Water Quality of Lake Erhai in Southwest China and Its Projected Status in the near Future
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Model
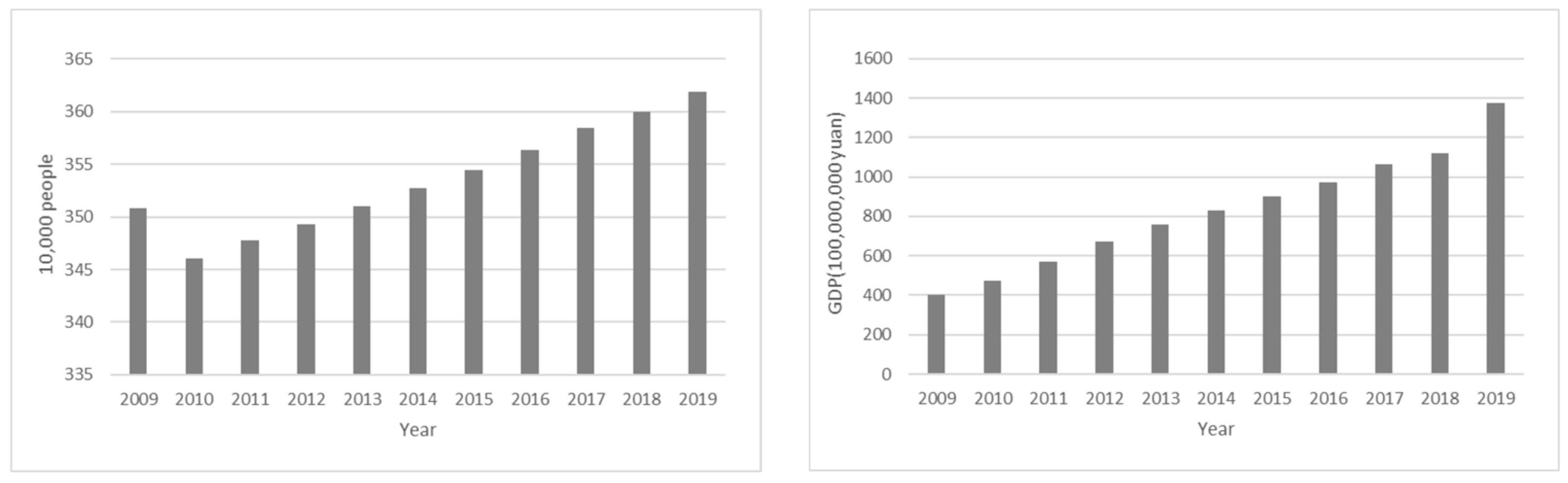
2.1. Study Area and Data Sources
2.2. Methods and Models
2.3. Parameter Calibration and Model Verification
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Annual Water Quality Changes
