Soil Salt and Water Regulation in Saline Agriculture Based on Physical Measures with Model Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
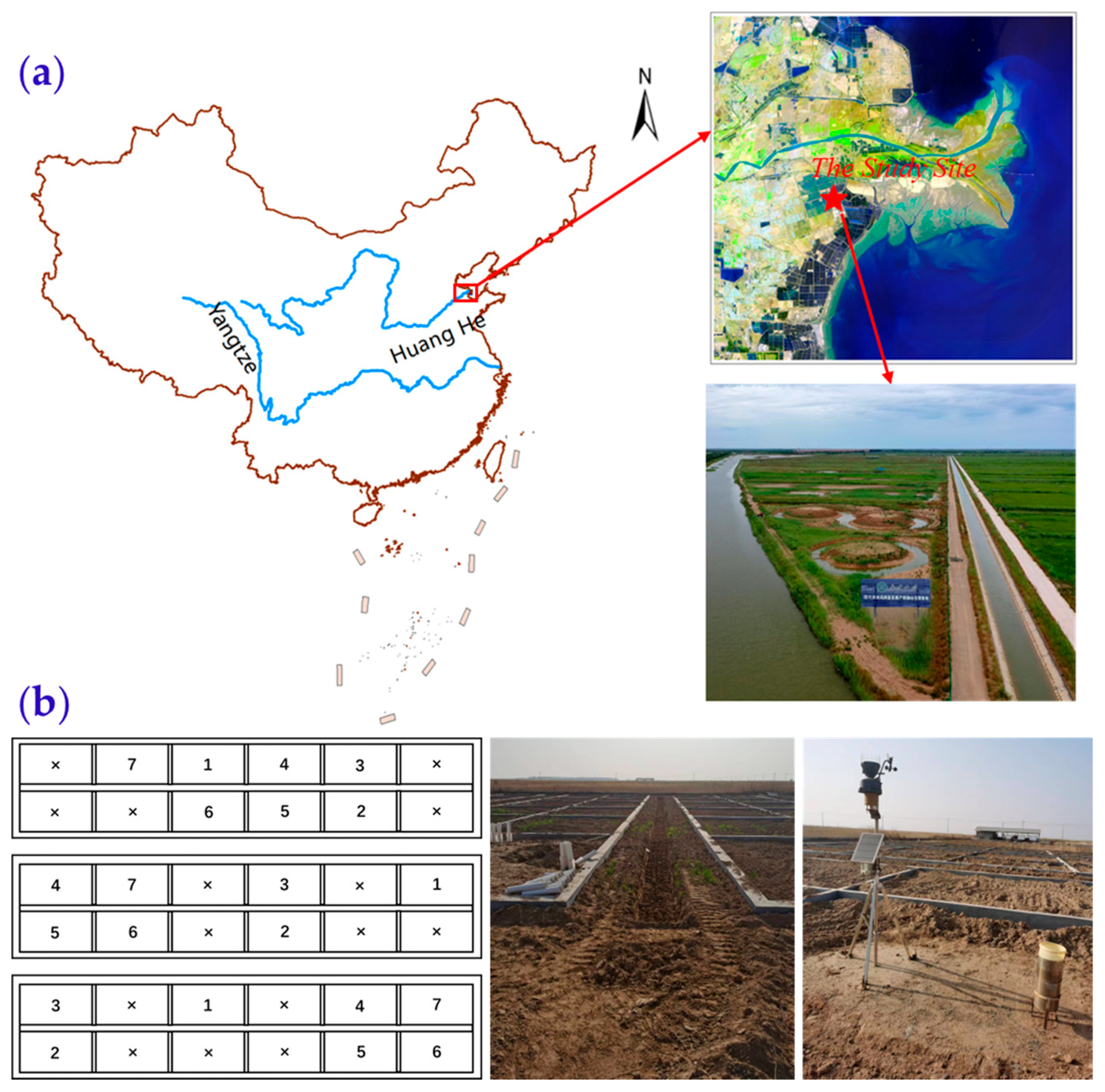
2.1. Study Area and Site Characterization
2.2. Field Experiment
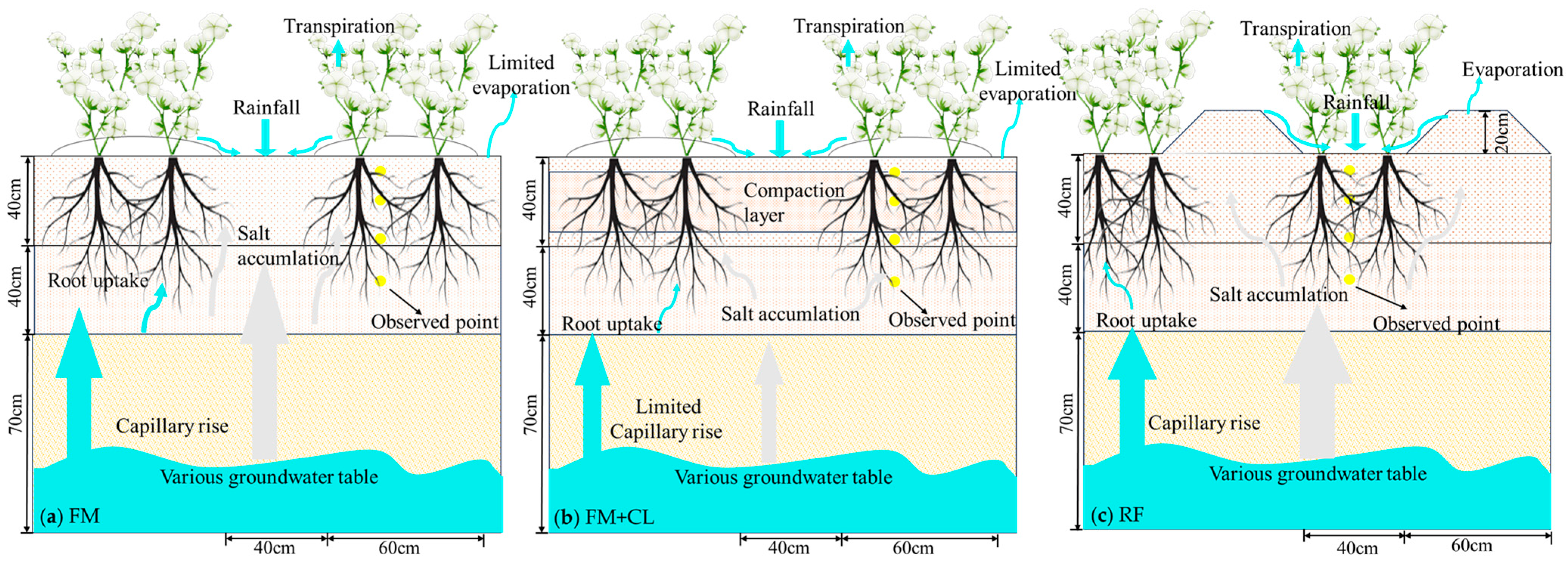
2.2.1. Experiment Design
2.2.2. Field and Laboratory Measurements
2.3. Simulation of the Coupled Water Flow and Solute Transport
2.3.1. Water Flow
2.3.2. Root Water Uptake
2.3.3. Estimation and Partition of Evapotranspiration
2.3.4. Solute Transport
2.3.5. Initial and Boundary Conditions
2.3.6. Statistical Analysis
2.4. The Groundwater Effect and Salt Accumulation
3. Results
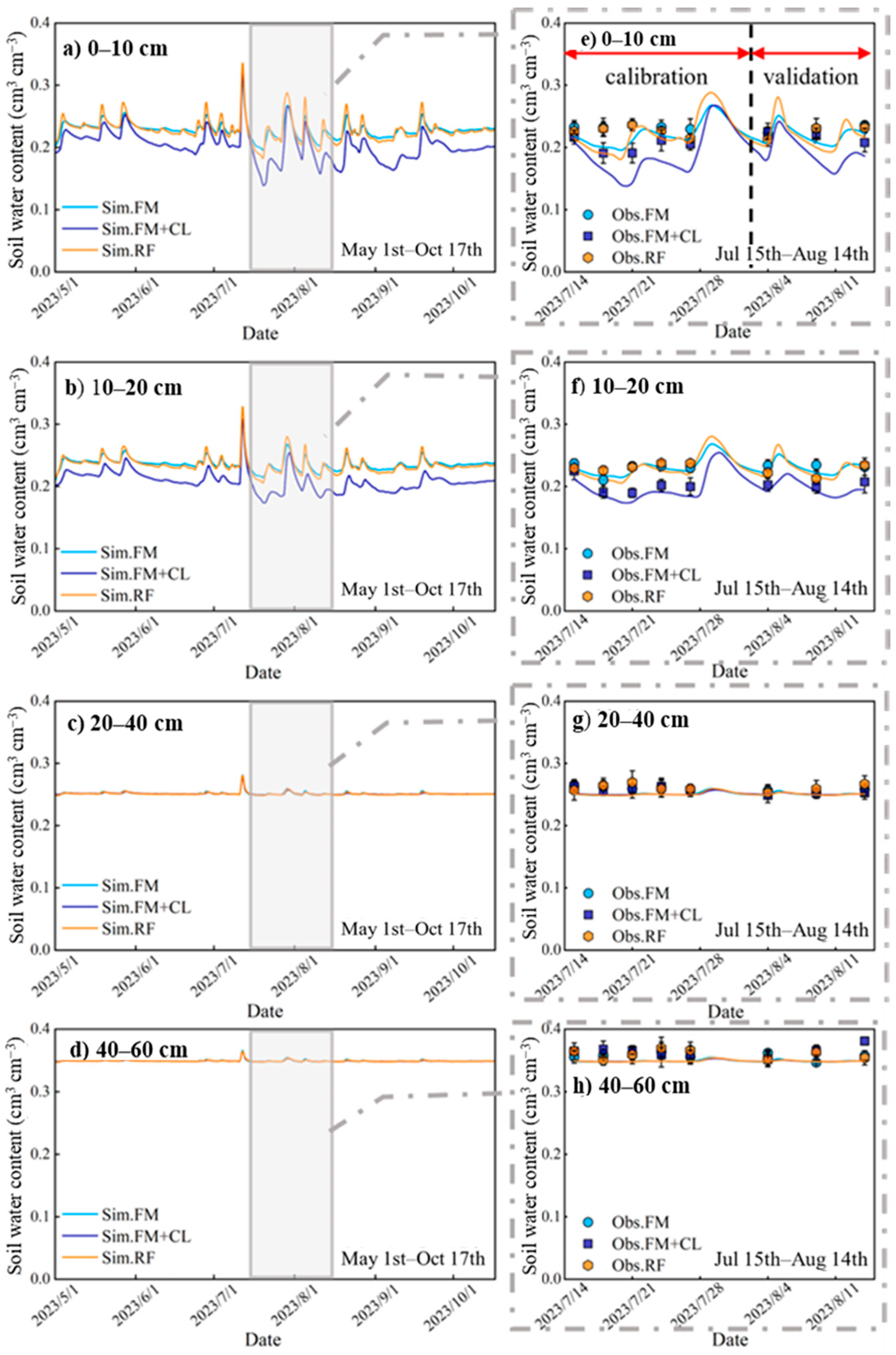
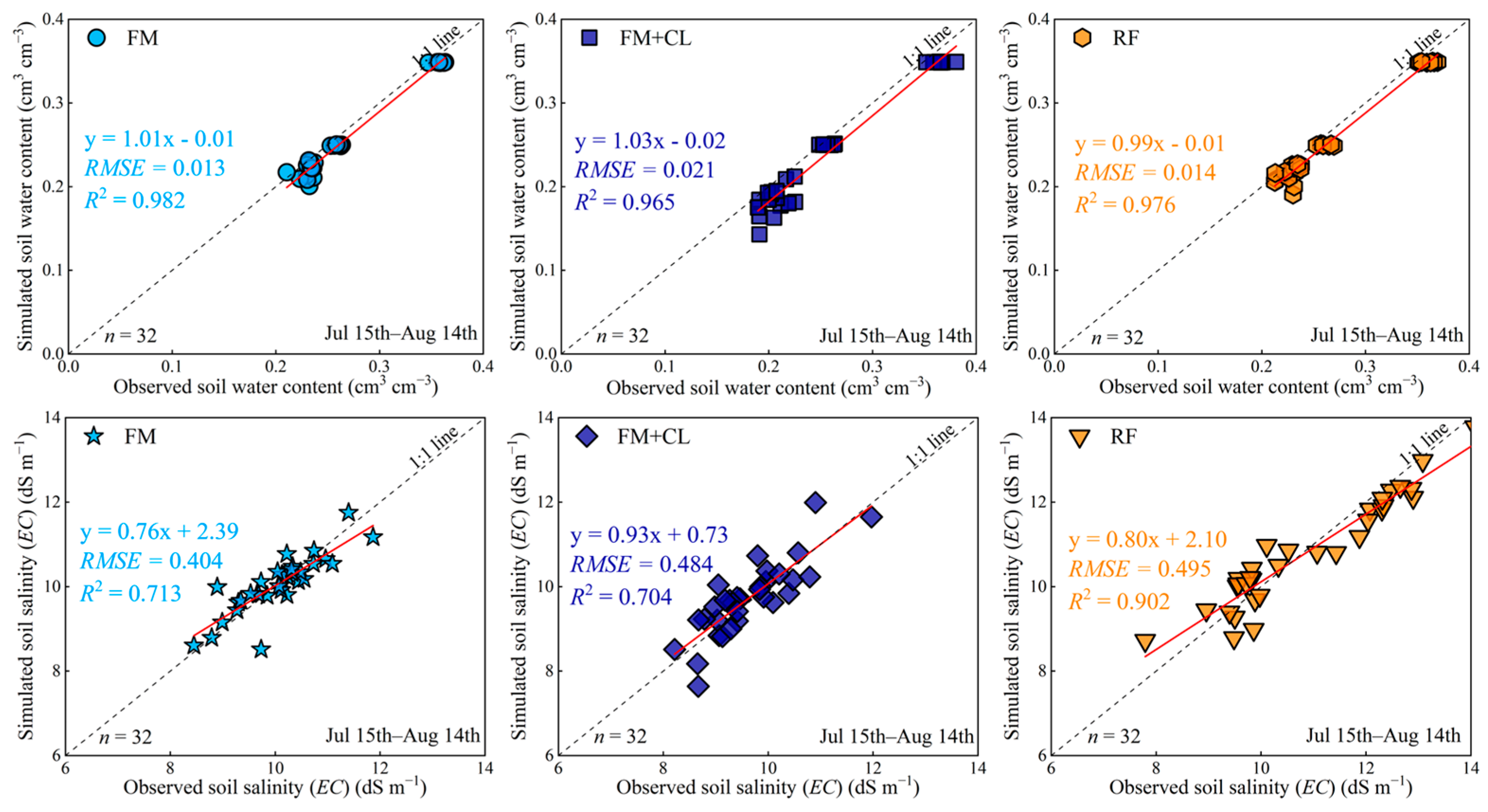
3.1. Model Performance
3.2. Soil Water Dynamic
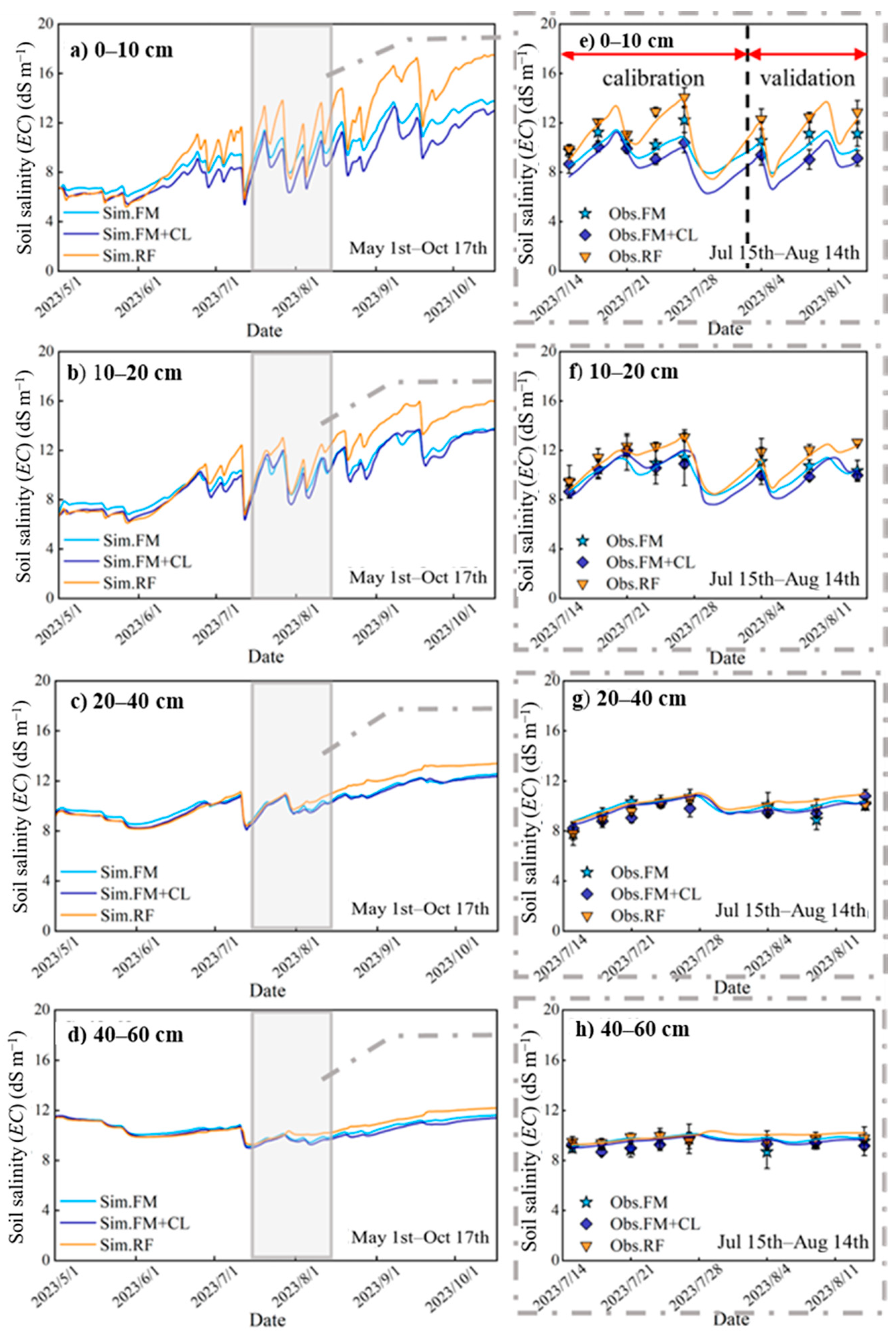
3.3. Changes in Soil Salinity
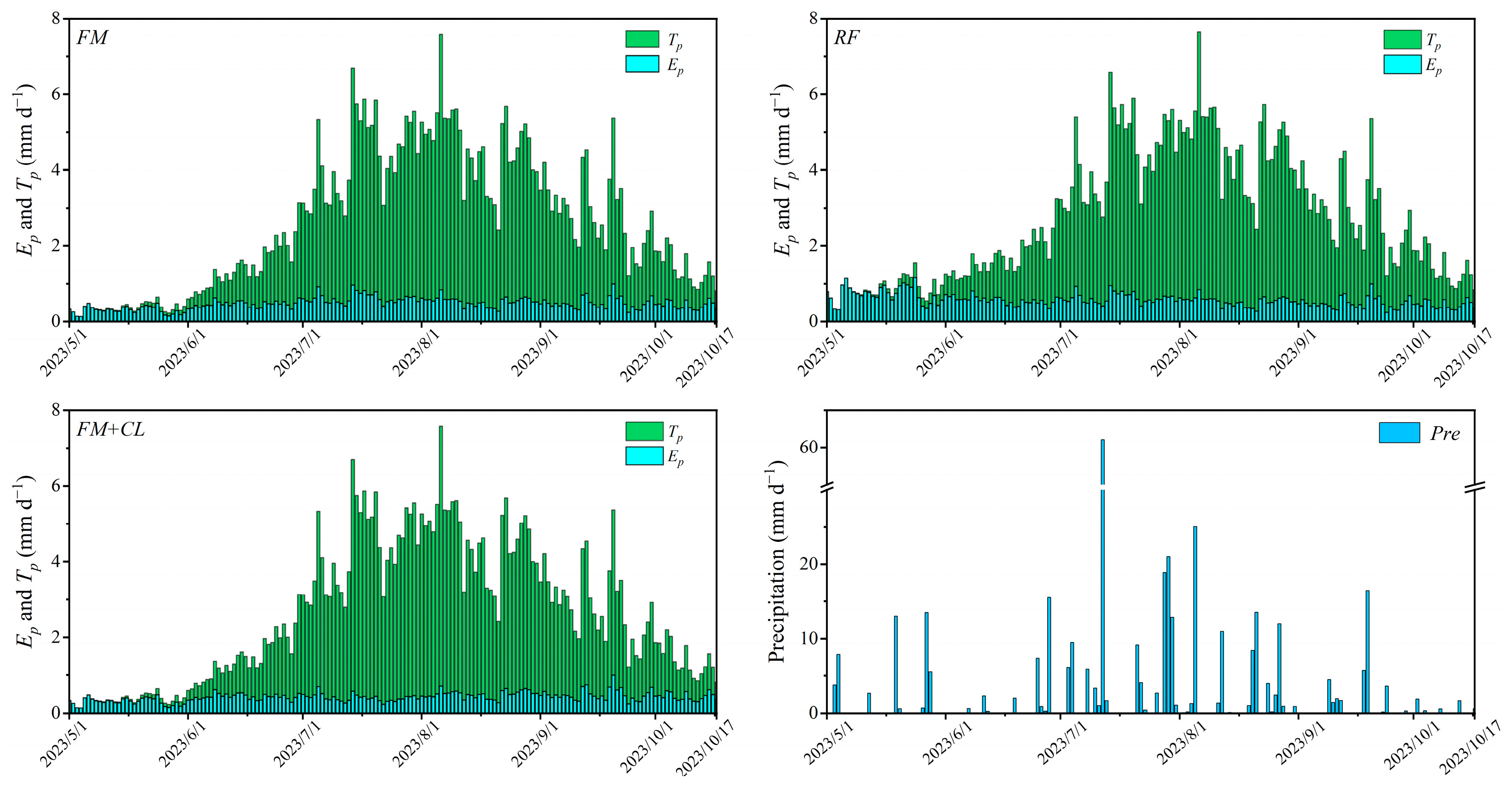
3.4. Actual Crop Transpiration and Water–Salt Stress
3.5. Influences of the Shallow Saline Groundwater on Crop Transpiration
4. Discussion
4.1. Efficient Use of Water Resources
4.2. The Effects of Soil Compaction on Saline Agroecosystems
