Effects of Salinity Level on Microplastic Removal in Simulated Waters Using Agglomeration–Micro-Flotation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.1.1. Microplastic Samples
2.1.2. Environmental Matrices
2.2. Microplastic Removal Experiments
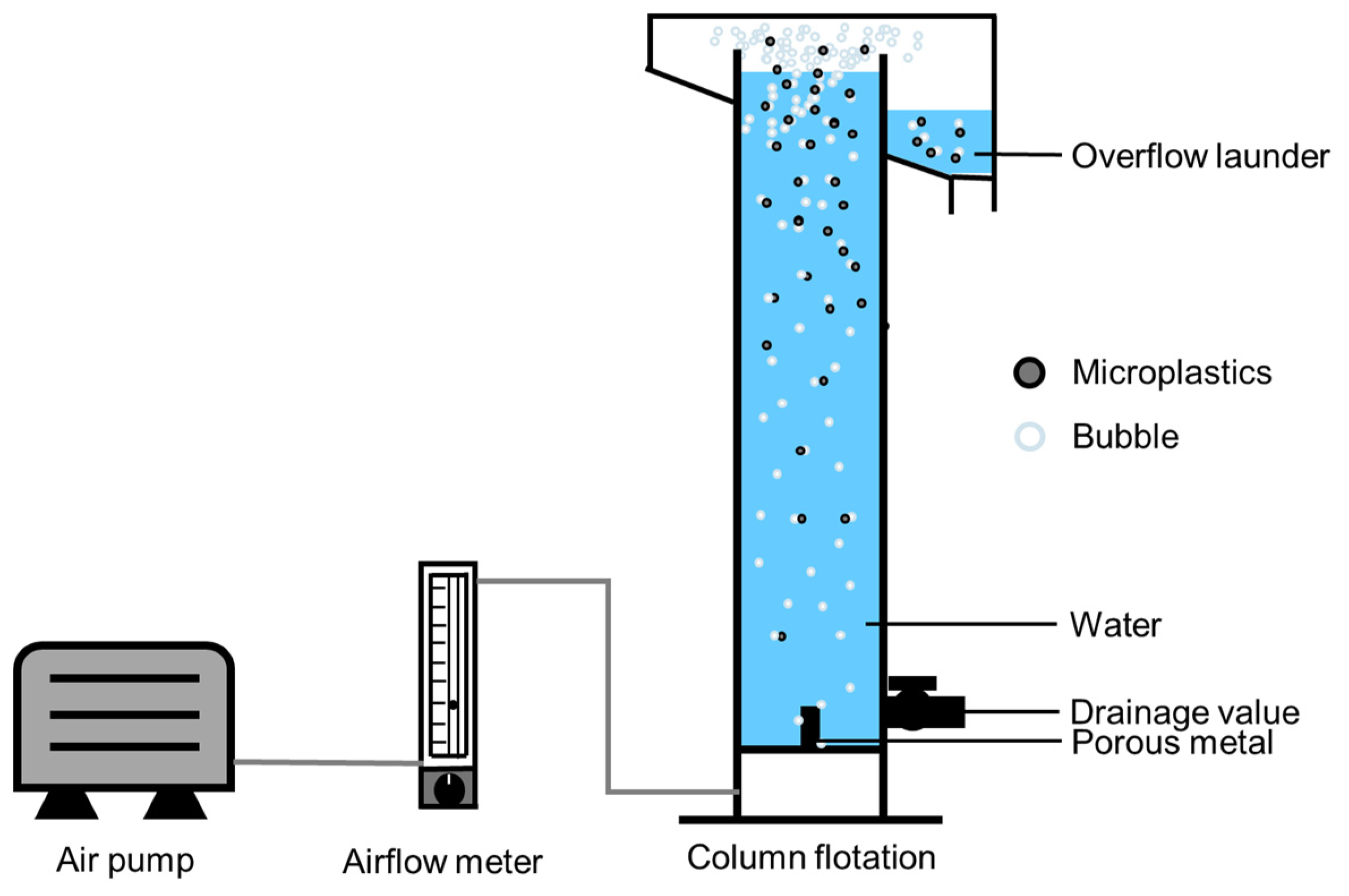
2.2.1. Agglomeration Procedure and Column Flotation Setup
