Characteristics of Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Heavy Rainfall and Surface Runoff Generating Processes in the Mountainous Areas of Northern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
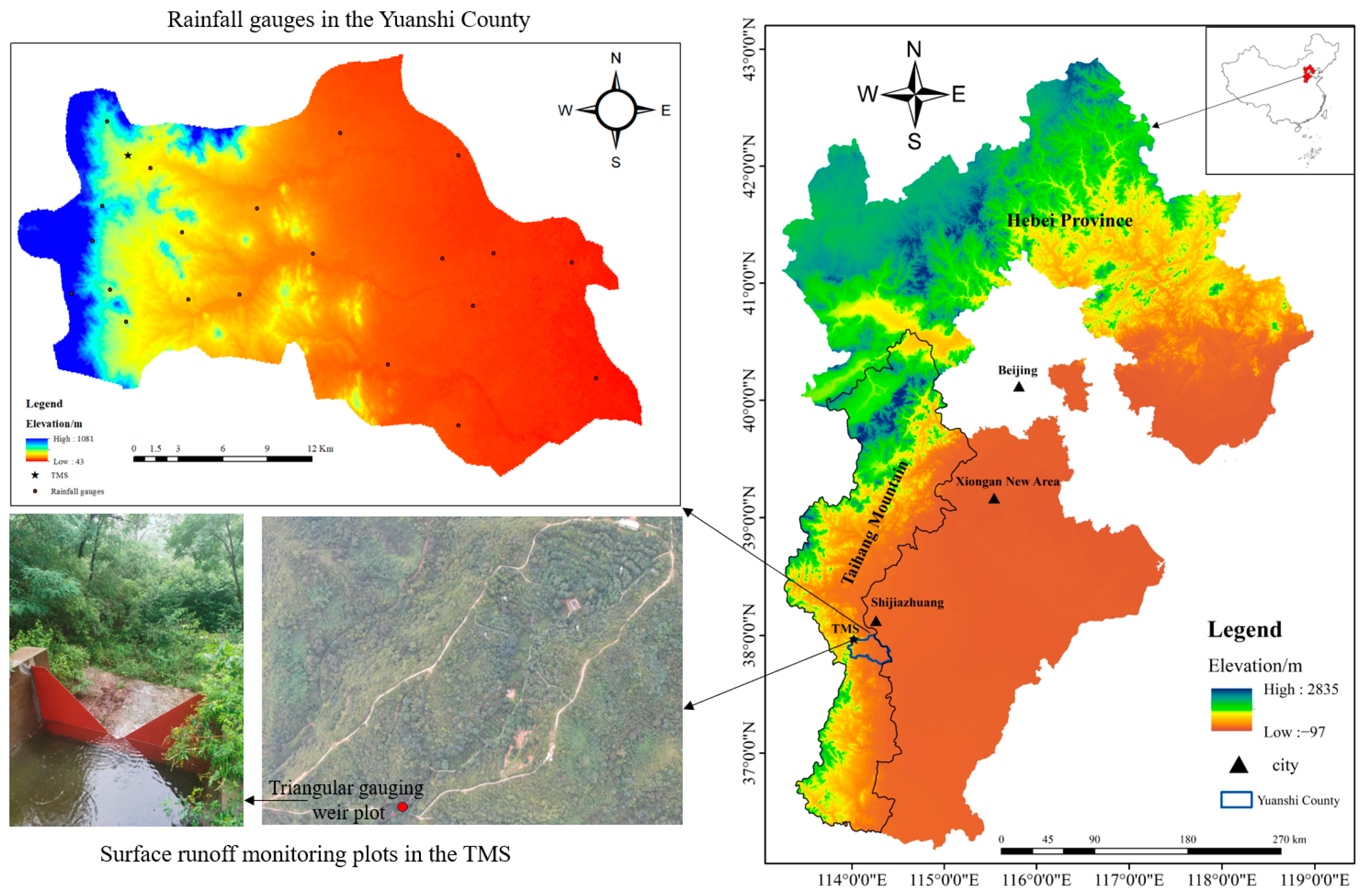
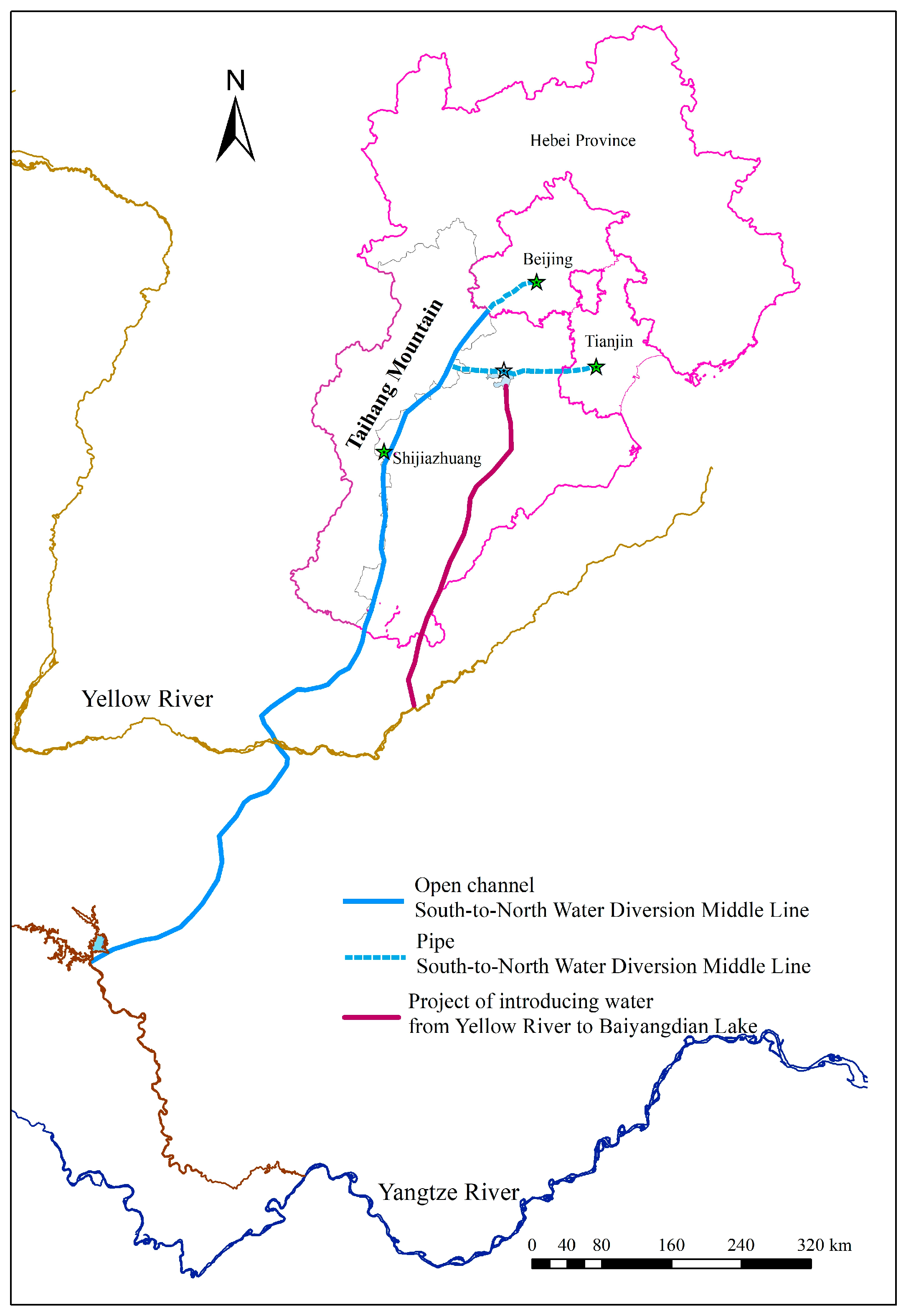
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. Rainfall Monitoring
2.2.2. Surface Runoff Monitoring
2.3. Homogeneity and Trend Test
2.4. Runoff Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
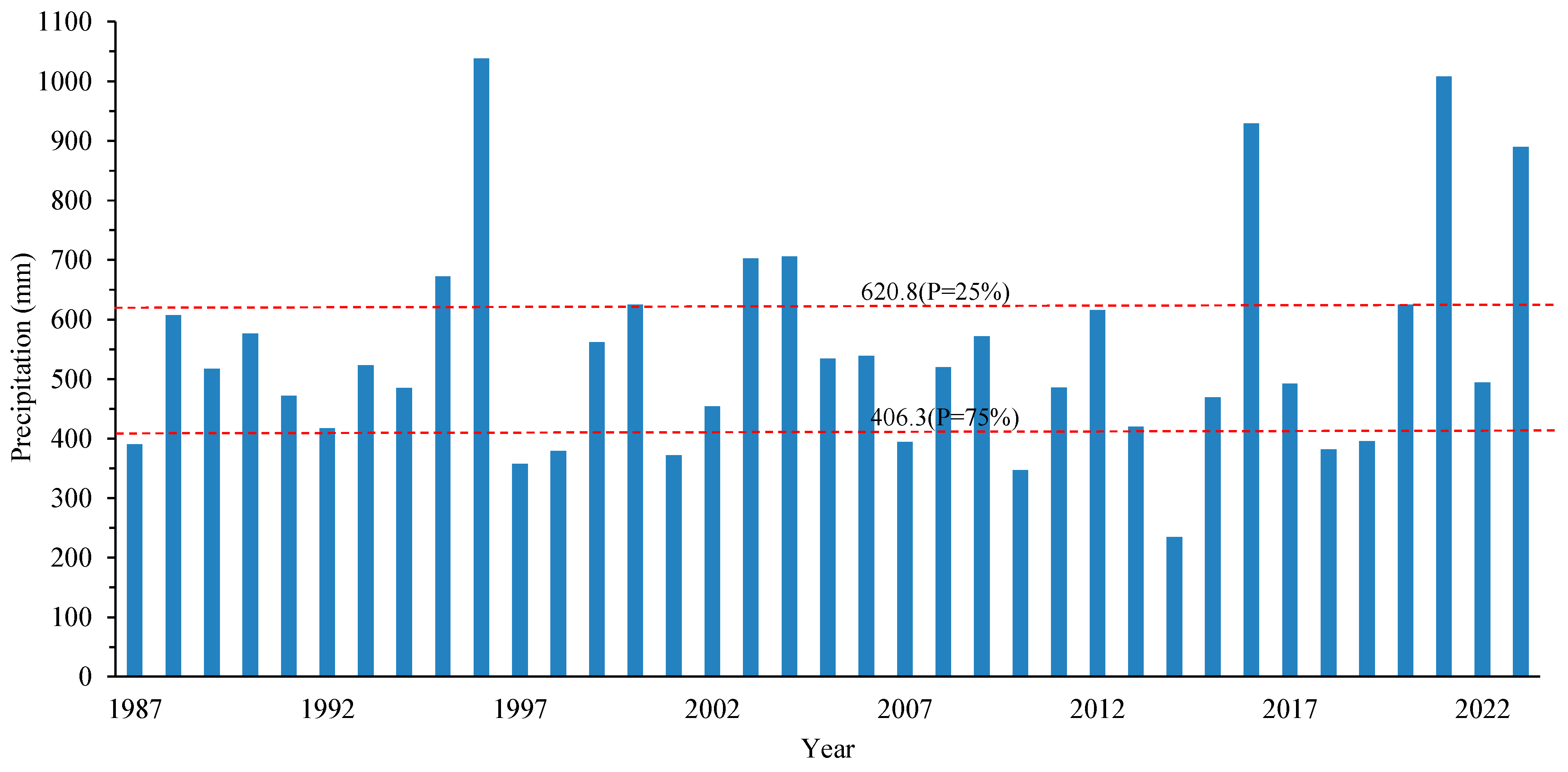
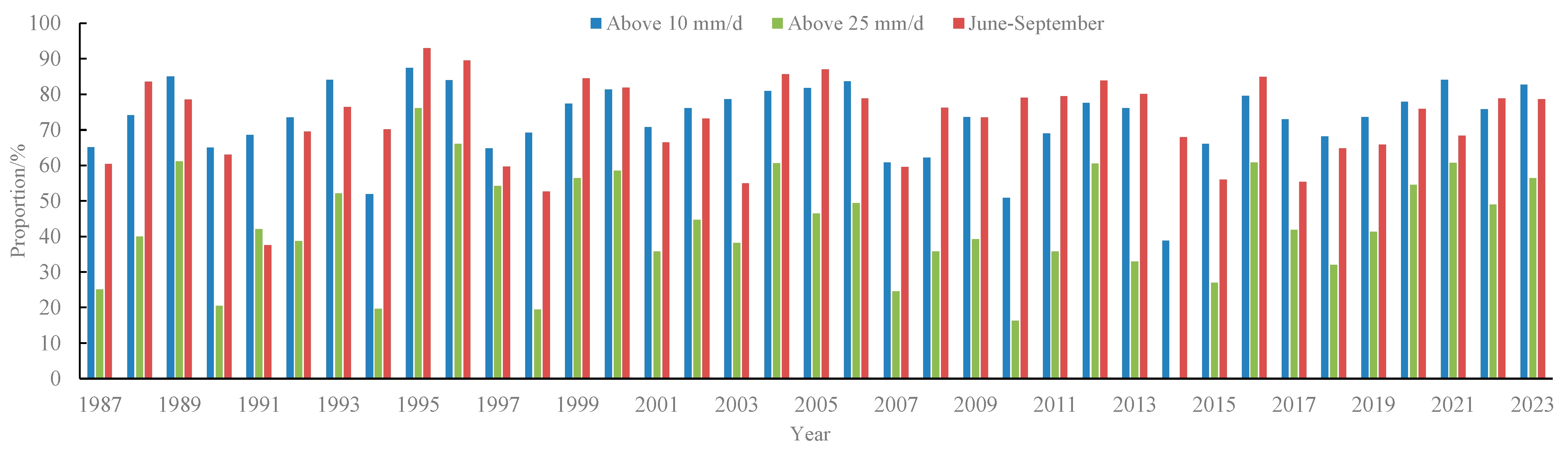
3.1. Annual Rainfall Characteristics
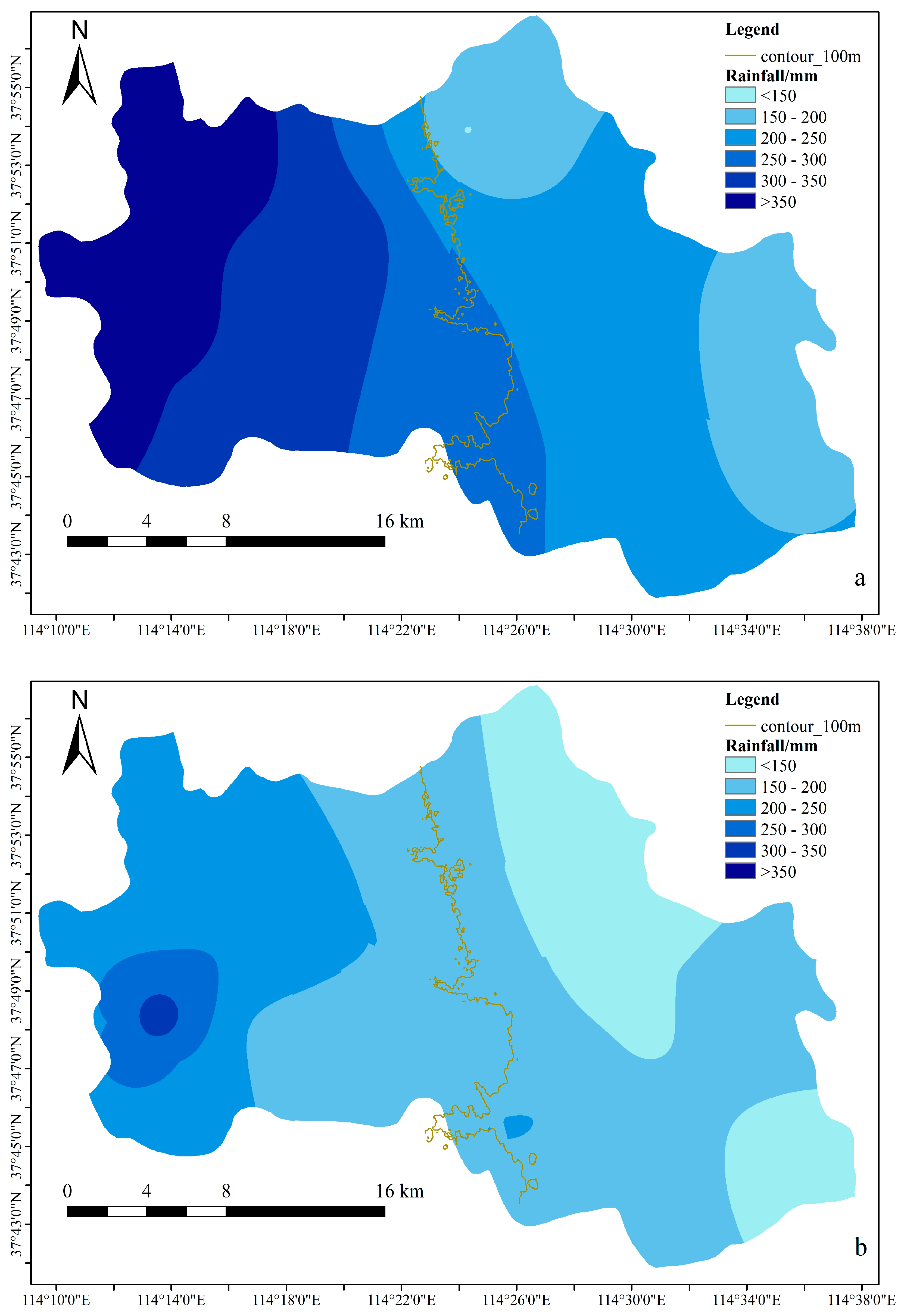
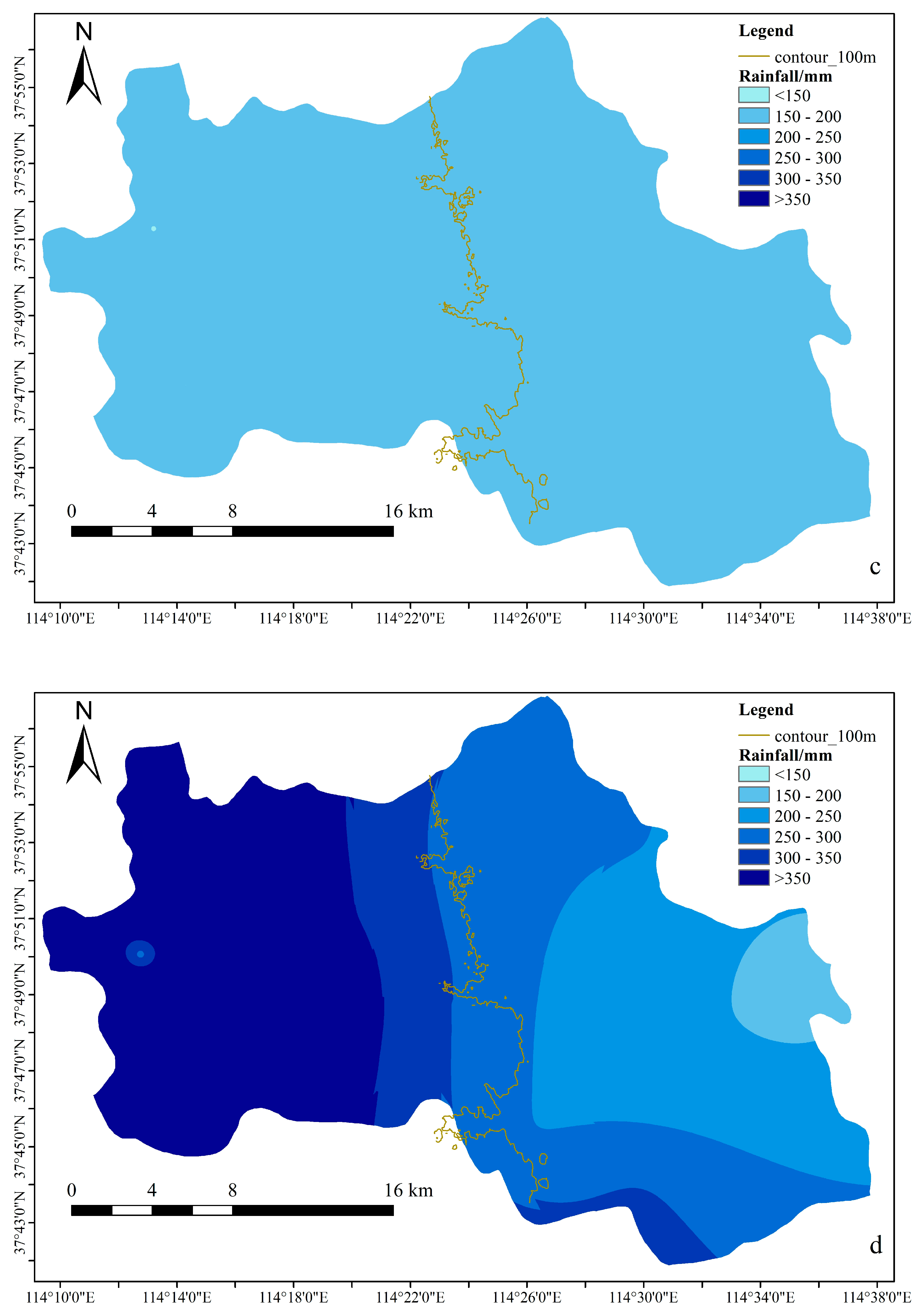
3.2. Rainfall Spatial Characteristics
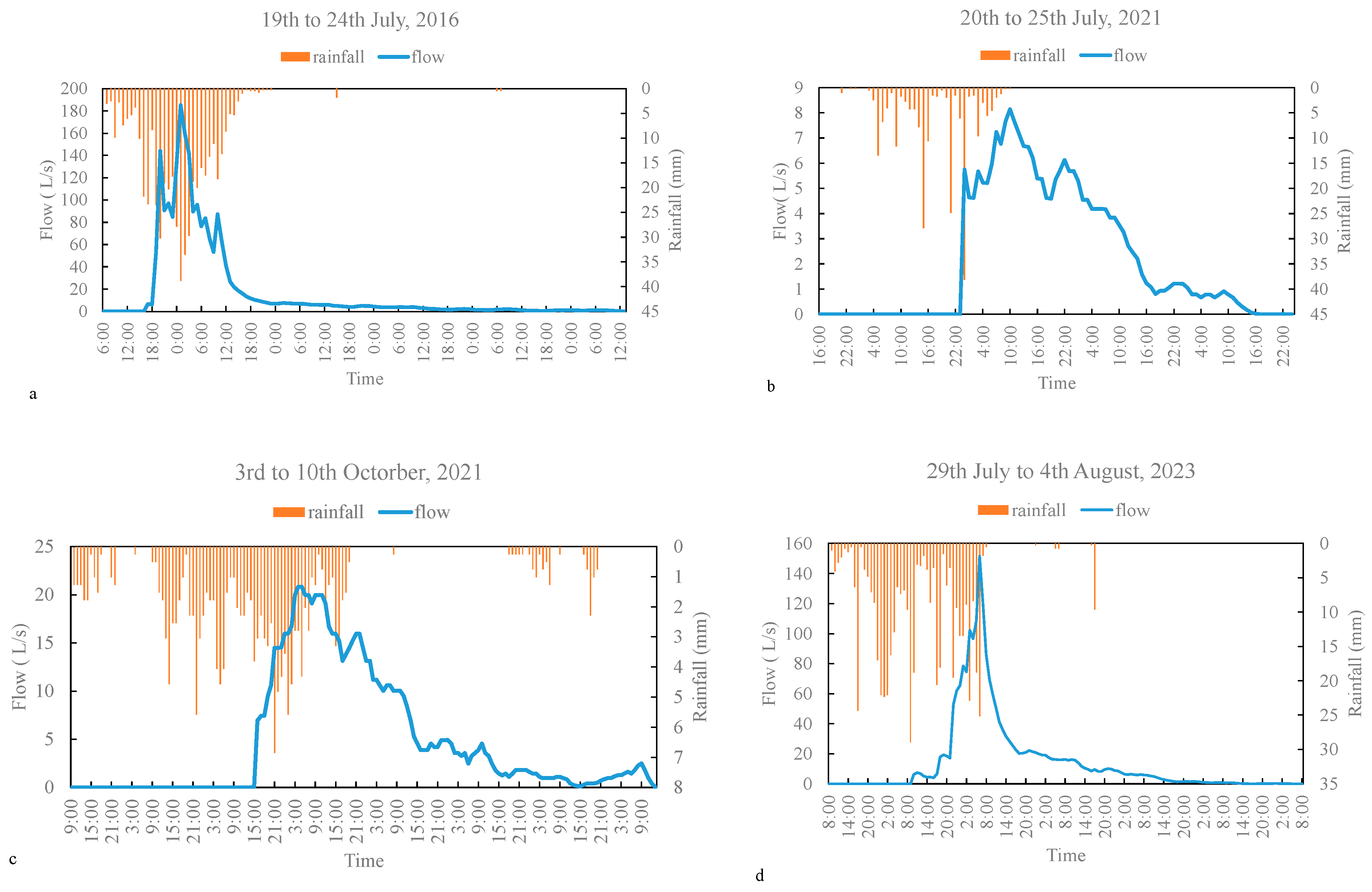
3.3. Surface Runoff Generating Processes
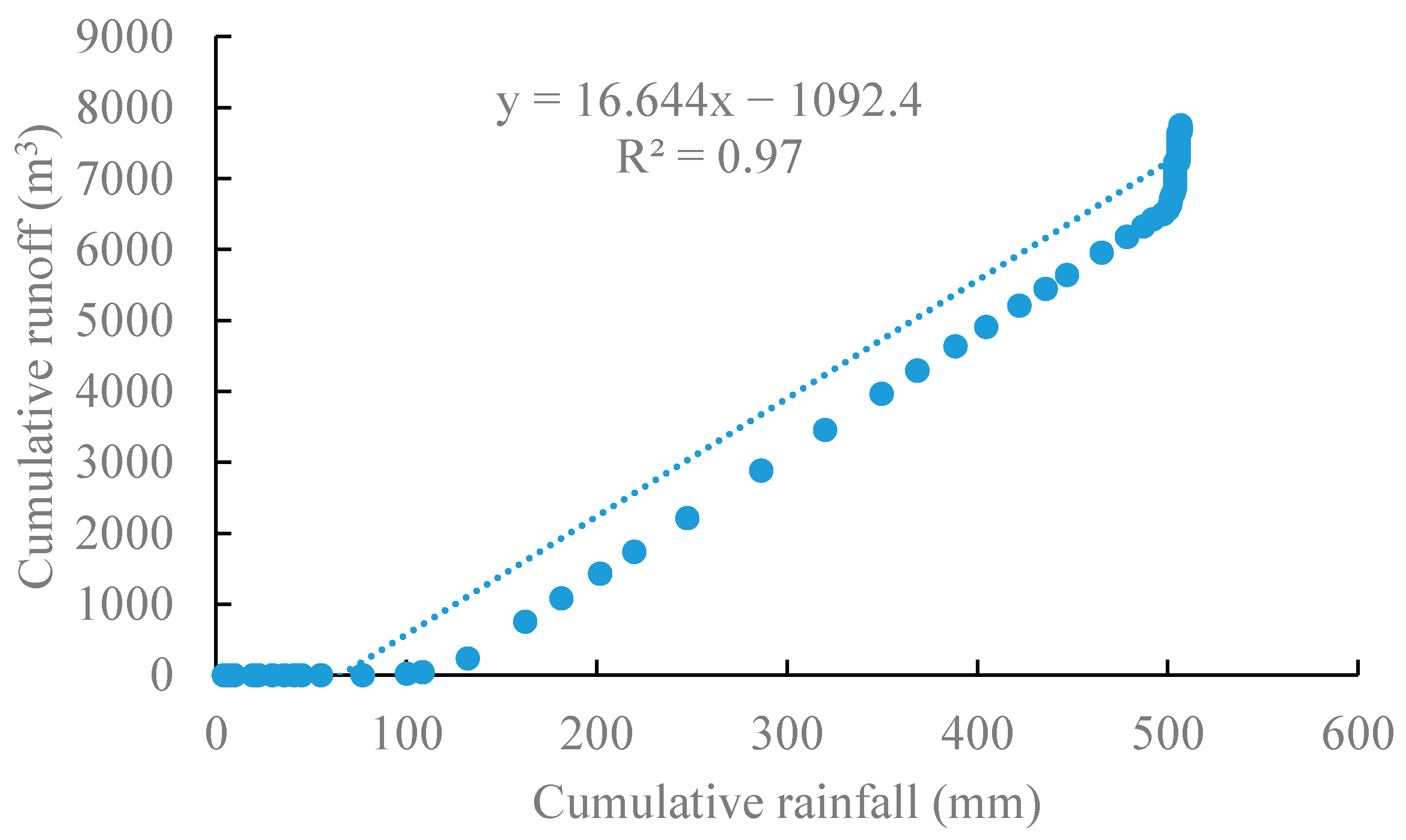
3.4. Contributions of Precipitation on Variation in Runoff
4. Discussion
4.1. Forms of Surface Runoff Generating
4.2. Indications of Surface Runoff Generating Processes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fei, K.; Deng, L.; Zhang, L.; Sun, T.; Wu, Y.; Fan, X.; Dong, Y. Lateral transport of soil total carbon with slope runoff and interflow: Effects of rainstorm characteristics under simulated rainfall. Catena 2019, 179, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; Shi, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Q. Straw returning on sloping farmland reduces the soil and water loss via surface flow but increases the nitrogen loss via interflow. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 339, 108154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Liu, J.; Gao, H.; Qi, F.; Wang, F.; Zhang, M. Surface and subsurface runoff generation processes and their influencing factors on a hillslope in northern China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 906, 167372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, F.; van Meerveld, I.; Weiler, M. Long-term changes in runoff generation mechanisms for two proglacial areas in the Swiss Alps II: Subsurface flow. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2021WR030223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Mena, M.; Carrillo-Lopez, E.; Boix-Fayos, C.; Almagro, M.; García Franco, N.; Díaz-Pereira, E.; Montoya, I.; de Vente, J. Long-term effectiveness of sustainable land management practices to control runoff, soil erosion, and nutrient loss and the role of rainfall intensity in Mediterranean rainfed agroecosystems. Catena 2020, 187, 104352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Su, D.; Li, P.; He, Z. Experimental study of the impact of rainfall characteristics on runoff generation and soil erosion. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424–425, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Jia, F.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Y. Effects of surficial condition and rainfall intensity on runoff in a loess hilly area, China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, M.A.; Kavian, A. Effects of rainfall patterns on runoff and soil erosion in field plots. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Abla, M.; Lü, D.; Yan, R.; Ren, Q.; Ren, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Lin, P.; et al. Effects of vegetation and rainfall types on surface runoff and soil erosion on steep slopes on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2018, 170, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, P.; Gusarov, A.V.; Yu, Y. Effects of land uses and rainfall regimes on surface runoff and sediment yield in a nested watershed of the Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 44, 404277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güçlü, Y.S. Improved visualization for trend analysis by comparing with classical Mann-Kendall test and ITA. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124674. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Wang, G. Insight into runoff decline due to climate change in China’s Water Tower. Water Supply 2012, 12, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Wang, S.