4.3. Implications and Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferguson, C.R.; Pan, M.; Oki, T. The Effect of Global Warming on Future Water Availability: CMIP5 Synthesis. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 7791–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, T. Water Resources Management and Adaptation to Climate Change. In Water Security, Climate Change and Sustainable Development; Biswas, A.K., Tortajada, C., Eds.; Water Resources Development and Management; Springer: Singapore, 2016; pp. 27–40. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. The Impacts of Climate Change on Water Resources and Agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, B. Food Security and Food Self-sufficiency in China: From Past to 2050. Food Energy Secur. 2014, 3, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Wang, X.; Smith, P.; Fan, J.; Lu, Y.; Emmett, B.; Li, R.; Dorling, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, S.; et al. Soil Quality Both Increases Crop Production and Improves Resilience to Climate Change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Zhu, A.; Ali, T.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, F.; Huang, J.; Davis, K.F. Crop Switching Can Enhance Environmental Sustainability and Farmer Incomes in China. Nature 2023, 616, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Cultivated Land Protection and Rational Use in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 106, 105454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, R.; Deng, Y.; Ma, P.; Lin, H.; Wang, J. Mapping the Yellow River Delta Land Subsidence with Multitemporal SAR Interferometry by Exploiting Both Persistent and Distributed Scatterers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 148, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Jian, Z.; Sun, Y.; Pan, F.; Han, H.; Liu, Q.; Mei, Y. Ecological Sustainability and High-Quality Development of the Yellow River Delta in China Based on the Improved Ecological Footprint Model. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Yang, J.; Yao, R.; Xie, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. Soil Water-Salt Control and Yield Improvement under the Effect of Compound Control in Saline Soil of the Yellow River Delta, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 263, 107455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Liu, G.; Tian, G.; Chen, S.; Huang, C.; Chen, S.; Liu, Q.; Chang, J.; Shi, Y. Geospatial-Temporal Analysis of Land-Use Changes in the Yellow River Delta during the Last 40 Years. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 2004, 47, 1008–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, P.