Preparation of CS/PVA/POP Nanofiber Membranes and Adsorption Behavior for Hg(II) Ions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Preparation of Adsorbents
2.3.1. Preparation of POP
2.3.2. Preparation of CS/PVA/POP Nanofiber Membranes
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
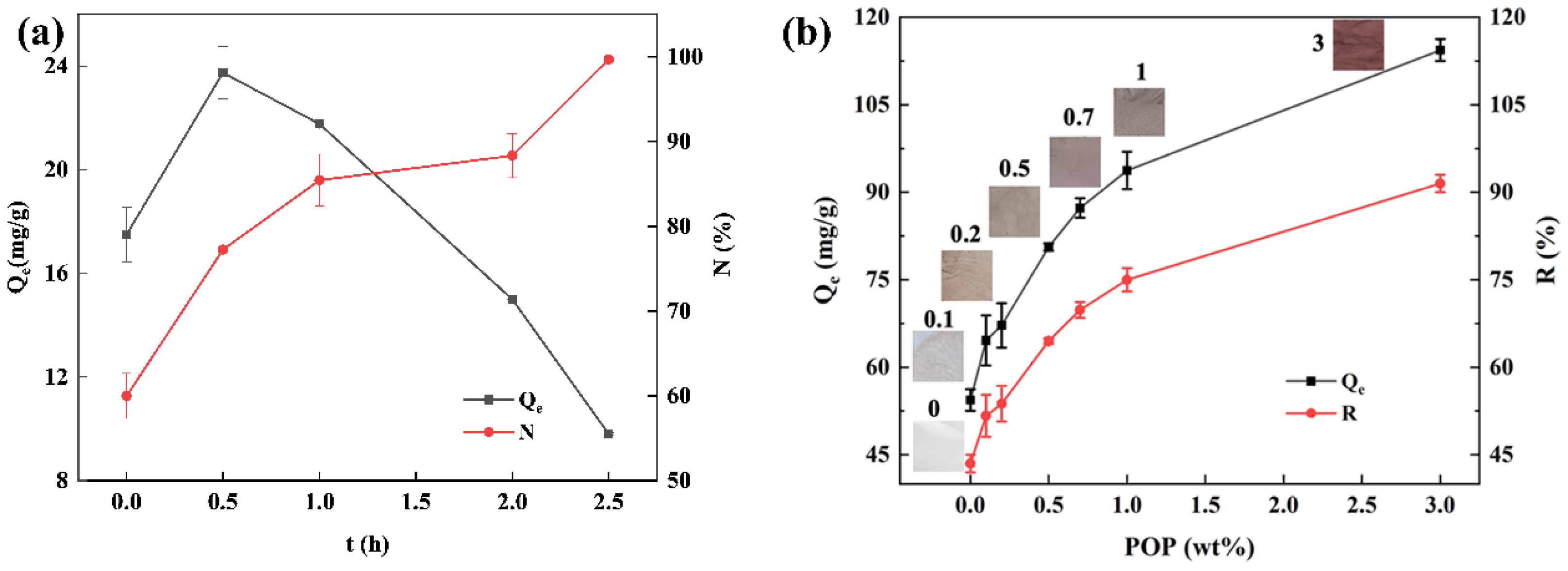
3.1. Effect of Glutaraldehyde Crosslinking Time
3.2. Effect of POP Loadings on Adsorption
3.3. Characterization of CS/PVA/POP
3.3.1. FT-IR Analysis
3.3.2. XRD Analysis
3.3.3. SEM Analysis
3.4. Adsorption Properties
3.4.1. Effect of pH
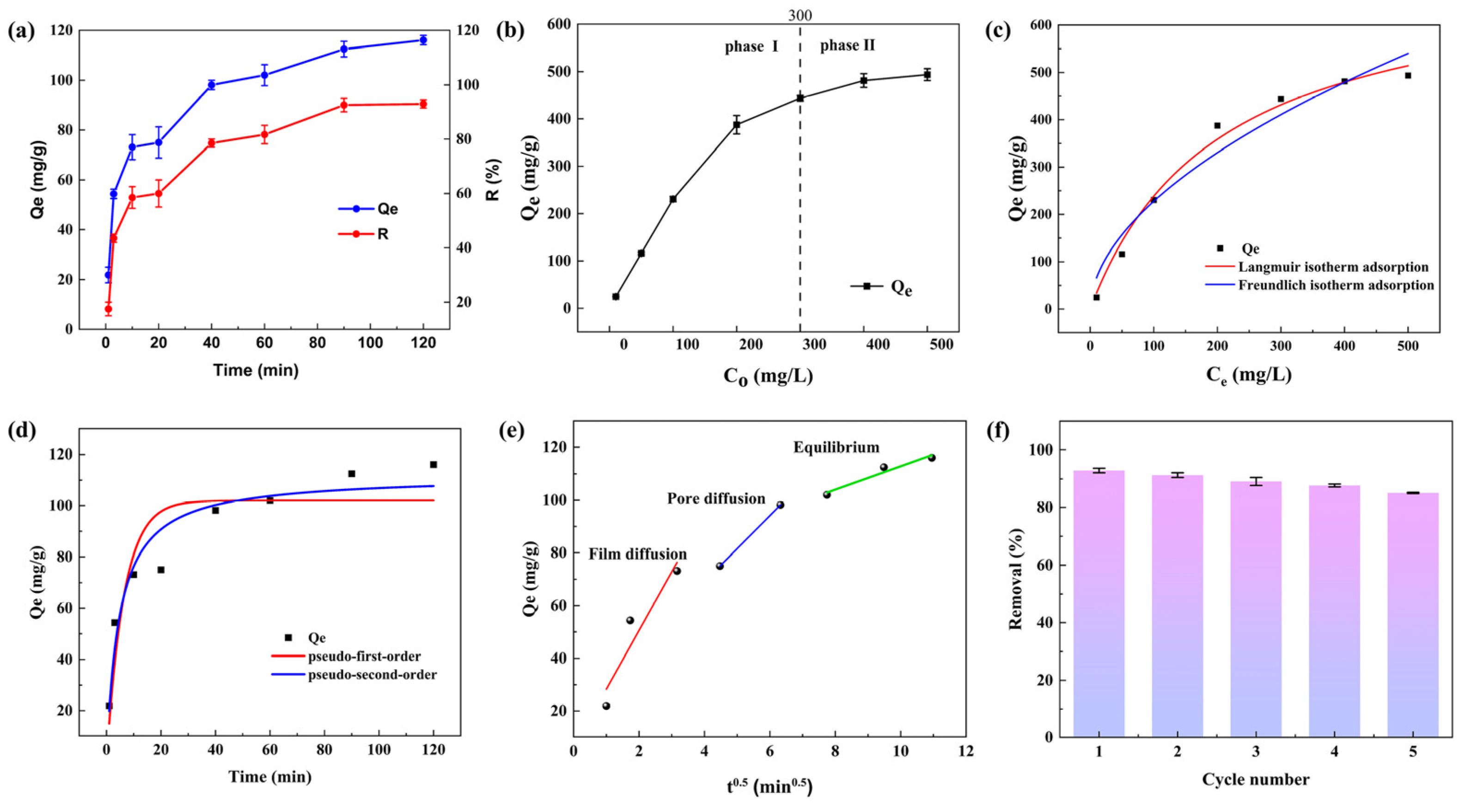
3.4.2. Effect of Contact Time
3.4.3. Effect of Initial Hg(II) Ion Concentration
3.4.4. Sorption Isotherm Models
3.4.5. Sorption Kinetics
Fitting of Pseudo-First-Order and Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Models
Intraparticle Diffusion Model
3.5. Reusability
3.6. Adsorption Mechanism
3.7. Comparison with the Related Adsorbents
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CS | Chitosan |
| PVA | polyvinyl alcohol |
| POP | porous organic polymer |
References
- Mohmood, I.; Lopes, C.B.; Lopes, I.; Tavares, D.S.; Soares, A.M.; Duarte, A.C.; Trindade, T.; Ahmad, I.; Pereira, E. Remediation of mercury contaminated saltwater with functionalized silica coated magnetite nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557–558, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naushad, M.; Ahamad, T.; AlOthman, Z.A.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H. Green and eco-friendly nanocomposite for the removal of toxic Hg(II) metal ion from aqueous environment: Adsorption kinetics & isotherm modelling. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 279, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen, J.K.; Rissanen, T.H.; Voutilainen, S.; Tuomainen, T.P. Mercury as a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2007, 18, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Gorain, B.; Choudhury, H.; Roychoudhury, S.; Sengupta, P. Environmental and occupational exposure of metals and female reproductive health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 62067–62092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.K.; Dolgova, N.V.; Nehzati, S.; Korbas, M.; Cotelesage, J.J.H.; Sokaras, D.; Kroll, T.; O’Donoghue, J.L.; Watson, G.E.; Myers, G.J.; et al. Molecular Fates of Organometallic Mercury in Human Brain. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 1756–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Li, P.; Fu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Lin, C.J. Mercury pollution in China: Implications on the implementation of the Minamata Convention. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2022, 24, 634–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Duan, X. Chemical precipitation of heavy metals from wastewater by using the synthetical magnesium hydroxy carbonate. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, L.; Osborne, J.W.; Benjamin, L.K. Harnessing microbes for heavy metal remediation: Mechanisms and prospects. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 197, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarle, S.; Ratto, M.; Rovatti, M. Mercury removal from water by ion exchange resins adsorption. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2971–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Huangfu, X.; Ma, J. Removal of trace mercury(II) from aqueous solution by in situ formed Mn-Fe (hydr)oxides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Huang, J.; Gao, C.; Xu, G.; Wang, G.; Zhang, B.; Duan, C. Effective and reusable 3D CuxS nanocluster structured magnetic adsorbent for mercury extraction from wastewater. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, L.; Srivastav, A.L.; Kaushal, J.; Nguyen, X.C. Recent advances in nanomaterial developments for efficient removal of Hg(II) from water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 62851–62869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayar, J.; Ali, N.; Dong, Y.; Ahmad, U.; Anjum, M.M.; Khan, G.R.; Zaib, M.; Jalal, A.; Ali, R.; Ali, L. Biochar-based adsorption for heavy metal removal in water: A sustainable and cost-effective approach. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N. Recent modifications of chitosan for adsorption applications: A critical and systematic review. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 312–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Ren, Z. A novel benzothiazole modified chitosan with excellent adsorption capacity for Au(III) in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 1918–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, Y.; Hu, J.; Chen, Q.; Wu, Y. Preparation of new diatomite-chitosan composite materials and their adsorption properties and mechanism of Hg(II). R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saheed, I.O.; Oh, W.D.; Suah, F.B.M. Chitosan modifications for adsorption of pollutants—A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayach, J.; Duma, L.; Badran, A.; Hijazi, A.; Martinez, A.; Bechelany, M.; Baydoun, E.; Hamad, H. Enhancing Wastewater Depollution: Sustainable Biosorption Using Chemically Modified Chitosan Derivatives for Efficient Removal of Heavy Metals and Dyes. Materials 2024, 17, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, R.S.; Beppu, M.M. Interaction of natural and crosslinked chitosan membranes with Hg(II) ions. Colloids Surf. A 2006, 279, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabadi, M.; Irani, M.; Ismaeili, J.; Piri, H.; Parnian, M.J. Electrospun nanofiber membrane of PEO/Chitosan for the adsorption of nickel, cadmium, lead and copper ions from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 220, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Chen, K.H.; Lai, Y.R.; Chiu, C.Y.; Lee, H.C.; Chang, Y.K. Electrospinning of Quaternized Chitosan-Poly(vinyl alcohol) Composite Nanofiber Membrane: Processing Optimization and Antibacterial Efficacy. Membranes 2022, 12, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, C.W.; Lin, M.C.; Huang, C.H.; Lai, M.F.; Shiu, B.C.; Lin, J.H. Preparation of Needleless