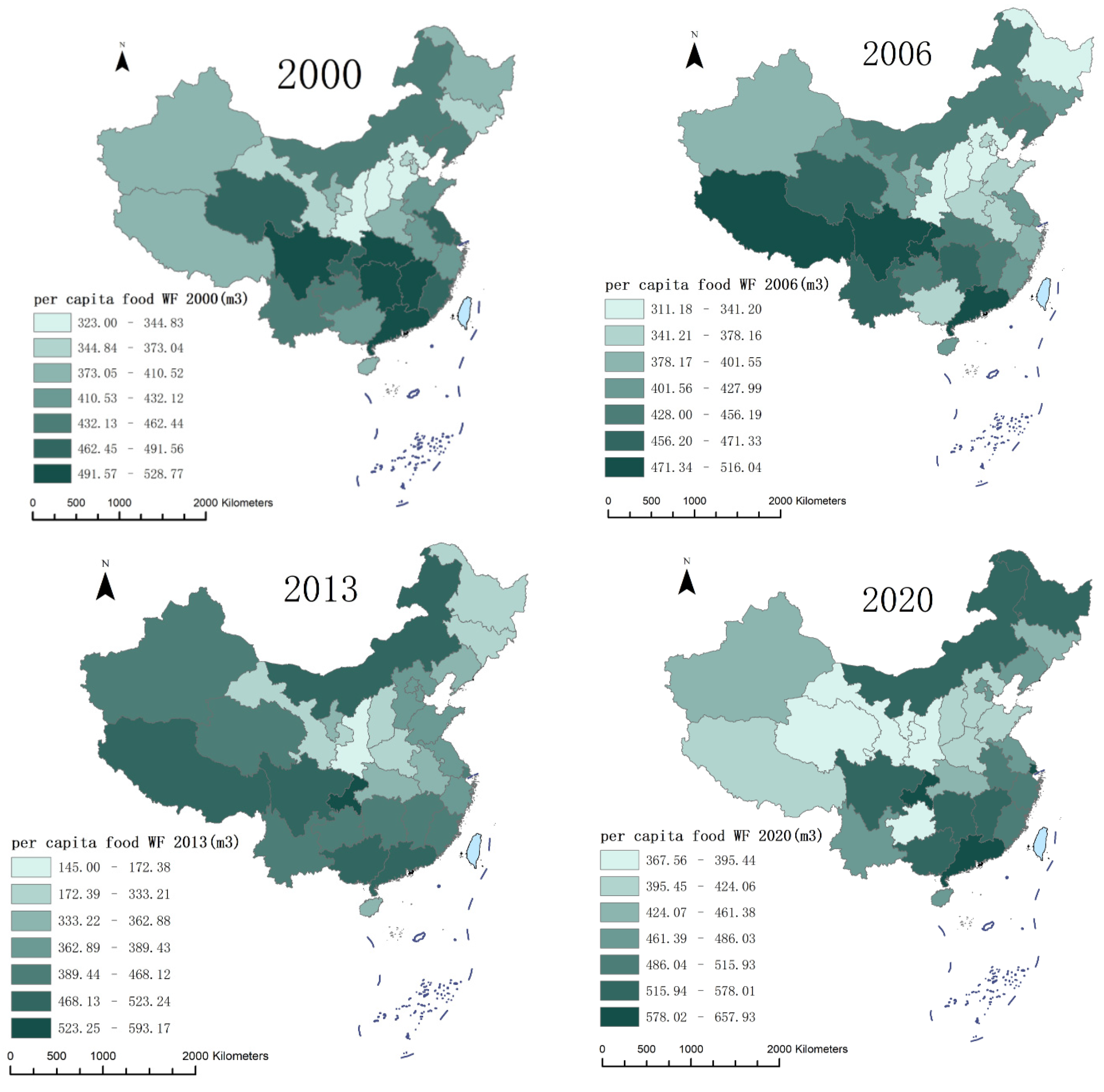
3.2. Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Evolution of Urban and Rural Residents’ per Capita Food Consumption WF
3.3. Analysis of Key Factors Influencing Urban and Rural Residents’ Food WF
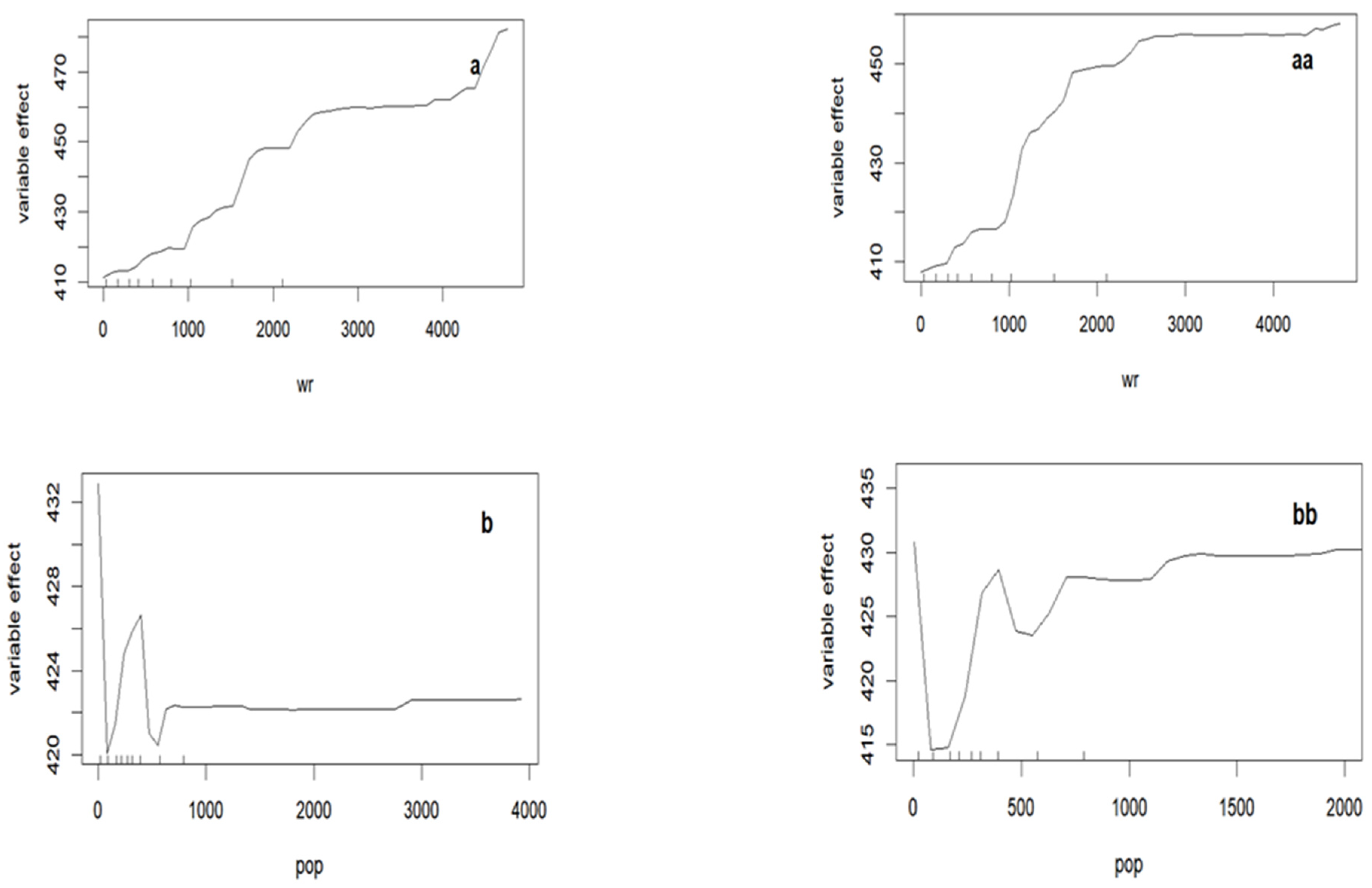
3.3.1. Identification of Key Factors Impacting Urban and Rural Residents’ per Capita Food WF
3.3.2. Analysis of the Key Influencing Factors of per Capita Food WF of Urban and Rural Residents
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in the per Capita Food WF of Urban and Rural Residents
4.2. Temporal and Spatial Changes in the per Capita Food WF of Urban and Rural Residents
4.3. Primary Driving Factors for the per Capita Food WF of Urban and Rural Residents
5. Conclusions
6. Recommendations
7. Research Contribution, Deficiencies, and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO; IFAD; UNICEF; WFP; WHO. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2018: Building Climate Resilience for Food Security and Nutrition; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.D.; Duan, C.Q.; Yang, S.M.; Ji, K. Overview of Hydrological and Water Resources Responses to Land Use/Cover Change. J. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. China Water Resources Bulletin; China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Jiang, W.Q.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, C.J.; Sun, Q. Impact of Changes in Urban and Rural Residents’ Dietary Structure on China’s Water Resources Demand: From the Perspective of Nutrient Balance. Resour. Sci. 2021, 43, 1662–1674. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Guo, Y.; He, P.; Searchinger, T.D.; Chen, Y.; Springmann, M.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Mauzerall, D.L. Environmental and Human Health Trade-Offs in Potential Chinese Dietary Shifts. One Earth 2022, 5, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tai, A.P.K.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shaddick, G.; Yan, X.; Lam, H.-M. Dietary Shifts Can Reduce Premature Deaths Related to Particulate Matter Pollution in China. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, Q. Impact of Urban and Rural Food Consumption on Water Demand in China—From the Perspective of Water Footprint. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 34, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X. The Evolution Process, Characteristics and Adjustment of Chinese Dietary Guidelines: A Global Perspective. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 193, 106964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blas, A.; Garrido, A.; Willaarts, B.A. Food Consumption and Waste in Spanish Households: Water Implications Within and Beyond National Borders. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gao, B.; Hu, Y.; Huang, W.; Cui, S. Environmental Effects of Sustainability-Oriented Diet Transition in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 158, 104802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Hu, H.; Yu, M. Water Footprint of Food Consumption by Chinese Residents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Hu, R.; Yin, T.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Muhammad, T.; Chen, X.; Li, Y. Spatial-Temporal Footprints Assessment and Driving Mechanism of China Household Diet Based on CHNS. Foods 2021, 10, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.F.; Santo, R.E.; Scatterday, A.P.; Fry, J.P.; Synk, C.M.; Cebron, S.R.; Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y.; de Pee, S.; Bloem, M.W. Country-Specific Dietary Shifts to Mitigate Climate and Water Crises. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2020, 62, 101926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.L.; Feng, X.W.; Dong, Y.Y.; Zhang, X. A Global Comparison of Carbon-Water-Food Nexus Based on Dietary Consumption. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2022, 73, 102489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlow, H.J.; Hayes, W.K.; Soret, S.; Carter, R.L.; Schwab, E.R.; Sabate, J. Diet and the Environment: Does What You Eat Matter? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Zhang, C.; Martens, P.; Cao, X. A Comparative Study on the Dietary Ecological Footprint in Contemporary China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.M. Study on the Development of Food Consumption and Nutrition between Urban and Rural Residents in China. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Fang, C.; Bai, Y.; Sun, B.; Liao, X.; Liu, Z. Regional Inequality and Urban-Rural Difference of Dietary Water Footprint in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 199, 107236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F. Study on Water Footprint of Food Consumption for Rural Residents in China and Its Influencing Factors. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Factors Analysis of Water Consumption in China Based on the Random Forest Model—Perspectives of Physical Water, Production Water Footprint, and Consumption Water Footprint. Ph.D. Thesis, Renmin University of China, Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.Z.; Liu, S.B. Impacts of driving factors and the regional difference of dietary water footprint in China. Yellow River 2017, 39, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Sun, S.; Bao, C. Changes in water footprint of food consumption and influencing factors for urban and rural residents in China. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2019, 33, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.; Wu, S.