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, L. Sustainable Agricultural Water Management in the Yellow River Basin, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 288, 108473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, J. Modeling Strategies to Balance Salt Leaching and Nitrogen Loss for Drip Irrigation with Saline Water in Arid Regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 274, 107943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Yang, J.; Yao, R.; Wang, X.; Xie, W.; Li, P. Nitrate Leaching and NH3 Volatilization during Soil Reclamation in the Yellow River Delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Pang, H.; Li, Y. Buried Straw Layer plus Plastic Mulching Reduces Soil Salinity and Increases Sunflower Yield in Saline Soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Wang, G.; Kang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Wan, S. Soil Water and Salinity Dynamics under the Improved Drip-Irrigation Scheduling for Ecological Restoration in the Saline Area of Yellow River Basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 264, 107255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezborodov, G.A.; Shadmanov, D.K.; Mirhashimov, R.T.; Yuldashev, T.; Qureshi, A.S.; Noble, A.D.; Qadir, M. Mulching and Water Quality Effects on Soil Salinity and Sodicity Dynamics and Cotton Productivity in Central Asia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 138, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shao, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, M. Assessing Soil Water Balance to Optimize Irrigation Schedules of Flood-Irrigated Maize Fields with Different Cultivation Histories in the Arid Region. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 265, 107543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zeng, S.; Luo, X.; Fang, L.; Liang, Z.; Yang, W. Effects of Small Ridge and Furrow Mulching Degradable Film on Dry Direct Seeded Rice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Zhang, K.; Fan, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Cheng, M.; Zou, Y. Ridge-Furrow Plastic Mulching and Dense Planting with Reduced Nitrogen Improve Soil Hydrothermal Conditions, Rainfed Soybean Yield and Economic Return in a Semi-Humid Drought-Prone Region of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 217, 105291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunek, J.J.; Šejna, M.; Van Genuchten, M. The HYDRUS-2D Software Package for Simulating Water Flow and Solute Transport in Two Dimensional Variably Saturated Media, Version 2.0; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Riverside, CA, USA, 1998.
