Abstract
A comprehensive understanding of water-quality spatiotemporal variations is essential for the long-term management of aquatic environments. However, the absence of indicators that fully capture the extent of eutrophication, the lack of long-term water-quality monitoring data, and the complexity of water pollutants sources have limited research on pollution characteristics and eutrophication assessments in plain river network areas. In this study, based on the monitoring data of water-quality indicators in the Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal (Changzhou section), the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of nutrient salts, as well as the eutrophication status of the water body, were revealed by using the comprehensive trophic level index (TLI) method. Meanwhile, the main sources of water pollutants were defined, and targeted control measures were proposed. The results showed that water-quality deterioration is more pronounced during the non-flood season, with significantly higher concentrations of ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) and total phosphorus (TP) compared to the flood season. Additionally, the analysis of the nitrogen-to-phosphorus (N:P) ratio suggested that some sampling sites exhibited phosphorus limitation. The eutrophication assessment indicated that most sections are eutrophic, with S8 and S2 being the most heavily polluted and at risk of cyanobacterial blooms. The primary sources of pollutants were identified as agricultural runoff, domestic sewage, and industrial discharges. To address these issues, it was recommended to reduce external pollution sources while focusing on internal control (1. Enhance the management of livestock and poultry farming; 2. Upgrade wastewater purification facilities; 3. Establish ecological protection zones along the riverbanks) and enhance aquatic ecosystem restoration. A coordinated and watershed-wide approach is crucial to improving water quality in this region. The findings of this study provide a scientific basis for the protection of the water environment and pollution control in plain river network areas.
1. Introduction
As industrialization and urbanization accelerate, water pollution has emerged as a major global concern in environmental protection [1]. Among the various water pollution issues, eutrophication is particularly prominent [2,3,4,5]. Eutrophication occurs when excessive amounts of nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, enter water bodies, leading to the overgrowth of algae, mass fish die-offs, and severe imbalances in aquatic ecosystems [6,7,8]. Due to the detrimental effects of eutrophication on the environment, society, and economy, it is crucial to thoroughly investigate its causes and develop targeted mitigation and management strategies.
Rivers are generally less prone to eutrophication than relatively static water bodies like lakes, owing to their unique hydrodynamic characteristics [9,10,11]. However, as nutrients accumulate in water bodies, the risk of eutrophication increases significantly, especially in seasonally variable rivers [12,13]. Seasonally variable rivers rely heavily on rainfall recharge with an uneven distribution of water over time scales [14,15]. The water level is high during the flood season, while the water level decreases in the non-flood season, and some tributaries even experience flow interruption. Therefore, conducting analyses of nutrient spatiotemporal variations, assessing eutrophication, and identifying primary pollution sources in seasonally variable rivers is essential for providing the scientific basis needed to prevent eutrophication in these water bodies.
As one of the longest and oldest man-made rivers in the world, the Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal serves as a crucial north–south waterway in China [16,17]. Located at the heart of the Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal, Changzhou is a key industrial city in China with an aquatic ecosystem that has been impacted by urban expansion, agricultural activities, and navigation [18,19,20]. The combination of these factors has resulted in a uniquely complex set of water environmental challenges in the region. Since 2005, Changzhou has implemented a series of comprehensive water environment-remediation measures targeting the Changzhou section of the Grand Canal, yielding significant results with annual improvements in water quality [21]. Notably, during the 13th Five-Year Plan period, the water quality in key river sections improved markedly, with all national and provincial water-quality monitoring sites meeting the required assessment standards. This indicates that Changzhou’s aquatic environment is gradually recovering, and the overall improvement in water quality has established a solid foundation for the city’s sustainable development.
