Research on the Recovery Technology and Application of Copper Resources from Mine Wastewater at High Altitudes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Equipment
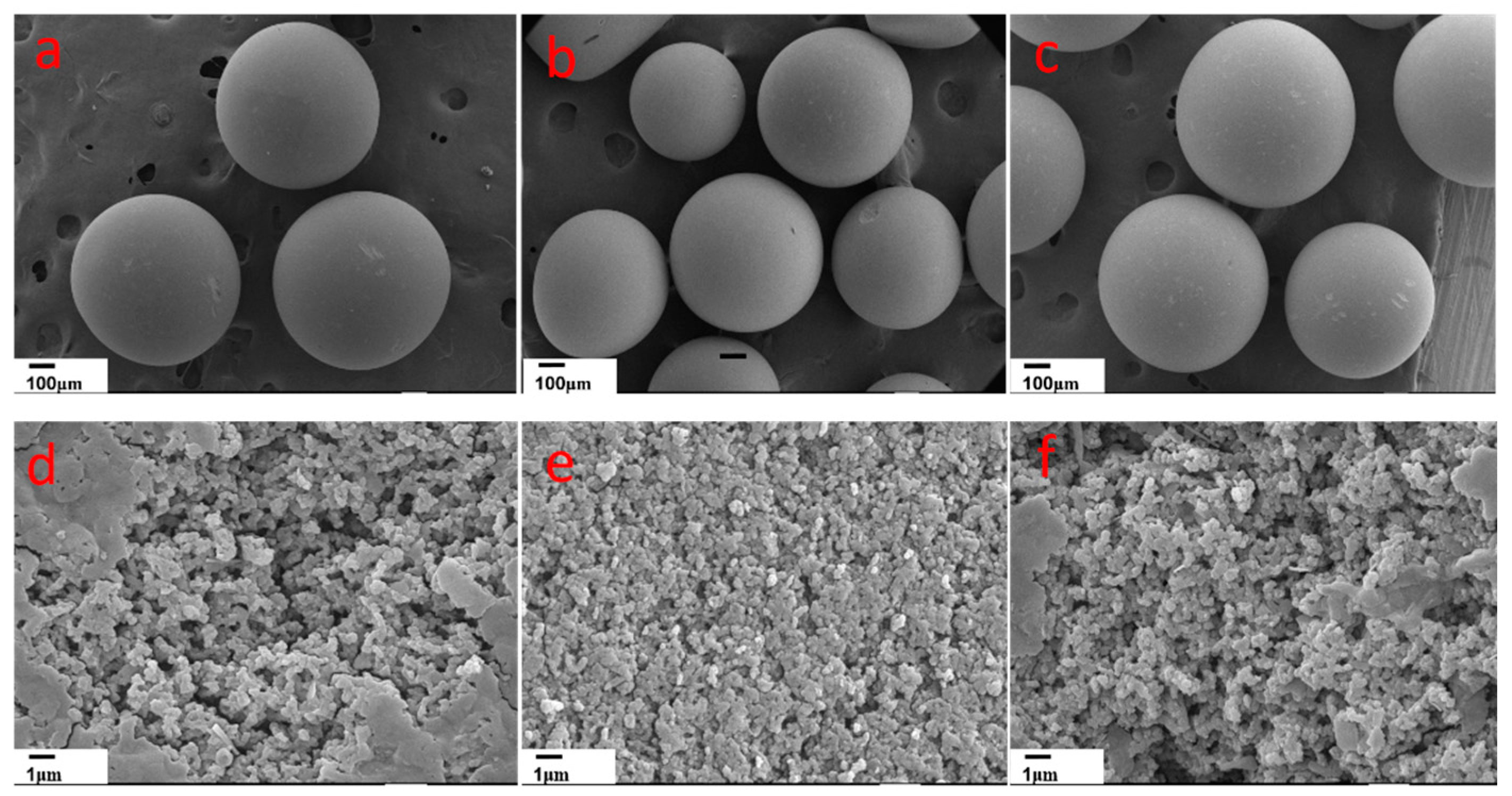
2.2. Characterization Methods
2.3. Experimental Methods
3. Results and Discussion
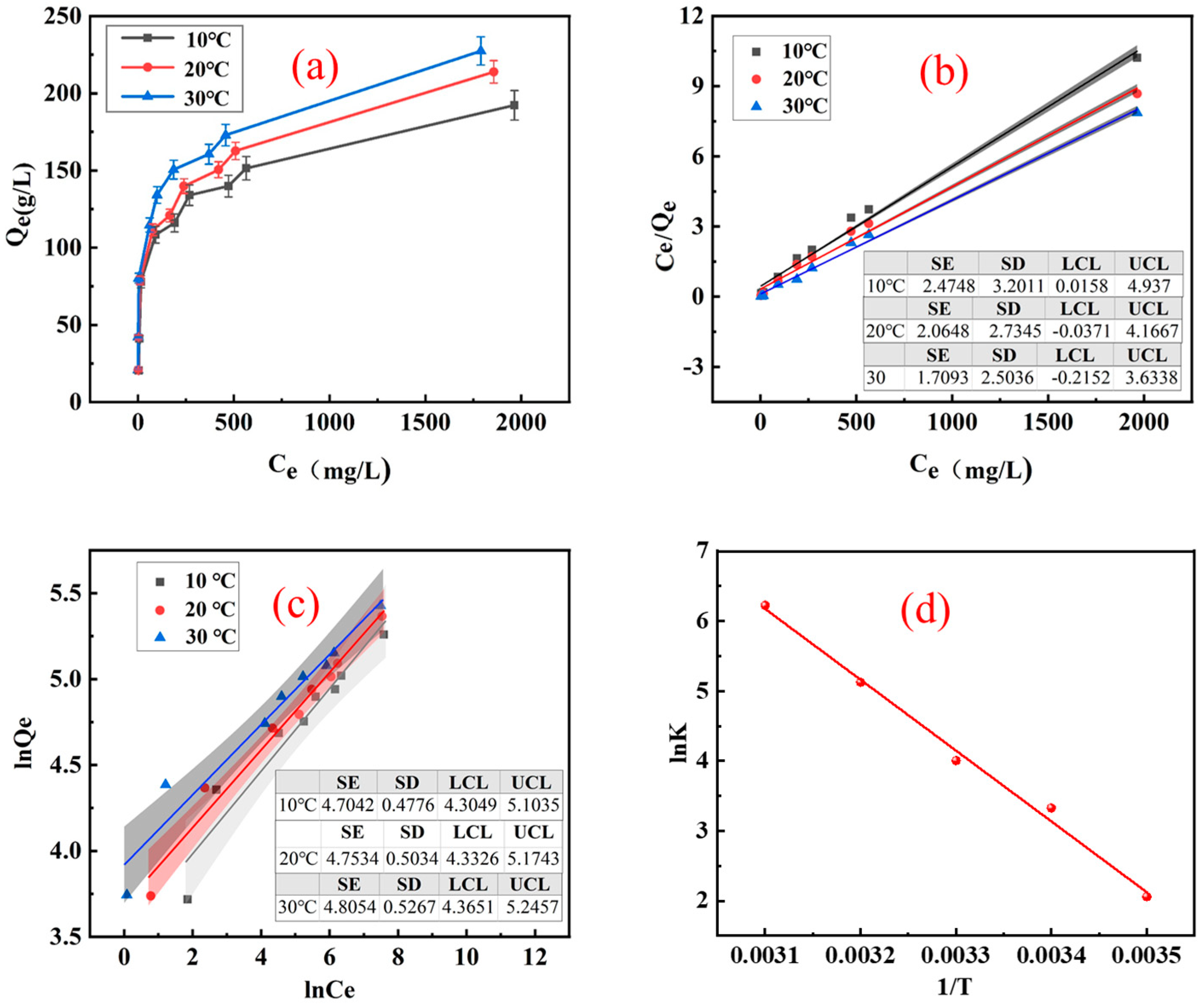
3.1. Adsorption Performance of Resin
3.2. Desorption
3.3. Nanofiltration
3.4. Electrowinning
3.5. Regeneration
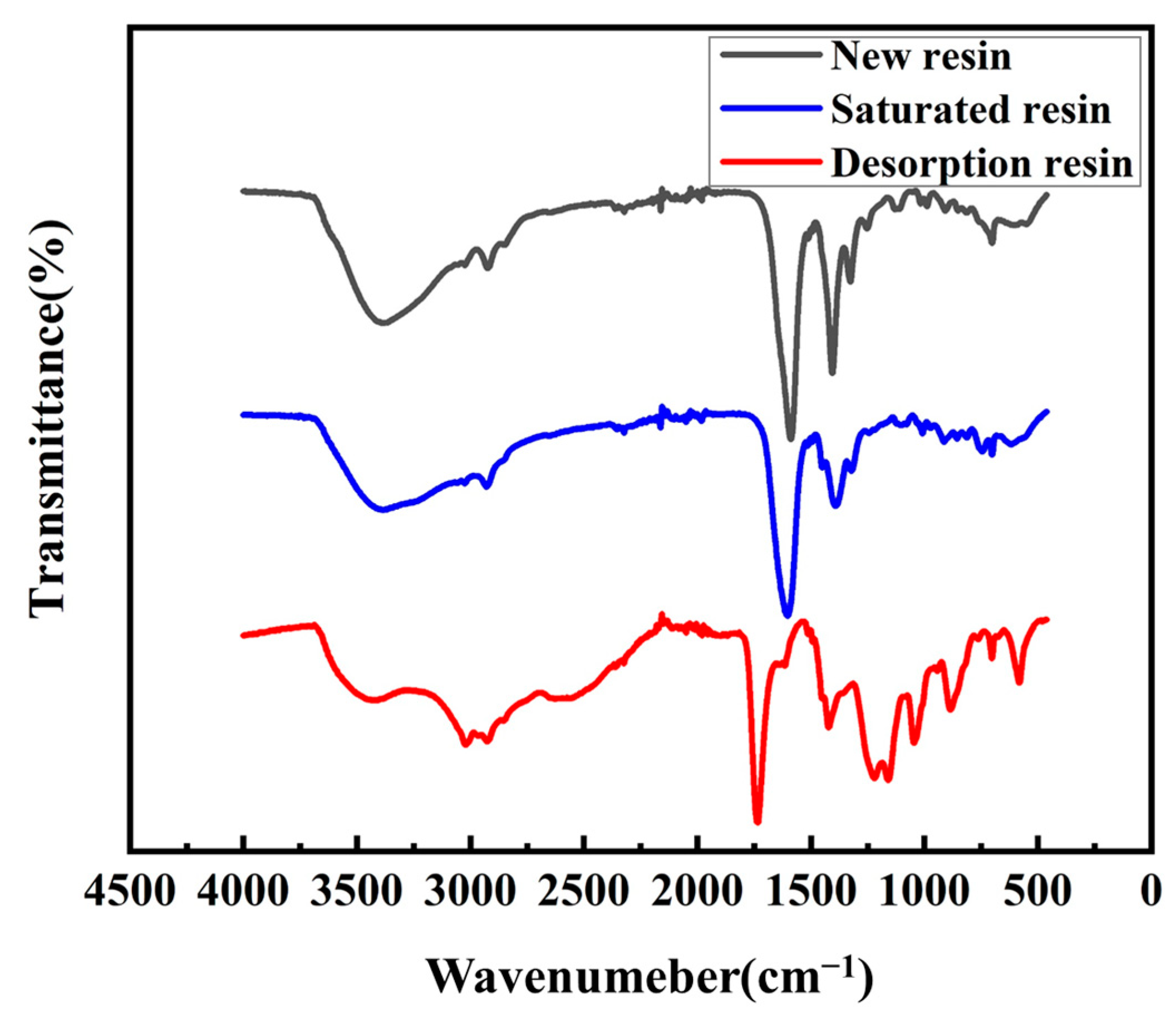
3.6. Adsorption Mechanism Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, S.; Liu, Z.W.; Mao, Q.; Ye, H.; Tian, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L. Leaching characteristics and environmental impact of heavy metals in tailings under rainfall conditions: A case study of an ion-adsorption rare earth mining area. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 281, 116642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, D.; Ren, F.; Huang, L. Spatiotemporal variation of soil heavy metals in China: The pollution status and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 161768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cravotta, C.; Trahan, M. Limestone drains to increase pH and remove dissolved metals from acidic mine drainage. Appl. Geochem. 1999, 14, 581–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Feng, W.; Li, X. Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Water Bodies around Typical Copper Mines in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Sun, J.; Ai, C.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y. Moderate permeability enhanced microbial community turnover and copper extraction during bioleaching of low-grade copper ores. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chang, Z.; El Kolaly, W.; Fan, F.; Li, M. Progress in the treatment of copper(II)-containing wastewater and wastewater treatment systems based on combined technologies: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 58, 104746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulungulungu, G.A.; Mao, T.; Han, K. Efficient removal of high-concentration copper ions from wastewater via 2D g-C3N4 photocatalytic membrane filtration. