The Importance of Nonconventional Water Resources under Water Scarcity
Abstract
:1. Prolegomena
2. Nonconventional Water Resources
2.1. Currently Available Nonconventional Water Resources
2.2. Potential Nonconventional Water Resources
2.3. Treated Wastewater
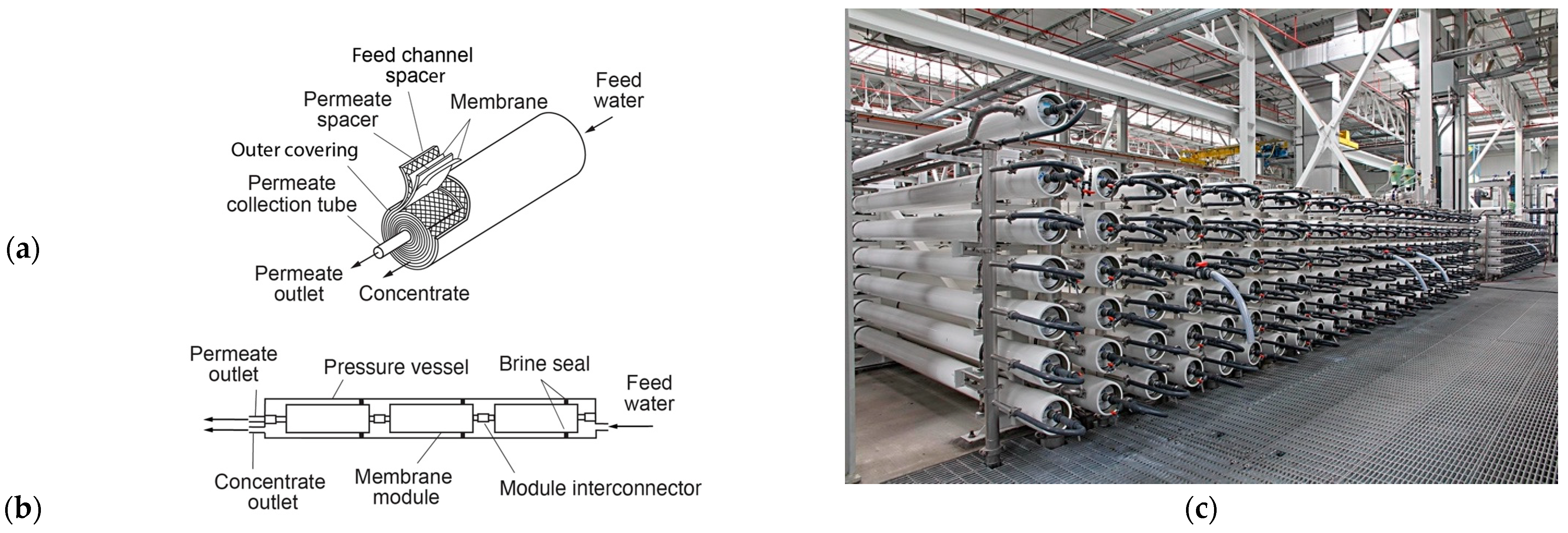
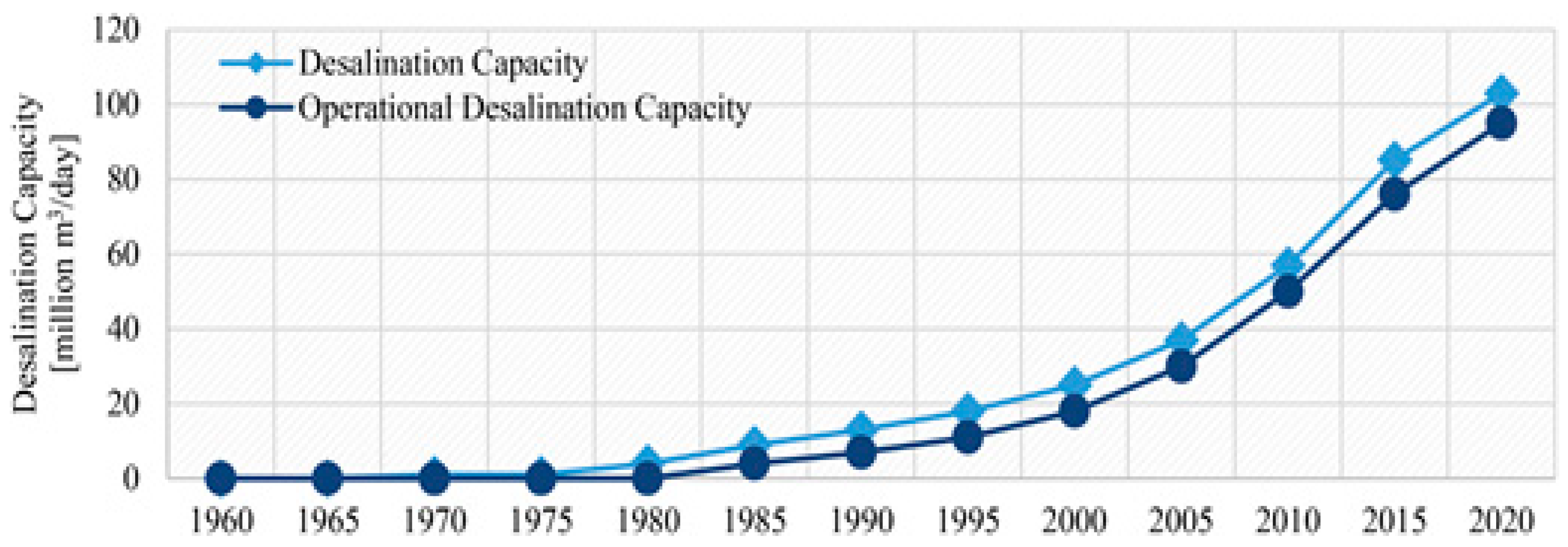
2.4. Sea, Saline, and Brackish Water

2.5. Harvested Rainwater
2.6. Recharged Groundwater
2.7. Agricultural Drainage Water
2.8. Cloud-Seeded Water
2.9. Dew and Fog Water
2.10. Fossil Water
2.11. Iceberg Water
3. Challenges for NWR
4. Epilogue and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tzanakakis, V.A.; Paranychianakis, N.V.; Angelakis, A.N. Water Supply and Water Scarcity. Water 2020, 12, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanakakis, V.A.; Capodaglio, A.G.; Angelakis, A.N. Insights into Global Water Reuse Opportunities. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimidastenaei, Z.; Avellán, T.; Sadegh, M.; Kløve, B.; Haghighi, A.T. Unconventional water resources: Global opportunities and challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarza, L.; Novo, C. What Are Non-Conventionalwater Resources? Smart Water Magazine. 2024. Available online: https://smartwatermagazine.com/q-a/what-are-non-conventional-water-resources (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Boretti, A.; Rosa, L. Reassessing the projections of the world water development report. npj Clean Water 2019, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. AQUASTAT. 2021. Available online: https://www.fao.org/aquastat/en/ (accessed on 28 March 2024).
