Abstract
Few studies have addressed the coupling of arsenic (As) and nitrogen (N) geochemistry in natural soil. This research focused on the vertical distribution and coupling behavior of As and N in coastal wetland sediments. Pore water and sediment from barren wetlands and coastal wetlands near three estuaries (Guanhe River, Sheyang River, and Liangduo River) in central Jiangsu Province of China with Spartina alterniflora (S. alterniflora) were sampled, which were analyzed for total As content and speciation and N inorganic fractions. The bacterial community was investigated through 16s rDNA sequencing; diversity indices were calculated. The As change trend in pore water of surface sediment with increasing depth was opposite to that of NO3−, possibly because NO3− promoted arsenite (As(III)) oxidation to arsenate (As(V)). Increased NO3− contents seemed to mitigate As toxicity. The vertical distribution of NH4+ indicated anaerobic ammonium oxidation and iron (Fe) ammonium oxidation to reduce Fe oxides, resulting in As release, especially in the deeper sediment. High-throughput sequencing analysis revealed some potential bacteria possibly involved in As-N geochemical coupling, such as Bacillus and Psychrobacter, which can couple denitrification with As oxidation, and Sva1033, which may favor ammonium oxidation-induced As release. Our results suggest that the N-driven oxidation of As(III) and the ammonium oxidation-induced As release can be relevant to As-N coupling processes in the coastal wetland and emphasize the importance of microorganisms in such processes. This research deepens our understanding of As-N coupling in natural coastal wetlands, providing a theoretical basis for controlling As pollution.
1. Introduction
Arsenic contamination is a global environmental issue that has aroused significant attention worldwide. This toxic metalloid can cause severe environmental problems and adversely affect human health and marine life. Not all As chemical species have the same toxicity: while inorganic As is more toxic than organic As, As(III) is more active and more toxic than other As species [1,2]. Arsenic is generally more abundant in sediments than in water [3] because sediments act as an internal source to release As into the overlying water, with an estimated release of 0.5 × 104 tons per year [4]. The transportation of As at the sediment-water interface involves various physicochemical reactions such as adsorption/desorption, precipitation/dissolution, redox reactions, and also microbial activities [5,6]. Therefore, sediments are a crucial source of As in aquatic systems.
Arsenic belongs to Group 15 (nitrogen group) of the periodic table, and numerous studies have demonstrated that its geochemical behavior is closely associated with other elements such as Fe, S, and P. For instance, Fe oxides can adsorb As and subsequently release it under reducing conditions; sulfur compounds can either adsorb or release As, depending on the prevailing redox status, and P can compete with As(V) for adsorption sites, thereby influencing As mobility [7,8]. In recent years, an increasing number of studies have revealed that As is also closely related to the geochemical behavior of the main element in its group, nitrogen, particularly inorganic nitrogen [9,10].
Current research indicates that nitrate (NO3−) and ammonium (NH4+) can affect the biogeochemical behaviors of As, including its speciation, transport, transformation, and release through microbial processes [10,11]. Under anaerobic conditions, NO3− can inhibit the microbial-mediated reduction of As(V), while certain microorganisms can couple the oxidation of As(III) with the reduction of NO3−, utilizing As(III) as an electron donor and NO3− as an electron acceptor [12,13]. Microorganisms such as Azoarcus, Sinorhizobium, Pseudomonas, and Paracoccus are known to participate in this process [14,15]. The anaerobic oxidation of As coupled with denitrification is predominantly observed in the surface soil of paddy fields [10] For example, Zhang et al. (2017) [16] added NO3− to anaerobic paddy soils to promote the oxidation of As(III) to As(V), thereby reducing As mobility, but only a limited number of studies have documented this process in anaerobic sediments, aquatic environments, and reactors [17].
The relationship between As and N behaviors is occasionally influenced by iron. Specifically, Fe(II) can be oxidized to iron oxides by nitrate-reducing Fe(II) oxidizers or by nitrite produced during denitrification, which facilitates the adsorption and fixation of As(V) onto Fe oxides [18,19,20]. Moreover, in environments with high NH4+ concentrations, As content correspondingly increases due to anaerobic ammonium oxidation and feammox, leading to Fe oxides or hydroxides reduction, thus promoting As release [11]. Some studies have even demonstrated that anaerobic ammonium oxidation can directly couple with As reduction [21].
Total As concentration and As speciation in vertical pore water and sediment in relation to depth, as well as their coupling with changes in N concentration in pore water, remain poorly understood in natural soils [22,23]. Currently, most research only focuses on microcosm experiments using constructed wetland paddy soils [10] and laboratory experiments with isolated soil bacteria [13], which limits the comprehensive understanding of As-N coupling behavior. Therefore, it is essential to expand research on natural soils to achieve a more thorough comprehension of the biogeochemical mechanisms underlying As-N coupling.
Coastal wetlands, unique ecological systems, are situated between terrestrial and marine environments and play a crucial role in global element biogeochemical cycles. Wetlands can retain and store pollutants such as As and N from terrestrial sources before they reach the ocean. In estuarine and coastal regions, various NO3− reduction pathways occur prior to N entering the ocean, making these areas vital for the N cycle [24,25]. Numerous studies have demonstrated that nitrification, denitrification, and anaerobic ammonium oxidation processes are prevalent in coastal wetlands [26]. At the same time, coastal wetlands are influenced by redox conditions (tidal effects) and the mixing of freshwater and seawater, resulting in diverse and complex microbial community structures. This complexity makes them an ideal natural laboratory to analyze the biogeochemical interrelations between N and As. In this study, we chose a coastal wetland in the Jiangsu Province (China) as the study area to investigate the vertical variation pattern of As and N and their inorganic speciation in natural soil; the effect of NO3− and NH4+ on the transportation and transformation of As and the role of microorganisms in these processes were also investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Sites
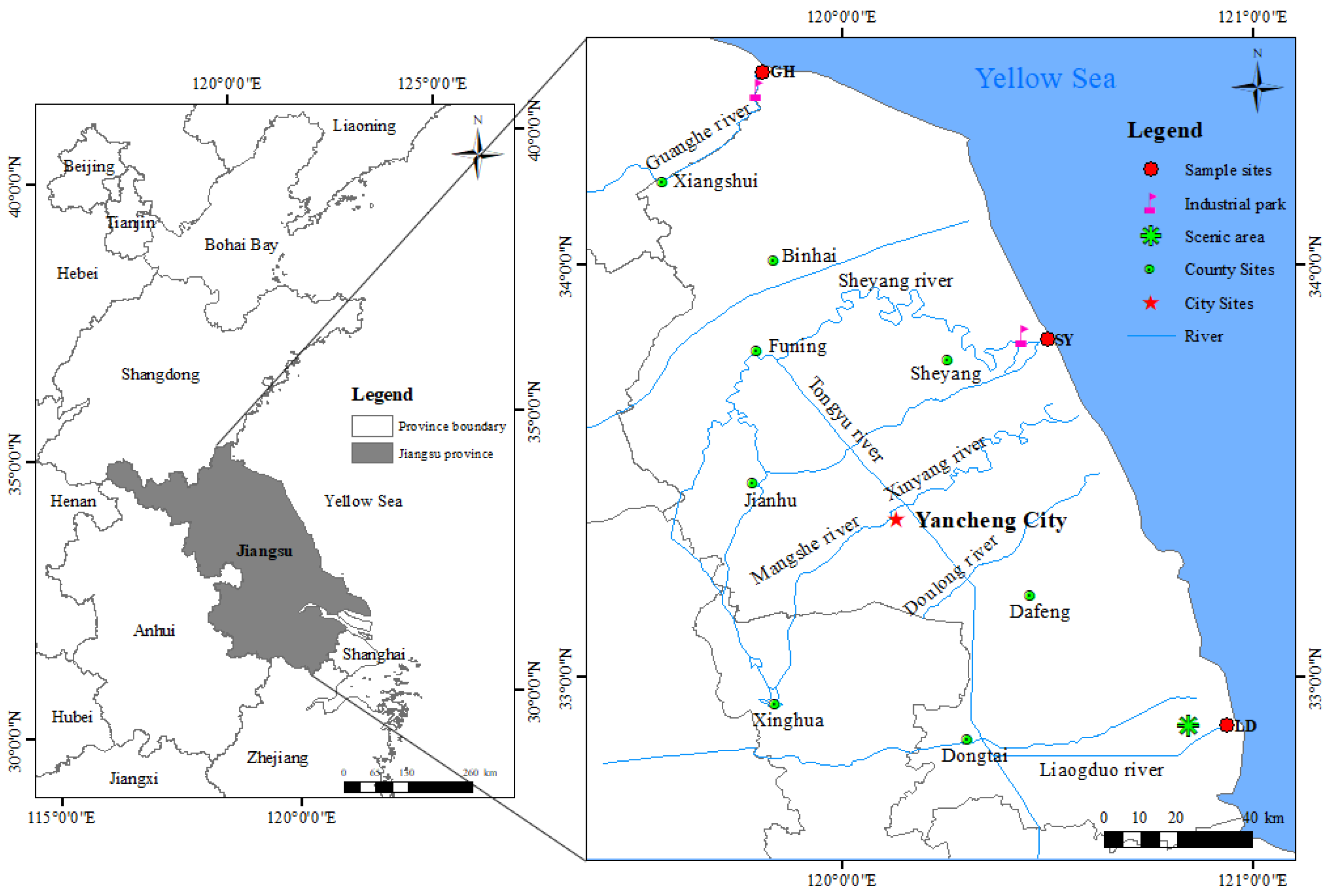
The study area is situated in the coastal wetland of central Jiangsu Province (Figure 1), which serves as a crucial stopover for migratory birds traveling between East Asia and Australia. This wetland is the largest contiguous coastal wetland system in China, spanning 5100 km2. The primary sources of sediment in this region are the old Yellow River and the Yangtze River estuaries [27].
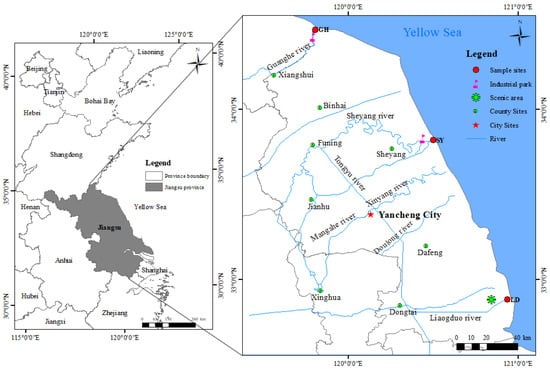
Figure 1.
Study area and sampling sites in a coastal wetland near Guanhe River (GH), Sheyang River (SY), and Liangduo River (LD) estuaries, Jiangsu Province, China.
During April and June 2023, three sediment-type samples were collected near Yancheng city, in Jiangsu Province, from intertidal coastal wetlands close to the Guanhe River (GH), Sheyang River (SY), and Liangduo River (LD) estuaries; geographic coordinates: 34°46′ N, 119°80′ E; 33°81′ N, 120°50′ E; and 32°88′ N, 119°80′ E, respectively. At these sampling sites, we obtained soil cores from two distinct habitats: barren wetland (G) and coastal wetland with S. alterniflora (C). The distribution of the sampling sites and the physicochemical properties of the sediment samples are presented in Figure 1 and Table S1, respectively. Each soil core, approximately 45 cm in length, was sectioned at 1 cm intervals on-site to obtain stratified samples, which were immediately placed in anaerobic sealed bags and transported on ice to the laboratory. Samples were subsequently stored in a −20 °C freezer until further processing.