There are various methods currently employed to evaluate water quality, including water-quality indicators, comprehensive pollution index, and eutrophication evaluations [22,23,24,25]. Among these, the comprehensive trophic level index (TLI) serves as a quantitative assessment method that effectively identifies critical areas of water-quality deterioration [26,27,28,29,30]. The TLI is not only a valuable tool for evaluating water quality but also a crucial decision-support instrument for riverine ecological protection and management. Recent research has made significant strides in understanding river pollution characteristics, causes of eutrophication, and management strategies. For instance, Romanelli et al. [31] combined nitrate isotope analysis with traditional chemical and biological assessment methods to investigate eutrophication processes in freshwater ecosystems. This approach enhances the precision of understanding eutrophication causes and provides a scientific foundation for remediation measures. Similarly, He et al. [7] developed two statistical models, Artificial Neural Networks and Logistic Regression models, to predict microcystin concentrations in rivers and the likelihood of exceeding regulatory thresholds. These studies offer advanced tools and methodologies for pollution warning and management. Nevertheless, existing research still falls short in terms of detailed analysis of pollution sources in specific regions, particularly with regard to dynamic monitoring of eutrophication [32,33]. Additionally, comprehensive water-quality indicators that fully reflect the extent of eutrophication remain scarce. The lack of long-term monitoring data and the complexity of pollution sources further complicate water-quality research and management [34]. Addressing these challenges requires more refined and continuous monitoring and research efforts to more effectively protect and improve riverine ecological environments.
The main objective of the present study is to analyze the spatiotemporal variation characteristics of water-quality indicators and evaluate the degree of eutrophication in the Changzhou section of the Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal. The ultimate goal is to recognize the sources of pollution and propose science-based remediation measures and management strategies. The specific contents of the research are as follows: (1) To evaluate the current status of water resources and employ cluster analysis to delineate the periods of the flood season and non-flood season. This categorization provides a foundation for further analysis of water-quality trends across different timeframes; (2) To analyze the spatial and temporal distribution of major pollutants (TN, TP, NH3-N) to identify the main concentration areas and sources of pollutants; (3) To assess the degree of eutrophication of water bodies using the TLI method and explore the mechanisms of external pollutant inputs and internal cycling processes; and (4) To investigate sources of water pollution and put forward targeted measures and management recommendations. The outcomes of this research are expected to provide a scientific basis for improving water quality and controlling the eutrophication process, thereby promoting the long-term sustainable development of the aquatic ecosystem in plain river network areas.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
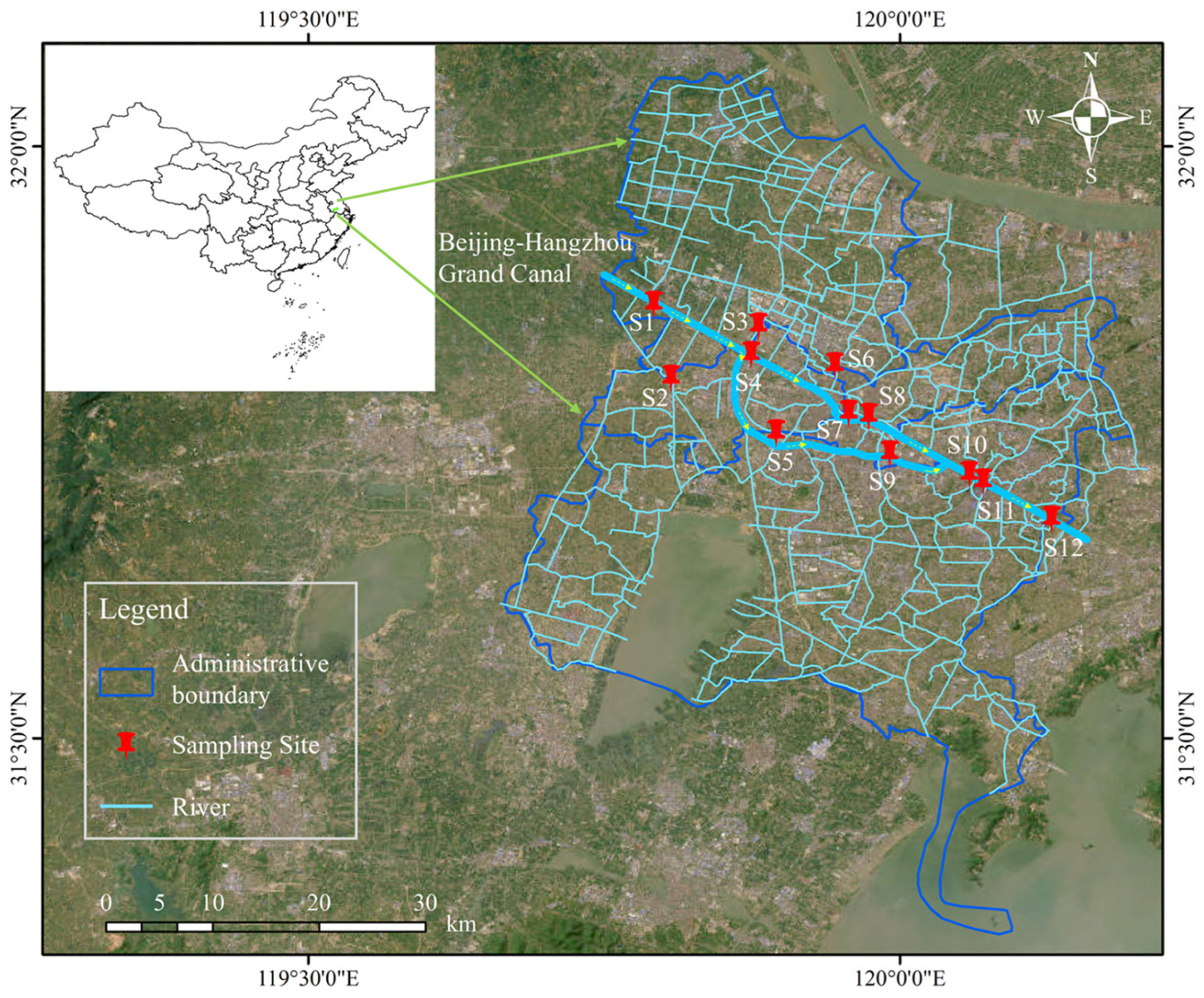
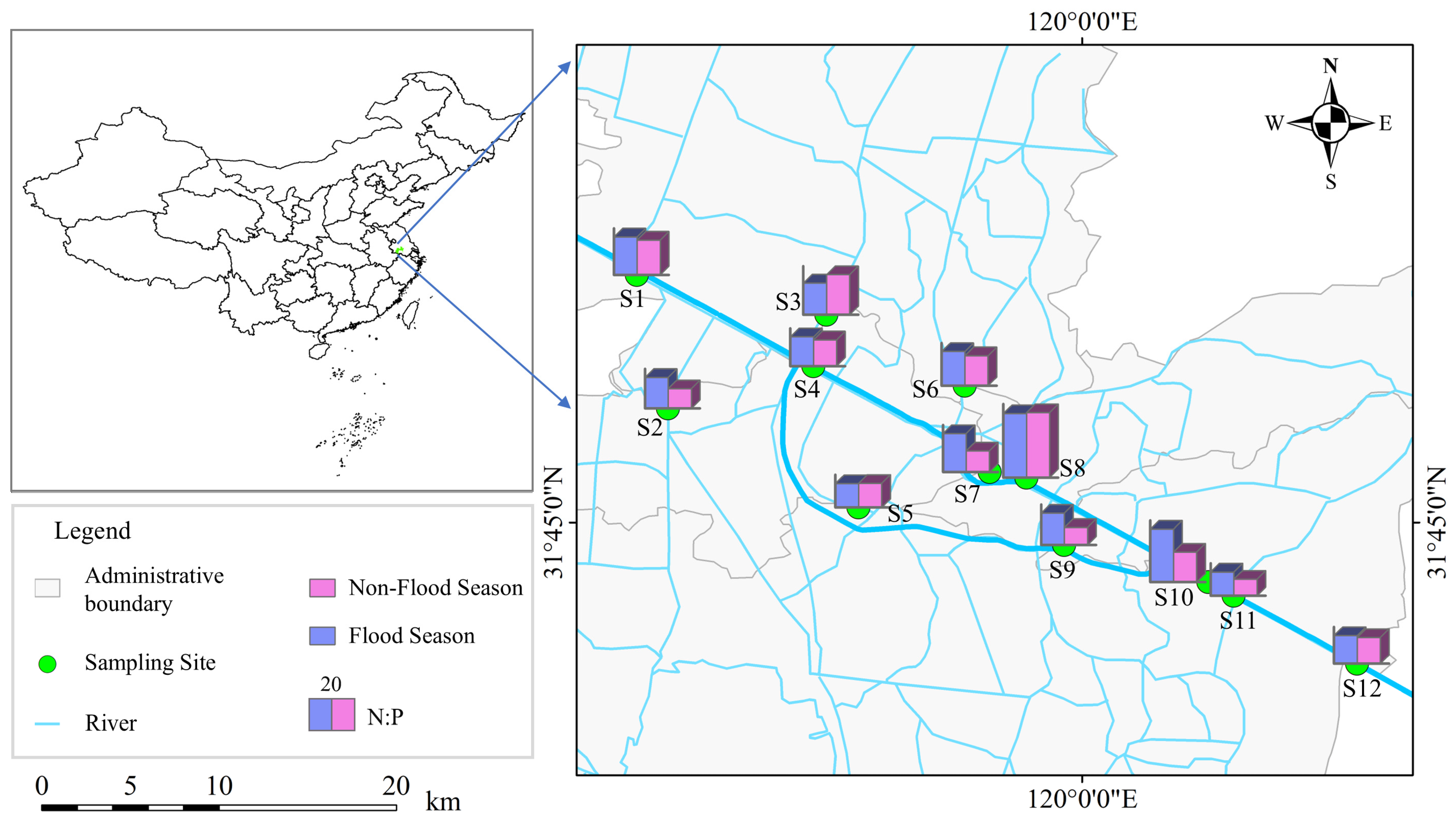
The Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal is the longest man-made waterway in the world, which extends 1794 km. It connects Beijing and Hangzhou, running through multiple provinces and cities in Eastern China. The Changzhou section, a critical part of the canal, spans 44.7 km and flows through the Xinbei, Zhonglou, Tianning, and Wujin Districts of Changzhou before entering Wuxi. Along its course, there are five tributaries that feed into the Changzhou section of the canal, namely the Xinmen River, the Desheng River, the Zaogang River, the Dingtang Harbor, and the Sanshan Harbor. The canal connects with the Wuyi Canal, Cailing Harbor, and Wujin Harbor, which further link to Gehu and Taihu, creating an extensive water network in the southern part of the Changzhou section. The water system within the Changzhou region is highly complex, comprising rivers such as Guan River, Beishi River, Dongshi River, Nanshi River, the Grand Canal, Xishi River, and Suoqiao River. These rivers form a densely interconnected network that plays a vital role in supporting waterway transportation, agricultural irrigation, and urban development in Changzhou [18,21], as shown in Figure 1. In this study, S1, S2, and S7 are designated as control points for agricultural, industrial, and commercial activities, respectively.
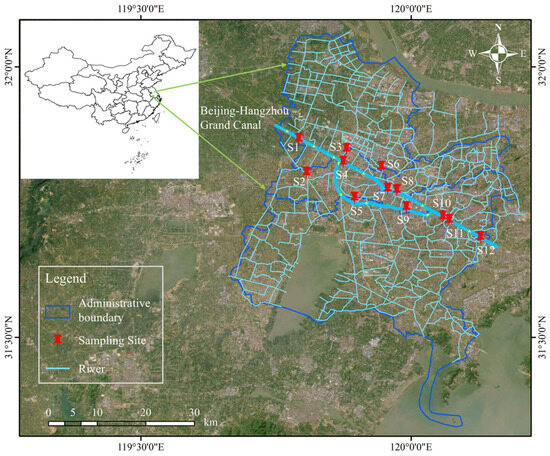
Figure 1.
