Fouling Community Characteristics in Sea Cage Farms in Leizhou Bay, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
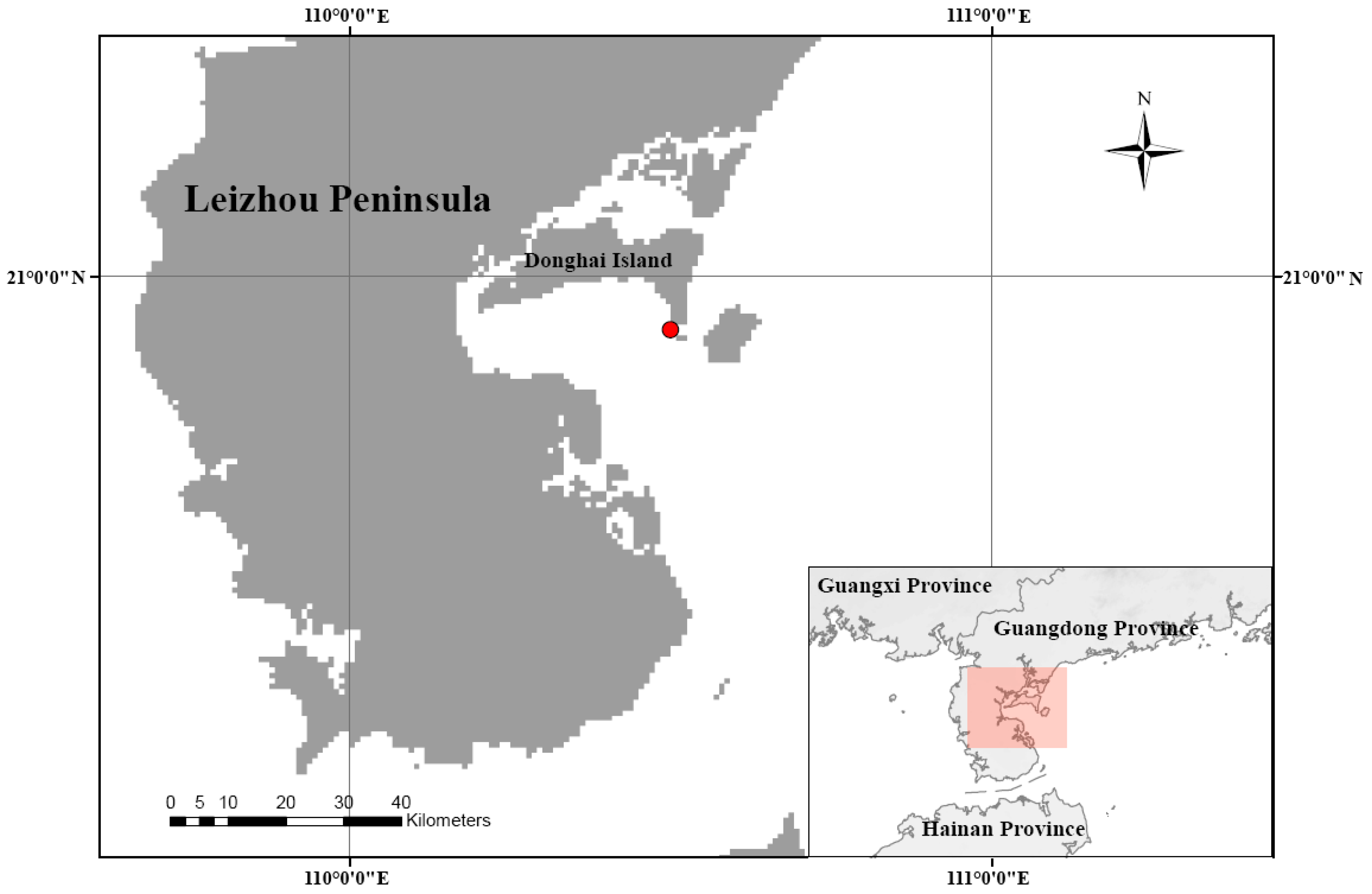
2.1. Survey Area
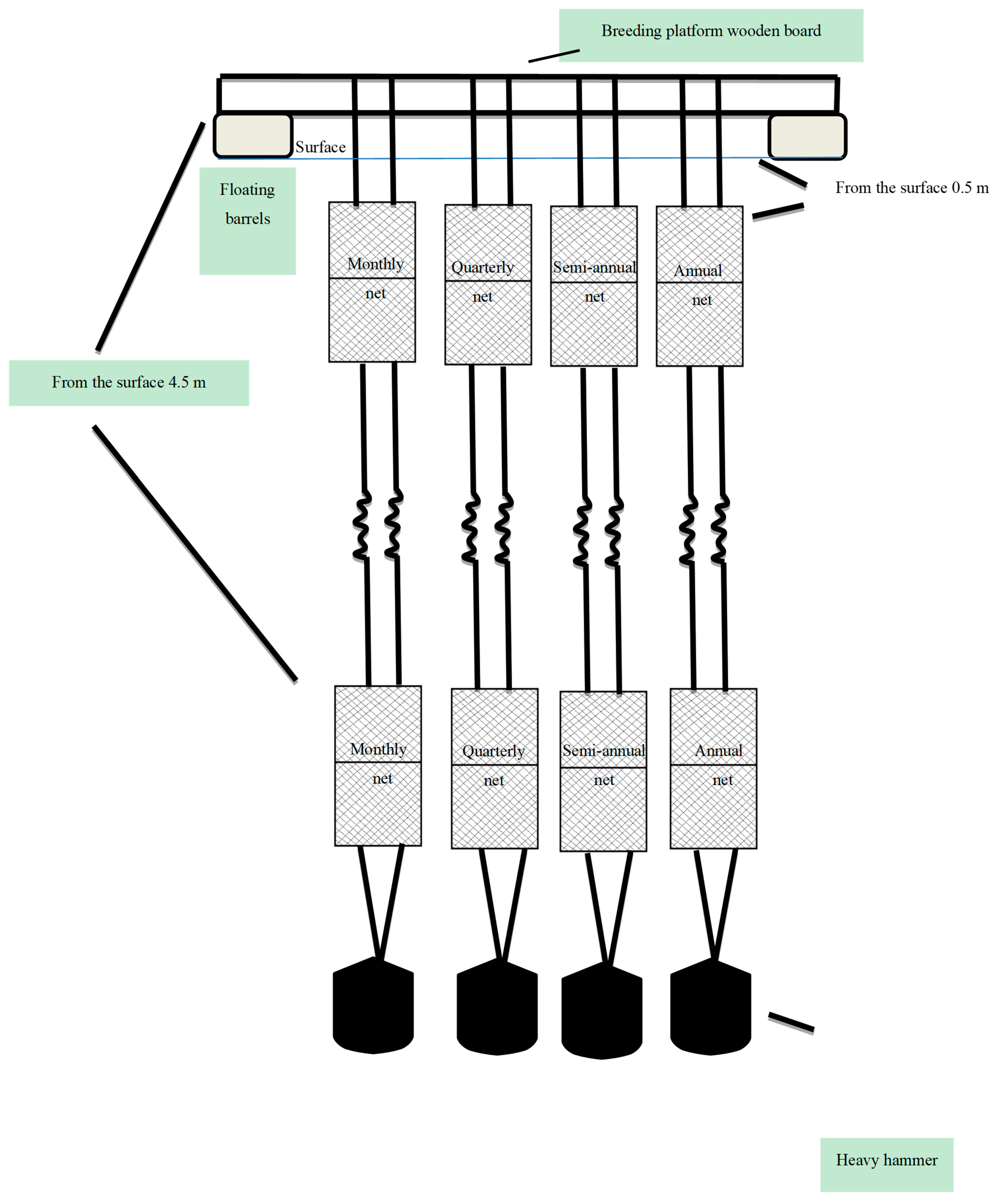
2.2. Sampling Methodology
2.3. Environmental Variables
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
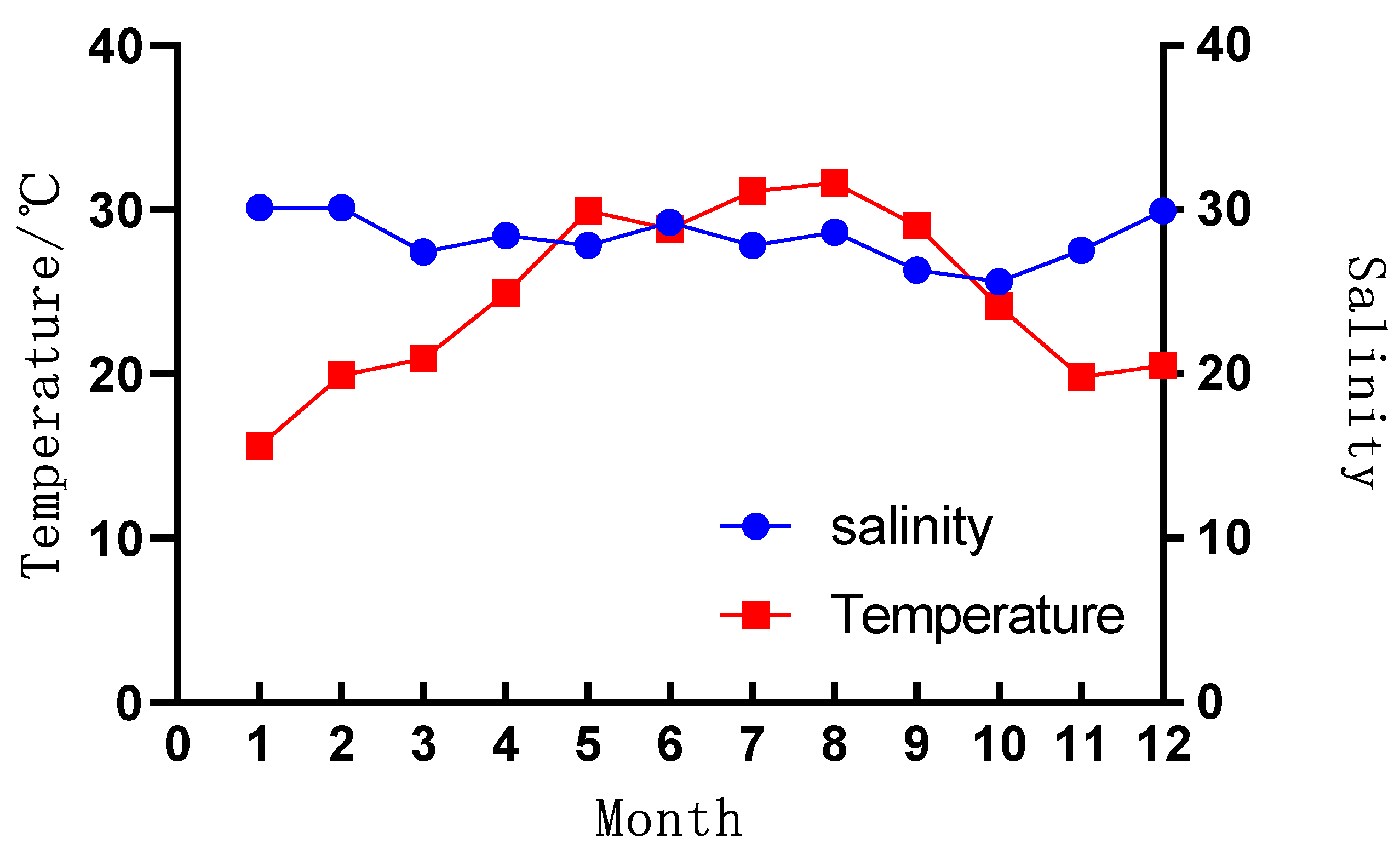
3.1. Environmental Characteristics
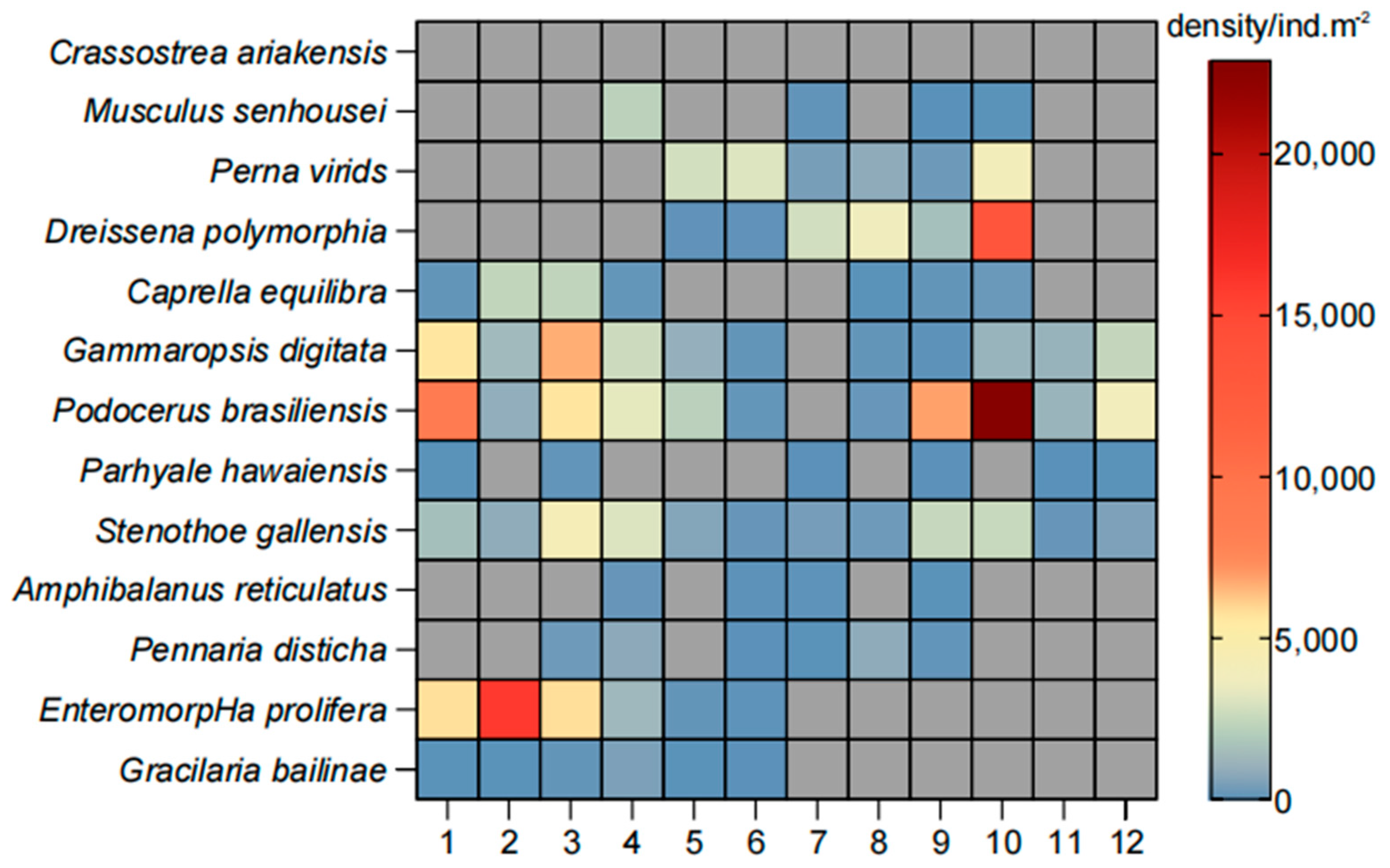
3.2. Species Composition
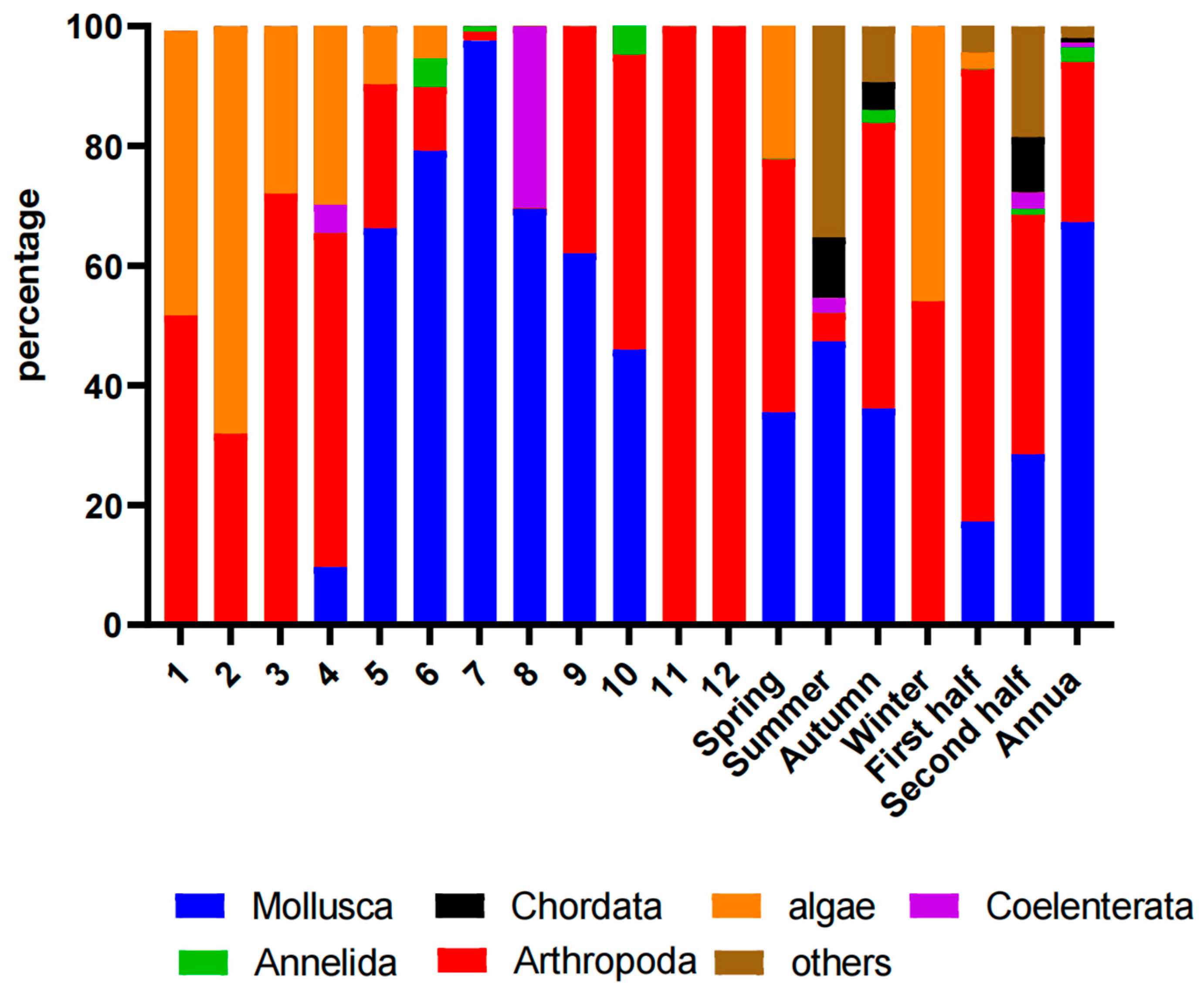
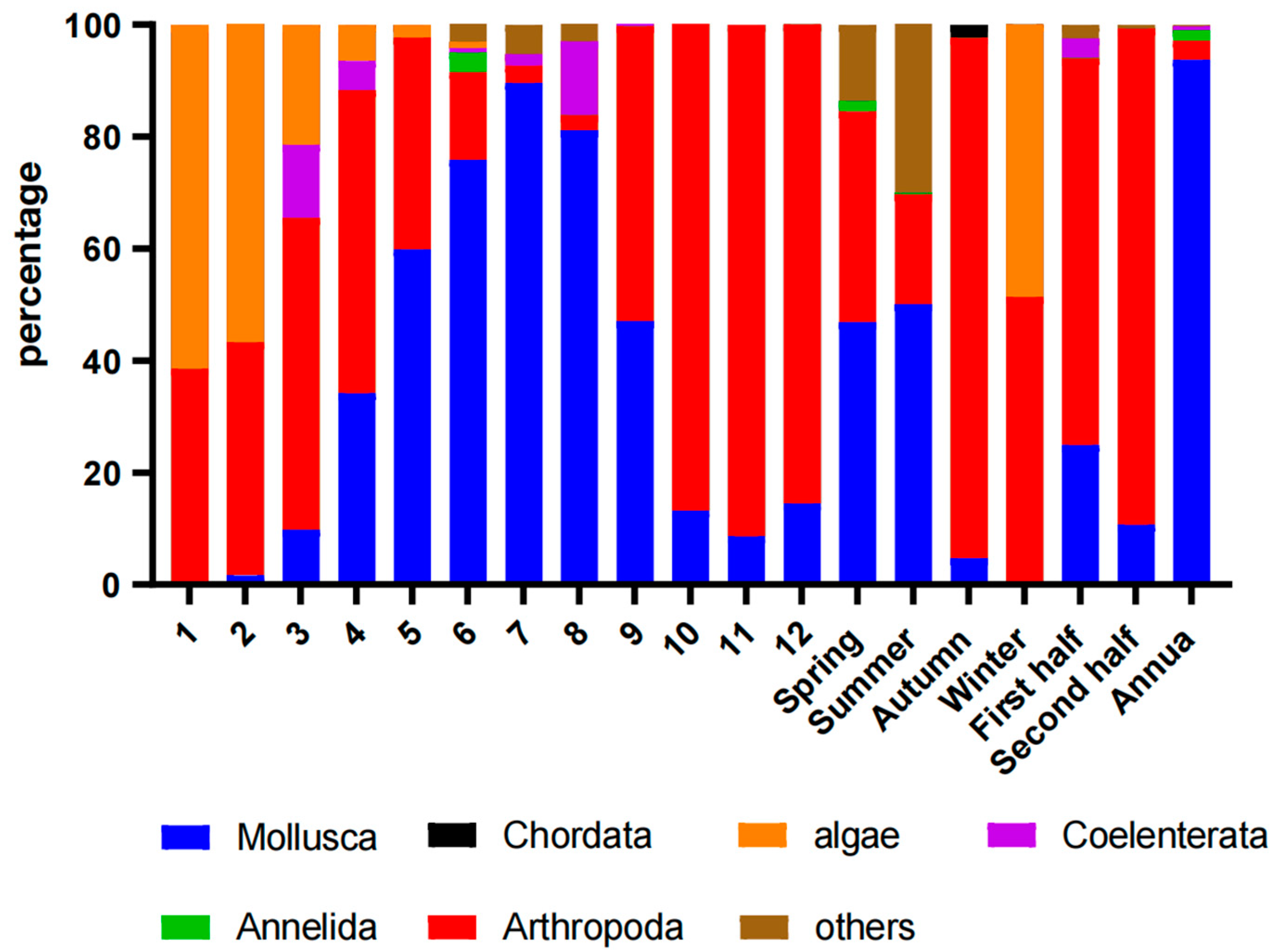
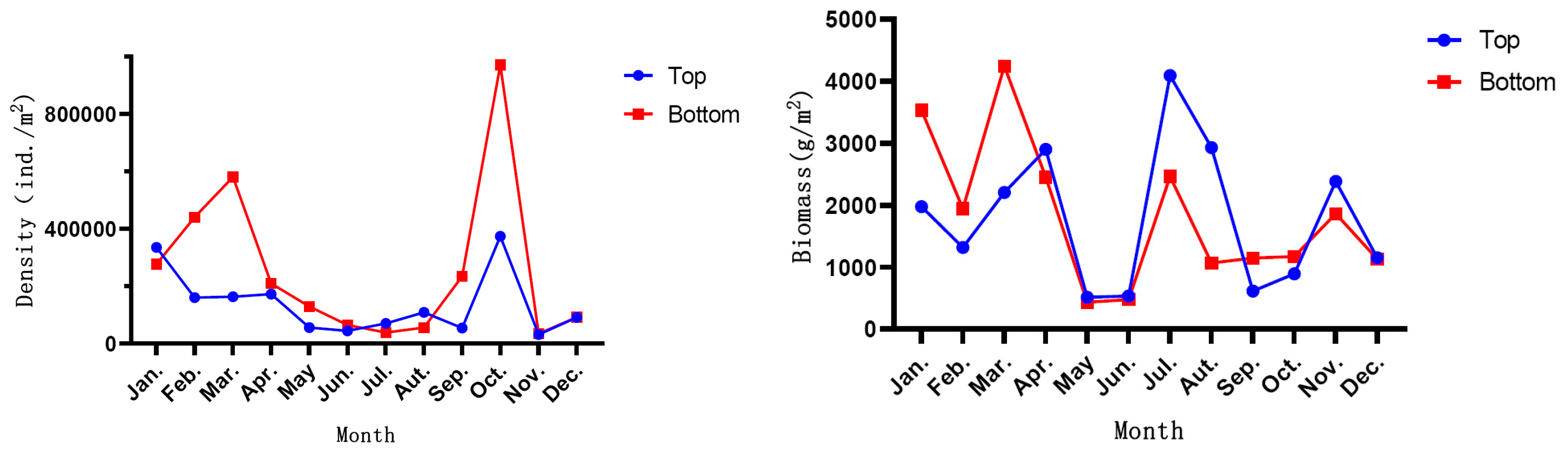
3.3. Settlement Rate and Its Spatiotemporal Variation
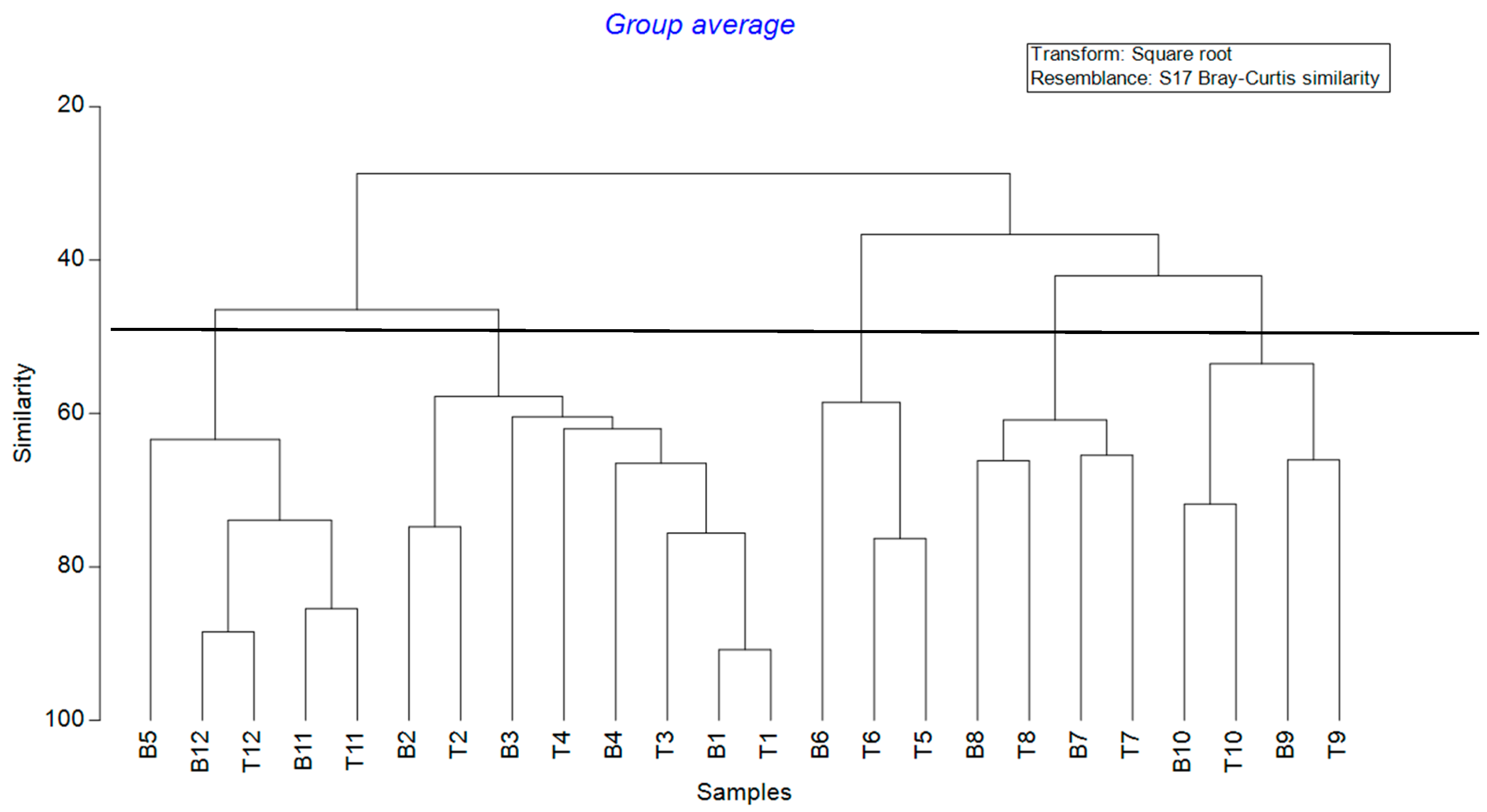
3.4. Seasonal Succession of Communities
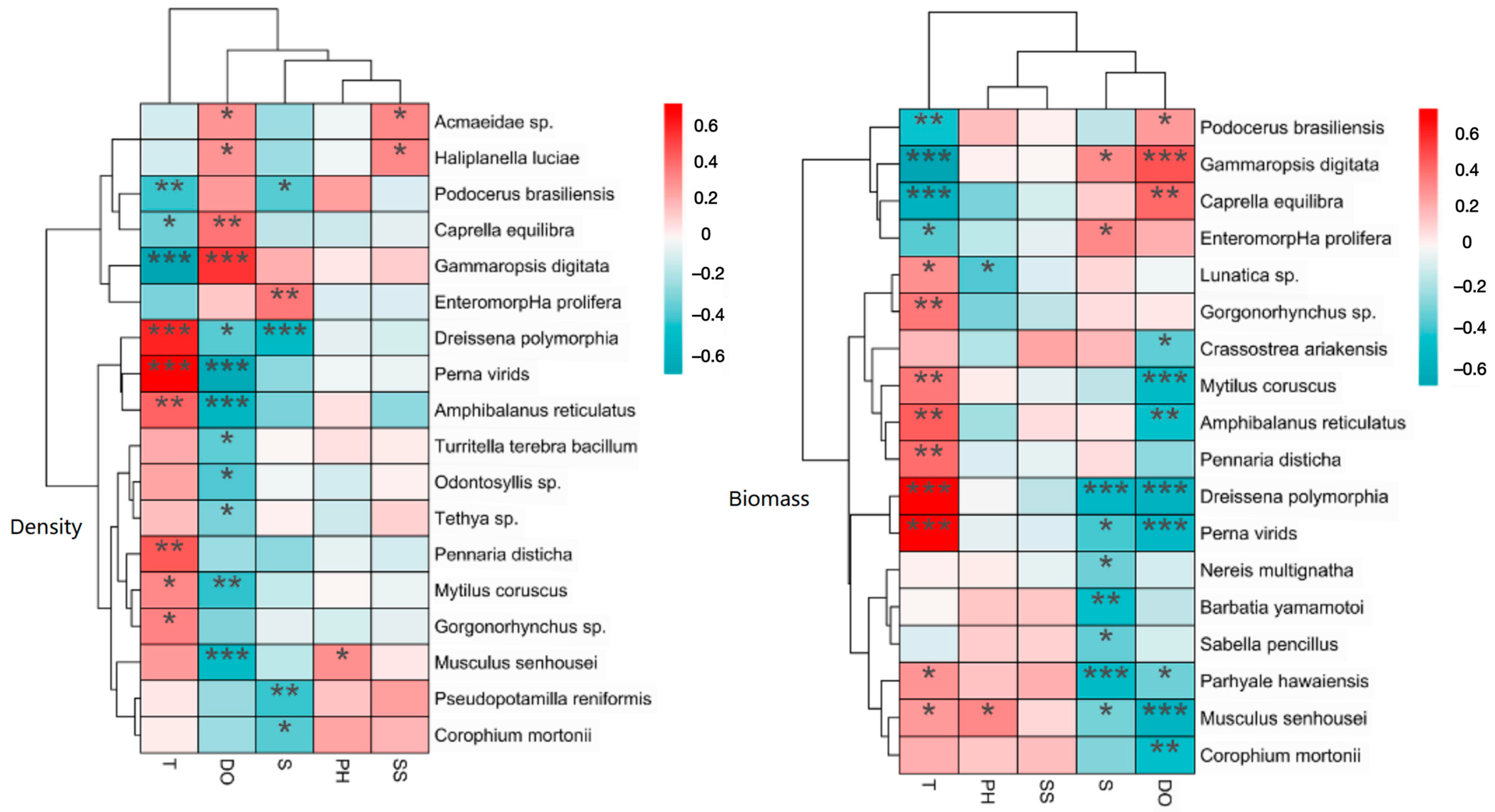
3.5. Correlation of Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, K.; Cong, W.; Gui, T.; Xing, T.; Wu, L. Effect and Remediation of Biofouling on Marine Aquaculture. Mater. Rep. 2020, 34, 78–81. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2018 Report. Guide Fish. Wealth Creat. 2018, 21, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Sun, Y.; He, J.; Chu, Y.; Sun, Z. Research progress of deep-water cage cleaning technology and devices. Fish. Mod. 2021, 48, 472–485. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, D.; Huang, Z. Fouling Organisms on Mariculture Cages in Daya Bay, China. J. Fish. Chin. 1990, 14, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, K.; Erdogan, U.H.; Cavas, L. Prevention of biofouling on aquaculture nets with ecofriendly antifouling paint formulation. Color. Technol. 