Assessment and Seasonal Monitoring of Groundwater Quality in Landfill-Affected Regions of China: Findings from Xiangyang
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Strategy
2.3. Field Investigations
- Detailed surveys of landfill infrastructure, including containment systems, leachate collection mechanisms, and surrounding drainage patterns.
- Observations of potential pollution pathways, such as leachate seepage, cracks in landfill liners, and visible discoloration of nearby vegetation.
- Recording hydrogeological data, including aquifer characteristics and groundwater flow directions, to understand the movement of contaminants.
2.4. Analytical Methods
| Parameter Category | Analytical Method | Equipment | Method Reference | QC Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Control Ions (K, Na, Ca, Mg) | ICP-OES/EDTA Titration | Thermo Fisher iCAP PRO (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) | HJ 776-2015 [24], DZ/T 0064.13/14-2021 [25] | Recovery: 70–120% (≤10 MDL), 70–130% (>10 MDL) |
| Anions (SO₄2−, Cl−, NO₃−, NO₂−, F−) | Ion Chromatography | Thermo Fisher AQ-1100 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) | HJ 84-2016 [26] | Recovery: 80–120% |
| Heavy Metals | ICP-MS | Thermo Fisher iCAP RQ (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) | HJ 700-2014 [27] | Recovery: 70–130%, RSD ≤20% |
| Mercury, As, Se, Sb | Atomic Fluorescence | Beijing Kechuang AFS-8500 (Beijing Kechuang Haiguang Instrument Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) | HJ 694-2014 [28] | Recovery: 70–130%, RSD ≤20% |
| Volatile Organic Compounds | Purge-and-Trap GC-MS | Agilent 8860-5977B (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) | HJ 639-2012 [29] | Recovery: 60–130%, RSD ≤30% |
| PCBs and Organochlorine Pesticides | GC | Agilent 8860 (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) | SL 497-2010 [30] | Recovery: 70–120%, RSD ≤30% |
| PAHs | HPLC | Agilent 1260II (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) | HJ 478-2009 [31] | Recovery: 60–120%, RSD ≤30% |
| Conventional Parameters (pH, TDS, DO) | Multiple Methods | Various | Multiple Standards | Method-specific |
2.5. Data Analysis and Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Groundwater Quality Assessment
3.2. Pollution Patterns and Key Contaminants
3.3. Seasonal Variations in Contamination
3.4. Source Attribution and Pollution Dynamics
3.5. Additional Water Quality Indicators
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Recommendations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Yue, J.; Su, Y.; Cheng, W.; Sun, S.; Chen, X.; Shi, D.; Liu, B. Emerging contaminants in landfill leachate and groundwater: A case study of hazardous waste landfill and municipal solid waste landfill in Northeastern China. Water 2024, 16, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baderna, D.; Maggioni, S.; Boriani, E.; Gemma, S.; Molteni, M.; Lombardo, A.; Colombo, A.; Bordonali, S.; Rotella, G.; Lodi, M.; et al. A combined approach to investigate the toxicity of an industrial landfill’s leachate: Chemical analyses, risk assessment and in vitro assays. