Strontium Isotopes and Rare Earth Elements as Tracers of Water–Rock Interactions in Taiwan Hot Springs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Background and Sampling
3. Analytical Methods
4. Results
4.1. Major Element Compositions
4.2. Sr Concentration and Sr Isotope
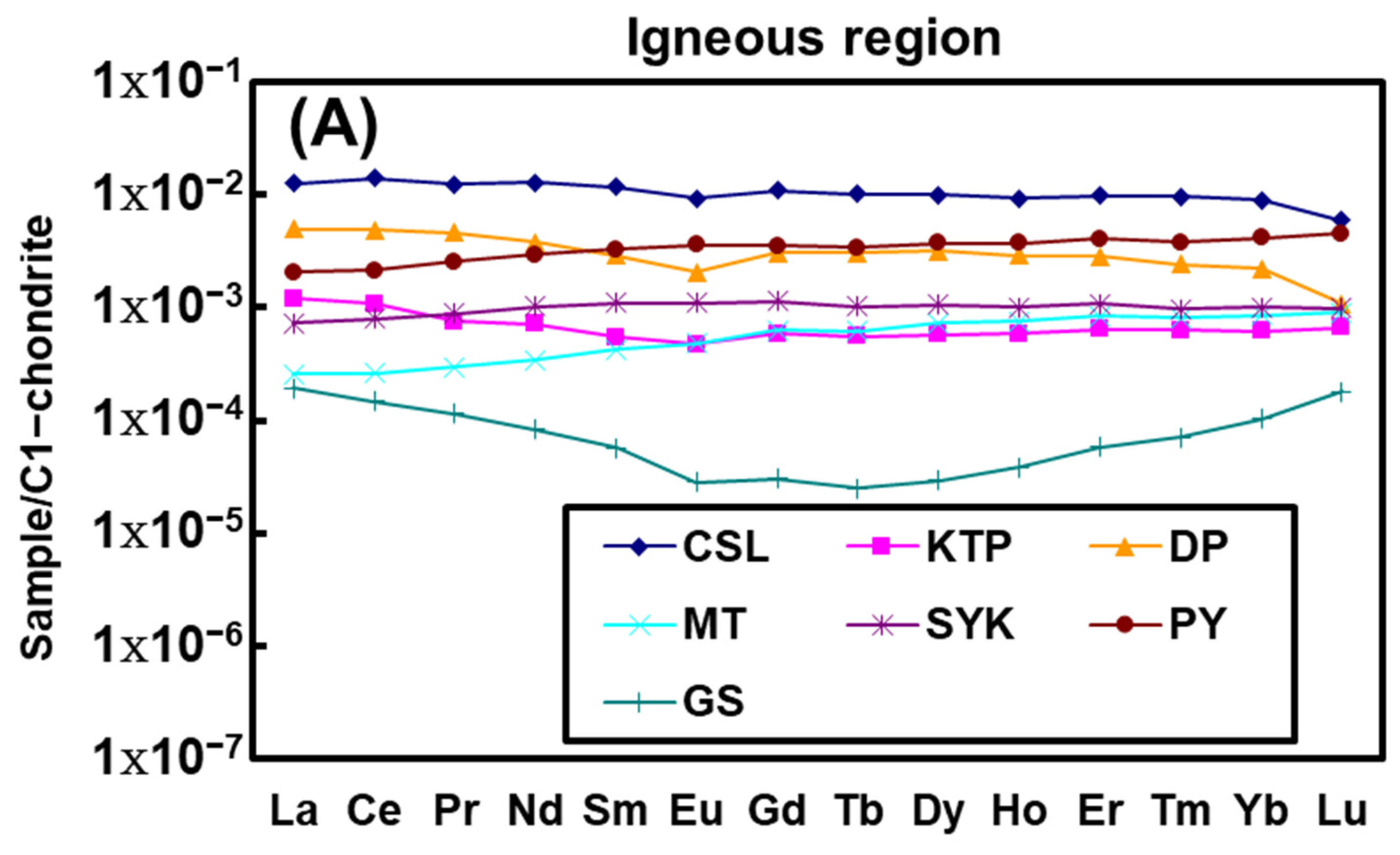
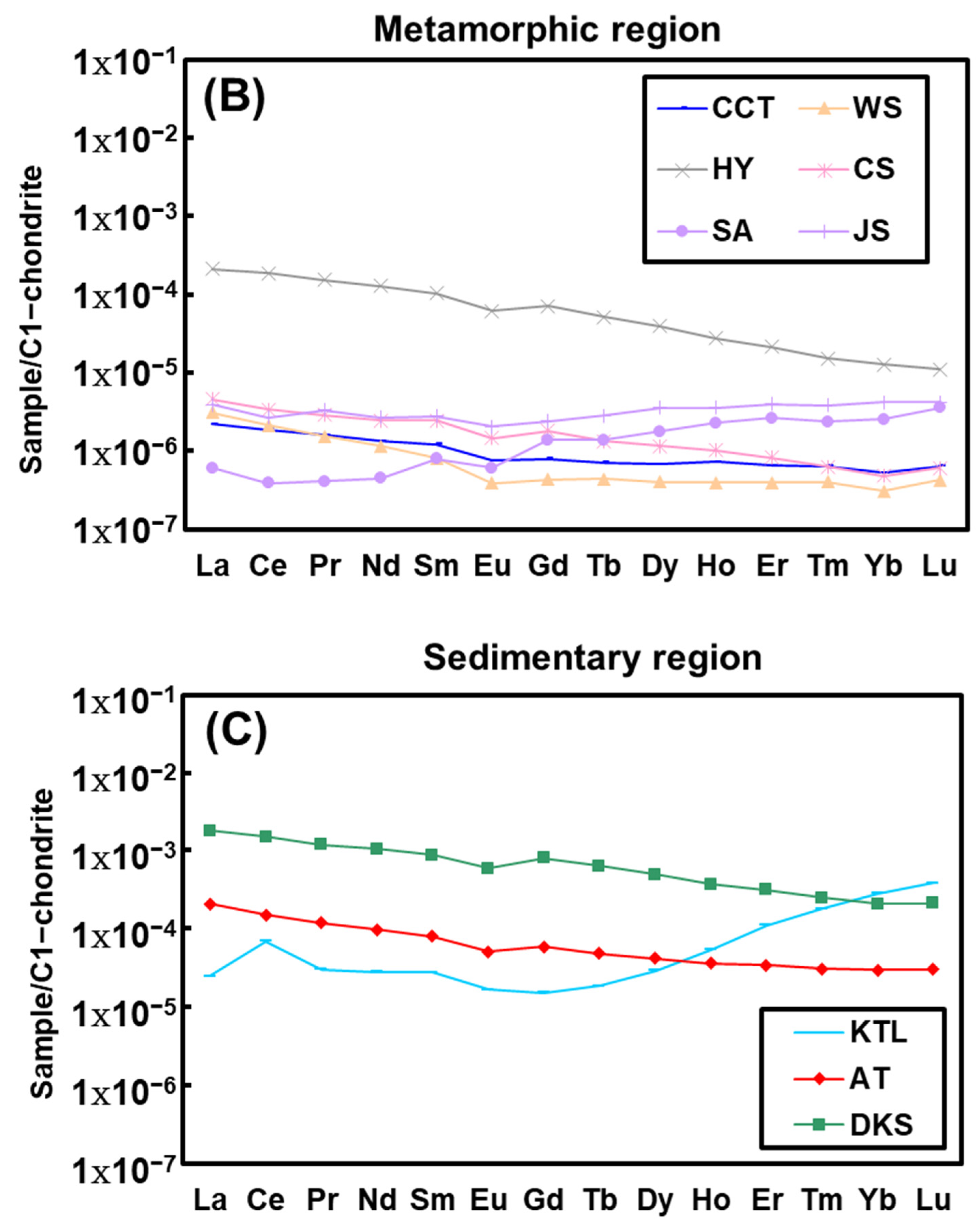
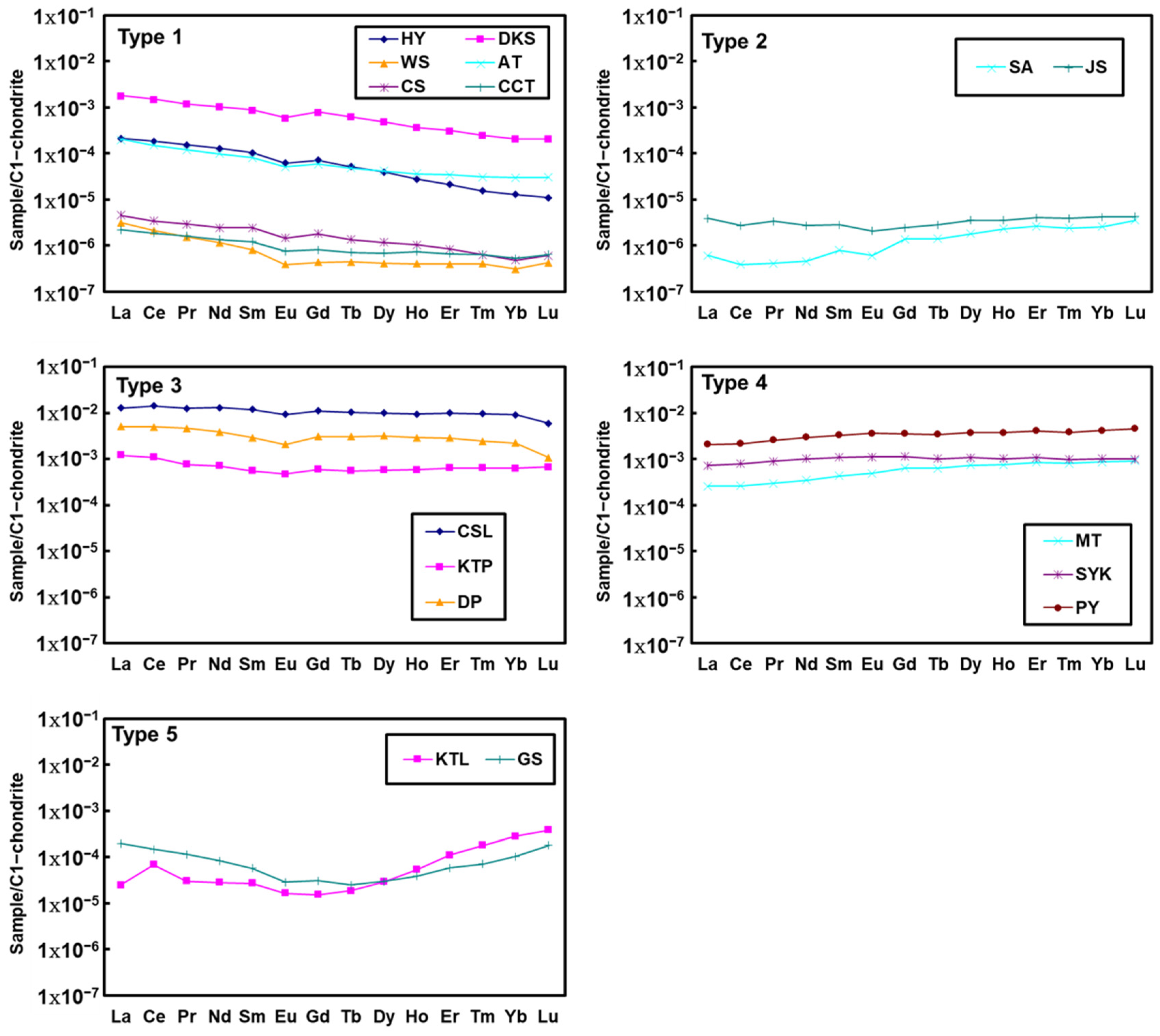
4.3. REEs Compositions
5. Discussion
5.1. Division of Water-Type by Major Component
5.2. Water–Rock Interaction Revealed by Sr Isotope
5.3. Hot Spring REE Patterns
5.4. Water–Rock Interaction Revealed by REE Compositions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.-H. Chemical Characteristics of Thermal Waters in the Central Range of Taiwan, R.O.C. Chem. Geol. 1985, 49, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Liu, K.-K.; Shieh, Y.-N. Geochemical and Isotopic Studies of Bauxitization in the Tatun Volcanic Area, Northern Taiwan. Chem. Geol. 1988, 68, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-F.; Sung, M. The Redox Potential of Hot Springs in Taiwan. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2009, 20, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-M.; Song, S.-R.; Chen, Y.-L.; Tsao, S. Characteristics and Origins of Hot Springs in the Tatun Volcano Group in Northern Taiwan. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2011, 22, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, J.-S.; Liao, L.; Kar, S.; Liu, C.-C.; Li, Z. Hydrochemistry of Hot Springs in Geothermal Fields of Central, Northern, and Northeastern Taiwan: Implication on Occurrence and Enrichment of Arsenic. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, J.P.; Liu, C.-C.; Nath, B.; Bundschuh, J.; Kar, S.; Jean, J.-S.; Bhattacharya, P.; Liu, J.-H.; Atla, S.B.; Chen, C.-Y. Biogeochemical Characteristics of Kuan-Tzu-Ling, Chung-Lun and Bao-Lai Hot Springs in Southern Taiwan. J. Environ. Sci. Health—Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2011, 46, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.-H.; Yeh, H.-F. Factors Controlling of Thermal Water Hydrogeochemical Characteristics in Tatun Volcano Group, Taiwan. Water 2020, 12, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, H.-C.; Pi, J.-L.; You, C.-F.; Shieh, Y.-T.; Lu, H.-Y.; Huang, K.-F.; Liu, H.-C.; Chung, C.-H. Hydrogeology Constrained by Multi-Isotopes and Volatiles Geochemistry of Hot Springs in Tatun Volcanic Group, Taiwan. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, C.; Wallace, M. Origin and Classification of Springs and Historical Review with Current Applications. Environ. Geol. 1994, 24, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afşin, M.; Kuşcu, I.; Elhatip, H.; Dirik, K. Hydrogeochemical Properties of CO2-Rich Thermal-Mineral Waters in Kayseri (Central Anatolia), Turkey. Environ. Geol. 2006, 50, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okan, Ö.Ö.; Çetindağ, B. Hydrogeochemical and Isotopic Investigation of the Kolan Geothermal Field, Southeastern Turkey. Environ. Geol. 2005, 48, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planer-Friedrich, B.; London, J.; Mccleskey, R.B.; Nordstrom, D.K.; Wallschläger, D. Thioarsenates in Geothermal Waters of Yellowstone National Park: Determination, Preservation, and Geochemical Importance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5245–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, R.; Truesdell, A. Chemical Indicators of Subsurface Temperature Applied to Hot Spring Waters of Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming, U.S.A. Geothermics 1970, 2, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Morita, J.; Iwaki, C.; Ueda, A. Geochemical Evaluation of Geothermal Resources in Toyama Prefecture, Japan, Based on the Chemical and Isotopic Characteristics of Hot Spring Waters. Geothermics 2021, 93, 102071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariner, R.H.; Rapp, J.B.; Willey, L.M.; Presser, T.S. The Chemical Composition and Estimated Minimum Thermal Reservoir Temperatures of the Principal Hot Springs of Northern and Central Nevada; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1974.
