Time-Varying Reliability Analysis of the Majiagou Landslide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
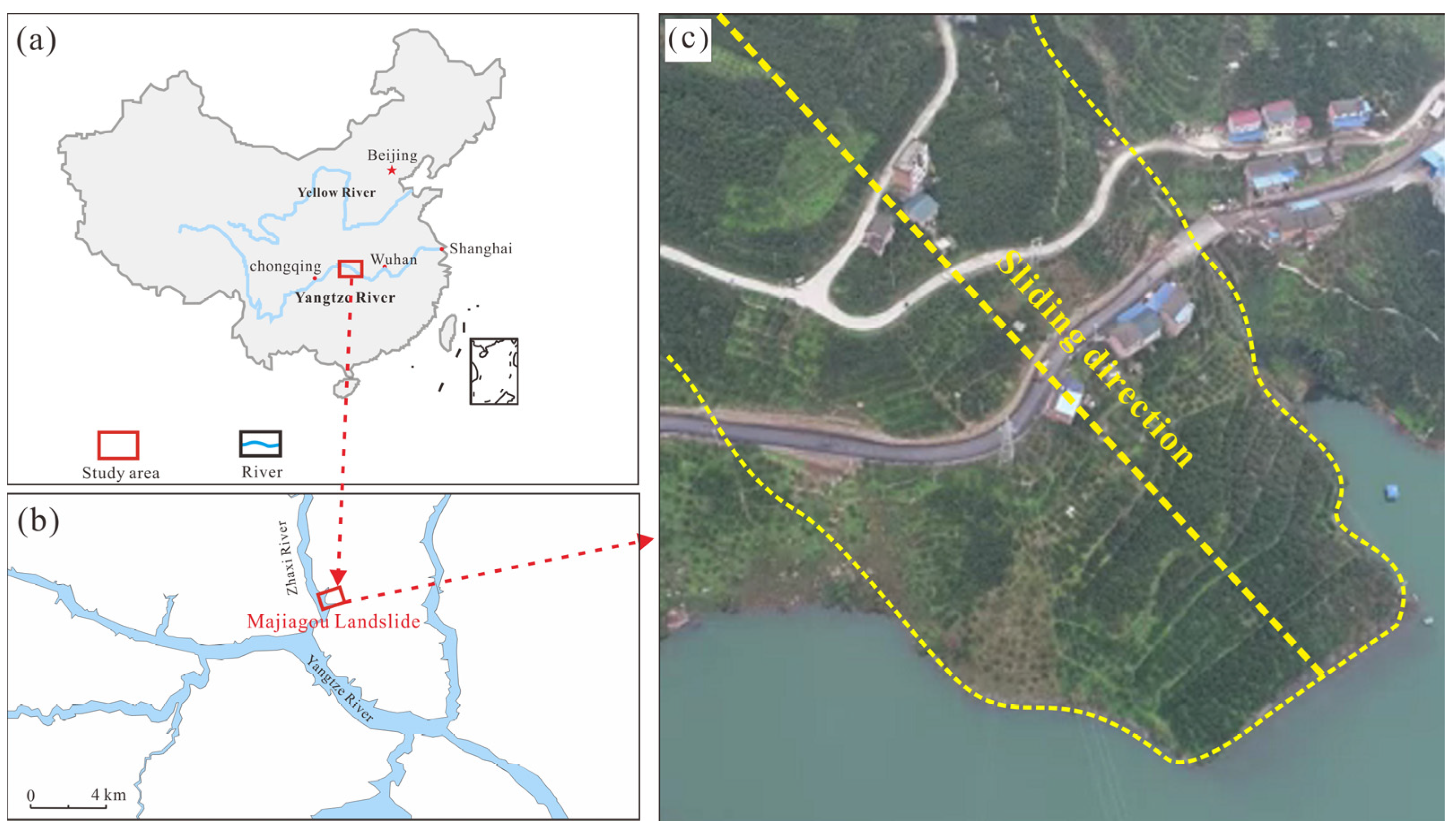
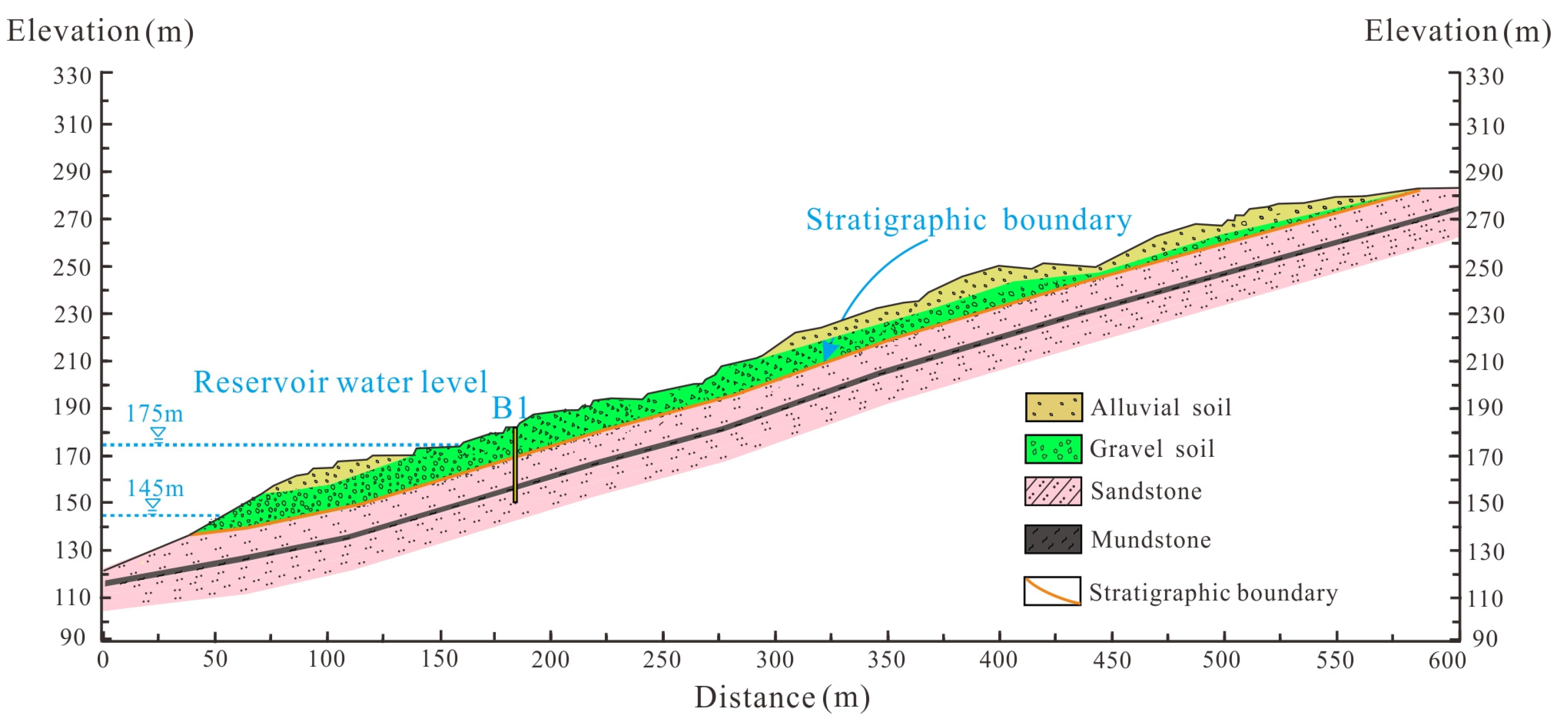
2. Geological Setting of Majiagou Landslide
