Relationship Between Aquatic Factors and Sulfide and Ferrous Iron in Black Bloom in Lakes: A Case Study of a Eutrophic Lake in Eastern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
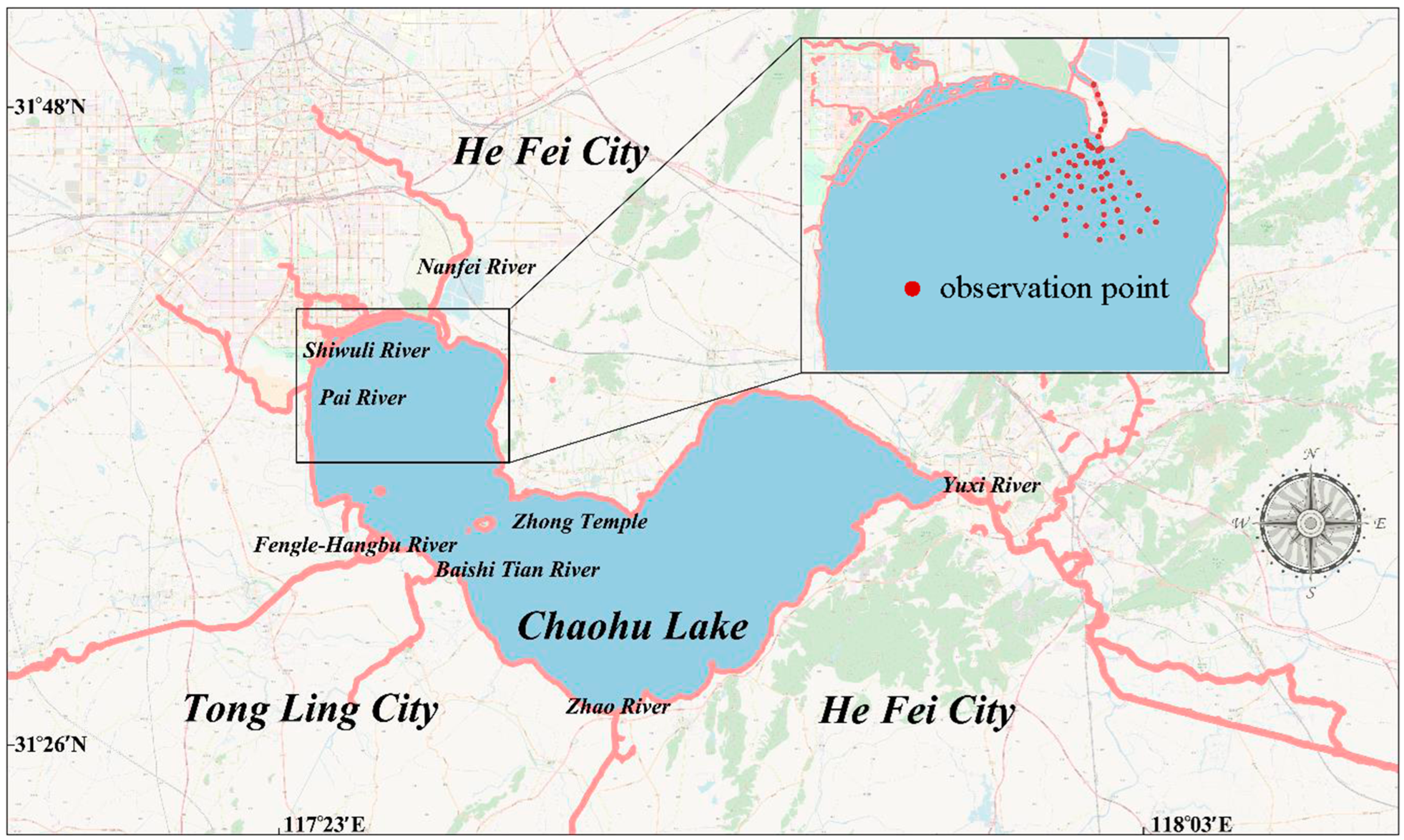
2. Study Region and Data Source
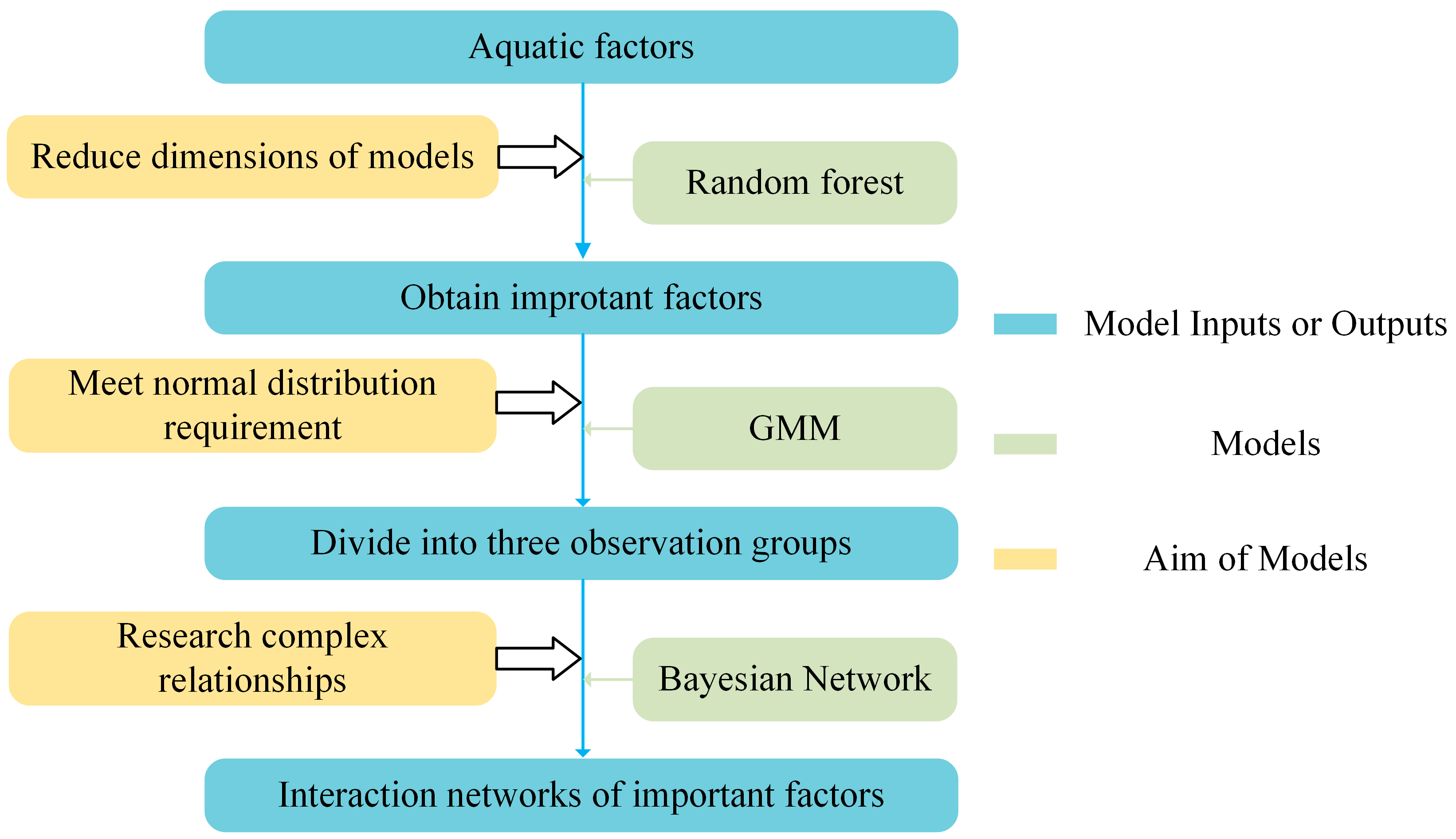
3. Methods
3.1. Random Forest
3.2. Gaussian Mixture Model
3.3. Bayesian Network
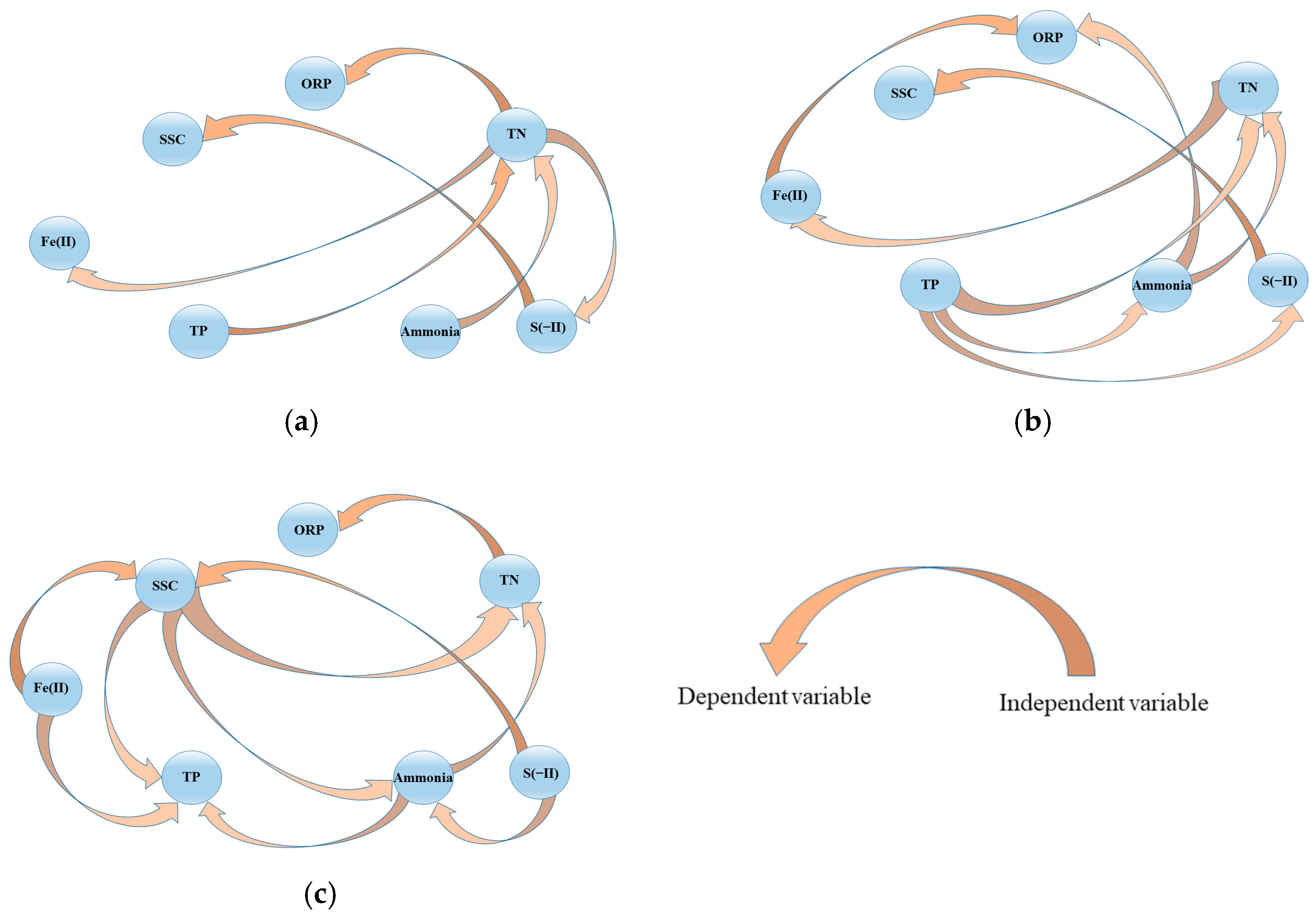
4. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, C.X. Progress and Prospect in Formation of Black Bloom in Lake Taihu: A Review. J. Lake Sci. 2015, 27, 553–566. [Google Scholar]
- Lazaro, T.R. Urban Hydrogy; Ann Arbor Science Publishers, Inc.: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Stahl, J.B. Black Water and Two Peculiar Types of Stratification in an Organically Loaded Strip-Mine Lake. Water Res. 1979, 13, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, B.; Ludlam, S.D. The Black Water Chemocline of Meromictic Lower Mystic Lake, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Intl. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2001, 86, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Lu, J.; Zhu, G.W.; Gao, M.Y.; Wen, L.; Yao, M.; Nie, Q. Occurence Characteristics of Black Patch Events and Their Influencing Factors in Lake Taihu During 2009 and 2017. J. Lake Sci. 2018, 30, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L. Doing Battle with the Green Monster of Taihu Lake. Science 2007, 317, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.C.; Xu, Z.A.; Wu, D.H. Relationships between Accumulation and Dying of Cyanobacteria and Black Spot. J. Hydroecol. 2012, 33, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.H.