Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Impact of Functional Head Groups and Chain Lengths of PFAS Degradation Using Ultrasound Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Details of Simulations
2.2. Physical Experimental Materials
2.3. Apparatus and Measurements
2.4. Ultrasound Reactor Tank
2.5. Chemical Analysis
2.6. Correlation Between Simulation and Experimental Data
3. Results and Discussion
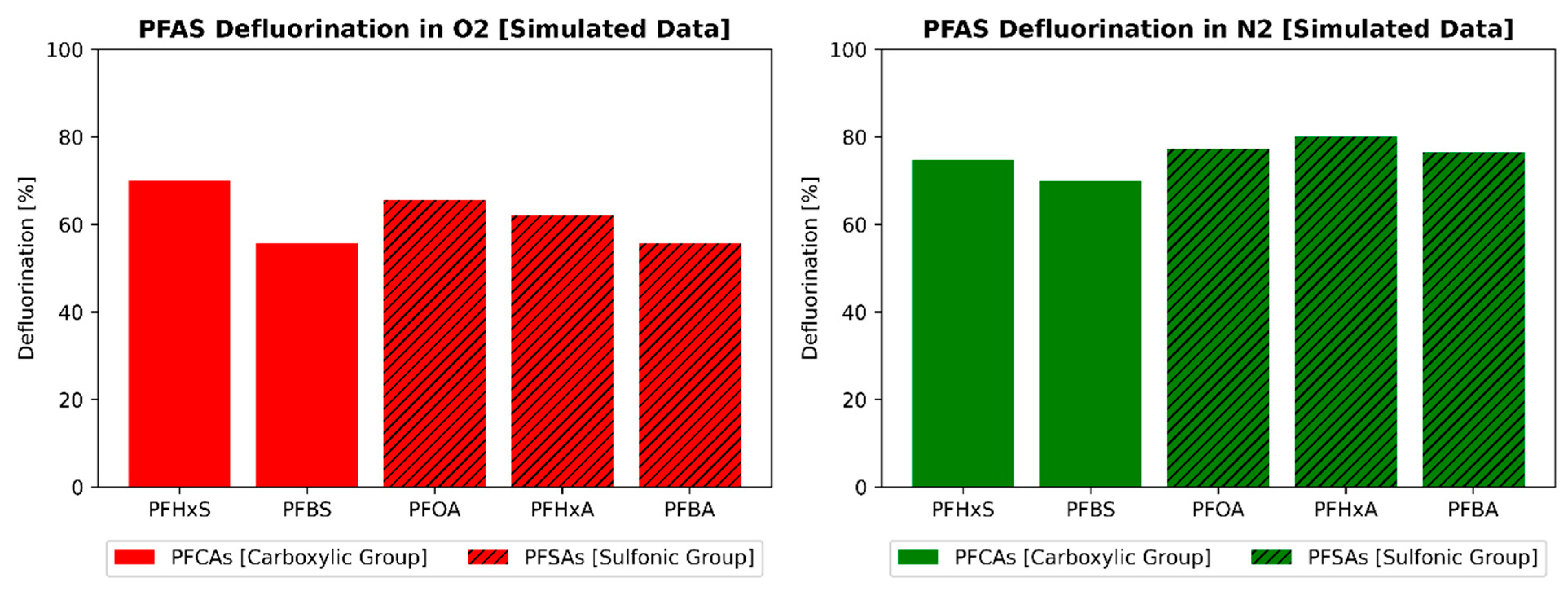
3.1. Impact of Functional Head Group and Chain Length
3.2. Impact of Chain Length
3.3. Influence of the Sonolytic Environment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pelch, K.E.; Reade, A.; Wolffe, T.A.; Kwiatkowski, C.F. PFAS health effects database: Protocol for a systematic evidence map. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meegoda, J.N.; Kewalramani, J.A.; Li, B.; Marsh, R.W. A review of the applications, environmental release, and remediation technologies of Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meegoda, J.N.; de Souza, B.B.; Casarini, M.M.; Kewalramani, J.A. A Review of PFAS Destruction Technologies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.H.; Long, G.C.; Porter, R.C.; Anderson, J.K. Occurrence of select perfluoroalkyl substances at U.S. Air Force aqueous film-forming foam release sites other than fire-training areas: Field-validation of critical fate and transport properties. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräunig, J.; Baduel, C.; Heffernan, A.; Rotander, A.; Donaldson, E.; Mueller, J.F. Fate and redistribution of perfluoroalkyl acids through AFFF-impacted groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596-597, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, A.G.; Jones, K.C.; Sweetman, A.J. A first global production, emission, and environmental inventory for perfluorooctane sulfonate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meegoda, J.; Kewalramani, J.; Marsh, R.; de Souza, B.B.; Dahanayake, M. Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Subjects: Polymer Science, Scholarly Community Encyclopedia Polymer Science 2021. Available online: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/6459 (accessed on 29 March 2022).
