Evaluating the Effectiveness of the “River Chief System”: An Empirical Study Based on the Water Quality Data of Coastal Rivers in Guangdong Province
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Research Design and Data
3.1. Model Specification
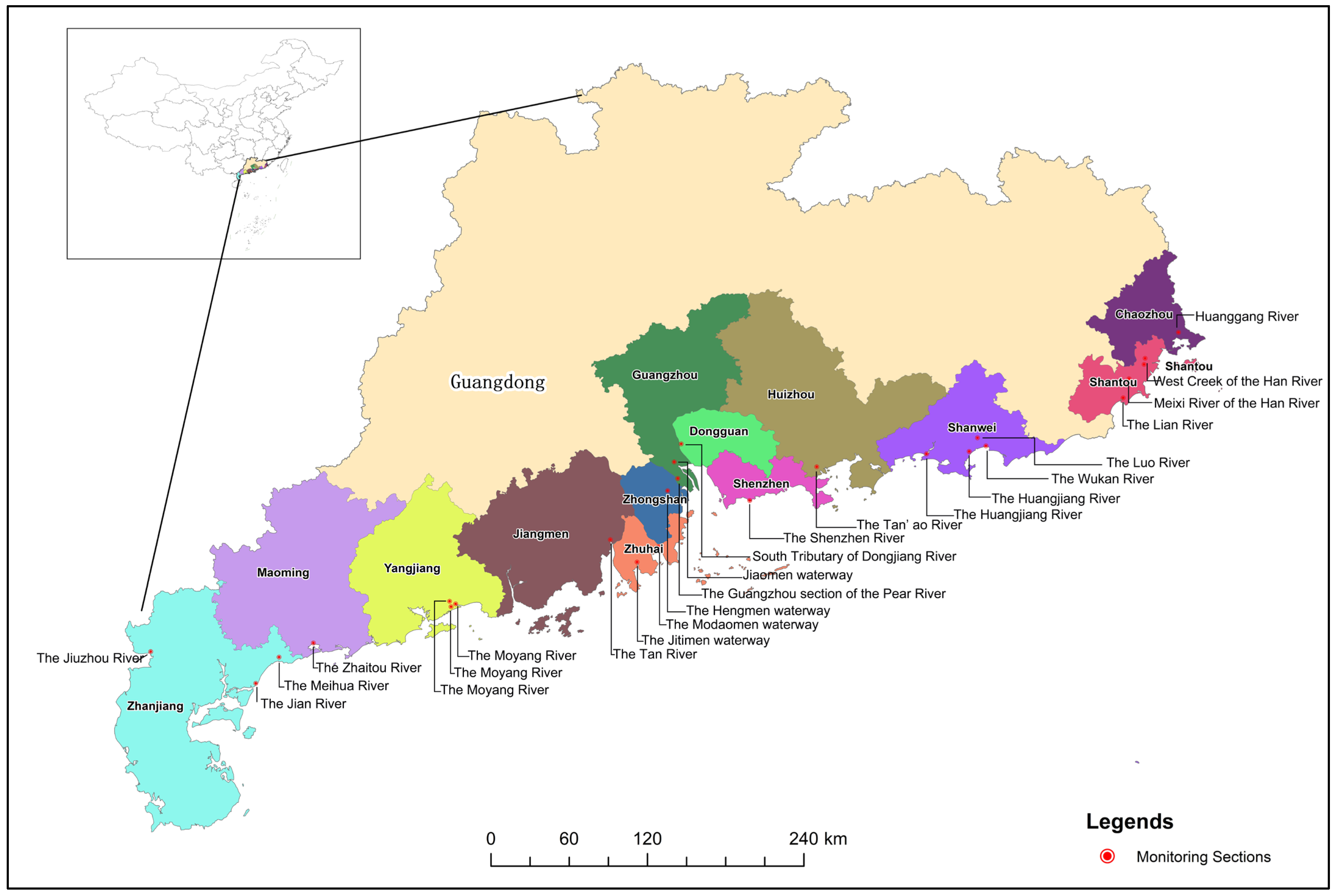
3.2. Data Source and Operationalization
3.2.1. Operationalization of Variables
3.2.2. Descriptive Statistics
4. Empirical Analysis Results
4.1. Basic Regression Results
4.2. Robustness Test
5. Conclusions and Discussion
5.1. Research Findings
5.2. Policy Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sigman, H. Transboundary spillovers and decentralization of environmental policies. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2005, 50, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helland, E.; Whitford, A.B. Pollution Incidence and Political Jurisdiction: Evidence from the TRI. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2003, 46, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Brombal, D.; Farah, P.D.; Moriggi, A.; Critto, A.; Zhou, Y.; Marcomini, A. China’s water environmental management towards institutional integration. A review of current progress and constraints vis-a-vis the European experience. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipscomb, M.; Mobarak, A.M. Decentralization and Pollution Spillovers: Evidence from the Re-drawing of County Borders in Brazil. Rev. Econ. Stud. 2017, 84, 464–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. The historical evolution, functional change and development guarantee of the River Chief System. Environ. Prot. 2017, 16, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.N.; Zeng, D. The dilemma and reflection of water environment governance innovation by river chief system—Based on the perspective of collaborative governance. J. Beijing Coll. Politics Law 2019, 2, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Cai, M.M. Critique of the “River Chief System” based on the perspective of new institutional economics. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2011, 21, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, L. Boundary of river chief: A reflection on the administrative power of watershed pollution control. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2022, 32, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Chen, X.N. Exploring a better policy process theory: A comparative study based on China’s water policy. Public Adm. Policy Rev. 2020, 9, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, M.E.; Li, P.; Zhao, D. Water pollution progress at borders: The role of changes in China’s political promotion incentives. Am. Econ. J. Econ. Policy 2015, 7, 223–242. Available online: https://www.aeaweb.org/articles?id=10.1257/pol.20130367 (accessed on 12 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.R.; Jin, G. Policy effect of environmental governance of local governments in China—Based on the evolution of “River Chief System”. Soc. Sci. China 2018, 5, 92–115+206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shi, X.; Wu, H.Q.; Liu, L.W. Trade-off between economic development and environmental governance in China: An analysis based on the effect of river chief system. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 60, 101403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.H.; Wang, T.T.; Gao, H.G. The transition from the “Administrative Unit” river chief system to the “River Basin Unit” river chief system—A quasi-natural experiment based on the River Chief System policy in the Yellow River Basin. J. Dongbei Univ. Financ. Econ. 2022, 144, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.W.; Wu, J.; Cai, H.Y. Research on the ecological environment governance effect of “River Chief System” in Xiangjiang River Basin. Soft Sci. 2022, 36, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yuan, H. See fewer. Is China’s river chief policy effective? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in the Yangtze River economic belt. China J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.F.; Zhou, J.G. How the River Chief System was formed: Function, deep structure and mechanism conditions. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2020, 30, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.H. Institutional economics analysis of the River Chief System. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2018, 28, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M. The River Chief System: A Case Study of Cross-Departmental Collaboration in Chinese Government River Basin Governance. J. Beijing Adm. Coll. 2015, 3, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.C.; Zhu, Y.C. The Impact of Technological Integration on Public Participation in Water Governance within the Context of the River Chief System: An Empirical Analysis Based on Survey Data from 5 Provinces. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2022, 32, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.N. The Implementation Boundaries of Technology-Embedded Collaborative Governance: A Case Study of “Internet Plus Water Governance” in City S. Discovery 2019, 208, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.K. The Environmental Legal Insights of Wuxi’s ‘River Chief System. Ecological Security and Legal Construction for Environmental Risk Prevention. In Proceedings of the 2011 National Conference on Environmental and Resources Law; Fuzhou University: Fuzhou, China, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 183–186. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Y.Y. The Pros and Cons, Controversies, and Improvements of the River Chief System. China Environ. Manag. 2019, 11, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.H.; Zhou, Y.D.; Deng, Z.J. The effectiveness of “River Chief System” policy: An empirical study based on environmental monitoring samples of China. Water 2021, 13, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B. An Overview of Policy Evaluation Methods. Stat. Manag. 2021, 36, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, H.J. The Current Research Status and Potential Issues of the Domestic Double-Difference Method. Res. Quant. Econ. Tech. Econ. 2015, 32, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L. Breakpoint Regression Design in Social Science Research: Recent Representative Studies and Prospects. Public Manag. Rev. 2021, 3, 140–159. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.Z.; Zhao, H. Can the ‘River Chief System’ Contribute to the Protection of Water Resources? An Empirical Analysis Based on Experience Data from Hubei Province. J. Cent. China Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2020, 54, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angrist, J.D.; Pischke, J.S. Mostly Harmless Econometrics: An Empiricist’s Companion; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2008; Available online: https://press.princeton.edu/books/ebook/9781400829828/mostly-harmless-econometrics#preview (accessed on 12 November 2023).