2020, 136, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, S.; Lu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, J.; Wang, X. Community Structure of Macrobenthic Crustacean with the Relationship of Affected Factors in the East Coastal of Leizhou Peninsula. J. Guangdong Ocean. Univ. 2021, 41, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Callow, M. Ship fouling: Problems and solutions. Chem. Ind. Lond. 1990, 54, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Sammarco, P.W.; Atchison, A.D.; Boland, G.S. Expansion of coral communities within the northern gulf of Mexico via offshore oil and gas platforms. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 280, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Yan, W.; Dong, Y.; Wang, H.; Yan, Y.; Liang, G. Marine fouling of offshore installations in the northern beibu gulf of China. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2006, 58, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Yan, W.X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, H.J.; Yan, Y.; Liang, G.H. Marine fouling on floating installations west of dongsha islands, the northern south China Sea. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2009, 63, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, W.; Wu, Z.; Song, X.; Wang, J.; Yan, T. Biofouling on deep-sea submersible buoy systems off xisha and dongsha islands in the northern south China Sea. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 104, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.W.; Li, Z.; Lin, H.S.; Liu, K.; Huang, Y.Q.; Lin, J.H.; He, B.X.; Mou, J.F.; Zhang, S.Y.; Ma, L.; et al. Community structure and its spatio-temporal patterns of marine fouling organisms in xinghua bay, China. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2019, 38, 578–584. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Lin, H.S.; Li, Z.; He, X.B.; Huang, Y.Q.; Lin, J.H.; Mou, J.F.; Zhang, S.Y.; Ma, L.; Quan, J.J.; et al. Community structure of macro-fouling organisms in the northeastern waters of the pingtan island, East China Sea. Haiyang Xuebao 2020, 42, 70–82. [Google Scholar]
- Qvarfordt, S.; Kautsky, H.; Malm, T. Development of fouling communities on vertical structures in the Baltic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 67, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.S.; Wang, J.J.; Liu, W.; Liu, K.; Zhang, S.Y.; He, X.B.; Huang, Y.Q.; Lin, J.H.; Mou, J.F.; Zheng, C.X.; et al. Fouling community characteristics in subtropical coastal waters of the southwestern East China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 36, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Huang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yu, S.; Liu, K.; Mou, J.; Lin, J.; He, X.; Fu, S.; et al. Biofouling characteristics in Xinghua Bay of Fujian, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 9, 1107087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, J.K.; Grizzle, R.E. Successional