2.2.2. Series Experiments
2.2.3. Parallel Experiments
2.2.4. Bubble Size Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
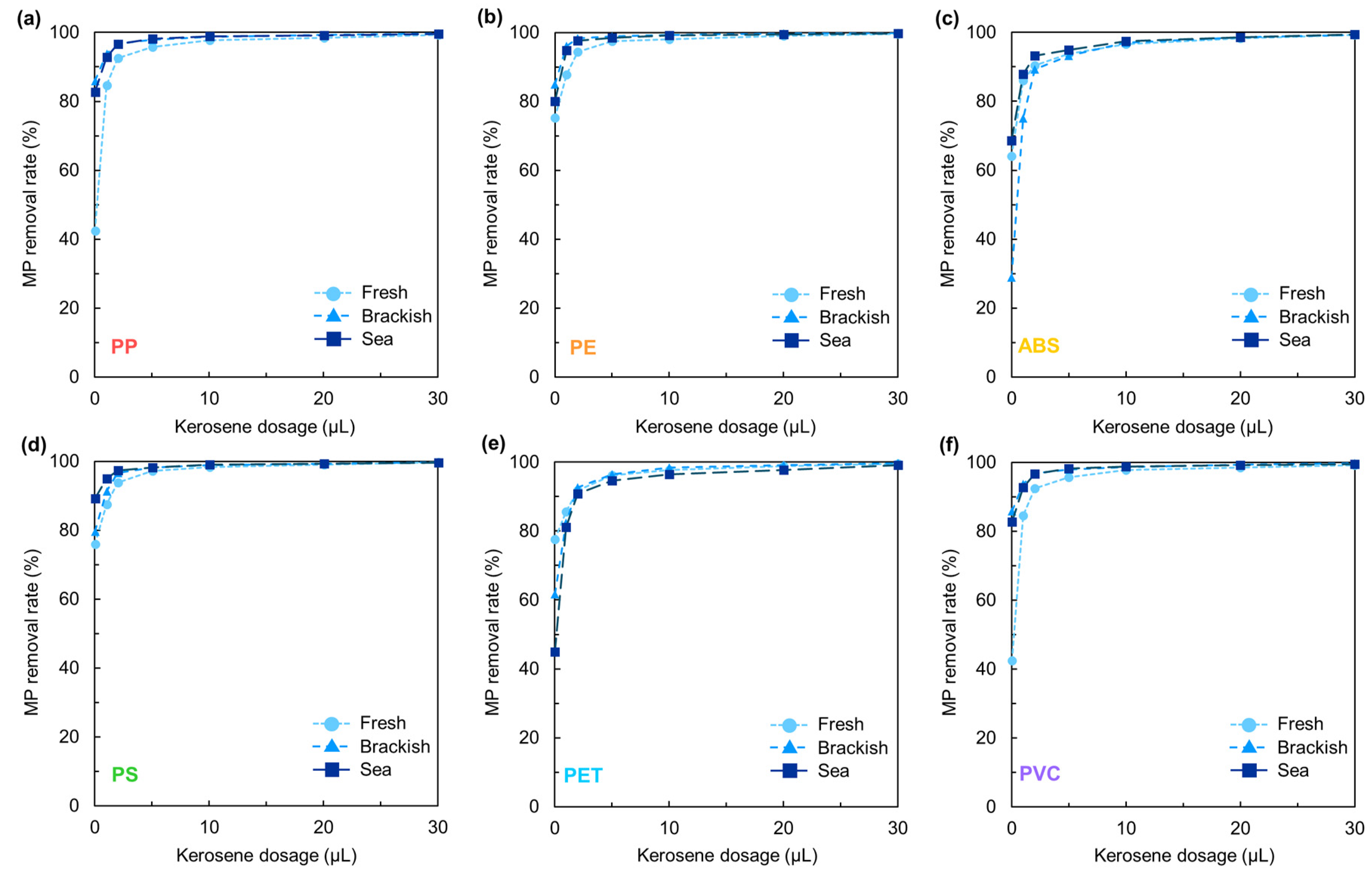
3.1. Effects of Plastic Type and Kerosene Dosage on the Removal Rate in Simulated Freshwater
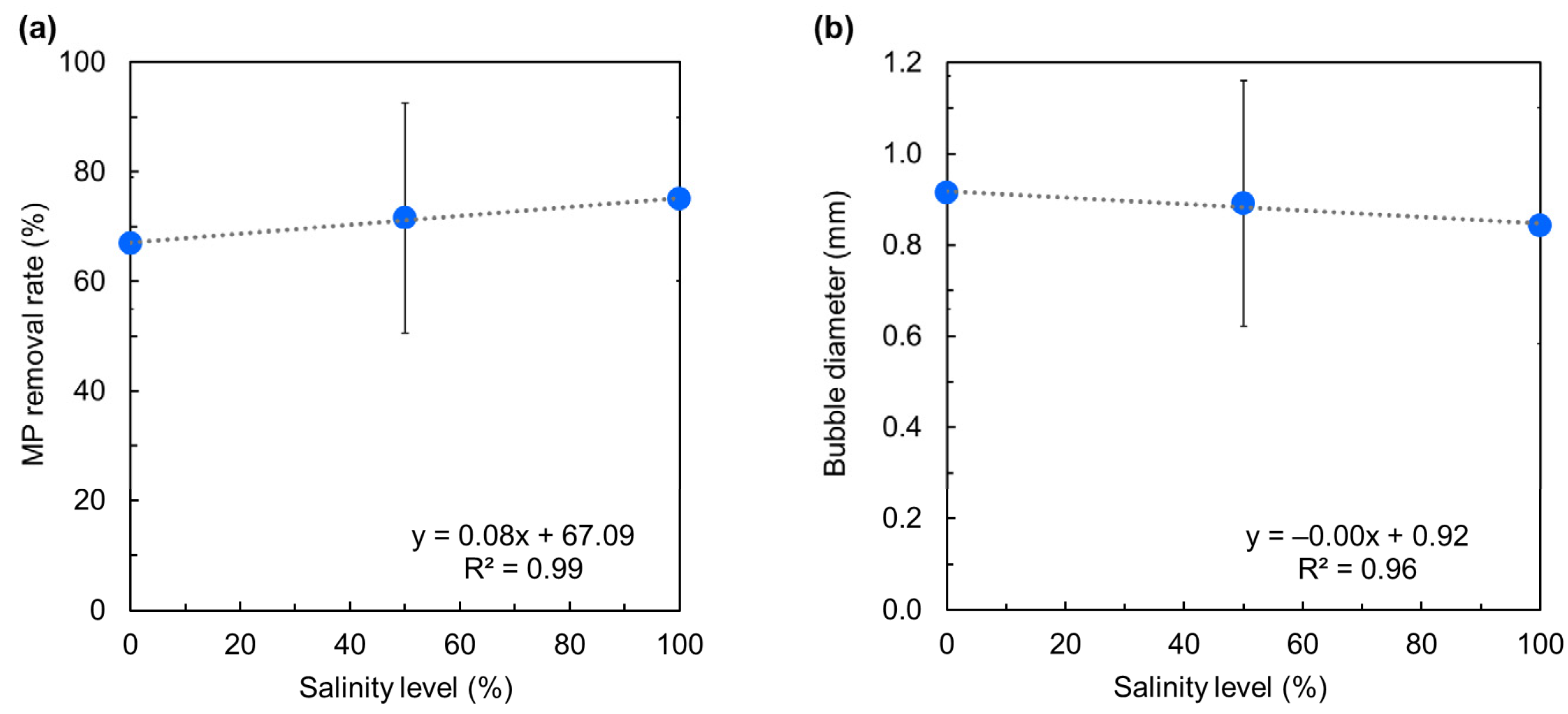
3.2. Effects of Salinity Levels on the Removal Rate of Microplastics
3.3. Effects of Kerosene Dosage on the Removal Rate of Microplastics at Different Salinity Levels
3.3.1. Series Experiments
3.3.2. Parallel Experiments
4. Conclusions
- Without kerosene, low-density MPs (i.e., PP and PE) exhibited the highest removal rates, followed by medium-density MPs (i.e., ABS and PS) and high-density MPs (i.e., PET and PVC).