2.1. Geographical Environment Feature
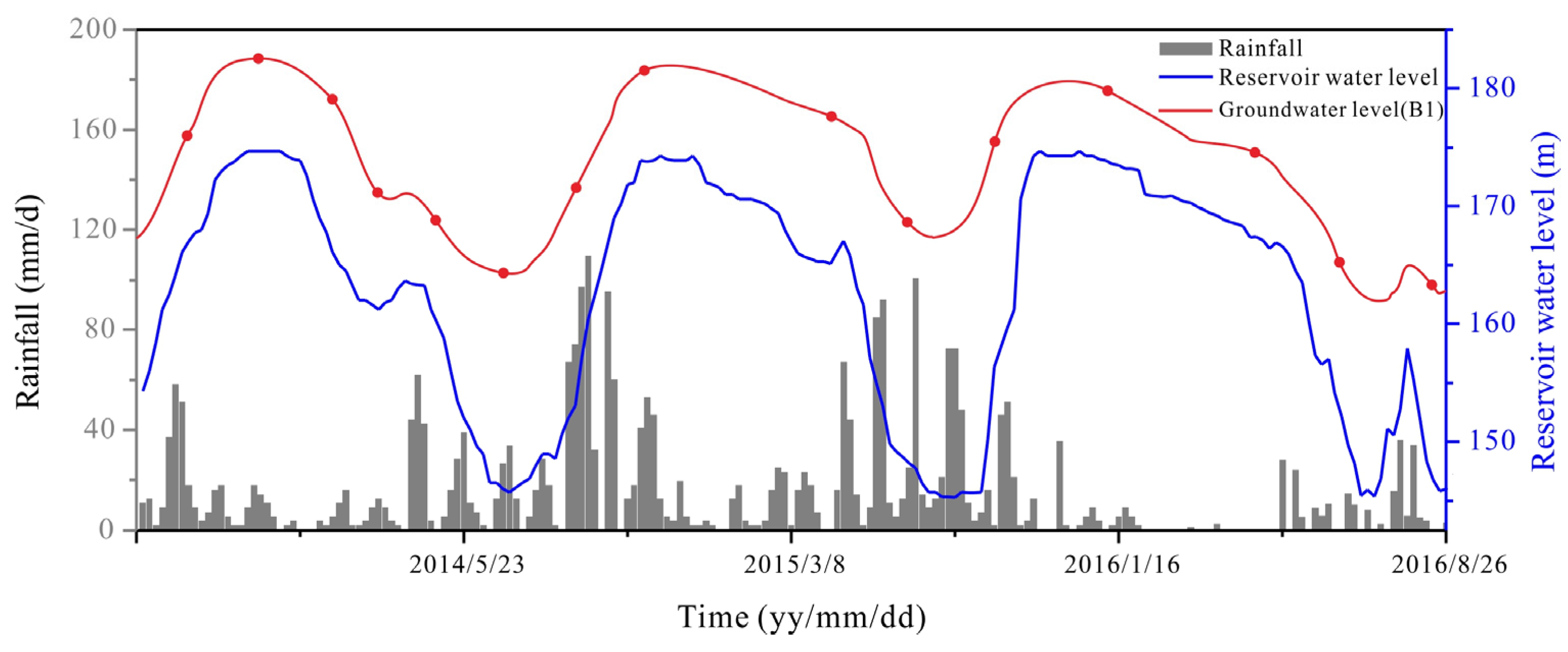
2.2. Hydrometeorological Characteristics
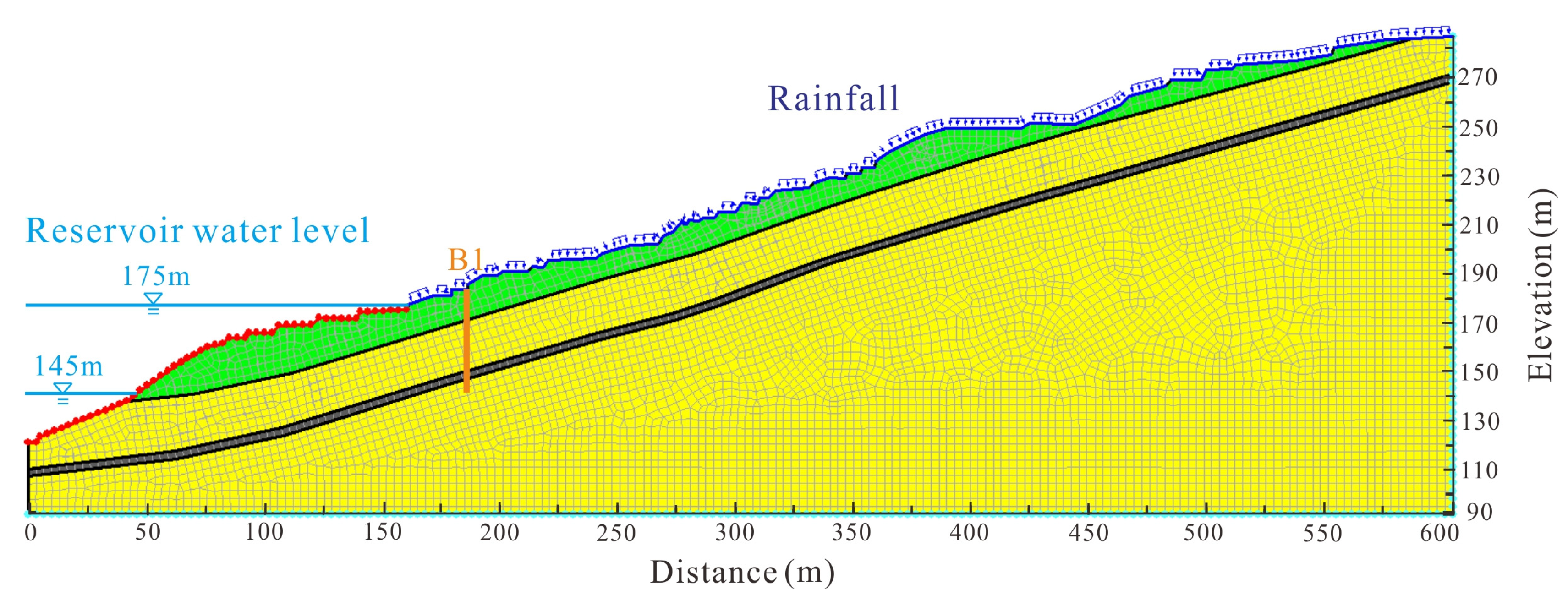
3. Numerical Model Establishment
4. Results
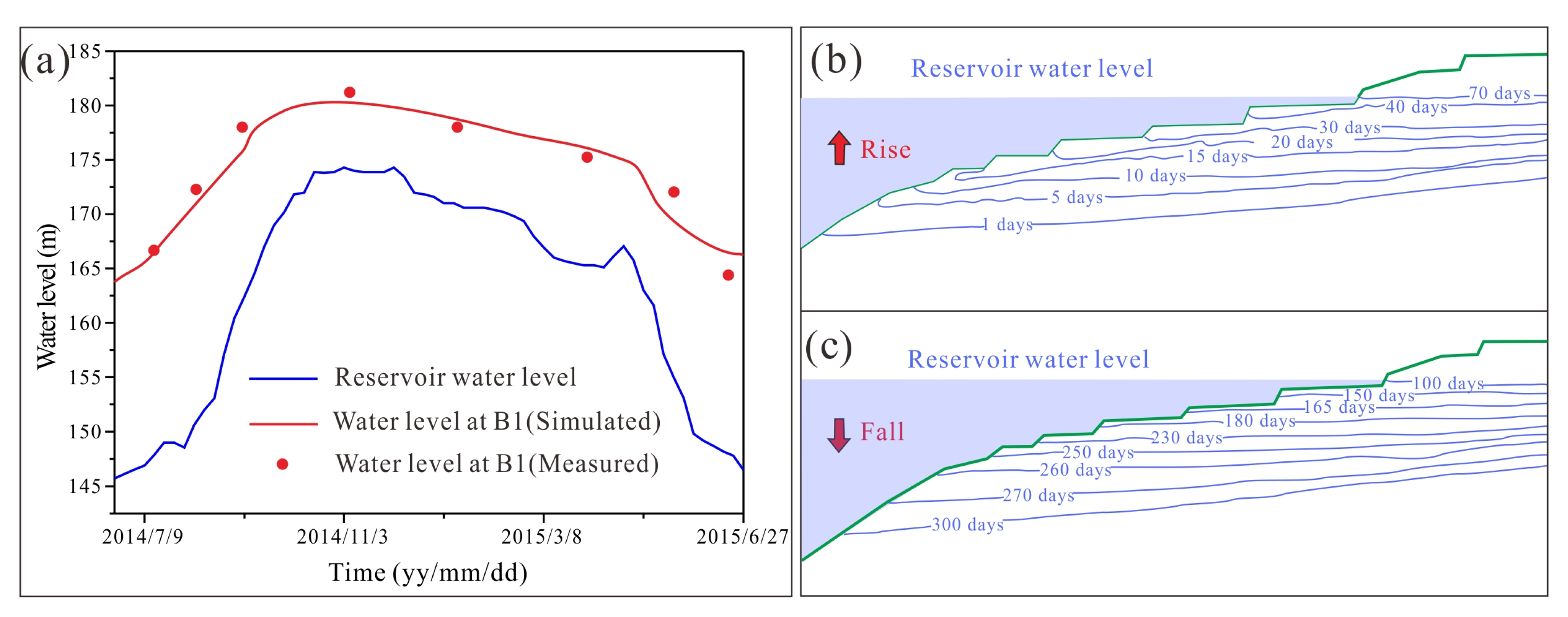
