Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Net Anthropogenic Phosphorus Inputs (NAPIs) and Their Impacts in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Using Monte Carlo Simulations and Sensitivity Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
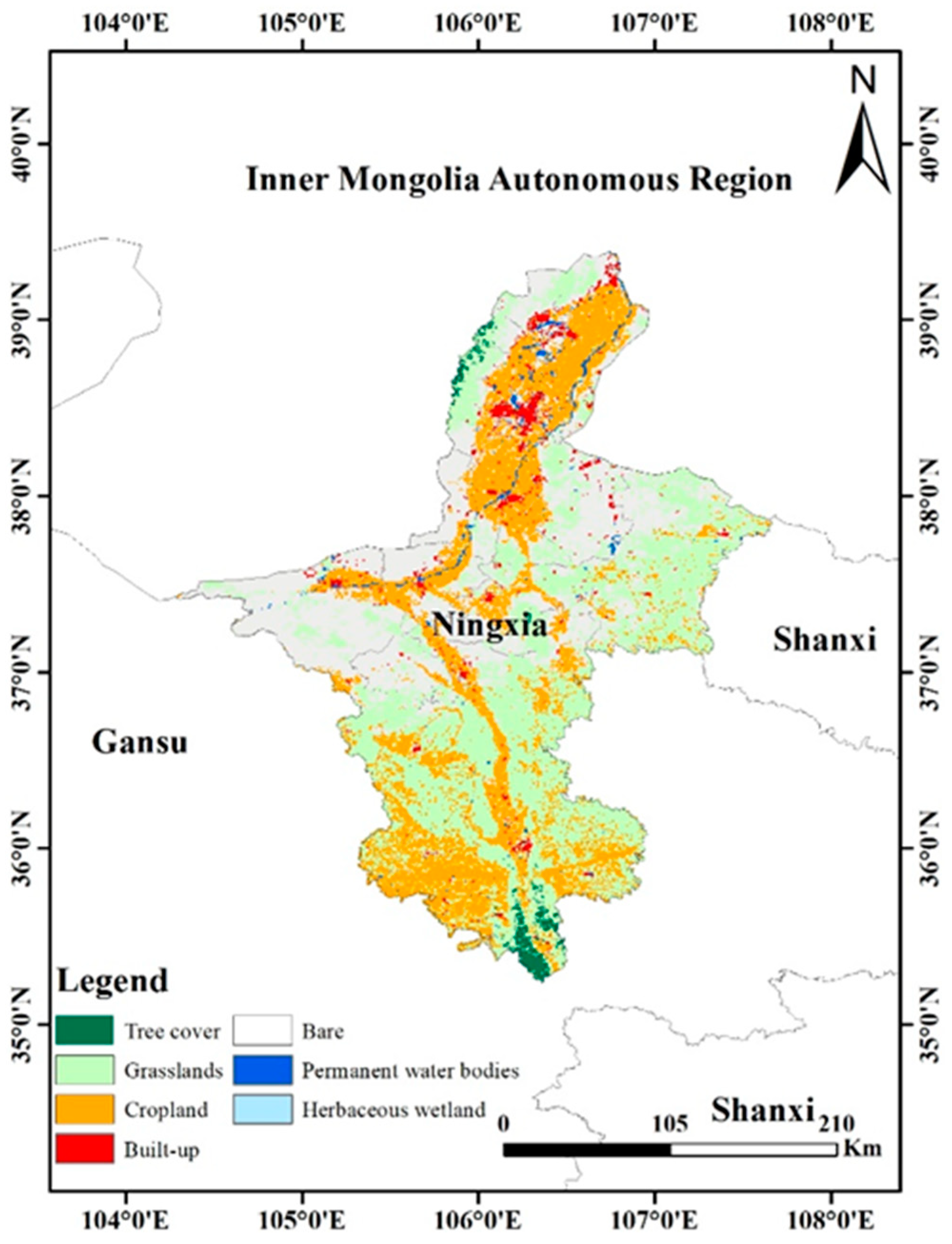
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Analysis
2.3. Estimation of the Net Anthropogenic Phosphorus Inputs
2.3.1. Calculation of Pim
2.3.2. Calculation of Pfer
2.3.3. Calculation of Pnf
2.4. Effects of Parameter Values on NAPI
2.4.1. Monte Carlo Method
2.4.2. Sensitivity Index Method
3. Results
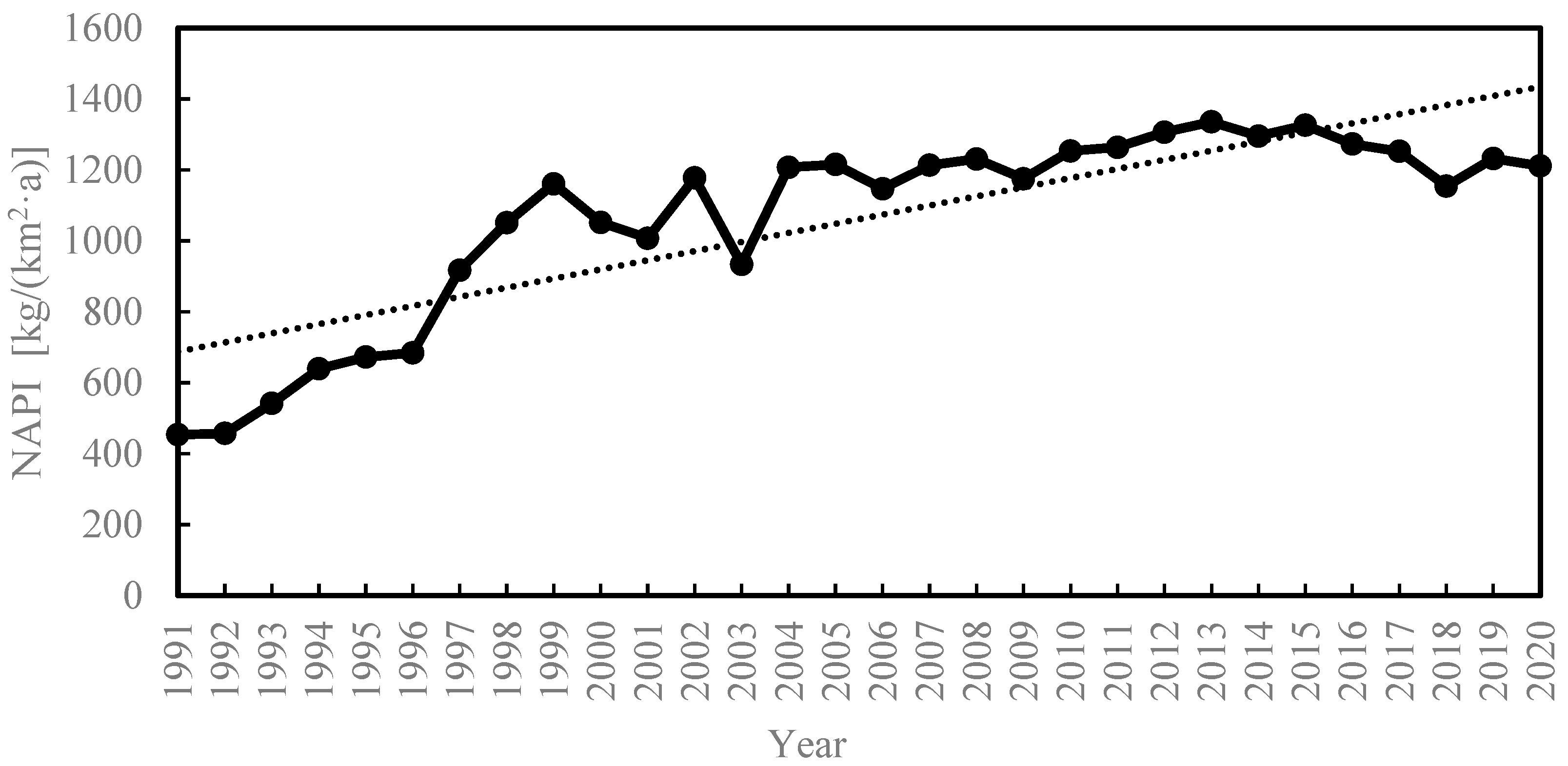
3.1. Interannual Variation Characteristics of NAPI
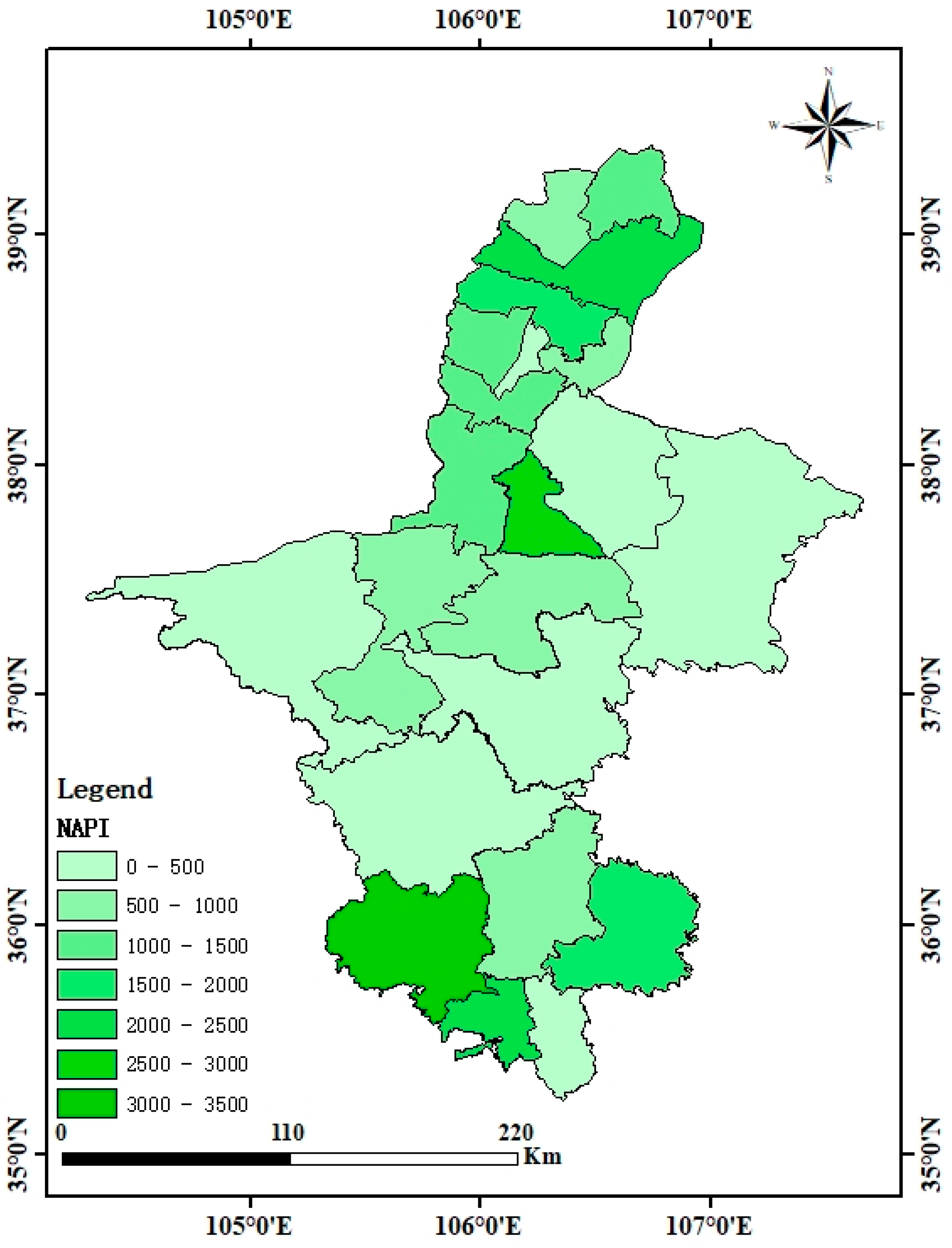
3.2. Spatial Variation Characteristics of NAPI
3.3. Uncertainty Analysis of NAPI
3.4. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, D. Toxicity Load Model of Non-point Source Phosphorus Pollution. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2019, 44, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Wang, L.J.; Chen, J.X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, S.; Liu, D. Characteristics of phosphorus pollution in rivers entering the West Dongting Lake. Res. Environ. Sci. 2018, 31, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Filippelli, G.M. The global phosphorus cycle: Past, present, and future. Elements 2008, 4, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouy, W.; Huang, H.B.; Cai, G.Q. Temporal and spatial characteristics of diffuse phosphorus pollution in the watershed without monitoring data at Chaohu Lake. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2014, 34, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Howarth, R.; Chan, F.; Conley, D.J.; Garnier, J.; Doney, S.C.; Marino, R.; Billen, G. Coupled biogeochemical cycles: Eutrophication and hypoxia in temperate estuaries and coastal marine ecosystems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, R.W. Coastal nitrogen pollution: A review of sources and trends globally and regionally. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Shi, Z.M.; Liao, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.Y. Source apportionment and evaluation of potentially toxic elements, P and Se, for paddy soils in the western margin of Chengdu Plain, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2022, 42, 327–338. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, M. Research on the Construction and Application of ArcGIS-Based Watershed Phosphorus Index Model. Master’s Thesis, Anhui Agricultural University, Hefei, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J. Spatial Distribution and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals and Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Different Land Use Patterns in the Caohai Watershed of Guizhou. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guiyang, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Hu, M.; Guo, Y.; Dahlgren, R.A. Influence of legacy phosphorus, land use, and climate change on anthropogenic phosphorus inputs and riverine export dynamics. Biogeochemistry 2015, 123, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Swaney, D.P.; Hong, B.; Howarth, R.W. Anthropogenic Phosphorus Inputs to a River Basin and Their Impacts on Phosphorus Fluxes Along Its Upstream-Downstream Continuum. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 3273–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Swaney, D.P.; Hong, B.; Howarth, R.W.; Han, H.; Li, X. Net anthropogenic phosphorus inputs and riverine phosphorus fluxes in highly populated headwater watersheds in China. Biogeochemistry 2015, 126, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, M.J.; Weller, D.E.; Jordan, T.E.; Sigwart, K.J.; Sullivan, K.J. Net anthropogenic phosphorus inputs: Spatial and temporal variability in the Chesapeake Bay region. Biogeochemistry 2008, 88, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, R.W.; Anderson, D.; Church, T.; Greening, H.; Hopkinson, C.; Huber, W.; Marcus, N.; Naiman, R.; Segerson, K.; Sharpley, A. Clean Coastal Waters—Understanding and Reducing the Effects of Nutrient Pollution; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Howarth, R.W.; Billen, G.; Swaney, D.; Townsend, A.; Jaworski, N.; Lajtha, K.; Downing, J.A.; Elmgren, R.; Caraco, N.; Jordan, T.; et al. Regional nitrogen budgets and riverine N & P fluxes for the drainages to the North Atlantic Ocean: Natural and human influences. Biogeochemistry 1996, 35, 75–139. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Bosch, N.; Allan, J.D. Spatial and temporal variation in phosphorus budgets for 24 watersheds in the Lake Erie and Lake Michigan basins. Biogeochemistry 2011, 102, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tian, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, C. Net anthropogenic phosphorus inputs (NAPI) index application in Mainland China. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Swaney, D.P.; Mörth, C.M.; Smedberg, E.; Hägg, H.E.; Humborg, C.; Howarth, R.W.; Bouraoui, F. Evaluating regional variation of net anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus inputs (NANI/NAPI), major drivers, nutrient retention pattern and management implications in the multinational areas of Baltic Sea basin. Ecol. Model. 