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, J.H. Analysis of Black Water Aggregation in Taihu Lake. Water Sci. Eng. 2011, 4, 374–385. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Liu, X.H.; Zhu, G.W.; Qin, B.Q.; Gao, G. Long-Term Modis Observations of Cyanobacterial Dynamics in Lake Taihu: Responses to Nutrient Enrichment and Meteorological Factors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Ding, S.; Yao, L.; Shen, Q.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Xua, D. Dynamics of Phosphorus-Iron-Sulfur at the Sediment-Water Interfaceinfluenced by Algae Blooms Decomposition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, C.; Yin, H.B.; Fan, C.X. The Main Sulfur-Containing Odorous Compounds and Their Forming Mechanisms in Waters During Bio-Induced Black Bloom. J. Lake Sci. 2015, 27, 583–590. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Fan, C.X.; He, W.; Deng, J.C.; Yin, H.B. Sulfur-Containing Amino Acid Methionine as the Precursor of Volatile Organic Sulfur Compounds in Algea-Induced Black Bloom. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.X.; Shen, Q.S. Identification of Black Suspended Particles in the Algae-Induced Black Bloom Water Column. J. Lake Sci. 2015, 27, 591–598. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, N.H.; Qian, X.; Kong, F.X. Analysis of Meteorological Factors of Forming Feculent and Anaerobic Water Aggreation Induced by Algal Bloom in Taihu Lake. Environ. Sci. 2011, 32, 401–408. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.F.; He, J.; Fan, C.X.; Zhang, L.; Shen, Q.S.; Zhong, J.C.; Yan, S.H. Environment Effects of Algae-Caused Black Spots: Impacts on Fe-Mn-S Cycles in Water-Sediment Interface. Environ. Sci. 2010, 31, 2652–2660. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.F.; Fan, C.X.; Zhang, L.; Shen, Q.S.; Wang, Z.D.; Han, S.Q. Environment Effects of Algae-Caused Black Spots Iii: Impacts on Fe-S-P Cycle in Water-Sediment Interface. China Environ. Sci. 2014, 34, 3199–3206. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Q.S.; Fan, C.X.; Liu, C.; Chen, C. The Limiting Factor to the Outbreak of Lake Black Bloom:Roles of Ferrous Iron and Sulfide Ions. Clean Soil Air Water 2018, 46, 1800305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, D.E., Jr.; Linda, S.B.; Hodgson, L.M. Relations between Color and Some Limnological Characteristics of Florida Lakes. JAWRA 1984, 20, 323–329. [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura, N.; Utsumi, M.; Wei, B.; Iwami, N.; Okano, K.; Kawauchi, Y.; Maekawa, T. Assessment for the Complicated Occurrence of Nuisance Odours from Phytoplankton and Environmental Factors in a Eutrophic Lake. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2004, 9, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzialowski, A.R.; Smith, V.H.; Huggins, D.G.; de Noyelles, F.; Lim, N.-D.; Baker, D.S.; Beurya, J.H. Development of Predictive Models for Geosmin-Related Taste and Odor in Kansas, USA, Drinking Water Reservoirs. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2829–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Wang, L.; Hua, Z.L.; Ding, S.M. The Relationships of Velocity, Dissolved Oxygen with Fe2+, S2− in Black Bloom Region on Nanfei River Estuary of Lake Chaohu. J. Lake Sci. 2016, 28, 710–717. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.L.; Wang, L.; Hua, Z.L. The Relationships of Different Concentration Fe2+, S2− with Hydrodynamics, Do in Black Bloom Water Based on Quantile Regression Method. China Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 627–633. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.L.; Cheng, H.M.; Cheng, J.L. Identifying the Driving Factors of Black Bloom in Lake Bay through Bayesian Lasso. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brieman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraley, C.; Rafery, A.E. Model-Based Clustering, Discriminant Analysis, and Density Estimation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2002, 97, 611–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, J. Causality: Models, Reasoning and Inference, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F. Mornitoring and Analytic Method for Water and Waste Water; China Environmental Publisher: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 88–129. [Google Scholar]
- Cline, J.D. Spectrophotometric Determination of Hydrogen Sulfide in Natural Waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1969, 14, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.F.; Shen, Q.S.; Zhang, L.; Fan, C.X.; Zhong, J.C.; Yan, S.H. Environment Effects of Algae-Caused Black Spots: Driving Effects on the N,P Changes in the Water-Sediment Interface. Environ. Sci. 2010, 31, 2917–2924. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.H.; Ma, Q. Monitoring and Analysis on “Black Water Aggregation” in Lake Taihu, 2009. J. Lake Sci. 2010, 22, 481–487. [Google Scholar]