- Sherif, M.; Liaqat, M.U.; Baig, F.; Al-Rashed, M. Water resources availability, sustainability and challenges in the GCC countries: An overview. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Asano, T.; Bahri, A.; Jimenez, B.E.; Tchobanoglous, G. Water reuse: From ancient to modern times and the future. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.; Angelakis, A.; Angelakis, A. The evolution of sanitation and wastewater management throughout the centuries: Past, present, and future. In Evolution of Sanitation and Wastewater Management through the Centuries; Angelakis, A., Rose, J., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2014; pp. 507–528. [Google Scholar]
- SERL. An Investigation of Sewage Spreading on Five California Soils; Sanitary Engineering Research Laboratory, Technical Bulletin No. 12 I.E.R. Series 37; University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- SERL. Studies in Water Reclamation; Sanitary Engineering Research Laboratory, Department of Engineering, Technical Bulletin No. 13 I.E.R. Series 37; University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, R.V.J.; Harold, B.; Gotaas, H.B.; Bacon, V.W. Economic and Technical Status of Water Reclamation from Sewage and Industrial Wastes. J. AWWA 1952, 44, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodaglio, A.G. Taking the water out of “wastewater”: An ineluctable oxymoron for urban water cycle sustainability. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 2030–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tan, C.; Wang, Y.; Ma, B.; Welacky, T. Soil phosphorus loss in tile drainage water from long-term conventional-and non-tillage soils of Ontario with and without compost addition. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, J. Mixing waters: The reuse of agricultural drainage water in Egypt. Geoforum 2014, 57, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecconet, D.; Bolognesi, S.; Piacentini, L.; Callegari, A.; Capodaglio, A.G. Bioelectrochemical greywater treatment for non-potable reuse and energy recovery. Water 2021, 13, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecconet, D.; Callegari, A.; Hlavínek, P.; Capodaglio, A.G. Membrane bioreactors for sustainable, fit-for-purpose greywater treatment: A critical review. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 745–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Muteen, A.; Mondal, P. Treatment of greywater using waste biomass derived activated carbons and integrated sand column. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UN-Water. United Nations-Water Analytical Brief on Unconventional Water Resources; UN-Water: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Tzanakakis, V.A.; Capodaglio, A.G.; Dercas, N. A Critical Review of Water Reuse: Lessons from Prehistoric Greece for Present and Future Challenges. Water 2023, 15, 2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanaseer, N.; Hindiyeh, M.; Al-Assaf, R. Hydrological and environmental impact of wastewater treatment and reuse on Zarqa River Basin in Jordan. Environments 2020, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainardis, M.; Cecconet, D.; Moretti, A.; Callegari, A.; Goi, D.; Freguia, S.; Capodaglio, A.G. Wastewater fertigation in agriculture: Issues and opportunities for improved water management and circular economy. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 296, 118755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinivella, R.; Bargiggia, R.; Zanoni, G.; Callegari, A.; Capodaglio, A.G. High-Strength, Chemical Industry Wastewater Treatment Feasibility Study for Energy Recovery. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewumi, J.; Ilemobade, A.; Van Zyl, J. Treated wastewater reuse in South Africa: Overview, potential and challenges. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 55, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baawain, M.S.; Al-Mamun, A.; Omidvarborna, H.; Al-Sabti, A.; Choudri, B.S. Public perceptions of reusing treated wastewater for urban and industrial applications: Challenges and opportunities. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 1859–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leviston, Z.; Nancarrow, B.E.; Tucker, D.I.; Porter, N.B. Predicting community behaviour: Indirect potable reuse of wastewater through Managed Aquifer Recharge. Land Water Sci. Rep. 2006, 2906, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Nancarrow, B.E.; Leviston, Z.; Po, M.; Porter, N.B.; Tucker, D.I. What drives communities’ decisions and behaviours in the reuse of wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domènech, L.; Saurí, D. Socio-technical transitions in water scarcity contexts: Public acceptance of greywater reuse technologies in the Metropolitan Area of Barcelona. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 55, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodaglio, A.G. Fit-for-purpose urban wastewater reuse: Analysis of issues and available technologies for sustainable multiple barrier approaches. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 1619–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC—European Council. Directive Concerning Urban Wastewater Treatment (91/271/EEC: UWWTD); European Council: Brussels, Belgium, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- EU. EU Regulation 2020/741 of the European Parliament and of the council of 25 May 2020 on minimum requirements for water reuse. Off. J. Eur. Union 2020, L 177/32, 32–55. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, A.; Durham, B. Water recycling and reuse in EUREAU countries: Trends and challenges. Desalination 2008, 218, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. Water Reuse Symposium. Water Reuse Review. 2023. Available online: https://watereuse.org/civicrm/mailing/view/?id=3377 (accessed on 31 January 2024).
- Hunter, A.; Sundaram, V.; Hunter, A. Advanced Level, Microconstituents and Contaminants of Emerging Concern (Non-PFAS), PFAS, Research and Innovation, Water Reuse and Reclamation. In Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation; Water Environment Federation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quench. What Are Total Dissolved Solids and Are They Safe to Drink? Quench Water Experts. 2022. Available online: https://quenchwater.com/blog/total-dissolved-solids/ (accessed on 31 January 2024).