- Qi, Z.; Feng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, A.; Zhang, Z. Spatial Distribution and Simulation of Soil Moisture and Salinity under Mulched Drip Irrigation Combined with Tillage in an Arid Saline Irrigation District, Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 201, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, J. Irrigation Planning in Cotton through Simulation Modeling. Irrig. Sci. 1996, 17, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Šimůnek, J.; Shi, H.; Chen, N.; Hu, Q. Optimizing Drip Irrigation with Alternate Use of Fresh and Brackish Waters by Analyzing Salt Stress: The Experimental and Simulation Approaches. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 219, 105355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.; Qi, J.; Suo, L.; Pan, Y.; Song, B.; Chen, X. Effect of Saline Land Reclamation by Constructing the “Raised Field -Shallow Trench” Pattern on Agroecosystems in Yellow River Delta. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 261, 107345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Chu, X.; Xing, Q.; Li, D.; Yu, J.; Luo, Y.; Wang, G.; Mao, P.; Rafique, R. Effects of Episodic Flooding on the Net Ecosystem CO 2 Exchange of a Supratidal Wetland in the Yellow River Delta. JGR Biogeosci. 2015, 120, 1506–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Sun, B.; Chu, X.; Xing, Q.; Song, W.; Xia, J. Precipitation Events Reduce Soil Respiration in a Coastal Wetland Based on Four-Year Continuous Field Measurements. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 256–257, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Han, G.; Zhou, D.; Fu, Y.; Guan, B.; Wang, G.; Ning, K.; Wu, H.; Wang, J. The Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Soil Salinity in Coastal Zone of the Yellow River Delta. Environ. Earth Sci 2014, 72, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.J. Study on Salt Tolerance of Crop and Cropping System Optimization in Hetao Irrigation District; China Agricultural University: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Xin, C.; Li, W.; Tan, W.; Zhang, D.; Luo, Z. Characteristics of Salinity and Fertility in Coastal Saline Cotton Fields in Shandong and Their Effects on Cotton Emergence. Cotton Sci. 2009, 21, 290–295. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirement; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 300, p. D05109. [Google Scholar]
- Hansson, K.; Šimůnek, J.; Mizoguchi, M.; Lundin, L.; Genuchten, M.T. van Water Flow and Heat Transport in Frozen Soil: Numerical Solution and Freeze–Thaw Applications. Vadose Zone J. 2004, 3, 693–704. [Google Scholar]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A Closed-form Equation for Predicting the Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaap, M.G.; Leij, F.J.; Van Genuchten, M.T. Rosetta: A Computer Program for Estimating Soil Hydraulic Parameters with Hierarchical Pedotransfer Functions. J. Hydrol. 2001, 251, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feddes, R.A.; Kowalik, P.J.; Zaradny, H. Simulation of Field Water Use and Crop Yield; Centre for Agricultural Publishing and Documentation: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1978; pp. 194–209. [Google Scholar]
- Šimůnek, J.; Hopmans, J.W. Modeling Compensated Root Water and Nutrient Uptake. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrugt, J.A.; Hopmans, J.W.; Šimunek, J. Calibration of a Two-Dimensional Root Water Uptake Model. Soil Sci. Soc Am. J. 2001, 65, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T.; U.S. Salinity Laboratory. A Numerical Model for Water and Solute Movement in and Below the Root Zone; United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service U.S. Salinity Laboratory: Riverside, CA, USA, 1987.
