Mechanism of Enhanced Fluoride Adsorption Using Amino-Functionalized Aluminum-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instruments and Experimental Reagents
2.2. Preparation of NH2-MIL-101 (Al)
2.3. Characterization Methods for NH2-MIL-101 (Al)
- (1)
- X-ray Diffraction Analysis (XRD)
- (2)
- Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
- (3)
- Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
- (4)
- Specific Surface Area and Pore Size Analysis (BET)
2.4. Adsorption Experiment and Analysis
2.4.1. Adsorption Experiment
2.4.2. Adsorption Kinetics
- (1)
- Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Model
- (2)
- Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model
2.4.3. Adsorption Isotherms
- (1)
- Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm Model
- (2)
- Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization Analysis of NH2-MIL-101 (Al)
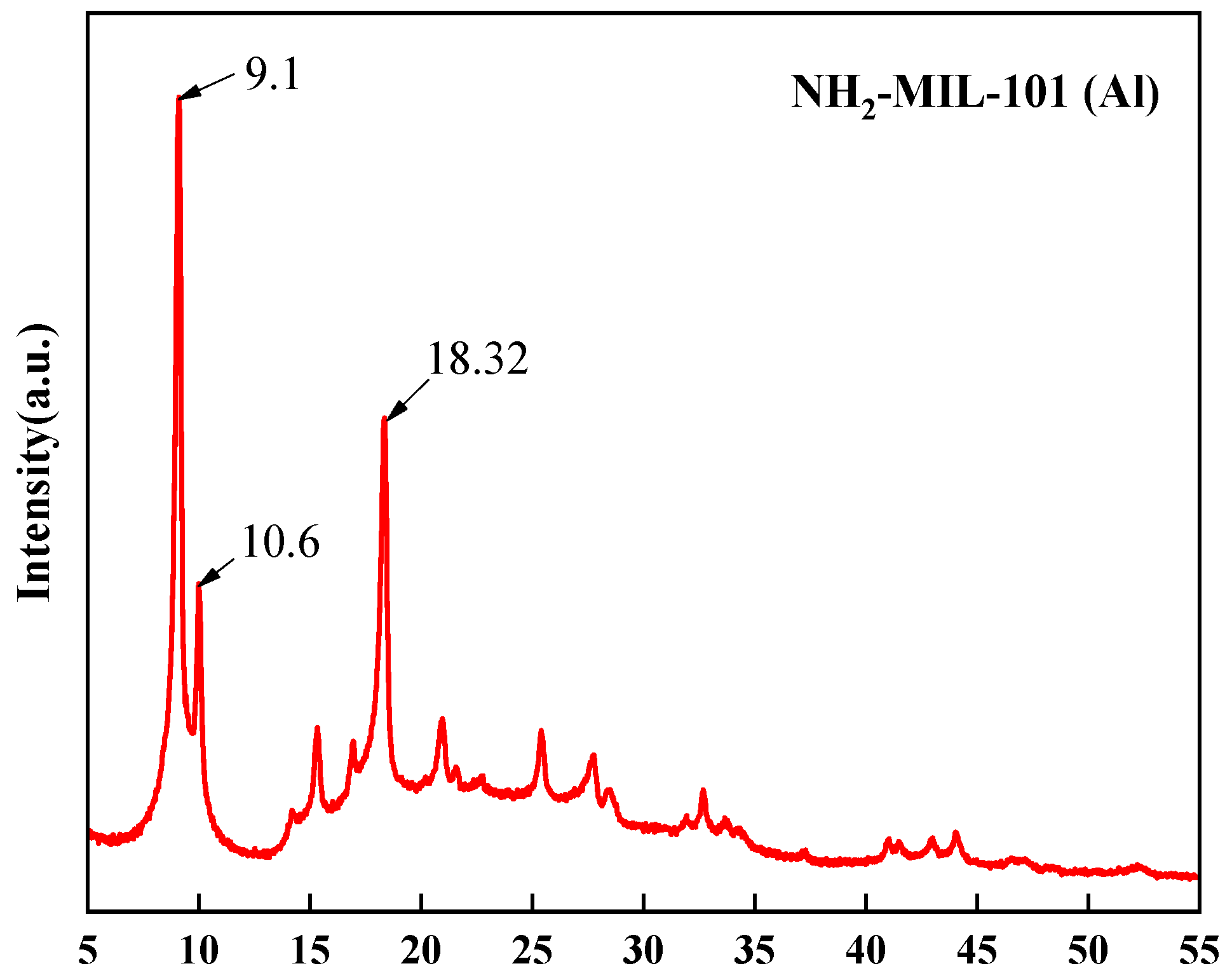
3.1.1. X-ray Diffraction Analysis (XRD)
3.1.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
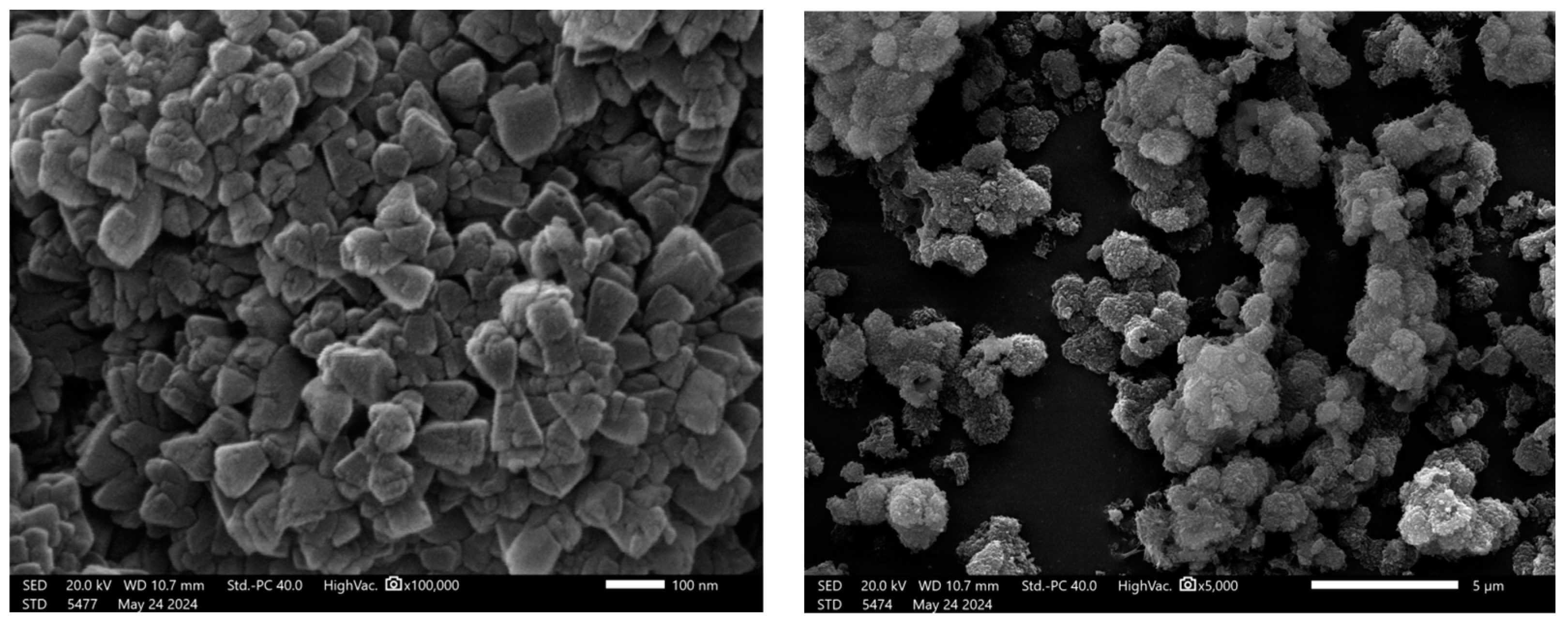
3.1.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.1.4. Specific Surface Area and Pore Size Analysis (BET)
3.2. Effect of Material Dosage on Adsorption Performance
3.3. Effect of Initial Fluoride Solution Concentration on the Defluorination Efficiency of NH2-MIL-101 (Al)
3.4. Effect of Solution pH on Fluorination Removal of NH2-MIL-101 (Al)
3.5. Effect of Reaction Time on Defluorination Using NH2-MIL-101 (Al)
3.6. Adsorption Kinetics Analysis
3.6.1. Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Model
3.6.2. Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model
3.7. Adsorption Isotherm Analysis
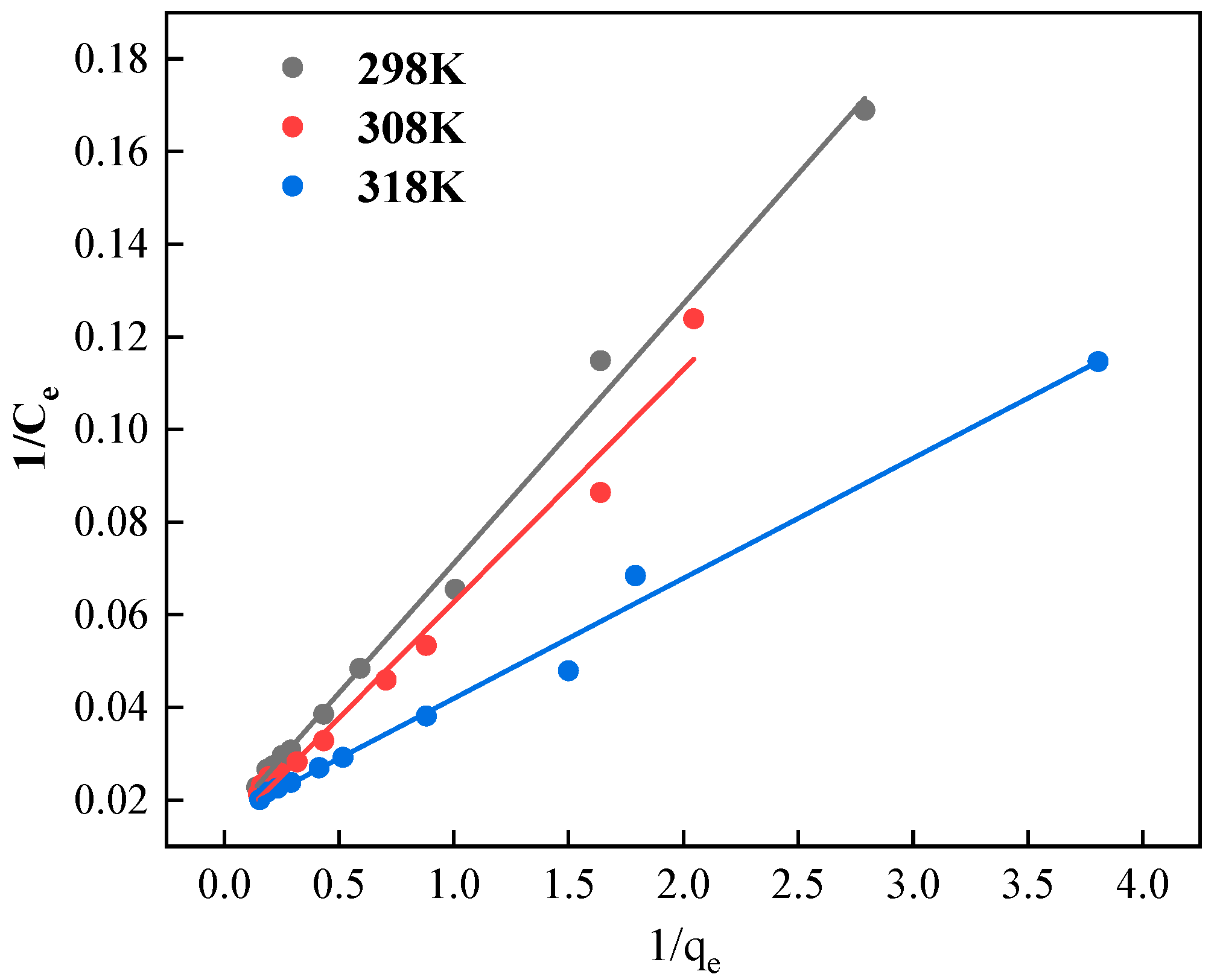
3.7.1. Langmuir Model
3.7.2. Freundlich Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kabir, H.; Gupta, A.K.; Tripathy, S. Fluoride and human health: Systematic appraisal of sources, exposures, metabolism, and toxicity. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 1116–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Mukherjee, K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Saha, B. Sources and toxicity of fluoride in the environment. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2013, 39, 2881–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Du, J. Removal Performance of Fluoride Ions from Drinking Water Using Metal Salt-Modified Activated Magnesium Oxide. J. Environ. Eng. 2023, 17, 2181–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, T. Advances in Functional Fluoride Removal Adsorbents for Drinking Water and Fluoride-Containing Wastewater. Environ. Chem. 2024, 43, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.Y.H.; Kuo, Y.L.; Liu, J.C. Fluoride at waste oyster shell surfaces—Role of magnesium. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wambu, E.W.; Ambusso, W.O.; Onindo, C.; Muthakia, G.K. Review of fluoride removal from water by adsorption using soil adsorbents—An evaluation of the status. J. Water Reuse Desalination 2016, 6, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Lataye, D.H.; Wasewar, K.L. Removal of fluoride from aqueous solution by using bael (Aegle marmelos) shell activated carbon: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. J. Fluor. Chem. 2017, 194, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradpisheh, Z.; Mirzaei, M.; Mahvi, A.H.; Mokhtari, M.; Azizi, R.; Fallahzadeh, H.; Ehrampoush, M.H. Impact of drinking water fluoride on human thyroid hormones: A case-control study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5749-2006; Sanitary Standards for Drinking Water. Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China and National Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Srivastava, S.; Flora, S. Fluoride in drinking water and skeletal fluorosis: A review of the global impact. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2020, 7, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasin, C.P.; Pathan, A.; Patel, R.V. An Evaluation of Carbon Nanotube-based and Activated Carbon-based Nanocomposites for Fluoride and Other Pollutant Removal from Water: A Review. Curr. Mol. Med. 2024, 9, 16–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.K.; Raghav, R.; Pandey, R. Recent advancements in fluoride impact on human health: A critical review. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2023, 20, 100305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, J.; Hussain, I.; Sharma, K. Fluoride and health hazards: Community perception in a fluorotic area of central Rajasthan (India): An arid environment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 162, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Thakur, S.K.; Sarkar, A.; Shekhar, S. Worldwide contamination of water by fluoride. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2016, 14, 291–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.; Mukhopadhyay, D.K. Human health hazards due to arsenic and fluoride contamination in drinking water and food chain. In Groundwater Development and Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 351–369. [Google Scholar]
- Sunkari, E.D.; Adams, S.J.; Okyere, M.B.; Bhattacharya, P. Groundwater fluoride contamination in Ghana and the associated human health risks: Any sustainable mitigation measures to curtail the long term hazards? Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 16, 100715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutai, I.K.; Kiriamiti, H.K.; M’Arimi, M.; Tewo, R.K. Fluoride removal from water using Al(OH)3-surface modified diatomite mixed with brick: Optimization, isotherm and kinetic studies. Aims Environ. Sci. 2024, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Chai, L.; Tang, C.; Li, B.; Yang, Z. Comparison of the degradation of molecular and ionic ibuprofen in a UV/H2O2 system. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 2174–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Su, R.; Yao, H.; Zhang, A.; Xiang, S.; Huang, L. Degradation of trimethoprim by sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes: Kinetics, mechanisms, and effects of natural water matrices. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 62572–62582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, R.; Dai, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Ouyang, D. Metronidazole degradation by UV and UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation processes: Kinetics, mechanisms, and effects of natural water matrices. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Su, R. Environmental impact of waste treatment and synchronous hydrogen production: Based on life cycle assessment method. Toxics 2024, 12, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorski, J.; Berg, M. Global analysis and prediction of fluoride in groundwater. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, N.; Derakhshani, R.; Sayadi, M.H. Approaches for the Efficient Removal of Fluoride from Groundwater: A Comprehensive Review. Toxics 2024, 12, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.J.; Zhang, C.; Ma, J.Q.; Sun, W.Q.; Shah, K.J. Review of fluoride removal technology from wastewater environment. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 299, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Xue, R.; Ma, X.; Zeng, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, S. Targeted improvement of narrow micropores in porous carbon for enhancing trace benzene vapor removal: Revealing the adsorption mechanism via experimental and molecular simulation. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2024, 671, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, J.; Hu, C.Z.; Qu, J.H. Sulfate Doping Promotes Agglomeration of Calcium Fluoride Crystals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 4450–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, R.; Zhang, H.; Chen, F.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L. Applications of single atom catalysts for environmental management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.Y.; Zhang, W.J.; Che, J.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Chen, Y.Q. Controllable and selective fluoride precipitation from phosphate-rich wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, B.L.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.P.; Zhou, F.; Guo, Y.C.; Yang, Y.H. Nanometer lanthanum hydroxide modified anionic polymer for deep fluoride removal: Adsorption properties and mechanism study. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2023, 33, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipplook, M.; Tanaka, H.; Sudare, T.; Hagio, T.; Saito, N.; Teshima, K. Nanoarchitectonics Solution Plasma Polymerization of Amino-Rich Carbon Nanosorbents for Use in Enhanced Fluoride Removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 7038–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, B.S.; Kumar, P.S.; Rangasamy, G.; Badawi, M.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Membrane-based removal of fluoride from groundwater. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 488, 150880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Li, C.J.; Chen, W.L.; Fang, H.P.; Huang, F.; Zhang, Y.L.; Pan, L.; Zheng, Y.C.; et al. Ionic liquid-functionalized transition-metal oxides as highly recyclable and efficient nano-adsorbent for fluoride removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 351, 128003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.Q.; Wang, Z.R.; Li, P.C.; Zhou, X.J.; Shen, S.S. Preparation of a positive porous polyvinylidene fluoride membrane and its removal of mercury containing wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 287, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, C.C.; Lerner, J.E.C.; Bertola, N.C.; Zaritzky, N.E. Synthesis and characterization of functional calcium-phosphate-chitosan adsorbents for fluoride removal from water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 264, 130553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.X.; Xiao, Y.J.; Lu, T.X.; He, G.C.; Ding, Z.X.; Wang, D.L.; Zhang, P.; Hu, Y.L. MgO modified sucrose-derived porous carbon composite for fluoride adsorption. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.R.D.; Jurado-Davila, I.V.; De Oliveira, J.T.; Nunes, K.G.P.; Estumano, D.C.; de Oliveira, R.A.; Carissimi, E.; Féris, L.A. Exploring Key Parameters in Adsorption for Effective Fluoride Removal: A Comprehensive Review and Engineering Implications. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.X.; Zhou, X.M.; Li, J.F.; Li, F.; Li, X.D.; Yu, J.X.; Guo, L.; Song, G.P.; Xiao, C.Q.; Zhou, F.; et al. Efficient removal of phosphate and fluoride from phosphogypsum leachate by lanthanum-modified zeolite: Synchronous adsorption behavior and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.L.; Wang, S.Y.; Shi, K.; Xiong, H.X. Adsorption removal of fluoride from polluted drinking waters using Mn-Al-La oxide. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 7122–7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.R.; Zhang, H.; Lu, J.X.; Cui, Y.G.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Xue, J.; Cao, H. Advanced magnetic adsorbents for enhanced phosphorus and fluoride removal from wastewater: Mechanistic insights and applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 353, 128195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Qi, T.; Chen, R.; Su, R.; Zeng, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, S. Experimental and theoretical calculations insight into acetone adsorption by porous carbon at different pressures: Effects of pore structure and oxygen groups. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2023, 646, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, H.; Morimoto, K.; Saito, T.; Hara, J. Simultaneous removal of arsenate and fluoride using magnesium-based adsorbents. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Messaoudi, N.; Franco, D.S.P.; Gubernat, S.; Georgin, J.; Senol, Z.M.; Cigeroglu, Z.; Allouss, D.; El Hajam, M. Advances and future perspectives of water defluoridation by adsorption technology: A review. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Gabbaï, F.P. Phosphonium boranes for the selective transport of fluoride anions across artificial phospholipid membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 5298–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Z.; Pan, S.L.; Zhang, M.; Qi, J.W.; Sun, X.Y.; Gu, C.; Wang, L.J.; Li, J.S. Modified hydrous zirconium oxide/PAN nanofibers for efficient defluoridation from groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanasekaran, P.; Sai, P.M.S.; Gnanasekar, K.I. Fixed bed adsorption of fluoride by Artocarpus hirsutus based adsorbent. J. Fluor. Chem. 2017, 195, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, L.Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Fu, D.D.; Zhao, Y.P. FeOOH-graphene oxide nanocomposites for fluoride removal from water: Acetate mediated nano FeOOH growth and adsorption mechanism. J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 2017, 490, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.C.; Kitagawa, S. Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5415–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiftlik, A.; Semerci, T.G.; Sahin, O.; Semerci, F. Two-dimensional metal-organic framework nanostructures based on 4,4′-sulfonyldibenzoate for photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes. Cryst. Growth Des. 2021, 21, 3364–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Xie, C.; Alhassan, S.I.; Huang, S.; Chen, R.; Xiang, S.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L. Oxygen reduction reaction in the field of water environment for application of nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Tian, F.K.; Deng, Y.X.; Yang, L.L.; Zhang, H.H.; Zhao, D.S.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.T.; Fan, L.M. Cluster-based multifunctional copper(ii) organic framework as a photocatalyst in the degradation of organic dye and as an electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Cryst. Growth Des. 2021, 21, 4242–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.K.; Li, Z.S.; Cheng, F.H.; Dai, X.R.; Wang, H.Q.; Luo, Y.T.; Huang, L. Advances in the degradation of emerging contaminants by persulfate oxidation technology. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Su, R. Cobalt-based mof material activates persulfate to degrade residual ciprofloxacin. Water 2024, 16, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolkou, A.K.; Zouboulis, A.I. Fluoride Removal from Water Sources by Adsorption on MOFs. Separations 2023, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, Q.; Tang, H.; Hu, Y.C.; Wang, W.L. MOFs-Based Photoelectrochemical Sensing Interface and Its Applications. Prog. Chem. 2024, 36, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.L.; Song, J.Y.; Zhao, J.Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Yang, W.S.; Hu, J.P. Novel MOF(Zr)-on-MOF(Ce/La) adsorbent for efficient fluoride and phosphate removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.X.; Han, J.Z.; Huang, X.H.; Qiu, S.; Liu, X.H.; Liu, L.L.; Zhao, M.J.; Qu, J.W.; Zou, J.L.; Zhang, J. Organic pollutants removal from aqueous solutions using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as adsorbents: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xu, W.; Su, R.; Shao, L.; Zeng, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, H. Insights