- Eltawil, M.A.; Zhengming, Z.; Yuan, L. A review of renewable energy technologies integrated with desalination systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 2245–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmoez, W.; Mahmoud, M.S.; Farrag, T.E. Water desalination using humidification/dehumidification (HDH) technique powered by solar energy: A detailed review. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 52, 4622–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistocchi, A.; Bleninger, T.; Breyer, C.; Caldera, U.; Dorati, C.; Ganora, D.; Millán, M.; Paton, C.; Poullis, D.; Herrero, F.S. Can seawater desalination be a win-win fix to our water cycle? Water Res. 2020, 182, 115906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Valipour, M.; Choo, K.-H.; Ahmed, A.T.; Baba, A.; Kumar, R.; Toor, G.S.; Wang, Z. Desalination: From ancient to present and future. Water 2021, 13, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Taroudakis, M.; Tchobanoglous, G. Thalassocracy in the Bronze Age and Its Relationship to Sustainability. Ann. Archaeol. 2024, 6, 2639–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, E.D. Fundamentals of Water Desalination; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Asano, T.; Burton, F.L.; Leverenz, H.; Tsuchihashi, R.; Tchobanoglous, G. Water Reuse: Issues, Technologies, and Applications; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zolghadr-Asli, B.; McIntyre, N.; Djordjević, S.; Farmani, R.; Pagliero, L. A closer look at the history of the desalination industry: The evolution of the practice of desalination through the course of time. Water Supply 2023, 23, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haut, B.; Zheng, X.-Y.; Mays, L.; Han, M.; Passchier, C.; Angelakis, A.N. Chapter 3: Evolution of rainwater harvesting and heritage in urban areas through the millennia: A sustainable technology for increasing water availability. In Water and Heritage: Material, Conceptual, and Spiritual Connections; Willems, W.J.H., van Schaik, H.P.J., Eds.; Sidestone Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 37–56. [Google Scholar]
- Mucheru-Muna, M.; Waswa, F.; Mairura, F. Socio-economic factors influencing utilisation of rain water harvesting and saving technologies in Tharaka South, Eastern Kenya. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 194, 150–159. [Google Scholar]
- Toosi, A.S.; Tousi, E.G.; Ghassemi, S.A.; Cheshomi, A.; Alaghmand, S. A multi-criteria decision analysis approach towards efficient rainwater harvesting. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannopoulos, S.; Antoniou, G.; Kaiafa-Saropoulou, M.; Angelakis, A. Historical development of rainwater harvesting and use in Hellas: A preliminary review. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2017, 17, 1022–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mays, L.; Antoniou, G.P.; Angelakis, A.N. History of Water Cisterns: Legacies and Lessons. Water 2013, 5, 1916–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoyiannis, D.; Patrikiou, A.; Ostigard, T. Water control in Ancient Greek cities. Water Urban. 2013, 130–148. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, A. Evolution of rainwater harvesting and use in Crete, Hellas, through the millennia. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2016, 16, 1624–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, A.; Voudouris, K.; Tchobanoglous, G. Evolution of water supplies in the Hellenic world focusing on water treatment and modern parallels. Water Supply 2020, 20, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oweis, T.; Hachum, A.; Bruggeman, A. The Role of Indigenous Knowledge in Improving Present Water-Harvesting Practices. In Indigenous Water Harvesting Systems in West Asia and North Africa; Oweis, T., Hachum, A., Bruggeman, A., Eds.; ICARDA: Aleppo, Syria, 2004; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mays, L.W. A brief history of water filtration/sedimentation. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2013, 13, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Dercas, N.; Tzanakakis, V.A. Water Quality Focusing on the Hellenic World: From Ancient to Modern Times and the Future. Water 2022, 14, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.Y.; Angelakis, A. Chinese and Greek ancient urban hydro-technologies: Similarities and differences. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2018, 18, 2208–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handia, L.; Tembo, J.M.; Mwiindwa, C. Potential of rainwater harvesting in urban Zambia. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2003, 28, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glendenning, C.; Van Ogtrop, F.; Mishra, A.; Vervoort, R. Balancing watershed and local scale impacts of rain water harvesting in India—A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 107, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehri, M.; Malekinezhad, H.; Ilderomi, A.R.; Talebi, A.; Hosseini, S.Z. Studying the effect of rain water harvesting from roof surfaces on runoff and household consumption reduction. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 43, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.F.; Jahan, C.S.; Mazumder, Q.H. Rainwater harvesting: Practiced potential for integrated water resource management in drought-prone Barind tract, Bangladesh. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 9, 100267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngigi, S.N. What is the limit of up-scaling rainwater harvesting in a river basin? Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2003, 28, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmreich, B.; Horn, H. Opportunities in rainwater harvesting. Desalination 2009, 248, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Capodaglio, A.G.; Valipour, M.; Krasilnikoff, J.; Ahmed, A.T.; Mandi, L.; Tzanakakis, V.A.; Baba, A.; Kumar, R.; Zheng, X. Evolution of Floods: From Ancient Times to the Present Times (ca 7600 BC to the Present) and the Future. Land 2023, 12, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosmin, N.; Jauhari, A.S.; Mustaamal, A.H.; Husin, F.; Hassan, M.Y. Experimental study for the single-stage and double-stage two-bladed Savonius micro-sized turbine for rain water harvesting (RWH) system. Energy Procedia 2015, 68, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgert, L.; Austin, P.; Picchione, K. Improving water security through rainwater harvesting: A case from Guatemala and the potential for expanding coverage. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2016, 32, 765–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, L.; Olofsson, B.; Saurí, D.; Palau-Rof, L. A breakthrough in urban rain-harvesting schemes through planning for urban greening: Case studies from Stockholm and Barcelona. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 51, 126678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurí, D.; Palau-Rof, L. Urban drainage in Barcelona: From hazard to resource? Water Altern. 2017, 10, 475–492. [Google Scholar]
- Yannopoulos, S.; Giannopoulou, I.; Kaiafa-Saropoulou, M. Investigation of the current situation and prospects for the development of rainwater harvesting as a tool to confront water scarcity worldwide. Water 2019, 11, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, I.A.; Christie, A.; Gilpin, A.-M. Water Quality of Roof-Harvested Drinking Water Tanks in a Rural Area near a Gold and Copper Mine: Potential Health Risk from a Layer of Metal-Enriched Water and Sediment. Water 2024, 16, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Liu, Y.; Gao, L. Stormwater treatment for reuse: Current practice and future development–A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, D.K. Annotated Bibliography on Artificial Recharge of Ground Water through 1954; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1959.
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Kanyerere, T. A review of the managed aquifer recharge: Historical development, current situation and perspectives. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2020, 118, 102887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwer, H. Artificial recharge of groundwater: Hydrogeology and engineering. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinzer, O.E. General principles of artificial ground-water recharge. Econ. Geol. 1946, 41, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, A.R.; Singh, S. Rainfall Assessment and Water Harvesting Potential in an Urban area for artificial groundwater recharge with land use and land cover approach. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 5215–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, I.; Dissanayake, D.; Mayadunna, B.; Weerasekera, W. An approach to delineate groundwater recharge potential sites in Ambalantota, Sri Lanka using GIS techniques. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Eliassen, R. The indirect cycle of water reuse. Water Wastes Eng. 1969, 6, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zaresefat, M.; Derakhshani, R.; Nikpeyman, V.; GhasemiNejad, A.; Raoof, A. Using artificial intelligence to identify suitable artificial groundwater recharge areas for the Iranshahr basin. Water 2023, 15, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekar, P.R.; Mathew, A. Assessing groundwater potential zones and artificial recharge sites in the monsoon-fed Murredu river basin, India: An integrated approach using GIS, AHP, and Fuzzy-AHP. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 23, 100994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lena, F.; Berardi, M.; Masciale, R.; Portoghese, I. Network dynamics for modelling artificial groundwater recharge by a cluster of infiltration basins. Hydrol. Process. 