Source, Transport, and Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements in Fluvial Sediments from a Typical Small Urban Basin (East Tiaoxi River, Eastern China)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Measurement
2.3. Indication of REE Parameters and Enrichment Assessment
2.3.1. REE Fractionation and Anomaly Parameters
2.3.2. Assessment of Enrichment and Ecological Risk
2.4. Statistical Analysis and Visualization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of REEs in Surface Sediments
3.1.1. Distribution Characteristics of REE Concentration
3.1.2. REE Fractionation Patterns and Anomalies
3.2. Impacts of Geochemical Composition on REE Concentrations and Fractionation
3.3. Distribution and Degree of REE Enrichment
3.3.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics
3.3.2. Degree of REE Enrichment and Potential Source
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barrat, J.-A.; Bayon, G. Practical guidelines for representing and interpreting rare earth abundances in environmental and biological studies. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saputro, S.P.; Godang, S.; Priadi, B.; Basuki, N.I.; Himawan, B. Geochemical study of Al–Fe–Ti enrichment in rock weathering: Implications for the recognizing of igneous protolith and the enrichment of REE in soil profile. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 140, 105259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Pourret, O.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, M. Distribution of rare earth elements in sediments of the North China Plain: A probe of sedimentation process. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 134, 105089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhong, Q.; Han, G. Discrimination of brewing technologies and assessment of health risks based on rare earth elements: Evidence of fingerprint in Chinese famous vinegars. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. Sources and geochemical behaviors of rare earth elements in suspended particulate matter in a wet-dry tropical river. Environ. Res. 2023, 218, 115044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakhmouradian, A.R.; Wall, F. Rare Earth Elements: Minerals, Mines, Magnets (and More). Elements 2012, 8, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.L.B.; Hatje, V.; Pedreira, R.M.A.; Boening, P.; Pahnke, K. REE fractionation and human Gd footprint along the continuum between Paraguacu River to coastal South Atlantic waters. Chem. Geol. 2020, 532, 119303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommasi, F.; Thomas, P.J.; Pagano, G.; Perono, G.A.; Oral, R.; Lyons, D.M.; Toscanesi, M.; Trifuoggi, M. Review of Rare Earth Elements as Fertilizers and Feed Additives: A Knowledge Gap Analysis. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 81, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bispo, F.H.A.; de Menezes, M.D.; Fontana, A.; Sarkis, J.E.d.S.; Gonçalves, C.M.; de Carvalho, T.S.; Curi, N.; Guilherme, L.R.G. Rare earth elements (REEs): Geochemical patterns and contamination aspects in Brazilian benchmark soils. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.; Mirlean, N.; Johannesson, K.H. Rare earth elements as tracers of sediment contamination by fertilizer industries in Southern Brazil, Patos Lagoon Estuary. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 129, 104965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwenzi, W.; Mangori, L.; Danha, C.; Chaukura, N.; Dunjana, N.; Sanganyado, E. Sources, behaviour, and environmental and human health risks of high-technology rare earth elements as emerging contaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dushyantha, N.; Batapola, N.; Ilankoon, I.M.S.K.; Rohitha, S.; Premasiri, R.; Abeysinghe, B.; Ratnayake, N.; Dissanayake, K. The story of rare earth elements (REEs): Occurrences, global distribution, genesis, geology, mineralogy and global production. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 122, 103521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Han, G.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S. Spatial Distribution and Sources of Rare Earth Elements in Urban River Water: The Indicators of Anthropogenic Inputs. Water 2023, 15, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Han, G. Rare earth elements reveal the human health and environmental concerns in the largest tributary of the Mekong river, Northeastern Thailand. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Xu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, G. Rare Earth Element Patterns in the Karst Terrains of Guizhou Province, China: Implication for Water/Particle Interaction. Aquat. Geochem. 2009, 15, 457–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayon, G.; Toucanne, S.; Skonieczny, C.; André, L.; Bermell, S.; Cheron, S.; Dennielou, B.; Etoubleau, J.; Freslon, N.; Gauchery, T.; et al. Rare earth elements and neodymium isotopes in world river sediments revisited. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 170, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, S.; Su, N.; Yin, P.; Wang, Z. Rare earth element geochemistry of the sediments from small rivers draining southeast China. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2018, 38, 139–149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Wang, Q.; Huang, X.; Yun, J.; Hu, Q.; Yang, G. Adsorption of amino acids at clay surfaces and implication for biochemical reactions: Role and impact of surface charges. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 183, 110458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, B.A.; Alam, M.S.; Flynn, S.L.; Chen, N.; Hao, W.; Ramachandran Shivakumar, K.; Swaren, L.; Gutierrez Rueda, D.; Konhauser, K.O.; Alessi, D.S.; et al. Rare Earth Element Adsorption to Clay Minerals: Mechanistic Insights and Implications for Recovery from Secondary Sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 7217–7227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gu, X.; Lian, M.; Wang, J.; Xin, M.; Wang, B.; Ouyang, W.; He, M.; Liu, X.; Lin, C. Occurrence, geochemical characteristics, enrichment, and ecological risks of rare earth elements in sediments of “the Yellow river−Estuary−bay” system. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 319, 121025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, P.; Prego, R.; Mil-Homens, M.; Caçador, I.; Caetano, M. Sources and distribution of yttrium and rare earth elements in surface sediments from Tagus estuary, Portugal. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Chen, C.; Chen, Q.; Huang, J. Difference in the Contribution of Driving Factors to Nitrogen Loss With Surface Runoff Between the Hill and Plain Agricultural Watersheds. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2024, 129, e2023JG007931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Deng, J.; Zhang, H.; Peng, J. Suspended solids transport rate of the rivers around western Lake Taihu. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2018, 38, 3682–3687. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover datasets and its dynamics in China from 1985 to 2023. In Earth System Science Data; Zenodo: Geneve, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 13. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Han, G.; Zeng, J.; Zhou, W. Distribution, fractionation and sources of rare earth elements in suspended particulate matter in a tropical agricultural catchment, northeast Thailand. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grawunder, A.; Lonschinski, M.; Händel, M.; Wagner, S.; Merten, D.; Mirgorodsky, D.; Büchel, G. Rare earth element patterns as process indicators at the water–solid interface of a post–mining area. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 96, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution: An Examination of the Geochemical Record Preserved in Sedimentary Rocks; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1985; 312p. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Lin, C.; Yu, R.; Yan, Y.; Hu, G.; Wang, Q. Spatial distribution and source appointment of rare earth elements in paddy soils of Jiulong River Basin, Southeast China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 200, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rétif, J.; Zalouk-Vergnoux, A.; Briant, N.; Poirier, L. From geochemistry to ecotoxicology of rare earth elements in aquatic environments: Diversity and uses of normalization reference materials and anomaly calculation methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 158890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, D.; Mackenzie, L.L.; Chen, B. Sedimentological and geochemical characteristics of sediments and their potential correlations to the processes of desertification along the Keriya River in the Taklamakan Desert, western China. Geomorphology 2021, 375, 107560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahlf, P.; Laukert, G.; Hathorne, E.C.; Vieira, L.H.; Frank, M. Dissolved neodymium and hafnium isotopes and rare earth elements in the Congo River Plume: Tracing and quantifying continental inputs into the southeast Atlantic. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2021, 294, 192–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Han, G.; Yang, K. Assessment and sources of heavy metals in suspended particulate matter in a tropical catchment, northeast Thailand. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 265, 121898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galhardi, J.A.; Leles, B.P.; de Mello, J.W.V.; Wilkinson, K.J. Bioavailability of trace metals and rare earth elements (REE) from the tropical soils of a coal mining area. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 134484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.R.; McLennan, S.M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev. Geophys. 1995, 33, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Xu, S.; Chi, Q.; Nie, L.; Zhang, B.; Yao, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Liu, D.; et al. China soil geochemical baselines networks: Data characteristics. Geol. China 2016, 43, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, R.A. Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Ou, X.; Chen, J. Calculation of Toxicity Coefficient of Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Rare Earth Elements. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 104, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godwyn-Paulson, P.; Jonathan, M.P.; Rodríguez-Espinosa, P.F.; Rodríguez-Figueroa, G.M. Rare earth element enrichments in beach sediments from Santa Rosalia mining region, Mexico: An index-based environmental approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Chi, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Nie, L.; Liu, D.; Xu, S.; Wu, H.; Gao, Y. Geochemical Background and Distribution of Rare Earth Elements in China: Implications for Potential Prospects. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2020, 41, 747–758. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.Y.; Jung, H.S.; Choi, M.S.; Li, C.X. The rare earth element compositions of the Changjiang (Yangtze) and Huanghe (Yellow) river sediments. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 201, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Han, G. Distribution, provenance, contamination, and probabilistic ecological risk of rare earth elements in surface sediments of Jiulong River estuary and adjacent watershed. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2024, 254, 107205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Yang, K.; Zeng, J. Spatio-Temporal Distribution and Environmental Behavior of Dissolved Rare Earth Elements (REE) in the Zhujiang River, Southwest China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 108, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrosino, P.; Sadeghi, M.; Albanese, S.; Andersson, M.; Lima, A.; De Vivo, B. REE contents in solid sample media and stream water from different geological contexts: Comparison between Italy and Sweden. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 133, 176–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderton, D.H.M.; Pearce, J.A.; Potts, P.J. Rare earth element mobility during granite alteration: Evidence from southwest England. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1980, 49, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Wünnemann, B.; Gao, S.; Zhang, Y. Early Holocene tidal flat evolution in a western embayment of East China Sea, in response to sea level rise episodes. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 250, 106642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Jian, X.; Pan, H. Bias in sediment chemical weathering intensity evaluation: A numerical simulation study. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2023, 246, 104574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.L.; Hu, Z.G.; Ju, J.T.; Zhu, L.P. Variations in trace element (including rare earth element) concentrations with grain sizes in loess and their implications for tracing the provenance of eolian deposits. Quat. Int. 2011, 236, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.Y.; Li, W.; Xie, G.Q.; Cai, L.