- Byrne, R.H.; Sholkovitz, E.R. Chapter 158 Marine Chemistry and Geochemistry of the Lanthanides; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 23, pp. 497–593. ISBN 0168-1273. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, S.J.; Jacobsen, S.B. Nd and Sr Isotopic Systematics of River Water Suspended Material: Implications for Crustal Evolution. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1988, 87, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Wang, C.-L.; Gao, L.-Y.; Zhang, C.-X.; Wang, Z.-B.; Wang, C.; Meng, D.; Shang, P.-Q. Evidence from REE and Trace Element Geochemistry for Genesis of Yangjiaowei Fluorite Deposit in Northern Fujian. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2022, 43, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nothdurft, L.D.; Webb, G.E.; Kamber, B.S. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry of Late Devonian Reefal Carbonates, Canning Basin, Western Australia: Confirmation of a Seawater REE Proxy in Ancient Limestones. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.R.; Wang, J.; Huang, W.; Xie, G.; Tatsumoto, M. Major Element, REE, and Pb, Nd and Sr Isotopic Geochemistry of Cenozoic Volcanic Rocks of Eastern China: Implications for Their Origin from Suboceanic-Type Mantle Reservoirs. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1991, 105, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Lyons, W.B. Rare-Earth Element Geochemistry of Colour Lake, an Acidic Freshwater Lake on Axel Heiberg Island, Northwest Territories, Canada. Chem. Geol. 1995, 119, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, R.P.T.; Verweij, W. Geochemistry of Some Rare Earth Elements in Groundwater, Vierlingsbeek, The Netherlands. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1320–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banner, J.L.; Wasserburg, G.J.; Dobson, P.F.; Carpenter, A.B.; Moore, C.H. Isotopic and Trace Element Constraints on the Origin and Evolution of Saline Groundwaters from Central Missouri. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammons, C.H.; Wood, S.A.; Pedrozo, F.; Varekamp, J.C.; Nelson, B.J.; Shope, C.L.; Baffico, G. Hydrogeochemistry and Rare Earth Element Behavior in a Volcanically Acidified Watershed in Patagonia, Argentina. Chem. Geol. 2005, 222, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Dulski, P. Distribution of Yttrium and Rare-Earth Elements in the Penge and Kuruman Iron-Formations, Transvaal Supergroup, South Africa. Precambrian Res. 1996, 79, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulaksiz, S.; Bau, M. Contrasting Behaviour of Anthropogenic Gadolinium and Natural Rare Earth Elements in Estuaries and the Gadolinium Input into the North Sea. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 260, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.W. Mobility and Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements during Weathering of a Granodiorite. Nature 1979, 279, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duddy, L.R. Redistribution and Fractionation of Rare-Earth and Other Elements in a Weathering Profile. Chem. Geol. 1980, 30, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J.-J.; Viers, J.; Dupré, B.; Polve, M.; Ndam, J.; Muller, J.