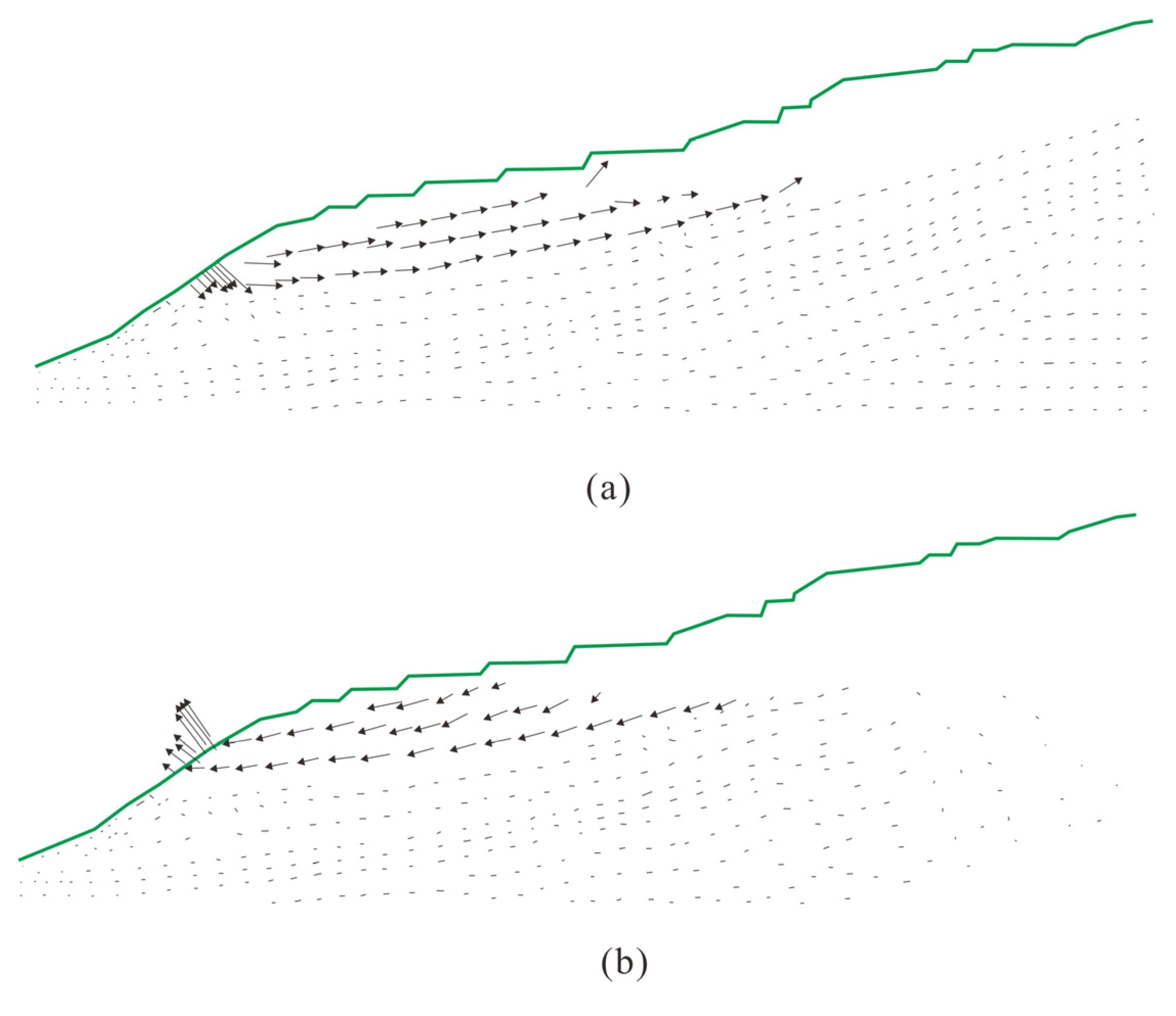
4.1. Seepgage Field
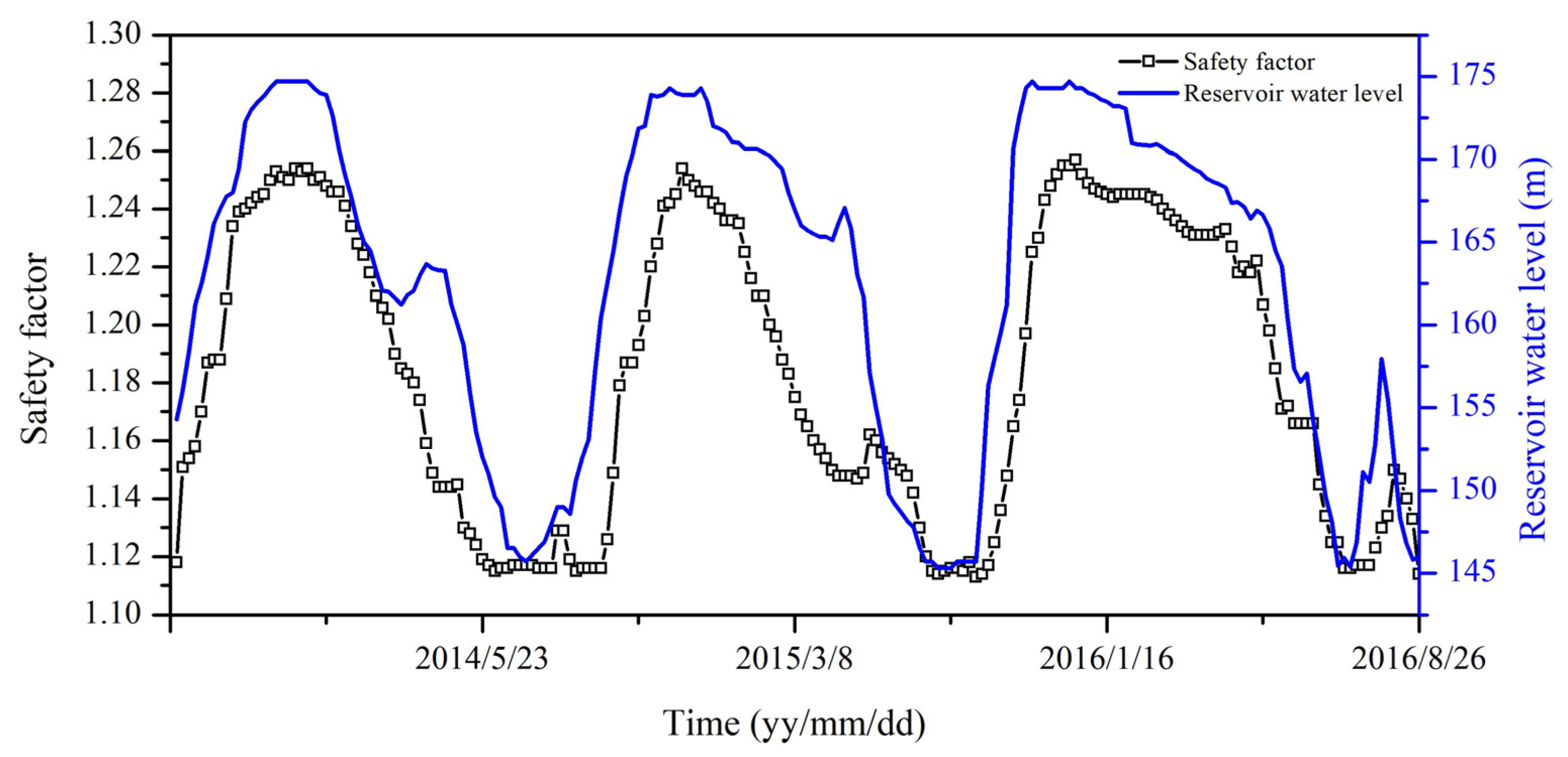
4.2. Landslide Stability
4.2.1. Effect of Rainfall on Landslide Stability
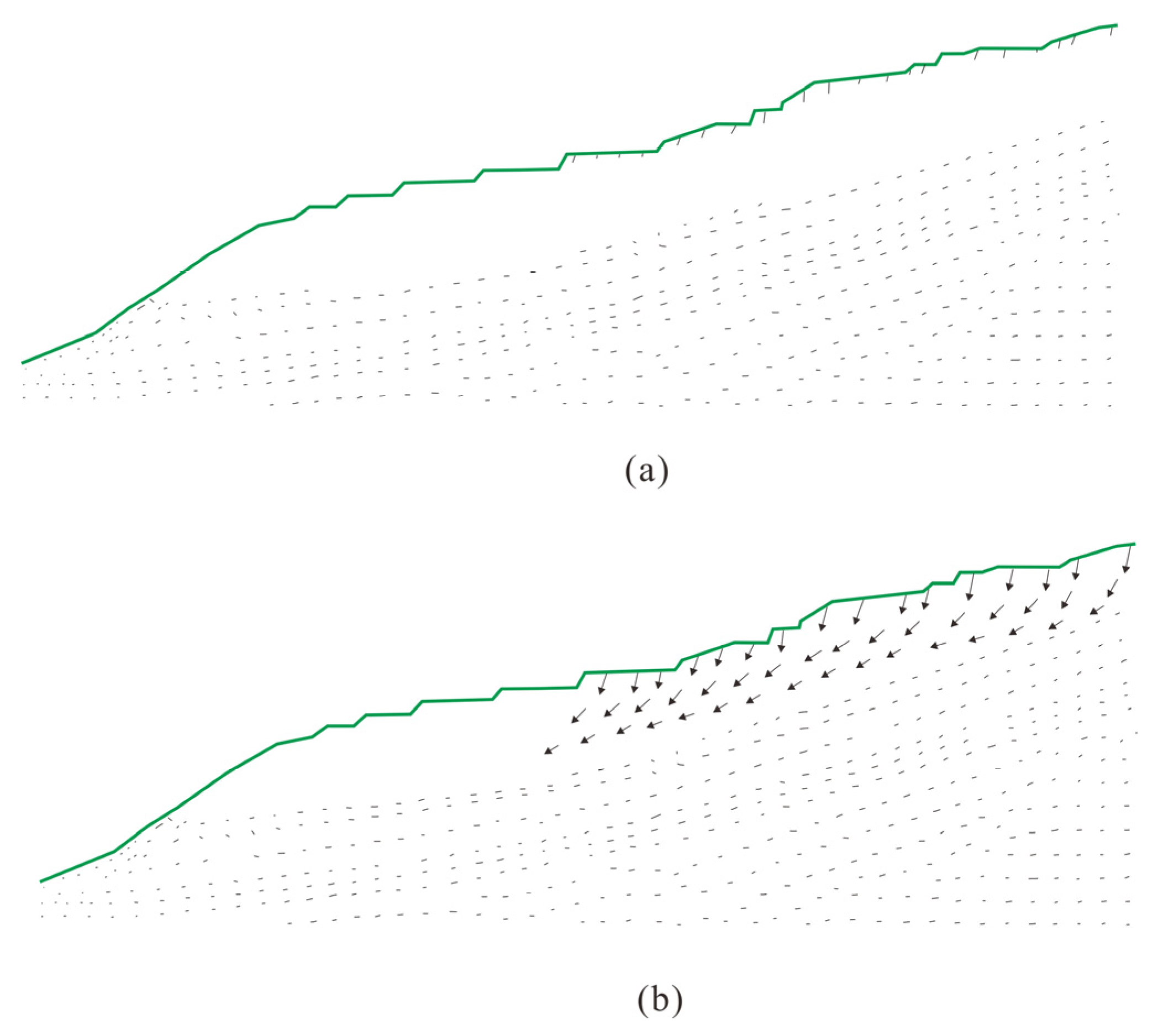
4.2.2. Effect of RWL Fluctuation on Landslide Stability