- Increasing kerosene dosage significantly improved removal rates by promoting MP agglomeration, increasing apparent particle size, and enhancing particle–bubble collision probability.
- Higher salinity levels (i.e., 50–100%) improved MP removal due to bubble stabilization and suppressed bubble coalescence caused by dissolved ions.
- The technique remained effective across all salinity levels, and the influence of MP density on removal rate diminished at higher salinities.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeong, E.; Lee, J.Y.; Redwan, M. Animal exposure to microplastics and health effects: A review. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Shi, W.; Tang, Y.; Han, Y.; Du, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, W.; Sun, C.; Liu, G. The toxic impacts of microplastics (MPs) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) on haematic parameters in a marine bivalve species and their potential mechanisms of action. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 147003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutkar, P.R.; Gadewar, R.D.; Dhulap, V.P. Recent trends in degradation of microplastics in the environment: A state-of-the-art review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 11, 100343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Wang, D.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Guo, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Xing, M. Microplastics pollution and risk assessment in water bodies of two nature reserves in Jilin Province: Correlation analysis with the degree of human activity. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julapong, P.; Srichonphaisarn, P.; Meekoch, T.; Tabelin, C.B.; Juntarasakul, O.; Phengsaart, T. The Influence of Textile Type, Textile Weight, and Detergent Dosage on Microfiber Emissions from Top-Loading Washing Machines. Toxics 2024, 12, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juntarasakul, O.; Julapong, P.; Srichonphaisarn, P.; Meekoch, T.; Janjaroen, D.; Tabelin, C.B.; Phengsaart, T. Weave structures of polyester fabric affect the tensile strength and microplastic fiber emission during the laundry process. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, A.; Irfan, M.; Mumtaz, M.; Qadir, A. Spatial distribution of microplastics in soil with context to human activities: A case study from the urban center. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbalaei, S.; Hanachi, P.; Walker, T.R.; Cole, M. Occurrence, sources, human health impacts and mitigation of microplastic pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 36046–36063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Jalalah, M.; Alsareii, S.A.; Harraz, F.A.; Almadiy, A.A.; Zheng, Y.; Thakur, N.; Salama, E.S. Microplastics (MPs) in wastewater treatment plants sludges: Substrates, digestive properties, microbial communities, mechanisms, and treatments. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, F.; Wang, Y.; Peng, L.; Liu, D. Adsorption behaviour of microplastics on the heavy metal Cr (VI) before and after ageing. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez-Pedriza, A.; Jaumot, J. Interaction of environmental pollutants with microplastics: A critical review of sorption factors, bioaccumulation and ecotoxicological effects. Toxics 2020, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Wang, X.; Dong, H.; Ciren, N.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhuoga, S.; Jia, X.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Y. Microplastics in remote region of the world: Insights from the glacier of Geladandong, China. Appl. Geochem. 2024, 168, 106026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissen, R.; Chawchai, S. Microplastics on beaches along the eastern Gulf of Thailand—A preliminary study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 157, 111345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heshmati, S.; Makhdoumi, P.; Pirsaheb, M.; Hossini, H.; Ahmadi, S.; Fattahi, H. Occurrence and characterization of microplastic content in the digestive system of riverine fishes. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.R.A.; Luza, K.M.B.; Subebe, M.J.B.; Tabelin, C.B.; Phengsaart, T.; Arima, T.; Sena, R.; Butalid, R.; Escabarte, A.B.; Mazahery, A.R.F.; et al. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) microplastics affect angiogenesis and central nervous system (CNS) development of duck embryo. Emerg. Contam. 2025, 11, 100433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefano, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; et al. Plasticenta: First evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihart, A.J.; Garcia, M.A.; El Hayek, E.; Liu, R.; Olewine, M.; Kingston, J.D.; Castillo, E.F.; Gullapalli, R.R.; Howard, T.; Bleske, B.; et al. Bioaccumulation of microplastics in decedent human brains. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawab, A.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, M.T.; Nafees, M.; Khan, I.; Ihsanullah, I. Human exposure to microplastics: A review on exposure routes and public health impacts. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 16, 100487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhou, N.; Chen, Y.; Ling, Z.; Xiang, P. Microplastics in the human body: A comprehensive review of exposure, distribution, migration mechanisms, and toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 946, 174215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, E.G.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Ma, L.; Zeng, E.Y.; Shi, H. A review of microplastics in table salt, drinking water, and air: Direct human exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3740–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuri, G.; Karanasiou, A.; Lacorte, S. Microplastics: Human exposure assessment through air, water, and food. Environ. Int. 2023, 179, 108150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangeliou, N.; Grythe, H.; Klimont, Z.; Heyes, C.; Eckhardt, S.; Lopez-Aparicio, S.; Stohl, A. Atmospheric transport is a major pathway of microplastics to remote regions. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayal, L.; Yadav, K.; Dey, U.; Das, K.; Kumari, P.; Raj, D.; Mandal, R.R. Recent advancement in microplastic removal process from wastewater-a critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 16, 100460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; Matis, K.A. Flotation in water and wastewater treatment. Processes 2018, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuerstenau, M.C.; Jameson, G.J.; Yoon, R.H. Froth Flotation: A Century of Innovation; SME: Littleton, CO, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Zhang, M.N.; Li, Y.L.; Lau, E.V. Improving micro-fine mineral flotation via micro/nano technologies. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 520–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Fornasiero, D.; Ralston, J. Influence of dissolved gas on bubble–particle heterocoagulation. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1998, 94, 1983–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, D.H.; Kim, M.S. Feasibility of carbon dioxide bubbles as a collector in flotation process for water treatment. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.—AQUA 2013, 62, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, M.S.K.A.; Evans, G.M.; Donne, S.W. Bubble size measurement in electroflotation. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, J.A.; Dobby, G. Column flotation. In Flotation Science and Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1990; pp. 291–329. [Google Scholar]
- Subrahmanyam, T.V.; Forssberg, K.E. Fine particles processing: Shear-flocculation and carrier flotation—A review. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1990, 30, 265–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Li, B.; Zhan, H.; Xie, G. Discrimination of six flotation kinetic models used in the conventional flotation and carrier flotation of− 74 μm coal fines. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 13813–13821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Almatrafi, E.; Hu, T.; Zhou, C.; Song, B.; Zeng, Z.; Zeng, G. Efficient removal of microplastics from wastewater by an electrocoagulation process. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollah, M.Y.A.; Schennach, R.; Parga, J.R.; Cocke, D.L. Electrocoagulation (EC)—Science and applications. J. Hazard Mater. 2001, 84, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julapong, P.; Ekasin, J.; Katethol, P.; Srichonphaisarn, P.; Juntarasakul, O.; Numprasanthai, A.; Tabelin, C.B.; Phengsaart, T. Agglomeration-Flotation of Microplastics Using Kerosene as Bridging Liquid for Particle Size Enlargement. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornn, V.; Ito, M.; Shimada, H.; Tabelin, C.B.; Jeon, S.; Park, I.; Hiroyoshi, N. Agglomeration-Flotation of Finely Ground Chalcopyrite and Quartz: Effects of Agitation Strength during Agglomeration Using Emulsified Oil on Chalcopyrite. Minerals 2020, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alioua, W.; Lapointe, M. Fiber-based super-bridging agents enable efficient contaminant removal via settling and screening: Impact on microplastics, textile fibers, and turbidity. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HiMedia Laboratories. “Artificial Sea Water Salts Broth”. M1942 2013. Available online: https://exodocientifica.com.br/_technical-data/M1942.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Yoon, R.H. The role of hydrodynamic and surface forces in bubble–particle interaction. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2000, 58, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, R.; Hu, K.C. On the collision rate of small particles in turbulent flows. J. Fluid Mech. 1999, 391, 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, S.; Laskowski, J.S. Froth flotation in saline water. KONA Powder Part. J. 2011, 29, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. The UN Sustainable Development Goals. United Nations, New York, 2015. Available online: http://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/summit/ (accessed on 5 March 2025).





