Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in the Surface Waters of China: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Assembly
2.2. Data Analysis
2.3. Heterogeneity Analysis and Publication Bias Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatial Distribution Patterns
3.2. Pollution Sources Analysis
3.3. Correlation Between Pollution and Hydrological Parameters
3.4. Comparison with Global Data
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Buser, A.M.; Cousins, I.T.; Demattio, S.; Drost, W.; Johansson, O.; Ohno, K.; Patlewicz, G.; Richard, A.M.; Walker, G.W.; et al. A New OECD Definition for Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15575–15578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abunada, Z.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Bashir, M.J.K. An Overview of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in the Environment: Source, Fate, Risk and Regulations. Water 2020, 12, 3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, F.; Dutta, R.; Barbeau, B.; Berube, P.; Mohseni, M. PFAS removal by ion exchange resins: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Zhang, M.; Yang, D. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in Chinese surface waters: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’eon, J.C.; Mabury, S.A. Exploring Indirect Sources of Human Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylates (PFCAs): Evaluating Uptake, Elimination, and Biotransformation of Polyfluoroalkyl Phosphate Esters (PAPs) in the Rat. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiplinger, J.L.; Richmond, T.G.; Osterberg, C.E.J.C.R. Activation of Carbon-Fluorine Bonds by Metal Complexes. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 373–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, J.W.; Jenkins, T.M.; Rankin, K.; Naile, J.E. Decades-Scale Degradation of Commercial, Side-Chain, Fluorotelomer-Based Polymers in Soils and Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logeshwaran, P.; Sivaram, A.K.; Surapaneni, A.; Kannan, K.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M. Exposure to perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) but not perflurorooctanoic acid (PFOA) at ppb concentration induces chronic toxicity in Daphnia carinata. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Mallula, S.; Golovko, S.A.; Golovko, M.Y.; Xiao, F. In Vivo Generation of PFOA, PFOS, and Other Compounds from Cationic and Zwitterionic Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in a Terrestrial Invertebrate (Lumbricus terrestris). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7378–7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jiao, X.