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Wu, J.; Meng, Y.Q. Genesis of the Wangu Au deposit in the Jiangnan orogenic belt: Constraints from texture, trace element, and in-situ Sr isotope of scheelite. Ore Geol. Rev. 2025, 176, 106375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.H.; Choi, M.S. REE geochemistry of fine-grained sediments from major rivers around the Yellow Sea. Chem. Geol. 2009, 266, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A. The aqueous geochemistry of the rare-earth elements and yttrium: 1. Review of available low-temperature data for inorganic complexes and the inorganic REE speciation of natural waters. Chem. Geol. 1990, 82, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wu, P.; Wei, G.; Yang, Y.; Ji, S.; Ma, L.; Zhou, J.; Tan, W.; Zhu, J.; Takahashi, Y. Enrichment and fractionation of rare earth elements (REEs) in ion-adsorption-type REE deposits: Constraints of an iron (hydr)oxide-clay mineral composite. Am. Mineral. 2025, 110, 114–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, Z. Rare Earth Element Compositions of the Sediments from the Major Tributaries and the Main Stream of the Changjiang River. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2011, 30, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, C.; Cai, J. Heavy mineral compositions of the Changjiang (Yangtze River) sediments and their provenance-tracing implication. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2009, 35, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.; Sipos, P.; Jakab, G.; Szalai, Z.; Kalicz, P.; Madarász, B. Improving the reliability of using rare earth elements as soil erosion tracers. CATENA 2024, 243, 108175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.Y.; Xu, Z.F. Geochemical Behaviors of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) in Karst Soils under Different Land-Use Types: A Case in Yinjiang Karst Catchment, Southwest China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özen, Y. Distribution and origin of rare earth elements (REEs) in topsoils and soil profiles of southern Konya (Turkey): Implication for controls on the dynamics of REEs in soils and bedrocks. CATENA 2024, 246, 108352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, B.; Bera, B.; Roy, S.h.; Adhikary, P.P.; Sengupta, D.; Shit, P.K. Assessment of non-carcinogenic health risk of heavy metal pollution: Evidences from coal mining region of eastern India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 47275–47293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, R.; Teng, Y.; Wu, J. Contamination characteristics, ecological risk and source identification of trace metals in sediments of the Le’an River (China). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 125, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simbanegavi, T.T.; Gwenzi, W. Chapter 11—Ecological health risks of high-technology rare earth elements. In Emerging Contaminants in the Terrestrial-Aquatic-Atmosphere Continuum; Gwenzi, W., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