3.2. Monthly Water Quality Changes
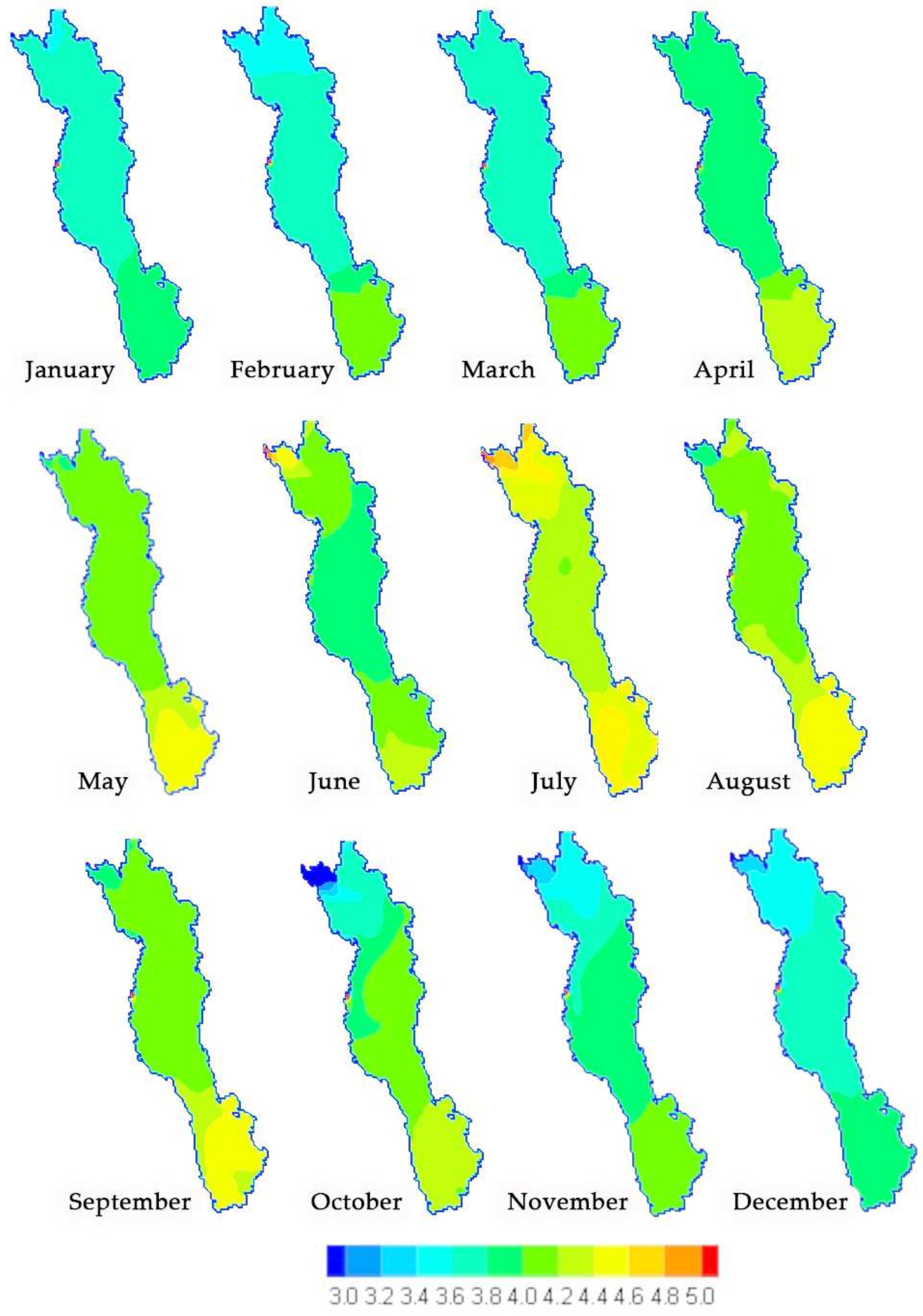
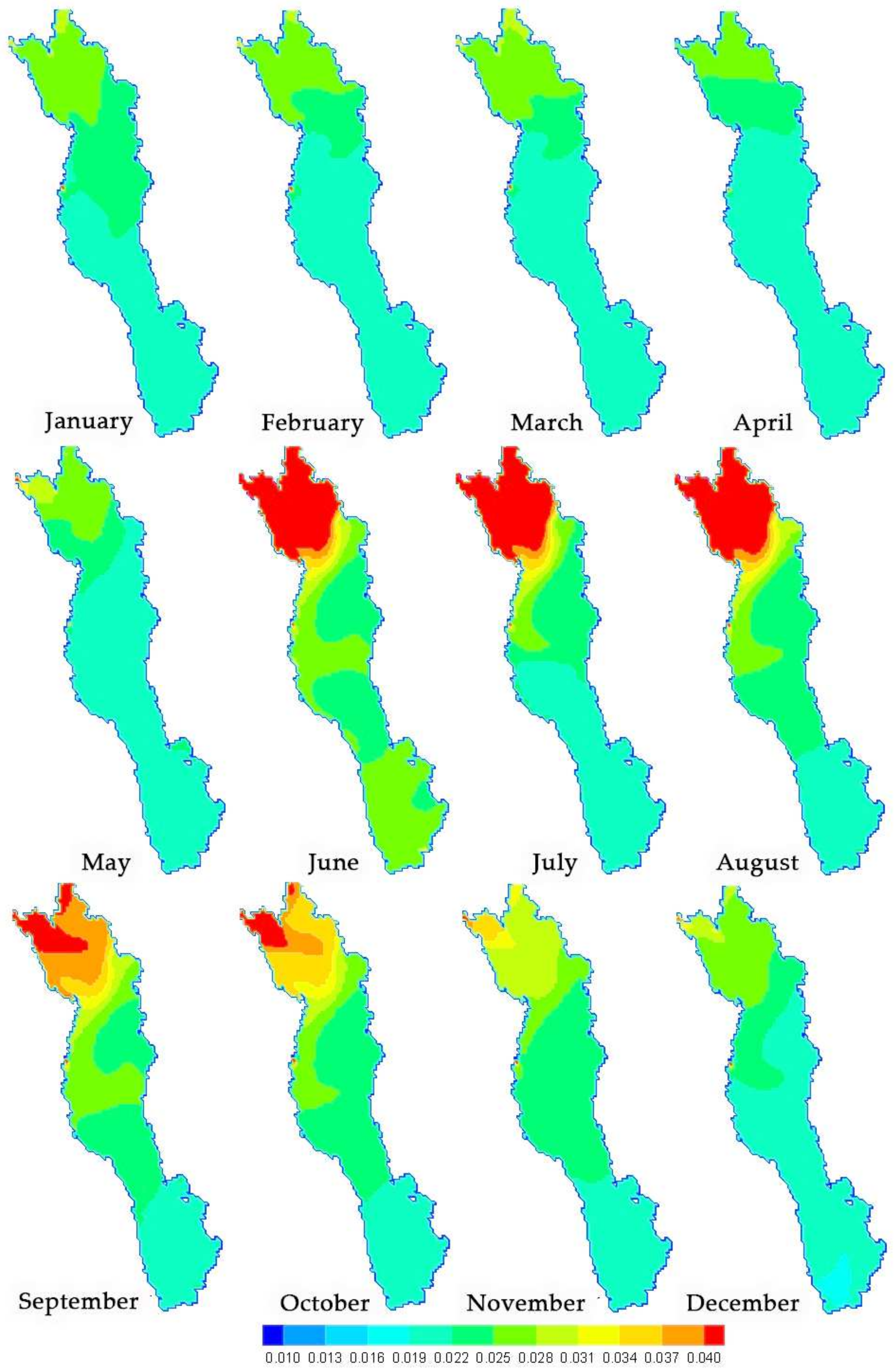
3.3. Spatial Variation of Water Quality
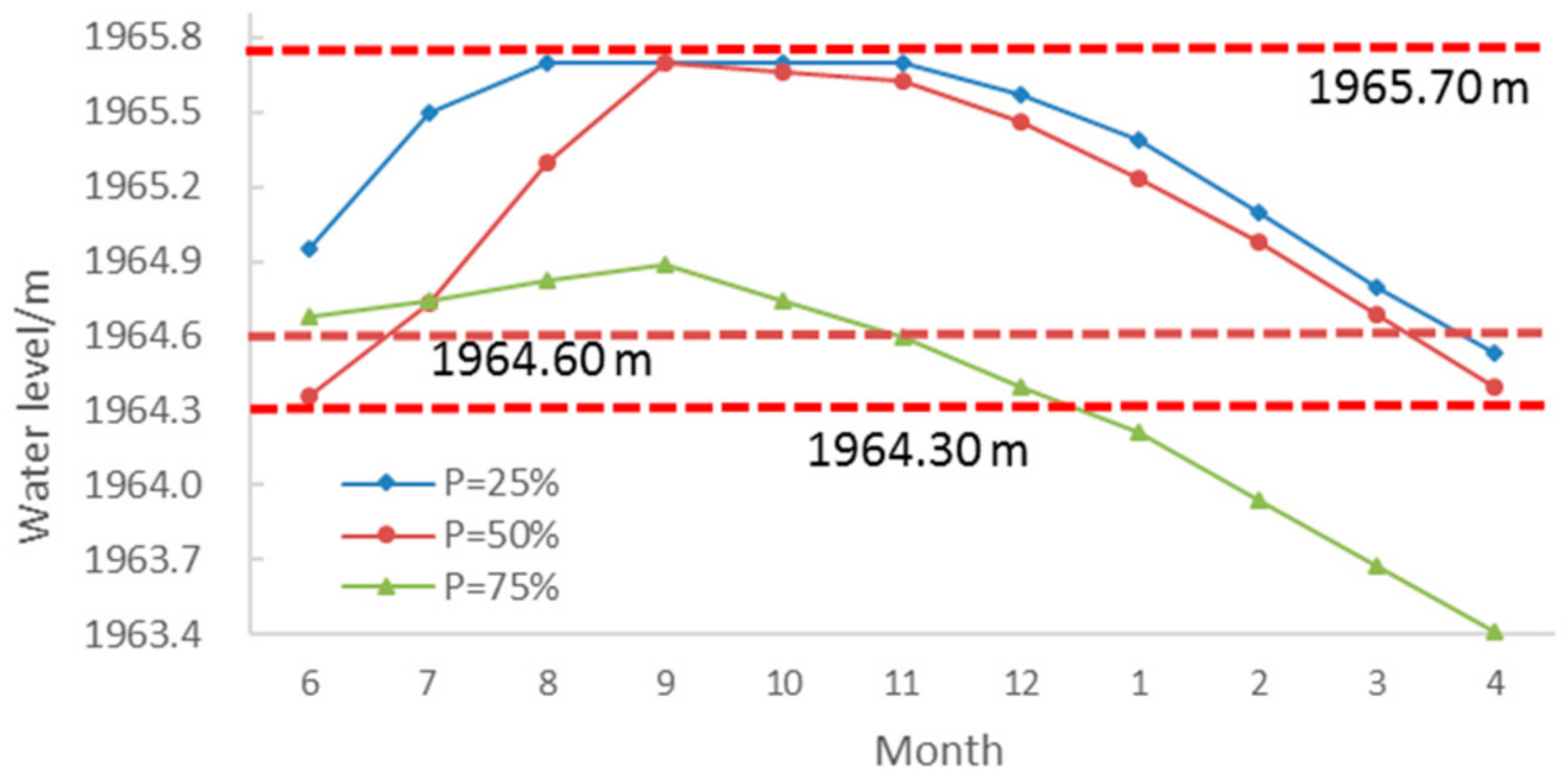
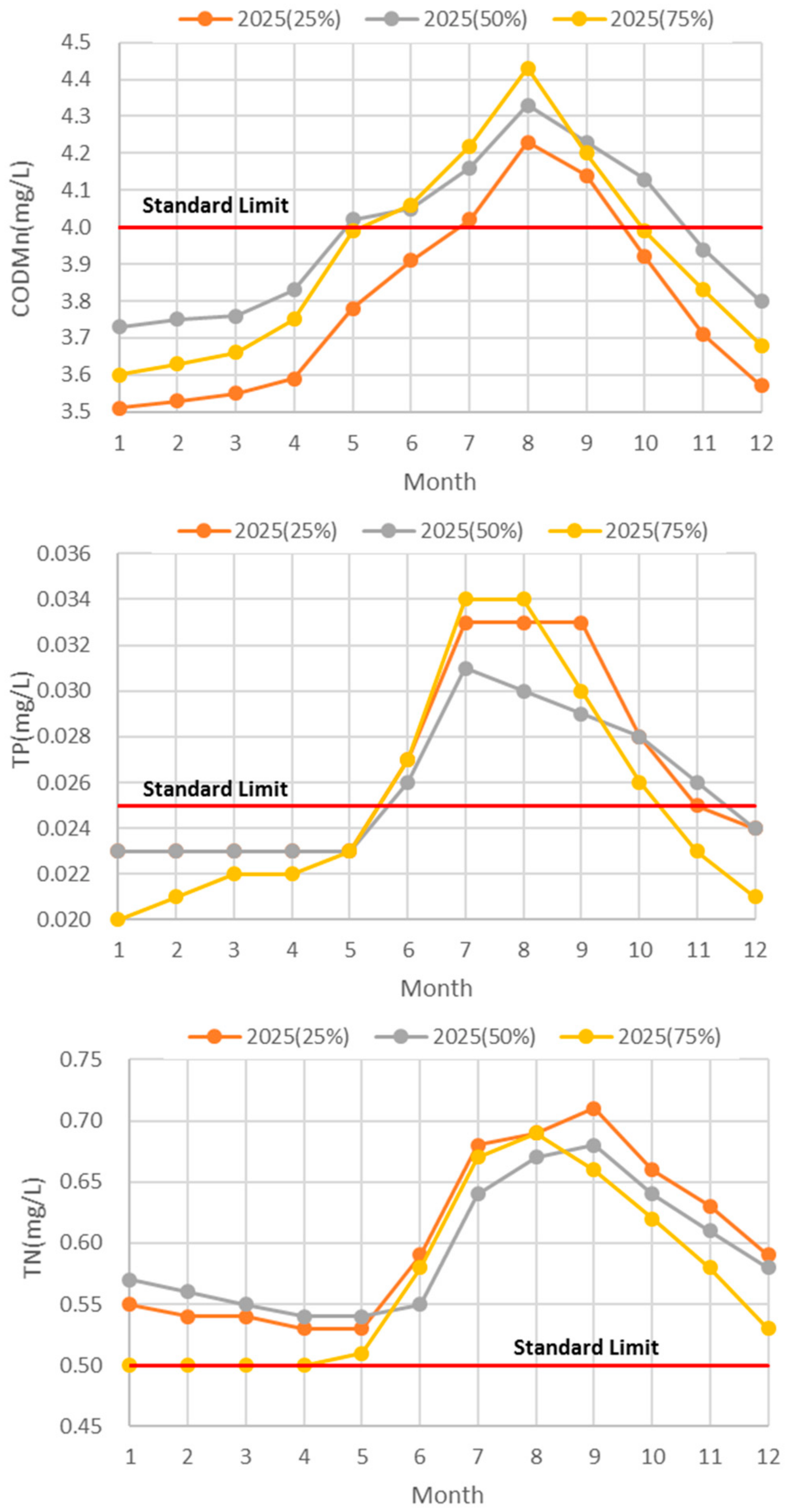
3.4. Water Quality Prediction of Lake Erhai
4. Conclusions