Locations of main river reaches and sampling sites of Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal (Changzhou Section), arrows indicate the direction of river flows.
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
In order to assess the spatial and temporal variation characteristics of water pollution and the status of eutrophication comprehensively, 12 representative water-quality sampling sites were established in 2021 along the Changzhou section of the Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal (Table 1). These sampling points were carefully selected based on the hydrological characteristics and channel configuration, ensuring coverage of critical areas. The water-quality indicators in the present study include water temperature (WT), pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), permanganate index (CODMn), ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N), total phosphorus (TP), and total nitrogen (TN), all of which were obtained from hydrological monitoring stations and water-quality monitoring stations with a monitoring frequency of once per day.

Table 1.
Information of sampling sites in the Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal (Changzhou section).
The comprehensive trophic level index (TLI) is a widely used method for evaluating the degree of eutrophication in water bodies by considering multiple water-quality parameters [28,29,30]. The water-quality parameters include TN, NH3-N, TP, DO, CODMn, transparency, and chlorophyll-a, which reflect the eutrophication status of the water body to some extent. To address the limitations of traditional univariate linear regression in calculating correlations, the present study employed an improved comprehensive weighted index method recommended by the China National Environmental Monitoring Center [35]. TP, TN, and CODMn were selected as evaluation factors to assess the nutrient status of the Changzhou section of the Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal. TLI integrates several water-quality parameters such as nitrogen, phosphorus, chlorophyll-a, and water transparency. The general formula for TLI can be expressed as follows:
where TLI represents the comprehensive trophic level index, TLIj denotes the trophic state index for the j-th parameter, and Wj is the corresponding weight assigned to the trophic state index of the j-th parameter.
where rij is the correlation between the j-th parameter and the reference parameter, while m denotes the number of primary parameters that are closely related to the reference parameter. The weight Wj for each parameter can be adjusted based on the strength of these correlations, ensuring that the most influential parameters contribute appropriately to the overall TLI.
To provide a more intuitive reflection of the eutrophication status of water bodies, the present study employed a continuous numerical scale from 0 to 100 to classify the trophic status and qualitatively evaluate water quality. This grading method enhances the practicality and interpretability of the water-quality assessment. Within the same trophic state, a higher TLI indicates a higher degree of nutrient enrichment and poorer water quality. The specific grading and evaluation criteria are detailed in Table 2. This continuous classification approach allows for a more precise representation of the water quality across different trophic levels.

Table 2.
Criteria for eutrophication assessment.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. An Overview of Water Resources
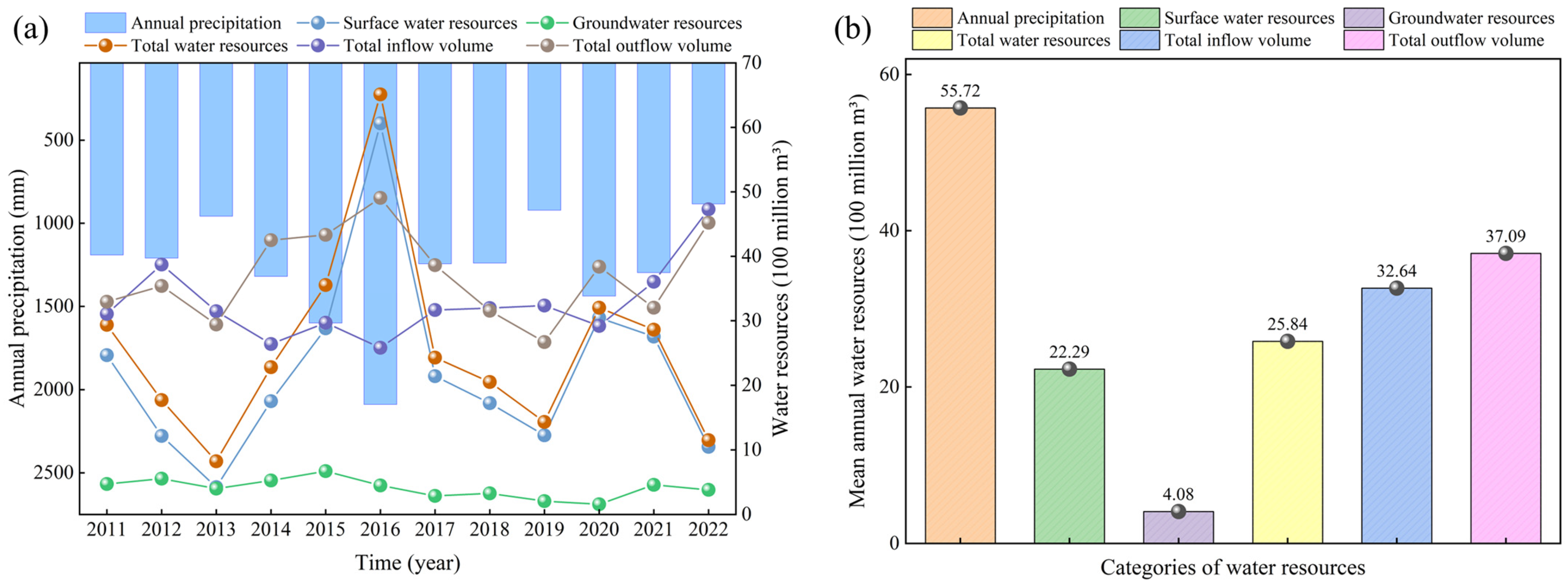
The effective management and regulation of regional water resources are critical to maintaining and improving water quality, particularly in light of decreasing resource volumes, which could adversely affect river water quality [36,37,38]. The statistics of water resources in Changzhou City, China, were shown in Figure 2. According to the Changzhou Water Resources Bulletin published by the Changzhou City Water Conservancy Bureau, the trends of total water resources and surface water resources are highly consistent with annual precipitation. The total water resources and surface water resources have experienced significant fluctuations during the period from 2011 to 2022, which were primarily influenced by annual precipitation. The year 2016 marked the peak of this period, with an annual precipitation of 2089.3 mm, resulting in total water resources and surface water resources reaching 6511 million m3 and 6062 million m3, respectively. Since then, both of these two indicators declined annually until 2020. In contrast, the groundwater resources and the total inflow and outflow volumes remained relatively stable, which indicated that these water sources were less influenced by annual precipitation.
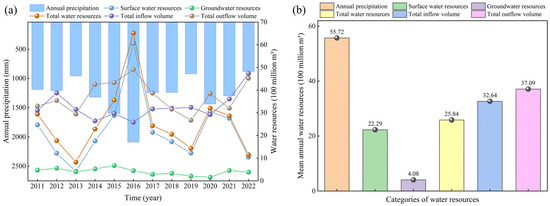
Figure 2.
Water resources statistics for the period from 2011–2022 in Changzhou, China. (a) Variations of water resources, (b) Average multi-year water resources.
The multi-year average total water resources stand at 2584 million m3, with an average annual precipitation of 5572 million m3 and surface water resource volume of 2229 million m3, while groundwater resources account for 408 million m3. This distribution underscores the dominance of surface water resources, with groundwater contributing a smaller share of the total water resources of Changzhou City. Furthermore, data on the water flow in major rivers indicate that there is a significant disparity between water supply and demand. The total inflow volume is 3264 million m3, while the total outflow volume is 3709 million m3, reflecting a reduction in water resources.