Electrospinning Polyvinyl Alcohol/Water-Soluble Chitosan Nanofibrous Membranes: Antibacterial Property and Filter Efficiency. Polymers 2022, 14, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amani, A.; Kalajahi, S.T.; Yazdian, F.; Mirzababaei, S.; Rashedi, H.; Faramarzi, M.A.; Vahidi, M. Immobilization of urease enzyme on chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol electrospun nanofibers. Biotechnol. Prog. 2022, 38, e3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurisingal, J.F.; Yun, H.; Hong, C.S. Porous organic materials for iodine adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 131835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelnaby, M.M.; Saleh, T.A.; Zeama, M.; Abdalla, M.A.; Ahmed, H.M.; Habib, M.A. Azo-Linked Porous Organic Polymers for Selective Carbon Dioxide Capture and Metal Ion Removal. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 14535–14543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fang, Y.; Yu, J.; Gao, W.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, X. A silsesquioxane-porphyrin-based porous organic polymer as a highly efficient and recyclable absorbent for wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorginpour, F.; Moradinia, S.; Daneshi, M.; Zali-Boeini, H. Novel sulfur-containing porous organic polymer as a nanotrap for rapid removal of mercury(ii) from environmental waters. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 3694–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.Y.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, Y.X.; Sun, X.H.; Hu, J.S. Efficient selective uptake of Hg(II) using a porous organic polymer rich in N and S atoms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hense, D.; Strube, O.I. Glutaraldehyde Cross-Linking of Salt-Induced Fibrinogen Hydrogels. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 6927–6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.T.; Gong, J.; Gu, X.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Dong, J.; Shen, X.Y. Fabrication and Characterization of Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Chitosan Blend Nanofibers Produced by Electrospinning Method. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 67, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, A.; Beni, A.A. A Novel Fixed-Bed Reactor Design Incorporating an Electrospun PVA/Chitosan Nanofiber Membrane. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.Y.; Dong, M.; Wang, Y.W.; Chen, Y.T.; Wang, H.Z.; Su, C.Y.; Wang, W. Thioether-Based Fluorescent Covalent Organic Framework for Selective Detection and Facile Removal of Mercury(II). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3031–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajalakshmi, K.; Muthusamy, S.; Xie, M.; Nam, Y.S.; Lee, B.; Lee, K.B.; Xu, Y.J.; Xie, J.M. Fabrication of thiophene decorated side chain entanglement free COFs for highly regenerable mercury extraction. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattwick, H.; Kingshuk, R.; Kingshuk, N.; Debanjan, C.; Dhanya, P.; Yogesh, G.; Satishchandra, O.; Ramanathan, V. High and Reversible Lithium Ion Storage in Self-Exfoliated Triazole-Triformyl Phloroglucinol-Based Covalent Organic Nanosheets. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1702170. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H.; Li, Q.; Cao, X.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Jiang, X.H.; Li, M.; Hua, M.; Zhang, Z.B. Removal of uranium(VI) from aqueous solutions by CMK-3 and its polymer composite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 285, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Zeng, B.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, S.X.; Hu, T.; Zhang, L.B. A systematic review of metal organic frameworks materials for heavy metal removal: Synthesis, applications and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 460, 141710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.; Heller, W. The adsorption of cis- and trans- azobenzene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1939, 61, 2228–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian, S. Kinetic models of sorption: A theoretical analysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 276, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Mckay, G. The kinetics of sorption of basic dyes from aqueous solution by sphagnum moss peat. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 1998, 76, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilson, R.E.; Amundson, N.R. Intraparticle diffusion and conduction in porous catalysts-I: Single reactions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1961, 13, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Singh, N.; Tiwari, S.; Tiwari, S.K.; Dhakate, S.R. Cerium functionalized PVA–chitosan composite nanofibers for effective remediation of ultra-low concentrations of Hg(II) in water. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 16622–16630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Deliyanni, E.A. Mercury(II) removal with modified magnetic chitosan adsorbents. Molecules 2013, 18, 6193–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Sun, C.; Ma, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, C.; Xu, Q.; Wang, C.; Chen, H. Removal and recovery of Hg(II) from aqueous solution using chitosan-coated cotton fibers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, R.; Gao, W.; Li, M. Sulfur-modified Chitosan Hydrogel as an Adsorbent for Removal of Hg(II) from Effluents. Fiber Polym. 2017, 18, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Meng, X.; Yue, Q.; Yin, W.; Gao, Y.; Fang, P.; Shen, L. Thiolene click chemistry synthesis of a novel magnetic mesoporous silica/chitosan composite for selective Hg(II) capture and high catalytic activity of spent Hg(II) adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Dang, Q.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Xu, Q.; Liu, H.; Ji, X.; Zhang, B.; Cha, D. Novel amidinothiourea-modiffed chitosan microparticles for selective removal of Hg(II) in solution. Carbohyd. Polym. 