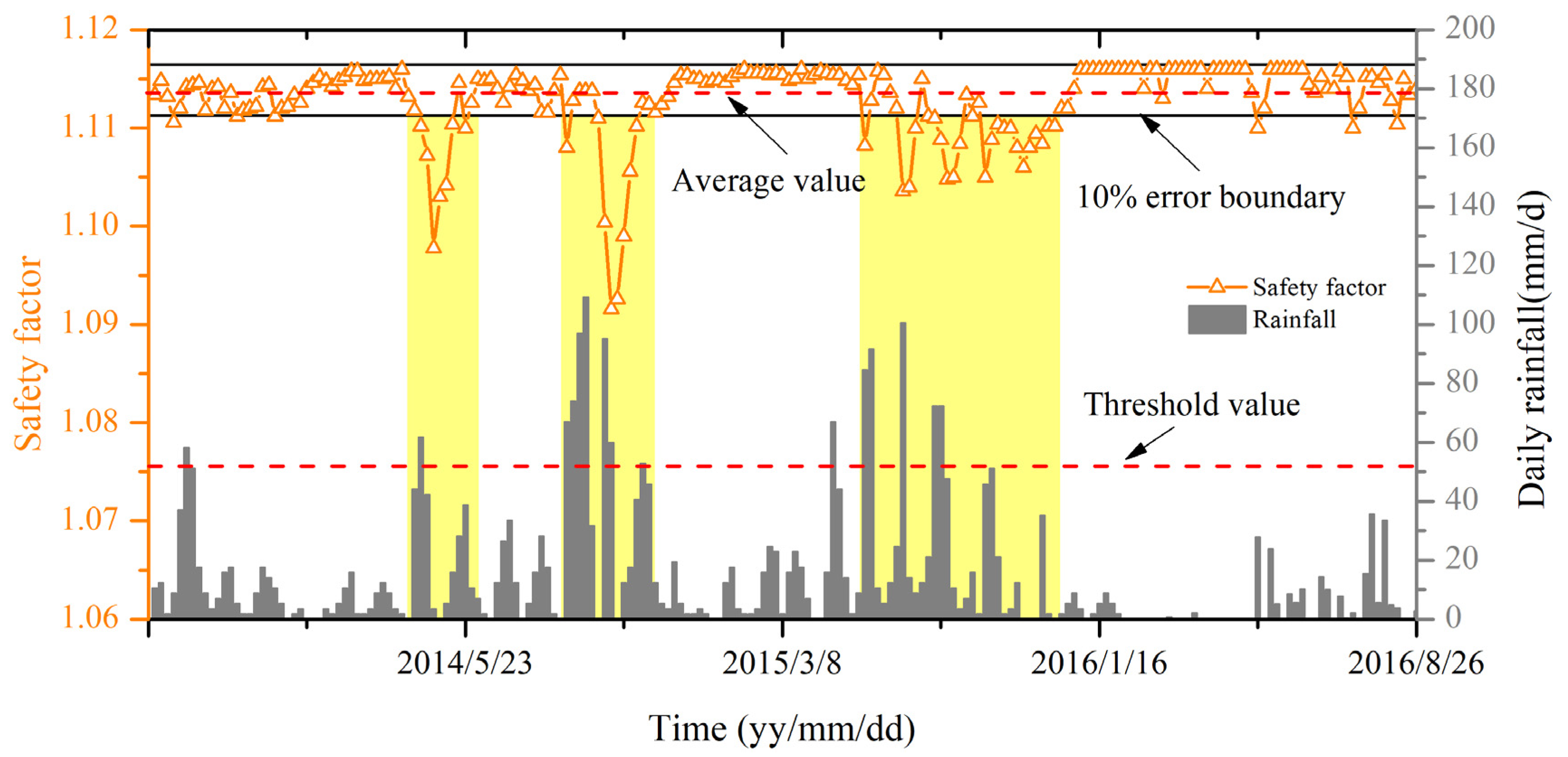
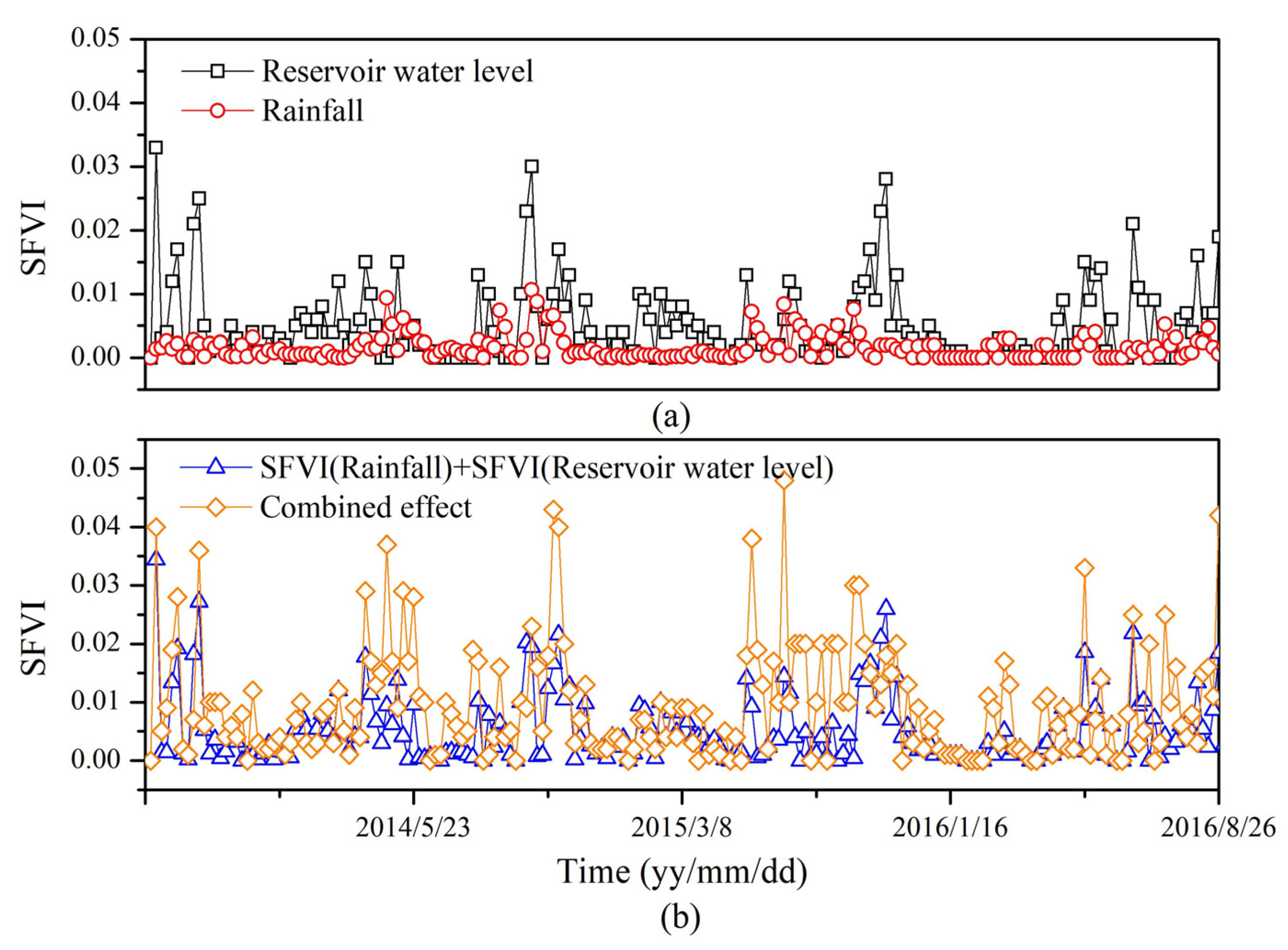
4.2.3. Combined Effect of Rainfall and RWL Fluctuation on Landslide Stability
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The RWL fluctuation is identified as the most critical factor influencing the stability of the Majiagou landslide. Specifically, when the RWL rapidly decreases from 165 m to 145 m, at an average rate of 0.859 m/d, the safety factor experiences the most significant decline.
- (2)
- Rainfall has a limited impact on the safety factor. Only when rainfall exceeds 50 mm/day does the safety factor of the slope experience a noticeable decline. At lower levels of precipitation, the impact on landslide stability is negligible.