3.2. Temporal Clustering Characteristics
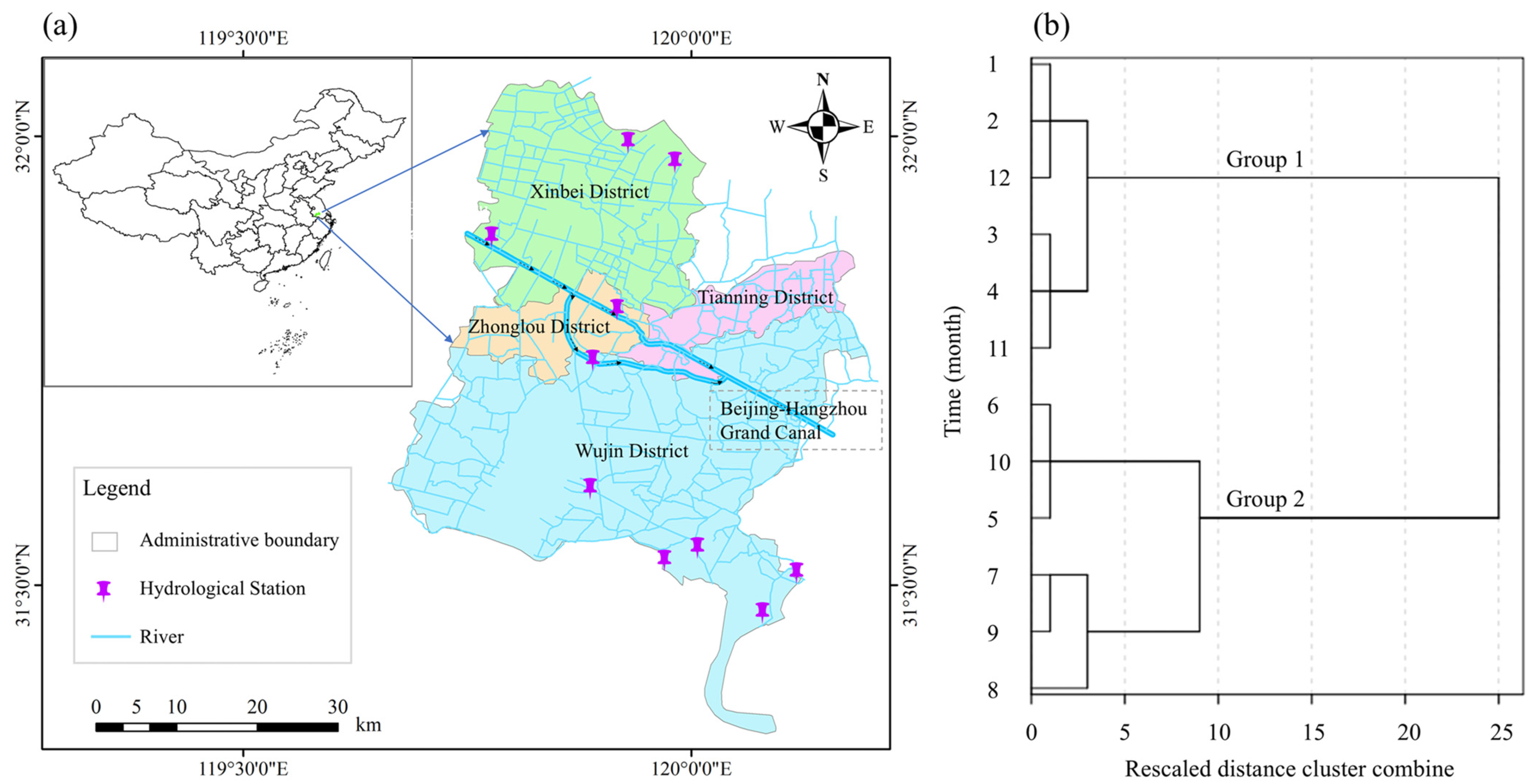
Water quality is influenced by several factors such as seasonal precipitation, variations in flow, and human activities [39,40]. The variations in water quality during flood and non-flood seasons reflect distinct processes: during the flood season, changes in water quality highlight the impact of increased precipitation on pollutant dispersion and dilution, whereas in the non-flood season, lower flow conditions reveal the pollutant accumulation and self-purification capacity of water bodies. The definition of flood season is based on the significant increase of precipitation and water level in the region, usually occurring during specific periods of the year. Conversely, the non-flood season corresponds to periods with relatively lower precipitation and water levels. To accurately delineate the flood season and non-flood season in Changzhou, this study conducted a time cluster analysis [32] of the monthly average water level data from 10 hydrological stations in 2021 (Figure 3a). Using the function of Analyze–Classification–Hierarchical Cluster in SPSS software (Version 20), the water level data from the hydrological stations were input as variables, and the 12 months were labeled as cases. The furthest-neighbor method was selected for clustering, generating a dendrogram (Figure 3b) based on the similarity of water levels between months. The results of the dendrogram show two groups: (1) Non-flood season (November to April) is characterized by lower precipitation and water levels, with water-quality analysis focusing on pollutant accumulation and the self-purification ability of the water body; (2) Flood season (May to October) is marked by increased precipitation and a significant rise in water levels, where water-quality analysis primarily focuses on the processes of pollutant dispersion and dilution. This temporal classification provides a scientific basis for further analysis of the spatial and temporal variations of water quality during flood and non-flood seasons.
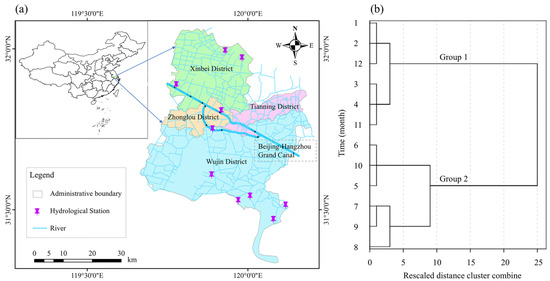
Figure 3.
Delineation of flood and non-flood seasons. (a) Locations of hydrological stations; (b) Temporal clustering dendrogram, where group 1 and group 2 represent the non-flood and flood season, respectively, arrows indicate the direction of river flows.