- Speybroeck, N. Classification and Regression Trees. Int. J. Public Health 2012, 57, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Antia, S.T.; Edwin, R.; Bodan, Z. Comparison of Support Vector Machine and Random Forest Algorithms for Invasive and Expansive Species Classification Using Airborne Hyperspectral Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetnik, V.; Liaw, A.; Tong, C.; Culberson, J.C.; Sheridan, R.P.; Feuston, B.P. Random Forest: A Classification and Regression Tool for Compound Classification and Qsar Modeling. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2003, 43, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Wang, L.; Cheng, J.L.; He, C.D.; Cheng, H.M. Recognizing Crucial Aquatic Factors Influencing Greenhouse Gas Emissions in the Eutrophication Zone of Taihu Lake, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrucca, L.; Fop, M.; Murphy, T.B. Mclust 5 Clustering, Classification and Density Estimation Using Gaussian Finite Mixture Models. R J. 2016, 8, 289–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraley, C.; Rafery, A.E. Model-Based Methods of Classification: Using the Mclust Software in Chemomertics. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearl, J. Probabilistic Reasoning in Intelligent Systems: Networks of Plausible Inference; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, S.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Neapolitan, R.E. Learning Bayesian Networks; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Scutari, M. Learning Bayesian Networks with the Bnlearn R Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 35, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3838-2002; National Surface Water Quality Standard. State Environmental Protection Administration (China): Beijing, China, 2002.
