Combining Fluorescent Organic Substances, Ions, and Oxygen-18 to Trace Diverse Water Sources of River Flow in a Hilly Catchment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
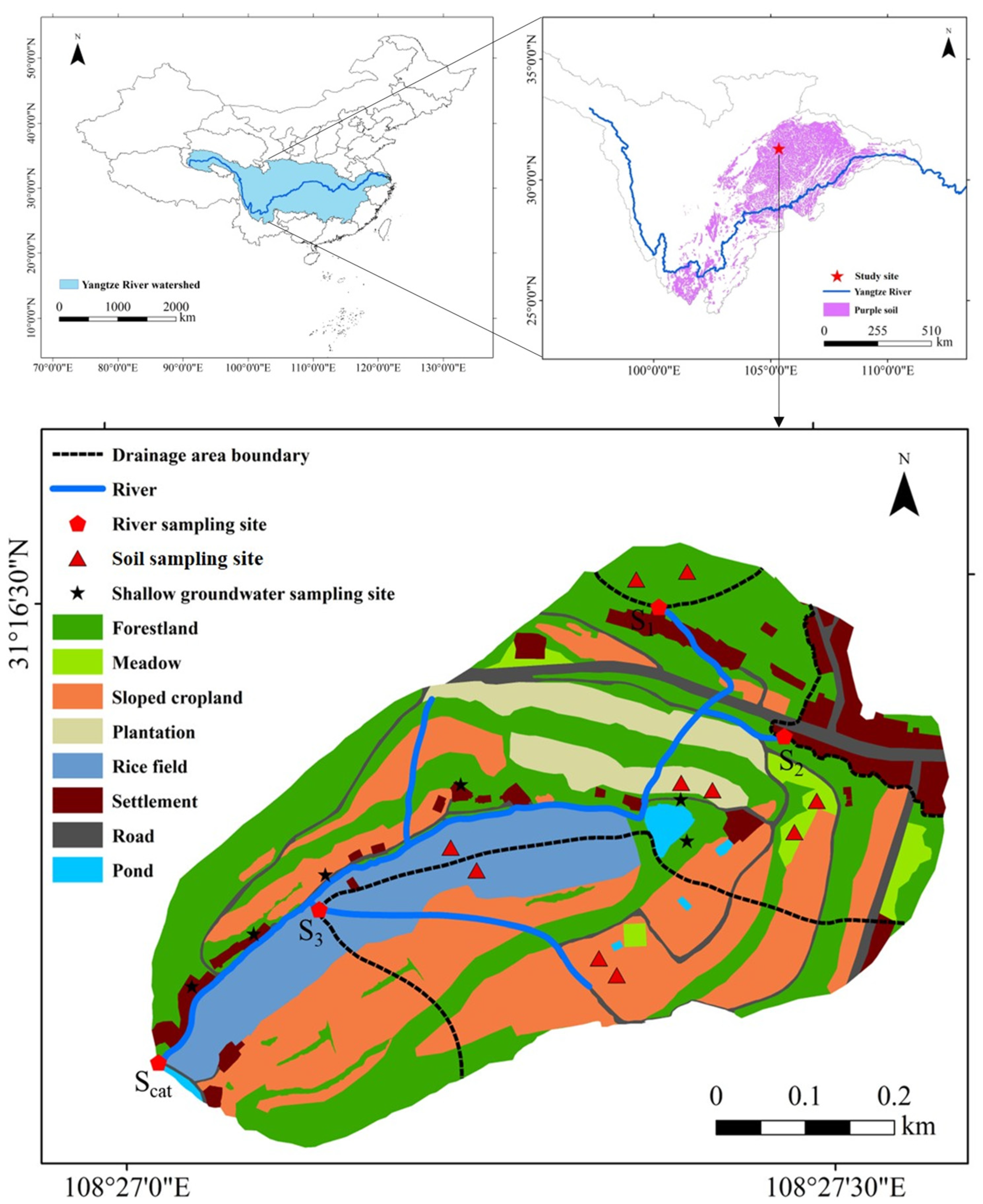
2.1. Catchment Characteristics
2.2. Water Sampling and Analyses
2.3. River Water Sources and Tracers
2.4. Hydrograph Separation
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Differences in Hydrochemical Parameters and δ18O Between Various Water Sources
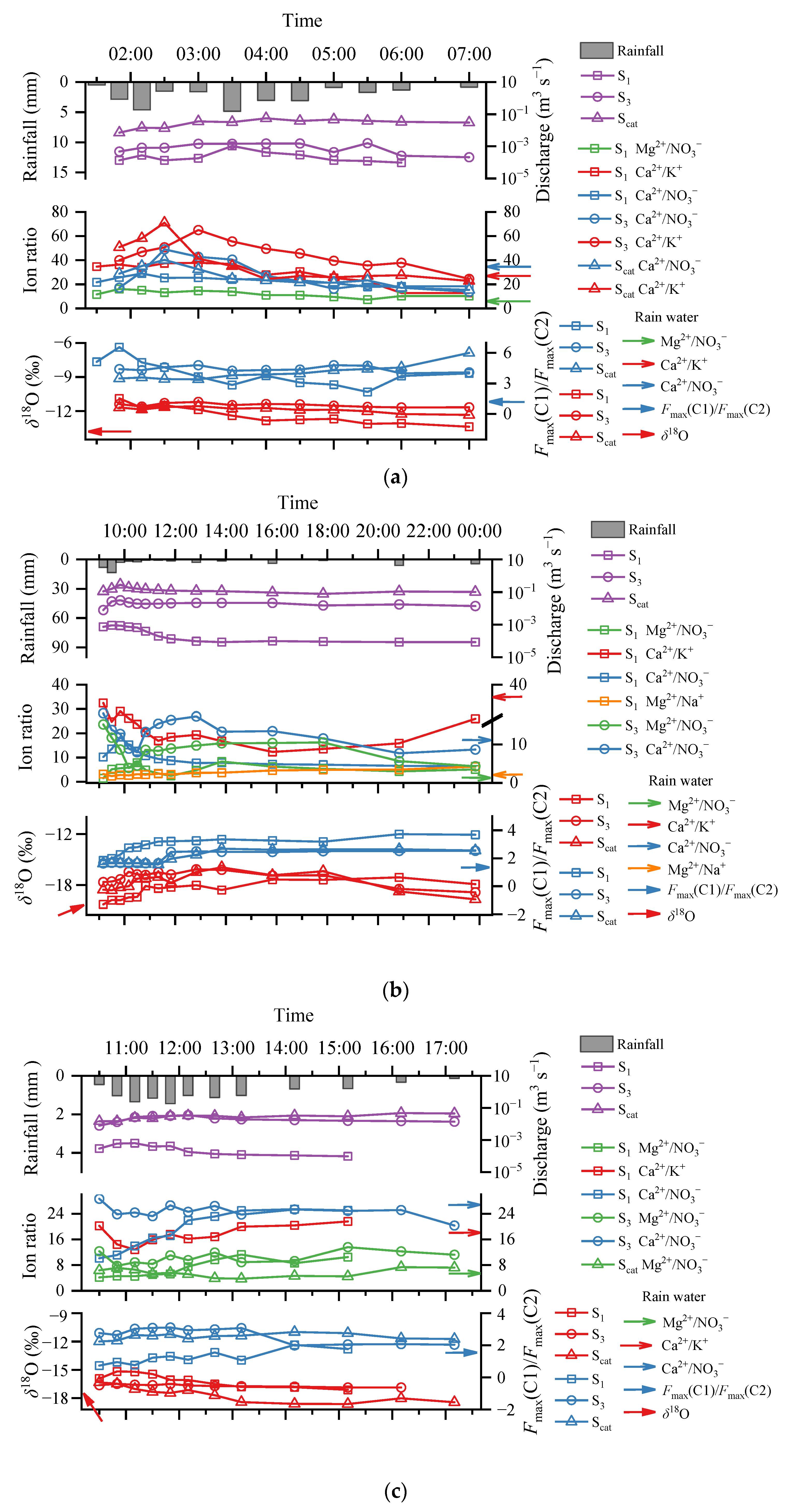
3.2. Temporal Changes in River Discharge, Hydrochemical Parameters, and δ18O During Rainfall
3.3. Performance of Hydrochemical Parameters in the Separation of River Hydrographs in a Drainage Area with a Single Vegetation Cover Type by Comparing with δ18O
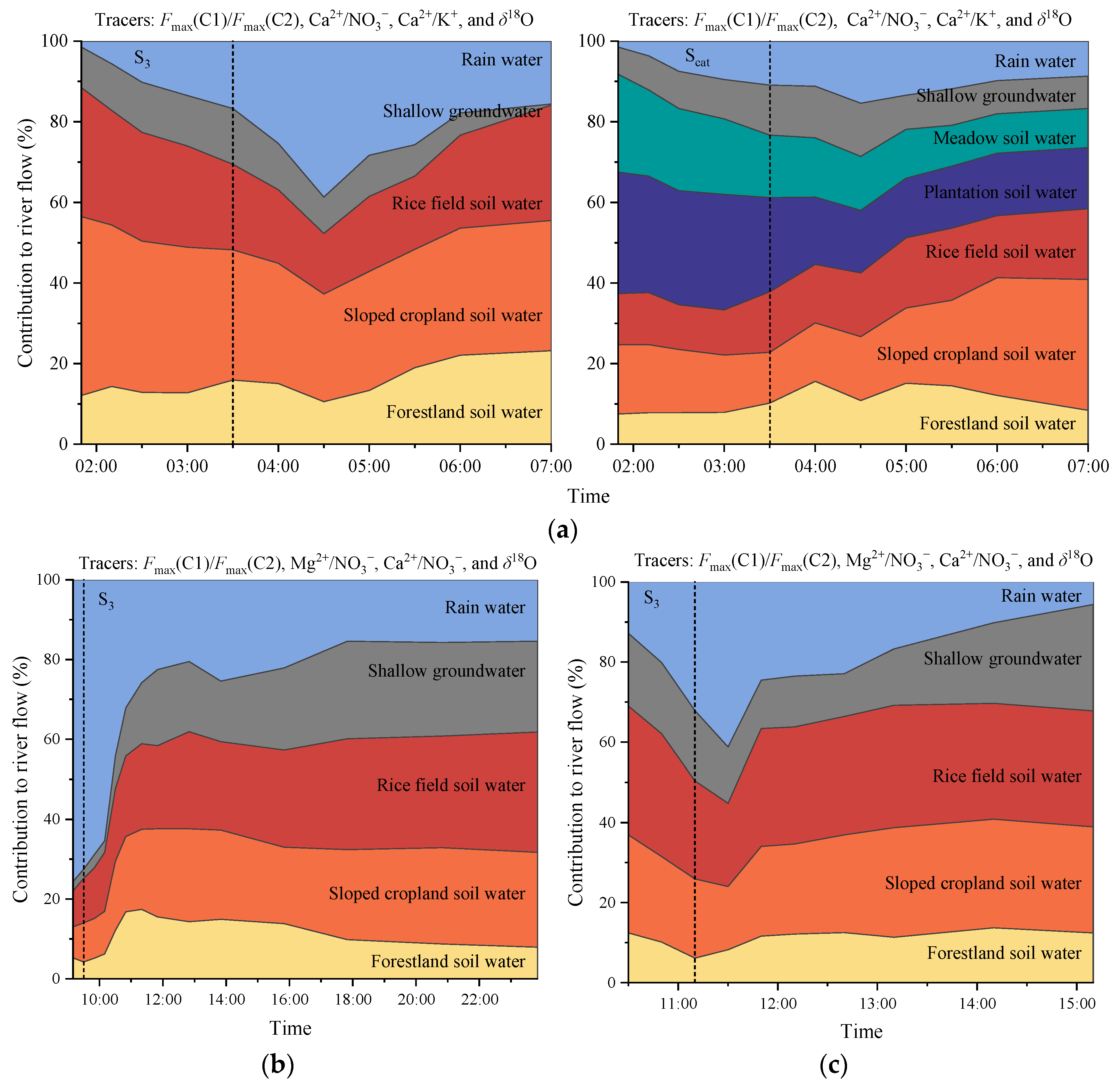
3.4. Performance of Multiple Tracers in the Separation of River Hydrographs in Drainage Areas with Multiple Land-Use Types
4. Discussion
4.1. Selection of Multiple Tracers
4.2. Applicability of Multiple Tracers to River Hydrograph Separation
4.3. Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, D.W.; Yang, Y.T.; Xia, J. Hydrological cycle and water resources in a changing world: A review. Geo. Sus. 2021, 2, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musie, M.; Sen, S.; Chaubey, I. Hydrologic responses to climate variability and human activities in Lake Ziway Basin, Ethiopia. Water 2020, 12, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei, M.A.; Amekudzi, L.K.; Wemegah, D.D.; Preko, K.; Gyawu, E.S.; Obiri-Danso, K. The impact of climate and land-use changes on the hydrological processes of Owabi catchment from SWAT analysis. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2019, 25, 100620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhang, X.P.; Shi, X.N.; Yu, Z.L.; Liu, K.S.; Liu, Z. Identifying river water sources using end-member mixing analysis in a subtropical monsoon basin China. Hydrol. Process. 2023, 37, e14824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.J.; Gao, L.; Geris, J.; Verrot, L.; Peng, X.H. Assessment of water sources and their contributions to streamflow by end-member mixing analysis in a subtropical mixed agricultural catchment. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 203, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.W.; Baranov, V.; Mendoza-Lera, C.; Nikolakopoulou, M.; Harjung, A.; Kolbe, T.; Balasubramanian, M.N.; Vaessen, T.N.; Ciocca, F.; Campeau, A.; et al. Using multi-tracer inference to move beyond single-catchment ecohydrology. Earth Sci. Rev. 2016, 160, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, M.S.; Park, H.Y.; Shin, H.S.; Lee, B.J.; Hur, J. Separately tracking the sources of hydrophobic and hydrophilic dissolved organic matter during a storm event in an agricultural watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 162347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buerge, I.J.; Buser, H.R.; Kahle, M.; Mueller, M.D.; Poiger, T. Ubiquitous occurrence of the artificial sweetener acesulfame in the aquatic environment: An ideal chemical marker of domestic wastewater in groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4381–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenot, A.; Benoît, M.; Carignan, J.; France-Lanord, C. Insights into stable isotope characterization to monitor the signification of soil water sampling for environmental studies dealing with soil water dynamics through the unsaturated zone. C. R. Geosci. 2015, 347, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Liu, Z.Q.; Xiong, K.N.; He, Q.F.; Li, Y.; Cai, L.L.; Chen, Y. Migration of dissolved organic matter in the epikarst fissured soil of south China karst. Land 2023, 12, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Haddix, M.L.; Kroeger, M.E.; Stewart, C.E. The role of plant input physical-chemical properties, and microbial and soil chemical diversity on the formation of particulate and mineral-associated organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 168, 108648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, R.D.; Porcal, P.; Hejzlar, J.; Paule-Mercado, M.C.; Haaland, S.; Gundersen, C.B.; Orderud, G.I.; Eikebrokk, B. Distinguishing between sources of natural dissolved organic matter (DOM) based on its characteristics. Water 2023, 15, 3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lu, Y.H.; Edmonds, J.W.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Das, O.; Liu, J.; Zheng, C.M. Hydrological and land use control of watershed exports of dissolved organic matter in a large arid river basin in northwestern China. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.X.; Cui, J.F.; Cheng, J.H.; Tang, X.Y. A novel tool for tracing water sources of streamflow in a mixed land-use catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, B.; Shanley, J.B.; Kirchner, J.W.; Norris, D.; Adler, T.; Bristol, C.; Harpold, A.A.; Perdrial, J.N.; Rizzo, D.M.; Sterle, G.; et al. Streams as mirrors: Reading subsurface water chemistry from stream chemistry. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR029931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerge, I.J.; Poiger, T.; Müller, M.D.; Buser, H.R. Caffeine, an anthropogenic marker for wastewater contamination of surface waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatesman, T.A.; Liljedahl, A.K.; Douglas, T.A.; Debolskiy, M.V.; Trainor, T.P.; Gaedeke, A. Glacier contribution to lowland streamflow: A multi-year, daily geochemical hydrograph separation study in subarctic Alaska. Chem. Geol. 2023, 621, 121368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladouche, B.; Probst, A.; Viville, D.; Idir, S.; Baque, D.; Loubet, M.; Probst, J.L.; Bariac, T. Hydrograph separation using isotopic, chemical and hydrological approaches (Strengbach catchment, France). J. Hydrol. 2001, 242, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma, J.L.J.; Grabs, T.; Futter, M.N.; Bishop, K.H.; Laudon, H.; Koehler, S.J. Riparian zone control on base cation concentration in boreal streams. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 3849–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Q.S.; Li, P.H.; Liu, C.; Cui, J.F.; Guan, Z.; Tang, X.Y. Concentration and spectroscopic characteristics of DOM in surface runoff and fracture flow in a cropland plot of a loamy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Guan, Z.; Cheng, J.H.; Tang, X.Y.; Xian, Q.S. Ambient temperature modulates dissipation and redistribution of chlorpyrifos and 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol in paddy field. Soil Sediment Contam. 2022, 31, 533–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cheng, J.H.; Xian, Q.S.; Cui, J.F.; Tang, X.Y.; Wang, G.X. Dynamics and sources of colloids in shallow groundwater in lowland wells and fracture flow in sloping farmland. Water Res. 2019, 156, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W. Hydrological Processes and Colloid Transport in the Sloping Farmland of Purple Soil. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, UCAS, Chengdu, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, J.R.; Barnard, H.R.; Coulombe, R.; McDonnell, J.J. Ecohydrologic separation of water between trees and streams in a Mediterranean climate. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 3, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.G.; Patrickson, S.J.; Ehleringer, J.R. Water extraction times for plant and soil materials used in stable isotope analysis. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, S.; Fulda, C.; Schäfer, W. A multi-tracer study in a shallow aquifer using age dating tracers 3H, 85Kr, CFC-113 and SF6—indication for retarded transport of CFC-113. J. Hydrol. 2001, 248, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, B.C.; Jackson, A.L.; Ward, E.J.; Parnell, A.C.; Phillips, D.L.; Semmens, B.X. Analyzing mixing systems using a new generation of Bayesian tracer mixing models. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, J.B.; Ferguson, J.M. Estimating the diets of animals using stable isotopes and a comprehensive Bayesian mixing model. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e28478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models: Part I. A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhao, P.; Wang, C.; Tang, J.L. Tracing water flow from sloping farmland to streams using oxygen-18 isotope to study a small agricultural catchment in southwest China. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 134, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, W.; Tang, J.L. Mixing of event and pre-event water in a shallow Entisol in sloping farmland based on isotopic and hydrometric measurements. SW China. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 3478–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkel, C.; Correa-Barahona, A.; Martinez-Martinez, M.; Granados-Bolanos, S.; Venegas-Cordero, N.; Gutierrez-Garcia, K.; Blanco-Ramirez, S.; Quesada-Mora, R.; Solano-Rivera, V.; Mussio-Mora, J.; et al. Headwaters drive streamflow and lowland tracer export in a large-scale humid tropical catchment. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 3824–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffland, E.; Kuyper, T.W.; Comans, R.N.J.; Creamer, R.E. Eco-functionality of organic matter in soils. Plant Soil 2020, 455, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbadegesin, L.A. Leaching of Veterinary Antibiotics in Purple Soil Orchard and Farmland. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, UCAS, Chengdu, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell, J.J. A rationale for old water discharge through macropores in a steep, humid catchment. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 2821–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasechko, S.; Kirchner, J.W.; Welker, J.M.; McDonnell, J.J. Substantial proportion of global streamflow less than three months old. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, J.W. Quantifying new water fractions and transit time distributions using ensemble hydrograph separation: Theory and benchmark tests. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 303–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Kalbitz, K. Cycling downwards—Dissolved organic matter in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 52, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, J.S.; Zhan, L.C.; Ma, F.Y.; Yan, J.H.; Wang, T. Study on groundwater recharge based on chloride mass balance and hydrochemistry in the irrigated agricultural area, North China Plain. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.H.; Wu, J.H.; Gao, X.Y.; Guo, W.Y.; Chen, W.Q. Hydrochemical background levels and threshold values of phreatic groundwater in the greater Xi’an region, China: Spatiotemporal distribution, influencing factors and implication to water quality management. Expo. Health. 2023, 15, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayo-Olagbende, G.O.; Ewulo, B.S. Ionic mobility of cations as affected by redox status of two different soil types. Bulg. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 6, 18–32. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Gao, X.B.; Li, C.C.; Wang, H.; Kang, C.Q.; Wang, W.Z.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Z.; Xiong, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.X. Combining hydrodynamics, geochemical and multiple isotopic tracers to understand the hydrogeological functioning of karst groundwater system in Jinci, northern China. J. Hydrol. 