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggen, T.; Moeder, M.; Arukwe, A. Municipal landfill leachates: A significant source for new and emerging pollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5147–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Shi, G.; He, L.; Wei, L.; Shi, Q. A review of groundwater contamination near municipal solid waste landfill sites in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Yang, X.; Xu, P.; Wan, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, D.; Razzaq, A. Linking Water Quality Indicators in Stable Reservoir Ecosystems: Correlation Analysis and Ecohydrological Implications. Water 2024, 16, 3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, P. Appraisal of shallow groundwater quality with human health risk assessment in different seasons in rural areas of the Guanzhong Plain (China). Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, G.; Yuan, Y.; Xi, B.; Li, R. Assessment of the impact of landfills on groundwater quality in Eastern China: A comprehensive analysis of inorganic solutes. Environ. Earth Sci. 2024, 83, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Li, T.; Hu, S.; Zhou, X. Evaluation of Human Health Risks Associated with Groundwater Contamination and Groundwater Pollution Prediction in a Landfill and Surrounding Area in Kaifeng City, China. Water 2023, 15, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Liu, Y.; You, S.; Zeng, G.; Tan, X.; Hu, X.; Hu, X.; Huang, L.; Li, F. Spatial distribution, health risk assessment and statistical source identification of the trace elements in surface water from the Xiangjiang River, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 9400–9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Hu, L.; Han, Y.; Dong, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ying, G. Non-target and target screening of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in landfill leachate and impact on groundwater in Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mepaiyeda, S.; Madi, K.; Gwavava, O.; Baiyegunhi, C. Geological and geophysical assessment of groundwater contamination at the Roundhill landfill site, Berlin, Eastern Cape, South Africa. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Su, Y.; Miao, K. Modelling Groundwater Flow and Contaminant Migration in Heterogeneous Fractured Media at a Municipal Solid Waste Landfill in Nanjing Lishui, China. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 8391260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, J. Review of groundwater nitrate pollution from municipal landfill leachate and its health effects. Expo. Health 2024, 16, 123–135. [Google Scholar]
