Evaluation of Various Land Use Metrics for Enhancing Stream Water Quality Predictions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Land Use and Water Quality Monitoring Data
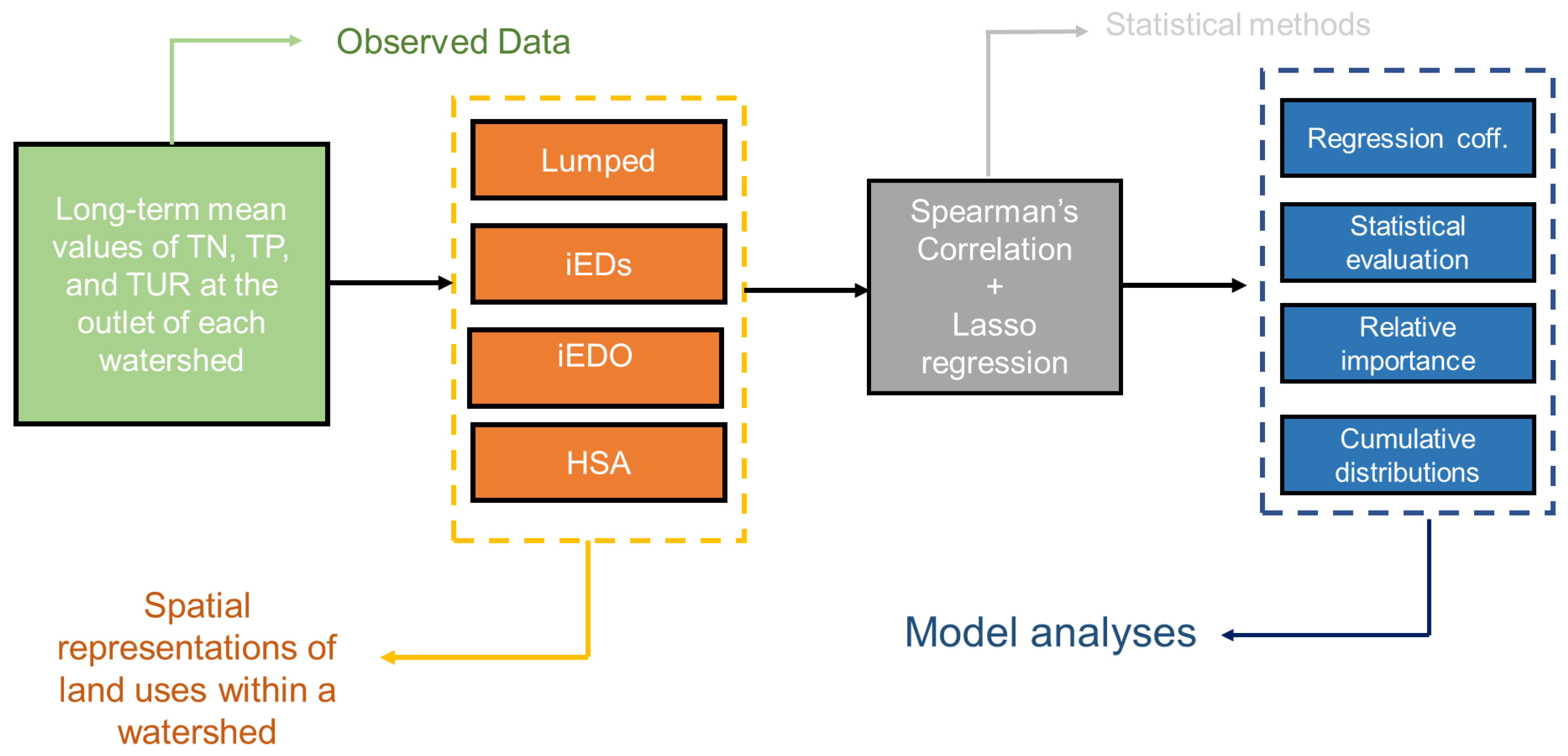
2.3. Model Development
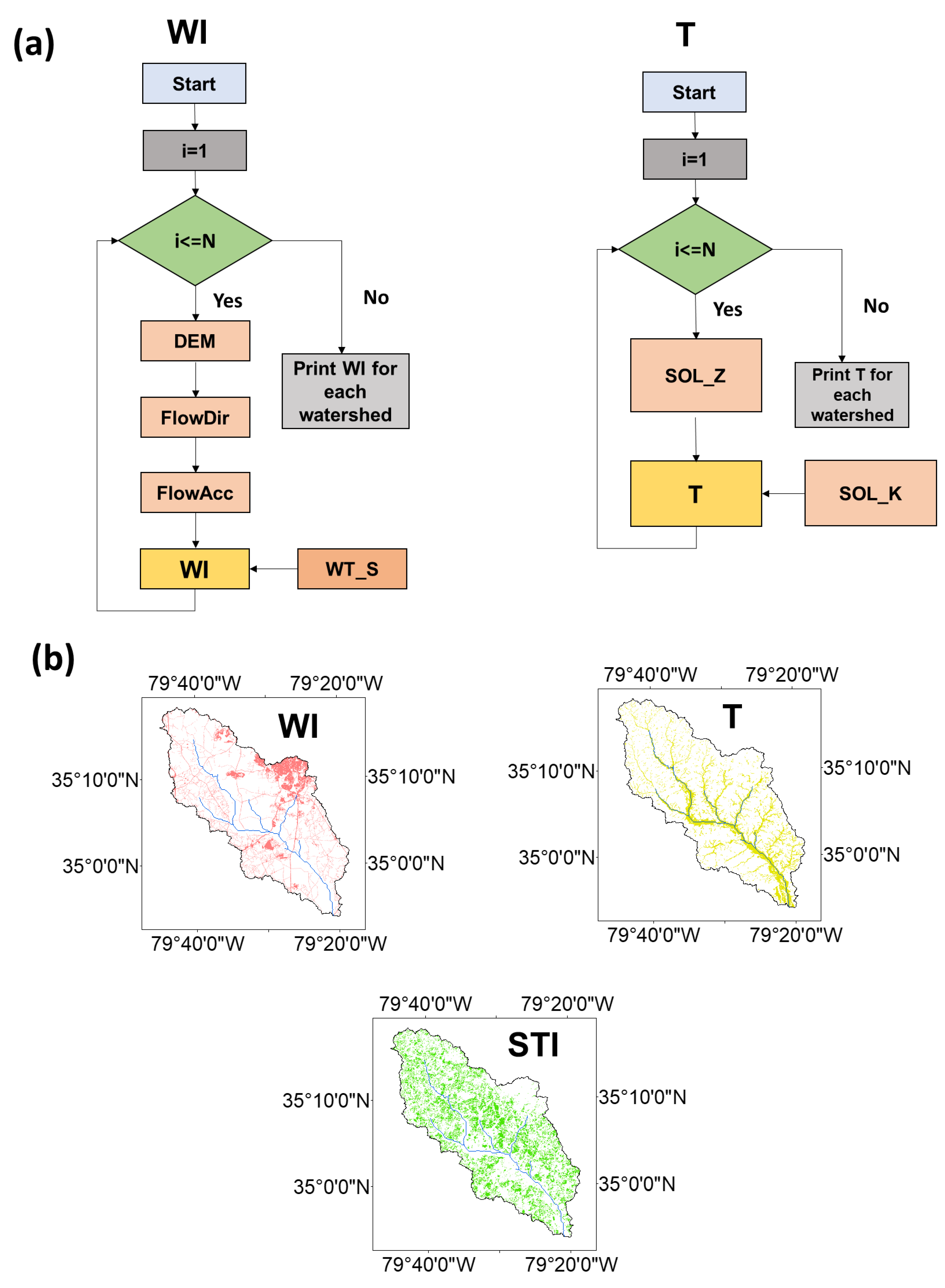
2.3.1. Inverse-Distance Weighted Metrics
2.3.2. Hydrological Sensitive Areas
2.3.3. Statistical Analysis
LASSO Regression
Model Validation
3. Result
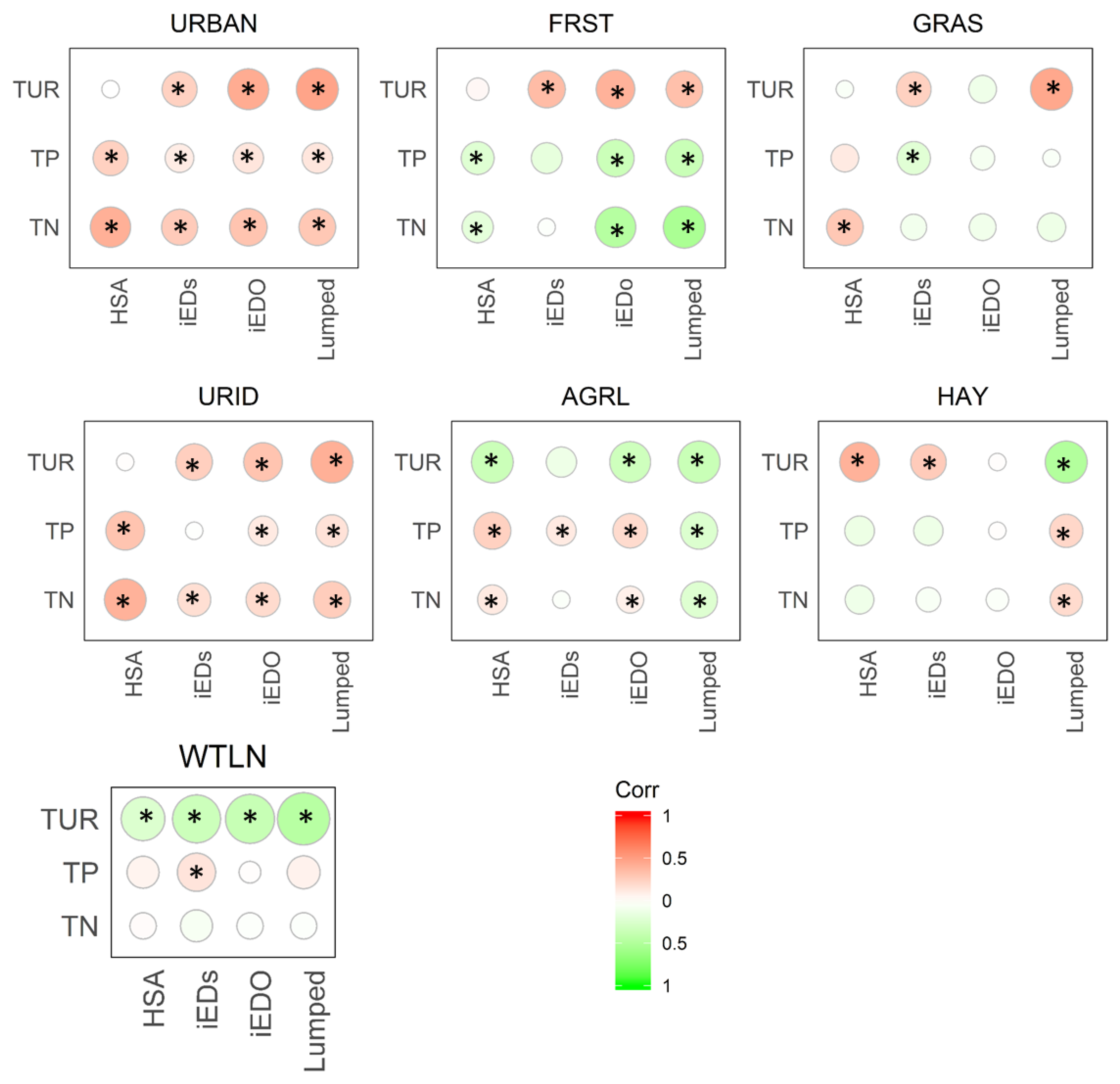
3.1. Visualization of Data and Correlations
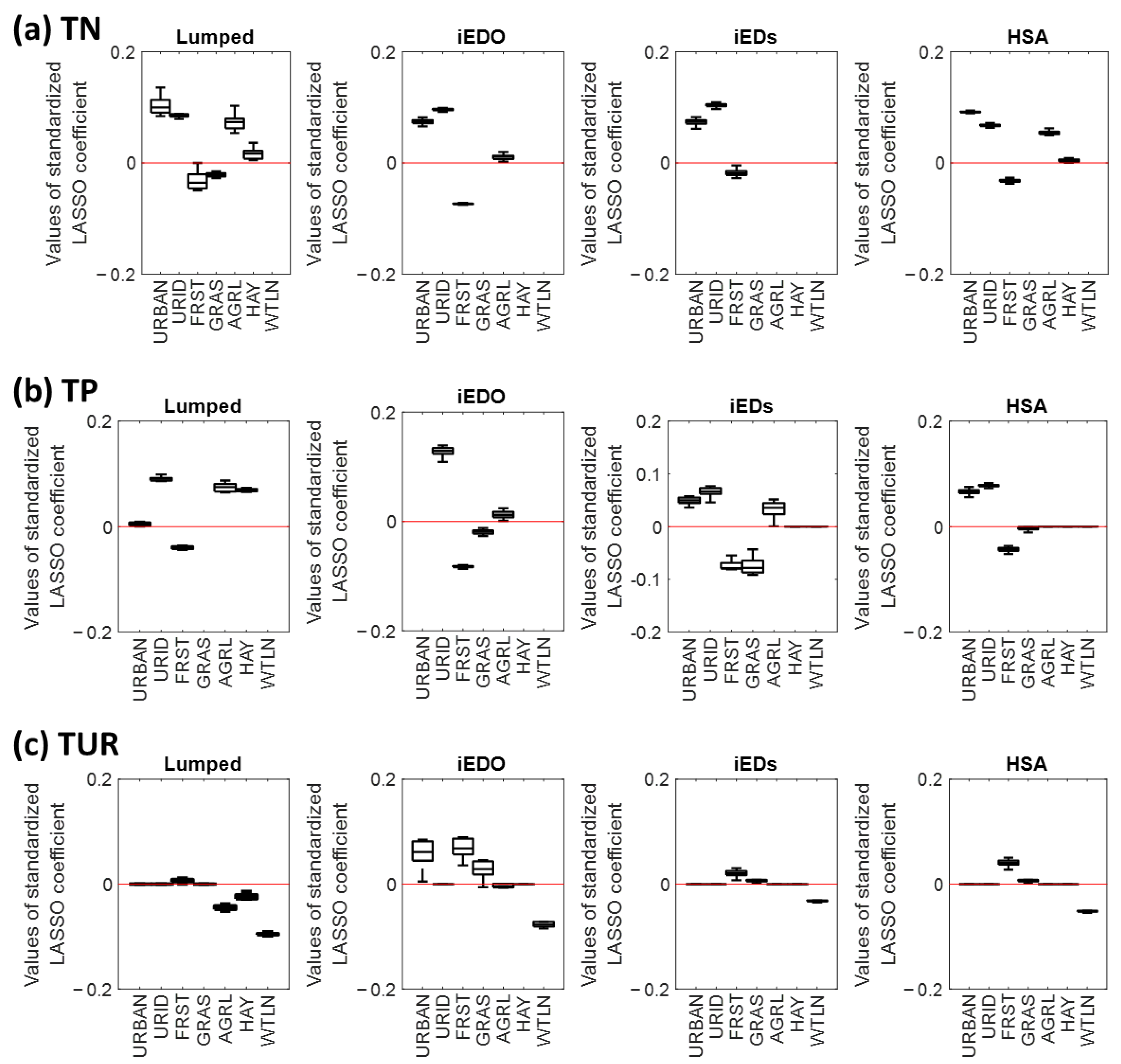
3.2. Relationship Between Water Quality Constituents and Land Use Variables
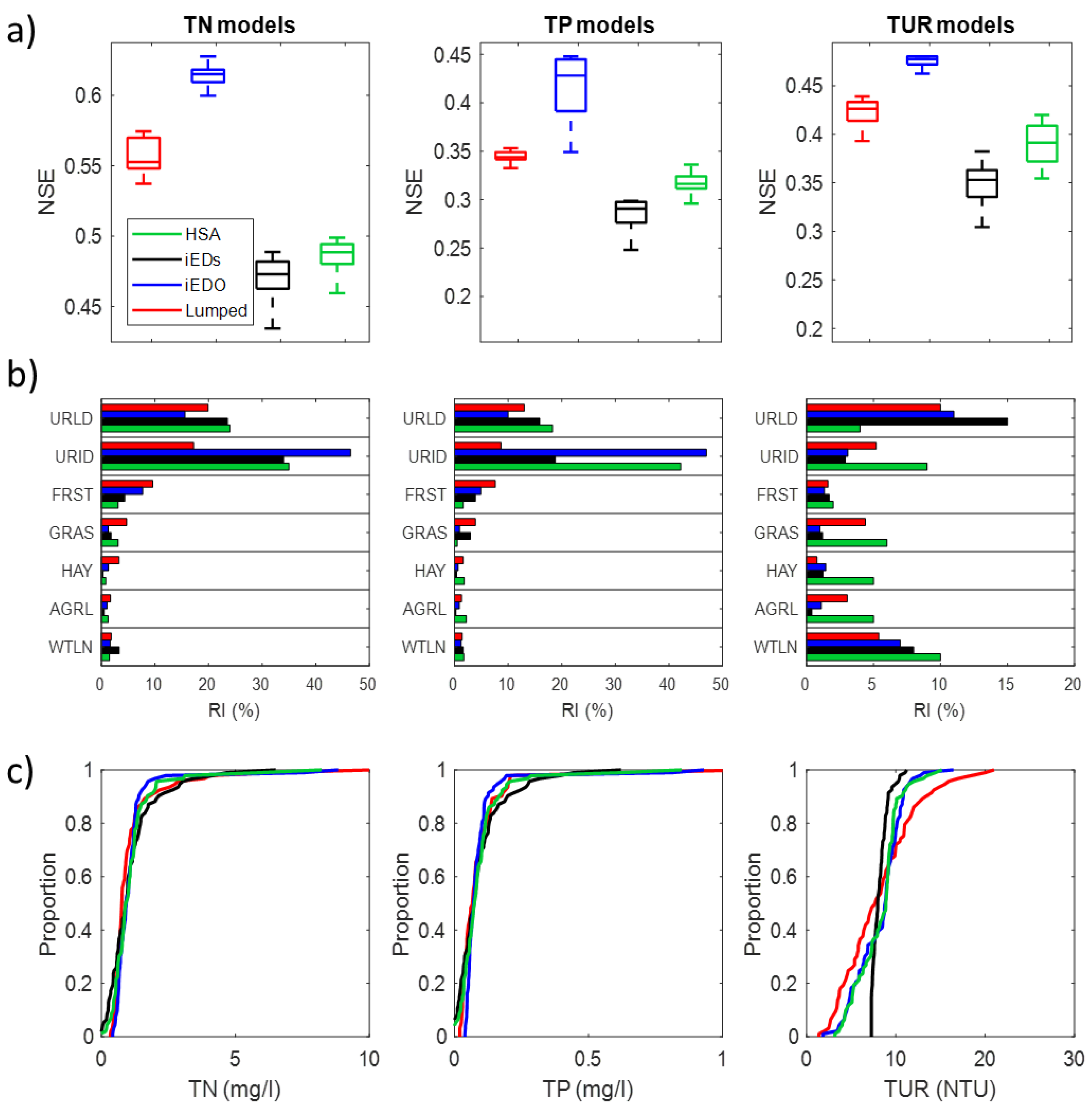
3.3. Model Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdul-Aziz, O.I.; Ishtiaq, K.S.; Tang, J.; Moseman-Valtierra, S.; Kroeger, K.D.; Gonneea, M.E.; Mora, J.; Morkeski, K. Environmental controls, emergent scaling, and predictions of greenhouse gas (GHG) fluxes in coastal salt marshes. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2018, 123, 2234–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.D. Landscapes and riverscapes: The influence of land use on stream ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2004, 35, 257–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A. Land use and water quality. In Encyclopedia of Hydrological Sciences; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, C.J.; Webb, J.A. Interactive effects of urban stormwater drainage, land clearance, and flow regime on stream macroinvertebrate assemblages across a large metropolitan region. Freshw. Sci. 2016, 35, 324–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.T.Y.; Chen, W. Modeling the relationship between land use and surface water quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 66, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzin, A.; Archaimbault, V.; Belliard, J.; Chauvin, C.; Delmas, F.; Pont, D. Ecological assessment of running waters: Do macrophytes, macroinvertebrates, diatoms and fish show similar responses to human pressures? Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, R.F.V.; Varandas, S.G.P.; Pacheco, F.A.L.; Pereira, V.R.; Santos, C.F.; Cortes, R.M.V.; Fernandes, L.F.S. Impacts of land use conflicts on riverine ecosystems. Land Use Policy 2015, 43, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.L.; Ringler, N.H. The response of fish and macroinvertebrate assemblages to multiple stressors: A comparative analysis of aquatic communities in a perturbed watershed (Onondaga Lake, NY). Ecol. Indic. 2014, 41, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, T.d.S.; Pessoa, L.A.; Vieira, L.; Cionek, V.d.M.; Singh, S.K.; Benedito, E.; do Couto, E.V. Evaluating land use impacts on water quality: Perspectives for watershed management. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Kennen, J.G.; Giri, S.; Walter, T.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Reassessing the relationship between landscape alteration and aquatic ecosystem degradation from a hydrologically sensitive area perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2850–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnahit, A.O.; Mishra, A.K.; Khan, A.A. Quantifying climate, streamflow, and watershed control on water quality across Southeastern US watersheds. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Park, S.R.; Lee, S.W. Effect of Land Use on Stream Water Quality and Biological Conditions in Multi-Scale Watersheds. Water 2023, 15, 4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, K.A.; Jiang, J.; Wang, P. Land use impacts on surface water quality by statistical approaches. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2018, 4, 231–250. [Google Scholar]
