Water Quality Estimation Using Gaofen-2 Images Based on UAV Multispectral Data Modeling in Qinba Rugged Terrain Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
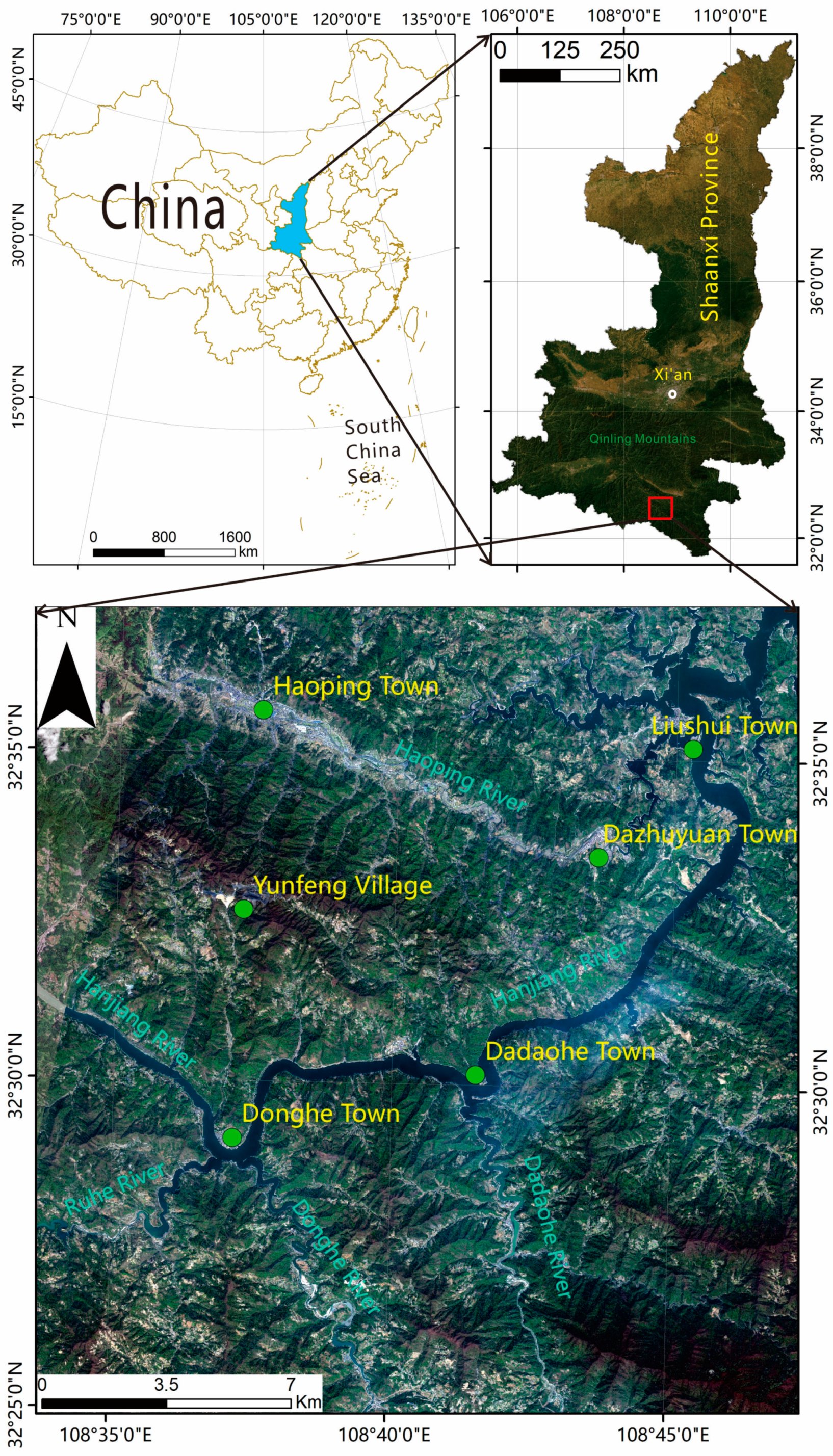
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Multispectral Data Acquisition and Preprocessing for UAVs
2.3. Water Sample Collection
2.4. Data Acquisition and Processing of Gaofen-2 Data
2.5. Establishment of UAV Multispectral Water Quality Estimation Model
2.6. Comparison of Multispectral Images from UAVs and Gaofen-2
3. Results
3.1. Relative Deviation between UAV and Gaofen-2 Multispectral Images
3.2. Establishment of Water Quality Estimation Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Yan, T.; Sun, T. Growing water scarcity, food security and government responses in China. Glob. Food Secur. 2017, 14, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Bing, H.; Peng, J.; Dong, F.; Gao, J.; Arhonditsis, G. Characterizing the river water quality in China: Recent progress and on-going challenges. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Ministry of Ecological Environment Announced the Environmental Quality of Surface Water in the Fourth Quarter of 2022 and from January to December in China. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywdt/xwfb/202301/t20230129_1014067.shtml (accessed on 29 January 2023).