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, S.; Xu, Z. Arable land and water footprints for food consumption in China: From the perspective of urban and rural dietary change. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savelli, E.; Mazzoleni, M.; Di Baldassarre, G.; Cloke, H.; Rusca, M. Urban water crises driven by elites’ unsustainable consumption. Nat. Sustain. 2023, 6, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.B.; Liu, X.F.; Zhao, Y.G.; Li, K. Study on water footprint of main grain crops production in Shanxi Province. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2018, 32, 135–136. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.Z.; Liu, S.B. Analysis of regional differences and driving factors of dietary water footprint in China. Yellow River 2017, 39, 39–40. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.; Geng, C.; Zhai, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, L. Impact of food consumption patterns change on agricultural water requirements: An urban-rural comparison in China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; MacDonald, G.K.; Galloway, J.N.; Geng, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, S. A new dietary guideline balancing sustainability and nutrition for China’s rural and urban residents. iScience 2022, 25, 105048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Wu, J.; Zhu, J.; Bang-Changa, S. A review of technologies on random forests. Stat. Inf. Forum 2011, 26, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Kan, A.; Zeng, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, M.; Ciren. Spatial distribution pattern and influencing factors of Tibet’s population based on the random forest model. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 664–680. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Tang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Han, M.; Jiang, W. Identification and evolution of key influencing factors of China’s carbon intensity based on machine learning. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 2592–2603. [Google Scholar]
- Tyralis, H.; Papacharalampous, G.; Langousis, A. A Brief Review of Random Forests for Water Scientists and Practitioners and Their Recent History in Water Resources. Water 2019, 11, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, M.A.Y. A global assessment of the water footprint of farm animal products. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 401–415. [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra, A.Y. Virtual Water Trade: Proceedings of the International Expert Meeting on Virtual Water Trade. 2003. Available online: https://ihedelftrepository.contentdm.oclc.org/digital/collection/p21063coll3/id/10351/ (accessed on 18 May 2022).