-C.; Gai, N.; Li, X.-J.; Wang, X.-C.; Lu, G.-H.; Piao, H.-T.; Rao, Z.; Yang, Y.-L. Perfluorinated compounds in soil, surface water, and groundwater from rural areas in eastern China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 211, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.I.; Lee, T.-Y.; Seo, H.; Kim, D.; Kim, D.; Cui, R.; An, Y.-J. Ecological risk assessment for perfluorooctanoic acid in soil using a species sensitivity approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 121150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Ye, J.; Qin, H.; Long, Y.; Li, Y. Influence of perfluorooctanoic acid on proteomic expression and cell membrane fatty acid of Escherichia coli. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Yu, Z.; Feng, L.; Wang, Y. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) induced embryotoxicity and disruption of cardiogenesis. Toxicol. Vitr. 2013, 27, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Abbasi, A.; Chen, G. Fate, distribution, and transport dynamics of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in the environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tri, D.V.; Anh, N.T.; Luu, T.L.; Trippel, J.; Wagner, M. Electrochemical degradation of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) in water with persulfate catalyst support. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 363, 132076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding-Marjanovic, K.C.; Houtz, E.F.; Yi, S.; Field, J.A.; Sedlak, D.L.; Alvarez-Cohen, L. Aerobic Biotransformation of Fluorotelomer Thioether Amido Sulfonate (Lodyne) in AFFF-Amended Microcosms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7666–7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia-Avendaño, S.; Duy, S.V.; Sauvé, S.; Liu, J. Generation of Perfluoroalkyl Acids from Aerobic Biotransformation of Quaternary Ammonium Polyfluoroalkyl Surfactants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9923–9932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, J.M.; MacLeod, M.; Cousins, I.T. Comparative Assessment of the Global Fate and Transport Pathways of Long-Chain Perfluorocarboxylic Acids (PFCAs) and Perfluorocarboxylates (PFCs) Emitted from Direct Sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5830–5836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Guo, Q.; Peng, Z.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, R. Current status and risk assessment of perfluoroalkyl acids in surface water and sediments of the Yellow River in Shandong, China. Emerg. Contam. 2025, 11, 100391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, G.; Liu, C.; Hao, Q.; Wu, L. Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) in Surface Water, Groundwater and Sediments of the Jin River Basin, Southeastern China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 108, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydebreck, F.; Tang, J.; Xie, Z.; Ebinghaus, R. Alternative and Legacy Perfluoroalkyl Substances: Differences Between European and Chinese River/Estuary Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8386–8395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, T. Are perfluoroalkyl substances in water and fish from drinking water source the major pathways towards human health risk? Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 181, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; Sun, P.; Yin, C.; Li, X.; Yu, L.; Ren, G.; Peng, L.; Wang, F. Distribution and potential health risks of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in water, sediment, and fish in Dongjiang River Basin, Southern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 99501–99510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, B.; Hu, H.; Zhang, T.; Yamazaki, E.; Taniyasu, S.; Yamashita, N.; Sun, H. Distribution and primary source analysis of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances with different chain lengths in surface and groundwater in two cities, North China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 108, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Du, P.; Liu, S.; Lv, J.; Xu, F.; Meng, W.; Xu, J. Distribution, source characterization and inventory of perfluoroalkyl substances in Taihu Lake, China. Chemosphere 2015, 127, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Q.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sheng, N.; Dai, J. Elevated concentrations of perfluorohexanesulfonate and other per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in Baiyangdian Lake (China): Source characterization and exposure assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Cheng, X.; Hua, X.; Jiang, B.; Tian, C.; Tang, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, H.; Lin, T.; Liao, Y.; et al. Emerging and legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water, sediment, and air of the Bohai Sea and its surrounding rivers. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Ding, T.-T.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Liang, H.-Y.; Du, S.-L.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.-X. Environmental exposure and ecological risk of perfluorinated substances (PFASs) in the Shaying River Basin, China. Chemosphere 2023, 339, 139666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, L.; Pan, X.