2.2. Sample Processing
The initially collected wet sediment sample without any treatment was used for bacterial DNA extraction. Then each stratified sample was centrifuged at room temperature at 8000 rpm for 12 min. The supernatant was subsequently filtered through a 0.22 μm sterile filter to obtain “pore water”, further utilized to measure As concentration and speciation and inorganic N fractions. Another portion of the soil was freeze-dried using a freeze-dryer. The freeze-dried soil was then ground using a mortar and passed through a 100-mesh sieve. These sieved soil samples were utilized as experimental materials for subsequent determinations of total Fe, total As, and As speciation.
2.3. Physico-Chemical Analysis
The pH and electrical conductivity (EC) of bulk soil samples were determined using the methods described by Liu et al. (2020) [28]. NO3− concentration in the pore water was measured by assessing the absorbance at 220 and 275 nm with a full-wavelength scanner, and the concentrations were calculated accordingly. Soil inorganic nitrogen was extracted with KCl (1 mol/L), extractant: soil ratio, 10:1. After shaking in an oscillator for 2 h, the supernatant was subsequently filtered through a 0.45 μm filter, and the filtrate was analyzed for NO2−, NO3−, and NH4+ as described by Zhang et al. (2021) [29] using an ultraviolet–visible spectrophotometer (UV–Vis, Persee, Shanghai, China).
The concentration of different As species in the soil and total As content in pore water were determined using atomic fluorescence spectrometry (HPLC-AFS, Persee, Shanghai, China). To determine As speciation, soil samples were extracted with 0.6 M phosphoric acid and 0.1 M ascorbic acid, followed by ultrasonic shaking at 80 °C for 30 min [30]. After cooling to room temperature, the samples were centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 20 min. One mL aliquot of the supernatant was then centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 15 min. The final supernatant was filtered through a 0.22 μm sterile filter and analyzed for As speciation within 24 h to prevent As(III) oxidation.
The concentration of total Fe in solution samples was determined using atomic absorption spectrophotometry following a three-step acid digestion process [31] (AAS-TAS990, Persee, Shanghai, China). Certified reference material (GBW–07452) was utilized for quality assurance. The sum of the extracted As species was compared to the total As provided by the standard reference material, with recovery rates ranging from 100.9% to 104.2%.
2.4. Bacterial DNA Extraction and 16s rDNA Sequencing
Microbial DNA was extracted from soil samples at various depths (1, 10, 20, 30, and 40 cm) using an E.Z.N.A. Stool DNA kit (Omega Biotek, Norcross, GA, USA), following the manufacturer´s protocol. The 16S rDNA V3–V4 region of the prokaryotes rRNA gene was amplified via PCR, employing the following thermal profile: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 2 min, followed by 27 cycles consisting of denaturation at 98 °C for 10 s, annealing at 62 °C for 30 s, and extension at 68 °C for 30 s, concluding with a final extension at 68 °C for 10 min. The primers used were 341-F: 5′-CCT ACG GGNGGC WGC AG-3′; 806-R: 5′-GGA CTA CHVGGG TAT CTAAT-3′, with a unique 8 bp barcode sequence assigned to each sample. PCR amplifications were conducted in triplicate using 50-μL mixtures that included 5 μL of 10 × KOD buffer, 5 μL of 2.5 mM dNTPs, 1.5 μL of each primer (5 μM), 1 μL of KOD polymerase, and 100 ng of template DNA. Amplicons were extracted from 2% agarose gels, purified using an AxyPrep DNA Gel Extraction Kit (Axygen Biosciences, Union City, CA, USA), according to the manufacturer`s instructions, and quantified using a Qubit® 3.0 (Life Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The purified amplicons were pooled in equimolar quantities and subjected to paired-end sequencing (2 × 250) on an Illumina Novaseq 6000 Platform (Nanjing GenePioneer Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China), following standard protocols.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS 27.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Pearson correlation analysis was utilized to examine the relationships between various parameters and the associations between them and microbial communities, with a p-value < 0.05 (two-tailed) regarded as statistically significant. Spearman coefficient analysis was used to examine the correlation between microbial diversity and soil elements. A nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) analysis was utilized to analyze the differences in microbial community structure between barren wetlands (G) and the coastal wetlands with S. alterniflora (C). The t-test was employed to assess differences in dissolved arsenic (dAs) in pore water and arsenic species concentrations in sediments across the three sampling sites, as well as to evaluate differences in microbial diversity between the barren wetland (G) and the coastal wetland with S. alterniflora (C). In t-tests and one-way ANOVA, a p-value < 0.05 was considered significant. In addition, mantel tests and a heatmap of the geochemical parameters and microbial community clusters were performed using the R software packages (vegan, ggplot2, v.4.1.1).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Arsenic and Nitrogen Vertical Distribution in Pore Water
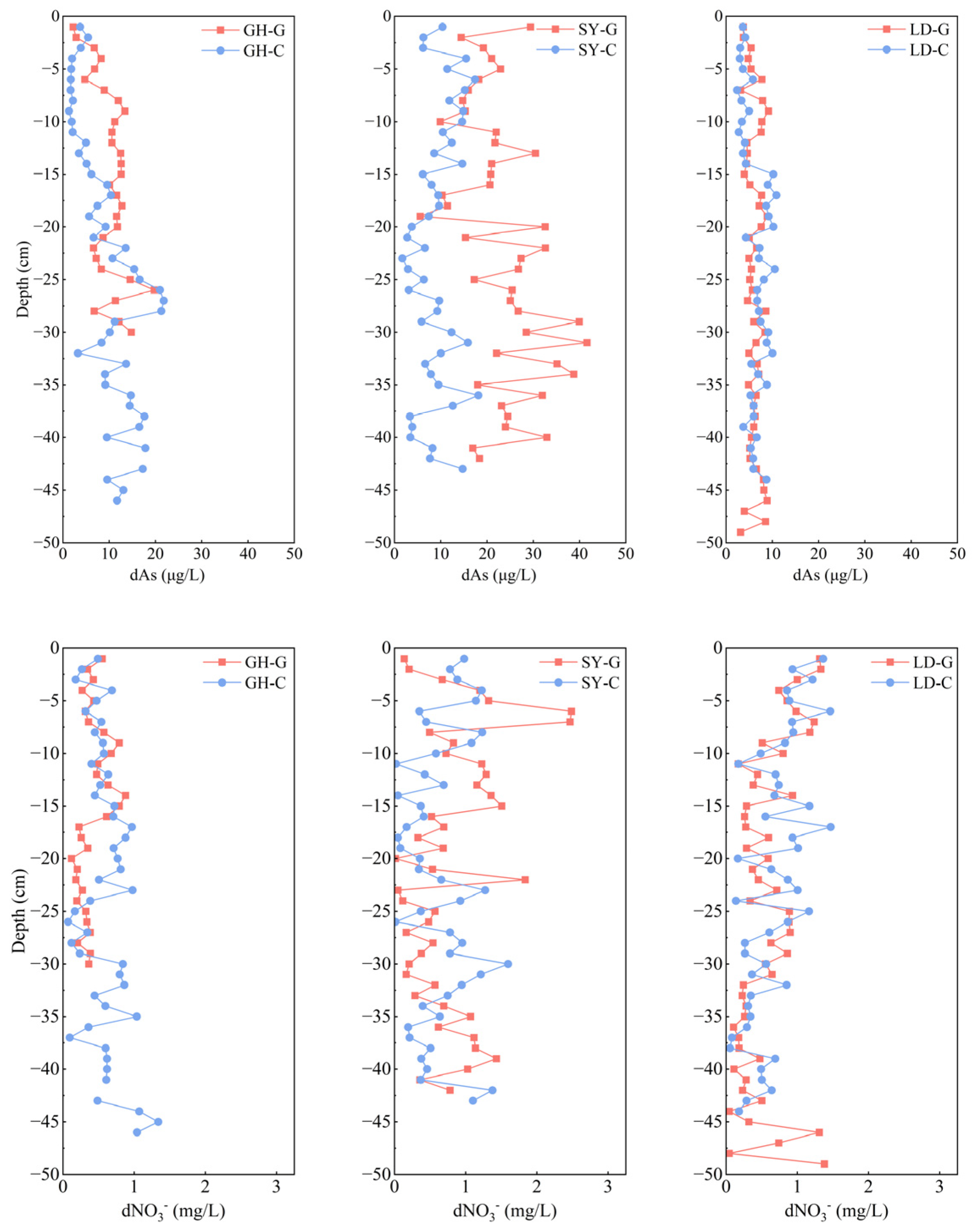
In most sampling sites, dAs of pore water generally showed little change or increased with depth, but dAs of SY-G decreased with depth (0–24 cm) and then increased (24–30 cm) (Figure 2, upper panel). The dAs concentration in the pore water of the uppermost surface layer (0–1 cm) was lower than the average, probably due to the oxidation of As(III) to As(V) under relative oxidizing conditions; As(V) is more readily adsorbed by soil particles, thus reducing pore water As levels [32]. On the other hand, the dAs concentration in the pore water of the barren wetland varied from north to south, increased from GH to SY, and decreased from SY to LD (Table S2). In comparison to the study of dAs concentration in the pore water of the Yangtze River Delta estuary, where it is industrially developed, arsenic concentrations in the pore water of GH-G and SY-G at comparable depths were generally higher than those in this study, only approaching those of GH and SY at a depth of 15 cm. As concentrations at LD-G were consistently lower than those observed in the Yangtze River Delta estuary, as reported before [22]. This spatial heterogeneity may be attributed to the land-use type surrounding the three sampling sites, both onshore and offshore, as the more northern sites in this study (GH and SY) are in proximity to ports and industrial parks developed over a longer period, thus, typically showing higher dAs concentrations. In contrast, the LD site had the lowest average dAs concentration in this research. This sampling site, located near the Tiaozini Scenic Area, lacks nearby ports or industrial parks and has only a few aquaculture households (Figure 1, Table S2). According to a previous study [33], aquaculture does not influence As accumulation significantly. However, the vertical distribution of dAs in pore water also showed slight differences across sites. For example, in GH-G and GH-C samples, dAs concentrations increased with depth, with average concentrations of 10.1 μg/L and 9.5 μg/L, respectively (Figure 2, upper panel). This trend is consistent with previous findings indicating that dAs concentrations in porewater typically increase with depth, as vertical transport driven by hydraulic percolation and gravitational forces facilitates the migration of dissolved arsenic into deeper sediments [34,35]. Additionally, a significant positive correlation was observed between pore water As concentration and soil pH at SY-G and GH-G (Table S3). It may be speculated that higher pH increases the negative surface charge by forming hydroxide ions, which facilitates As a result desorption from Fe oxide. Thus, when the pH value increases, As(III) is more likely released into the surrounding solution.
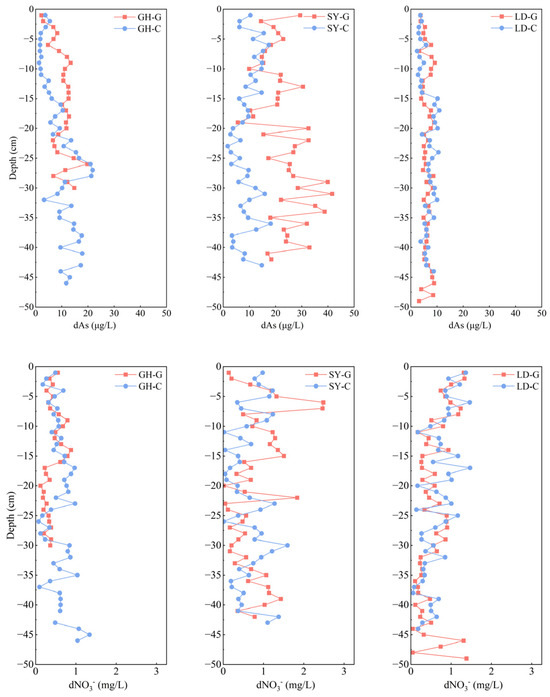
Figure 2.