- Aghapour, S.; Bina, B.; Tarrahi, M.; Amiri, F.; Ebrahimi, A. Comparative health risk assessment of nitrate in drinking groundwater resources of urban and rural regions (Isfahan, Iran), using GIS. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, E.; Morales, P.; Zamora, G.; Sánchez, E.; Calderón, E.; De Jesús Alba Romero, J.; Rincón, E. Consumption of water contaminated by nitrate and its deleterious effects on the human thyroid gland: A review and update. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2020, 32, 984–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.; Parvez, F.; Zoeller, R.; Hocevar, B.; Kamendulis, L.; Rohlman, D.; Eunus, M.; Graziano, J. Thyroid hormones and neurobehavioral functions among adolescents chronically exposed to groundwater with geogenic arsenic in Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilpazeer, F.; Munir, M.; Baloch, M.; Shafiq, I.; Iqbal, J.; Saeed, M.; Abbas, M.; Shafique, S.; Aziz, K.; Mustafa, A.; et al. A Comprehensive Review of the Latest Advancements in Controlling Arsenic Contaminants in Groundwater. Water 2023, 15, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toolabi, A.; Bonyadi, Z.; Paydar, M.; Najafpoor, A.; Ramavandi, B. Spatial distribution, occurrence, and health risk assessment of nitrate, fluoride, and arsenic in Bam groundwater resource, Iran. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 12, 100543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilkarnjanakul, W.; Watchalayann, P.; Chotpantarat, S. Spatial distribution and health risk assessment of As and Pb contamination in the groundwater of Rayong Province, Thailand. Environ. Res. 2021, 204, 111838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, M.; Bommarito, P.; George, A.; Yelton, S.; Cable, P.; Coyte, R.; Karr, J.; Vengosh, A.; Gray, K.; Fry, R. Assessment of inorganic contamination of private wells and demonstration of effective filter-based reduction: A pilot-study in Stokes County, North Carolina. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ164-2020; Water Quality—Determination of Inorganic Anions by Ion Chromatography. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020.
- GB/T 14848-2017; Groundwater Quality Standard. China National Standardization Management Committee: Beijing, China, 2017.
- GB3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- HJ 776-2015; Water Quality—Determination of 32 Elements—Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015.
- DZ/T 0064.13/14-2021; Water Quality—Determination of Heavy Metals—ICP-OES. China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- HJ 84-2016; . Water Quality—Determination of Inorganic Anions (F⁻, Cl⁻, NO₂⁻, Br⁻, NO₃⁻, PO43−, SO32−, SO42−)—Ion Chromatography. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- HJ 700-2014; Water Quality—Determination of 65 Elements—Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014.
- HJ 694-2014; Water Quality—Determination of Mercury, Arsenic, Selenium, Bismuth and Antimony—Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014.
- HJ 639-2012; Water Quality—Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds—Purge and Trap/Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- SL 497-2010; . Water Quality—Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons—High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China, China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2010.