- Frumin, G.T.; Gildeeva, I.M. Eutrophication of water bodies—A global environmental problem. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2014, 84, 2483–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T. Design and Implementation of Water Pollution Monitoring Visualization Based on IDL. Master’s Degree, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Shi, Q.; Abdusalih, N.; Pan, X. Review on Monitoring of Lake Water Quality with the Remote Sensing Technology in Arid Areas of the West China. J. Agric. Sci. 2005, 26, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Bouraoui, F.; Grizzetti, B. Modelling mitigation options to reduce diffuse nitrogen water pollution from agriculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branch, R.A. Remote Sensing of Water Surface Variability Near River Mouths. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, H.-J.; He, Y.-C.; Chusnah, W.N.; Jaelani, L.M.; Chang, C.-H. Multi-Reservoir Water Quality Mapping from Remote Sensing Using Spatial Regression. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Ye, H.; Sun, D.; Yue, J.; Yang, G.; Hu, J. An automated, high-performance approach for detecting and characterizing broccoli based on UAV remote-sensing and transformers: A case study from Haining, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 114, 103055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Xiao, J.; Bonafoni, S.; Berger, C.; Deilami, K.; Zhou, Y.; Frolking, S.; Yao, R.; Qiao, Z.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite Remote Sensing of Surface Urban Heat Islands: Progress, Challenges, and Perspectives. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xia, K.; Feng, H.; Fang, Y. Inversion of water quality elements in small and micro-size water region using multispectral image by UAV. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, R.; Zhang, H.; Yue, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Mei, S. A wavelet theory based remote sensing inversion of chlorophyll a concentrations for inland lakes in arid areas using TM image data. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Adjovu, G.E.; Stephen, H.; James, D.; Ahmad, S. Overview of the Application of Remote Sensing in Effective Monitoring of Water Quality Parameters. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, B. A Semi-Empirical Retrieval Method of Above-Ground Live Forest Fuel Loads by Combining SAR and Optical Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang, S. Study on the artificial neural network model for water quality remote sensing inversion in the Wei River. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2009, 24, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Yan, J. Application of GA-SVM for multispectral remote sensing inversion of water quality parameters in the Wei River. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 13, 740–744. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Q.; Shen, H.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, H.; Tan, W.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. Deep learning in environmental remote sensing: Achievements and challenges. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Fan, M.; Qin, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H. Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Algorithms in Automatic Identification and Extraction of Water Boundaries. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, A.; Wang, H.; Ma, J. Remote sensing inversion of water quality of Fuyang river based on UAV multi-spectrral images. Geomat. Spat. Inf. Technol. 2022, 3, 81–85. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Lv, T. Geological Characteristics and Stone-bearing Coal Analysis of Dove Formation in Shuanglong Area, Ankang City. Coal 2014, 23, 52–53. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, H.; Ke, H. Temporal and Spatial Variation and Influencing Factors of Heavy Metals in the Water of the Chenjiagou River in a Certain Place. Northwestern Geol. 2023, 4, 169–183. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Ma, H. Thought on the characteristics and comprehensive utilization of stone coal. Shaanxi Coal 2013, 1, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z. Geological Characteristics of the Stone Coal Belt in Haoping, Ankang City. Value Eng. 2014, 33, 310–311. [Google Scholar]
- Choosumrong, S.; Hataitara, R.; Sujipuli, K.; Chitpan, M. Bananas diseases and insect infestations monitoring using multi-spectral camera RTK UAV images. Spat. Inf. Res. 2023, 31, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Feng, H.; Jin, X.; Yuan, H.; Li, Z.; Zhou, C.; Yang, G.; Tian, Q. A Comparison of Crop Parameters Estimation Using Images from UAV-Mounted Snapshot Hyperspectral Sensor and High-Definition Digital Camera. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 11893-89; Water Quality-Determination of Total Phosphorus-Ammonium Molybdate Spectrophotometric Method. China Environmental Science Press Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 1990.
- HJ 828-2017; Water Quality-Determination of the Chemical Oxygen Demand-Dichromate Method. China Environmental Science Press Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2017.
- HJ 636-2012; Water Quality-Determination of Total Nitrogen-Alkaline Potassium Persulfate Digestion UV Spectrophotometric Method. China Environmental Science Press Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Liang, S.; Wei, H.; Gan, F.; Chen, L.; Xiao, C. Preliminary Application Evaluation of GF-2 Satellite Data in Remote Sensing Geological Survey. Spacecr. Recovery Remote Sens. 2015, 4, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Prieto-Amparan, J.A.; Villarreal-Guerrero, F.; Martinez-Salvador, M.; Manjarrez-Domínguez, C.; Santellano-Estrada, E.; Pinedo-Alvarez, A. Atmospheric and Radiometric Correction Algorithms for the Multitemporal Assessment of Grasslands Productivity. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X. Variational Pansharpening for Hyperspectral Imagery Constrained by Spectral Shape and Gram–Schmidt Transformation. Sensors 2018, 18, 4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, R.; Balzter, H.; Kolo, K. Predicting Land Use/Land Cover Changes Using a CA-Markov Model under Two Different Scenarios. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, S.; Qin, X.; Zhao, N.; Liang, L. Mapping of Urban Surface Water Bodies from Sentinel-2 MSI Imagery at 10 m Resolution via NDWI-Based Image Sharpening. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Han, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, D.; Fan, J.; Sun, G.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Study on the inversion of COD in water bodies in Guangzhou based on remote sensing. Sci. Technol. Innov. 2021, 9, 38–39. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Kuang, R.; Li, J.; Hu, M. Inversion Model of TN, TP Concentration Based on Measured Spectral Reflectance Data in Poyang Lake. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 9, 2088–2094. [Google Scholar]
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. China Environmental Science Press Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2002.