-P. Solid/Liquid REE Fractionation in the Lateritic System of Goyoum, East Cameroon: The Implication for the Present Dynamics of the Soil Covers of the Humid Tropical Regions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 273–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, D.; Stille, P.; Probst, A.; Gauthier-lafaye, F.; Pourcelot, L.; Del Nero, M. Characterization and Migration of Atmospheric REE in Soils and Surface Waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2002, 66, 3339–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H.; Upstill-Goddard, R.; Sholkovitz, E.R. The Rare Earth Elements in Rivers, Estuaries, and Coastal Seas and Their Significance to the Composition of Ocean Waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 971–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.R. The Aquatic Chemistry of Rare Earth Elements in Rivers and Estuaries. Aquat. Geochem. 1995, 1, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Tang, J.; Daniels, J.M.; Bounds, W.J.; Burdige, D.J. Rare Earth Element Concentrations and Speciation in Organic-Rich Blackwaters of the Great Dismal Swamp, Virginia, USA. Chem. Geol. 2004, 209, 271–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannigan, R.E.; Sholkovitz, E.R. The Development of Middle Rare Earth Element Enrichments in Freshwaters: Weathering of Phosphate Minerals. Chem. Geol. 2001, 175, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viers, J.; Wasserburg, G.J. Behavior of Sm and Nd in a Lateritic Soil Profile1 1Associate Editor: G. R. Helz. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, 2043–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.-F.; Liao, W.-L.; Huang, K.-F.; Chung, C.-H.; Liu, Z. Sediment Source Variation Using REEs, Sr, and Nd Isotopic Compositions: A Case Study in MD05-2901, Northwestern South China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 10, 1292802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.-M.; Høgdahl, O.; Philippot, J.C. Rare Earth Element Supply to the Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 1976, 81, 3119–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keasler, K.M.; Loveland, W.D. Rare Earth Elemental Concentrations in Some Pacific Northwest Rivers. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1982, 61, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.R. The Geochemistry of Rare Earth Elements in the Amazon River Estuary. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 2181–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stordal, M.C.; Wasserburg, G.J. Neodymium Isotopic Study of Baffin Bay Water: Sources of REE from Very Old Terranes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1986, 77, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, K.H.; Farnham, I.M.; Guo, C.; Stetzenbach, K.J. Rare Earth Element Fractionation and Concentration Variations along a Groundwater Flow Path within a Shallow, Basin-Fill Aquifer, Southern Nevada, USA. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 2697–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.G.; Greig, A.; Collerson, K.D.; Kamber, B.S. Rare Earth Element and Yttrium Variability in South East Queensland Waterways. Aquat. Geochem. 2006, 12, 39–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, A.; Siciliano, A.; Spampinato, M.; Morello, R.; Trancone, G.; Race, M.; Guida, M.; Fabbricino, M.; Spasiano, D.; Fratino, U. A Multi-Disciplinary Approach Based on Chemical Characterization of Foreshore Sediments, Ecotoxicity Assessment and Statistical Analyses for Environmental Monitoring of Marine-Coastal Areas. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 202, 106780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michard, A. Rare Earth Element Systematics in Hydrothermal Fluids. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweed, S.O.; Weaver, T.R.; Cartwright, I.; Schaefer, B. Behavior of Rare Earth Elements in Groundwater during Flow and Mixing in Fractured Rock Aquifers: An Example from the Dandenong Ranges, Southeast Australia. Chem. Geol. 2006, 234, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, B.C.; Corder, G.D.; Ali, S.H. Sustainability of Rare Earths—An Overview of the State of Knowledge. Minerals 2013, 3, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, A.; Ghoreyshinia, S.; Mehrabi, B.; Delavari, M. Rare Earth Elements Geochemistry in Springs from Taftan Geothermal Area SE Iran. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2015, 304, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatipoğlu Temizel, E.; Gültekin, F.; Fırat Ersoy, A. Major, Trace, and Rare Earth Element Geochemistry of the Ayder and İkizdere (Rize, NE Turkey) Geothermal Waters: Constraints for Water–Rock Interactions. Geothermics 2020, 86, 101810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Huang, T.; Tian, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, Y. Geochemical Behaviors of Rare Earth Elements in Granite-Hosted Geothermal Systems in SE China. Geothermics 2023, 115, 102826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Xing, L.; Zhan, Y.; Li, F.; Shao, J.; Niu, H.; Liang, X.; Li, C. Geochemical Behaviors of Rare Earth Elements in Groundwater along a Flow Path in the North China Plain. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2016, 117, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dia, A.; Gruau, G.; Olivié-Lauquet, G.; Riou, C.; Molénat, J.; Curmi, P. The Distribution of Rare Earth Elements in Groundwaters: Assessing the Role of Source-Rock Composition, Redox Changes and Colloidal Particles. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2000, 64, 4131–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.J.; Palmer, M.R.; Sturchio, N.C.; Kemp, A.J. The Rare Earth Element Geochemistry of Acid-Sulphate and Acid-Sulphate-Chloride Geothermal Systems from Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming, USA. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Usui, A.; Pracejus, B.; Mita, N.; Kanai, Y.; Irber, W.; Dulski, P. Geochemistry of Low-Temperature Water–Rock Interaction: Evidence from Natural Waters, Andesite, and Iron-Oxyhydroxide Precipitates at Nishiki-Numa Iron-Spring, Hokkaido, Japan. Chem. Geol. 1998, 151, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, P.; Dulski, P.; Savascin, Y.; Conrad, M. Rare Earth Elements, Yttrium and Pb Isotope Ratios in Thermal Spring and Well Waters of West Anatolia, Turkey: A Hydrochemical Study of Their Origin. Chem. Geol. 2004, 206, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.R.; Edmond, J.M. Controls over the Strontium Isotope Composition of River Water. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1992, 56, 2099–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, D.C.; Bacon, J.R. Strontium Isotopes as Indicators of Mineral Weathering in Catchments. CATENA 1994, 22, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullen, T.D.; Krabbenhoft, D.P.; Kendall, C. Kinetic and Mineralogic Controls on the Evolution of Groundwater Chemistry and 87Sr/86Sr in a Sandy Silicate Aquifer, Northern Wisconsin, USA. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 1807–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosbois, C.; Négrel, P.; Fouillac, C.; Grimaud, D. Dissolved Load of the Loire River: Chemical and Isotopic Characterization. Chem. Geol. 2000, 170, 179–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.R.; Jacobsen, S.B.; Poreda, R.J.; Dowling, C.B.; Aggarwal, P.K. Large Groundwater Strontium Flux to the Oceans from the Bengal Basin and the Marine Strontium Isotope Record. Science 2001, 293, 1470–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, S.; Fullagar, P.D. Strontium Isotope Systematics of Base Flow in Piedmont Province Watersheds, Georgia (USA). Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 1571–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.S.; You, C.F.; Chung, C.H.; Huang, K.F.; Zhou, C. Mg and Sr Isotopes in Cap Dolostone: Implications for Oceanic Mixing after a Neoproterozoic Snowball Earth Event. Water 2023, 15, 2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-W.; Huang, S.-T.; Wang, R.-M.; Chen, W.-F.; Chung, C.-H.; You, C.-F. Strontium Isotopic Composition as Tracers for Identifying Groundwater Recharge Sources in the Choushui River Alluvial Plain, Western Taiwan. Water 2024, 16, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paces, J.B.; Wurster, F.C. Natural Uranium and Strontium Isotope Tracers of Water Sources and Surface Water-Groundwater Interactions in Arid Wetlands—Pahranagat Valley, Nevada, USA. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataille, C.; Laffoon, J.; Bowen, G. Mapping Multiple Source Effects on the Strontium Isotopic Signatures of Ecosystems from the Circum-Caribbean Region. Ecosphere 2012, 3, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, H.; Song, X.; Zhang, Q.; Burford, M. Strontium Concentrations and Isotope Ratios in a Forest-River System in the South Qinling Mts., China. Water Res. 2016, 93, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppe, J. A Retrodeformable Cross Section of Northern Taiwan. Proc. Geol. Soc. China 1980, 23, 46–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Daly, J.S.; Tian, Y.; Tyrrell, S.; Sun, X.; Badenszki, E.; Qin, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Guo, R. Sedimentary Provenance Perspectives on the Evolution of the Major Rivers Draining the Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2022, 232, 104151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.S. Geotectonic Evolution of Late Cenozoic Arc-Continent Collision in Taiwan. Tectonophysics 1990, 183, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.-T. Geothermal Update Report, Taiwan, Republic of China. In 1985 International Symposium on Geothermal Energy; Geothermal Resources Council: El Centro, CA, USA, 1985; pp. 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Huff, E.A.; Huff, D.R. TRU Spec and RE Spec Chromatography: Basic Studies and Applications. In Proceedings of the 34th ORNL/DOE Conference on Analytical Chemistry in Energy Technology, Gatlinburg, TN, USA, 5–7 October 1993; p. HD193. [Google Scholar]
- Yeghicheyan, D.; Carignan, J.; Valladon, M.; Coz, M.; Le Cornec, F.; Rouelle, M.; Robert, M.; Aquilina, L.; Aubry, E.; Churlaud, C.; et al. A Compilation of Silicon and Thirty One Trace Elements Measured in the Natural River Water Reference Material SLRS-4 (NRC-CNRC). Geostand. Newsl.-J. Geostand. Geoanalysis. 2001, 25, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-C.; Hsiao, J.-C.; Huang, W.-L. The Investigation of Water Quality and Arsenic Concentration of Hot Springs in Tatun Volcanic Group. Bull. Cent. Geol. Surv. 2010, 23, 67–90. [Google Scholar]
- Anders, E.; Grevesse, N. Abundances of the Elements: Meteoritic and Solar. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Hung, J.-J. Aquatic Chemistry of Lakes and Reservoirs in Taiwan. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 1997, 8, 405–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.S. An Introduction to the Geology of Taiwan Explanatory Text of the Geologic Map of Taiwan; The Ministry of Economic Affairs, R.O.C.: Taipei, China, 1975.