- HJ 478-2009; Water Quality—Determination of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons—Liquid-Liquid Extraction-High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Adimalla, N.; Qian, H.; Nandan, M.J. Groundwater chemistry integrating the pollution index of groundwater and evaluation of potential human health risk: A case study from hard rock terrain of south India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, S.; Azarnivand, A.; Chitsaz, N. Groundwater quality classification derivation using Multi-Criteria-Decision-Making techniques. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 78, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Sun, Z. Evaluation of Shallow Groundwater Contamination and Associated Human Health Risk in an Alluvial Plain Impacted by Agricultural and Industrial Activities, Mid-west China. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobeloch, L.; Salna, B.; Hogan, A.; Postle, J.; Anderson, H. Blue babies and nitrate-contaminated well water. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odiyo, J.; Makungo, R. Chemical and Microbial Quality of Groundwater in Siloam Village, Implications to Human Health and Sources of Contamination. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayub, R.; Messier, K.P.; Serre, M.L.; Mahinthakumar, K. Non-point source evaluation of groundwater nitrate contamination from agriculture under geologic uncertainty. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2019, 33, 939–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakida, F.T.; Lerner, D.N. Non-agricultural sources of groundwater nitrate: A review and case study. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratiwi, W.H.; Putri, G.L.; Pratama, M.A.; Zulkarnain, F.; Priadi, C.R. Health risk analysis of nitrite, nitrate, and heavy metal pollution in groundwater near landfill area: A case study of the Sumur Batu village in Bekasi, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 633, 012015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiddee, P.; Naidu, R.; Wong, M.H. Metals and polybrominated diphenyl ethers leaching from electronic waste in simulated landfills. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 252, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Tong, X.; Currell, M.J.; Cao, G.; Jin, M.; Tong, C. Evaluation of the impact of an uncontrolled landfill on surrounding groundwater quality, Zhoukou, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 136, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrete-Bolagay, D.; Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Chuya-Sumba, C.; De Sousa, F.B.; Whitehead, D.; Alexis, F.; Guerrero, V.H. Persistent organic pollutants: The trade-off between potential risks and sustainable remediation methods. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Li, Q.; Zheng, M.; Su, G.; Lin, S.; Wu, M.; Li, C.; Wang, Q.; Tao, Y.; Dai, L.; et al. Recent advances in the removal of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) using multifunctional materials: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjito, H.; Suntoro, S.; Gunawan, T.; Maskuri, M. Underground Leachate Distribution Based on Electrical Resistivity in Piyungan Landfill, Bantul. Indones. J. Geogr. 