2025, 648, 132375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Jiang, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.H.; Xu, L.L.; Qu, Z.H. Interaction between groundwater and surface water in the Qujiang River basin in China: Evidence from chemical isotope measurements. Water 2023, 15, 3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhang, W.; Song, S.B.; McKenzie, B.M. Within-year changes in hydraulic properties of a shallow entisol in farmland and forestland. Vadose Zone J. 2015, 14, vzj2014-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jencso, K.G. Hydrologic Connectivity Between Landscapes and Streams: Transferring Reach and Plot Scale Understanding to the Catchment Scale. Ph.D. Thesis, Montana State University, Bozeman, MT, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Outram, F.N.; Cooper, R.J.; Suennenberg, G.; Hiscock, K.M.; Lovett, A.A. Antecedent conditions, hydrological connectivity and anthropogenic inputs: Factors affecting nitrate and phosphorus transfers to agricultural headwater streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 545, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Rain Characteristics * | River Flow Depth § | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event No. (date) | PNRD | Amount | Time Duration | Imax | ||||
| (day) | (mm) | (h) | (mm (30 min)−1) | (mm) | ||||
| S1 | S2 | S3 | Scat | |||||
| 1 (28 June 2023) | 23 | 25.95 | 5.67 | 6.93 | 0.29 | 2.40 | 0.73 | 1.64 |
| 2 (27 July 2023) | 9 | 54.51 | 14.67 | 20.16 | 0.47 | 36.29 | 4.27 | 17.16 |
| 3 (25 August 2023) | 2 | 10.44 | 6.67 | 2.17 | 0.02 | 5.67 | 1.69 | 1.82 |
| Rain Event No. | Qualified Multiple Tracers for Distinguishing Water Sources of Streamflow * | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S3 | Scat | |
| 1 | Fmax(C1)/Fmax(C2), Mg2+/NO3−, Ca2+/K+, Ca2+/NO3−, and δ18O | Fmax(C1)/Fmax(C2), Ca2+/NO3−, Ca2+/K+, and δ18O | Fmax(C1)/Fmax(C2), Ca2+/NO3−, Ca2+/K+, and δ18O |
| 2 | Fmax(C1)/Fmax(C2), Mg2+/NO3−, Ca2+/K+, Ca2+/NO3−, Mg2+/Na+, and δ18O | Fmax(C1)/Fmax(C2), Mg2+/NO3−, Ca2+/NO3−, and δ18O | |
| 3 | Fmax(C1)/Fmax(C2), Mg2+/NO3−, Ca2+/K+, Ca2+/NO3−, and δ18O | Fmax(C1)/Fmax(C2), Mg2+/NO3−, Ca2+/NO3−, and δ18O | |
| Rain Event No | Weir | Water Source Proportions in River Flow (%) * | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rain Water | Forestland Soil Water | Plantation Soil Water | Sloped Cropland Soil Water | Rice Field Soil Water | Meadow Soil Water | Settlement Runoff | Shallow Groundwater | ||