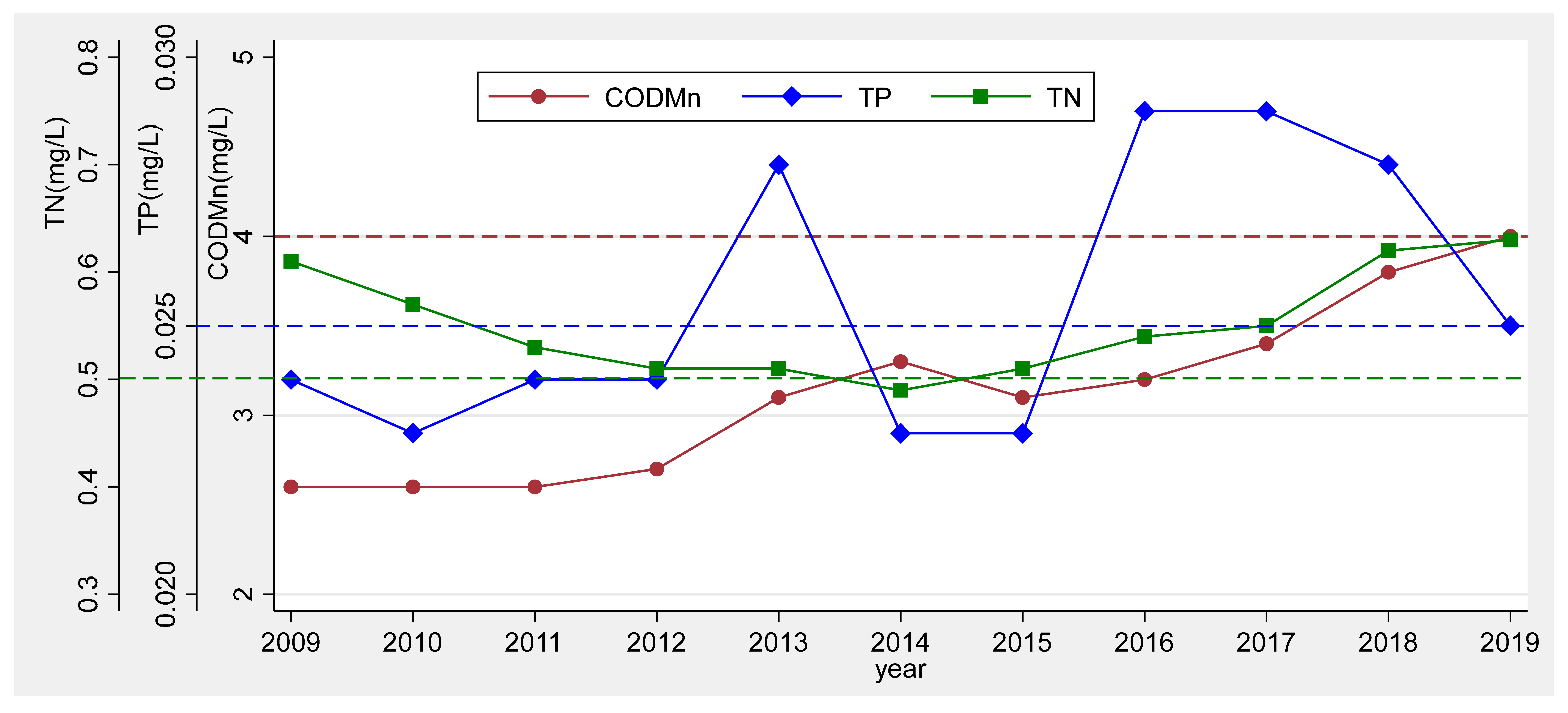
- According to the average annual concentrations of CODMn, TP, and TN in Lake Erhai, the concentration of TP decreased after 2016, but the concentrations of CODMn and TN showed an increasing trend. This was mainly because the protection measures implemented for Lake Erhai prevented TP from entering the lake. However, the