- (3)
- The interaction between rainfall and RWL fluctuation forms a nonlinear, mutually reinforcing mechanism. This interaction does not merely have an additive effect; rather, it amplifies the reduction in slope stability in a disproportionate manner.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, H.M.; Wasowski, J.; Juang, C.H. Geohazards in the three Gorges Reservoir Area, China—Lessons learned from decades of research. Eng. Geol. 2019, 261, 105267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Shi, B.; Zhang, L. Prediction of landslide sharp increase displacement by SVM with considering hysteresis of groundwater change. Eng. Geol. 2021, 280, 105876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Zhu, H.H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, B.; Schenato, L.; Pasuto, A. Subsurface multi-physical monitoring of a reservoir landslide with the fiber-optic nerve system. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL098211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Li, C.; Hu, X.; Wang, L.; Criss, R.; Su, A.; Xiong, C. Deformation response of the Huangtupo landslide to rainfall and the changing levels of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2015, 74, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.W.; Zhang, Y.M.; Huo, Z.T.; Matsumoto, T.; Huang, B.L. The July 14, 2003 Qianjiangping landslide, three gorges reservoir, China. Landslides 2004, 1, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Hu, X.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, G.; Liu, C.; Xu, C.; Liu, Z. Displacement behaviour and potential impulse waves of the Gapa landslide subjected to the Jinping Reservoir fluctuations in Southwest China. Geomorphology 2022, 397, 108013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizzo, A.; Girolamo, P.D.; Risio, M.D.; Maistri, A.; Petaccia, A. Great landslide events in Italian artificial reservoirs. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. 2005, 5, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolin, H.; Yueping, Y.; Renjiang, L.; Peng, Z.; Zhen, Q.; Yang, L.; Kaikai, X. Three-dimensional experimental investigation on hazard reduction of landslide-generated impulse waves in the Baihetan Reservoir, China. Landslides 2023, 20, 2017–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shi, A.; Xu, W.; Yan, L.; Wang, H.; Tian, L.; Xie, W.C. Numerical investigation of landslide-induced waves: A case study of Wangjiashan landslide in Baihetan Reservoir, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Gao, W.; Hu, R. Physical modeling for large-scale landslide with chair-shaped bedrock surfaces under precipitation and reservoir water fluctuation conditions. Water 2022, 14, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, B.; Zhu, H.; Yu, X.B.; Han, H.; Fan, X. PSO-SVM-based deep displacement prediction of Majiagou landslide considering the deformation hysteresis effect. Landslides 2021, 18, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zheng, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, C. Parameter inversion and deformation mechanism of Sanmendong landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir region under the combined effect of reservoir water level fluctuation and rainfall. Eng. Geol. 2016, 205, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleotti, P.; Chowdhury, R. Landslide hazard assessment: Summary review and new perspectives. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 1999, 58, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Hu, X.; Ishfaq, U.B.E.; He, K.; Ali, R.; Sanaullah, M.; Ali, U. InSAR-based deformation analysis around the Qiaoqi reservoir, Baoxing, Southwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2025, 84, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Chen, G.; Gong, S.; Sun, H.; Chantat, K. Analysis of rainfall-induced landslide using the extended DDA by incorporating matric suction. Comput. Geotech. 2021, 135, 104145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafle, L.; Xu, W.J.; Zeng, S.Y.; Nagel, T. A numerical investigation of slope stability influenced by the combined effects of reservoir water level fluctuations and precipitation: A case study of the Bianjiazhai landslide in China. Eng. Geol. 2022, 297, 106508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Suk, J.; Kim, H.; Jeong, S. Modeling of rainfall-induced landslides using a full-scale flume test. Landslides 2021, 18, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Idinger, G.; Wu, W. Centrifuge modelling of rainfall-induced slope failure in variably saturated soil. Acta Geotech. 2021, 16, 2899–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyelowe, K.C.; Ebid, A.M.; Hanandeh, S.; Kamchoom, V. Evaluating the slope behavior for geophysical flow prediction with advanced machine learning combinations. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyelowe, K.C.; Ebid, A.M.; Mahdi, H.A.; Baldovino, J.A. Selecting the safety and cost optimized geo-stabilization technique for soft clay slopes. Civ. Eng. J. 2023, 9, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyelowe, K.C.; Sujatha, E.R.; Aneke, F.I.; Ebid, A.M. Solving geophysical flow problems in Luxembourg: SPH constitutive review. Cogent. Eng. 2022, 9, 2122158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, H.; Xie, W. Deformation mechanism of deposit landslide induced by fluctuations of reservoir water level based on physical model tests. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.S.; Xu, G.L.; Zhang, D.Q.; Liu, H.Y. Stability analysis of Gongjiacun landslide in the three Gorges Reservoir area under the action of reservoir water level fluctuation and rainfall. Nat. Hazards 2022, 114, 1647–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.L.; Qi, S.C.; Lv, P.F.; Yang, X.G.; Zhou, J.W. Hydraulic response and stability of a reservoir slope with landslide potential under the combined effect of rainfall and water level fluctuation. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 1647–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Tang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, L.; Guo, F. Failure mechanism of colluvial landslide influenced by the water level change in the three gorges reservoir area. Geofluids 2021, 1, 6865129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, B.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Y.; Inyang, H.I. Kinematics, triggers and mechanism of Majiagou landslide based on FBG real-time monitoring. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jia, C.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, W. Centrifuge modeling test on reactivation of ancient landslide under sudden drop of reservoir water and rainfall. Acta Geotech. 2024, 19, 5651–5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.J.; Wang, Y.J.; Dong, X.Y. Influence of reservoir water level variations on slope stability and evaluation of landslide tsunami. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 4891–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Kang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zou, Y. Deformation Mechanism of Large-Scale Ancient Reservoir Landslides Driven by the Monitoring Data and Numerical Simulation. Geol. J. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Hu, B.; Yi, Q.; Yao, W.; Ma, C. The coupling effect of rainfall and reservoir water level decline on the Baijiabao landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Geofluids 2017, 1, 3724867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, S.; Wang, R.; Xiao, M. Stability analysis of a typical landslide mass in the Three Gorges Reservoir under varying reservoir water levels. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Gu, D.M.; Song, Y.X.; Cen, D.F.; Zeng, B. Towards a complete understanding of the triggering mechanism of a large reactivated landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Eng. Geol. 2018, 238, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Pan, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, F.; Chen, Y.; Sun, W. Deformation characteristics, mechanisms, and influencing factors of hydrodynamic pressure landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir: A case study and model test study. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2021, 80, 3513–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Sun, Q.; Hu, J.; Lu, Z.; Zhu, K.; Ye, X.; Li, Z. Investigating kinematics and triggers of slow-moving reservoir landslide using an improved MT-InSAR method. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2023, 14, 2289835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, H.; Zhang, D.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Shi, B.; Liu, Y. Strain distribution based geometric models for characterizing the deformation of a sliding zone. Eng. Geol. 2019, 263, 105300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; Wu, Y.; Miao, F.; Li, L.; Xue, Y. Time-varying reliability analysis of Majiagou landslide based on weakening of hydro-fluctuation belt under wetting-drying cycles. Landslides 2021, 18, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, H.; Han, H.; Shi, B. Fiber optic monitoring of an anti-slide pile in a retrogressive landslide. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. 2024, 16, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wu, H.; Han, H.; Yan, Y.; Shi, B. Shear deformation calculation of landslide using distributed strain sensing technology considering the coupling effect. Landslides 2023, 20, 1583–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Meng, Z.; Shi, B.; Zha, F.; Wei, G.; Yu, L.; Song, X. A method for monitoring of monopile horizontal displacement of offshore wind turbine based on UWFBG and boundary reconstruction. Measurement 2025, 252, 117384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.L.; Huang, D.; Peng, J.B.; Tomás, R. Influence of permeability on the stability of dual-structure landslide with different deposit-bedding interface morphology: The case of the three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Eng. Geol. 2022, 296, 106480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

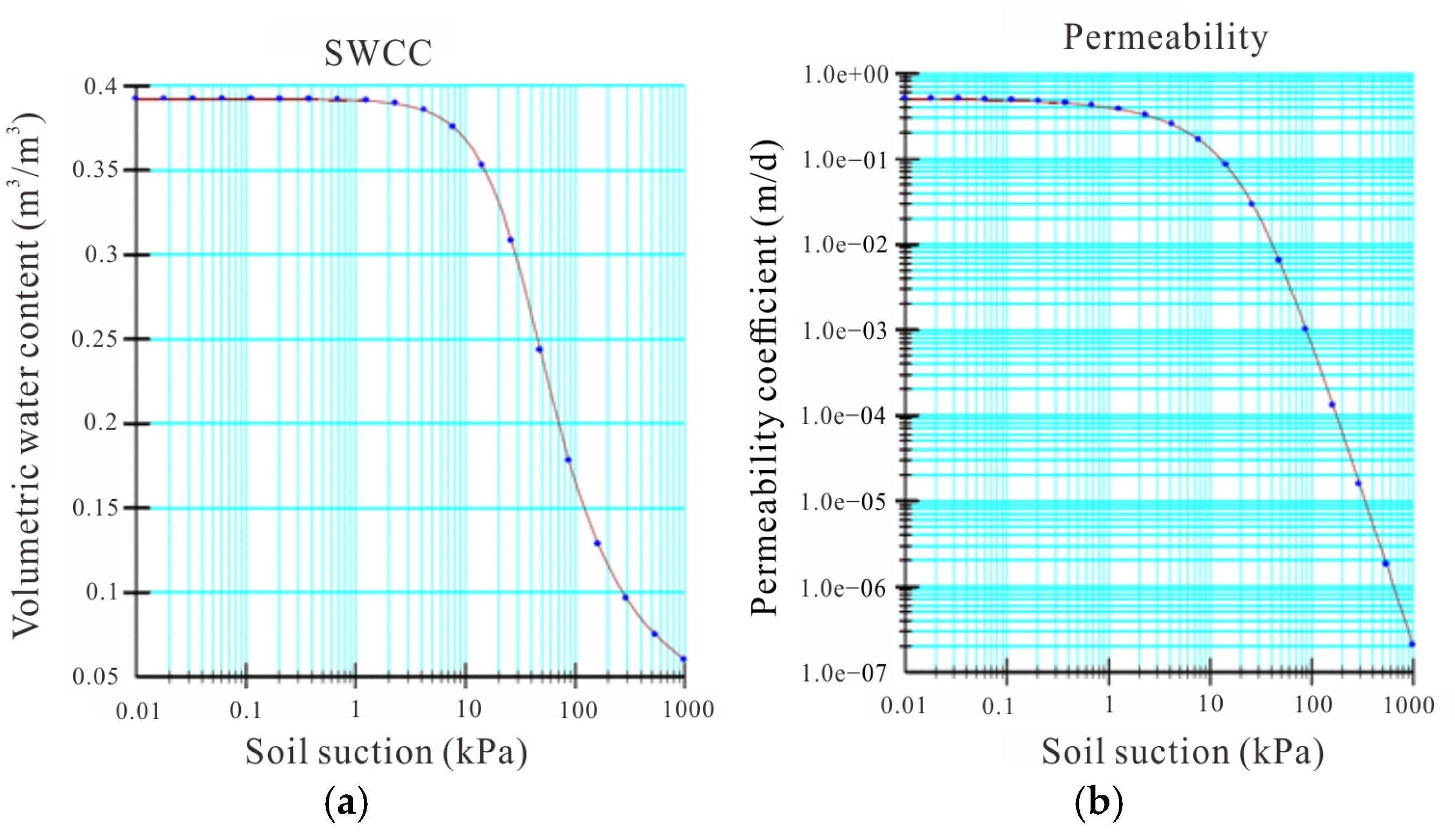

| Element | Unit Weight γ (kN/m3) | Friction Angel φ (kN/m3) | Cohension c (Kpa) | Permeability Coefficient k (cm/s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural | Saturated | Natural | Saturated | Natural | Saturated | ||
| Gravel soil | 21.14 | 22.05 | 19.31 | 17.68 | 18.32 | 16.21 | 8.25 × 10−4 |
| Mudstone | 21.84 | 22.52 | 17.18 | 15.26 | 27.30 | 25.15 | 1.13 × 10−6 |
| Bedrock | 26 | - | 39 | - | 3000 | - | - |
| Monitoring Time | 22 July 2014 | 11 August 2014 | 5 September 2014 | 16 November 2014 | 7 January 2015 | 6 April 2015 | 14 May 2015 | 21 June 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monitored water level (m) | 168.3 | 172.1 | 178 | 180.5 | 176.3 | 175.1 | 172.1 | 163.5 |
| Simulated water level (m) | 167.5 | 171.6 | 176.2 | 179.1 | 177.1 | 175.8 | 169.8 | 166.0 |
| Absolute error (m) | 0.8 | 0.5 | 1.8 | 1.4 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 2.3 | 2.5 |
| Relative error | 0.47% | 0.29% | 1.01% | 0.77% | 0.45% | 0.39% | 1.34% | 1.53% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lan, C.; Zhang, H.; Hu, G.; Song, X.; Sun, H. Time-Varying Reliability Analysis of the Majiagou Landslide. Water 2025, 17, 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081185
Lan C, Zhang H, Hu G, Song X, Sun H. Time-Varying Reliability Analysis of the Majiagou Landslide. Water. 2025; 17(8):1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081185
Chicago/Turabian StyleLan, Chun, Hui Zhang, Guangqing Hu, Xiaojin Song, and Heng Sun. 2025. "Time-Varying Reliability Analysis of the Majiagou Landslide" Water 17, no. 8: 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081185
APA StyleLan, C., Zhang, H., Hu, G., Song, X., & Sun, H. (2025). Time-Varying Reliability Analysis of the Majiagou Landslide. Water, 17(8), 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081185