- Viard, B.; Fu, S. The effect of Beijing’s driving restrictions on pollution and economic activity. MPRA Pap. 2011, 125, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.E.; Doyle, O.; Stancanelli, E. The impact of terrorism on individual well-being: Evidence from the Boston Marathon bombing. Econ. J. 2020, 130, 2065–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Lemieux, T. Regression discontinuity designs in economics. J. Econ. Lit. 2010, 48, 281–355. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/20778728 (accessed on 12 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Chen, J.S.; Quan, Z.Y.; Liu, X.Y. The Seventh Anniversary of the Comprehensive Implementation of the River and Lake Chief System: How Guangdong Can Bite Down the Hard Bones of Water Control? Dong, X.Y., Ed.; Southern Metropolis Daily, 12 November 2023; Volume 147, pp. A08–A11. [Google Scholar]

| Variables | Unit | Sample Size | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | \ | 1131 | 7.309 | 0.425 | 6.00 | 9.00 |
| DO | mg/L | 1131 | 1.736 | 0.485 | −1.427 | 2.965 |
| CODMn | mg/L | 1131 | 1.243 | 0.544 | −0.693 | 2.965 |
| BOD | mg/L | 1129 | 0.778 | 0.783 | −1.609 | 2.879 |
| NH3-N | mg/L | 1130 | 1.025 | 0.688 | −1.022 | 3.726 |
| COD | mg/L | 1130 | 2.549 | 0.606 | 0.000 | 4.205 |
| TN | mg/L | 1122 | 1.024 | 0.688 | −1.021 | 3.726 |
| TP | mg/L | 1131 | −1.989 | 0.927 | −4.605 | 2.033 |
| Population (annual) | Persons/m2 | 1131 | 7.055 | 0.962 | 5.758 | 9.088 |
| Temperature (monthly) | °C | 1131 | 23.867 | 5.003 | 13.000 | 31.200 |
| Rainfall (monthly) | mm | 1131 | 1080.389 | 1204.395 | 0.000 | 5778.134 |
| GDP | CNY billion | 1131 | 6.589 | 0.8 | 5.039 | 9.091 |
| Arable land area (annual) | Hectares | 1131 | 4.507 | 0.919 | 2.869 | 6.139 |
| Urban-construction land area (annual) | Hectares | 1131 | 5.066 | 1.028 | 2.833 | 7.022 |
| Secondary industry outputs (annual) | Billions | 1131 | 3.427 | 0.871 | 1.806 | 5.847 |
| Variables | Sample Mean | Before the RCS | After the RCS | t Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.309 (0.012) | 7.327 (0.018) | 7.297 (0.017) | 0.030 (0.025) |
| DO | 1.736 (0.014) | 1.686 (0.023) | 1.769 (0.018) | −0.084 *** (0.029) |
| CODMn | 1.243 (0.016) | 1.315 (0.027) | 1.194 (0.019) | 0.121 *** (0.032) |
| BOD | 0.778 (0.023) | 1.062 (0.031) | 0.585 (0.030) | 0.477 *** (0.045) |
| NH3-N | −0.823 (0.039) | −0.531 (0.060) | −1.020 (0.050) | 0.049 *** (0.079) |
| COD | 2.549 (0.018) | 2.744 (0.027) | 2.417 (0.022) | 0.327 *** (0.035) |
| TN | 1.024 (0.020) | 0.997 (0.037) | 1.043 (0.023) | −0.045 (0.041) |
| TP | −1.989 (0.028) | −1.759 (0.051) | −2.144 (0.028) | 0.384 *** (0.055) |
| pH | DO | CODMn | BOD | NH3-N | COD | TN | TP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCS’s full implementation | −0.041 (0.051) | 0.060 ** (0.030) | −0.111 * (0.059) | −0.138 ** (0.066) | −0.218 *** (0.045) | −0.162 *** (0.052) | −0.054 (0.064) | −0.153 * (0.080) |
| Population | −0.008 (0.026) | −0.018 (0.027) | −0.024 (0.035) | −0.025 (0.049) | 0.261 *** (0.092) | −0.025 (0.040) | −0.035 (0.031) | −0.119 *** (0.024) |
| Temperature | −0.002 (0.003) | −0.008 *** (0.003) | 0.003 (0.003) | 0.004 (0.005) | −0.024 *** (0.008) | −0.000 (0.004) | −0.014 *** (0.004) | −0.003 (0.003) |
| Rainfall | −0.001 *** (0.000) | −0.000 *** (0.000) | −0.000 * (0.000) | −0.000 * (0.000) | 0.000 * (0.000) | −0.000 (0.000) | 0.000 (0.000) | 0.000 (0.000) |
| GDP | 0.092 *** (0.007) | −0.605 *** (0.092) | 0.505 *** (0.128) | 0.584 *** (0.146) | 1.102 *** (0.262) | 0.013 (0.015) | 0.447 *** (0.088) | 0.403 *** (0.153) |
| Arable land area | −0.114 *** (0.020) | −0.005 (0.134) | 0.234 *** (0.025) | 0.169 *** (0.036) | 0.512 *** (0.065) | 0.246 *** (0.026) | 0.318 *** (0.028) | 0.134 *** (0.023) |
| Urban-construction land area | −0.098 *** (0.027) | −0.013 (0.024) | 0.070 * (0.036) | 0.184 *** (0.042) | 0.194 ** (0.077) | 0.185 *** (0.038) | 0.321 *** (0.028) | 0.167 *** (0.031) |
| Secondary industry outputs | 0.005 (0.064) | 0.249 *** (0.081) | −0.392 *** (0.131) | −0.551 *** (0.141) | −0.999 *** (0.255) | −0.226 ** (0.115) | −0.280 *** (0.083) | −0.390 ** (0.152) |