Vertical distribution of dissolved As (dAs) (upper panel) and dissolved NO3− (d NO3−) (bottom panel) in pore water samples taken at different depths in three sampling sites in a coastal wetland of Jiangsu Province. G: barren wetland; C: coastal wetland with Spartina alterniflora.
Unlike As, dNO3− concentration in pore water tended to increase from north to south (Figure 2, lower panel). More elevated temperatures, enhanced sunlight, intensified biological activity, and human agricultural practices, particularly aquaculture [36], may have resulted in greater NO3− concentrations at the surface layer of LD (0–1 cm) compared with the other sampling sites, in line with previous data [37]. Additionally, NO3− concentrations were elevated in the 0–5 cm layer across all sampling sites compared to those at depths exceeding 20 cm. This phenomenon is likely due to significant nitrification occurring in the aerobic surface layer and the potential NO3− lateral transport via water flow in the coastal wetland, as suggested before [38] It is worth noting that, except for SY-G, all sampling sites exhibited high dNO3− and low dAs concentrations in the uppermost surface layer (0–1 cm). This pattern may be explained by the preference of microorganisms to utilize NO3− as an electron acceptor rather than reduce As when NO3− concentrations are elevated, and a higher NO3− concentration may create an oxidizing environment for Fe and As, which facilitates As oxidation and its subsequent adsorption by soil Fe oxides, alongside an increase in soil Fe content from 27 to 31 cm (Figure S1), thereby leading to a reduction in As concentration in pore water, as previously reported in flooded paddy soils [39]. Concurrently, the predominant presence of Proteobacteria in the 0–1 cm soil layer across all samples (Figure 3a) suggests their involvement in NO3− utilization as an electron acceptor to oxidize As(III), which might be subsequently adsorbed by the soil [40]. Interestingly, at the GH-G site, the amplicon sequence variants (ASVs)-based numbers of Shewanella were found to be 42 and 109 at 20 and 30 cm, respectively. These findings reinforce the idea that some bacteria, such as Shewanella, can utilize Fe oxides as the primary electron acceptor when NO3− concentration is low, facilitating As release [41].
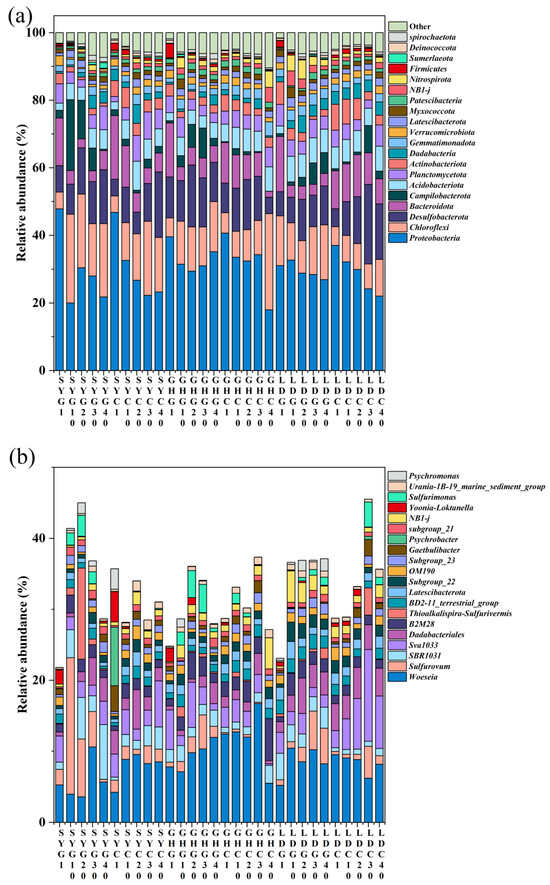
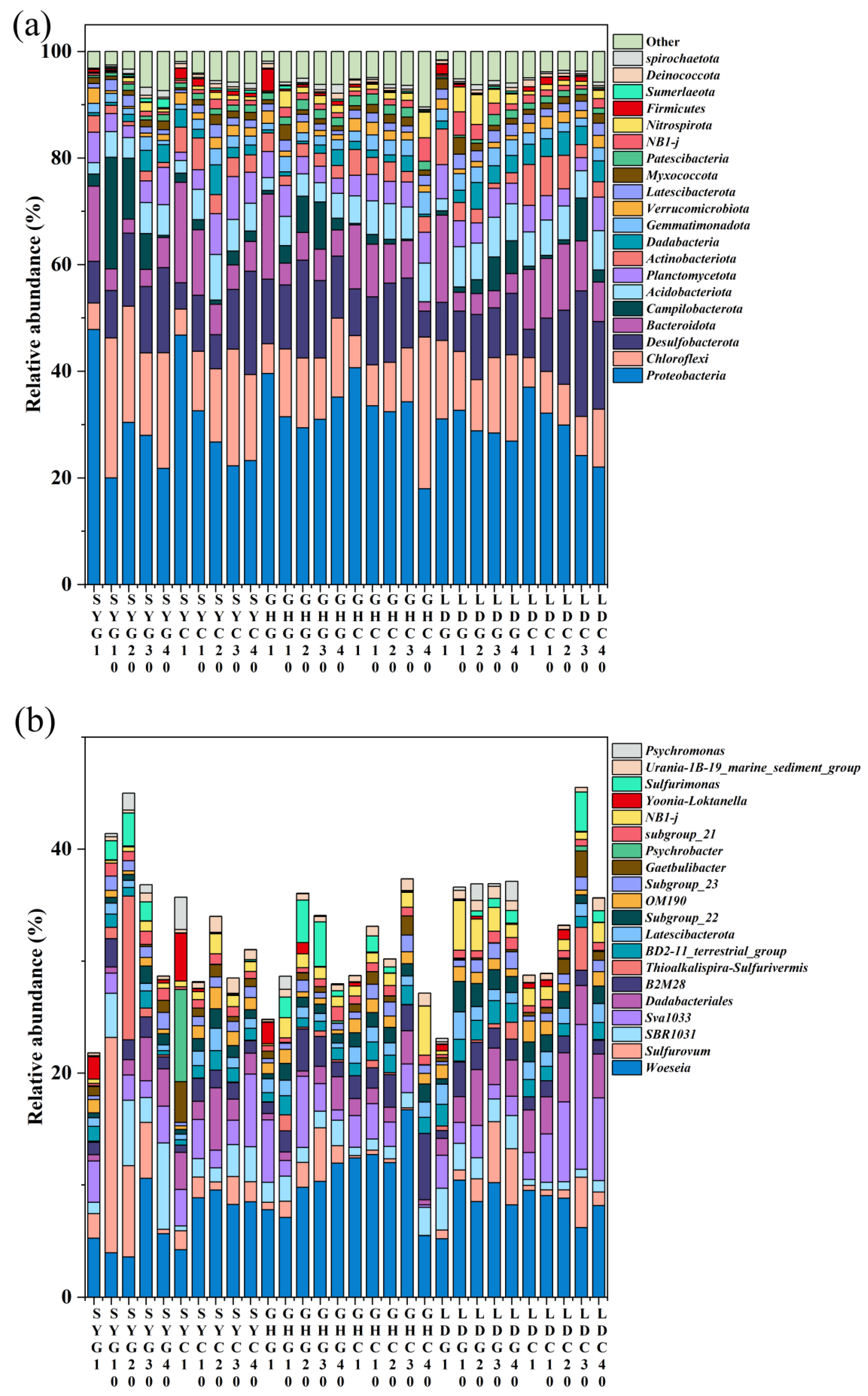
Figure 3.
Vertical distribution of microbial communities at phylum (a) and genus (b) levels in a coastal wetland of Jiangsu Province. The combination of letters and numbers on the X-axis identifies each specific site and depth of sampling (in cm).
3.2. Total Arsenic and Arsenic Species in Sediment
Total As concentrations in the sediments were determined by summing the concentrations of As(III) and As(V). Consistent with the results of previous research, only inorganic As was detected in the sediment samples. Methylated As and more complex organic-As species, such as arsenosugars and arsenobetaine, are predominantly found in biological tissues [42,43].
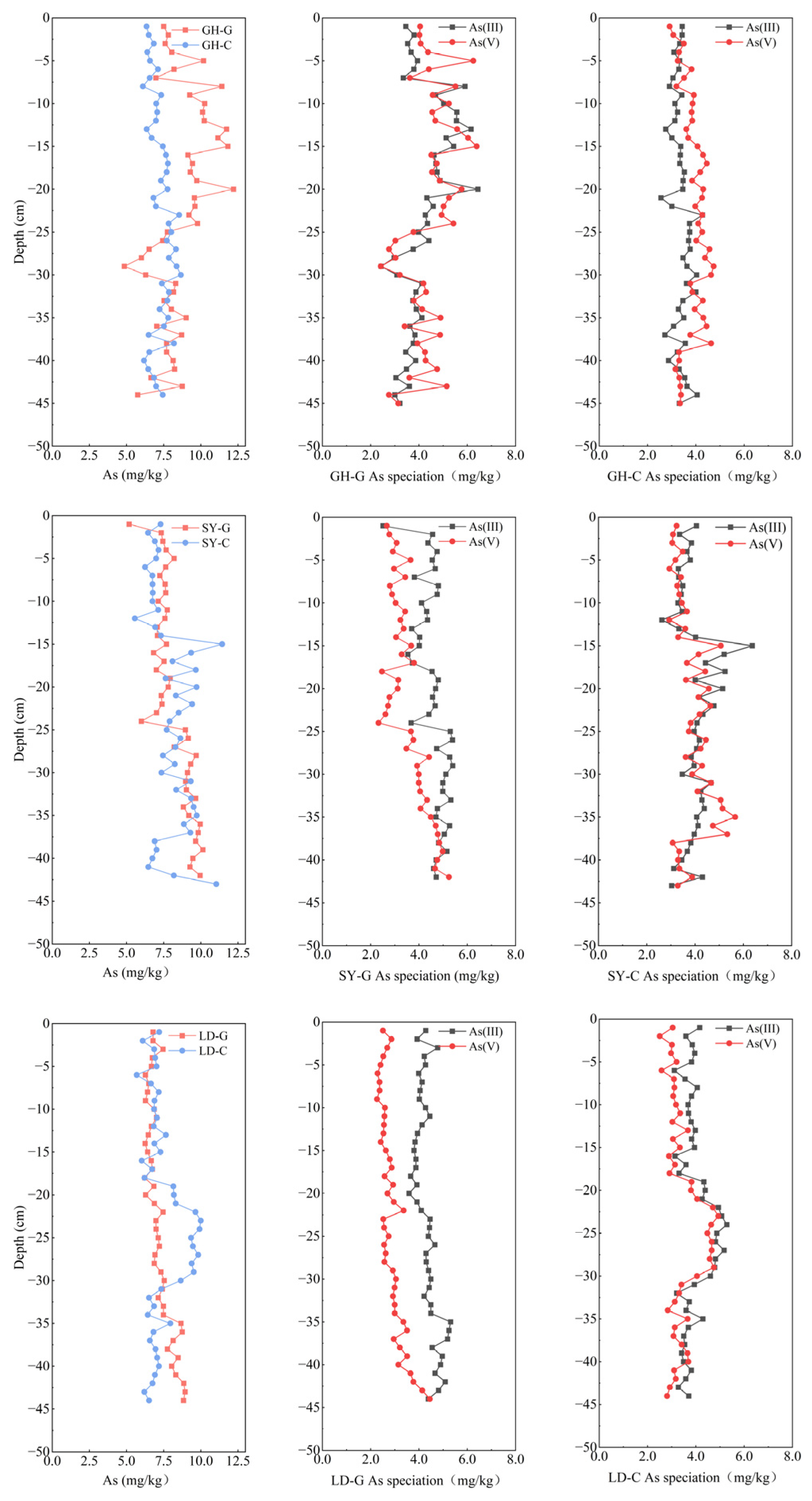
Arsenic levels in the sediment across sampling sites matched the findings of pore water analysis, with As concentrations in the LD-G and LD-C sediments, the most southern sector, slightly lower than those at the other two sites (Figure 4; Table S2). Significance difference analysis (Table S4) indicates that total As concentrations in the sediments of LD were significantly different from those in the sediments of GH and SY. Furthermore, the average variance at LD sampling sites was lower than that at GH and SY (−0.6 and −0.7, respectively), an observation that we primarily ascribe to variations in land use near the sampling locations. At the three sampling sites, we found in the sediment As concentrations slightly inferior to those reported before for the surface of Yangtze River Estuary sediments, 10.3 mg/kg [44], but closer to those found in the coastal sediments of Zhejiang Province, 8.7 mg/kg [45]. This suggests that As pollution in the coastal soils of Jiangsu Province is not currently severe. Liu et al. (2015) [27] reported total As concentrations in sediment cores from the northern Jiangsu barren wetland ranging from 10 to 20 mg/kg, which is higher than the concentrations observed in this study. However, according to Zhang et al. (2024) [46], soil As concentrations in China are expected to rise continuously over the next decades. Given that Jiangsu is one of China`s most developed regions in terms of industry and agriculture, it may face more severe soil As pollution in the future. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor As levels in this region.