2023, 37, e14876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.-R.; Kim, G.-B. Optimum interval of artificial groundwater recharge wells, considering injection rate and economic feasibility. Geosci. J. 2023, 27, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Laghari, Y.; Wei, Y.-C.; Wu, L.; He, A.-L.; Liu, G.-Y.; Yang, H.-H.; Guo, Z.-Y.; Leghari, S.J. Groundwater Depletion and Degradation in the North China Plain: Challenges and Mitigation Options. Water 2024, 16, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstensen, M.V.; Hashemi, F.; Hoffmann, C.C.; Zak, D.; Audet, J.; Kronvang, B. Efficiency of mitigation measures targeting nutrient losses from agricultural drainage systems: A review. Ambio 2020, 49, 1820–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlotman, W.; Smedema, L.; Rycroft, D. Modern Land Drainage: Planning, Design and Management of Agricultural Drainage Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, R.S.; Abuarab, M.E.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Baioumy, M.; Mokhtar, A. Assessment of environmental and toxicity impacts and potential health hazards of heavy metals pollution of agricultural drainage adjacent to industrial zones in Egypt. Chemosphere 2023, 318, 137872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayaalp, N. Anoxic Treatment of Agricultural Drainage Water in a Venturi-Integrated Membrane Bioreactor. Membranes 2023, 13, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnashar, W.; Abd-Elhamid, H.F.; Zeleňáková, M.; Elyamany, A. Value Engineering Approach to Evaluate the Agricultural Drainage Water Management Strategies. Water 2023, 15, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduljaleel, Y.; Awad, A.; Al-Ansari, N.; Salem, A.; Negm, A.; Gabr, M.E. Assessment of Subsurface Drainage Strategies Using DRAINMOD Model for Sustainable Agriculture: A Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Bano, H.; Rather, R.A.; Ahmad, S. Cloud seeding; its prospects and concerns in the modern world—A review. Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 2018, 6, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadargi, J.D.; Dateer, R.B.; Kalubarme, R.S.; Truong, N.T.N.; Pawar, S.H. A Novel Approach of Developing AgI Loaded Silica Aerogels for Possible Application as Cloud Seeding Material. Silicon 2023, 15, 5547–5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Yaghoubi, S. Optimization models for cloud seeding network design and operations. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2024, 312, 1146–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freud, E.; Koussevitzky, H.; Goren, T.; Rosenfeld, D. Cloud microphysical background for the Israel-4 cloud seeding experiment. Atmos. Res. 2015, 158, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nioras, D.; Ellinas, K.; Constantoudis, V.; Gogolides, E. How different are fog collection and dew water harvesting on surfaces with different wetting behaviors? ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 48322–48332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beysens, D. The formation of dew. Atmos. Res. 1995, 39, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO. International Meteorological Vocabulary, 2nd ed.; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, M.M.; Kara-Ali, A.; Assad, M. Potential of harvesting water from fog and dew water over semi-arid and arid regions in Syria. Water Supply 2022, 22, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beysens, D. Dew Water; River Publishers: Aalborg, Denmark, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kaseke, K.F.; Wang, L. Fog and dew as potable water resources: Maximizing harvesting potential and water quality concerns. GeoHealth 2018, 2, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beysens, D. Dew nucleation and growth. Comptes Rendus Phys. 2006, 7, 1082–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gindel, I. Irrigation of plants with atmospheric water within the desert. Nature 1965, 207, 1173–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberger, Y.; Loboda, I.; Garner, W. The influence of autumn dewfall on spatial and temporal distribution of nematodes in the desert ecosystem. J. Arid Environ. 1989, 16, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharan, G. Dew Harvest: To Supplement Drinking Water Sources in Arid Coastal Belt of Kutch; Foundation Books; Centre for Environment Education: Ahmedabad, India, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Clus, O.; Ortega, P.; Muselli, M.; Milimouk, I.; Beysens, D. Study of dew water collection in humid tropical islands. J. Hydrol. 