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 623, 126714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Garg, S.; Waite, T.D. Electrochemical treatment of wastewaters containing metal-organic complexes: A one-step approach for efficient metal complex decomposition and selective metal recovery. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Deng, J.; Xiong, W.; Cheng, M.; Liu, J.; Zhou, C.; Yang, Y. Boosting active hydrogen generation via ruthenium single atoms for efficient electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2025, 365, 124943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, F.; Song, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Wang, W. Mechanistic insights into ultrafast degradation of electron-rich emerging pollutants by waste cyanobacteria resource utilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 155918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jabari, M. Kinetic models for adsorption on mineral particles comparison between Langmuir kinetics and mass transfer. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2016, 6, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; Wu, L.; He, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Ge, L.; Bakangura, E.; Xu, T. Ion exchange membranes: New developments and applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 522, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afridi, M.N.; Lee, W.-H.; Kim, J.-O. Effect of phosphate concentration, anions, heavy metals, and organic matter on phosphate adsorption from wastewater using anodized iron oxide nanoflakes. Environ. Res. 2019, 171, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, X. Enhanced adsorption of copper ions from aqueous solution by two-step DTPA-modified magnetic cellulose hydrogel beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 211, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N.N.R.; Ang, W.L.; Teow, Y.H.; Mohammad, A.W.; Hilal, N. Nanofiltration membrane processes for water recycling, reuse and product recovery within various industries: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Huo, M. Enhanced resource recovery from wastewater using electrochemical-osmotic system with nanofiltration membranes. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 186, 106555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, X.; Xu, Z.; Tian, Q. Recent advancements in aqueous electrowinning for metal recovery: A comprehensive review. Miner. Eng. 2024, 216, 108897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duyen, L.T.; Bac, B.H. Adsorption–desorption behavior of halloysite clay for Cu2+ ions and recovery of copper by electrodeposition method. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, W.; Feng, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, H.; Ge, L.; Lv, H. Geochemical Characteristics of Primary Halos and Prospecting Significance of the Qulong Porphyry Copper–Molybdenum Deposit in Tibet. Minerals 2023, 13, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Qu, X.; Song, Y. Porphyry Copper Deposit Prognosis in the Middle Region of the Bangonghu–Nujiang Metallogenic Belt, Tibet, Using ASTER Remote Sensing Data. Resour. Geol. 2018, 68, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arief, V.O.; Trilestari, K.; Sunarso, J.; Indraswati, N.; Ismadji, S. Recent Progress on Biosorption of Heavy Metals from Liquids Using Low Cost Biosorbents: Characterization, Biosorption Parameters and Mechanism Studies. CLEAN—Soil Air Water 2008, 36, 937–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávila-Guzmán, N.E.; de Jesús Cerino-Córdova, F.; Soto-Regalado, E.; Rangel-Mendez, J.R.; Díaz-Flores, P.E.; Garza-Gonzalez, M.T.; Loredo-Medrano, J.A. Copper Biosorption by Spent Coffee Ground: Equilibrium, Kinetics, and Mechanism. CLEAN—Soil Air Water 2013, 41, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Tang, J.; Lü, P.; Luo, M.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Leng, Q. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Dating of Intermediate-Acidic Intrusive Rocks and Molybdenite Re-Os Dating from the Bangpu Mo (Cu) Deposit, Tibet and its Geological Implication. Acta Geol. Sin.