| Yearly Effects | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Regional Effects | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Constant | 7.887 *** (0.267) | 5.331 *** (0.421) | −2.100 *** (0.439) | −2.570 *** (0.516) | −8.974 *** (0.923) | 0.781 * (0.435) | −3.388 *** (0.341) | −1.434 *** (0.444) |
| Policy effect with polynomial interaction coefficient test (prob > F) | 0.279 | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.009 | 0.005 | 0.213 | 0.002 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.165 | 0.216 | 0.215 | 0.274 | 0.231 | 0.211 | 0.259 | 0.147 |
| Sample size | 780 | 780 | 780 | 780 | 780 | 780 | 780 | 780 |
| Polynomial order | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| pH | DO | CODMn | BOD | NH3-N | COD | TN | TP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before and after 12 Periods (First-Order) | ||||||||
| The RCS’s full implementation | −0.012 (0.058) | 0.022 (0.050) | −0.035 (0.077) | −0.012 (0.015) | −0.011 * (0.006) | −0.014 * (0.007) | −0.007 (0.014) | −0.009 (0.017) |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.359 | 0.335 | 0.354 | 0.389 | 0.327 | 0.329 | 0.395 | 0.278 |
| Climate factors | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Sample size | 312 | 312 | 312 | 312 | 312 | 312 | 312 | 312 |
| Before and after 20 Periods (Second-Order) | ||||||||
| The RCS’s full implementation | −0.035 (0.044) | 0.033 * (0.017) | −0.054 * (0.028) | −0.076 ** (0.038) | −0.125 ** (0.029) | −0.098 ** (0.047) | −0.033 (0.028) | −0.079 * (0.041) |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.205 | 0.275 | 0.263 | 0.311 | 0.278 | 0.278 | 0.308 | 0.197 |
| Climate factors | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Sample size | 520 | 520 | 520 | 520 | 520 | 520 | 520 | 520 |
| Before and after 36 Periods (Excluding Guangzhou and Shenzhen, Third-Order) | ||||||||
| The RCS’s full implementation | −0.040 (0.077) | 0.063 ** (0.032) | −0.129 * (0.068) | −0.142 ** (0.068) | −0.232 *** (0.041) | −0.181 *** (0.054) | −0.057 (0.058) | −0.160 * (0.077) |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.124 | 0.192 | 0.187 | 0.205 | 0.197 | 0.184 | 0.207 | 0.115 |
| Climate factors | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Sample size | 792 | 792 | 792 | 792 | 792 | 792 | 792 | 792 |
| pH | DO | CODMn | BOD | NH3-N | COD | TN | TP | pH | DO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The RCS’s full implementation | −0.192 (0.203) | −0.255 (0.215) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Virtual breakpoint (six periods ahead) | - | - | 0.004 (0.012) | 0.013 (0.042) | −0.012 (0.022) | −0.025 (0.038) | −0.003 (0.003) | −0.009 (0.012) | 0.004 (0.003) | −0.002 (0.012) |
| Socioeconomic variables | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 792 | 792 | 792 | 792 | 792 | 792 | 792 | 792 | - | - |
| Polynomial order | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, K.; Yao, J.; Huang, Y.; Ling, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y. Evaluating the Effectiveness of the “River Chief System”: An Empirical Study Based on the Water Quality Data of Coastal Rivers in Guangdong Province. Water 2024, 16, 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050790
Yang K, Yao J, Huang Y, Ling H, Yang Y, Zhang L, Chen D, Liu Y. Evaluating the Effectiveness of the “River Chief System”: An Empirical Study Based on the Water Quality Data of Coastal Rivers in Guangdong Province. Water. 2024; 16(5):790. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050790
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Kun, Jinrui Yao, Yin Huang, Huiyan Ling, Yu Yang, Lin Zhang, Diyun Chen, and Yuxian Liu. 2024. "Evaluating the Effectiveness of the “River Chief System”: An Empirical Study Based on the Water Quality Data of Coastal Rivers in Guangdong Province" Water 16, no. 5: 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050790
APA StyleYang, K., Yao, J., Huang, Y., Ling, H., Yang, Y., Zhang, L., Chen, D., & Liu, Y. (2024). Evaluating the Effectiveness of the “River Chief System”: An Empirical Study Based on the Water Quality Data of Coastal Rivers in Guangdong Province. Water, 16(5), 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050790