- Aryal, A.; Aryal, B. Income Distribution and Its Effect on Food Expenditure, Non-Food Expenses and Savings in Households of a Developing Economy. J. Econ. Financ. Account. Stud. 2023, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verba, D.; Kudinova, A.; Tkachenko, O.; Samiilenko, A. Plotting Engel curves for commodities “food” and “education” in the context of Ukrainian households’ well-being evaluation. Financ. Credit Act. Probl. Theory Pract. 2023, 2, 3974. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Q.; Yi, F.; Tian, X. Disparate changes of living standard in China: Perspective from Engel’s coefficient. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2022, 15, 481–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiffen, M. Population density, economic growth and societies in transition: Boserup reconsidered in a Kenyan case-study. Dev. Chang. 2010, 26, 31–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.M.; Zhang, P.Y.; Yu, C.; Li, G.Y.; Wang, C.X. Theoretical and practical issues of China’s new urbanization. Scientia Geogr. Sin. 2014, 34, 641–647. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.B.; Li, R.D.; Song, X.F. Correlation analysis of regional urbanization and ecological environment coupling in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2005, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Li, R.D.; Song, X.F. Analysis of coupling degree between urbanization and ecological environment in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2005, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S. Water footprints in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei: A perspective from comparisons between urban and rural consumptions in different regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variable Type | Variable Name | Symbol | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| natural factors | total water resources | wr | 100 million cubic meters |
| per capita water resources | wr_p | cubic meters | |
| economic factors | gross domestic product (GDP) | GDP | trillion |
| per capita gross domestic product | GDP_p | CNY ten thousand | |
| the proportion of food expenditure in total expenditure | food | percentage | |
| the proportion of output value of the primary industry in total output value | agri | percentage | |
| social factors | population density | pop | persons per square kilometer |
| urbanization rate | urb | percentage | |
| average years of education per capita | edu | year | |
| technological factors | crop yield per unit area | yield | kilograms per hectare |
| total agricultural machinery power | power | ten thousand kilowatts | |
| dietary water footprint intensity | intensity | percentage |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.; Zhang, T.; Yu, W.; Shen, D.; Wang, W. China’s Water Footprint on Urban and Rural Food Consumption: A Spatial–Temporal Evolution and Its Driving Factors Analysis from 2000 to 2020. Water 2024, 16, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16020247
Song Z, Zhang T, Yu W, Shen D, Wang W. China’s Water Footprint on Urban and Rural Food Consumption: A Spatial–Temporal Evolution and Its Driving Factors Analysis from 2000 to 2020. Water. 2024; 16(2):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16020247
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Zixuan, Tingting Zhang, Wenmeng Yu, Dajun Shen, and Weijia Wang. 2024. "China’s Water Footprint on Urban and Rural Food Consumption: A Spatial–Temporal Evolution and Its Driving Factors Analysis from 2000 to 2020" Water 16, no. 2: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16020247
APA StyleSong, Z., Zhang, T., Yu, W., Shen, D., & Wang, W. (2024). China’s Water Footprint on Urban and Rural Food Consumption: A Spatial–Temporal Evolution and Its Driving Factors Analysis from 2000 to 2020. Water, 16(2), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16020247