2018, 50, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Chen, G.; Zhou, P.; Xu, H.; Qiong, A.; Duo, B.; Lu, X.; Wang, Z.; Han, Z. Factors influencing groundwater contamination near municipal solid waste landfill sites in the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 211, 111913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes Flores, C.A.; Ferreira Albuquerque Cunha, H.; Cavalcanti da Cunha, A. Hydrometeorological characterization and estimation of landfill leachate generation in the Eastern Amazon/Brazil. PeerJ 2023, 11, e14686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, F.; Tareq, S.M. Impact of landfill leachate contamination on surface and groundwater of Bangladesh: A systematic review and possible public health risks assessment. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Verma, A.; Rajamani, P. Impact of landfill leachate on groundwater quality: A review. In A Review of Landfill Leachate; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 93–107. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, U.; Reddy, B.; Singh, V.; Singh, A.; Kesari, K.; Tripathi, P.; Kumar, P.; Tripathi, V.; Simal-Gándara, J. Potential Environmental and Human Health Risks Caused by Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria (ARB), Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARGs) and Emerging Contaminants (ECs) from Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Landfill. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Careghini, A.; Mastorgio, A.; Saponaro, S.; Sezenna, E. Bisphenol A, nonylphenols, benzophenones, and benzotriazoles in soils, groundwater, surface water, sediments, and food: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 22, 5711–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrie, B.; Barden, R.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. A review on emerging contaminants in wastewaters and the environment: Current knowledge, understudied areas and recommendations for future monitoring. Water Res. 2015, 72, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Huang, J.; Wang, B.; Deng, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, G. Contaminants of emerging concern in landfill leachate in China: A review. Emerg. Contam. 2018, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, H.; Karmakar, S.; Kumar, R.; Kadambala, P. A long-term comparative assessment of human health risk to leachate-contaminated groundwater from heavy metal with different liner systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 2911–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regadío, M.; Ruiz, A.I.; Rodríguez-Rastrero, M.; Cuevas, J. Containment and attenuating layers: An affordable strategy that preserves soil and water from landfill pollution. Waste Manag. 2015, 46, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 14848-2017; Standard for Groundwater Quality. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