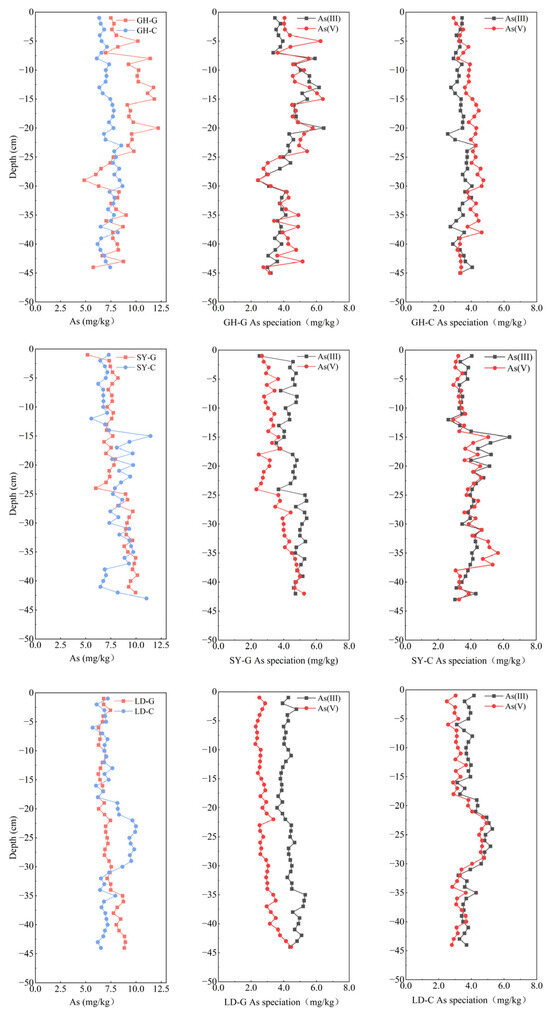
Figure 4.
Vertical distribution of total As (left) and As speciation (center, right) in sediment samples taken at different depths in three sampling sites in a coastal wetland of Jiangsu Province. G: barren wetland; C: coastal wetland with Spartina alterniflora.
In most samples, As(III) content was slightly higher than As(V) content, representing 37.5–64.8% of total As (Figure 4), a fact that may be attributed to tidal fluctuations in the coastal wetland, which probably create an anoxic, reductive environment in sediments, thereby increasing the possibility of As reduction. This observation is consistent with previous findings in other regions, where As(III) typically predominated over As(V) under reductive conditions. For instance, Guo et al. (2019) [47] reported that As(III) accounted for 40–70% of total As in the sediments of the northern East China Sea. Similarly, Mamindy-Pajany et al. (2013) [48] found that As(III) constituted 70–80% of the total As in surface soils at a Mediterranean coastal dock, which was attributed to pollution from nearby industrial areas and metallurgical activities. Moreover, the proportion of As(V) at GH-G and GH-C exceeded that recorded at SY and LD, likely due, as reported before, to the larger soil particle size and lower content of Fe oxides and organic matter at SY and LD, which may have resulted in reduced As adsorption [49,50]. Both As(III) and As(V) concentrations gradually decreased beyond 20 cm at GH-G, with As(V) surpassing the As(III) level, which reached a minimum of 42.3% of total As. At GH-C, As(V) content was generally higher than As(III) content but displayed a decreasing trend beyond 30 cm, declining from 56.6 to 47.6%.
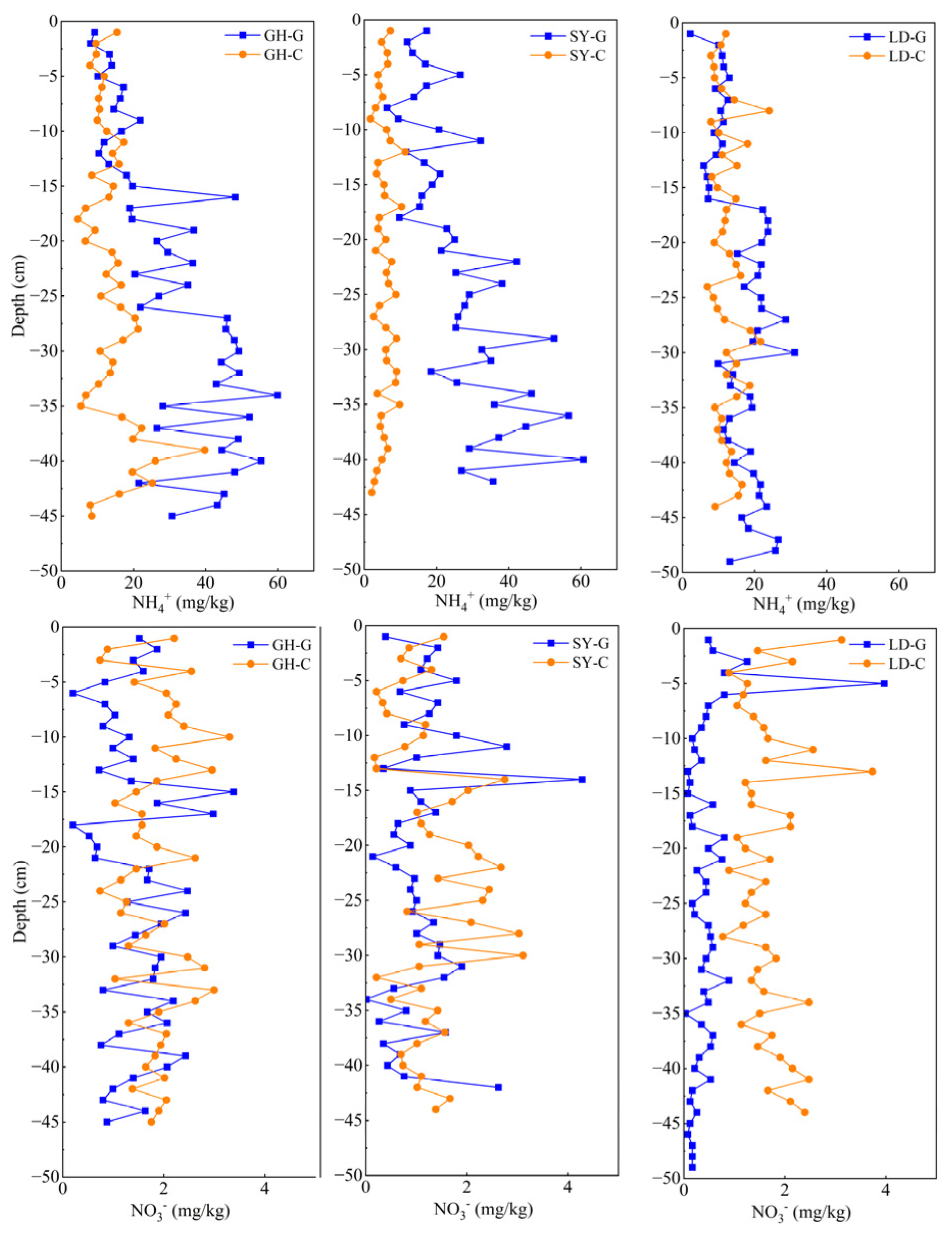
The significant decrease in total As concentration at 25–30 cm in GH may be attributed to the NH4+ increase observed (Figure 5). This rise could have promoted the dissolution of Fe oxides or hydroxides, thereby causing As(V) release from the soil matrix, in line with reported data [21]. In contrast, at SY-G and LD-G, As(V) gradually increased with depth, while the proportion of As(III) decreased, ultimately falling to 47.4%, with a corresponding rise in As(V). The increase in As(V) at SY-G and LD-G, along with the significant positive correlations between sediment NO3− and both total As and total Fe (Table S5), suggests that NO3− may act as an electron acceptor, promoting Fe oxidation and subsequent As adsorption, thereby enhancing sediment Fe and As contents.
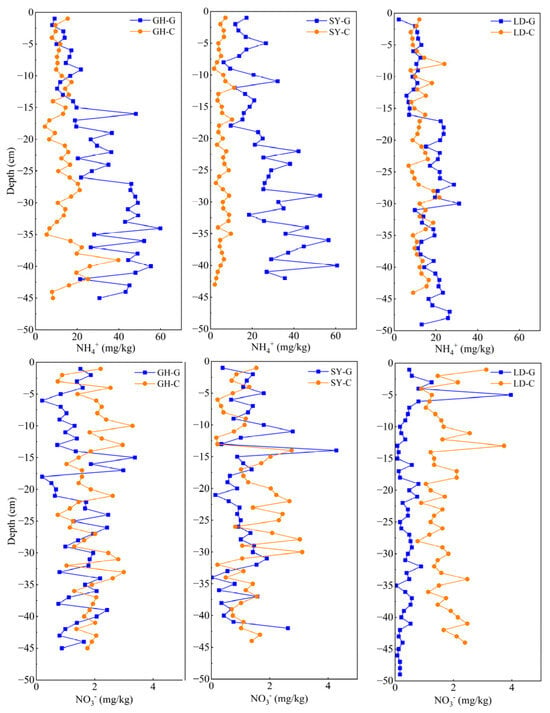
Figure 5.
Vertical distribution of NH4+ (upper panel) and NO3− (bottom panel) in sediment samples taken at different depths in three sampling sites in a coastal wetland of Jiangsu Province. G: barren wetland; C: coastal wetland with Spartina alterniflora.
3.3. Vertical Distribution of Nitrogen Species in the Sediments
NH4+ concentration in the sediment increased with depth in most cases at all sampling sites (Figure 5, upper panel). It has been reported that organic matter mineralization within sediments contributes to NH4+ rise [51,52]. NH4+ concentration in barren wetland sediments was generally higher than that with S. alterniflora. This disparity may be attributed to geographical differences, with barren wetland sediments acting as a sink for NH4+ before its eventual entry into the ocean [53]. On the other hand, S. alterniflora is known to absorb NH4+ [54].