- DB61-262-1997; Dividing the Functional Zones of Surface Water Bodies in the Hanjiang River System (Shaanxi Section). China Environmental Science Press Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 1998.
- Xu, Y.; Chen, H.; Ke, H.; Gong, H.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z. Analysis of White Pollution of River Aluminum in Stone Coalmining Area in Haoping River Basin and Its Causes. Northwestern Geol. 2023, 4, 128–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Chan, N.W.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Kung, H.-T.; Li, X.; Guo, T.; Wang, W.; Cao, N. Water Quality Index (WQI) as a Potential Proxy for Remote Sensing Evaluation of Water Quality in Arid Areas. Water 2021, 13, 3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, M.H.; Melesse, A.M.; Reddi, L. A Comprehensive Review on Water Quality Parameters Estimation Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Sensors 2016, 16, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Mu, X.; Chen, P.; Wang, B.; Choi, J.; Park, H.; Xu, S.; Wu, Y.; Yang, H. Machine learning-based inversion of water quality parameters in typical reach of the urban river by UAV multispectral data. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koparan, C.; Koc, A.B.; Privette, C.V.; Sawyer, C.B. In Situ Water Quality Measurements Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) System. Water 2018, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essam, S.; Zhang, Y.; Suliman, A. Mapping concentrations of surface water quality parameters using a novel remote sensing and artificial intelligence framework. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 1023–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Sandau, R.; Bries, K.; D’Errico, M. Small satellites for global coverage: Potential and limits. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Zhao, G.; Gao, P.; Cui, K.; Li, T. Inversion of soil salinity in coastal winter wheat growing area based on sentinel satellite and unmanned aerial vehicle multi-spectrum: A case study in kenli district of the Yellow River Deltae. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2020, 53, 5005. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zan, M.; Munige, M. Estimation of above ground biomass of Populus euphratica forest using UAV and satellite remotesensing. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 77. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Liang, Z.; Wang, B.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S. UAV and satellite re-mote sensing images based above ground biomass inversion in the meadows of Shengjin Lake. J. Lake Sci. 2019, 31, 517. [Google Scholar]
- Cillero, C.; Domínguez, G.; Delgado, M. An UAV and satellite multispectral data approach to monitor water quality in small reservoirs. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Meng, Q.; Bo, L. Monitoring analysis and evaluation of physical and chemical indicators of Yinghu water quality. China Fish. 2023, 6, 68–70. [Google Scholar]





| Multispectral Bands (nm) | Spatial Resolution (cm) | Focal Length (mm) | Field of VIEW (°) | Aperture |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 450/560/650/730/840 | 10 | 5.74 | 62.7 | f/2.2 |
| Sensors | Bands | Spectral Range (nm) | Spatial Resolution of Subsatellite Point (m) | Swath Width (km) | Sway (°) | Pass Frequency (Day−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAN | 1 | 450~900 | 0.8 | 20 | ±26 | 1 |
| MSI | 1 | 450~520 | 3.2 | 20 | ±26 | 1 |
| 2 | 520~590 | |||||
| 3 | 630~690 | |||||
| 4 | 770~890 |
| Parameters | Models | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD) | 0.804 | |
| Total phosphorus (TP) | 0.808 | |
| Total nitrogen (TN) | 0.9177 |
| Class I | Class II | Class III | Class IV | Class V | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | ≤15 | ≤15 | ≤20 | ≤30 | ≤40 |
| TP | ≤0.02 | ≤0.1 | ≤0.2 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.4 |
| TN | ≤0.2 | ≤0.5 | ≤1.0 | ≤1.5 | ≤2.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, D.; Cao, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.; Yang, M. Water Quality Estimation Using Gaofen-2 Images Based on UAV Multispectral Data Modeling in Qinba Rugged Terrain Area. Water 2024, 16, 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050732
Han D, Cao Y, Yang F, Zhang X, Yang M. Water Quality Estimation Using Gaofen-2 Images Based on UAV Multispectral Data Modeling in Qinba Rugged Terrain Area. Water. 2024; 16(5):732. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050732
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Dianchao, Yongxiang Cao, Fan Yang, Xin Zhang, and Min Yang. 2024. "Water Quality Estimation Using Gaofen-2 Images Based on UAV Multispectral Data Modeling in Qinba Rugged Terrain Area" Water 16, no. 5: 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050732
APA StyleHan, D., Cao, Y., Yang, F., Zhang, X., & Yang, M. (2024). Water Quality Estimation Using Gaofen-2 Images Based on UAV Multispectral Data Modeling in Qinba Rugged Terrain Area. Water, 16(5), 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050732