—Engl. Ed. 2012, 86, 1225–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Huang, J. Anisole-modified hyper-cross-linked resins for efficient adsorption of aniline from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 569, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y. Decontamination of Bisphenol A from Aqueous Solution by Graphene Adsorption. Langmuir 2012, 28, 8418–8425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lei, S.; Liang, L. Preparation of porous activated carbon from semi-coke by high temperature activation with KOH for the high-efficiency adsorption of aqueous tetracycline. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 530, 147187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, N.; Ansari, R.; Khodavirdilo, B. Removal of Copper ions from aqueous solutions using polymer derivations of poly (styrene-alt-maleic anhydride). Egypt. J. Pet. 2017, 26, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Liu, F.; Pei, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wei, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, A.; Xing, B. Citric Acid Enhanced Copper Removal by a Novel Multi-amines Decorated Resin. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Ling, C.; Yuan, R.; Liu, F.; Li, A. Bridging effects behind the coadsorption of copper and sulfamethoxazole by a polyamine-modified resin. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.C.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C.; Anastopoulos, I. A critical review of the estimation of the thermodynamic parameters on adsorption equilibria. Wrong use of equilibrium constant in the van’t hoof equation for calculation of thermodynamic parameters of adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 273, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; He, J.; Han, P.; Zeng, M.; Gao, X.; He, Q. Adsorption mechanism for tetracycline onto magnetic fe3o4 nanoparticles: Adsorption isotherm and dynamic behavior, location of adsorption sites and interaction bonds. Vacuum 2022, 195, 110634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Shen, Z.; Hu, X.; Schulman, E.; Cui, C.; Guo, Q.; Tian, H. Adsorption of tetracycline by shrimp shell waste from aqueous solutions: Adsorption isotherm, kinetics modeling, and mechanism. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 3467–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Element | Cu | Ca | Mg | Al | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (mg/L) | 100 | 150 | 67 | 25 | 59 |