pollution control measures did not have a noticeable effect on reducing CODMn and TN concentrations due to the complex relationship between carbon and nitrogen inputs and water quality in Lake Erhai.
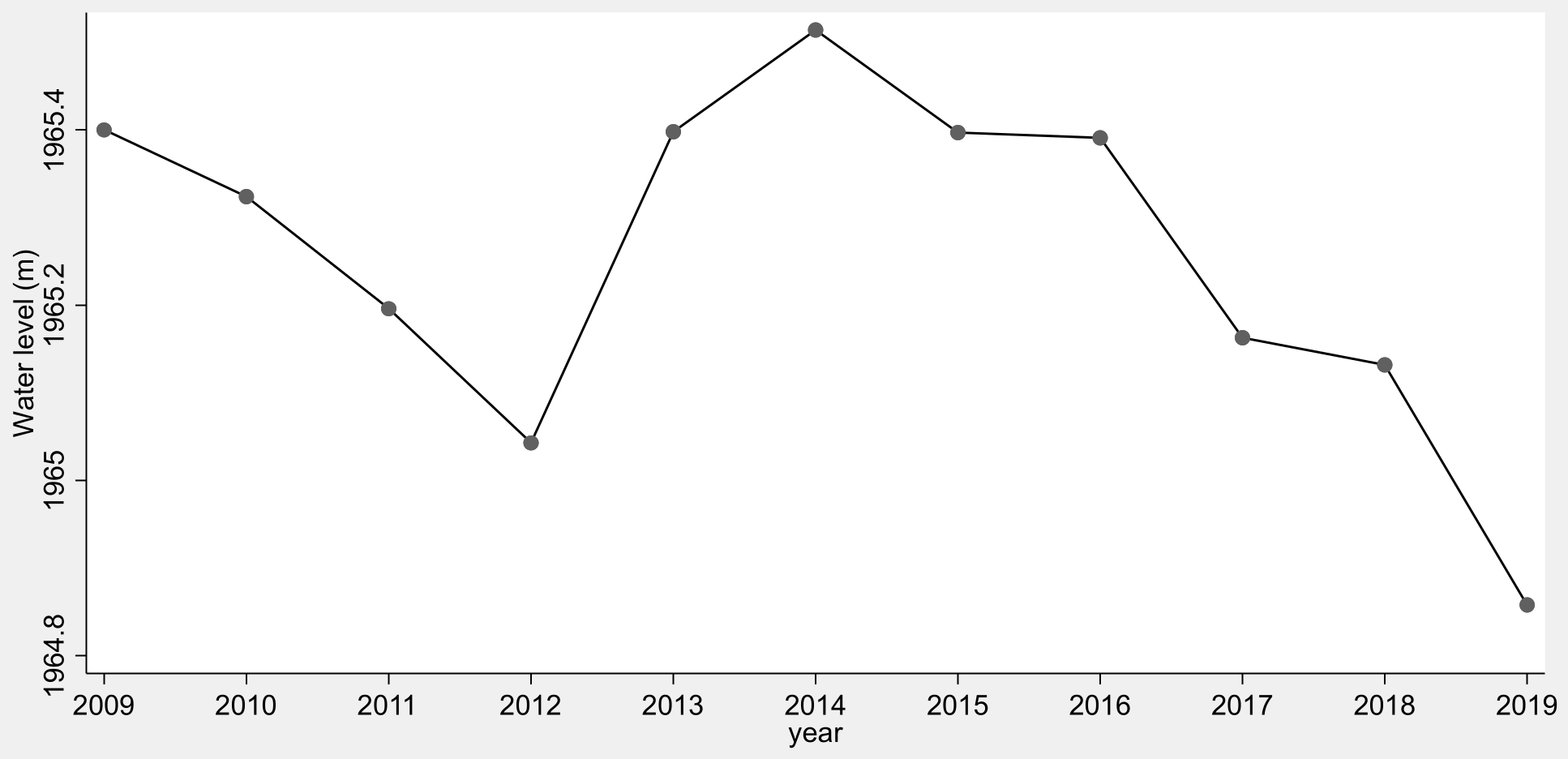
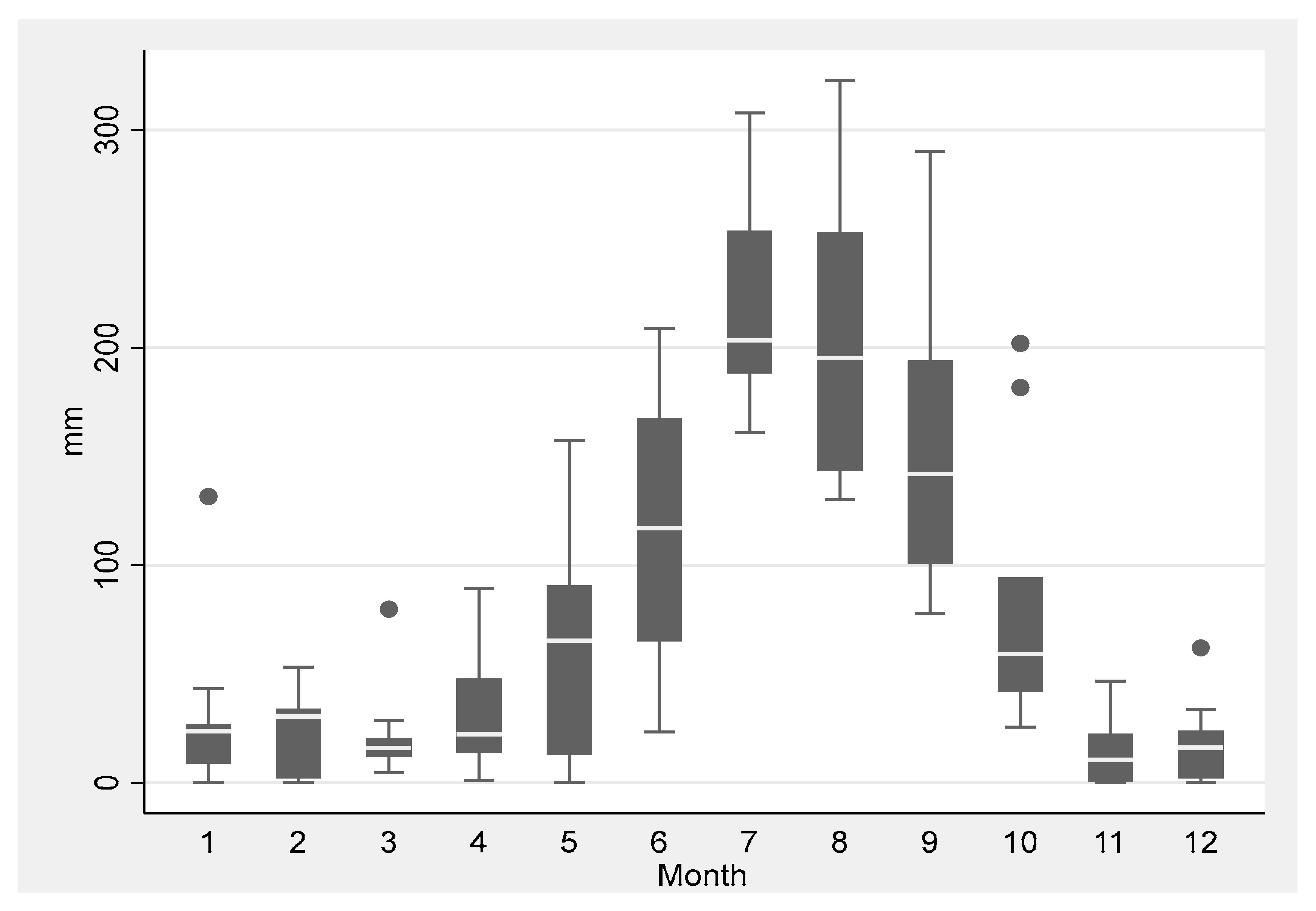
- The water quality of Lake Erhai was better in winter and spring than in summer and autumn, and the southern lake water quality was better than the northern lake water quality. In summer and autumn, pollutants enter Lake Erhai with rainfall, which is the main reason why the water quality of Lake Erhai is better in winter and spring than in summer and autumn. The water quality of the southern lake is better than that of the northern lake because there are more agricultural enterprises and larger agricultural non-point sources adjacent to the northern lake. These findings indicate that non-point source pollution is still the main source of pollution in Lake Erhai, and rainfall is the main driving force of pollution exceeding the water quality standard.