2012, 227, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Swaney, D.P.; Mccrackin, M.; Svanbäck, A.; Humborg, C.; Gustafsson, B.; Yershova, A.; Pakhomau, A. Advances in NANI and NAPI accounting for the Baltic drainage basin: Spatial and temporal trends and relationships to watershed TN and TP fluxes. Biogeochemistry 2017, 133, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Gao, B.; Yan, C.A.; Liu, Y. Evolution of anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus inputs to Lake Poyang Basin and its’ effect on water quality of lake. Acta Sci. Circumstantiate 2016, 36, 3137–3145. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.S.; Su, J.J.; Du, X.Z.; Li, X.-Y. Net anthropogenic nitrogen input to Huaihe River Basin, China during 1990–2010. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 26, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.X. Analysis on total phosphorus and total nitrogen pollution in Erhai Lake. Yunnan Environ. Sci. 2006, 25, 113–115. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Lei, Q.L.; Luo, J.F.; Lindsey, S.; Qin, L.; Zhai, L.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Li, W. Impact of human activities on phosphorus flows on an early eutrophic plateau: A case study in Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136851.1–136851.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Wu, Y.; Lv, Z.-J.; Gao, S.-J.; Chu, Z.S.; Pang, Y. Characteristics and Spatial Distribution of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in Erhai Lake Basin and Its Classified Control Strategy. Res. Environ. Sci. 2020, 33, 2474–2483. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.C.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Gao, W. Estimating multiple spatiotemporal driving forces of anthropogenic phosphorus inputs to Yangtze River Economic Belt. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 43, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, J.D.; Zhang, X.M.; Wei, T.X. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of net nitrogen and phosphorus input from human activity: A case study of Hangzhou section of Qiandao Lake Basin. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 41, 2831–2842. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, C.N.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Xu, R.; Li, H.; Zou, T.; Tang, Q.; Liu, W.; Nie, C.; Zhao, Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Input from Human Activities in Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Circle. Res. Environ. Sci. 2022, 35, 1596–1604. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.H.; Mao, Y.P.; Zhang, H. Characteristics of anthropogenic net input of nitrogen and phosphorus and suggestions on pollution control in Pearl River Delta. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2022, 16, 2049–2060. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Lei, Q.L.; Du, X.Z.; An, M.; Liu, X.; Qiu, W.; Wu, S.; Liu, H. Spatio-temporal variation and the impacts from parameters analysis of net anthropogenic phosphorus inputs in Henan province. China Environ. Sci. 2022, 42, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.J.; Zhang, A.P.; Yang, S.Q.; Yang, S.Q. Investigation of agricultural non-point source pollution in Ningxia irrigation district and analysis of its factors. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2009, 27, 256–260. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.Z.; Qing, W.Z.; Hui, Z.; Hussain, H.A.; Shaaban, M.; Yang, Z. Pathways of nitrogen loss and optimized nitrogen management for a rice cropping system in arid irrigation region, northwest China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 268, 110702. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Li, A.; Wang, X.S.; Kong, D.; Qiu, S.; He, Y.; Yin, Y.S.; Liu, Y.F.; Liu, R.B. Spectral Method for Predicting Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and potassium in small Amount of Compound Fertilizer. Chin. J. Lasers 2021, 48, 158–166. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, X.J. Study on Plant Species Selection and Wastewater Purification Efficiency in Constructed Wetlands in Beijing. Bachelor’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W. Study on Estating Models for Estimation of Per Capita Domestic Wastewater Discharge. Bachelor’s Thesis, Suzhou University of Science and Technology, Suzhou, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ficklin, D.L.; Luo, Y.; Iris, T.; Edwin, S.; Maurer, P. Development and application of a hydroclimatological stream temperature model within the Soil and Water Assessment Tool. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W01511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Zhang, W.S. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics and division analysis of provincial net anthropogenic phosphorus input in mainland China in recent twenty years. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2019, 28, 540–547. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.P.; Xiao, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y. Spatial dstribution of the net anthropogenic phosphorus input (NAPI) to the Dongting Lake basin, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 2404–2414. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pei, W.; Du, X.Z.; Lei, Q.L.; Yan, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chen, M.; Wu, S.; Liu, H. Spatiotemporal variation of net anthropogenic nitrogen input at county level and the impacts from parameters: A case study of Henan Province. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 41, 4447–4456. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, H.B.; Hu, J.W.; Rui, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, N. Drivers of change behind the spatial distribution and fate of typical trace organic pollutants in fresh waste leachate across China. Water Res. 2024, 263, 122170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.S.; Lei, Q.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yen, H.; Wang, H.; Zhai, L.; Liu, H.; Huang, C.; Ren, T.; Zhou, J.; et al. Effects of anthropogenic activities on long-term changes of nitrogen budget in a plain river network region: A case study in the Taihu Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, W.; Yan, T.Z.; Lei, Q.L.; Zhang, T.; Fan, B.; Du, X.; Luo, J.; Lindsey, S.; Liu, H. Spatio-temporal variation of net anthropogenic nitrogen inputs (NANI) from 1991 to 2019 and its impacts analysis from parameters in Northwest China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Crop Type | P (%) | Appropriate Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Wheat | 0.044~0.188 (5) | 0.167 (8) |
| Beans | 0.373~0.465 (6) | 0.418 (6) |
| Rice | 0.074~0.230 (4) | 0.082 (8) |
| Corn | 0.151~0.244 (5) | 0.196 (8) |
| Potato | 0.029~0.052 (4) | 0.046 (7) |
| Rapeseed | 0.210~0.612 (3) | 0.250 (6) |
| Vegetable | 0.012~0.035 (4) | 0.028 |
| Grape | 0.008~0.016 | 0.013 (6) |
| Livestock Types | Scope of Phosphorus Intake [kg/(capita·a)] | Appropriate Parameters [kg/(capita·a)] | Scope of Phosphorus Excretion [kg/(capita·a)] | Appropriate Parameters [kg/(capita·a)] | Proportion of Edible Portion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dairy | 13.90~26.13 (5) | 14.99 | 6.54~22.80 | 9.78 (4) | 79.5 |
| Beef | 5.11~10.99 (5) | 5.74 (6) | 3.48~9.49 (4) | 3.84 (4) | 79.5 |
| Pork | 1.21~3.59 (6) | 3.48 | 0.32~0.63 (5) | 0.49 | 87.1 |
| Poultry | 0.03~0.18 (4) | 0.09 | 0.003~0.03 (4) | 0.018 (5) | 85.0 |
| Sheep | 1.22~3.81 (5) | 1.26 (6) | 0.17~1.06 | 0.89 | 75.7 |