Notably, we found a positive correlation between As content in pore water and NH4+ concentration in the sediment of both GH-G and GH-C sites (Tables S3 and S6), suggesting that NH4+ may induce Fe(III) reduction, leading to the release of absorbed As from Fe oxides or hydroxides, as already indicated [9]. Furthermore, both total sediment As and NH4+ concentrations increased with depth, likely due to stronger reducing conditions in deeper soil layers [55]. Under these conditions, As can be released from iron oxides and become more readily transported downward, enriching in As pore water at deeper layers, as described [56].
The aforementioned findings indicate that NH4+ plays a relevant role in As geochemical cycling. In the case of LD-G, NH4+ concentration tended to be uniform with depth in the upper layers, at an average value of 15.7 mg/kg, but it slowly fluctuated and increased beyond 15 cm. In contrast, in LD-C samples, NH4+ exhibited a more pronounced increasing trend at depths of 20–30 cm. Decreases in As(III) and As(V) concentrations were also observed, along with a reduction in Fe (Figure 4 and Figures S1–S3). It is plausible that ammonia-induced reduction of Fe(III) resulted in the release of As from the sediment. This pattern further supports the hypothesis that NH4+-induced Fe(III) reduction leads to As release from the sediments [9].
NO3− concentrations in the sediments from the other two sampling sites (GH and SY) exhibited an increasing trend from 1 to 15 cm, followed by a decreasing trend (Figure 5, lower panel). This pattern is consistent with the results by Li et al. (2022) [23] in 1 m deep sediment cores at forest and wetland sites. To explain this phenomenon, it has been suggested that NO3− might replace O2 as an electron acceptor during the transition from oxygenated to anoxic conditions, facilitating the oxidation of elements such as Fe and As [57]. The lower As concentration in the pore water of surface sediments found in this study further supports this idea. Additionally, a positive correlation between NO3− and total sedimentary As in SY-C (Table S7) suggests that increased NO3− concentrations inhibit the dissolution, reduction, and release of As and Fe, thereby leading to As accumulation in the sediments. Compared to SY and LD, the lower NO3− concentration in LD-G is probably the consequence of minimal anthropogenic activity, while LD-C exhibited higher NO3− concentrations, likely due to the strong nitrogen-fixing ability of S. alterniflora, as documented before [58].
3.4. Microbial Analysis in Sediment
3.4.1. Microbial Diversity
In the high pH and high salinity soil environment of Jiangsu province coastal wetlands, alpha-diversity was assessed using the ACE index, Shannon index, and observed species to elucidate biodiversity in estuarine soils. The results of these analyses are presented in Table S8. The finding that Good’s coverage was ≥96% indicates that the bacterial ASVs in each sample were well represented.
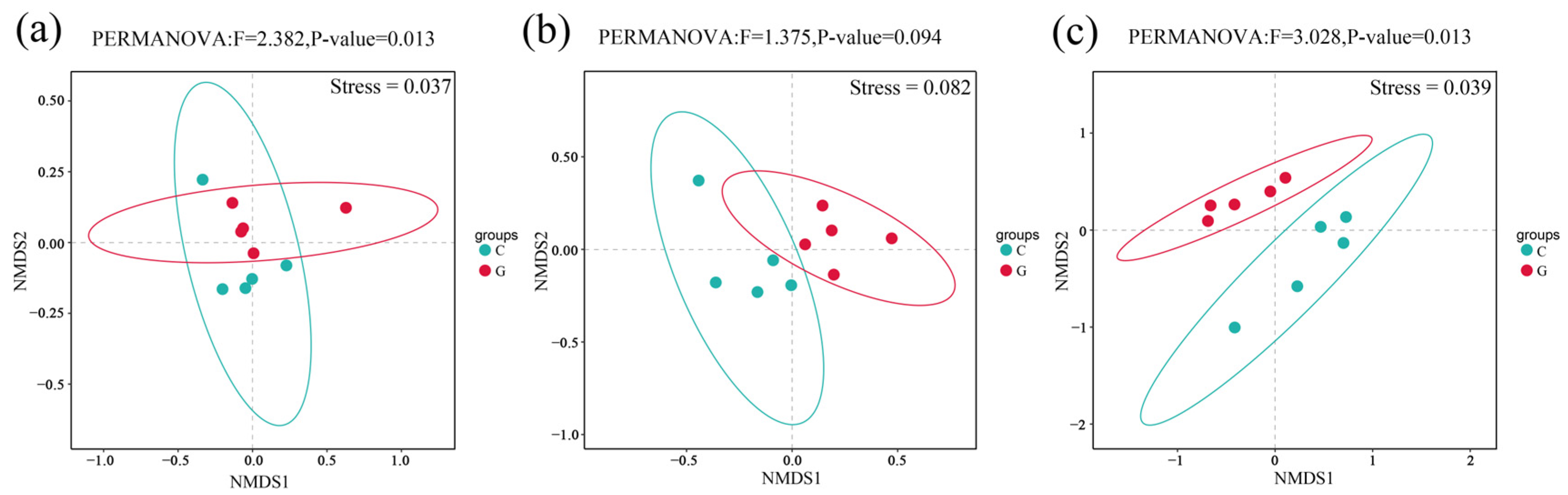
A nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) analysis based on ASV levels and Bray–Curtis distance, conducted using R software (v.3.6.1; R Core Team, 2019), revealed significant differences in the bacterial community composition between barren wetland and coastal wetland with Spartina alterniflora across all sampling sites (Figure 6). Notably, samples from SY displayed considerable overlap (Figure 6b). The NMDS model had a stress value of 0.082, indicating a well-fitted model. The PERMANOVA results (F = 1.375, p = 0.094) suggest no statistically significant difference between the barren wetland and the coastal wetland with S. alterniflora, indicating a relatively similar microbial community composition at this site.
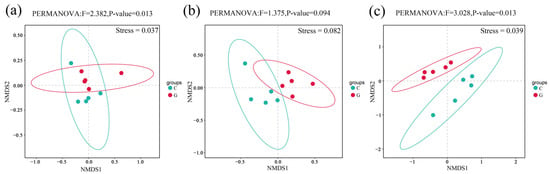
Figure 6.
A nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) analysis of microbial community structure under different environmental conditions across three sampling sites. (a) GH, (b) SY, (c) LD.
In contrast, the overlap was minimal for samples from the GH and LD sites (Figure 6a,c), where stress values were 0.037 and 0.039, respectively, both below 0.05, indicating a highly reliable NMDS model. The PERMANOVA results showed F-values of 2.382 (p = 0.013) for GH and 3.028 (p = 0.013) for LD, suggesting significant differences in bacterial community composition between the barren and vegetated wetlands at these sites. A higher F-value corresponds to greater dissimilarity between groups, with LD exhibiting the most pronounced divergence. The significant differences observed in GH and LD (p < 0.05) suggest distinct microbial community compositions, whereas the SY site shows higher similarity between conditions. In this regard, Wang et al. (2023) [59] found that increased NH4+ concentrations could influence soil microbial community structures. Given the higher NH4+ concentrations detected in the barren wetland soil compared to the sediment of the coastal wetland with S. alterniflora, it can be inferred that NH4+ may contribute to the differences in microbial community structure between these environments.
Microbial diversity at SY-G and SY-C displayed a significant variation with depth, whereas this did not occur at GH and LD (Table S8). At SY-C samples, ACE, observed species (Obs), and Shannon diversity indices peaked at a depth of 10 cm, to gradually decline at deeper strata. Generally, the alpha diversity of soil bacterial communities is influenced by various abiotic and biotic factors, including soil properties and vegetation. Different types of halophyte vegetation may impact the diversity and richness of soil bacterial communities. Previous studies have indicated that soils dominated by halophytes exhibit greater microbial diversity compared to barren wetland sediments [60,61]. However, the significance in the three indices—ACE, Obs, and Shannon—between barren wetland and coastal wetland sediments with S. alterniflora were all found to be p > 0.05 (Table S9), suggesting no significant difference in diversity between the two sample types.
As shown in Table 1, the three indices were significantly negatively correlated with soil EC but not with soil ammonia nitrogen. This finding aligns with data published by An et al. (2019) [62], who identified salinity as a crucial factor influencing bacterial communities and indicated that high salinity conditions may lead to reduced alpha diversity in wetland sediments. Additionally, Wang et al. (2023) [59] found that nitrogen input appears to have only a minor effect on microbial diversity. Thus, in the unique environment of barren wetlands, higher salinity levels are usually associated with lower microbial diversity. In this study, we calculated an average Shannon diversity index in the barren wetland and coastal wetland by S. alterniflora (Zhejiang province) of 10.1 and 9.8, respectively, which exceed those reported by Gu et al. (2022) [61] in a comparable study (8.26 and 9.74) and tend to reveal a greater microbial species richness and a more even microbial distribution in the sediments of the study area. Consequently, and in line with other reports [63], we consider that microorganisms are likely to play a crucial role in the As-N coupling cycle.

Table 1.
Correlation between soil physicochemical properties and microbial diversity.
3.4.2. Microbial Community Composition and Potential Arsenic-Nitrogen Coupling Functional Microorganisms
The distribution of microbial communities at both the phylum and genus levels in sediment samples is depicted in Figure 3a,b, respectively. A total of 162 phyla and 818 genera were identified, with the twenty most dominant phyla and genera presented in the figure. The four dominant phyla were Proteobacteria, Chloroflexi, Desulfobacterota, and Bacteroidota, exhibiting relative abundances of 18–48%, 5–26%, 5–24%, and 2–16%, respectively (Figure 3a). These findings align with the results of Luo et al. (2024) [64], who also identified Proteobacteria, Desulfobacterota, and Bacteroidota as the predominant bacterial phyla in coastal wetlands.
Previous research has demonstrated that Proteobacteria, Chloroflexi, and Bacteroidota encompass bacteria with denitrification capabilities [65,66]. In our study, Proteobacteria and Bacteroidota were abundant taxa in the surface layer (0–1 cm) of both barren wetlands and coastal wetlands with S. alterniflora across the three sampling sites, whereas Chloroflexi had a lower relative abundance in the surface layer (0–1 cm) but was more prevalent in subsurface layers.
Firmicutes and Nitrospirota, which ranked among the top twenty phyla, have also been implicated in As and N biogeochemical processes [67,68]. Importantly, some genera within Proteobacteria and Firmicutes demonstrate high tolerance to arsenic and possess the capability to oxidize As(III). Nitrospirota, recognized for its strong ammonia oxidation, can convert NH4+ directly to NO3− or oxidize NO2– to NO3–, thereby influencing nitrogen cycling in aquatic environments [69]. Furthermore, some studies have identified the presence of As(V) reductase encoded by the ArsC gene within Nitrospirota [68]. Further investigation is needed to elucidate the possible role of Nitrospirota members of this phylum in the interaction between arsenic and nitrogen.
At the family level, the dominant taxa included Woeseiaceae (~16.4%), Anaerolineaceae (~13.6%), Rhodobacteraceae (~6.2%), Flavobacteriaceae (~5.4%), and Sulfurovaceae (~4.9%) (Figure S4). Among them, Woeseiaceae and Anaerolineaceae were the most abundant, associated with carbon and nitrogen cycling as well as organic matter degradation [70,71]. Since family-level analysis provides only a general overview, we further examined the microbial composition at the genus level to better understand the functional roles of key taxa in the biogeochemical cycling of arsenic and nitrogen.