- Based on the prediction results, this study concluded that the water quality of Lake Erhai could not be fundamentally improved through the measures of the “seven actions” and “eight key battles” for comprehensive water pollution control in the Erhai basin. By 2025, the water quality of Lake Erhai will still fail to meet the Class II water quality standard due to the large quantity of non-point source pollutants entering the lake and the decrease in natural water resources in the basin. Finally, two recommendations were made, including supplementary non-point source pollution control measures and the diversion of water from external basins, which will promote the continuous improvement of water quality in Lake Erhai.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, J.; Jones, R.T.; Yang, X.; John, A. The Holocene vegetation history of Lake Erhai, Yunnan province southwestern China: The role of climate and human forcings. Holocene 2006, 16, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisma, D.; Sun, S.; Song, X.; Thomasse, E. Sedimentation in Erhai lake, Yunnan province, China. J. Lake Sci. 2000, 12, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Yuan, G.; Cao, T.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, L.; Zhang, M.; Ni, L.; Wang, S. Succession of submerged macrophyte communities in relation to environmental change in Lake Erhai over the past 50 years. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Peng, W.; Li, H.; Mao, Z. Evolution of eutrophication in the Erhai Lake and its relevantresearch progress. J. China Inst. Water Resour. Hydropower Res. 2005, 3, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qian, X.; Li, X.; Wei, Z.; Hu, S. Long-term trend of eutrophication state of Lake Erhai in 1988-2013 and analyses of its socio-economic drivers. J. Lake Sci. 2018, 30, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ceng, H. Analysis of environment status of Erhai basin. Yunnan Geogr. Enviroment Res. 2002, 14, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H. Discussion of Water Environmental Changes in Erhai Lake. Environ. Sci. Surv. 2018, 37, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, H.; Li, L. Study on Temporal and Spatial Variation of Phosphorus Load in Erhai inflow riversand Eutrophication in Erhai Lake in 2015. Pearl River 2017, 38, 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z. Carrying out lake protection and promoting ecological civilization Construction—Taking Erhai Lake as an example. Creation 2022, 30, 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q. Study on pretection and management mode of Plateau Lake-A case study of Erhai Lake. Yunnan Water Power 2022, 38, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W. Eutrophication and Recovery in Experimental Lakes: Implications for Lake Management. Science 1974, 184, 897–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W. The dilemma of controlling cultural eutrophication of lakes. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 4322–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechmann, M.E.; Berge, D.; Eggestad, H.O.; Vandsemb, S.M. Phosphorus transfer from agricultural areas and its impact on the eutrophication of lakes—Two long-term integrated studies from Norway. J. Hydrol. 2005, 304, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R. Effect of water level on environment of Erhai Lake. In Collected Works Scientific on Erhai Lake in Yunnan; The Nationalities Publishing House of Yunnan: Kunming, China, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. Analysis of temporal and spatial changes of total nitrogen of Erhai Lake from 1985 to 2019. Environ. Sci. Surv. 2020, 39, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Su, J.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, R.; Wu, J. Study on the evolution characteristics of water quality and its key impact factors of Erhai Lake. J. China Inst. Water Resour. Hydropower Res. 2022, 20, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, L. Water quality evaluation and source analysis of pollutants of the Erhai Lake. Water Resour. Power 2021, 39, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Yu, B.; Zhou, R.; Wang, Y. Correlating analysis of water environment pollution and water envi-roment change in Erhai River Basin. J. Cent. China Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2020, 54, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, G.; Guo, Z.; Ye, P. Climate impacts and Its effects on water quality of Erhai Lake during the period of 1989–2019 in Dali area, Yunnan. Geoscience 2022, 36, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; An, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, H. Changes in Water Environment in Erhai Lake and Its Influencing Factors. Water 2021, 13, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M. Water quality characteristics and pollution load estimation of main rivers around Erhai Lake. Yangtze River 2022, 53, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Gao, S.; Ye, B.; Chu, Z.; Hou, Z.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, B. Nitrogen and phosphorus pollution characteristics of surface runoff and the impacts of land use on runoff water quality in rainy season in the western Erhai Lake basin. Res. Enviromental Sci. 2018, 31, 1891–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Xiang, S.; Chu, Z.; Xue, L.; Ye, B. Relationship between agricultural land and water quality of inflow river in Erhai Lake basin. Enviromental Sci. 2015, 36, 4005–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wu, Y.; Hou, Z.; Chu, Z.; Rao, J. Water quality characteristics of irrigation and drainage ditches in western Erhai Lake basin and the effect of land uses. J. Enviromental Eng. Technol. 