| Year | Pfer [kg/(km2·a)] | Pim [kg/(km2·a)] | NAPI [kg/(km2·a)] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1998 | 665~712/677 | 86~174/113 | 790~1053/1051 |
| 2003 | 645~697/653 | 130~225/149 | 843~1032/933 |
| 2008 | 827~902/851 | 101~167/118 | 1039~1284/1231 |
| 2013 | 984~1091/1001 | 98~160/110 | 1208~1396/1336 |
| 2018 | 810~859/822 | 101~192/131 | 1146~1402/1154 |
| NAPI | 1993 | 1998 | 2003 | 2008 | 2013 | 2018 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | Min | Max | |
| Yinchuan | 659 | 759 | 1122 | 1279 | 1189 | 1247 | 1285 | 1324 | 1150 | 1241 | 1370 | 1584 |
| Yongning | 897 | 1144 | 764 | 1277 | 958 | 1241 | 1341 | 1784 | 1524 | 1660 | 1478 | 1573 |
| Helan | 1215 | 1404 | 1954 | 2278 | 2029 | 2341 | 2221 | 2593 | 2174 | 2309 | 2311 | 2781 |
| Dawukou | 148 | 156 | 140 | 150 | 380 | 413 | 220 | 396 | 413 | 578 | 279 | 660 |
| Pingluo | 859 | 1242 | 625 | 1042 | 1358 | 2322 | 2649 | 3543 | 3194 | 3338 | 3263 | 3515 |
| Huinong | 433 | 478 | 426 | 439 | 514 | 586 | 781 | 894 | 957 | 1012 | 821 | 1014 |
| Litong | 990 | 1188 | 1594 | 2052 | 1836 | 1926 | 1874 | 1999 | 2072 | 2312 | 2228 | 2509 |
| Qingtongxia | 463 | 565 | 841 | 978 | 1011 | 1221 | 1247 | 1351 | 1224 | 1521 | 1127 | 1347 |
| Hongsipu | 278 | 314 | 421 | 496 | 500 | 532 | 511 | 741 | 784 | 860 | 710 | 845 |
| Zhongwei | 243 | 279 | 392 | 456 | 433 | 463 | 389 | 484 | 418 | 522 | 357 | 405 |
| Zhongning | 233 | 276 | 220 | 287 | 471 | 544 | 524 | 559 | 557 | 693 | 547 | 792 |
| Lingwu | 495 | 604 | 469 | 753 | 441 | 574 | 473 | 597 | 551 | 742 | 644 | 751 |
| Yanchi | 181 | 284 | 125 | 353 | 121 | 268 | 147 | 401 | 225 | 549 | 178 | 427 |
| Tongxin | 200 | 312 | 267 | 477 | 535 | 703 | 574 | 661 | 560 | 744 | 308 | 554 |
| Guyuan | 764 | 1205 | 801 | 1289 | 1026 | 1341 | 1114 | 1452 | 1259 | 1331 | 1044 | 1271 |
| Haiyuan | 255 | 396 | 242 | 401 | 287 | 384 | 306 | 542 | 312 | 593 | 207 | 448 |
| Xiji | 602 | 739 | 941 | 1179 | 2059 | 2447 | 2563 | 2880 | 2895 | 3370 | 2773 | 3070 |
| Longde | 486 | 522 | 453 | 524 | 690 | 845 | 1248 | 1647 | 1879 | 2058 | 1880 | 2114 |
| Jingyuan | 156 | 201 | 159 | 210 | 164 | 220 | 170 | 254 | 340 | 499 | 325 | 514 |
| Pengyang | 332 | 383 | 654 | 747 | 867 | 1023 | 1159 | 1578 | 1674 | 1992 | 1542 | 1880 |
| Index | Sensitivity |
|---|---|
| 0.00 ≤ |I| ≤ 0.05 | Small to negligible |
| 0.05 ≤ |I| ≤ 0.20 | Medium |
| 0.20 ≤ |I| ≤ 1.00 | High |
| |I| ≥ 1.00 | Very high |
| Parameters | Year | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1991 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | Average | |