- King, R.S.; Baker, M.E.; Whigham, D.F.; Weller, D.E.; Jordan, T.E.; Kazyak, P.F.; Hurd, M.K. Spatial considerations for linking watershed land cover to ecological indicators in streams. Ecol. Appl. 2005, 15, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.S.G.; Morgan, J.W.; McDonnell, M.J.; Mccarthy, M.A. Plant traits and local extinctions in natural grasslands along an urban–rural gradient. J. Ecol. 2005, 93, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, E.E.; Sheldon, F.; Darnell, R.; Bunn, S.E.; Harch, B.D. A comparison of spatially explicit landscape representation methods and their relationship to stream condition. Freshw. Biol. 2011, 56, 590–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paringit, E.C.; Nadaoka, K. Sediment yield modelling for small agricultural catchments: Land-cover parameterization based on remote sensing data analysis. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 1845–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, B.W.; Bott, T.L.; Jackson, J.K.; Kaplan, L.A.; Newbold, J.D.; Standley, L.J.; Hession, W.C.; Horwitz, R.J. Riparian deforestation, stream narrowing, and loss of stream ecosystem services. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14132–14137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.; Cumberland, S.A.; Bradley, C.; Buckley, C.; Bridgeman, J. To what extent can portable fluorescence spectroscopy be used in the real-time assessment of microbial water quality? Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliva, L.; Williams, D.D. Buffer zone versus whole catchment approaches to studying land use impact on river water quality. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3462–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, C.R.; Dolédec, S.; Norris, R.; Peacock, K.; Arbuckle, C. The influence of scale and geography on relationships between stream community composition and landscape variables: Description and prediction. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 768–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, B.W.; Newbold, J.D. Streamside forest buffer width needed to protect stream water quality, habitat, and organisms: A literature review. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2014, 50, 560–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, Z. Assessing the impacts of land use on downstream water quality using a hydrologically sensitive area concept. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 213, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Hall, C.; Drewes, D.; Messinger, G.; Prato, T.; Hale, K.; Van Abs, D. Hydrologically sensitive areas, land use controls, and protection of healthy watersheds. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2014, 140, 04014011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlett, J.D. Principles of Forest Hydrology; University of Georgia Press: Athens, GA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Homer, C.G.; Fry, J.A.; Barnes, C.A. The National Land Cover Database; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Alnahit, A.O.; Mishra, A.K.; Khan, A.A. Stream water quality prediction using boosted regression tree and random forest models. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2022, 36, 2661–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, R.M.; De Cicco, L.A. User Guide to Exploration and Graphics for RivEr Trends (EGRET) and DataRetrieval: R Packages for Hydrologic Data; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, S.V.; Swanson, F.J.; McKee, W.A.; Cummins, K.W. An ecosystem perspective of riparian zones. Bioscience 1991, 41, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z. Assessing critical source areas in watersheds for conservation buffer planning and riparian restoration. Environ. Manag. 2009, 44, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, B.P.; Fleming, M.; Schneider, R.L.; Richards, B.K.; Archibald, J.; Qiu, Z.; Walter, M.T. Evaluating topographic wetness indices across central New York agricultural landscapes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3279–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.T.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Mehta, V.K.; Thongs, D.; Zion, M.; Schneiderman, E. Refined conceptualization of TOPMODEL for shallow subsurface flows. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 2041–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, B.K.P. Hill shading and the reflectance map. Proc. IEEE 1981, 69, 14–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, J.; McGlynn, B.L. A new triangular multiple flow direction algorithm for computing upslope areas from gridded digital elevation models. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W04501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauke, J.; Kossowski, T. Comparison of values of Pearson’s and Spearman’s correlation coefficients on the same sets of data. Quaest. Geogr. 2011, 30, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Cox, D.R. An analysis of transformations. J. R. Stat. Soc. Series B Stat. Methodol. 