2022, 12, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Research on Environmental Impact of the Dianzhong Water Di-version Project Using Erhai Lake as a Regulation and Storage Reservoir. Enviromental Sci. Surv. 2021, 40, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yang, Z.; Tang, X.; Lv, X.; Zhu, J.; Dou, J.; Yang, S.; Meng, L. Three-dimensional modeling and characteristics of hydrodynamic processes in Erhai Lake. J. Kunming Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2013, 38, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Numerical Simulation of Hydrodynamic-Water Quality in Lake Erhai Based on EFDC Model; Chinese Research Academy of Enviromental Sciences: Beijing, China, 2020; 96p. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Duan, L.; Wen, X.; Li, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Effects of Seasonal Variation on Water Quality Parameters and Eutrophication in Lake Yangzong. Water 2022, 14, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.; Hou, P.; Wen, X.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Seasonal Stratification Charac-teristics of Vertical Profiles and Water Quality of Lake Lugu in Southwest China. Water 2022, 14, 2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Chang, F.; Wen, X.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H. Seasonal Variation in the Water Quality and Eutrophication of Lake Xingyun in Southwestern China. Water 2022, 14, 3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Tang, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, S. Analysis of the change trend of water resources in Erhai basin. Yunnan Water Power 2018, 34, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamau, P.; Ellsworth, T.; Boast, C.; Simmons, F. Tillage and cropping effects on preferential flow and solute transport. Soil Sci. 1996, 161, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacic, D.A.; David, M.B.; Gentry, L.E.; Starks, K.M.; Cooke, R.A. Effectiveness of constructed wetlands in reducing nitrogen and phosphorus export from agricultural tile drainage. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 29, 1262–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosse, P.J.; Baker, D.B. Context for re-evaluating agricultural source phosphorus loadings to the Great Lakes. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 91, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, A.M. Municipal point source and agricultural nonpoint source contributions to coastal eutrophication. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1982, 18, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Transverse/longitudinal diffusion coefficient | 4 | m2/s |
| Decay coefficient of CODMn | 0.001 | d−1 |
| Sediment release rate of CODMn | 0–200 | mg/(m2·d) |
| Decay coefficient of TP | 0.005 | d−1 |
| Sediment release rate of TP | 0–5 | mg/(m2·d) |
| Decay coefficient of TN | 0.004 | d−1 |
| Sediment release rate of TN | 0–50 | mg/(m2·d) |
| Pollutant | Monitoring Site | Measured (mg/L) | Simulated (mg/L) | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CODMn | Longkan | 3.73 | 3.53 | 5.36 |
| Tacun | 3.76 | 3.54 | 5.85 | |
| Xiaoguanyi | 3.76 | 3.52 | 6.38 | |
| Huxin | 3.69 | 3.52 | 4.61 | |
| Taoyuan | 3.81 | 3.54 | 7.09 | |
| TP | Longkan | 0.028 | 0.026 | 7.14 |
| Tacun | 0.026 | 0.027 | −3.85 | |
| Xiaoguanyi | 0.029 | 0.028 | 3.45 | |
| Huxin | 0.026 | 0.028 | −7.69 | |
| Taoyuan | 0.029 | 0.031 | −6.90 | |
| TN | Longkan | 0.59 | 0.64 | −8.47 |
| Tacun | 0.59 | 0.61 | −3.39 | |
| Xiaoguanyi | 0.62 | 0.60 | 3.23 | |
| Huxin | 0.61 | 0.60 | 1.64 | |
| Taoyuan | 0.67 | 0.73 | −8.96 |
| Types of Pollutants | Rainy Season (June to September) | Dry Season (October to May of the Following Year) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical oxygen demand | 6801 | 3923 |
| TP | 93 | 35 |
| TN | 1088 | 658 |
| Pollutant | Northern Rivers | Western Rivers | Southern Rivers | Eastern River |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical oxygen demand | 5610.7 | 4079.7 | 895.9 | 137.0 |
| TP | 43.6 | 67.7 | 14.0 | 2.5 |
| TN | 675.6 | 892.8 | 159.3 | 18.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, T.; Ma, W.; Chen, J.; Duan, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, H. Water Quality of Lake Erhai in Southwest China and Its Projected Status in the near Future. Water 2024, 16, 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070972
Xu T, Ma W, Chen J, Duan L, Li H, Zhang H. Water Quality of Lake Erhai in Southwest China and Its Projected Status in the near Future. Water. 2024; 16(7):972. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070972
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Tianbao, Wei Ma, Jun Chen, Lizeng Duan, Huayu Li, and Hucai Zhang. 2024. "Water Quality of Lake Erhai in Southwest China and Its Projected Status in the near Future" Water 16, no. 7: 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070972
APA StyleXu, T., Ma, W., Chen, J., Duan, L., Li, H., & Zhang, H. (2024). Water Quality of Lake Erhai in Southwest China and Its Projected Status in the near Future. Water, 16(7), 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070972