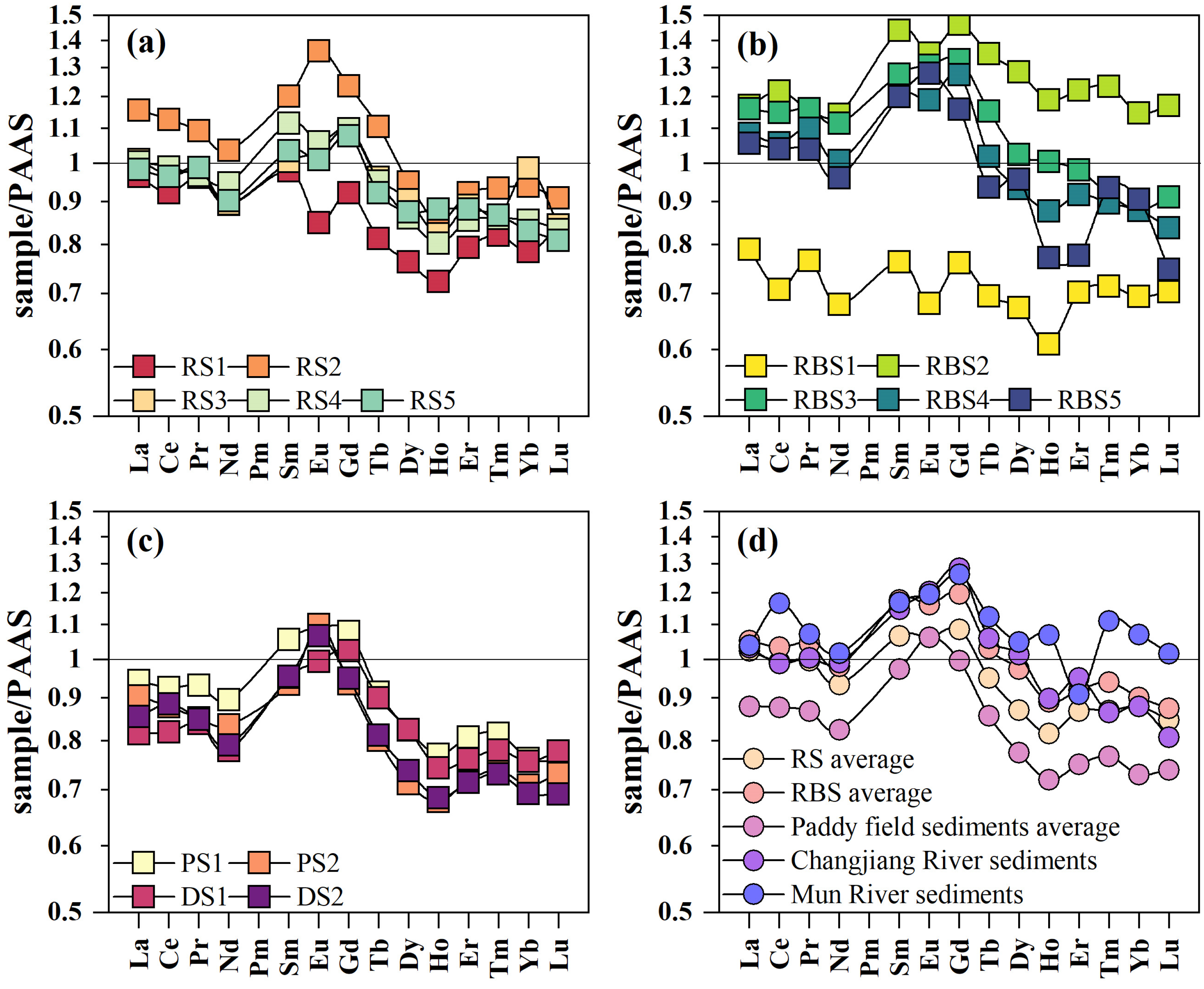

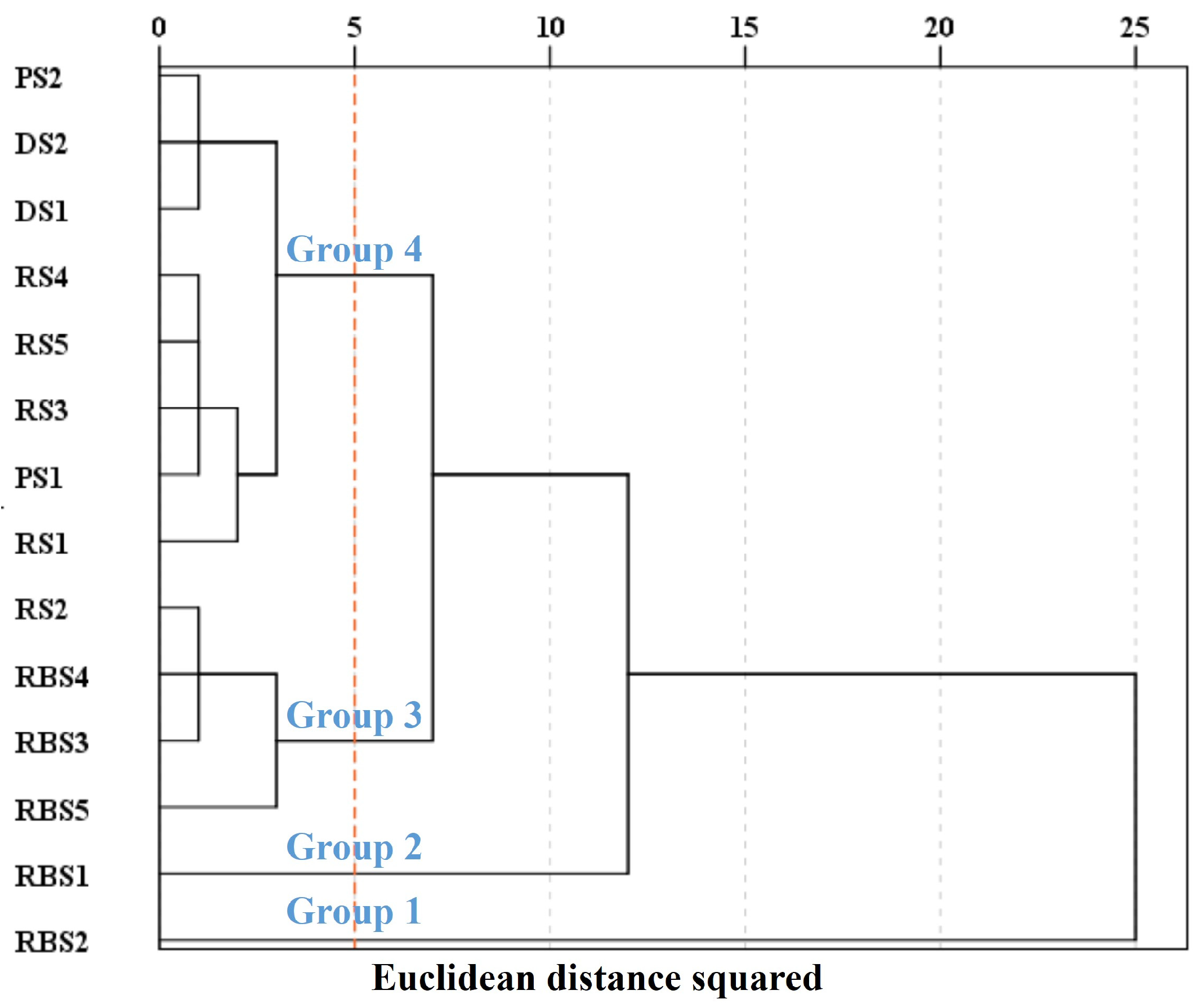
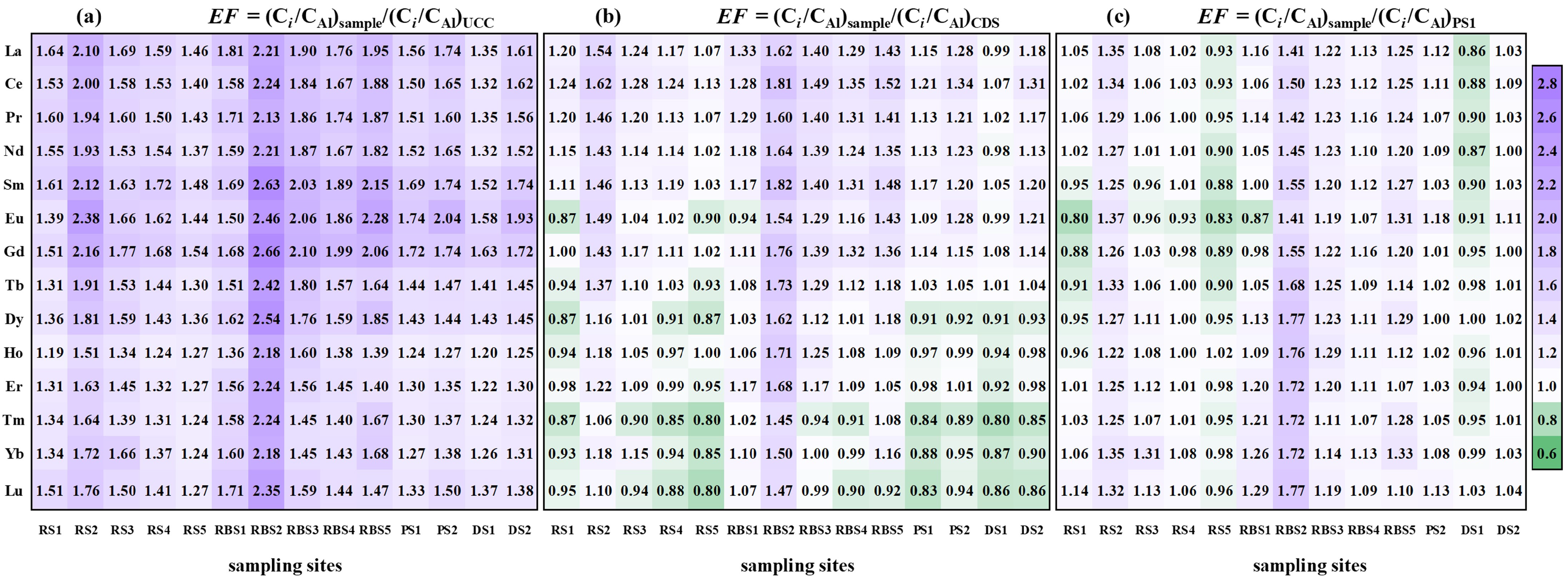

| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ∑REE | Al | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | mg/kg | % | |
| UCC 1 | 30.00 | 64.00 | 7.10 | 26.00 | 4.50 | 0.88 | 3.80 | 0.64 | 3.50 | 0.80 | 2.30 | 0.33 | 2.20 | 0.32 | 146.37 | 8.04 |
| CDS 2 | 32.00 | 62.00 | 7.40 | 27.40 | 5.10 | 1.10 | 4.50 | 0.70 | 4.30 | 0.80 | 2.40 | 0.40 | 2.50 | 0.40 | 151.00 | 6.30 |
| PS1 3 | 36.01 | 73.63 | 8.22 | 30.35 | 5.86 | 1.18 | 5.03 | 0.71 | 3.86 | 0.76 | 2.30 | 0.33 | 2.15 | 0.33 | 170.71 | 6.19 |
| Component | Units | Riparian Sediments (RSs) | Riverbed Sediments (RBSs) | Paddy Field Sediments | RSs + RBSs | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg 1 | Max 2 | Min 3 | Avg | Max | Min | Avg | Max | Min | Avg | ||
| La | mg/kg | 39.08 | 44.17 | 36.81 | 40.20 | 44.72 | 30.16 | 33.59 | 36.01 | 31.15 | 39.64 |
| Ce | mg/kg | 79.13 | 89.69 | 73.40 | 82.31 | 97.02 | 56.31 | 69.80 | 73.63 | 65.22 | 80.72 |
| Pr | mg/kg | 8.80 | 9.65 | 8.49 | 9.22 | 10.25 | 6.76 | 7.66 | 8.22 | 7.41 | 9.01 |
| Nd | mg/kg | 31.67 | 35.12 | 30.25 | 33.25 | 38.73 | 23.03 | 27.96 | 30.35 | 26.38 | 32.46 |
| Sm | mg/kg | 5.92 | 6.67 | 5.43 | 6.53 | 7.99 | 4.23 | 5.40 | 5.86 | 5.18 | 6.22 |
| Eu | mg/kg | 1.15 | 1.47 | 0.92 | 1.25 | 1.46 | 0.74 | 1.15 | 1.19 | 1.07 | 1.20 |
| Gd | mg/kg | 5.06 | 5.76 | 4.30 | 5.58 | 6.82 | 3.54 | 4.64 | 5.03 | 4.36 | 5.32 |
| Tb | mg/kg | 0.74 | 0.86 | 0.63 | 0.80 | 1.04 | 0.54 | 0.66 | 0.71 | 0.62 | 0.77 |
| Dy | mg/kg | 4.07 | 4.44 | 3.57 | 4.56 | 6.01 | 3.15 | 3.62 | 3.86 | 3.33 | 4.32 |
| Ho | mg/kg | 0.81 | 0.87 | 0.72 | 0.88 | 1.18 | 0.60 | 0.71 | 0.76 | 0.67 | 0.85 |
| Er | mg/kg | 2.47 | 2.63 | 2.26 | 2.62 | 3.48 | 2.00 | 2.14 | 2.30 | 2.03 | 2.55 |
| Tm | mg/kg | 0.35 | 0.38 | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.50 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.37 |
| Yb | mg/kg | 2.48 | 2.78 | 2.21 | 2.54 | 3.24 | 1.96 | 2.06 | 2.15 | 1.95 | 2.51 |
| Lu | mg/kg | 0.37 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.38 | 0.51 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.37 |
| ∑REE | mg/kg | 182.10 | 204.71 | 169.67 | 190.50 | 222.92 | 133.62 | 160.03 | 170.71 | 151.53 | 186.30 |
| ∑LREE | mg/kg | 158.68 | 178.63 | 148.94 | 164.98 | 190.70 | 116.27 | 139.01 | 148.21 | 130.16 | 161.83 |
| ∑MREE | mg/kg | 16.94 | 19.19 | 14.84 | 18.72 | 23.32 | 12.20 | 15.48 | 16.63 | 14.67 | 17.83 |
| ∑HREE | mg/kg | 6.48 | 6.89 | 5.89 | 6.80 | 8.90 | 5.15 | 5.54 | 5.87 | 5.26 | 6.64 |
| (La/Yb)N | 4 | 1.17 | 1.23 | 1.02 | 1.18 | 1.32 | 1.02 | 1.21 | 1.28 | 1.08 | 1.17 |