-Y.S.; Gillies, R.R.; Kravitz, B.; Hipps, L.; Rasch, P.J. Increasing water cycle extremes in California and in relation to ENSO cycle under global warming. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8657. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Chiew, F.H.; Charles, S.; Podger, G. Future climate and runoff projections across South Asia from CMIP5 global climate models and hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 18, 92–109. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, X.; Li, W.; Li, J.; He, L.; Mao, J.; Han, L. Future climate change and urban growth together affect surface runoff in a large-scale urban agglomeration. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 99, 104970. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, D.; Min, Z. Effects of grass vegetation coverage and position on runoff and sediment yields on the slope of Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 259, 107231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Hu, C.; Ping, J. Study on the influence of vegetation change on runoff generation mechanism in the Loess Plateau, China. Water Supply 2020, 21, 683–695. [Google Scholar]
- Astuti, I.S.; Sahoo, K.; Milewski, A.; Mishra, D.R. Impact of land use land cover (LULC) change on surface runoff in an increasingly urbanized tropical watershed. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 4087–4103. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.K.; Jia, Y.W.; Hao, C.P.; Li, X.X.; Qiu, Y.Q.; Niu, C.W. Evolution law and attribution analysis of vertical distribution of blue water and green water in Taihang Mountain region. South—North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 16, 64–73, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Qi, F.; Liu, J.; Gao, H.; Fu, T.; Wang, F. Characteristics and spatial–temporal patterns of supply and demand of ecosystem services in the Taihang Mountains. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 109932. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. Evolution of habitat quality and association with land-use changes in mountainous areas: A case study of the Taihang Mountains in Hebei Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107967. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, W.W.; Qi, S.L.; Zhou, C.H.; Zhang, W.J. Spatial analysis of soil and water loss sensitivity based on USLE and GIS—A case study of Taihang Mountain area in Hebei Province. Geogr. Res. 2014, 33, 614–624, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Geng, S.; Shi, P.; Zong, N.; Zhu, W. Using soil survey database to assess soil quality in the heterogeneous Taihang mountains, North China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Ge, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, B.; Zhang, W.; Ding, G. Modern pollen-vegetation relationships in the Taihang Mountains: Towards the quantitative reconstruction of land-cover changes in the North China Plain. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107928. [Google Scholar]
- Sakakibara, K.; Tsujimura, M.; Song, X.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal variation of the surface water effect on the groundwater recharge in a low-precipitation region: Application of the multi-tracer approach to the Taihang Mountains, North China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 545, 132–144. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Hou, X.; Cao, J. Identifying the driving impact factors on water yield service in mountainous areas of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region in China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.W.; Hao, C.P.; Niu, C.W.; Qiu, Y.Q.; Du, J.K.; Xu, F.; Liu, H. Spatial-temporal variations of precipitation and runoff and analyses of water-heat-human-land matching characteristics in a typical mountainous area of China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 2288–2302, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Zhang, Y.Y. Water resource and pollution safeguard for Xiongan New Area construction and its sustainable development. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2017, 32, 1199–1205, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Geng, S.; Shi, P.; Song, M.; Zong, N.; Zu, J.; Zhu, W. Diversity of vegetation composition enhances ecosystem stability along elevational gradients in the Taihang Mountains, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 594–603. [Google Scholar]
- Hirabayashi, Y.; Mahendran, R.; Koirala, S.; Konoshima, L.; Yamazaki, D.; Watanabe, S.; Kim, H.; Kanae, S. Global flood risk under climate change. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 816–821. [Google Scholar]
- Najafi, M.R.; Zhang, Y.; Martyn, N. A flood risk assessment framework for interdependent infrastructure systems in coastal environments. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 64, 102516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, T.G. Evidence for intensification of the global water cycle: Review and synthesis. J. Hydrol. 2006, 319, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, S.H.; Wahab, A.K.A.; Shahid, S.; Asaduzzaman; Dewan, A. Low impact development techniques to mitigate the impacts of climate-change-induced urban floods: Current trends, issues and challenges. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 62, 102373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.; Libera, D.A.; Wang, G.; Li, Z.; Wang, D. Verification of a new spatial distribution function of soil water storage capacity using conceptual and SWAT models. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2020, 25, 04020007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Johnson, F.; Marshall, L. Assessing the Potential Robustness of Conceptual Rainfall-Runoff Models Under a Changing Climate. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 5030–5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajiki, M.; Schoups, G.; Franssen, H.J.H.; Najafinejad, A.; Bahremand, A. recursive bayesian estimation of conceptual rainfall-runoff model errors in real-time prediction of streamflow. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR025237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Y. Experimental analysis of infiltration process and hydraulic properties in soil and rock profile in the Taihang Mountains, North China. Water Supply 2021, 22, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Han, S. Using temperature effect on seepage variations as proxy for phenological processes of basin-scale vegetation communities. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Zou, G.R.; Yin, W.S.; Zheng, H.R. Irrigation District Water Measurement Workbook; Water Resources and Hydropower Press: Beijing, China, 1984. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, V.; Pollak, C. Methods in Climatology; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1950. [Google Scholar]
- Swed, F.S.; Eisenhart, C. Tables for testing randomness of grouping in a sequence of alternatives. Ann. Math. Stat. 1943, 14, 66–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, R.M.; Santos, C.A.G.; Moreira, M.; Corte-Real, J.; Silva, V.C.L.; Medeiros, I.C. Rainfall and river flow trends using Mann–Kendall and Sen’s slope estimator statistical tests in the Cobres River basin. Nat. Hazards 2015, 77, 1205–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Gocic, M.; Trajkovic, S. Analysis of changes in meteorological variables using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s slope estimator statistical tests in Serbia. Glob. Planet. Change 2013, 100, 172–182. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Miao, C.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Gou, J. Is the runoff coefficient increasing or decreasing after ecological restoration on China’s Loess Plateau? Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2021, 9, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Yu, X.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Ding, M. Using four approaches to separate the effects of climate change and human activities on sediment discharge in karst watersheds. Catena 2022, 212, 106118. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Li, P.; Zhao, B.; Xu, R.; Zhao, G.; Sun, W.; Mu, X. Use of double mass curves in hydrologic benefit evaluations. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 4639–4646. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.P. Log-Pearson Type III Distribution BT—Entropy-Based Parameter Estimation in Hydrology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Song, X.; Xia, L.; Fu, N.; Feng, D.; Li, H.; Li, Y. Modelling the effects of climate change on transpiration and evaporation in natural and constructed grasslands in the semi-arid Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 302, 107077. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, R.E. The role of infiltration in the hydrologic cycle. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1933, 14, 446–460. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.J. The Xinanjiang model applied in China. J. Hydrol. 1992, 135, 371–381. [Google Scholar]
- Dunne, T.; Price, A.G.; Colbeck, S.C. The generation of runoff from subarctic snowpacks. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 677–685. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, S.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Pan, H.; Li, W.; Ran, Q. From rainfall to runoff: The role of soil moisture in a mountainous catchment. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, T.; Black, R.D. An experimental investigation of runoff production in permeable soils. Water Resour. Res. 1970, 6, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, D. Environmental Soil Physics: Fundamentals, Applications, and Environmental Considerations; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Haihe River Water Conservancy Commission, MWR. Haihe River Water Resources Bulletin 2021; Haihe River Water Conservancy Commission, MWR: Beijing, China, 2022. (In Chinese)