2008, 361, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gido, B.; Friedler, E.; Broday, D.M. Assessment of atmospheric moisture harvesting by direct cooling. Atmos. Res. 2016, 182, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, J. Fog harvesting: An alternative source of water supply on the West Coast of South Africa. GeoJournal 2004, 61, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, M.; Heng, X.; Oza, M.; Luo, C. Enhancement of fog-collection efficiency of a Raschel mesh using surface coatings and local geometric changes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 508, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürsoy, M.; Harris, M.; Carletto, A.; Yaprak, A.; Karaman, M.; Badyal, J. Bioinspired asymmetric-anisotropic (directional) fog harvesting based on the arid climate plant Eremopyrum orientale. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 529, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margat, J.; Foster, S.; Droubi, A. Concept and importance of non-renewable resources. Non-Renew. Groundw. Resour. A Guideb. Soc.-Sustain. Manag. Water-Policy Mak. 2006, 10, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- USGS. Mineral Commodity Summaries 2022. 2022. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs2022/mcs2022.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Mazzoni, A.; Heggy, E.; Scabbia, G. Forecasting water budget deficits and groundwater depletion in the main fossil aquifer systems in North Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2018, 53, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eik, K.; Marchenko, A. Model tests of iceberg towing. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Siriwardana, N. Water transportation via icebergs towing. In Unconventional Water Resources; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 199–212. [Google Scholar]
- Karimidastenaei, Z.; Klöve, B.; Sadegh, M.; Haghighi, A.T. Polar Ice as an Unconventional Water Resource: Opportunities and Challenges. Water 2021, 13, 3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.I.; Muscolo, A.; Farooq, M.; Ahmad, W. Sustainable use and management of non-conventional water resources for rehabilitation of marginal lands in arid and semiarid environments. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 221, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdandoost, F.; Noruzi, M.M.; Yazdani, S.A. Sustainability assessment approaches based on water-energy Nexus: Fictions and nonfictions about non-conventional water resources. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.I.; Hussain, M.I.; Zafar, A.; Ahmad, K.; Ashraf, M.A.; Ahmed, M.; ALrashidi, A.A.; ALHaithloul, H.A.S.; Alghanem, S.M.; Khan, M.I. Ecological risk assessment and bioaccumulation of trace element, copper, in wheat varieties irrigated with non-conventional water resources in a semi-arid tropics. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 269, 107711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanakakis, V.A.; Angelakis, A.N. Climate, Water, Soil. Water 2023, 15, 4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Water Resource | Important Nonconventional Applications |
|---|---|
| Currently available nonconventional water resources | |
| Treated wastewater | Agricultural and landscape irrigation, toilet flushing, industrial applications, drinking water, high-purity industrial uses, hydroponics, etc. |
| Sea, saline, and brackish water | Drinking water; industrial applications; irrigation. |
| Harvested rainwater | Drinking water with or without treatment; landscape irrigation. |
| Recharged groundwater | Drinking water with or without treatment; agricultural use; industrial applications with treatment. |
| Potentially available nonconventional water resources | |
| Agricultural drainage water Cloud-seeded water | Secondary irrigation. If captured drinking water with treatment; irrigation. |
| Dew and Fog water | Drinking water; landscape irrigation. |
| Fossil water | Irrigation; drinking water with treatment. |
| Iceberg towed water | Drinking water; irrigation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angelakis, A.N.; Tchobanoglous, G.; Capodaglio, A.G.; Tzanakakis, V.A. The Importance of Nonconventional Water Resources under Water Scarcity. Water 2024, 16, 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16071015
Angelakis AN, Tchobanoglous G, Capodaglio AG, Tzanakakis VA. The Importance of Nonconventional Water Resources under Water Scarcity. Water. 2024; 16(7):1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16071015
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngelakis, Andreas N., George Tchobanoglous, Andrea G. Capodaglio, and Vasileios A. Tzanakakis. 2024. "The Importance of Nonconventional Water Resources under Water Scarcity" Water 16, no. 7: 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16071015
APA StyleAngelakis, A. N., Tchobanoglous, G., Capodaglio, A. G., & Tzanakakis, V. A. (2024). The Importance of Nonconventional Water Resources under Water Scarcity. Water, 16(7), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16071015