At the genus level, the microbial composition was similar to that at the family level, and the twenty most dominant genera are presented in Figure 3b. The primary dominant genera include Woeseia (~16.71%), Sulfurovum (~19.3%), SBR1031 (~7.7%), and Sva1033 (~12.9%). Woeseia, from the Woeseiaceae family, was the most abundant genus across all soil samples and has been previously observed in various marine sediments; it may play a significant role in nitrogen geochemical cycling within coastal wetlands [72]. Sulfurovum is an anaerobic chemolithotroph that utilizes either sulfur or thiosulfate as an energy source, with carbon dioxide serving as the sole carbon source. Nitrate acts as the sole terminal electron acceptor for this microorganism [73]. Notably, Sva1033 was also identified as a dominant genus by Luo et al. (2024) [74] and is recognized as a dissimilatory iron reducer [75]. Other dominant genera with relatively high average abundances were Thiobacillus (~0.72%), Halomonas (~2.34%), and Bacillus (~0.25%). These genera may be involved in the biogeochemical coupling of arsenic and nitrogen in estuarine wetlands [76,77,78].
3.5. Interactions of Microorganisms with Arsenic and Nitrogen
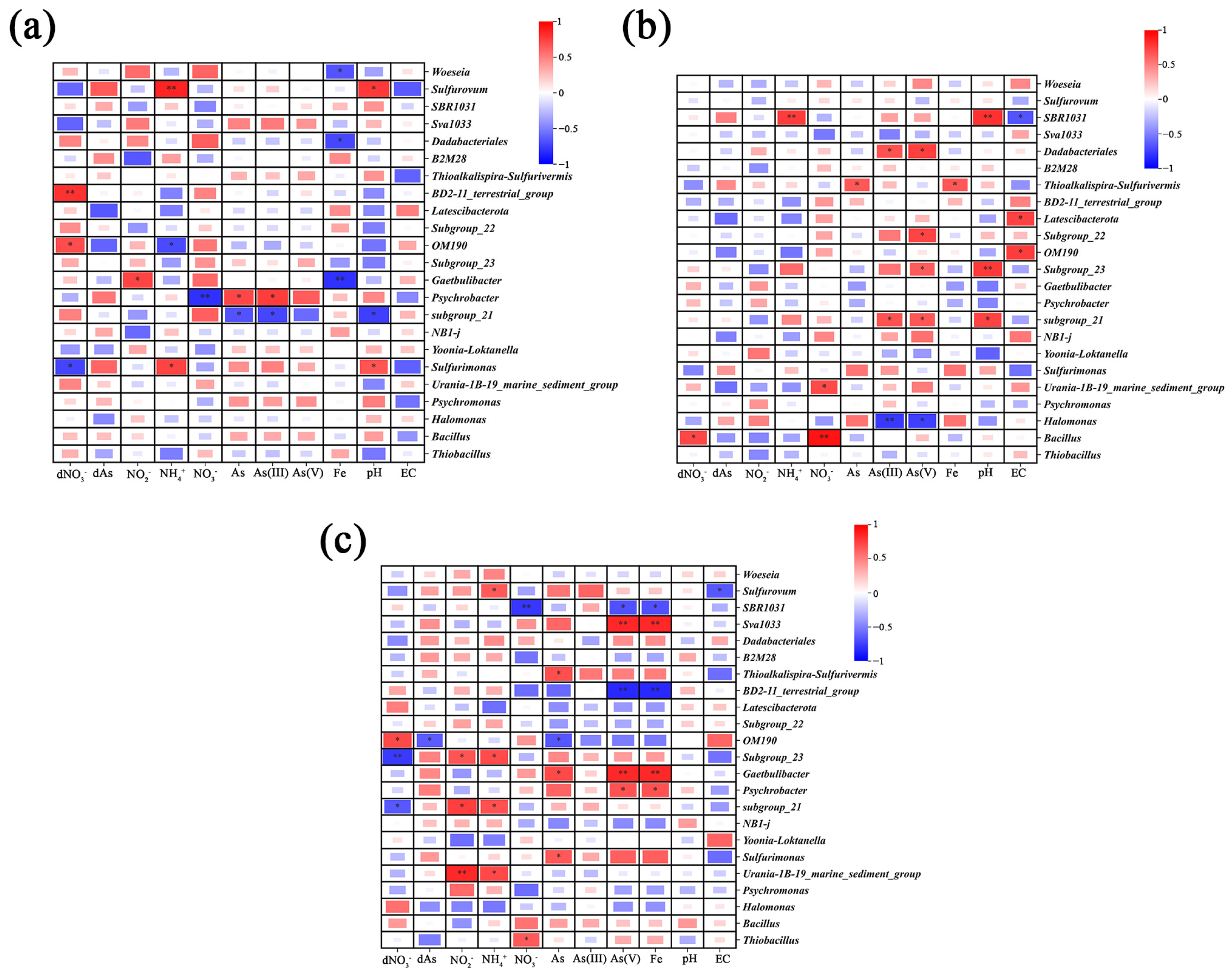
To further investigate the influence of microorganisms on As-N coupling behaviors, we analyzed the relationships between microbial communities and geochemical indicators such as N and Fe (Figure 7). Numerous studies have indicated that NO3− reduction coupled with As oxidation primarily occurs in suboxic environments [10,16], potentially within the surface soil layers (approximately 0–20 cm) of paddy fields. In this study, we observed that NO3− concentrations and total As in pore water at depths of 1–15 cm increased in the intertidal zone of the GH sampling site. Additionally, NO3− in pore water exhibited a significant positive correlation with soil As(V), suggesting that NO3− may act as an electron acceptor to oxidize As(III) under suboxic conditions, thereby increasing As(V) in the sediment. Furthermore, total As in pore water showed a significant positive correlation with total As in the soil (Table S6), indicating vertical transport of As and its accumulation in the lower soil layers. In the GH-C site, both pore water NO3− and As concentrations gradually increased in the 1–20 cm soil layer.
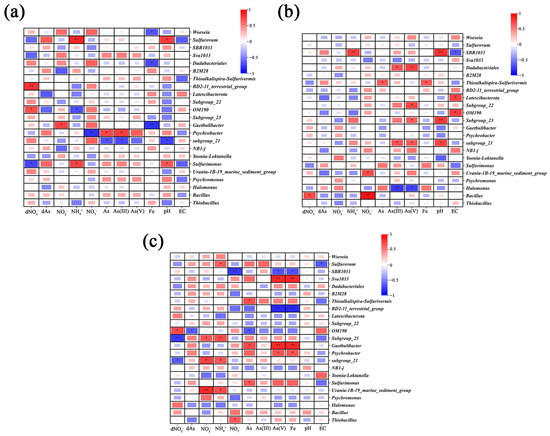
Figure 7.
Heatmap of correlations between microbial communities, pore water, and soil physicochemical parameters. (a): GH, (b): SY, (c): LD. Red: positive correlations; blue: negative correlations. Color intensity reflects the strength of the correlation. * and ** indicate significant correlations at p < 0.05 and p < 0.01, respectively.
A significant positive correlation was also observed between pore water NO3− and sediment As(V). Interestingly, Psychrobacter was identified at the GH sampling site; this microorganism was reported to possess strong denitrifying capabilities [66]. Psychrobacter was significantly negatively correlated with sediment NO3− (r = −0.81, p < 0.01) (Figure 7a); we speculate that this bacterium could have contributed to reducing nitrate availability as an electron acceptor and decreasing the potential for As(III) oxidation. Supporting this hypothesis, Psychrobacter was significantly positively correlated with As(III) concentration in SY (Figure 7a). This aligns with previous observations in the Hetao Plain, where Psychrobacter abundance exhibited positive correlations with As concentration, which was assigned to its strong resistance to this contaminant [66]. Additionally, NO3− in pore water was significantly negatively correlated with soil As(V) in the LD-G site at a depth of 1–40 cm (Table S10), likely due to the absence of electron acceptors necessary for As(III) oxidation.
In this study, the microbial genus SBR1031 demonstrated a negative correlation with both NO3− and As(V) levels in LD (Figure 7c). Previous studies showed that SBR1031 could facilitate NO3− removal processes, such as denitrification and anammox, in reactors, and its abundance was negatively correlated with NO3− concentration [79]. Therefore, we speculate that similar processes could have taken place and indirectly influenced As release in the coastal wetland here studied.
Bacillus exhibited significant positive correlations with sediment NO3− (r = 0.93, p < 0.01) and dissolved NO3− in pore water (r = 0.72, p < 0.05) in SY-G and SY-C, indicating that Bacillus is capable of utilizing NO3− as an electron acceptor under anaerobic conditions. There are reports showing that Bacillus can oxidize As(III) using NO3− as the electron acceptor [76]. Importantly, a gradual decrease in pore water As was observed at non-surface soil layers (31–40 cm), with NO3− in pore water showing a significant negative correlation with total As, alongside an increase in soil As(V) and a decrease in As(III), suggesting As(III) oxidation. The Mantel analysis further supports the conclusion that denitrification is closely linked to As dynamics in these environments (Figure S5). Significant correlations between denitrification-related microbial communities and As levels in the soil (p < 0.05) suggest that NO3− reduction may influence As transformation. This reinforces previous findings that many bacteria in these environments, including Bacillus and Psychrobacter, possess both denitrification and As oxidation capabilities. The strong association observed in the Mantel analysis highlights the potential for denitrification-driven changes in arsenic speciation in coastal wetlands. These results underscore the need for further research on isolating and culturing functionally relevant bacteria, which could provide valuable insights into the biotechnological potential for managing As pollution in coastal and marine ecosystems.
In this study, it was found that NH4+ may play a significant role in the reduction and release of As. Sediment NH4+ concentrations exhibited significant positive correlations with Fe, As(V), total As, and NO2− in the sediment, as well as total As in pore water of LD-G at depths of 1–40 cm (Table S10). Therefore, NH4+ may contribute to the reduction and release of As within the sediment. In this sense, a previous study indicated that NH4+ could act as an electron donor in the induced reduction of Fe oxide minerals, thereby facilitating As mobilization in groundwater [67]. This process likely involves Fe-mediated anaerobic NH4+ oxidation, which produces ferrous ions [72] and subsequently releases As(V) adsorbed onto iron oxides, promoting As mobilization in groundwater. Additionally, Xiu et al. (2024) [9] found high As enrichment in groundwater and attributed this phenomenon to bacterial anaerobic ammonium oxidation, which can induce Fe (III) reduction, and also noted that ammonia-oxidizing archaea predominantly exist in soil and marine sediments. Considering these observations, further research is needed to investigate the presence of ammonia-oxidizing genes in coastal wetland communities that might mediate the coupling reaction between As and NH4+ transformations.
We also found significant positive correlations between Sva1033 abundance and Fe (r = 0.85, p < 0.01) and As(V) (r = 0.85, p < 0.01) in LD-G and LD-C (Figure 7c). Previous studies by Baloza et al. (2023) [75] indicated that Sva1033 is significantly correlated with Fe and plays a crucial role in iron reduction. Given the close association between Fe and As(V), where As(V) is readily adsorbed onto Fe oxides or hydroxides, it can be inferred that Sva1033 may influence As desorption and its release into pore water [73]. The Mantel analysis at the LD site further supports the connection between N and Fe cycling (Figure S6), revealing that both anammox bacteria and iron-reducing bacteria are significantly associated with ammonium. Additionally, a strong positive correlation between Fe and As was observed, suggesting that Fe reduction may facilitate As mobilization in this environment. The observed relationships suggest that microbially mediated Fe reduction may not only influence As speciation and release but could also be closely linked to nitrogen transformation processes.