| P intake of per person | 0.030 | 0.033 | 0.036 | 0.027 | 0.020 | 0.025 | 0.029 | 0.029 |
| P intake of cattle | 0.027 | 0.022 | 0.023 | 0.021 | 0.010 | 0.011 | 0.009 | 0.018 |
| P intake of pig | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.011 | 0.012 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.010 | 0.011 |
| P excretion of cattle | 0.071 | 0.080 | 0.077 | 0.074 | 0.068 | 0.070 | 0.065 | 0.072 |
| P excretion of pig | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.012 | 0.014 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 0.013 |
| P content of wheat | −0.033 | −0.033 | −0.029 | −0.028 | −0.032 | −0.032 | −0.033 | −0.031 |
| P content of corn | −0.022 | −0.021 | −0.021 | −0.019 | −0.024 | −0.023 | −0.030 | −0.023 |
| P fertilizer | 0.110 | 0.128 | 0.111 | 0.134 | 0.115 | 0.215 | 0.250 | 0.152 |
| Non-food P | 0.011 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.011 | 0.011 | 0.009 | 0.011 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, H.; Liu, X.; Lei, Q.; Luo, J.; Di, H.; Du, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Net Anthropogenic Phosphorus Inputs (NAPIs) and Their Impacts in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Using Monte Carlo Simulations and Sensitivity Analysis. Water 2024, 16, 3160. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223160
Ma H, Liu X, Lei Q, Luo J, Di H, Du X, Zhao Y, Zhang X, Liu H. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Net Anthropogenic Phosphorus Inputs (NAPIs) and Their Impacts in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Using Monte Carlo Simulations and Sensitivity Analysis. Water. 2024; 16(22):3160. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223160
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Hua, Xiaotong Liu, Qiuliang Lei, Jiafa Luo, Hongjie Di, Xinzhong Du, Ying Zhao, Xuejun Zhang, and Hongbin Liu. 2024. "Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Net Anthropogenic Phosphorus Inputs (NAPIs) and Their Impacts in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Using Monte Carlo Simulations and Sensitivity Analysis" Water 16, no. 22: 3160. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223160
APA StyleMa, H., Liu, X., Lei, Q., Luo, J., Di, H., Du, X., Zhao, Y., Zhang, X., & Liu, H. (2024). Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Net Anthropogenic Phosphorus Inputs (NAPIs) and Their Impacts in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Using Monte Carlo Simulations and Sensitivity Analysis. Water, 16(22), 3160. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223160