3.3. Water Pollution Characteristics
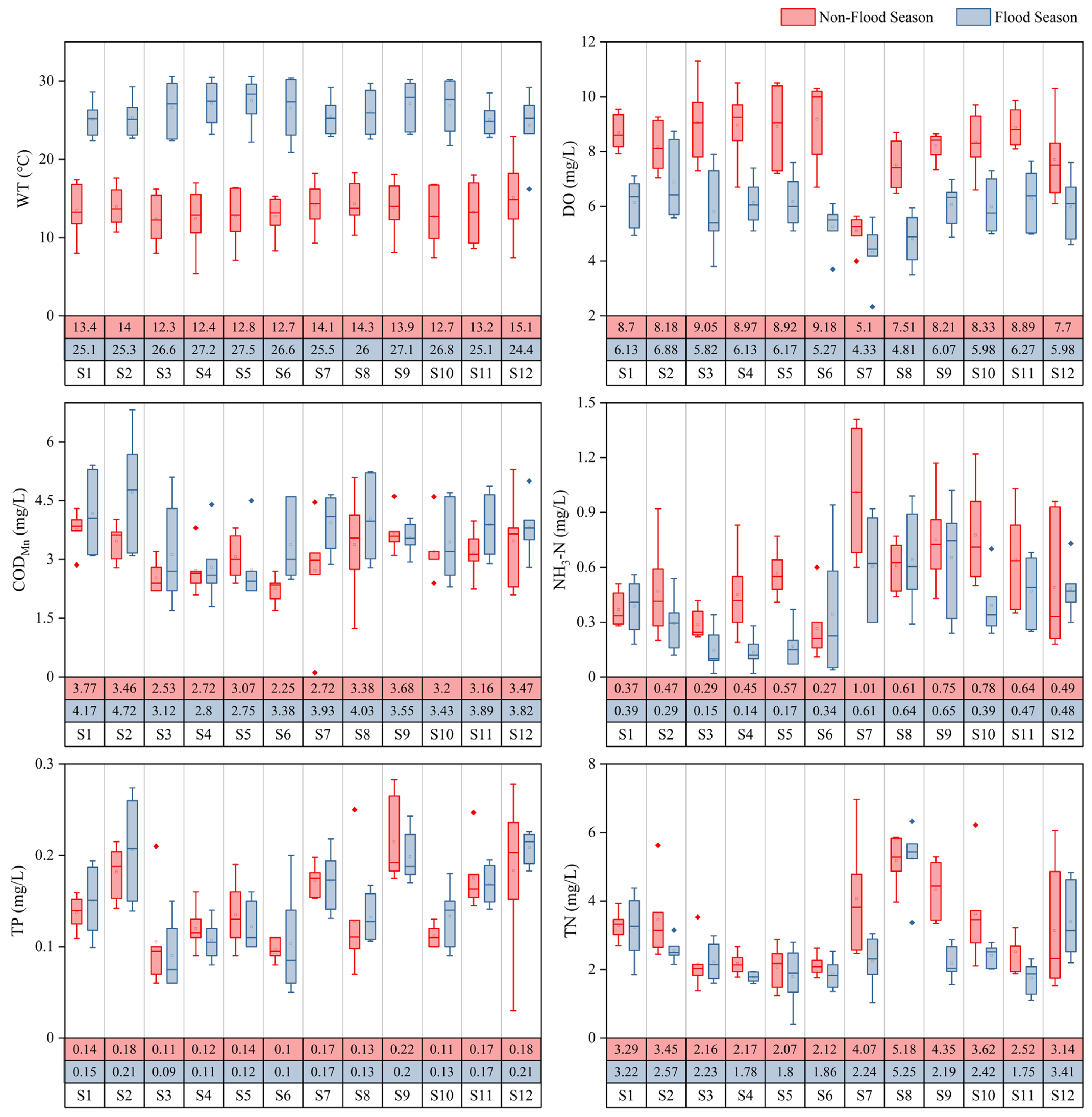
This study analyzed the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of water pollution in the Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal (Changzhou section) during the flood season and non-flood season using the water-quality indicators of WT, DO, CODMn, NH3-N, TP, and TN, as showed in Figure 4. WT is generally lower during the non-flood season compared to the flood season, which reflects the direct influence of seasonal temperature variations on water bodies. DO shows significantly higher concentrations in the non-flood season. This can be attributed to the lower WT during this period, which enhances oxygen solubility. Concurrently, a reduced input of external organic pollutants resulted in lower oxygen consumption. In contrast, higher temperatures can lead to oxygen saturation in water bodies during the flood season, limiting further increases in DO concentrations. CODMn exhibits higher concentrations during the flood season, particularly at sampling sites such as S2, S7, and S8. The average concentration of CODMn during the flood season (3.63 mg/L) is higher than the non-flood season (3.12 mg/L), which might be related to the influx of organic pollutants carried by storm runoff. NH3-N has a higher average concentration during the non-flood season (0.56 mg/L) compared to the flood season (0.39 mg/L), especially in S3, S6, and S8. The increase in NH3-N during the non-flood season may be linked to agricultural runoff and domestic sewage discharge while being coupled with the reduced dilution effect due to lower water flow. The concentration of TP is also higher during the non-flood season, with notable increases at S7, S8, and S9. The lower water flow during this period contributes to the accumulation of phosphorus, which may originate from domestic sewage and agricultural fertilizers. TN displays higher average concentrations during the non-flood season (3.18 mg/L), particularly at sections S7 and S9, with the highest levels observed at S8. Overall, the concentration of pollutants in water bodies is generally lower during the flood season compared to the non-flood season.
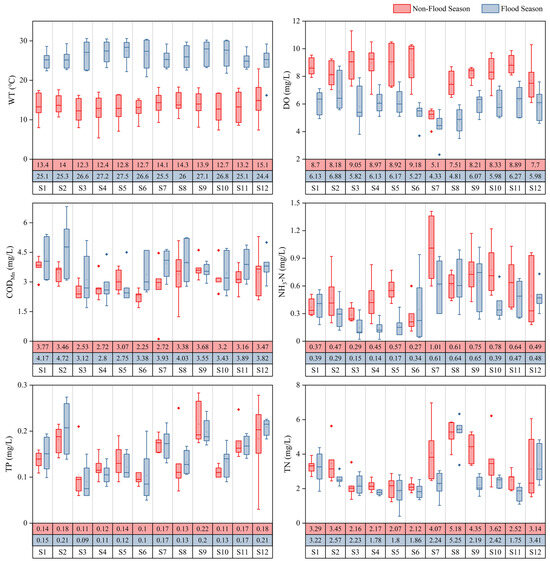
Figure 4.
The spatial-temporal variation characteristics of water-quality indicators. (The data in the table represent the average values of the indicators for the flood season and the non-flood season, respectively).
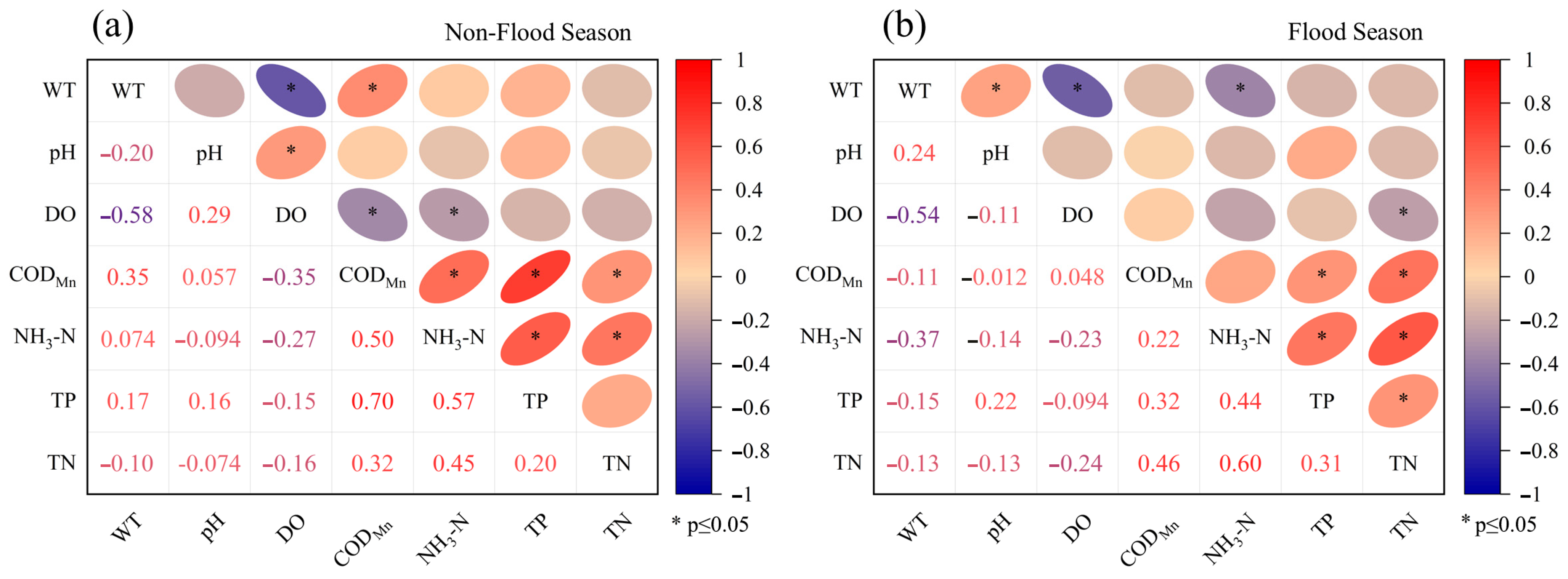
3.4. Correlation of Water-Quality Indicators
A correlation analysis was conducted on seven water-quality monitoring indicators during both non-flood and flood seasons to reveal the interrelationships among these indicators and their impact on water pollution under different seasonal conditions [25,27]. During the non-flood season (Figure 5a), the correlation analysis shows a moderate negative correlation between WT and DO (r = −0.58), indicating that the DO content increases as WT decreases. The pH shows low correlations with other indicators (−0.094–0.16), except for a modest positive correlation with DO (r = 0.29). This suggests that pH is likely influenced by independent pollution sources rather than being directly linked to other water-quality parameters. Additionally, DO exhibits negative correlations with other water-quality indicators, which implies that as concentrations of nutrients such as TN, TP, and organic pollutants increase, oxygen consumption intensifies, leading to a decrease in DO levels and weakening the self-purification capacity of the river. The moderate correlations among pollution indicators such as CODMn, NH3-N, TP, and TN suggest similar pollution sources or common pathways of pollutant dispersion. In the flood season (Figure 5b), the correlation analysis reveals a similar pattern to the non-flood season, with WT and DO continuing to show a moderate negative correlation (r = −0.54). The pH also maintains weak correlations with other indicators, consistent with the findings from the non-flood season. In general, there is some consistency between water-quality indicators under different seasonal conditions. In addition, the pollution conditions are complex in the Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal (Changzhou section), which is affected by multiple factors.