- Tranter, M.; Brown, G.; Raiswell, R.; Sharp, M.; Gurnell, A. A Conceptual Model of Solute Acquisition by Alpine Glacial Meltwaters. J. Glaciol. 1993, 39, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.C.; You, C.F.; Lin, F.J.; Chung, C.H.; Huang, K.F. Seasonal Variation in Long-Range Transported Dust to a Subtropical Islet Offshore Northern Taiwan: Chemical Composition and Sr Isotopic Evidence in Rainwater. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3386–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dia, A.N.; Cohen, A.S.; O’Nions, R.K.; Shackleton, N.J. Seawater Sr Isotope Variation over the Past 300 Kyr and Influence of Global Climate Cycles. Nature 1992, 356, 786–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L. Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of Late Pliocene-Quaternary Volcanic Rocks from the Northern Taiwan Volcanic Zone; National Taiwan University: Taipei, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.K.; Chen, C.H.; Shieh, Y.N. Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopic Compositions of Meteoric Waters from the Tatun Shan Area. Northern Taiwan. Bull. Inst. Earth Sci. Acad. Sin. 1984, 4, 159–175. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.L. Chemical Compositions of Hot Spring Waters in the Tatun Volcanic Area and Their Influence on Stream Waters; National Taiwan University: Taipei, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.L. Preliminary Geochemical and Isotopes Study of the Erren River Water; National Cheng Kung University: Tainan, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.J.-S.; Yang, H.-J. Sources and Genesis of the Chinkuashih Au–Cu Deposits in Northern Taiwan: Constraints from Os and Sr Isotopic Compositions of Sulfides. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 222, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G. Ten A Mineralogical and Geochemical Study of the Origin and Formation Mechanism of Linkou Laterite, Northern Taiwan; National Cheng Kung University, Department of Earth Sciences: Tainan, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, C.-Y.; Jahn, B.-M.; Mertzman, S.A.; Wu, T.-W. Subduction-Related Granitic Rocks of Taiwan. J. Southeast. Asian Earth Sci. 1996, 14, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yui, T.-F.; Heaman, L.; Lan, C.-Y. U-Pb and Sr Isotopic Studies on Granitoids from Taiwan and Chinmen-Lieyü and Tectonic Implications. Tectonophysics 1996, 263, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-L.; Chung, S.-L.; O’reilly, S.Y.; Sun, S.-S.; Shinjo, R.; Chen, C.-H. Geochemical Constraints for the Genesis of Post-Collisional Magmatism and the Geodynamic Evolution of the Northern Taiwan Region. J. Petrol. 2004, 45, 975–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Jahn, B.-M.; Lee, T.; Chen, C.-H.; Cornichet, J. Sm-Nd Isotopic Geochemistry of Sediments from Taiwan and Implications for the Tectonic Evolution of Southeast China. Chem. Geol. 1990, 88, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yui, T.F.; Lan, C.Y. Isotopic Compositions of Tananao Marble in the Tungao Area, Northeastern Taiwan: A Chronological Consideration. Spec. Publ. Cent. Geol. Surv. 1991, 5, 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.; Shannon, W. Rare-Earth Elements in Geothermal Waters from Oregon, Nevada, and California. J. Solid State Chem. 2003, 171, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlesworth, P.; Wood, S. The Aqueous Geochemistry of the Rare Earth Elements and Yttrium. Part 7. REE, Th and U Contents in Thermal Springs Associated with the Idaho Batholith. Appl. Geochem. 1998, 13, 861–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikawada, Y.; Fukai, M.; Oi, T. Specific REE Patterns Observed in Sulfurous Hot Springs from a Hydrothermal Alteration Area in Manza, Japan. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2013, 7, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanada, T.; Takamatsu, N.; Yoshiike, Y. Geochemical Interpretation of Long-Term Variations in Rare Earth Element Concentrations in Acidic Hot Spring Waters from the Tamagawa Geothermal Area, Japan. Geothermics 2006, 35, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, Y.; Iijima, A.; Kimura, S.; Kozawa, K. Preliminary Study on Evaluation of Rare Earth Elements in Hot Spring Water as a Geochemical Indicator Intended to Understand Hot Spring Water Flow. Hot Spring Sci. 2013, 63, 141–157. [Google Scholar]
- Deluca, F.; Mongelli, G.; Paternoster, M.; Zhu, Y. Rare Earth Elements Distribution and Geochemical Behaviour in the Volcanic Groundwaters of Mount Vulture, Southern Italy. Chem. Geol. 2020, 539, 119503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorović, M.; Đurović, M.Ć.; Štrbački, J.; Papic, P. Rare Earth Elements in Mineral Waters in Serbia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourret, O.; Van Der Ent, A.; Hursthouse, A.; Irawan, D.E.; Liu, H.; Wiche, O. The ‘Europium Anomaly’ in Plants: Facts and Fiction. Plant Soil. 2021, 476, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.; Doig, R. The Significance of Europium Anomalies in the REE Spectra of Granites and Pegmatites, Mont Laurier, Quebec. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1983, 47, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, P.; Dulski, P.; De Lucia, M. REY Patterns and Their Natural Anomalies in Waters and Brines: The Correlation of Gd and Y Anomalies. Hydrology 2021, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikawada, Y.; Ossaka, T.; Oi, T.; Honda, T. Experimental Studies on the Mobility of Lanthanides Accompanying Alteration of Andesite by Acidic Hot Spring Water. Chem. Geol. 2001, 176, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, P.; Dulski, P.; Salameh, E.; Geyer, S. Characterization of the Sources of Thermal Spring- and Well Water in Jordan by Rare Earth Element and Yttrium Distribution and Stable Isotopes of H2O. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 2006, 34, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, P.; Dulski, P.; Özgür, N. Partitioning of Rare Earths and Some Major Elements in the Kizildere Geothermal Field, Turkey. Geothermics 2008, 37, 132–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, M.G.; Lecomte, K.L.; Pasquini, A.I.; Formica, S.M.; Depetris, P.J. Sources of Dissolved REE in Mountainous Streams Draining Granitic Rocks, Sierras Pampeanas (Córdoba, Argentina). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 5355–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.J.; Komninou, A.; Yardley, B.W.D.; Palmer, M.R. Rare Earth Element Speciation in Geothermal Fluids from Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming, USA. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1998, 62, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, J.R.; Shock, E.L.; Sassani, D.C. Rare Earth Elements in Hydrothermal Systems: Estimates of Standard Partial Molal Thermodynamic Properties of Aqueous Complexes of the Rare Earth Elements at High Pressures and Temperatures. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 4329–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verplanck, P.L.; Nordstrom, D.K.; Taylor, H.E.; Kimball, B.A. Rare Earth Element Partitioning between Hydrous Ferric Oxides and Acid Mine Water during Iron Oxidation. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 1339–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmann, M.; Stille, P. Controls on Transport and Fractionation of the Rare Earth Elements in Stream Water of a Mixed Basaltic–Granitic Catchment Basin (Massif Central, France). Chem. Geol. 2008, 254, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Wu, Y.J. Volcanic Geology of the Tatun Geothermal Area, Northern Taiwan. Proc. Geol. Soc. China 1971, 14, 5–20. [Google Scholar]
- Dobson, P.; Gasperikova, E.; Spycher, N.; Lindsey, N.J.; Guo, T.R.; Chen, W.S.; Liu, C.H.; Wang, C.-J.; Chen, S.-N.; Fowler, A.P.G. Conceptual Model of the Tatun Geothermal System, Taiwan. Geothermics 2018, 74, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, I.T.; Golding, S.D. Rare Earth Element Fractionation in Authigenic Illite–Smectite from Late Permian Clastic Rocks, Bowen Basin, Australia: Implications for Physico-Chemical Environments of Fluids during Illitization. Chem. Geol. 2003, 193, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baar, H.J.W.; Bacon, M.P.; Brewer, P.G. Rare-Earth Distributions with a Positive Ce Anomaly in the Western North Atlantic Ocean. Nature 1983, 301, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, M.; Möller, P. Rare Earth Element Systematics of the Chemically Precipitated Component in Early Precambrian Iron Formations and the Evolution of the Terrestrial Atmosphere-Hydrosphere-Lithosphere System. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 2239–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.-P.; Kerrich, R.; Hendry, M.J. Distribution of the Rare Earth Elements in Porewaters from a Clay-Rich Aquitard Sequence, Saskatchewan, Canada. Chem. Geol. 2001, 176, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H.; Sholkovitz, E.R. Rare Earth Elements in the Pore Waters of Reducing Nearshore Sediments. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1987, 82, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.R.; Piepgras, D.J.; Jacobsen, S.B. The Pore Water Chemistry of Rare Earth Elements in Buzzards Bay Sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1989, 53, 2847–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wen, H.; Capezzuoli, E.; Brogi, A.; Liu, R.; Vaselli, O.; Wang, F.; Lu, Z.; You, Y.; Kele, S. Strontium Isotopes and Rare Earth Elements in Terrestrial Hot-Spring Deposits: Characterization and Geothermal Implications. GSA Bull. 2024, 136, 5009–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noack, C.W.; Dzombak, D.A.; Karamalidis, A.K. Rare Earth Element Distributions and Trends in Natural Waters with a Focus on Groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4317–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample ID | Sample Location | Geothermal Field | Type of Exposed Rock | pH | Temperature (°C) | Water Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSL | Chungshanlo | (1) | andesite | 3.2 | 74 | Acid SO4 |
| KTP | Kengtzuping | (1) | andesite | 2.5 | 82 | Acid SO4 |
| DP | Dapu | (1) | alluvium | 2.2 | 99 | SO4-Cl |
| MT | Ma-Tsao | (1) | andesite | 2.4 | 60 | Acid SO4 |
| SYK | Siaoyoukeng | (1) | tuff | 2.4 | 72 | Acid SO4 |
| PY | Payen | (1) | andesite | 2.3 | 91 | Acid SO4 |
| GS | Ginshan | (1) | alluvium | 2.5 | 57 | SO4-Cl |
| CCT | Changchuntzu | (2) | marble | - | - | - |
| CS | Chingshui | (2) | argillite | 6.7 | 64 | Na-HCO3 |
| JS | Jiaosi | (2) | metasandstone | 7.3 | 58 | Na-HCO3 |
| SA | Suao | (2) | slate and argillite | 5.5 | 21 | Na-HCO3 |
| WS | Wenshan | (2) | slate and schist | 7.4 | 46 | Neutral SO4 |