1964, 26, 211–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardsley, W.E.; Vetrova, V.; Liu, S. Toward creating simpler hydrological models: A LASSO subset selection approach. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 72, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilo, D.C.; Lombardo, L.; Mai, P.M.; Dou, J.; Huser, R. Handling high predictor dimensionality in slope-unit-based landslide susceptibility models through LASSO-penalized Generalized Linear Model. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 97, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, D.; Lee, T.S.; Ouarda, T.B.M.J.; Lee, J. Predictor selection for downscaling GCM data with LASSO. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D17116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Series B Stat. Methodol. 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuber, V.; Strimmer, K. High-dimensional regression and variable selection using CAR scores. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2011, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. Partial least squares structural equation modeling: Rigorous applications, better results and higher acceptance. Long Range Plann. 2013, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, S.S.; Groffman, P.M.; Band, L.E.; Shields, C.A.; Morgan, R.P.; Palmer, M.A.; Belt, K.T.; Swan, C.M.; Findlay, S.E.G.; Fisher, G.T. Interaction between urbanization and climate variability amplifies watershed nitrate export in Maryland. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5872–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, N.; Band, L.; Grove, M. Nitrogen input from residential lawn care practices in suburban watersheds in Baltimore County, MD. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2004, 47, 737–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.J.; Meyer, J.L. Streams in the urban landscape. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2001, 32, 333–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, B.; Chang, H. Effects of land cover, topography, and built structure on seasonal water quality at multiple spatial scales. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 209, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, C.; Weng, Q. Assessing surface water quality and its relation with urban land cover changes in the Lake Calumet Area, Greater Chicago. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 1096–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J. Spatially varying relationships between land use and water quality across an urbanization gradient explored by geographically weighted regression. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 376–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsegaye, T.; Sheppard, D.; Islam, K.R.; Tadesse, W.; Atalay, A.; Marzen, L. Development of chemical index as a measure of in-stream water quality in response to land-use and land cover changes. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2006, 174, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.; Cai, S.; Li, H.; Yang, G.; Li, Z.; Nie, X. Inferring land use and land cover impact on stream water quality using a Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach in the Xitiaoxi River Watershed, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 133, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


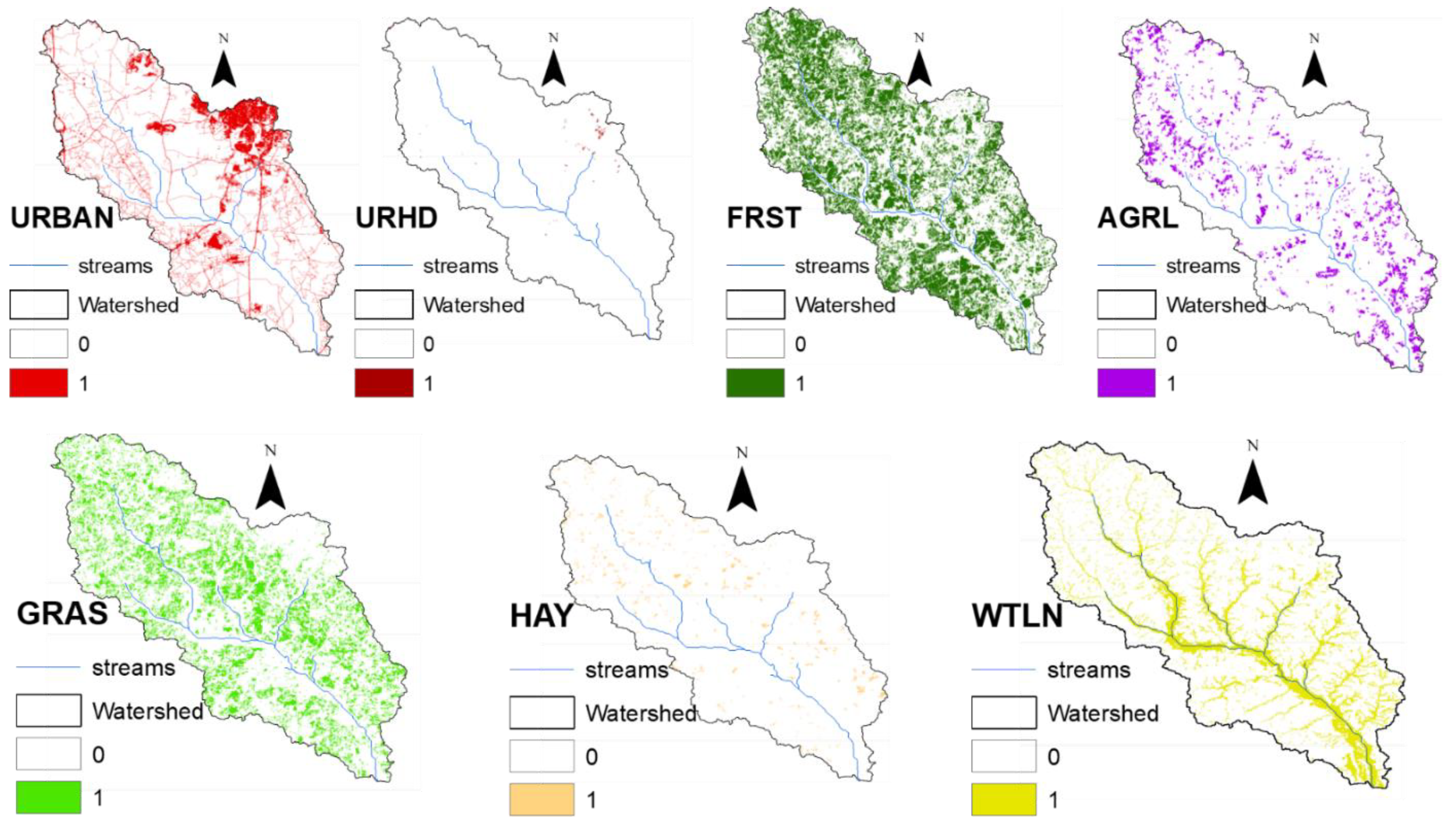

| Land Use Type | Definition | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | 25th Percentile | 50th Percentile | 75th Percentile | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| URBAN (%) | Total percent of urban land use | 10.5 | 6.9 | 2.1 | 5.1 | 8.3 | 14.5 | 33.6 |