- Maas, E.V.; Hoffman, G.J. Crop Salt Tolerance—Current Assessment. J. Irrig. Drain. Div. 1977, 103, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, J.T. Model for Predicting Evaporation from a Row Crop with Incomplete Cover. Water Resour. Res. 1972, 8, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Han, S.; Yang, Y.; Ai, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, F. Identifying Changes in Irrigation Return Flow with Gradually Intensified Water-Saving Technology Using HYDRUS for Regional Water Resources Management. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 194, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhai, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Jiang, R.; Lee Hill, R.; Si, B.; Hao, F. Simulation of Soil Water and Heat Flow in Ridge Cultivation with Plastic Film Mulching System on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 202, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimůnek, J.; Van Genuchten, M.T.; Jacques, D.; Hopmans, J.W.; Inoue, M.; Flury, M. 6.6 Solute Transport during Variably Saturated Flow-Inverse Methods. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 4 Physical Methods; Dane, J.H., Clarke Topp, G., Eds.; SSSA Book Series; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2018; pp. 1435–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Wang, Z.; Šimůnek, J.; He, Y.; Muhamma, R. Optimizing the Strategies of Mulched Brackish Drip Irrigation under a Shallow Water Table in Xinjiang, China, Using HYDRUS-3D. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 283, 108303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Wang, X.; Huo, Z.; Guan, H.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, G. Response of Shelterbelt Transpiration to Shallow Groundwater in Arid Areas. J. Hydrol. 2021, 592, 125611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassam, D.W.; Pagendam, D.E.; Hunter, H.M. Conceptualisation and Application of Models for Groundwater–Surface Water Interactions and Nitrate Attenuation Potential in Riparian Zones. Environ. Model. Softw. 2008, 23, 859–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qi, J.; Hu, Q.; Wang, Y. The “Groundwater Benefit Zone”, Proposals, Contributions and New Scientific Issues. In Soil Science—Emerging Technologies, Global Perspectives and Applications; Aide, M., Braden, I., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, Y.; Dai, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, P.; Huo, Z. Dependence of Evapotranspiration Validity on Shallow Groundwater in Arid Area-a Three Years Field Observation Experiment. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 286, 108411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, C.S.; Loheide, S.P. Groundwater-dependent Vegetation: Quantifying the Groundwater Subsidy. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, 2009WR008874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Huo, Z.; Qu, Z.; Xu, X.; Huang, G.; Steenhuis, T.S. Modeling Contribution of Shallow Groundwater to Evapotranspiration and Yield of Maize in an Arid Area. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylu, M.E.; Loheide, S.P.; Kucharik, C.J. Effects of Root Distribution and Root Water Compensation on Simulated Water Use in Maize Influenced by Shallow Groundwater. Vadose Zone J. 2017, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürsoy, S. Soil Compaction Due to Increased Machinery Intensity in Agricultural Production: Its Main Causes, Effects and Management. In Technology in Agriculture; Ahmad, F., Sultan, M., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Batey, T. Soil Compaction and Soil Management—A Review. Soil Use Manag. 2009, 25, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, M.A.; Anderson, W.K. Soil Compaction in Cropping Systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 82, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheb, M.R.; Venkatesh, R.; Shearer, S.A. A Review on the Effect of Soil Compaction and Its Management for Sustainable Crop Production. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 46, 417–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombi, T.; Keller, T. Developing Strategies to Recover Crop Productivity after Soil Compaction—A Plant Eco-Physiological Perspective. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 191, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivarajan, S.; Maharlooei, M.; Bajwa, S.G.; Nowatzki, J. Impact of Soil Compaction Due to Wheel Traffic on Corn and Soybean Growth, Development and Yield. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 175, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, M.T.D.; Debiasi, H.; Franchini, J.C.; Mastroberti, A.A.; Levien, R.; Leitner, D.; Schnepf, A. Soil Compaction Impacts Soybean Root Growth in an Oxisol from Subtropical Brazil. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 200, 104611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürsoy, S.; Türk, Z. Effects of Land Rolling on Soil Properties and Plant Growth in Chickpea Production. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mileusnić, Z.I.; Saljnikov, E.; Radojević, R.L.; Petrović, D.V. Soil Compaction Due to Agricultural Machinery Impact. J. Terramech. 2022, 100, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, K.; Geyer, M. Plastic Mulch Films in Agriculture: Their Use, Environmental Problems, Recycling and Alternatives. Environments 2023, 10, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Hu, Z.; Wu, F.; Guo, K.; Gu, F.; Cao, M. The Use and Recycling of Agricultural Plastic Mulch in China: A Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Li, X.; Šimůnek, J.; Shi, H.