| Type of Plastics | SG | D50 (µm) | Provider |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | 0.92 | ~600 | Showa Denko Materials Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan |
| Polyethylene (PE) | 0.97 | ~460 | Showa Denko Materials Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan |
| Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) | 1.03 | ~540 | Sumitomo Bakelite Co., Ltd., Shizuoka, Japan |
| Polystyrene (PS) | 1.06 | ~590 | Kyoei Sangyo Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan |
| Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | 1.31 | ~600 | Sanplatec Corp., Osaka, Japan |
| Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) | 1.38 | ~550 | Sanplatec Corp., Osaka, Japan |
| Test Item | Specification |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear |
| Color | Colorless |
| pH | 5.2–7.0 |
| Residual dissolved solids | 0–1.0 ppm |
| Chloride | Neg. |
| Electrical conductivity | 0–1.0 Microsiemens |
| Iron | Neg. |
| Tin | Neg. |
| Copper | Neg. |
| Hardness | Neg. |
| Component | Standard Seawater Specification (g/L) [38] | Simulated Seawater Specification (g/L) | Simulated Brackish Water Specification (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium chloride (NaCl) | 24.60 | ~24.60 | ~12.30 |
| Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) | 4.66 | ~4.66 | ~2.33 |
| Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) | 6.29 | ~6.29 | ~3.15 |
| Calcium chloride (CaCl2) | 1.36 | ~1.36 | ~0.68 |
| Potassium chloride (KCl) | 0.67 | ~0.67 | ~0.34 |
| Strontium (Sr) | – | N/A | N/A |
| Boron (B) | – | N/A | N/A |
| Lithium (Li) | – | N/A | N/A |
| Iodine (I) | – | N/A | N/A |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | – | N/A | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phengsaart, T.; Srichonphaisarn, P.; Khwathichak, W.; Bumrungsak, C.; Park, I.; Ito, M.; Villacorte-Tabelin, M.; Tabelin, C.B.; Jeon, S.; Haga, K.; et al. Effects of Salinity Level on Microplastic Removal in Simulated Waters Using Agglomeration–Micro-Flotation. Water 2025, 17, 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091264
Phengsaart T, Srichonphaisarn P, Khwathichak W, Bumrungsak C, Park I, Ito M, Villacorte-Tabelin M, Tabelin CB, Jeon S, Haga K, et al. Effects of Salinity Level on Microplastic Removal in Simulated Waters Using Agglomeration–Micro-Flotation. Water. 2025; 17(9):1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091264
Chicago/Turabian StylePhengsaart, Theerayut, Palot Srichonphaisarn, Worada Khwathichak, Chanatip Bumrungsak, Ilhwan Park, Mayumi Ito, Mylah Villacorte-Tabelin, Carlito Baltazar Tabelin, Sanghee Jeon, Kazutoshi Haga, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Salinity Level on Microplastic Removal in Simulated Waters Using Agglomeration–Micro-Flotation" Water 17, no. 9: 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091264
APA StylePhengsaart, T., Srichonphaisarn, P., Khwathichak, W., Bumrungsak, C., Park, I., Ito, M., Villacorte-Tabelin, M., Tabelin, C. B., Jeon, S., Haga, K., & Juntarasakul, O. (2025). Effects of Salinity Level on Microplastic Removal in Simulated Waters Using Agglomeration–Micro-Flotation. Water, 17(9), 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091264