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L. Isomeric specific partitioning behaviors of perfluoroalkyl substances in water dissolved phase, suspended particulate matters and sediments in Liao River Basin and Taihu Lake, China. Water Res. 2015, 80, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Tong, Y.; Li, F.; Cheng, F.; Huang, Z.; You, J. Legacy and Emerging Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances Behave Distinctly in Spatial Distribution and Multimedia Partitioning: A Case Study in the Pearl River, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 3492–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, C.; Han, J.; Sun, R.; Kong, X.; Wang, X.; He, X. Levels and spatial distribution of perfluoroalkyl substances in China Liaodong Bay basin with concentrated fluorine industry parks. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Liu, J.; Bao, K.; Chen, N.; Meng, B. Multicompartment occurrence and partitioning of alternative and legacy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in an impacted river in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Qv, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L. Natural biofilm as a potential integrative sample for evaluating the contamination and impacts of PFAS on aquatic ecosystems. Water Res. 2022, 215, 118244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Munoz, G.; Duy, S.V.; Zhang, L.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Yi, L.; Liu, M.; Sun, H.; Liu, J.; et al. Occurrence and Distribution of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Tianjin, China: The Contribution of Emerging and Unknown Analogues. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14254–14264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Ding, G.; Zhang, J.; Wei, L.; Xue, H.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Sun, Y. Occurrence and distribution of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in surface water and bottom water of the Shuangtaizi Estuary, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Xiao, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Huang, K.; Wang, J. Occurrence and ecotoxicological risk assessment of perfluoroalkyl substances in water of lakes along the middle reach of Yangtze River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, L.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dou, Z.; Yamazaki, E.; Yamashita, N.; Lin, B.-L.; et al. Occurrence and partitioning behavior of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in water and sediment from the Jiulong Estuary-Xiamen Bay, China. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Song, L.