- Fan, C.X.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Wu, Q.L. The Effects and Processes of Lake Sediment Interface; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Z.L.; Liu, X.D.; Chu, K.J.; Gu, L.; Wang, L. Numerical Simulation of Water Flow and Pollutant Transport Based on Boundary Fitting; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.L. Research on Parameters Sensitivity and Optimization Determination of Chaohu Lake Efdc Eutrophication Model; Hohai University: Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Scrucca, L. Dimension Reduction for Model-Based Clustering. Stat. Comput. 2010, 20, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, Q.M.; Wang, X.X.; Din, Y.; Sun, J.X. Reducing Organic Substances from Anaerobic Decomposition of Hydrophytes. Biogeochemistry 2009, 94, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vile, M.A.; Bridgham, S.D.; Wieder, R.K. Response of Anaerobic Carbon Mineralization Rates to Sulfate Amendments in a Boreal Peatland. Ecol. Appl. 2003, 13, 720–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartacek, J.; Manconi, I.; Sansone, G.; Murgia, R.; Lens, P. Divalent Metal Addition Restores Sulfide-Inhibited N2o Reduction in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Nitric Oxide 2010, 23, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Item *** | Minimum | Mean | SD * | Maximum | K–S Test (D/p) ** | Normal |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP (mg/L) | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.31 | 1.43 | 0.332/<0.01 | No |
| TP (mg/L) | 0.09 | 0.52 | 0.55 | 2.94 | 0.271/<0.01 | No |
| TN (mg/L) | 0.66 | 3.72 | 3.46 | 14.99 | 0.209/<0.01 | No |
| Ammonia (mg/L) | 0.33 | 3.00 | 2.94 | 12.44 | 0.287/<0.01 | No |
| S(−II) (mg/L) | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.203/<0.01 | No |
| Fe(II)(mg/L) | 0.24 | 1.27 | 0.94 | 5.51 | 0.279/<0.01 | No |
| pH | 6.83 | 7.94 | 0.39 | 8.35 | 0.193/0.011 | No |
| DO (mg/L) | 1.85 | 6.50 | 1.58 | 8.43 | 0.202/<0.01 | No |
| WT (°C) | 23.80 | 25.42 | 1.79 | 31.80 | 0.258/<0.01 | No |
| ORP (mV) | −86 | 117 | 53 | 168 | 0.209/<0.01 | No |
| COD (mg/L) | 61.33 | 78.74 | 8.00 | 110.86 | 0.194/0.011 | No |
| CHLA (mg/m3) | 17.06 | 47.98 | 24.64 | 165.46 | 0.210/<0.01 | No |
| SSC (mg/L) | 4 | 106 | 186 | 1188 | 0.331/<0.01 | No |
| Fe(II) | S(−II) | TN | TP | Ammonia | SSC | ORP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Worst | / | / | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.73 | 0.76 | 0.89 |
| Worse | 0.62 | 0.63 | 0.75 | / | 0.93 | 0.66 | 0.79 |
| Bad | 0.61 | 0.63 | 0.65 | / | 0.91 | 0.60 | 0.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Xu, C.; Niu, H.; Liu, N.; Xu, M.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J. Relationship Between Aquatic Factors and Sulfide and Ferrous Iron in Black Bloom in Lakes: A Case Study of a Eutrophic Lake in Eastern China. Water 2024, 16, 3120. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213120
Wang L, Xu C, Niu H, Liu N, Xu M, Wang Y, Cheng J. Relationship Between Aquatic Factors and Sulfide and Ferrous Iron in Black Bloom in Lakes: A Case Study of a Eutrophic Lake in Eastern China. Water. 2024; 16(21):3120. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213120
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Liang, Changlin Xu, Hao Niu, Nian Liu, Meiling Xu, Yulin Wang, and Jilin Cheng. 2024. "Relationship Between Aquatic Factors and Sulfide and Ferrous Iron in Black Bloom in Lakes: A Case Study of a Eutrophic Lake in Eastern China" Water 16, no. 21: 3120. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213120
APA StyleWang, L., Xu, C., Niu, H., Liu, N., Xu, M., Wang, Y., & Cheng, J. (2024). Relationship Between Aquatic Factors and Sulfide and Ferrous Iron in Black Bloom in Lakes: A Case Study of a Eutrophic Lake in Eastern China. Water, 16(21), 3120. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213120