| URID (%) | Total percent industrial urban land use | 7.4 | 9.7 | 0.4 | 2.0 | 2.8 | 9.7 | 43.0 |
| FRST (%) | Total percent forest land use | 1.3 | 1.8 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 1.3 | 8.1 |
| GRAS (%) | Total percentage of grassland use (e.g., Range-Brush) | 41.5 | 15.8 | 12.8 | 30.0 | 40.4 | 53.7 | 81.5 |
| HAY (%) | Total percent hay land (Range-Brush and Range-Grasses) | 11.2 | 6.3 | 1.2 | 7.2 | 9.6 | 15.3 | 24.7 |
| AGRL (%) | Total percent agricultural land use | 18.8 | 10.5 | 0.7 | 11.6 | 17.5 | 22.5 | 53.6 |
| WTLN (%) | Total percent wetland land use | 8.4 | 11.8 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 2.7 | 13.5 | 66.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alnahit, A.O.; Mishra, A.K.; Khan, A.A. Evaluation of Various Land Use Metrics for Enhancing Stream Water Quality Predictions. Water 2025, 17, 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060849
Alnahit AO, Mishra AK, Khan AA. Evaluation of Various Land Use Metrics for Enhancing Stream Water Quality Predictions. Water. 2025; 17(6):849. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060849
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlnahit, Ali O., Ashok. K. Mishra, and Abdul A. Khan. 2025. "Evaluation of Various Land Use Metrics for Enhancing Stream Water Quality Predictions" Water 17, no. 6: 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060849
APA StyleAlnahit, A. O., Mishra, A. K., & Khan, A. A. (2025). Evaluation of Various Land Use Metrics for Enhancing Stream Water Quality Predictions. Water, 17(6), 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060849