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Ma, H.; Cai, M.; Codling, G.; Ebinghaus, R.; et al. Occurrence and trends in concentrations of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in surface waters of Eastern China. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Yamazaki, E.; Yamashita, N.; Wang, X. Occurrence, partitioning behavior and risk assessments of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water, sediment and biota from the Dongshan Bay, China. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Lei, H.; Lu, Y.; Xie, X.; Wang, P.; Liao, J.; Liang, Z.; Sun, B.; Wu, Z. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in water and sediment from a temperate watershed in China: Occurrence, sources, and ecological risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 890, 164341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Shao, P.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gai, N. Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in Rivers and Drinking Waters from Qingdao, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.-G.; Yu, K.-F.; Wang, Y.-H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Guo, J. Perfluoroalkyl substances in the riverine and coastal water of the Beibu Gulf, South China: Spatiotemporal distribution and source identification. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Yan, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Pang, Y. Perfluoroalkyl substances in the surface water and fishes in Chaohu Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 75907–75920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cai, Y.; Ma, L.; Lin, X.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Perfluoroalkyl substances in water, sediment, and fish from a subtropical river of China: Environmental behaviors and potential risk. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.-G.; Ying, G.-G.; Zhao, J.-L.; Liu, Y.-S.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Zhang, Q.-Q. Spatiotemporal distribution and mass loadings of perfluoroalkyl substances in the Yangtze River of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomer-Vidal, P.; Jiang, L.; Mei, W.; Luo, C.; Lacorte, S.; Rigol, A.; Zhang, G. Plant uptake of perfluoroalkyl substances in freshwater environments (Dongzhulong and Xiaoqing Rivers, China). J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, X.; Ma, M.; Zheng, B.; Zhao, X. Occurrence, partition and environmental risk assessment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water and sediment from the Baiyangdian Lake, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, M.; Jin, X.; Liu, C.; Zheng, B.; Shen, J.; et al. High contamination, bioaccumulation and risk assessment of perfluoroalkyl substances in multiple environmental media at the Baiyangdian Lake. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wu, J.; Wei, X.; Xu, A.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z. Male reproductive toxicity of perfluorooctanoate (PFOA): Rodent studies. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 128608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longpré, D.; Lorusso, L.; Levicki, C.; Carrier, R.; Cureton, P. PFOS, PFOA, LC-PFCAS, and certain other PFAS: A focus on Canadian guidelines and guidance for contaminated sites management. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 18, 100752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southerland, E.; Birnbaum, L.S. What Limits Will the World Health Organization Recommend for PFOA and PFOS in Drinking Water? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 7103–7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lu, Y.; Wang, T.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, S.; Xie, S.; Xiao, Y.; Giesy, J.P. Occurrence and transport of 17 perfluoroalkyl acids in 12 coastal rivers in south Bohai coastal region of China with concentrated fluoropolymer facilities. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 190, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, G.W.; Church, T.R.; Miller, J.P.; Burris, J.M.; Hansen, K.J.; Lundberg, J.K.; Armitage, J.B.; Herron, R.M.; Medhdizadehkashi, Z.; Nobiletti, J.B.; et al. Perfluorooctanesulfonate and other fluorochemicals in the serum of American Red Cross adult blood donors. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 1892–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wang, P.; Meng, J.; Liu, S.; Lu, Y.; Khim, J.S.; Giesy, J.P. A review of sources, multimedia distribution and health risks of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) in China. Chemosphere 2015, 129, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igwe, P.U.; Chukwudi, C.C.; Ifenatuorah, F.C.; Fagbeja, I.F.; Okeke, C.A. A Review of Environmental Effects of Surface Water Pollution. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2017, 4, 128–137. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Shih, K. Adsorption of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) on alumina: Influence of solution pH and cations. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2925–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Simcik, M.F.; Gulliver, J.S. Mechanisms for removal of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) from drinking water by conventional and enhanced coagulation. Water Res. 2013, 47, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Taniyasu, S.; Lam, P.K.S.; Yamashita, N. Partitioning of perfluorooctanoate (PFOA), perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctane sulfonamide (PFOSA) between water and sediment. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Gibbes, B.; Wang, T.; Lockington, D. Coupling effects of tide and salting-out on perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) transport and adsorption in a coastal aquifer. Adv. Water Resour. 2022, 166, 104240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Jia, C.; Pan, G. Effect of salinity and sediment characteristics on the sorption and desorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate at sediment-water interface. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1343–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-X.; He, W.; Qin, N.; Kong, X.-Z.; He, Q.-S.; Yang, B.; Yang, C.; Jorgensen, S.E.; Xu, F.-L. Temporal-spatial distributions and ecological risks of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) in the surface water from the fifth-largest freshwater lake in China (Lake Chaohu). Environ. Pollut. 2015, 200, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.W.; Hamid, F.S.; Yusoff, I.; Chan, V. A review of PFAS research in Asia and occurrence of PFOA and PFOS in groundwater, surface water and coastal water in Asia. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 22, 100947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lein, N.P.H.; Fujii, S.; Tanaka, S.; Nozoe, M.; Tanaka, H. Contamination of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in surface water of the Yodo River basin (Japan). Desalination 2008, 226, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.-H.; Lee, D.-Y.; Jeong, D.-K.; Kuppusamy, S.; Lee, Y.B.; Park, B.-J.; Kim, J.-H. Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) concentrations in the South Korean agricultural environment: A national survey. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1841–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, H.; Luo, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, W.; Li, R. Evaluation and prediction of anthropogenic impacts on long-term multimedia fate and health risks of PFOS and PFOA in the Elbe River Basin. Water Res. 2024, 257, 121675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orenibi, E.; Illés, Á.; Sandil, S.; Endrédi, A.; Szekeres, J.; Dobosy, P.; Záray, G. Temporal and spatial distribution of inorganic fluoride, total adsorbable organofluorine, PFOA and PFOS concentrations in the Hungarian section of the Danube River. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 485, 136820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paige, T.; De Silva, T.; Buddhadasa, S.; Prasad, S.; Nugegoda, D.; Pettigrove, V. Background concentrations and spatial distribution of PFAS in surface waters and sediments of the greater Melbourne area, Australia. Chemosphere 2024, 349, 140791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