- Fenton, S.E.; Ducatman, A.; Boobis, A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Lau, C.; Ng, C.; Smith, J.S.; Roberts, S.M. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Toxicity and Human Health Review: Current State of Knowledge and Strategies for Informing Future Research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 606–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazzolo, S.; Caligiuri, I.; Sfriso, A.A.; Mauceri, M.; Rotondo, R.; Campagnol, D.; Canzonieri, V.; Rizzolio, F. Early Warnings by Liver Organoids on Short- and Long-Chain PFAS Toxicity. Toxics 2022, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahinroosta, R.; Senevirathna, L. A review of the emerging treatment technologies for PFAS contaminated soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 255, 109896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L.; Xie, Z.; Ebinghaus, R. Distribution of perfluoroalkyl compounds in seawater from Northern Europe, Atlantic Ocean, and Southern Ocean. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusseau, M.L.; Anderson, R.H.; Guo, B. PFAS concentrations in soils: Background levels versus contaminated sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, J.L.; Nadal, M. Human exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) through drinking water: A review of the recent scientific literature. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesy, J.P.; Kannan, K. Global Distribution of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate in Wildlife. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, K.Y.; Yamazaki, E.; Yamashita, N.; Taniyasu, S.; Murphy, M.B.; Horii, Y.; Petrick, G.; Kallerborn, R.; Kannan, K.; Murano, K.; et al. Transport of Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from an arctic glacier to downstream locations: Implications for sources. Sci. Total. Environ. 2013, 447, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, K.; Mabury, S.A.; Jenkins, T.M.; Washington, J.W. A North American and global survey of perfluoroalkyl substances in surface soils: Distribution patterns and mode of occurrence. Chemosphere 2016, 161, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reducing PFAS in Drinking Water with Treatment Technologies|US EPA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sciencematters/reducing-pfas-drinking-water-treatment-technologies (accessed on 22 January 2024).
- Pérez, F.; Nadal, M.; Navarro-Ortega, A.; Fàbrega, F.; Domingo, J.L.; Barceló, D.; Farré, M. Accumulation of perfluoroalkyl substances in human tissues. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischel, H.N.; A MacManus-Spencer, L.; Zhang, C.; Luthy, R.G. Strong associations of short-chain perfluoroalkyl acids with serum albumin and investigation of binding mechanisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 2423–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaballah, S.; Swank, A.; Sobus, J.R.; Howey, X.M.; Schmid, J.; Catron, T.; McCord, J.; Hines, E.; Strynar, M.; Tal, T. Evaluation of Developmental Toxicity, Developmental Neurotoxicity, and Tissue Dose in Zebrafish Exposed to GenX and Other PFAS. Environ. Heal. Perspect. 2020, 128, 47005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.D.; Hu, W.; De Coen, W.; Newsted, J.L.; Giesy, J.P. Binding of perfluorinated fatty acids to serum proteins. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 2639–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubel, F.A.; Sorenson, S.D.; Roach, D.E. Health status of plant workers exposed to fluorochemicals—A preliminary report. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 2010, 41, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, B.E.; Pinney, S.M.; Hines, E.P.; Fenton, S.E.; Ferguson, K.K. Associations between longitudinal serum perfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) levels and measures of thyroid hormone, kidney function, and body mass index in the Fernald Community Cohort. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWitt, J.C.; Peden-Adams, M.M.; Keller, J.M.; Germolec, D.R. Immunotoxicity of Perfluorinated Compounds: Recent Developments. Toxicol. Pathol. 2011, 40, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaunig, J.E.; Shinohara, M.; Iwai, H.; Chengelis, C.P.; Kirkpatrick, J.B.; Wang, Z.; Bruner, R.H. Evaluation of the chronic toxicity and carcinogenicity of perfluorohexanoic acid (PFHxA) in sprague-dawley rats. Toxicol. Pathol. 2015, 43, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Ronen, A. A Review on Removal and Destruction of Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) by Novel Membranes. Membranes 2022, 12, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogue, C. Incineration May Spread, Not Break Down PFAS, C&EN News 2020. Available online: https://cen.acs.org/environment/persistent-pollutants/Incincerators-spread-break-down-PFAS/98/web/2020/04 (accessed on 18 September 2022).