into CO2 capture in porous carbons from machine learning, experiments and molecular simulation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306, 122521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Su, R.; Ma, X.; Zeng, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, H. Porous carbon for oxygenated and aromatic VOCs adsorption by molecular simulation and experimental study: Effect pore structure and functional groups. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 605, 154708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ye, M.; Zhou, Y.; Su, R.; Huang, S.; Chen, Y.; Dai, X. Synergistic enhancement of oxytetracycline hydrochloride removal by UV/ZIF-67 (Co)-activated peroxymonosulfate. Water 2024, 16, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X.; Xie, Z.; Kuang, Q.; Zheng, L. The function of metal–organic frameworks in the application of MOF-based composites. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 2628–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almáši, M. A review on state of art and perspectives of Metal-Organic frameworks (MOFs) in the fight against coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. J. Coord. Chem. 2021, 74, 2111–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, B.; Sahoo, R.; Das, M.C. pH-stable MOFs: Design principles and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 493, 215301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, H.; Bagherian, G.; Forghani Tehrani, G. Application of NH2-MIL-101(Al) as a new adsorbent for defluoridation of aqueous solutions: Isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Int. J. Enivron. Sci. Technol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Crespo, P.; Ramos-Fernandez, E.V.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F. Synthesis and characterization of an amino functionalized MIL-101 (Al): Separation and catalytic properties. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 2565–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Su, R. Preparation of NH2-MIL-101(Fe) metal organic framework and its performance in adsorbing and removing tetracycline. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzilli, J.R.; Collaborators. Determination of Fluoride in Fluoride Tablets and Solutions by Ion-Selective Electrode: Collaborative Study. J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. 1984, 67, 682–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongphat, A.; Wongcharee, S.; Chaiduangsri, N.; Suwannahong, K.; Kreetachat, T.; Imman, S.; Suriyachai, N.; Hongthong, S.; Phadee, P.; Thanarat, P.; et al. Using excel solver’s parameter function in predicting and interpretation for kinetic adsorption model via batch sorption: Selection and statistical analysis for basic dye removal onto a novel magnetic nanosorbent. Chemengineering 2024, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannahong, K.; Wongcharee, S.; Kreetachat, T.; Imman, S.; Suriyachai, N.; Hongthong, S.; Rioyo, J.; Dechapanya, W.; Noiwimol, P. Comprehensive cost-benefit and statistical analysis of isotherm and kinetic models for heavy metal removal in acidic solutions using weakly base polymeric chelating resin as adsorbent. Water 2024, 16, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption isotherm models: Classification, physical meaning, application and solving method. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadipouya, S.; Ahmadijokani, F.; Molavi, H.; Rezakazemi, M.; Arjmand, M. CO2/CH4 separation by mixed-matrix membranes holding functionalized NH2-MIL-101(Al) nanoparticles: Effect of amino-silane functionalization. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2021, 176, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaeva, V.I.; Tarasov, A.L.; Starannikova, L.E.; Yampol’skii, Y.P.; Alent’ev, A.Y.; Kustov, L.M. Microwave-assisted synthesis of mesoporous metal-organic framework NH2-MIL-101(Al). Russ. Chem. Bull. 2015, 64, 2791–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.T.; Chi, L.N.; Wang, X.Z.; Wang, Y.; Sui, Y.M.; Xie, T.T.; Arandiyan, H. Effective and selective adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solution via trivalent-metals-based amino-MIL-101 MOFs. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 357, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Jia, X.; Hou, X.; Xia, R.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X. Characterization of magnetic aluminum-based metal-organic frameworks and their adsorption performance for fluoride in water. Environ. Sci. Res. 2021, 34, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y. Study on the Adsorption of Phosphorus and Fluorine in Water by ZIF-8 and NH2-MIL-101 (Al). Ph.D. Dissertation, Yunnan University, Kunming, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kamarehie, B.; Noraee, Z.; Jafari, A.; Ghaderpoori, M.; Karami, M.A.; Ghaderpoury, A. Data on the fluoride adsorption from aqueous solutions by metal-organic frameworks (ZIF-8 and Uio-66). Data Brief 2018, 20, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.L.; Krusnamurthy, P.A.P.; Nakajima, H.; Rashid, S.A. Adsorptive, kinetics and regeneration studies of fluoride removal from water using zirconium-based metal organic frameworks. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 18740–18752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaseelan, A.; Naushad, M.; Ahamad, T.; Viswanathan, N. Design and development of amine functionalized iron based metal organic frameworks for selective fluoride removal from water environment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.F.; Zhang, T.; Lv, L.; Chen, Y.X.; Tang, W.X.; Tang, S.W. Room-temperature synthesis of MIL-100(Fe) and its adsorption performance for fluoride removal from water. Colloid. Surf. A 2021, 624, 126791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.G.; Zhu, H.; Sun, T.S.; Liu, Y.B.; Han, T.; Lu, J.X.; Dai, H.L.; Zhai, L.Z. Synthesis and study of an efficient metal-organic framework adsorbent (MIL-96(Al)) for fluoride removal from water. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 3128179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Hua, L.; Li, H.; Han, X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, F.; He, L.; et al. Room-temperature methane conversion by graphene-confined single iron atoms. Chem 2018, 4, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehra, S.; Raghav, S.; Kumar, D. Biomaterial functionalized cerium nanocomposite for removal of fluoride using central composite design optimization study. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, U.; Behera, S.K.; Meikap, B.C. A novel acid modified alumina adsorbent with enhanced defluoridation property: Kinetics, isotherm study and applicability on industrial wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 868–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, G.J.; CouperthWaite, S.J.; Dawes, L.A.; Thompson, S.; Spencer, J. Activated alumina for the removal of fluoride ions from high alkalinity groundwater: New insights from equilibrium and column studies with multicomponent solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 187, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





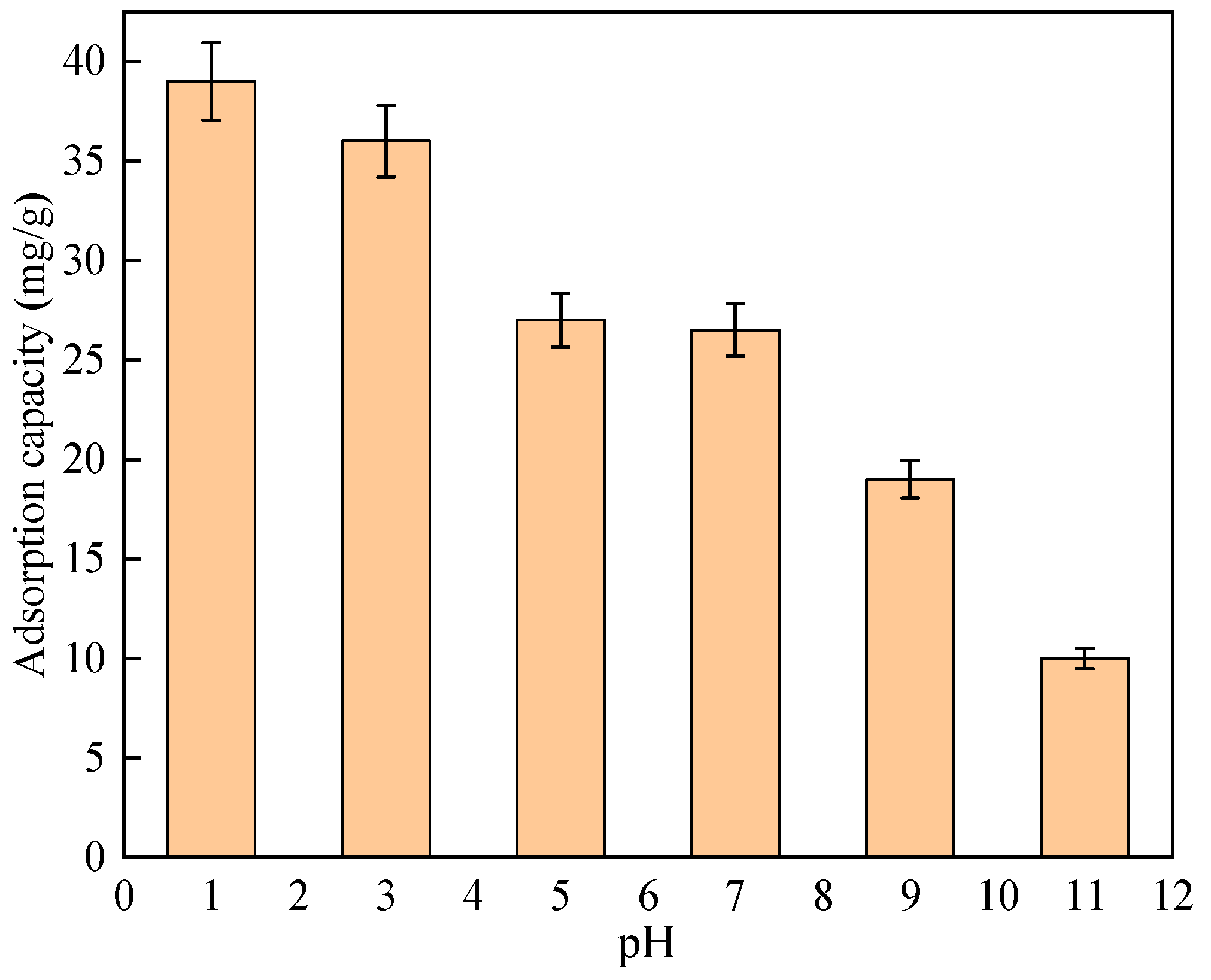




| (mg·g−1) | (min−1) | |
|---|---|---|
| 30.4 | −0.02346 | 0.95278 |
| qe (mg·g−1) | K2 (g/(mg·min)) | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 37.0 | 0.000373 | 0.99727 |
| Temperature/k | Slope | Intercept | qm | KL | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 0.01501 | 0.05606 | 67 | 0.2677 | 0.9942 |
| 308 | 0.01265 | 0.0501 | 79 | 0.2525 | 0.9801 |
| 318 | 0.016 | 0.02593 | 63 | 0.6170 | 0.9879 |
| Temperature/k | Slope | Intercept | 1/n | KF | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 1.1222 | 0.6731 | 0.6731 | 13.2520 | 0.9761 |
| 308 | 1.1954 | 0.6199 | 0.6199 | 15.6830 | 0.9547 |
| 318 | 1.3320 | 0.5199 | 0.5199 | 21.4822 | 0.9417 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ye, M.; Zhou, Y.; Su, R.; Huang, S.; Chen, Y.; Dai, X. Mechanism of Enhanced Fluoride Adsorption Using Amino-Functionalized Aluminum-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks. Water 2024, 16, 2889. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202889
Luo Y, Liu Z, Ye M, Zhou Y, Su R, Huang S, Chen Y, Dai X. Mechanism of Enhanced Fluoride Adsorption Using Amino-Functionalized Aluminum-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks. Water. 2024; 16(20):2889. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202889
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Yiting, Zhao Liu, Mingqiang Ye, Yihui Zhou, Rongkui Su, Shunhong Huang, Yonghua Chen, and Xiangrong Dai. 2024. "Mechanism of Enhanced Fluoride Adsorption Using Amino-Functionalized Aluminum-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks" Water 16, no. 20: 2889. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202889
APA StyleLuo, Y., Liu, Z., Ye, M., Zhou, Y., Su, R., Huang, S., Chen, Y., & Dai, X. (2024). Mechanism of Enhanced Fluoride Adsorption Using Amino-Functionalized Aluminum-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks. Water, 16(20), 2889. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202889