development of fouling communities on open ocean aquaculture fish cages in the western gulf of Maine, USA. Aquaculture 2007, 262, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliskovic, M.; Jelic-Mrcelic, G.; Antolic, B.; Anicic, I. The fouling of fish farm cage nets as bioindicator of aquaculture pollution in the Adriatic Sea (Croatia). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ba-Akdah, M.A.; Satheesh, S.; El-Sherbiny, M.M.O. Biofouling Community Development on Commercial Cage Nets Submerged in a Cage Aquaculture Facility in the Red Sea. Thalassas 2020, 36, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Yan, W.X. Fouling of offshore structures in China—A review. Biofouling 2003, 19 (Suppl. S1), 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruzzo, D.; Conlan, S.; Aldred, N.; Clare, A.S.; Høeg, J.T. Video observation of surface exploration in cyprids of balanus amphitrite: The movements of antennular sensory setae. Biofouling 2011, 27, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, N.N.; Gohad, N.V.; Orihuela, B.; Burg, T.C.; Birchfield, S.T.; Rittschof, D.; Mount, A.S. Development of an automated algorithm for tracking and quantifying barnacle cyprid settlement behavior. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 410, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Wang, G.C.; Xu, Y.; Sougrat, R.; Qian, P.Y. The effect of butenolide on behavioural and morphological changes of marine fouling species balanus amphitrite and bugula neritina. Biofouling 2011, 27, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasso, M.; Conlan, S.L.; Clare, A.S.; Werner, C. Active enzyme nanocoatings affect settlement of balanus amphitrite barnacle cyprids. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Yan, T.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Cheng, Z. Fouling acorn barnacles in China—A review. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2013, 31, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, M.; Wu, Q. Study for Developing Resources of Marine Culture and Propagation in Zhanjiang Harbor and Leizhou Bay. J. Zhanjiang Fish. Coll. 1993, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 12763.6-2007; Specifications for Oceanographic Survey—Part 6: Exchange of Oceanographic Survey Data. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China, Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Pinkas, L. Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna, and bonito in California waters. Fish. Bull. 1971, 152, 1–105. [Google Scholar]
- Wekemo Bioincloud, Correlation Analysis. Available online: https://bioincloud.tech (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- Hamilton, M.A.; Russo, R.C.; Thurston, R.V. Trimmed Spearman-Karber method for estimating median lethal concentrations in toxicity bioassays. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1977, 11, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, J.B.; Sun, X.L.; Chen, C.L. Trait fouling organism community in wastewater discharge area of desulfurized power plant in Zhanjiang Bay. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2018, 37, 395–403. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.S.; Cao, W.H.; Chen, D.; Xie, E.Y.; Yan, T. Review of fouling ascidians in the coastal waters of China. Ecol. Sci. 2018, 37, 186–191. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, T.; Li, Z.F.; Hu, Y.F.; Li, X.X.; Cao, W.H.; Luo, W.J.; Cheng, Z.Q. A review on the balanomorph barnacles in the coastal waters of China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 5230–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.L. Study on Ecology of Marine Fouling Organisms in Cage-Acquaculture Areas, Tong’an Bay. Master’s Thesis, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dziubińska, A.; Janas, U. Submerged objects-a nice place to live and develop. Succession of fouling communities in the Gulf of Gdańsk, Southern Baltic. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2007, 36, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogata, Y.; Tokikuni, N.; Yoshimura, E.; Sato, K.; Endo, N.; Matsumura, K.; Sugita, H. Salinity limitations on larval settlement of four barnacle species. Sess. Org. 2011, 28, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.H.; Yan, J.; Feng, M.P.; Han, S.S.; Lin, M.Q. Effect of salinity on larval development of the two common barnacles from the southeast coast of China. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2018, 37, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.Q.; Cai, L.Z.; Huang, R.J.; Zhou, X.P.; Fu, S.J.; Lin, H.S.; Huang, K. Species composition of trawling mollusk in Beibu Gulf and its environmental effect. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2010, 29, 617–622. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Yan, X.W.; Han, H.; Sang, S.T.; Zhai, Z.M.; Liu, Z.; Liang, J.; Chi, J.X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, G.F. The influence of salinity on hatching, growth and survival of larvae and juveniles in green mussel Perna viridis. J. Dalian Ocean Univ. 2013, 28, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.C.; Luo, Q.; Yuan, S.; Li, N.; Qin, T.T.; Liu, L.G.; Cheng, L.G. Water quality of shrimp ditch and its effects on crayfish yield in shrimp and rice co-cropping fields. Chin. Rural Water Hydropower 2022, 10, 158–162. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.G.; Xu, R.; Liu, C.C.; Qin, Y.T.; Cai, P. Characters of hypoxia area off the Yangtze River Estuary and its influence. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2012, 31, 588–593. [Google Scholar]

| Jan. | Feb. | Mar. | Apr. | May | Jun. | Jul. | Aug. | Sep. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L | Top | 55.4 | 0.8 | 11.6 | 77.8 | 44.3 | 22.8 | 55.6 | 33.6 | 33.0 | 11.6 | 55.9 | 55.8 |
| Bottom | 44.5 | 22.5 | 33.8 | 55.7 | 45.6 | 22.9 | 66.8 | 22.6 | 33.0 | 11.6 | 55.1 | 55.7 | |
| Species Name | Mean Density/ind.·m−2 | Mean Biomass/g·m−2 | IRI | Lifestyle | Functional Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perna viridis | 12,904.6 | 89.4 | 2592 | A | S |