- USEPA, Per-and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): Incineration to Manage PFAS Waste Streams Background. 2020. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2019-09/documents/technical_brief_pfas_incineration_ioaa_approved_final_july_2019.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2022).
- Gomez-Ruiz, B.; Gómez-Lavín, S.; Diban, N.; Boiteux, V.; Colin, A.; Dauchy, X.; Urtiaga, A. Efficient electrochemical degradation of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) from the effluents of an industrial wastewater treatment plant. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kewalramani, J.A.; de Souza, B.B.; Marsh, R.W.; Meegoda, J.N. Contributions of reactor geometry and ultrasound frequency on the efficiency of sonochemical reactor. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2023, 98, 106529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kewalramani, J.A.; Marsh, R.W.; Prajapati, D.; Meegoda, J.N. Kinetics effects of the power density and initial concentration on the sonochemical degradation of PFOS and PFOA in concentrated waste. J. Water Process. Eng. 2023, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kewalramani, J.A.; Wang, B.; Marsh, R.W.; Meegoda, J.N.; Freire, L.R. Coupled high and low-frequency ultrasound remediation of PFAS-contaminated soils. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2022, 88, 106063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidnell, T.; Wood, R.J.; Hurst, J.; Lee, J.; Bussemaker, M.J. Sonolysis of per- and poly fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): A meta-analysis. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2022, 87, 105944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meegoda, J.N.; Hewage, S.A.; Batagoda, J.H. Stability of Nanobubbles. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, B.B.; Hewage, S.A.; Kewalramani, J.A.; van Duin, A.C.; Meegoda, J.N. A ReaxFF-based molecular dynamics study of the destruction of PFAS due to ultrasound. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 122026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S. Sonochemistry. Science 1990, 247, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S. Ultrasound. Its Chemical, Physical, and Biological Effects. Science 1989, 243, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S. The Chemical Effects of Ultrasound. Sci. Am. 1989, 260, 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Suslick, K.S.; Price, G.J. Applications of Ultrasound to Materials Chemistry. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1999, 29, 295–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S.; Ertl, G.; Kniizinger, H.; Weitkamp, J. Sonocatalysis. In Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalysis; 1997; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Flint, E.B.; Suslick, K.S. The Temperature of Cavitation. Science 1991, 253, 1397–1399. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/2878744 (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- Chen, D.; Sharma, S.; Mudhoo, A. Handbook on Applications of Ultrasound: Sonochemistry for Sustainability; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA.
- Wu, T.Y.; Guo, N.; Teh, C.Y.; Hay, J.X.W. Theory and Fundamentals of Ultrasound. Adv. Ultrasound Technol. Environ. Remediat. 2013, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Juárez, J.A.; Graff, K.F. Power Ultrasonics: Applications of High-Intensity Ultrasound; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2014; pp. 1–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Pétrier, C. The use of power ultrasound for water treatment. In Power Ultrasonics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 939–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y. Advanced Oxidation Processes Using Ultrasound Technology for Water and Wastewater Treatment. Handb. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2015, 711–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didenko, Y.T.; McNamara, W.B., III; Suslick, K.S. Temperature of Multibubble Sonoluminescence in Water. J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103, 10783–10788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddingsaas, N.C.; Suslick, K.S. Intense Mechanoluminescence and Gas Phase Reactions from the Sonication of an Organic Slurry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 6718–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauterborn, W.; Mettin, R. Acoustic cavitation: Bubble dynamics in high-power ultrasonic fields. In Power Ultrasonics; Woodhead Publishing: Göttingen, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Guelfo, J.L.; Korzeniowski, S.; Mills, M.A.; Anderson, J.; Anderson, R.H.; Arblaster, J.A.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; Dasu, K.; Henry, B.J.; et al. Environmental Sources, Chemistry, Fate, and Transport of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: State of the Science, Key Knowledge Gaps, and Recommendations Presented at the August 2019 SETAC Focus Topic Meeting. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 3234–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, C.F.; Andrews, D.Q.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Bruton, T.A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Maffini, M.V.; Miller, M.F.; Pelch, K.E.; Reade, A.; et al. Scientific Basis for Managing PFAS as a Chemical Class. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horst, J.; McDonough, J.; Ross, I.; Houtz, E. Understanding and Managing the Potential By-Products of PFAS Destruction. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 2020, 40, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Lee, T.; Sahle-Demessie, E.; Ateia, M.; Nadagouda, M.N. Recent advances on PFAS degradation via thermal and nonthermal methods. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2023, 13, 100421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, B.B.; Meegoda, J. Insights into PFAS environmental fate through computational chemistry: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Xia, X.; Dong, J.; Xia, N.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y. Short- and long-chain perfluoroalkyl substances in the water, suspended particulate matter, and surface sediment of a turbid river. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendel, S.; Fetter, É.; Staude, C.; Vierke, L.; Biegel-Engler, A. Short-chain perfluoroalkyl acids: Environmental concerns and a regulatory strategy under REACH. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifuzzaman; Pellizzeri, S.; Attia, M.F.; Tharayil, N.; Anker, J.N.; Karanfil, T. Cationic polymer for selective removal of GenX and short-chain PFAS from surface waters and wastewaters at ng/L levels. Water Res. 2019, 163, 114874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Wu, S.; Lopez, I.J.; Chang, J.Y.; Karanfil, T.; Snyder, S.A. Adsorption of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in groundwater by granular activated carbons: Roles of hydrophobicity of PFAS and carbon characteristics. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duin, A.C.T.; Dasgupta, S.; Lorant, F.; Goddard, W.A. ReaxFF: A Reactive Force Field for Hydrocarbons. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 9396–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Srinivasan, S.G.; Neek-Amal, M.; Costamagna, S.; van Duin, A.C.T.; Peeters, F.M. Thermal properties of fluorinated graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 104114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LAMMPS Molecular Dynamics Simulator, (n.d.). Available online: https://www.lammps.org/index.html (accessed on 21 February 2022).
- Thompson, A.P.; Aktulga, H.M.; Berger, R.; Bolintineanu, D.S.; Brown, W.M.; Crozier, P.S.; Veld, P.J.I.; Kohlmeyer, A.; Moore, S.G.; Nguyen, T.D.; et al. LAMMPS - a flexible simulation tool for particle-based materials modeling at the atomic, meso, and continuum scales. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2022, 271, 108171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: An advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J. Cheminform. 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukowski, A. Visualization and analysis of atomistic simulation data with OVITO—The Open Visualization Tool. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 18, 015012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.J.; Sidnell, T.; Ross, I.; McDonough, J.; Lee, J.; Bussemaker, M.J. Ultrasonic degradation of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) correlated with sonochemical and sonoluminescence characterisation. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2020, 68, 105196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, S.S.; Cranmer, B.; Dooley, G.; Hanson, A.J.; Maraviov, S.; Mohanty, S.K.; Blotevogel, J.; Mahendra, S. Sonolytic destruction of Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in groundwater, aqueous Film-Forming Foams, and investigation derived waste. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.Y.; Vecitis, C.D.; Mader, B.T.; Hoffmann, M.R. Perfluorinated Surfactant Chain-Length Effects on Sonochemical Kinetics. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 9834–9842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecitis, C.D.; Park, H.; Cheng, J.; Mader, B.T.; Hoffmann, M.R. Kinetics and Mechanism of the Sonolytic Conversion of the Aqueous Perfluorinated Surfactants, Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA), and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) into Inorganic Products. J. Phys. Chem. A 2008, 112, 4261–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Vecitis, C.D.; Park, H.; Mader, B.T.; Hoffmann, M.R. Sonochemical Degradation of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in Groundwater: Kinetic Effects of Matrix Inorganics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippert, E. The Strengths of Chemical Bonds, von T. L. Cottrell. Butterworths Publications Ltd., London 1958. 2. Aufl., X, 317 S., geb.t—/32/—. Angew. Chem. 1960, 72, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, N.A.; Rodriguez-Freire, L.; Keswani, M.; Sierra-Alvarez, R. Effect of chemical structure on the sonochemical degradation of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2016, 2, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psillakis, E.; Cheng, J.; Hoffmann, M.R.; Colussi, A.J. Enrichment Factors of Perfluoroalkyl Oxoanions at the Air/Water Interface. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 8826–8829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruelle, P.; Kesselring, U.W. The Hydrophobic Effect. 3. A Key Ingredient in Predicting n-Octanol–Water Partition Coefficients. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 87, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldoveanu, S.; David, V. Front Matter, Modern Sample Preparation for Chromatography iii. 2021. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128214053010017?via%3Dihub (accessed on 22 February 2024).