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, Y. The Effects of Biodegradable and Plastic Film Mulching on Nitrogen Uptake, Distribution, and Leaching in a Drip-Irrigated Sandy Field. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 292, 106817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jia, W.; Yan, C.; Wang, J. Agricultural Plastic Mulching as a Source of Microplastics in the Terrestrial Environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horta, A.; Oliveira, A.R.; Azevedo, L.; Ramos, T.B. Assessing the Use of Digital Soil Maps in Hydrological Modeling for Soil-Water Budget Simulations—Implications for Water Management Plans in Southern Portugal. Geoderma Reg. 2024, 36, e00741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anlauf, R.; Schaefer, J.; Kajitvichyanukul, P. Coupling HYDRUS-1D with ArcGIS to Estimate Pesticide Accumulation and Leaching Risk on a Regional Basis. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.A.; Chen, W.; Lin, B.-S.; Seeboonruang, U. Comparison of Ensemble Machine Learning Methods for Soil Erosion Pin Measurements. Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Depth | Texture (%) | ρb | Soil Texture | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (cm) | Sand | Silt | Clay | (g cm−3) | |
| 0–40 | 59.67 | 34.81 | 5.52 | 1.36 | Sand loam |
| 40–80 | 19.34 | 71.47 | 9.19 | 1.41 | Silt loam |
| 80–150 | 14.91 | 68.30 | 16.69 | 1.44 | Silt loam |
| 11–28 (CL) * | 57.51 | 35.47 | 7.02 | 1.48 | Sand loam |
| Depth | θr | θs | α | n | Ks | DL | DT | Dw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (cm) | (cm3 cm−3) | (cm3 cm−3) | (cm−1) | (-) | (cm d−1) | (cm) | (cm) | (cm2 d−1) |
| 0–40 | 0.0345 | 0.384 | 0.0234 | 1.44 | 70.72 | 48 | 4.2 | 2.02 |
| 40–80 | 0.0454 | 0.386 | 0.0059 | 1.66 | 49.82 | 38 | 3.3 | 1.62 |
| 80–150 | 0.0748 | 0.483 | 0.0058 | 1.62 | 23.58 | 31 | 3.5 | 1.60 |
| 11–28 (CL) | 0.0328 | 0.360 | 0.0284 | 1.43 | 31.72 | 44 | 3.8 | 2.51 |
| Depth (cm) | Calibration (July 2023) | Validation (August 2023) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWC (cm3 cm−3) | EC (dS m−1) | SWC (cm3 cm−3) | EC (dS m−1) | ||
| 0–10 | RMSE | 0.016 | 0.542 | 0.019 | 0.525 |
| R2 | 0.958 | 0.656 | 0.937 | 0.621 | |
| 10–20 | RMSE | 0.021 | 0.558 | 0.024 | 0.561 |
| R2 | 0.962 | 0.721 | 0.949 | 0.618 | |
| 20–40 | RMSE | 0.011 | 0.524 | 0.012 | 0.511 |
| R2 | 0.978 | 0.778 | 0.966 | 0.702 | |
| 40–60 | RMSE | 0.012 | 0.493 | 0.009 | 0.322 |
| R2 | 0.981 | 0.819 | 0.977 | 0.867 | |
| Treatment | Growth Stage | P (mm) | EP (mm) | TP (mm) | ETP (mm) | TA (mm) | TA/TP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FM | Seedling | 48.6 | 15.1 | 4.0 | 19.1 | 4.0 | 0.99 |
| Squaring | 50.2 | 21.2 | 46.7 | 67.9 | 43.9 | 0.94 | |
| Flower boll | 176.4 | 27.1 | 163.8 | 190.9 | 150.4 | 0.92 | |
| Boll opening | 84.5 | 30.5 | 135.2 | 165.8 | 110.7 | 0.82 | |
| Total | 359.7 | 93.9 | 349.7 | 443.6 | 308.9 | 0.88 | |
| FM+CL | Seedling | 48.6 | 14.3 | 4.1 | 18.4 | 4.0 | 0.98 |
| Squaring | 50.2 | 21.3 | 47.7 | 69.0 | 44.8 | 0.94 | |
| Flower boll | 176.4 | 27.1 | 165.7 | 192.8 | 154.1 | 0.93 | |
| Boll opening | 84.5 | 30.5 | 136.6 | 167.1 | 116.1 | 0.85 | |
| Total | 359.7 | 93.2 | 354.1 | 447.3 | 319.0 | 0.91 | |
| RF | Seedling | 48.6 | 31.8 | 6.8 | 38.6 | 5.1 | 0.76 |
| Squaring | 50.2 | 22.8 | 49.1 | 71.9 | 41.7 | 0.85 | |
| Flower boll | 176.4 | 27.2 | 164.4 | 191.6 | 142.6 | 0.87 | |
| Boll opening | 84.5 | 30.7 | 135.8 | 166.6 | 99.2 | 0.73 | |
| Total | 359.7 | 112.5 | 356.2 | 468.7 | 288.6 | 0.81 |
| Treatment | Growth Stage | TP | Variable Head BC | Free Drainage BC | ΔTA * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mm) | TA (mm) | TA/TP | TA (mm) | TA/TP | (mm) | ||
| FM | Seedling | 4.0 | 4.0 | 0.99 | 4.0 | 0.99 | 0.0 |
| Squaring | 46.7 | 43.9 | 0.94 | 45.5 | 0.97 | −1.6 | |
| Flower boll | 163.8 | 150.4 | 0.92 | 149.6 | 0.91 | 0.8 | |
| Boll opening | 135.2 | 110.7 | 0.82 | 103.2 | 0.76 | 7.5 | |
| Total | 349.7 | 308.9 | 0.88 | 302.3 | 0.86 | 6.6 | |
| FM+CL | Seedling | 4.1 | 4.0 | 0.98 | 4.0 | 0.99 | 0.0 |
| Squaring | 47.7 | 44.8 | 0.94 | 45.6 | 0.98 | −0.8 | |
| Flower boll | 165.7 | 154.1 | 0.93 | 152.8 | 0.93 | 1.3 | |
| Boll opening | 136.6 | 116.1 | 0.85 | 104.2 | 0.77 | 11.9 | |
| Total | 354.1 | 319.0 | 0.91 | 306.6 | 0.88 | 12.4 | |
| RF | Seedling | 6.8 | 5.1 | 0.76 | 5.2 | 0.77 | −0.1 |
| Squaring | 49.1 | 41.7 | 0.85 | 42.8 | 0.87 | −1.1 | |
| Flower boll | 164.4 | 142.6 | 0.87 | 144.5 | 0.88 | −1.9 | |
| Boll opening | 135.8 | 99.2 | 0.73 | 95.3 | 0.70 | 3.9 | |
| Total | 356.2 | 288.6 | 0.81 | 287.8 | 0.81 | 0.8 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, W.; Yu, J.; Hu, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y. Soil Salt and Water Regulation in Saline Agriculture Based on Physical Measures with Model Analysis. Water 2024, 16, 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050719
Fu W, Yu J, Hu Q, Wang H, Zhao Y. Soil Salt and Water Regulation in Saline Agriculture Based on Physical Measures with Model Analysis. Water. 2024; 16(5):719. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050719
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Wenyuan, Jinyi Yu, Qiuli Hu, Haixia Wang, and Ying Zhao. 2024. "Soil Salt and Water Regulation in Saline Agriculture Based on Physical Measures with Model Analysis" Water 16, no. 5: 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050719
APA StyleFu, W., Yu, J., Hu, Q., Wang, H., & Zhao, Y. (2024). Soil Salt and Water Regulation in Saline Agriculture Based on Physical Measures with Model Analysis. Water, 16(5), 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050719