| (La/Sm)N | 4 | 0.96 | 1.01 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 1.03 | 0.81 | 0.90 | 0.97 | 0.86 | 0.93 |
| (Sm/Yb)N | 4 | 1.22 | 1.31 | 1.02 | 1.30 | 1.45 | 1.10 | 1.33 | 1.39 | 1.26 | 1.26 |
| Ce/Ce* | 4 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 1.05 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 1.04 | 0.99 | 0.98 |
| Eu/Eu* | 4 | 0.98 | 1.12 | 0.89 | 0.97 | 1.08 | 0.89 | 1.08 | 1.18 | 1.01 | 0.98 |
| Al | wt% | 6.23 | 6.91 | 5.63 | 5.60 | 6.31 | 4.47 | 5.79 | 6.19 | 5.31 | 5.91 |
| Ca | wt% | 0.60 | 0.95 | 0.31 | 1.03 | 2.17 | 0.31 | 1.18 | 2.93 | 0.36 | 0.82 |
| Fe | wt% | 3.12 | 3.41 | 2.74 | 3.06 | 3.56 | 1.90 | 3.04 | 3.90 | 2.41 | 3.09 |
| K | wt% | 1.35 | 2.41 | 0.86 | 1.01 | 1.87 | 0.63 | 1.25 | 1.34 | 1.16 | 1.18 |
| Mg | wt% | 0.69 | 0.81 | 0.45 | 1.04 | 2.51 | 0.24 | 0.61 | 0.83 | 0.36 | 0.87 |
| Mn | wt% | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.16 | 0.45 | 0.04 | 0.09 |
| Na | wt% | 0.77 | 1.13 | 0.67 | 0.88 | 0.98 | 0.77 | 0.64 | 0.73 | 0.48 | 0.83 |
| Ti | wt% | 0.33 | 0.37 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 0.42 | 0.16 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| Clay | % | 52.78 | 60.72 | 35.04 | 39.26 | 53.86 | 30.68 | 43.74 | 67.79 | 32.23 | 46.02 |
| Silt | % | 38.22 | 41.81 | 29.36 | 53.79 | 67.38 | 31.47 | 55.90 | 66.75 | 32.21 | 46.01 |
| pH | 4 | 7.31 | 7.61 | 6.85 | 7.64 | 7.93 | 7.31 | 7.04 | 7.51 | 6.26 | 7.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, B.; Liang, B.; Lin, Q.; Wang, W. Source, Transport, and Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements in Fluvial Sediments from a Typical Small Urban Basin (East Tiaoxi River, Eastern China). Water 2025, 17, 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091279
Yang K, Zhang Q, Wang B, Liang B, Lin Q, Wang W. Source, Transport, and Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements in Fluvial Sediments from a Typical Small Urban Basin (East Tiaoxi River, Eastern China). Water. 2025; 17(9):1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091279
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Kunhua, Qian Zhang, Bei Wang, Bin Liang, Qiang Lin, and Weijiao Wang. 2025. "Source, Transport, and Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements in Fluvial Sediments from a Typical Small Urban Basin (East Tiaoxi River, Eastern China)" Water 17, no. 9: 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091279
APA StyleYang, K., Zhang, Q., Wang, B., Liang, B., Lin, Q., & Wang, W. (2025). Source, Transport, and Fractionation of Rare Earth Elements in Fluvial Sediments from a Typical Small Urban Basin (East Tiaoxi River, Eastern China). Water, 17(9), 1279. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091279