| Podocerus brasiliensis | 68,832.2 | 341.3 | 2580 | M | D |
| Gammaropsis digitata | 24,896.0 | 264.1 | 2256 | M | D |
| Stenothoe gallensis | 19,056.3 | 140.9 | 1706 | M | D |
| Amphibalanus reticulatus | 322.5 | 8.9 | 939 | SE | S |
| Enteromorpha prolifera | 33,264.3 | 289.2 | 287 | A | PP |
| Dreissena polymorphia | 25,412.1 | 397.8 | 272 | A | S |
| Parhyale hawaiensis | 225.2 | 6.2 | 92 | M | D |
| Caprella equilibra | 6055.0 | 58.3 | 85 | M | D |
| Pennaria disticha | 2343.5 | 65.3 | 48 | SE | S |
| Gracilaria bailinae | 819.2 | 27.2 | 46 | A | PP |
| Musculus senhousei | 2603.3 | 46.1 | 37 | A | S |
| Crassostrea ariakensis | 0 | 7.9 | 29 | SE | S |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, L. Fouling Community Characteristics in Sea Cage Farms in Leizhou Bay, China. Water 2025, 17, 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040495
Zhang Y, Zhou J, Liu L. Fouling Community Characteristics in Sea Cage Farms in Leizhou Bay, China. Water. 2025; 17(4):495. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040495
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yanping, Jiali Zhou, and Li Liu. 2025. "Fouling Community Characteristics in Sea Cage Farms in Leizhou Bay, China" Water 17, no. 4: 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040495
APA StyleZhang, Y., Zhou, J., & Liu, L. (2025). Fouling Community Characteristics in Sea Cage Farms in Leizhou Bay, China. Water, 17(4), 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040495