The combined actions of multiple microbes may lead to additional coupling effects. For instance, Halomonas, an N-related microbe, showed in this study significant negative correlations with As(III) (r = −0.75, p < 0.05) and As(V) (r = −0.78, p < 0.01) in the SY site (Figure 7b). Halomonas is known for its high As tolerance and can absorb As for growth, thereby detoxifying As [77]. In addition, OM190 showed significantly positive correlations with dNO3− at two sampling sites (Figure 7a,c). A previous study suggests the potential ability of this microbe for anaerobic NH4+ oxidation [79], so it can be speculated that in the wetlands assessed, it could have also been involved in anaerobic NH4+ oxidation, while in this study, OM190 was positively correlated with As of LD (r = −0.66, p < 0.05), suggesting that OM190 might influence As-N coupling geochemical behavior. Therefore, how this microorganism would affect As-N coupling or whether the combination of more than two bacteria would affect this process is unknown and requires further research.
4. Conclusions
This study researched the vertical distribution of As and N and their coupling relationships in the natural soil of coastal wetlands, with a focus on possible microbial interactions. Under the special environment of coastal wetland, where aerobic and anaerobic conditions alternate, NO3− can act as an electron acceptor for the oxidation of As(III), especially in the more superficial surface sediments, and thus, As(V) might be more readily adsorbed by Fe oxides or hydroxides, thereby immobilizing As and reducing its toxicity. Additionally, microbes such as Bacillus and Psychrobacter may participate in denitrification, potentially promoting As oxidation processes directly or indirectly and helping immobilize and detoxify As. In the barren wetland of different sampling sites, the accumulation of NH4+ led to anaerobic NH4+ oxidation and Fe ammonium oxidation, resulting in the reduction of Fe oxides or hydroxides. This reduction can release As from the sediment interface into the water interface, thus increasing As mobility, and microbes such as Sva1033 and SBR1031 may be involved in these processes. This study provides important insights into the As-N geochemical coupling behavior in the natural soil of a coastal wetland, a point of great significance for the prevention and control of As pollution in coastal and marine ecosystems. Further research is needed to understand more deeply the role of specific microorganisms in these relevant interactions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w17091255/s1, Table S1. Physicochemical properties of overlying water and soil organic matter across sampling sites; Figure S1. Vertical profiles of sediment physicochemical parameters (NO2−, Fe, pH, EC) at GH site; Figure S2. Vertical profiles of sediment physicochemical parameters (NO2−, Fe, pH, EC) at SY site; Figure S3. Vertical profiles of sediment physicochemical parameters (NO2−, Fe, pH, EC) at LD site; Table S2. Statistical parameters of porewater and sediment characteristics with depth; Table S3. Pearson correlations between porewater-sediment parameters at GH-G site; Table S4. Spatial ANOVA of arsenic concentrations in sediments; Table S5. Pearson correlations between porewater-sediment parameters at SY-G site; Table S6. Pearson correlations between porewater-sediment parameters at GH-C site; Table S7. Pearson correlations between porewater-sediment parameters at SY-C site; Table S8. Bacterial community diversity indices across sediment depths; Table S9. Microbial diversity comparison between barren and Spartina alterniflora wetlands; Figure S4. Microbial community composition across sediment depths in Jiangsu coastal wetlands; Figure S5. Mantel test network for geochemical-microbial interactions at SY site; Table S10. Pearson correlations between porewater-sediment parameters at LD-G site; Table S11. Pearson correlations between porewater-sediment parameters at LD-C site; Figure S6. Mantel test network for geochemical-microbial interactions at LD site; Table S12. Functional microbial genera in denitrification, arsenic redox, iron reduction, and anammox processes. References [80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92] are citied in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Methodology: Y.Z. and L.X.; Software: Y.Z.; Formal analysis: L.D.; Investigation: Y.Z., S.K., Z.Z., K.L. and H.W.; Resources: T.L.; Data curation: H.G.; Writing—original draft: Y.Z.; Writing—review & editing: L.X.; Supervision: L.X.; Project administration: L.X.; Funding acquisition: L.X. and T.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by School-level research projects of the Yancheng Institute of Technology (xjr2021041 and 2023039), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20241974), and the Talents Project of Yancheng Institute of Technology.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chakraborty, S.; Bhar, K.; Saha, S.; Chakrabarti, R.; Pal, A.; Siddhanta, A. Novel arsenic nanoparticles are more effective and less toxic than As (III) to inhibit extracellular and intracellular proliferation of Leishmania donovani. J. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 2014, 187640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xiong, H.Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Wang, W.X. Transfer and bioavailability of inorganic and organic arsenic in sediment-water-biota microcosm. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 232, 105763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaffar, Z.; Cúrdia, J.; Borja, A.; Irigoien, X.; Carvalho, S. Consistent variability in beta-diversity patterns contrasts with changes in alpha-diversity along an onshore to offshore environmental gradient: The case of Red Sea soft-bottom macrobenthos. Mar. Biodivers. 2019, 49, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Yoshinaga, M.; Zhao, F.J.; Rosen, B.P. Earth abides arsenic biotransformations. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2014, 42, 443–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couture, R.M.; Gobeil, C.; Tessier, A. Arsenic, iron and sulfur co-diagenesis in lake sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 1238–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, F.Y.; Huo, S.L.; Zhang, J.T.; Zhang, L.; Xi, B.D.; Zhang, L.Y. Arsenic fractionation and contamination assessment in sediments of thirteen lakes from the East Plain and Yungui Plateau Ecoregions, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.W.; Liang, J.L.; Björn, L.O.; Li, J.T.; Shu, W.S.; Wang, Y.T. Phosphorus-arsenic interaction in the ‘soil-plant-microbe’ system and its influence on arsenic pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planer-Friedrich, B. Sulfur being an overlooked promoter of groundwater arsenic contamination. Nat. Water 2023, 1, 134–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, W.; Gai, R.X.; Chen, S.Z.; Ren, C.; Lloyd, J.R.; Bassil, N.M. Ammonium-enhanced arsenic mobilization from aquifer sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 3449–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Du, Y.H.; Li, X.M.; Li, F.B.; Qiao, J.T.; Chen, G. Insight into universality and characteristics of nitrate reduction coupled with arsenic oxidation in different paddy soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, T.N.; Liu, C.W.; Kao, Y.H.; Hsiao, S.S. Isotopic evidence of nitrogen sources and nitrogen transformation in arsenic-contaminated groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.M.; Qiao, J.T.; Li, S.; Häggblom, M.M.; Li, F.B. Bacterial communities and functional genes stimulated during anaerobic arsenite oxidation and nitrate reduction in a paddy soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2172–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chai, C.W.; ThomasArrigo, L.K.; Zhao, S.C.; Kretzschmar, R.; Zhao, F.J. Nitrite accumulation is required for microbial anaerobic iron oxidation, but not for arsenite oxidation, in two heterotrophic denitrifiers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4036–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.H. Impact of microorganisms on arsenic biogeochemistry: A review. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2014, 225, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, W.X.; Liu, B.B.; He, J.; Shen, Q.; Zhao, F.J. Anaerobic arsenite oxidation by an autotrophic arsenite-oxidizing bacterium from an arsenic-contaminated paddy soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5956–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.C.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, W.X.; Huang, K.; Tang, Z. Nitrate stimulates anaerobic microbial arsenite oxidation in paddy soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4377–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Sierra, R.; Field, J.A. Anoxic oxidation of arsenite linked to denitrification in sludges and sediments. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4569–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, J.; Prommer, H.; Kaksonen, A.H.; Sun, J.; Siade, A.J.; Yusov, A. Identifying and quantifying the intermediate processes during nitrate-dependent iron(II) oxidation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5771–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.X.; Chen, D.D.; Li, X.M.; Li, F.B. Microbially mediated coupling of nitrate reduction and Fe(II) oxidation under anoxic conditions. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.B.; Zhang, H.B.; Wang, H.F.; He, B.H.; Wang, H.X. Remediation of arsenic- and nitrate-contaminated groundwater through iron-dependent autotrophic denitrifying culture. Environ. Res. 2024, 257, 119239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; Kolton, M.; Häggblom, M.M.; Sun, X.Y.; Yu, K.; He, B. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to arsenate reduction, a novel biogeochemical process observed in arsenic-contaminated paddy soil. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2022, 335, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.Q.; Song, J.M.; Zhang, Y.T.; Yin, M.L.; Yuan, H.M.; Li, X.G. Unraveling seasonal shifts in microbial and geochemical mediated arsenic mobilization at the estuarine sediment-water interface under redox changes. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.H.; Siddique, M.S.; Liu, M.J.; Graham, N.; Yu, W.Z. The migration and microbiological degradation of dissolved organic matter in riparian soils. Water Res. 2022, 224, 119080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Velez, J.D.; Harvey, J.W.; Cardenas, M.B.; Kiel, B. Denitrification in the Mississippi River network controlled by flow through river bedforms. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.J.; Zheng, Y.L.; Liu, M.; Gong, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Yin, G.Y. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) bacterial diversity, abundance, and activity in marsh sediments of the Yangtze Estuary. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2013, 118, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.Z.; Liu, C.; Li, X.F.; Zheng, Y.L.; Dong, H.P.; Liang, X. High importance of coupled nitrification-denitrification for nitrogen removal in a large periodically low-oxygen estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Pan, S.M.; Sun, Z.Y.; Ma, R.F.; Chen, L.H.; Wang, Y. Heavy metal spatial variability and historical changes in the Yangtze River estuary and North Jiangsu tidal flat. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 98, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.D.; Mo, X.; Kong, W.J.; Song, Y. Soil bacterial diversity, structure, and function of Suaeda salsa in rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils in various habitats in the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Yan, Z.Z.; Li, X.Z. Iron plaque formation and rhizosphere iron bacteria in Spartina alterniflora and Phragmites australis on the redoxcline of tidal flat in the Yangtze River Estuary. Geoderma 2021, 392, 115000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, E.; Muñoz-Olivas, R.; Cámara, C.; Kumar Sengupta, M.; Ahamed, S. Arsenic speciation in rice, straw, soil, hair and nails samples from the arsenic-affected areas of Middle and Lower Ganga plain. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2007, 42, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, L.; Harmesa, H.; Kaysupi, M.T.; Kampono, I.; Prayitno, H.B.; Budiyanto, F. Determination of trace metal content in certified reference marine sediment by three acid digestion and flame atomic absorption Spectrometry. AIP Conf. Proc. 2022, 2493, 030015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.N.; Yin, N.Y.; Du, H.L.; Cai, X.L.; Cui, Y.S. The fate of arsenic adsorbed on iron oxides in the presence of arsenite-oxidizing bacteria. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmaki, E.G.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Pasias, I.N.; Baulard, C.; Papaharisis, L.; Efstathiou, C.E. Environmental impact of intensive aquaculture: Investigation on the accumulation of metals and nutrients in marine sediments of Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 485, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, R.; Jian, Y.T.; Ma, T. Spatial distribution and factors influencing the various forms of iron in alluvial–lacustrine clayey aquitard. Water 2023, 15, 3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.C.; Chen, Y.Z.; Ma, T.; Xiong, W. Impact of pressure on arsenic released from pore water in clayey sediment. Toxics 2022, 10, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Niu, L.L.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Xiao, N. Escalating arsenic contamination throughout Chinese soils. Nat. Sustain. 2024, 7, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, J.L.; Giblin, A.E.; Murphy, A.E.; Bulseco, A.N.; Deegan, L.A.; Johnson, D.S. Not all nitrogen is created equal: Differential effects of nitrate and ammonium enrichment in coastal wetlands. BioScience 2020, 70, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.H.; Ouyang, H.; Deng, W.; Zhu, Y.M.; Zhang, X.L.; Wang, Q.G. Spatial distribution characteristics of organic matter and total nitrogen of marsh soils in river marginal wetlands. Geoderma 2005, 124, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.J.