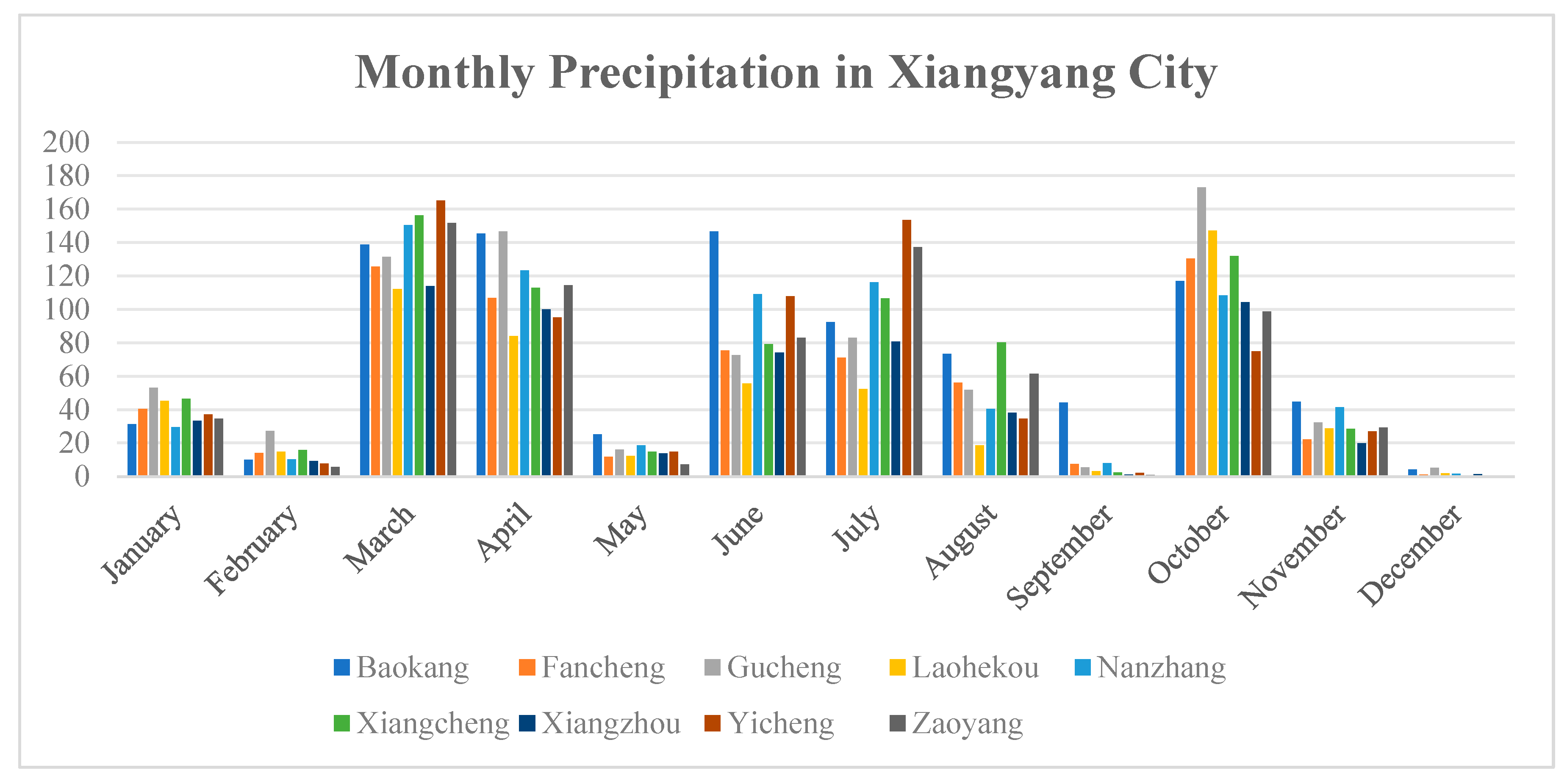

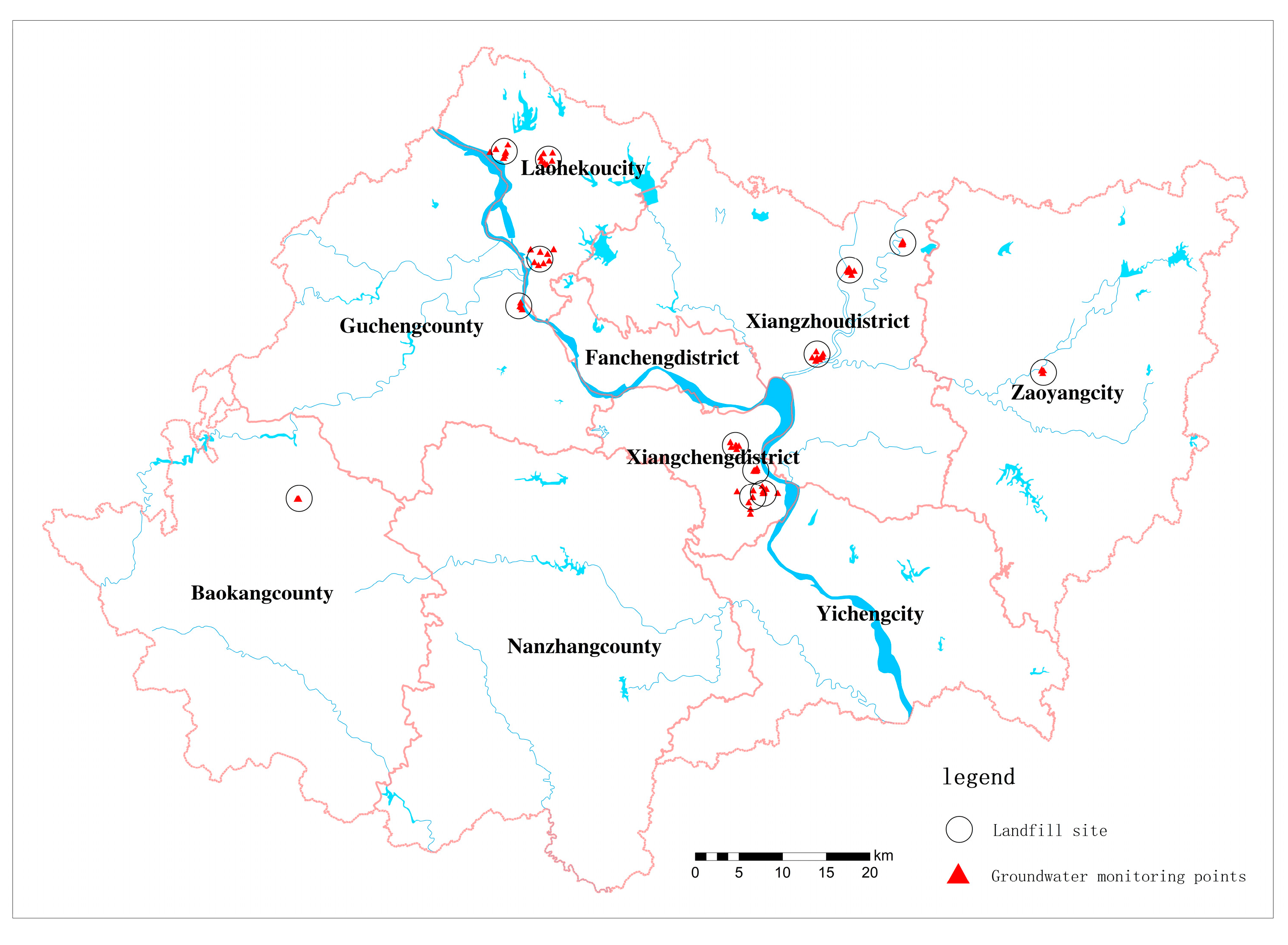
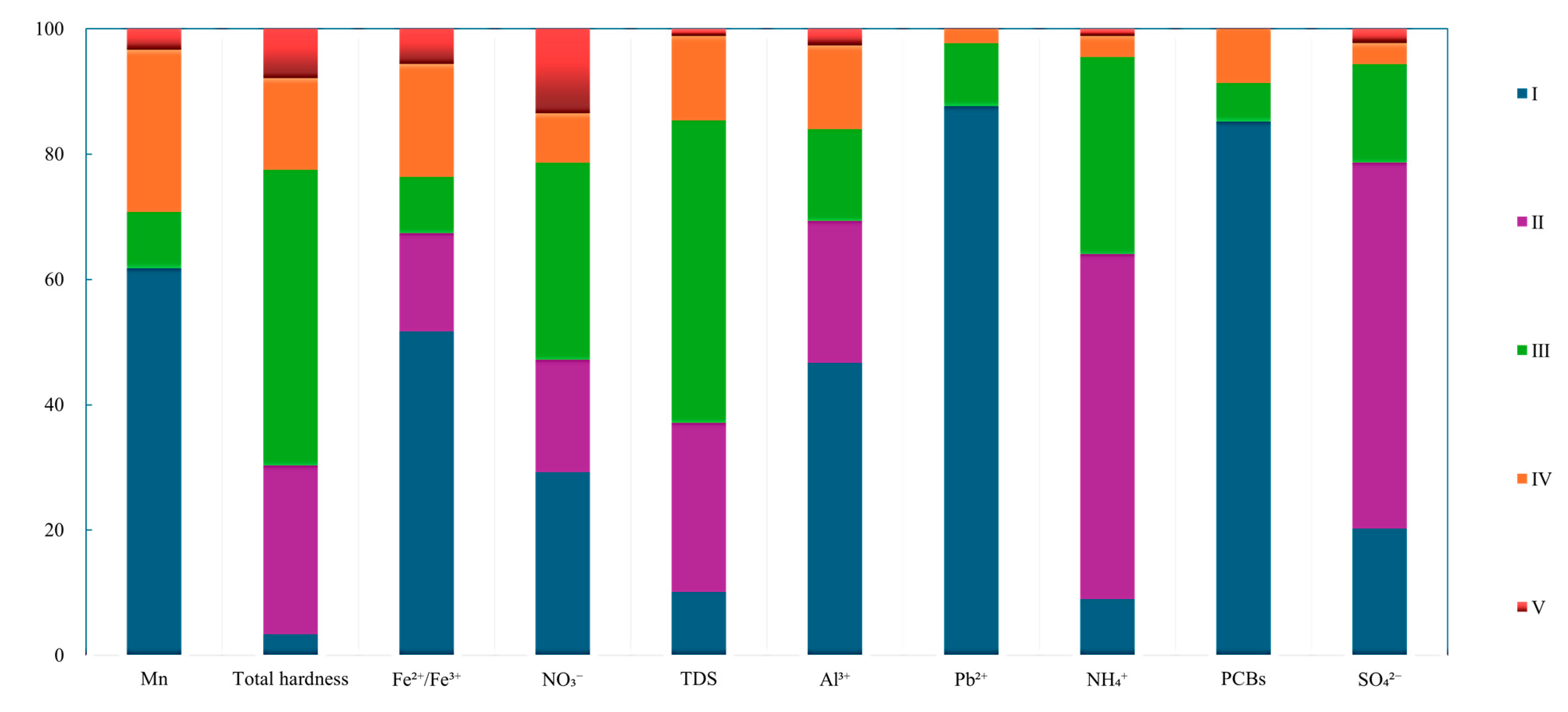
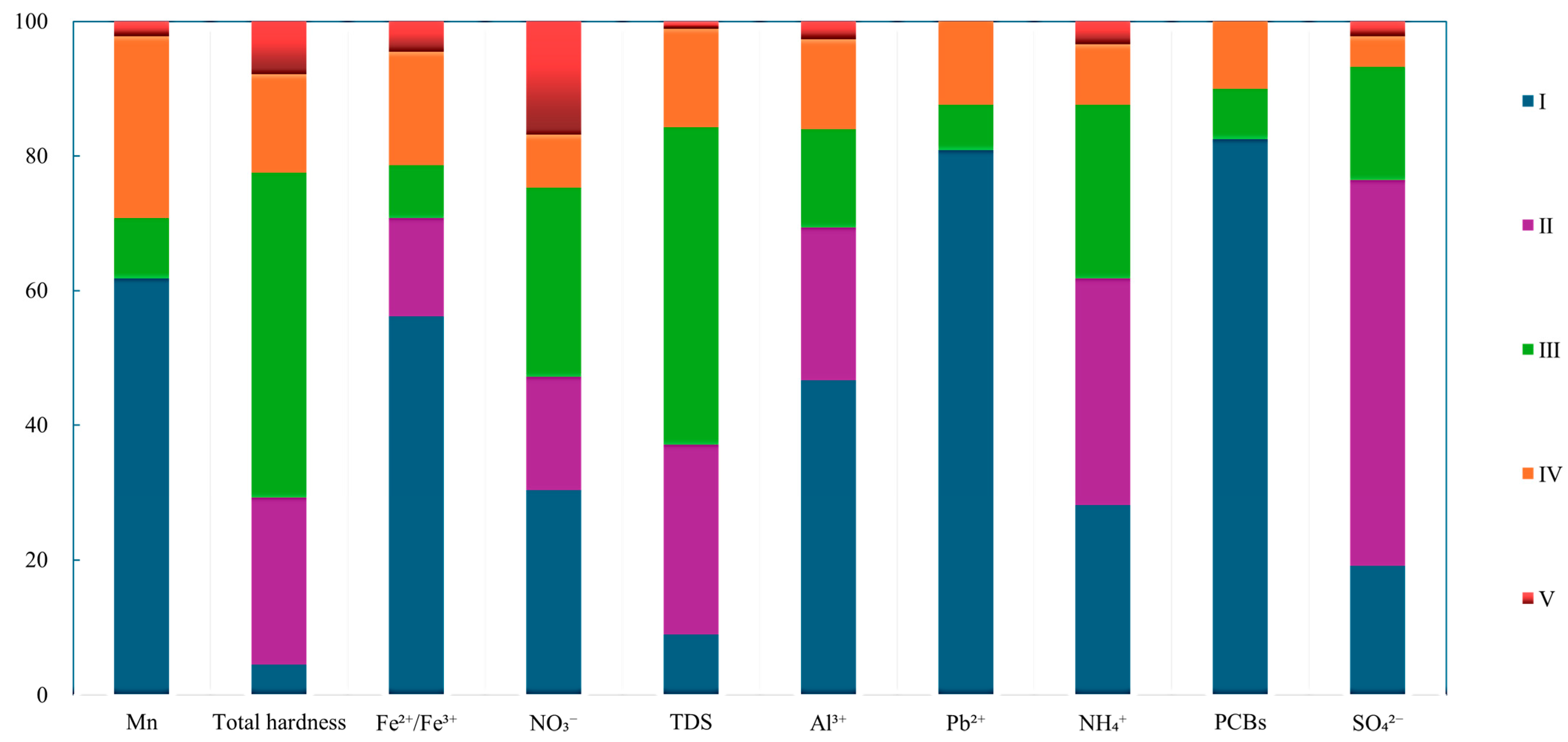
| No. | Counties and Urban Areas | Landfill Site (Coded) | Number of Monitoring Points (s) | Sample Data (Group) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Laohekou City | L1 | 7 | 14 |
| 2 | L2 | 7 | 14 | |
| 3 | L3 | 8 | 16 | |
| 4 | Zaoyang City | L4 | 5 | 10 |
| 5 | Gucheng County | L5 | 5 | 10 |
| 6 | Baokang County | L6 | 4 | 8 |
| 7 | Xiangcheng District | L7 | 8 | 16 |
| 8 | L8 | 5 | 10 | |
| 9 | L9 | 8 | 16 | |
| 10 | L10 | 8 | 16 | |
| 11 | Xiangzhou District | L11 | 8 | 16 |
| 12 | L12 | 8 | 16 | |
| 13 | L13 | 8 | 16 | |
| Total | 13 | 89 | 178 | |
| Indicator Type | Name of Index | Number of Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Natural control ions | Potassium (K), Calcium (Ca), Sodium (Na), Magnesium (Mg), Sulfate (SO42−), Chloride (Cl−), Carbonate (CO32−), Bicarbonate (HCO3−) | 8 |
| Conventional indicators | pH, Dissolved Oxygen (DO), Redox Potential (Eh), Conductivity, Color, Odor, Turbidity, Total Hardness, Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), Iron (Fe), Manganese (Mn), Copper (Cu), Zinc (Zn), Volatile Phenols, Synthetic Detergents (anionic), Permanganate Index, Nitrate (NO3−-N), Nitrite (NO2−-N), Ammonia (NH3-N), Fluoride (F−), Cyanide (CN−), Mercury (Hg), Arsenic (As), Selenium (Se), Cadmium (Cd), Chromium (Cr6+), Lead (Pb), Total Coliform Bacteria | 29 |
| Organo-Chlorine Pesticides | Hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH), Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT), p,p-DDT, Hexachlorobenzene | 4 |
| Halogenated Hydrocarbons | Trichloromethane (CHCl3), Dichloromonobromomethane, Tribromomethane (CHBr3), Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl4), Vinyl Chloride (C2H3Cl) | 5 |
| Halogenated Hydrocarbons | Chlorobenzene | 1 |
| Monocyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons | Benzene (C6H6), Toluene (C7H8), Ethylbenzene (C8H10), Xylene (C8H10), Styrene (C8H8) | 5 |
| Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) | Benzo(a)pyrene (BaP) | 1 |
| Inorganic Components | Total Phosphorus (P), Bromide (Br−), Thallium (Tl), Total Chromium (Cr) | 4 |
| Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) | Polychlorinated Biphenyl | 1 |
| Overall Organic Components | Total Organic Carbon (TOC) | 1 |
| Esters | Di(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate, Di(2-ethylhexyl) Adipate, Di(2-ethyl) Phosphate | 3 |
| No. | Landfill Site (Coded) | No. of Monitoring Sites | Monitoring Period | No. of Class I Wells (s) | No. of Class IV Wells (s) | No. of Class V Wells (s) | Comprehensive Water Quality Category | Indicators Exceeding Standards (Category IV and V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L1 | 7 | wet season | 2 | 2 | 3 | III | Total hardness, soluble total solids, chloride, manganese, aluminum, nitrate |
| dry season | 3 | 1 | 3 | |||||