| Kinetic Model | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Quasi-first-order kinetic equations | k1 (h−1) | −0.00827 |
| Qe (g/L) | 174.6 | |
| R2 | 0.9939 | |
| SE | 4.98965 | |
| SD | 0.10999 | |
| CLC | 4.98282 | |
| UCL | 4.99647 | |
| quasi-second-order kinetic equations | k2 (L·g−1·h−1) | −0.018 |
| Qe (g/L) | 174.6 | |
| R2 | 0.6406 | |
| SE | 1.0887 | |
| SD | 0.23957 | |
| CLC | 1.07384 | |
| UCL | 1.10357 |
| T (K) | Qe (mg/g−1) | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm (mg/g−1) | KL | R2 | n | KF | R2 | ||
| 283.15 | 192.2 | 195.3 | 0.012 | 0.989 | 3.265 | 22.69 | 0.896 |
| 293.15 | 213.8 | 216.9 | 0.013 | 0.985 | 3.632 | 30.27 | 0.940 |
| 303.15 | 227.5 | 229.9 | 0.015 | 0.988 | 4.122 | 40.85 | 0.947 |
| T (K) | ∆G (kJ·mol−1) | ∆H (kJ·mol−1) | ∆S (kJ·mol−1·K−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 283.15 | −4.847 | 80.978 | 0.301 | 0.971 |
| 293.15 | −8.108 | |||
| 303.15 | −10.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Yan, X.; Zhou, C.; Meng, Y. Research on the Recovery Technology and Application of Copper Resources from Mine Wastewater at High Altitudes. Water 2025, 17, 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060856
Wu J, Yan X, Zhou C, Meng Y. Research on the Recovery Technology and Application of Copper Resources from Mine Wastewater at High Altitudes. Water. 2025; 17(6):856. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060856
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jianhui, Xu Yan, Chengyun Zhou, and Yun Meng. 2025. "Research on the Recovery Technology and Application of Copper Resources from Mine Wastewater at High Altitudes" Water 17, no. 6: 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060856
APA StyleWu, J., Yan, X., Zhou, C., & Meng, Y. (2025). Research on the Recovery Technology and Application of Copper Resources from Mine Wastewater at High Altitudes. Water, 17(6), 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060856