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Liu, D.H.; Yin, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, B. Nitrate reduced arsenic redox transformation and transfer in flooded paddy soil-rice system. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.K.; Tran, H.T.; Park, Y.; Yu, J.; Lee, T. Microbial arsenite oxidation with oxygen, nitrate, or an electrode as the sole electron acceptor. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.B.; Zeng, X.C.; Chen, X.M.; Wu, W.W.; Wang, Y.X. Inhibitory effect of nitrate/nitrite on the microbial reductive dissolution of arsenic and iron from soils into pore water. Ecotoxicology 2019, 28, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, D.J.H. Arsenic in aquatic organisms: A review, emphasizing chemical speciation. Aquat. Toxicol. 1990, 16, 151–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorini, D.; Notti, A.; Halt, M.N.; Gambi, M.C.; Regoli, F. Levels and chemical speciation of arsenic in polychaetes: A review. Mar. Ecol. 2005, 26, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.F.; Li, F.L.; Dominech, S.; Wen, X.H.; Yang, S.Y. Heavy metals of surface sediments in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary: Distribution, speciation and environmental risks. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 198, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Q.; Ma, Y.Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, S.J.; Hu, Z. Levels and ecological risk of heavy metals in the surface sediments of tidal flats along the North Jiangsu coast, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 170, 112663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Dai, Z.; Wang, F.; Yang, S.; Cao, W. Geographical factor dominates spatial patterns of potential nitrate reduction rates in coastal wetland sediments in Fujian Province, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 12, 1399200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Li, L.G.; Zhai, W.W.; Xu, B.L.; Yin, X.L.; He, Y. Distribution of arsenic and its biotransformation genes in sediments from the East China Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamindy-Pajany, Y.; Bataillard, P.; Séby, F.; Crouzet, C.; Moulin, A.; Guezennec, A.-G. Arsenic in marina sediments from the Mediterranean coast: Speciation in the solid phase and occurrence of thioarsenates. Soil. Sediment. Contam. Int. J. 2013, 22, 984–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Yuan, Z.J.; Li, D.Q.; Zheng, M.H.; Nie, X.D.; Liao, Y.H. Effects of soil particle size on the adsorption, distribution, and migration behaviors of heavy metal(loid)s in soil: A review. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 1596–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.H.; Wang, Y.F.; Jiang, C.D.; Liu, Q.; Li, W.X. Heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of intertidal zone in central Jiangsu Province: Distribution, source, and assessment. Mar. Geol. Front. 2024, 40, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Han, Y.; Roelcke, M.; Nieder, R.; Cai, Z.C. Temperature dependence of gross N transformation rates in two Chinese paddy soils under aerobic condition. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.B.; Li, X.F.; Gao, D.Z.; Liu, M.; Cheng, L. Ammonium production and removal in the sediments of Shanghai river networks: Spatiotemporal variations, controlling factors, and environmental implications. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2017, 122, 2461–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Z.; Lu, Z.Y.; Tobias, C.R.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, K.; Yu, Q.B. Salt marsh expansion into estuarine mangrove mudflats reduces nitrogen removal capacity. Catena 2023, 232, 107459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.P.; Bi, Y.X.; Su, L.; Lei, Y.; Gong, L.; Dong, X.H. Unveiling the nitrogen and phosphorus removal potential: Comparative analysis of three coastal wetland plant species in lab-scale constructed wetlands. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Furman, A. Soil redox dynamics under dynamic hydrologic regimes—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 143026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.Q.; Fu, Q.L.; Hu, H.Q.; Zhu, J.; Liu, M.X. Comparing effects of ammonium and nitrate nitrogen on arsenic accumulation in brown rice and its dynamics in soil-plant system. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 2650–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, D.E.; Glazer, A.N.; Falkowski, P.G. The evolution and future of Earth’s nitrogen cycle. Science 2010, 330, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.X.; Xu, X.; Wang, M. Responses of soil nitrogen fixation to Spartina alterniflora invasion and nitrogen addition in a Chinese salt marsh. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Feng, J.G.; Ao, G.; Qin, W.K.; Han, M.G.; Shen, Y.W. Globally nitrogen addition alters soil microbial community structure, but has minor effects on soil microbial diversity and richness. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2023, 179, 108982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, D.R.; Kim, J.; Kang, H. Influences of different halophyte vegetation on soil microbial community at temperate salt marsh. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 75, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Shi, J.Y.; Rui, J.L.; Yu, Y.M.; Huang, W.B.; Lu, Z.N. Halophyte vegetation influences soil microbial community of coastal salt marsh. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2022, 21, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.X.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Yao, M.J.; Rui, J.P.; Zhang, S.H. Soil bacterial community structure in Chinese wetlands. Geoderma 2019, 337, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.Y.; Hu, Y.S.; Chen, S.K.; Guo, S.S. Effect of microbial communities on nitrogen and phosphorus metabolism in rivers with different heavy metal pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 87398–87411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.; Sun, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Zheng, Q.N.; Kong, S.; Xue, L. The alternation of flood and ebb tide induced arsenic release and migration from coastal tidal flat sediments in Yellow Sea wetlands: An ex-situ study. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 448, 141730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; Tan, Y.F.; Fan, Y.J.; Wu, J.; Yu, L.T. Insights into nitrite accumulation and microbial structure in partial denitrification (PD) process by the combining regulation of C/N ratio and nitrate concentration. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; Li, Q.H.; Gao, Q.F.; Shen, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.B. Comparative study on the treatment of swine wastewater by VFCW-MFC and VFCW: Pollutants removal, electricity generation, microorganism community. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, H.J. Mixotrophic denitrification for enhancing nitrogen removal of municipal tailwater: Contribution of heterotrophic/sulfur autotrophic denitrification and bacterial community. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 151940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.C.; Li, X.D.; Wu, Y.H.; Xu, X.W.; Liu, Y.X.; Shi, B.Z. Microbe-driven elemental cycling enables microbial adaptation to deep-sea ferromanganese nodule sediment fields. Microbiome 2023, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, T.; Goordial, J.; Lindsay, M.R.; McGonigle, J.; Booker, A.; Moser, D. Replicated life-history patterns and subsurface origins of the bacterial sister phyla Nitrospirota and Nitrospinota. ISME J. 2023, 17, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, C.J.; Hug, L.A.; Wrighton, K.C.; Thomas, B.C.; Williams, K.H.; Wu, D. Extraordinary phylogenetic diversity and metabolic versatility in aquifer sediment. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mußmann, M.; Pjevac, P.; Krüger, K.; Dyksma, S. Genomic repertoire of the Woeseiaceae/JTB255, cosmopolitan and abundant core members of microbial communities in marine sediments. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.T.; Li, M.; Niu, M.Y.; Fan, X.B.; Liang, W.Y.; Wang, F.P. Difference of nitrogen-cycling microbes between shallow bay and deep-sea sediments in the South China Sea. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannelli, D.; Chung, M.; Staley, J.; Starovoytov, V.; Le Bris, N.; Vetriani, C. Sulfurovum riftiae sp. nov., a mesophilic, thiosulfate-oxidizing, nitrate-reducing chemolithoautotrophic epsilonproteobacterium isolated from the tube of the deep-sea hydrothermal vent polychaete Riftia pachyptila. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 2697–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.; Qin, W.; Wang, Y.Z.; Sun, Y.; Kong, S. Arsenic mobility and microbial community composition in the sediments of coastal wetlands driven by tidal action. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 153, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baloza, M.; Henkel, S.; Kasten, S.; Holtappels, M.; Molari, M. The impact of sea ice cover on microbial communities in Antarctic shelf sediments. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, P.; Su, J.Q.; Hu, Z.Y.; Häggblom, M.M.; Zhu, Y.G. Genome sequence of the anaerobic bacterium Bacillus sp. strain ZYK, a selenite and nitrate reducer from paddy soil. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2014, 9, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Wang, L.R.; Gan, R.; Tong, T.; Bian, H.; Li, Z.Q. Signature arsenic detoxification pathways in Halomonas sp. strain GFAJ-1. Mbio 2018, 9, e00515-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecchin, S.; Colombo, M.; Cavalca, L. Exposure to different arsenic species drives the establishment of iron- and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria on rice root iron plaques. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, Ö.K.; Özen, V.; Wankel, S.D.; Orsi, W.D. Quantifying population-specific growth in benthic bacterial communities under low oxygen using H218O. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1546–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, X.; Luan, S.; Zhou, H.; Liu, L.; Qu, Y. Diversity and structure of soil bacterial community in intertidal zone of Daliao River estuary, Northeast China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Tian, X.; He, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhao, K. Nitrogen removal capability and mechanism of a novel heterotrophic nitrification–aerobic denitrification bacterium Halomonas sp. DN3. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 387, 129569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Song, X.; Cheng, X.; Huang, Z.; Dong, D.; Li, X. Enhanced denitrification of biodegradable polymers using Bacillus pumilus in aerobic denitrification bioreactors: Performance and mechanism. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 394, 130240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Aquino, A.; Kalinainen, N.; Auvinen, H.; Andreottola, G.; Puhakka, J.A.; Palmroth, M.R.T. Effects of inorganic ions on autotrophic denitrification by Thiobacillus denitrificans and on heterotrophic denitrification by an enrichment culture. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 165940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, T.; Shao, M.F.; Fang, H.H.P. Autotrophic denitrification in nitrate-induced marine sediment remediation and Sulfurimonas denitrificans-like bacteria. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Zhang, D.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zeng, W.; Lei, H. Identification of aerobic-denitrifying Psychrobacter cryohalolentis strain F5-6 and its nitrate removal at low temperature. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2022, 172, 105426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yin, N.; Cai, X.; Wang, Z.; Cui, Y. Arsenic redox transformation by Pseudomonas sp. HN-2 isolated from arsenic-contaminated soil in Hunan, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 47, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagade, A.; Nandre, V.; Paul, D.; Patil, Y.; Sharma, N.; Giri, A.; Kodam, K. Characterisation of hyper tolerant Bacillus firmus L-148 for arsenic oxidation. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, L.; Yang, R.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Cao, Z.G.; Zhang, X. Thiobacillus spp. and Anaeromyxobacter spp. mediate arsenite oxidation-dependent biological nitrogen fixation in two contrasting types of arsenic-contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, V.H.-C.; Chu, Y.-J.; Su, Y.-C.; Hsiao, S.-Y.; Wei, C.-C.; Liu, C.-W.; Liao, C.-M.; Shen, W.-C. Arsenite-oxidizing and arsenate-reducing bacteria associated with arsenic-rich groundwater in Taiwan. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2011, 123, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Zheng, Q.; Yu, J.; Liang, W.; Sun, Y.; Quan, G.; Zhou, F. Roles of nanoparticles in arsenic mobility and microbial community composition in arsenic-enriched soils. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 138, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Li, B.; Liu, X.; Yang, W.; Liu, Q. Starting-up performances and microbial community shifts in the coupling process (SAPD-A) with sulfide autotrophic partial denitrification (SAPD) and anammox treating nitrate and ammonium contained wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 331, 117298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.; Yu, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, X.; Deng, X.; Yu, J.; Chi, R. Recovery of anammox process performance after substrate inhibition: Reactor performance, sludge morphology, and microbial community. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 357, 127351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).