| 2 | L2 | 7 | wet season | 3 | 3 | 1 | III | Total hardness, soluble total solids, iron, manganese, aluminum, oxygen consumption, nitrite, nitrate |
| dry season | 3 | 3 | 1 | |||||
| 3 | L3 | 8 | wet season | 1 | 6 | 1 | III | Total hardness, iron, manganese, aluminum, ammonia nitrogen |
| dry season | 0 | 6 | 2 | |||||
| 4 | L4 | 5 | wet season | 0 | 4 | 1 | IV | Total hardness, chloride, iron, manganese, ammonia nitrogen, sodium, nitrite, fluoride, lead, carbon tetracloride, polychlorinated biphenyls (total amount) |
| dry season | 0 | 4 | 1 | |||||
| 5 | L5 | 5 | wet season | 0 | 4 | 1 | V | Iron, manganese, ammonia nitrogen, nitrite, lead, benzoa (a) pyrene, polychlorinated biphenyl (total amount), 6666 (total amount), DDT (total amount), hexachlorobenzene |
| dry season | 0 | 5 | 0 | |||||
| 6 | L6 | 4 | wet season | 0 | 2 | 2 | IV | Total hardness, sulfate, iron, manganese, ammonia nitrogen, nitrite, nitrate, lead, polychlorinated biphenyls (total amount) |
| dry season | 0 | 2 | 2 | |||||
| 7 | L7 | 8 | wet season | 3 | 4 | 1 | III | Total hardness, soluble total solids, sulfate, manganese, aluminum, nitrate |
| dry season | 3 | 4 | 1 | |||||
| 8 | L8 | 5 | wet season | 3 | 2 | 0 | III | Chlorides, nitrites |
| dry season | 3 | 2 | 0 | |||||
| 9 | L9 | 8 | wet season | 1 | 3 | 4 | III | Total hardness, soluble total solids, sulfate, chloride, iron, manganese, aluminum, oxygen consumption, ammonia nitrogen, nitrate |
| dry season | 1 | 3 | 4 | |||||
| 10 | L10 | 8 | wet season | 2 | 2 | 4 | III | Total hardness, soluble total solids, iron, manganese, aluminum, nitrates, iodide |
| dry season | 2 | 2 | 4 | |||||
| 11 | L11 | 8 | wet season | 0 | 4 | 4 | III | Zinc, aluminum, and nitrate |
| dry season | 0 | 4 | 4 | |||||
| 12 | L12 | 8 | wet season | 2 | 4 | 2 | IV | Total hardness, soluble total solids, sulfate, aluminum, nitrate, and arsenic |
| dry season | 2 | 4 | 2 | |||||
| 13 | L13 | 8 | wet season | 7 | 1 | 0 | III | Aluminium |
| dry season | 7 | 1 | 0 |
| Pollutant Type | Parameter | Monitoring Period | Number of Wells Exceeding Standard | Exceedance Rate (%) | Range of Exceedance (Times Over Limit) | Number of Affected Landfills | Landfill Site with Maximum Exceedance (Coded) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional indicators | Manganese | Wet season | 26 | 29.21 | 0.05–18.6 | 9 | L9 |
| Dry season | 26 | 29.21 | 0.26–18.3 | 9 | L9 | ||
| Nitrate | Wet season | 19 | 21.35 | 0.045–4.75 | 8 | L6 | |
| Dry season | 18 | 20.22 | 0.01–4.6 | 8 | L6 | ||
| Total Hardness | Wet season | 20 | 22.47 | 0.0234–2.62 | 9 | L9 | |
| Dry season | 20 | 22.47 | 0.013–2.55 | 9 | L9 | ||
| Iron | Wet season | 19 | 21.35 | 0.13–12.1 | 7 | L9 | |
| Dry season | 21 | 23.60 | 0.1–18.47 | 7 | L3 | ||
| Soluble total solids | Wet season | 14 | 15.73 | 0.05–1.82 | 6 | L9 | |
| Dry season | 13 | 14.61 | 0.01–1.76 | 6 | L9 | ||
| Aluminum | Wet season | 12 | 16.00 | 0.04–12.1 | 9 | L10 | |
| Dry season | 12 | 16.00 | 0.38–11.5 | 8 | L10 | ||
| Ammonia nitrogen | Wet season | 10 | 11.24 | 0.21–8.63 | 5 | L4 | |
| Dry season | 4 | 4.49 | 0.334–3.02 | 2 | L9 | ||