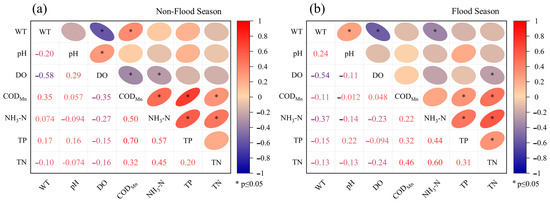
Figure 5.
Correlations characteristics of water-quality indicators.
3.5. N:P Ratio Characteristics
The nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratio (N:P) is a crucial factor influencing phytoplankton growth [41,42]. In natural water bodies, phytoplankton typically requires nitrogen and phosphorus in a molar ratio of approximately 16:1, a ratio also known as the Redfield ratio. A significant deviation from this ratio in water bodies can lead to increased limitation, thereby affecting the community structure and growth rate of phytoplankton [6,31]. For instance, when the N:P ratio exceeds 30, phosphorus will become the limiting factor for phytoplankton growth. Conversely, when the N:P ratio falls below 10, nitrogen becomes the limiting nutrient. The imbalance in nutrient elements can further exacerbate the degree of eutrophication, which could lead to algal blooms and water-quality deterioration [8]. In the present study, the spatiotemporal variations of the N:P ratios (Figure 6) indicated significant differences in nutrient status across different sampling sites. During the non-flood season, the average N:P ratio across sampling sites was 22.1, with most sites showing ratios between 10 and 30, suggesting relatively balanced nutrient conditions in these areas. However, S8 (39.8) and S10 (32.9) had N:P ratios above 30, indicating a strong phosphorus limitation at these locations. In contrast, the mean N:P ratio decreased to 18.2, implying a reduction in phosphorus limitation, which could be attributed to increased phosphorus input from rainfall during the flood season. Nevertheless, S8 (40.4) remained significantly higher than other sites, indicating a strong phosphorus limitation, which could be caused by insufficient external phosphorus input and restricted internal phosphorus release from this location.
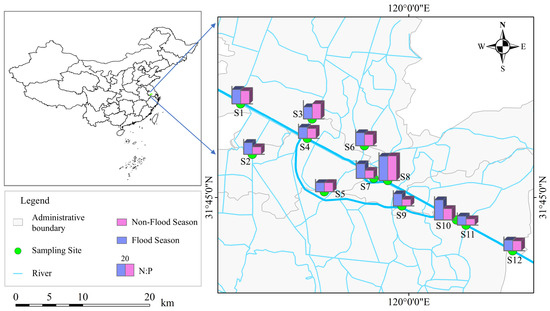
Figure 6.
Spatiotemporal variation characteristics of N:P ratio.
3.6. Evaluation of Eutrophication
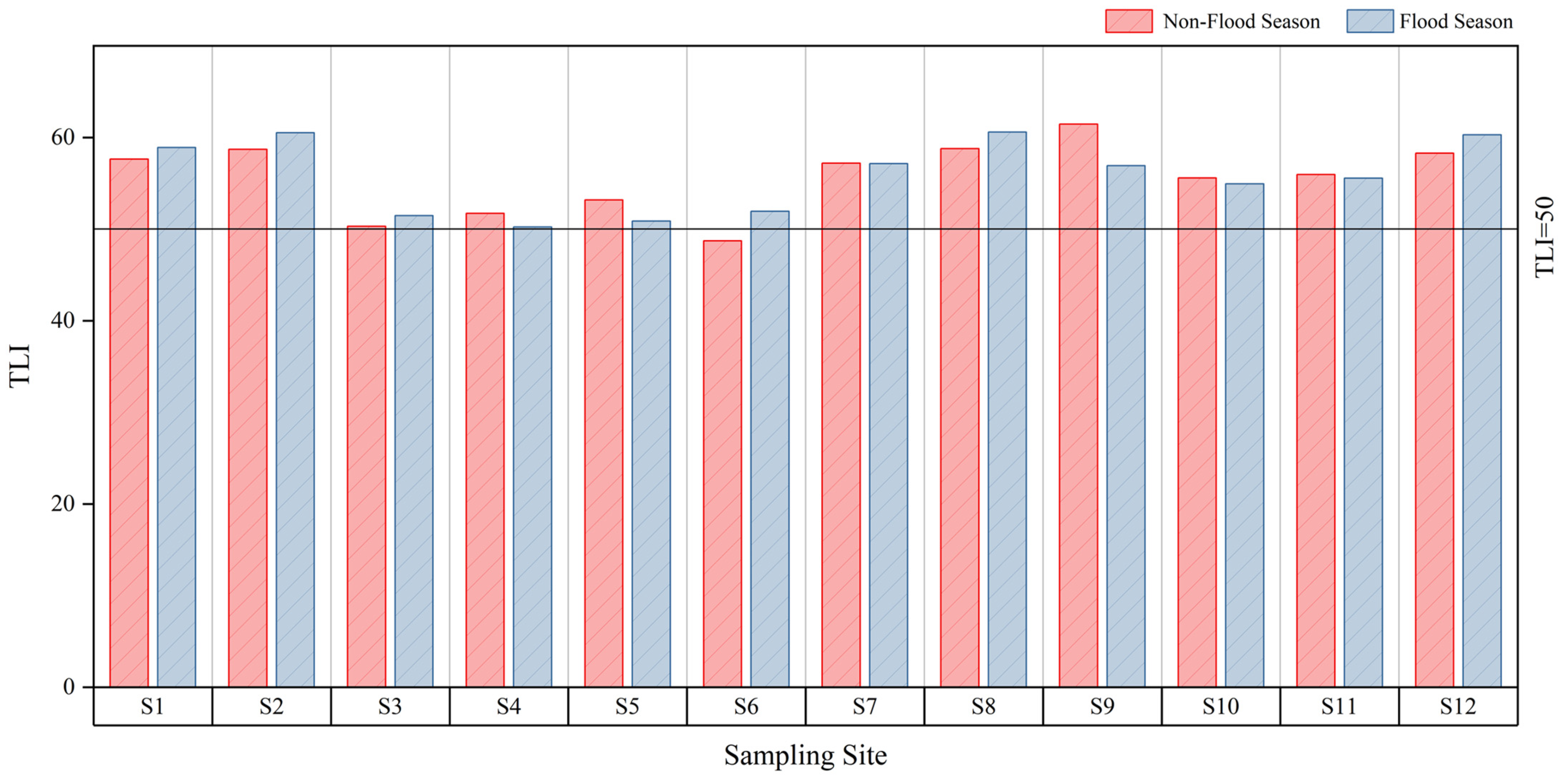
The nutrient status of the Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal (Changzhou section) was assessed using the comprehensive TLI method, and the eutrophication levels at 12 sampling sites during both the flood and non-flood seasons (Figure 7) were analyzed. The results indicate that the TLI across different sections were generally consistent between the flood and non-flood seasons, suggesting that seasonal variations had minimal impact on overall water quality [30]. TLI at S6 (48.71) was mesotrophic during the non-flood season, which reflects good water quality. In contrast, all other sections were in eutrophication, with TLI ranging from 50 to 70, which indicated a degree of water pollution. It is noteworthy that the TLI of S2, S8, and S12 during the flood season were 60.52, 60.59, and 60.28, respectively, and the TLI of S9 during the non-flood season was 61.45. These values classify the sections as moderately eutrophic, with a water-quality rating of moderate pollution.