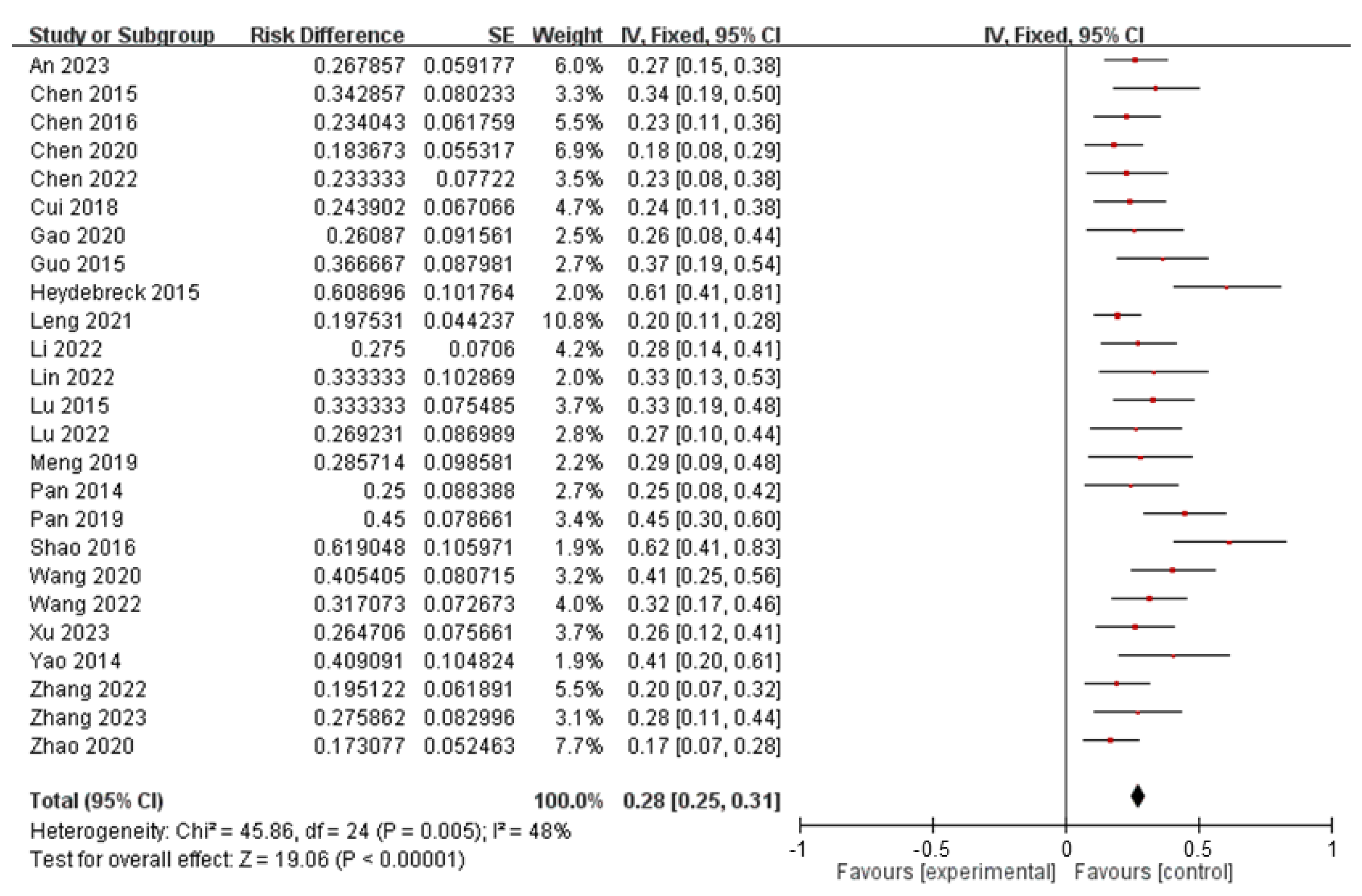

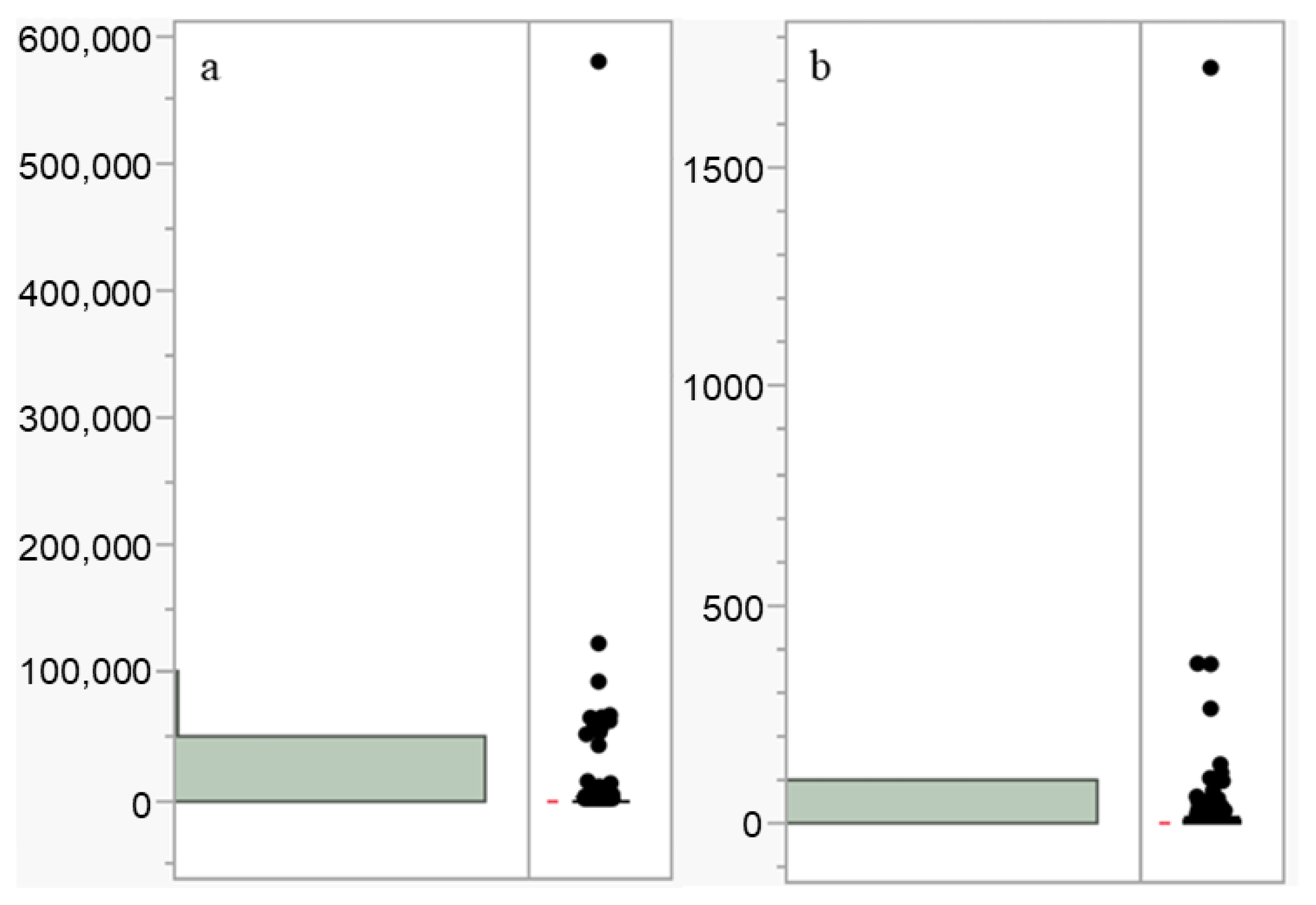
| Type | n | Mean (ng/L) | SE | Range (ng/L) | UCI | LCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFOA | 1141 | 1615.1703 | 558.5725 | [0.0001, 578,970] | 2711.116 | 519.2247 |
| PFOS | 1015 | 8.4082 | 58.0018 | [0.003, 1725.37] | 11.9907 | 4.8422 |
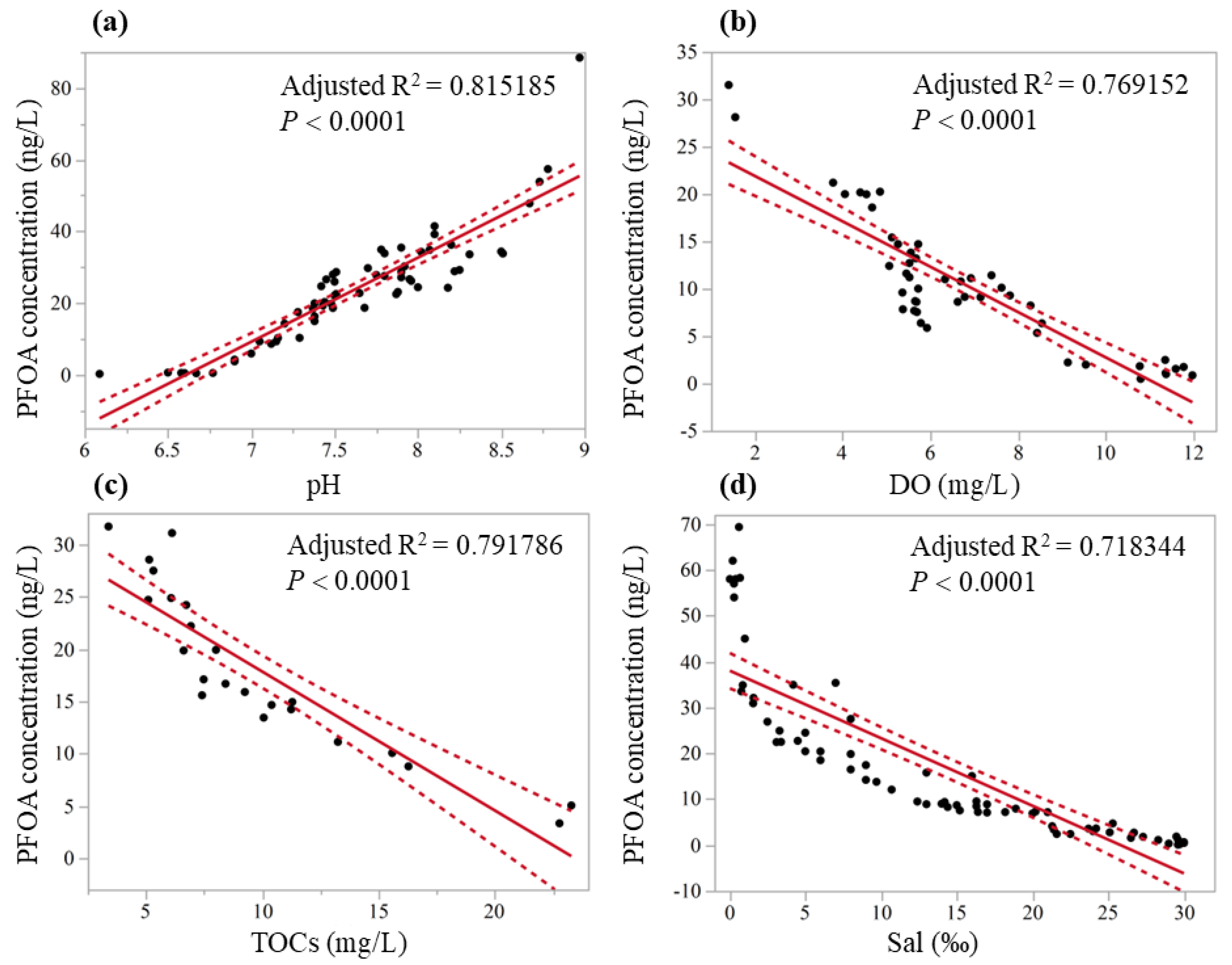
| Model | R2 | Adjusted R2 | F-Value | p | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration = (−155.33 + 23.49 × pH) | 0.818 | −0.815 | F1,63 = 278.88 | <0.0001 * | 64 |
| Concentration = (26.67 − 2.39 × DO) | 0.774 | 0.769 | F1,47 = 157.59 | <0.0001 * | 48 |
| Concentration = (31.13 − 1.33 × TOCs) | 0.801 | 0.792 | F1,22 = 84.66 | <0.0001 * | 23 |
| Concentration = (38.03 − 1.47 × Sal) | 0.722 | 0.718 | F1,71 = 182.08 | <0.0001 * | 72 |
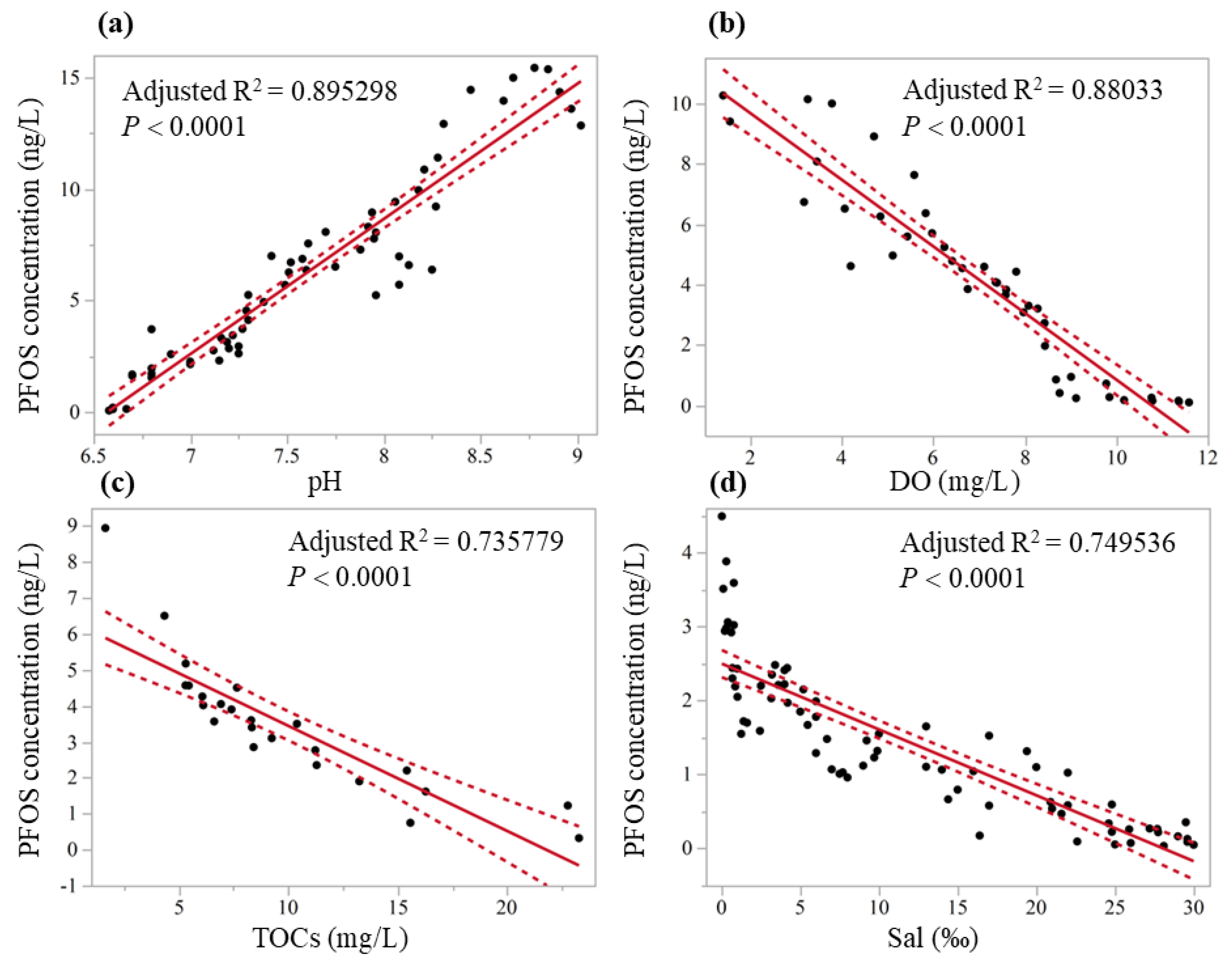
| Model | R2 | Adjusted R2 | F-Value | p | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration = (−39.89 + 6.07 × pH) | 0.897 | 0.895 | F1,59 = 505.51 | <0.0001 * | 60 |
| Concentration = (11.87 − 1.10 × DO) | 0.883 | 0.880 | F1,41 = 302.61 | <0.0001 * | 42 |
| Concentration = (6.37 − 0.29 × TOCs) | 0.747 | 0.736 | F1,23 = 65.05 | <0.0001 * | 24 |
| Concentration = (2.49 − 0.09 × Sal) | 0.753 | 0.750 | F1,74 = 222.45 | <0.0001 * | 75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, M.; Yin, R.; Wang, J.; You, M.; Wang, N.; Wong, Y.J.; Xiao, T. Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in the Surface Waters of China: A Meta-Analysis. Water 2025, 17, 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091275
Chang M, Yin R, Wang J, You M, Wang N, Wong YJ, Xiao T. Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in the Surface Waters of China: A Meta-Analysis. Water. 2025; 17(9):1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091275
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Mingdong, Ru Yin, Jianqiao Wang, Mengyang You, Nana Wang, Yong Jie Wong, and Tangfu Xiao. 2025. "Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in the Surface Waters of China: A Meta-Analysis" Water 17, no. 9: 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091275
APA StyleChang, M., Yin, R., Wang, J., You, M., Wang, N., Wong, Y. J., & Xiao, T. (2025). Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in the Surface Waters of China: A Meta-Analysis. Water, 17(9), 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091275