2021, 269, 118273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, C.; Liu, M. Mussel-inspired synthesis of magnetic polydopamine–chitosan nanoparticles as biosorbent for dyes and metals removal. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 61, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Highly selective adsorption of Hg(II) by the monodisperse magnetic functional chitosan nano-biosorbent. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2018, 296, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.J.; Xu, N.C.; Shi, L.; Huang, H.B.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhang, J.; Shen, J.L.; Li, H.L.; Chen, Y.L. Facile Synthesis of Porous Organic Polymer/Chitosan Composites and the Removal Effect of Hg(II). Rock. Miner. Anal. 2024, 43, 289–301. [Google Scholar]




| Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | n | KF ((mg/g)(L/mg)1/n) | R2 |
| 723.30 | 0.0049 | 0.9893 | 19.24 | 1.8635 | 0.9532 |
| C0 (mg/L) | 10 | 50 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RL | 0.5308 | 0.1845 | 0.1016 | 0.0535 | 0.0363 | 0.0275 | 0.0221 |
| Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | Qe (mg/g) | R2 | k2 [g/(mg·min)] | Qe (mg/g) | R2 |
| 0.158 | 102.03 | 0.8349 | 0.00192 | 111.87 | 0.9326 |
| Phase I (Film Diffusion) | Phase II (Pore Diffusion) | Phase III (Equilibrium) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | C1 | R12 | k2 | C2 | R22 | k3 | C3 | R32 |
| 22.47 | 4.88 | 0.9200 | 12.48 | 19.17 | 1 | 3.90 | 72.97 | 0.8934 |
| Absorbent | Qmax (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Germanium-modified CS/PVA nanofiber | 31.4 | [42] |
| CS–cotton fibers | 104.3 | [44] |
| Sulfur-modified CS Hydrogel | 186.9 | [45] |
| Mesoporous silica/CS composite | 478.5 | [46] |
| Amidinothiourea-modified CS particles | 322.5 | [47] |
| Diatomite-CS/PVA composite | 195.7 | [16] |
| Magnetic polydopamine–CS NPs | 245.2 | [48] |
| Monodisperse magnetic functional CS | 246.1 | [49] |
| Thiourea based POP | 1250 | [28] |
| POP/CS | 249.2 | [50] |
| CS/PVA/POP nanofibre membrane | 493.8 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Q.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, S.; Hu, J.; Chen, Z.; Reheman, A. Preparation of CS/PVA/POP Nanofiber Membranes and Adsorption Behavior for Hg(II) Ions. Water 2025, 17, 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060885
Zhou Q, Sun Y, Li Z, Sun S, Hu J, Chen Z, Reheman A. Preparation of CS/PVA/POP Nanofiber Membranes and Adsorption Behavior for Hg(II) Ions. Water. 2025; 17(6):885. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060885
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Qunhua, Yu Sun, Ziye Li, Siqin Sun, Jianshe Hu, Zhangpei Chen, and Aikebaier Reheman. 2025. "Preparation of CS/PVA/POP Nanofiber Membranes and Adsorption Behavior for Hg(II) Ions" Water 17, no. 6: 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060885
APA StyleZhou, Q., Sun, Y., Li, Z., Sun, S., Hu, J., Chen, Z., & Reheman, A. (2025). Preparation of CS/PVA/POP Nanofiber Membranes and Adsorption Behavior for Hg(II) Ions. Water, 17(6), 885. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060885