- Wang, Z.; Cousins, I.T.; Scheringer, M.; Hungerbühler, K. Fluorinated alternatives to long-chain perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids (PFCAs), perfluoroalkane sulfonic acids (PFSAs) and their potential precursors. Environ. Int. 2013, 60, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateia, M.; Maroli, A.; Tharayil, N.; Karanfil, T. The overlooked short- and ultrashort-chain poly- and perfluorinated substances: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 866–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shende, T.; Andaluri, G.; Suri, R. Chain-length dependent ultrasonic degradation of perfluoroalkyl substances. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2023, 15, 100509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, R.W.; Kewalramani, J.A.; de Souza, B.B.; Meegoda, J.N. The use of a fluorine mass balance to demonstrate the mineralization of PFAS by high frequency and high power ultrasound. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Freire, L.; Abad-Fernández, N.; Sierra-Alvarez, R.; Hoppe-Jones, C.; Peng, H.; Giesy, J.P.; Snyder, S.; Keswani, M. Sonochemical degradation of perfluorinated chemicals in aqueous film-forming foams. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sostaric, J.Z.; Riesz, P. Sonochemistry of surfactants in aqueous solutions: An EPR spin-trapping study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 11010–11019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.; Hoffmann, M.R. Sonochemical degradation of perfluorinated surfactants: Power and multiple frequency effects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isowamwen, O.; Li, R.; Holsen, T.; Thagard, S.M. Plasma-assisted degradation of a short-chain perfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS): Perfluorobutane sulfonate (PFBS). J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 456, 131691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, T.; Karanam, K.; Han, H.; Vo, H.N.P.; Shukla, P.; Firouzi, M.; Rudolph, V. Effect of different co-foaming agents on PFAS removal from the environment by foam fractionation. Water Res. 2023, 230, 119532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Nickelsen, M.; Chiang, S.-Y.; Woodard, S.; Wang, Y.; Liang, S.; Mora, R.; Fontanez, R.; Anderson, H.; Huang, Q. Treatment of perfluoroalkyl acids in concentrated wastes from regeneration of spent ion exchange resin by electrochemical oxidation using Magnéli phase Ti4O7 anode. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2021, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Multari, N.; Nau-Hix, C.; Woodard, S.; Nickelsen, M.; Thagard, S.M.; Holsen, T.M. Removal of Poly- and Per-Fluorinated Compounds from Ion Exchange Regenerant Still Bottom Samples in a Plasma Reactor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 13973–13980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shende, T.; Andaluri, G.; Suri, R. Frequency-dependent sonochemical degradation of perfluoroalkyl substances and numerical analysis of cavity dynamics. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narimani, M.; Khan, Y.; da Silva, G. A Detailed Chemical Kinetic Model for the Destruction of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS): Pyrolysis and Incineration of Short-Chain Perfluorinated Carboxylic and Sulfonic Acids. ChemRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Molecule Name | Chemical Formula | Acronym | Chain Length | Perfluorinated Carbon | Log (Kow) * | Functional Group | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perfluorooctanoic acid | C8HF15O2 | PFOA | Long | 7 | 5.11 | Carboxyl | PFCAs |
| Perfluorohexanesulphonic acid | C6HF13O3S | PFHxS | Long | 6 | - | Sulfonic | PFSAs |
| Perfluorohexanoic acid | C6HF11O2 | PFHxA | Short | 5 | 3.71 | Carboxyl | PFCAs |
| Perfluorobutane sulfonate | C4HF9O3S | PFBS | Short | 4 | 2.63 | Sulfonic | PFSAs |
| Perflurobutanoic acid | C4HF7O2 | PFBA | Short | 3 | 2.31 | Carboxyl | PFCAs |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bezerra de Souza, B.; Kewalramani, J.A.; Marsh, R.W.; Meegoda, J. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Impact of Functional Head Groups and Chain Lengths of PFAS Degradation Using Ultrasound Technology. Water 2025, 17, 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071025
Bezerra de Souza B, Kewalramani JA, Marsh RW, Meegoda J. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Impact of Functional Head Groups and Chain Lengths of PFAS Degradation Using Ultrasound Technology. Water. 2025; 17(7):1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071025
Chicago/Turabian StyleBezerra de Souza, Bruno, Jitendra A. Kewalramani, Richard W. Marsh, and Jay Meegoda. 2025. "Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Impact of Functional Head Groups and Chain Lengths of PFAS Degradation Using Ultrasound Technology" Water 17, no. 7: 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071025
APA StyleBezerra de Souza, B., Kewalramani, J. A., Marsh, R. W., & Meegoda, J. (2025). Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Impact of Functional Head Groups and Chain Lengths of PFAS Degradation Using Ultrasound Technology. Water, 17(7), 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071025