| HY | Hungyeh | (3) | slate and phyllite | 7.3 | 80 | Na-HCO3 |
| AT | Antung | (3) | sandstone and shale | 8.7 | 66 | SO4-Cl |
| KTL | Kuantzuling | (4) | silt and shale | 7.5 | 66 | Na-HCO3-Cl |
| DKS | Dakangshan | (4) | limestone | 7.4 | 21 | Na-HCO3-Cl |
| Sample ID | Na | K | Mg | Al | Si | Ca | Fe | Sr | *F− | *Cl− | *HCO3− | *SO42− | 87Sr/86Sr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSL | 23.4 | 10.5 | 18.3 | 56.3 | 41.4 | 50.7 | 78.1 | 0.15 | ND | 59.4 | ND | 212 | 0.70552 |
| KTP | 5.76 | 0.95 | 2.69 | 2.77 | 9.43 | 5.59 | 2.07 | 0.03 | 13.4 | 30 | ND | 349 | 0.70558 |
| DP | 2470 | 267 | 249 | 96.9 | 88.2 | 293 | 75.9 | 2.86 | 5.45 | 6320 | ND | 2070 | 0.71240 |
| MT | 16.9 | 6.65 | 13.7 | 4.9 | 63.3 | 45.7 | 3.39 | 0.1 | 1.62 | 19.6 | 17.1 | 234 | 0.70468 |
| SYK | 14.1 | 5.12 | 12.3 | 6.41 | 78.3 | 49.2 | 20.6 | 0.05 | 2.69 | 907 | ND | 1160 | 0.70601 |
| PY | 15.7 | 2.9 | 8.63 | 8.12 | 43.6 | 23.6 | 4.61 | 0.07 | ND | 55.4 | ND | 559 | 0.70516 |
| GS | 587 | 96.6 | 103 | 40.0 | 103 | 94.1 | 18.1 | 0.12 | 6.18 | 1430 | 219 | 254 | 0.70618 |
| CCT | 2.67 | 0.77 | 7.58 | 0.01 | 2.31 | 38.7 | 0.01 | 0.24 | - | - | - | - | 0.70817 |
| CS | 765 | 37.4 | 0.62 | 0.38 | 74.5 | 1.17 | 0.21 | 0.52 | 1.63 | 3.97 | 498 | 1.11 | 0.71495 |
| JS | 198 | 10.3 | 5.41 | 0.21 | 19.0 | 11.4 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 3.08 | 27.4 | 489 | 1.11 | 0.71571 |
| SA | 12.8 | 1.22 | 5.91 | 0.16 | 9.48 | 15.6 | 0.10 | 0.93 | ND | 10.5 | 117 | 21 | 0.71480 |
| WS | 122 | 10.4 | 37.0 | 0.11 | 19.3 | 188 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 2.61 | 16.5 | 221 | 790 | 0.71004 |
| HY | 388 | 13.5 | 1.89 | 0.29 | 48.2 | 9.64 | 0.27 | 3.20 | 1.23 | 106 | 714 | 71.5 | 0.71730 |
| AT | 587 | 5.18 | 0.16 | 0.64 | 28.4 | 97.7 | 0.29 | 0.14 | 4.97 | 724 | 25.5 | 422 | 0.70564 |
| KTL | 8440 | 266 | 23.9 | 0.2 | 9.3 | 21.4 | 0.25 | 3.42 | 7.44 | 3620 | 4860 | 37.4 | 0.71066 |
| DKS | 100 | 6.12 | 95.4 | 3.53 | 24.4 | 232 | 5.52 | 5.34 | ND | 492 | 311 | ND | 0.70931 |
| Sample ID | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ΣREE | (La/Yb)N | Ce/Ce* | Eu/Eu* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSL | 3000 | 8550 | 1110 | 5850 | 1740 | 518 | 2160 | 372 | 2430 | 523 | 1580 | 234 | 1480 | 144 | 29700 | 2.15 | 1.12 | 0.81 |
| KTP | 283 | 655 | 67.5 | 323 | 81 | 26.4 | 116 | 20.2 | 139 | 32.5 | 102 | 15.4 | 102 | 16.2 | 1980 | 1.81 | 1.14 | 0.83 |
| DP | 1180 | 2970 | 413 | 1740 | 427 | 116 | 600 | 111 | 776 | 161 | 450 | 58.6 | 364 | 26.1 | 9380 | 4.66 | 1.02 | 0.7 |
| MT | 60.6 | 157 | 26.4 | 157 | 62.8 | 27.3 | 125 | 22.5 | 177 | 41.8 | 135 | 19.5 | 140 | 22 | 1170 | 0.28 | 0.94 | 0.93 |
| SYK | 170 | 480 | 79.3 | 460 | 161 | 61.8 | 223 | 36.9 | 260 | 56.2 | 171 | 23.6 | 165 | 24.2 | 2370 | 0.73 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| PY | 482 | 1300 | 227 | 1340 | 488 | 201 | 690 | 123 | 899 | 206 | 646 | 92.1 | 671 | 111 | 7470 | 0.45 | 0.94 | 1.05 |
| GS | 45.6 | 88.2 | 10.2 | 37.6 | 8.39 | 1.6 | 6.01 | 0.9 | 7.14 | 2.13 | 9.19 | 1.71 | 16.8 | 4.37 | 240 | 1.08 | 0.98 | 0.68 |
| CCT | 0.52 | 1.14 | 0.14 | 0.61 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.1 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 3.26 | 3.44 | 1.00 | 0.76 |
| CS | 1.08 | 2.06 | 0.26 | 1.11 | 0.36 | 0.08 | 0.36 | 0.05 | 0.28 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 5.94 | 7.54 | 0.94 | 0.7 |
| JS | 0.92 | 1.64 | 0.3 | 1.22 | 0.41 | 0.12 | 0.48 | 0.1 | 0.86 | 0.2 | 0.64 | 0.09 | 0.68 | 0.1 | 7.76 | 0.92 | 0.75 | 0.79 |
| SA | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 0.2 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 0.43 | 0.13 | 0.42 | 0.06 | 0.42 | 0.09 | 2.64 | 0.17 | 0.78 | 0.58 |
| WS | 0.73 | 1.28 | 0.14 | 0.52 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.1 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 3.17 | 7.37 | 0.97 | 0.65 |
| HY | 50 | 112 | 13.7 | 57.6 | 15.3 | 3.47 | 13.9 | 1.86 | 9.58 | 1.53 | 3.38 | 0.37 | 2.08 | 0.27 | 285 | 19.4 | 1.02 | 0.72 |
| AT | 48.1 | 90.2 | 10.5 | 44.1 | 11.8 | 2.84 | 11.6 | 1.76 | 10.1 | 1.99 | 5.46 | 0.75 | 4.8 | 0.73 | 245 | 6.85 | 0.96 | 0.74 |
| KTL | 5.81 | 41.3 | 2.69 | 12.7 | 4 | 0.92 | 2.98 | 0.67 | 7.06 | 2.95 | 17.6 | 4.31 | 45.6 | 9.23 | 158 | 0.07 | 2.50 | 0.81 |
| DKS | 421 | 901 | 105 | 469 | 129 | 33.1 | 156 | 22.9 | 118 | 20.5 | 49.3 | 6.03 | 33.8 | 5.07 | 2470 | 8.6 | 1.03 | 0.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, C.-H.; You, C.-F.; Yeh, Y.-L. Strontium Isotopes and Rare Earth Elements as Tracers of Water–Rock Interactions in Taiwan Hot Springs. Water 2025, 17, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010071
Chung C-H, You C-F, Yeh Y-L. Strontium Isotopes and Rare Earth Elements as Tracers of Water–Rock Interactions in Taiwan Hot Springs. Water. 2025; 17(1):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010071
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Chuan-Hsiung, Chen-Feng You, and Yi-Ling Yeh. 2025. "Strontium Isotopes and Rare Earth Elements as Tracers of Water–Rock Interactions in Taiwan Hot Springs" Water 17, no. 1: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010071
APA StyleChung, C.-H., You, C.-F., & Yeh, Y.-L. (2025). Strontium Isotopes and Rare Earth Elements as Tracers of Water–Rock Interactions in Taiwan Hot Springs. Water, 17(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010071