| 1 | S1 | 44.9 ± 21.7 | 55.1 ± 21.7 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| (NU) | (NU) | ||||||||
| S3 | 18.1 ± 10.8 | 15.6 ± 4.1 | -- | 33.6 ± 5.3 | 23.2 ± 5.4 | -- | -- | 9.5 ± 3.9 | |
| (7.3–8.9) | (5.1–7.9) | (12.4–14.7) | (9.3–14.8) | (3.4–4.2) | |||||
| Scat | 9.4 ± 4.0 | 10.7 ± 3.17 | 21.1 ± 6.7 | 18.9 ± 6.3 | 14.7 ± 2.4 | 15.5 ± 5.1 | NS | 9.8 ± 2.2 | |
| (6.5–7.2) | (5.3–5.5) | (8.4–14.7) | (9.3–12.7) | (9.6–11.4) | (6.3–8.3) | (3.5–6.4) | |||
| 2 | S1 | 49.5 ± 25.5 | 50.5 ± 25.5 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| (NU) | (NU) | ||||||||
| S3 | 37.3 ± 23.2 | 10.9 ± 4.7 | -- | 18.0 ± 5.9 | 20.3 ± 6.4 | -- | -- | 13.5 ± 8.4 | |
| (12.6–14.3) | (4.3–4.6) | (7.9–10.2) | (10.2–11.5) | (5.2–5.6) | |||||
| 3 | S1 | 30.5 ± 23.8 | 69.5 ± 23.8 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| (NU) | (NU) | ||||||||
| S3 | 20.9 ± 10.5 | 11.0 ± 2.3 | -- | 23.2 ± 3.6 | 28.4 ± 3.3 | -- | -- | 16.4 ± 4.7 | |
| (10.8–12.2) | (7.6–8.7) | (10.4–11.2) | (9.2–11.8) | (5.7–8.4) | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.-X.; Ao, Y.-T.; Cui, J.-F.; Li, X.-Y.; Tang, X.-Y.; Cheng, J.-H.; Chen, L. Combining Fluorescent Organic Substances, Ions, and Oxygen-18 to Trace Diverse Water Sources of River Flow in a Hilly Catchment. Water 2025, 17, 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081222
Sun Z-X, Ao Y-T, Cui J-F, Li X-Y, Tang X-Y, Cheng J-H, Chen L. Combining Fluorescent Organic Substances, Ions, and Oxygen-18 to Trace Diverse Water Sources of River Flow in a Hilly Catchment. Water. 2025; 17(8):1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081222
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zhi-Xiang, Yan-Ting Ao, Jun-Fang Cui, Xiao-Yu Li, Xiang-Yu Tang, Jian-Hua Cheng, and Lu Chen. 2025. "Combining Fluorescent Organic Substances, Ions, and Oxygen-18 to Trace Diverse Water Sources of River Flow in a Hilly Catchment" Water 17, no. 8: 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081222
APA StyleSun, Z.-X., Ao, Y.-T., Cui, J.-F., Li, X.-Y., Tang, X.-Y., Cheng, J.-H., & Chen, L. (2025). Combining Fluorescent Organic Substances, Ions, and Oxygen-18 to Trace Diverse Water Sources of River Flow in a Hilly Catchment. Water, 17(8), 1222. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081222