| Sulfate | Wet season | 6 | 6.74 | 0.012–1.032 | 4 | L12 | |
| Dry season | 5 | 5.62 | 0.148–0.956 | 4 | L12 | ||
| Nitrite | Wet season | 2 | 2.25 | 0.5–1.62 | 2 | L5 | |
| Dry season | 5 | 5.62 | 0.27–10.10 | 4 | L6 | ||
| Chloride | Wet season | 5 | 5.62 | 0.3068–1.448 | 4 | L9 | |
| Dry season | 5 | 5.62 | 0.284–1.432 | 4 | L9 | ||
| Zinc | Wet season | 2 | 2.25 | 0.09–0.18 | 1 | L11 | |
| Dry season | 1 | 1.12 | 0.06 | 1 | L11 | ||
| Consumed oxygen | Wet season | 2 | 2.67 | 0.267–2.267 | 2 | L9 | |
| Dry season | 2 | 2.67 | 0.167–2.1 | 2 | L9 | ||
| Iodide | Wet season | 1 | 1.33 | 0.2526 | 1 | L10 | |
| Sodium | Wet season | 1 | 1.12 | 0.04405 | 1 | L4 | |
| Fluoride | Wet season | 1 | 1.12 | 0.04 | 1 | L4 | |
| Heavy metal indicators | Lead | Wet season | 11 | 12.36 | 0.14–7.6 | 4 | L6 |
| Dry season | 2 | 2.25 | 0.07–1.7 | 2 | L6 | ||
| Arsenic | Wet season | 3 | 3.37 | 0.38–3.13 | 2 | L12 | |
| Dry season | 3 | 3.37 | 0.26–2.86 | 2 | L12 | ||
| Organic pollutants | Polychlorinated biphenyl (Total) | Wet season | 8 | 10.00 | 0.42–2.82 | 2 | L5 |
| Dry season | 7 | 8.64 | 0.1–4.76 | 3 | L5 | ||
| Pesticides | Hexachlorobenzene | Wet season | 4 | 18.18 | 0.15–3.84 | 1 | L5 |
| Benzex (Total) | Dry season | 1 | 4.35 | 0.319 | 1 | L5 | |
| DDT (Total) | Dry season | 1 | 4.35 | 0.042 | 1 | L5 | |
| Halogenated hydrocarbon | Carbon tetrachloride | Wet season | 3 | 3.37 | 1.785–4.41 | 1 | L4 |
| Cycloaromatic hydrocarbons | Benzo(a)pyrene | Dry season | 2 | 2.47 | 3.38–4.72 | 1 | L5 |
| Metric | Count | Landfill Sites (Coded) |
|---|---|---|
| Total Organic Carbon (TOC) | 3 | L6, L5, L4 |
| Dichloromonobromomethane | 2 | L6, L4 |
| Bromide | 3 | L6, L5, L4 |
| Permanganate Index | 1 | L6 |
| Total Phosphorus | 2 | L6, L4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, J.; Yang, W.; Yang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wan, X.; Zhu, A.; He, Z.; Shrestha, R.P.; Razzaq, A. Assessment and Seasonal Monitoring of Groundwater Quality in Landfill-Affected Regions of China: Findings from Xiangyang. Water 2025, 17, 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040572
Du J, Yang W, Yang Q, Li Y, Wan X, Zhu A, He Z, Shrestha RP, Razzaq A. Assessment and Seasonal Monitoring of Groundwater Quality in Landfill-Affected Regions of China: Findings from Xiangyang. Water. 2025; 17(4):572. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040572
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Juan, Wenbing Yang, Qi Yang, You Li, Xiang Wan, Anan Zhu, Zhenzhu He, Rajendra Prasad Shrestha, and Amar Razzaq. 2025. "Assessment and Seasonal Monitoring of Groundwater Quality in Landfill-Affected Regions of China: Findings from Xiangyang" Water 17, no. 4: 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040572
APA StyleDu, J., Yang, W., Yang, Q., Li, Y., Wan, X., Zhu, A., He, Z., Shrestha, R. P., & Razzaq, A. (2025). Assessment and Seasonal Monitoring of Groundwater Quality in Landfill-Affected Regions of China: Findings from Xiangyang. Water, 17(4), 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040572