- Zhu, Z.W. Analysis of the July 18–19, 2016 heavy rain process in Hebei Province. Pract. Rural. Technol. 2019, 3, 17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]

| Test Item | Total Rainfall from 1987–2023 | Above I10 from 1987–2023 | Above I25 from 1987–2023 | Total Rainfall from 2014–2023 | Above I10 from 2014–2023 | Above I25 from 2014–2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZMK | 0.405 | 0.196 | 0.0392 | 1.61 | 2.33 ** | 1.79 * |
| Baseline Period | Changing Period | /m3 | /m3 | Tb/h | Tc/h | /m3 | /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19th to 24th July, 2016 | 66.27 | - | 117 | - | - | - | |
| 20th to 25th July, 2021 | - | 11.04 | - | 73 | 34.14 | 58.17 | |
| 3rd to 10th October, 2021 | - | 24.03 | - | 119 | 15.12 | 121.09 | |
| 29th July to 4th August, 2023 | - | 61.70 | - | 119 | 58.92 | 160.70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, X.; Cao, J.; Yang, H. Characteristics of Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Heavy Rainfall and Surface Runoff Generating Processes in the Mountainous Areas of Northern China. Water 2025, 17, 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070970
Hou X, Cao J, Yang H. Characteristics of Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Heavy Rainfall and Surface Runoff Generating Processes in the Mountainous Areas of Northern China. Water. 2025; 17(7):970. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070970
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Xianglong, Jiansheng Cao, and Hui Yang. 2025. "Characteristics of Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Heavy Rainfall and Surface Runoff Generating Processes in the Mountainous Areas of Northern China" Water 17, no. 7: 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070970
APA StyleHou, X., Cao, J., & Yang, H. (2025). Characteristics of Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Heavy Rainfall and Surface Runoff Generating Processes in the Mountainous Areas of Northern China. Water, 17(7), 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070970