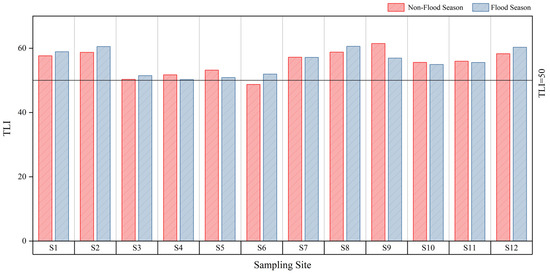
Figure 7.
Assessment of nutrition states of the rivers.
The analysis, combined with the geographic location and surrounding industrial structure, suggests that the eutrophication in these sections is closely linked to inputs from agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and domestic sewage within the watershed. Based on the annual TLI, the sampling sites were ranked in terms of eutrophication severity as follows: S8 > S2 > S12 > S9 > S1 > S7 > S11 > S10 > S5 > S4 > S3 > S6. This ranking indicates that S8 and S2 are the most severely polluted areas and should be prioritized for remediation efforts.
3.7. Water Pollution Sources and Preventive Measures
The eutrophication issue in the Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal (Changzhou section) exhibits significant regional variations, which are influenced by various factors such as human activities, geographic location, and climate conditions. Investigations reveal that the primary sources of eutrophication are agricultural non-point source pollution, domestic sewage pollution, and industrial pollution [21]. The combination of these pollution sources has led to mild eutrophication, compromising the ecological health of the water body. Agricultural non-point source pollution primarily originates from upstream and downstream agricultural activities, particularly pollutants from livestock and poultry farming that enter the river through surface runoff (S1, S3, S8). It increases the nitrogen and phosphorus content in the water body and promotes the eutrophication process. Domestic sewage pollution is mainly attributed to the aging and damaged sewage pipelines in the central old town area, which result in untreated sewage being directly discharged into the canal (S7, S10). The organic matter and nutrients in domestic sewage further burden the water body with pollution. Although pollution-causing enterprises along the main canal have been relocated, certain industries such as machinery and chemicals along smaller tributaries still pose a problem due to the discharge of characteristic pollutants (S2, S4, S5, S6, S9, S10, S11, S12). These pollutants exert specific ecological pressure on the aquatic ecosystem.
In view of the characteristics of eutrophication and its main pollution sources in the Changzhou section of the Grand Canal, the following water environment protection and remediation measures are proposed: (1) Enhance the management of livestock and poultry farming: Implement large-scale, controlled farming practices, apply fertilizers judiciously, and adopt refined livestock management. Construct wetlands and ecological ditches to improve agricultural wastewater treatment; (2) Upgrade wastewater purification facilities: Expand the coverage of the sewage network and strengthen regulatory oversight to ensure effective wastewater management; (3) Establish ecological protection zones along the riverbanks: Develop green ecological corridors, stock fish, and cultivate aquatic plants to enhance the natural purification capacity of the river. However, achieving long-term and stable water-quality improvement requires not only the application of scientific and technological measures and engineering solutions but also sustained efforts in policy enforcement, public participation, and raising environmental awareness.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, we have conducted a comprehensive analysis of the water pollution characteristics, the eutrophication level, and the primary sources of pollution in the Changzhou section of the Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal. It was found that the pollution of the river was significantly different between the flood season and the non-flood season. During the non-flood season, lower WT and higher DO levels were observed. However, concentrations of NH3-N, TP, and TN were relatively elevated, indicating more severe pollution during this period. Concentrations of CODMn increased significantly during the flood season, owing to the influx of organic pollutants from storm runoff. Additionally, the spatiotemporal variation in the nitrogen-to-phosphorus (N:P) ratio highlighted significant disparities in nutrient status across sampling sites. Phosphorus limitation was prevalent during the non-flood season, particularly at the S8, whereas this limitation was somewhat alleviated during the flood season. Despite these seasonal shifts, the water body remains moderately eutrophic overall, with sections S8 and S2 identified as the most heavily polluted, requiring immediate remediation. In summary, the study underscores the complexity of the water quality in the Changzhou section of the Grand Canal, which is influenced by multiple factors. The pollution issues are particularly pronounced during the non-flood season, when the water body’s self-purification capacity is diminished, heightening the risk of eutrophication. An investigation into pollution sources identified agricultural non-point source pollution, domestic sewage discharge, and industrial activities as the primary contributors to river water eutrophication. To address these challenges, the study proposes a series of comprehensive remediation measures, including optimizing agricultural practices, upgrading wastewater treatment facilities, and implementing ecological restoration initiatives. Furthermore, due to the limited focus of this study on microbial contamination and pollution source tracking, certain limitations exist in terms of in-depth pollution source identification, diversity analysis, and precise source characterization. Future research could consider the application of three-dimensional fluorescence or isotope-tracing techniques to enhance pollution source tracking, thereby refining water-quality assessment and management strategies. Therefore, sustained improvement in water quality will require an integrated approach, combining policy enforcement, public engagement, and heightened environmental awareness.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.H. and G.Z.; methodology, H.H. and G.Z.; software, H.H.; validation, S.T. and T.H.; formal analysis, H.H.; investigation, S.T.; resources, G.Z.; data curation, H.H.; writing—original draft preparation, H.H. and S.T.; writing—review and editing, H.H.; visualization, T.H.; supervision, G.Z.; project administration, G.Z.; funding acquisition, G.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Watershed Non-point Source Pollution Prevention and Control Technology and Application Demonstration (2021YFC3201502).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundations of China for their support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, J.; Han, J.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Yee Leung, K.M.; Snyder, S.A.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Which Micropollutants in Water Environments Deserve More Attention Globally? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasuriya, B.T.G.; Ghose, A.; Gheewala, S.H.; Prapaspongsa, T. Assessment of Eutrophication Potential from Fertiliser Application in Agricultural Systems in Thailand. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 154993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorzal-Almeida, S.; Bartozek, E.C.R.; Bicudo, D.C. Homogenization of Diatom Assemblages Is Driven by Eutrophication in Tropical Reservoirs. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maúre, E.d.R.; Terauchi, G.; Ishizaka, J.; Clinton, N.; DeWitt, M. Globally Consistent Assessment of Coastal Eutrophication. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Gan, X.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, C.; Wu, S.; Du, L. Research Status on Remediation of Eutrophic Water by Submerged Macrophytes: A Review. Process Saf. Environ. 2023, 169, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Fisher, T.R.; Buchanan, C.; Gustafson, A.B.; Karrh, R.R.; Murphy, R.R.; Testa, J.M.; Tian, R.; Tango, P.J. Nutrient Limitation of Phytoplankton in Three Tributaries of Chesapeake Bay: Detecting Responses Following Nutrient Reductions. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, H.; Zhuang, W.; Liang, D.; Ao, Y. Risk Prediction of Microcystins Based on Water Quality Surrogates: A Case Study in a Eutrophicated Urban River Network. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 275, 116651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvir, R.U.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J. Cyanobacterial Community Succession and Associated Cyanotoxin Production in Hypereutrophic and Eutrophic Freshwaters. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bing, H.; Peng, J.; Dong, F.; Gao, J.; Arhonditsis, G.B. Characterizing the River Water Quality in China: Recent Progress and on-Going Challenges. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Rong, N.; Jin, X.; Meng, X.; Han, S.; Zhang, D.; Shan, B. Dissolved Oxygen Variation in the North China Plain River Network Region over 2011–2020 and the Influencing Factors. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, L.M.; Carolina de Almeida Castilho, M.; Henry, R.; Ferragut, C. Epipelon, Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Responses to the Experimental Oligotrophication in a Eutrophic Shallow Reservoir. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, W.; Han, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, Y. Quantitative Study on Redistribution of Nitrogen and Phosphorus by Wetland Plants under Different Water Quality Conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.-I.; Koh, D.-C.; Cho, B.-W.; Jung, Y.-Y. Nutrient Dynamics in Stream Water and Groundwater in Riparian Zones of a Mesoscale Agricultural Catchment with Intense Seasonal Pumping. Agr. Water Manag. 2022, 261, 107336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shen, M.; Liu, W.; Ma, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D. Developing Remote Sensing Methods for Monitoring Water Quality of Alpine Rivers on the Tibetan Plateau. GIScience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1384–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X. Correlations between Water Quality and the Structure and Connectivity of the River Network in the Southern Jiangsu Plain, Eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jing, Z.; Huang, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, J.; Tan, L.; et al. On Conservation of World Heritage Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal for Enhancing Cultural Ecosystem Services. Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Influence of Urban Green Space Landscape Pattern on River Water Quality in a Highly Urbanized River Network of Hangzhou City. J. Hydrol. 2023, 621, 129602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X. A Longitudinal Functional Connectivity Comprehensive Index for Multi-Sluice Flood Control System in Plain Urban River Networks. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 128362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y.; He, J.; Sun, H. Influence of Ongoing Discharge from Multiple Wastewater Treatment Plants on Microplastic Patterns in Small-Scale Receiving Rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 932, 172880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, X.; Yin, C.; Xu, W.; Shi, W.; Qian, G.; Xun, Z. Inland Vessels Emission Inventory and the Emission Characteristics of the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal in Jiangsu Province. Process. Saf. Environ. 2018, 113, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, J.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z. Assessment and Prediction of the Water Ecological Carrying Capacity in Changzhou City, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Li, K.; Huang, T.; Wang, S.; Tang, Y.; Wen, G.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Cai, X. Extending Improvements of Eutrophication and Water Quality via Induced Natural Mixing after Artificial Mixing in a Stratified Reservoir. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 322, 116048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Rahman, A.; Olbert, A.I. A Comprehensive Method for Improvement of Water Quality Index (WQI) Models for Coastal Water Quality Assessment. Water Res. 2022, 219, 118532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, T.; Shen, S.-L.; Zhou, A. Indices and Models of Surface Water Quality Assessment: Review and Perspectives. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gai, R.; Guo, Z. A Water Quality Assessment Method Based on an Improved Grey Relational Analysis and Particle Swarm Optimization Multi-Classification Support Vector Machine. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1099668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczynski, A.; Smith, R.G.R.; Fraser, C.E.; Larned, S.T. Environmental Indicators of Lake Ecosystem Health in Aotearoa New Zealand: Current State and Trends. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 165, 112185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Zhou, C.; Peng, Y.; Jia, R.; Zhao, W.; Liang, S.; Xu, X.; Terada, A.; Wang, G. Space-for-Time Substitution Leads to Carbon Emission Overestimation in Eutrophic Lakes. Environ. Res. 2023, 219, 115175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Shi, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, S.; Sun, B.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z. Trophic Status of a Shallow Lake in Inner Mongolia: Long-Term, Seasonal, and Spatial Variation. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Lv, C.; Huang, L.; Shan, H.; Wang, H.; Wen, Z.; Yin, C.; Chou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ni, L.; et al. Seasonal Variation and Nutrient Jointly Drive the Community Structure of Macrophytes in Lakes with Different Trophic States. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1182823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; He, B.; Zhou, Y.; Kutser, T.; Toming, K.; Feng, Q.; Yang, X.; Fu, C.; Yang, F.; Li, W.; et al. Trophic State Assessment of Optically Diverse Lakes Using Sentinel-3-Derived Trophic Level Index. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 114, 103026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanelli, A.; Soto, D.X.; Matiatos, I.; Martínez, D.E.; Esquius, S. A Biological and Nitrate Isotopic Assessment Framework to Understand Eutrophication in Aquatic Ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, D.; Zhao, X.; Gao, L.; Liang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wu, Q.; Ren, K.; Li, R.; Yang, C.; et al. Estimation of Water Quality Variables Based on Machine Learning Model and Cluster Analysis-Based Empirical Model Using Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data in Inland Reservoirs, South China. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 342, 123104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heredia, C.; Guédron, S.; Point, D.; Perrot, V.; Campillo, S.; Verin, C.; Espinoza, M.E.; Fernandez, P.; Duwig, C.; Achá, D. Anthropogenic Eutrophication of Lake Titicaca (Bolivia) Revealed by Carbon and Nitrogen Stable Isotopes Fingerprinting. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhimathi, G.; Chellaswamy, C.; Selvan, T. Comprehensive River Water Quality Monitoring Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Gated Recurrent Units: A Case Study along the Vaigai River. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 365, 121567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China National Environmental Monitoring Center. Evaluation Methods and Classification Technical Regulations for Eutrophication Assessment of Lakes (Reservoirs) ([2001]090); China National Environmental Monitoring Center: Beijing, China, 2001. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.; Lv, X.; Yu, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Q. Intra-Annual Variation in the Attribution of Runoff Evolution in the Yellow River Source Area. CATENA 2023, 225, 107032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xia, J.; Zhou, M.; Deng, S.; Li, Q. Assessment of the Joint Impact of Rainfall and River Water Level on Urban Flooding in Wuhan City, China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 613, 128419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Weng, B.; Yan, D.; Bi, W.; Yang, Y.; Gong, X.; Wang, H. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Surface Water Resources in the Tibetan Plateau: Based on the Produce Water Coefficient Method Considering Snowmelt. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Dong, B.; Huang, G.; Tong, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, G. Study on the Sediment and Phosphorus Flux Processes under the Effects of Mega Dams Upstream of Yangtze River. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, M.T.H.; Thorslund, J.; Strokal, M.; Hofstra, N.; Flörke, M.; Ehalt Macedo, H.; Nkwasa, A.; Tang, T.; Kaushal, S.S.; Kumar, R.; et al. Global River Water Quality under Climate Change and Hydroclimatic Extremes. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, C.-Y.; Yue, F.-J.; Zhou, B.; Fu, X.; Ma, Z.-N.; Gong, Y.-Q.; Chen, S.-N. Chronic Increasing Nitrogen and Endogenous Phosphorus Release from Sediment Threaten to the Water Quality in a Semi-Humid Region Reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Song, Z.; Bouwman, A.F.; Ran, X. Phosphorus Depletion Is Exacerbated by Increasing Nitrogen Loading in the Bohai Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 352, 124119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).