Worldwide Research Progress and Trends in Application of Machine Learning to Wastewater Treatment: A Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
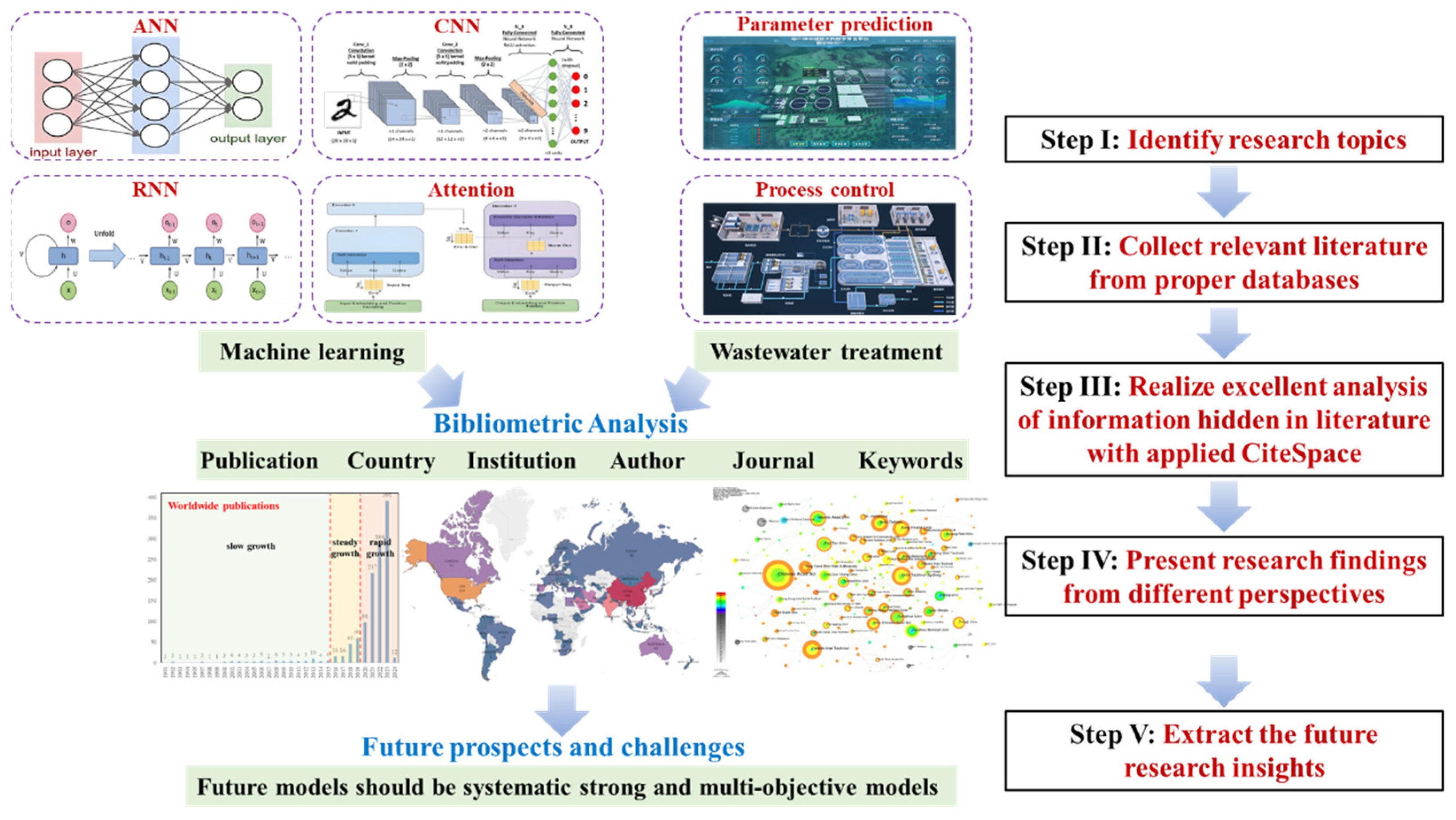
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Data Analysis Methods
3. Results
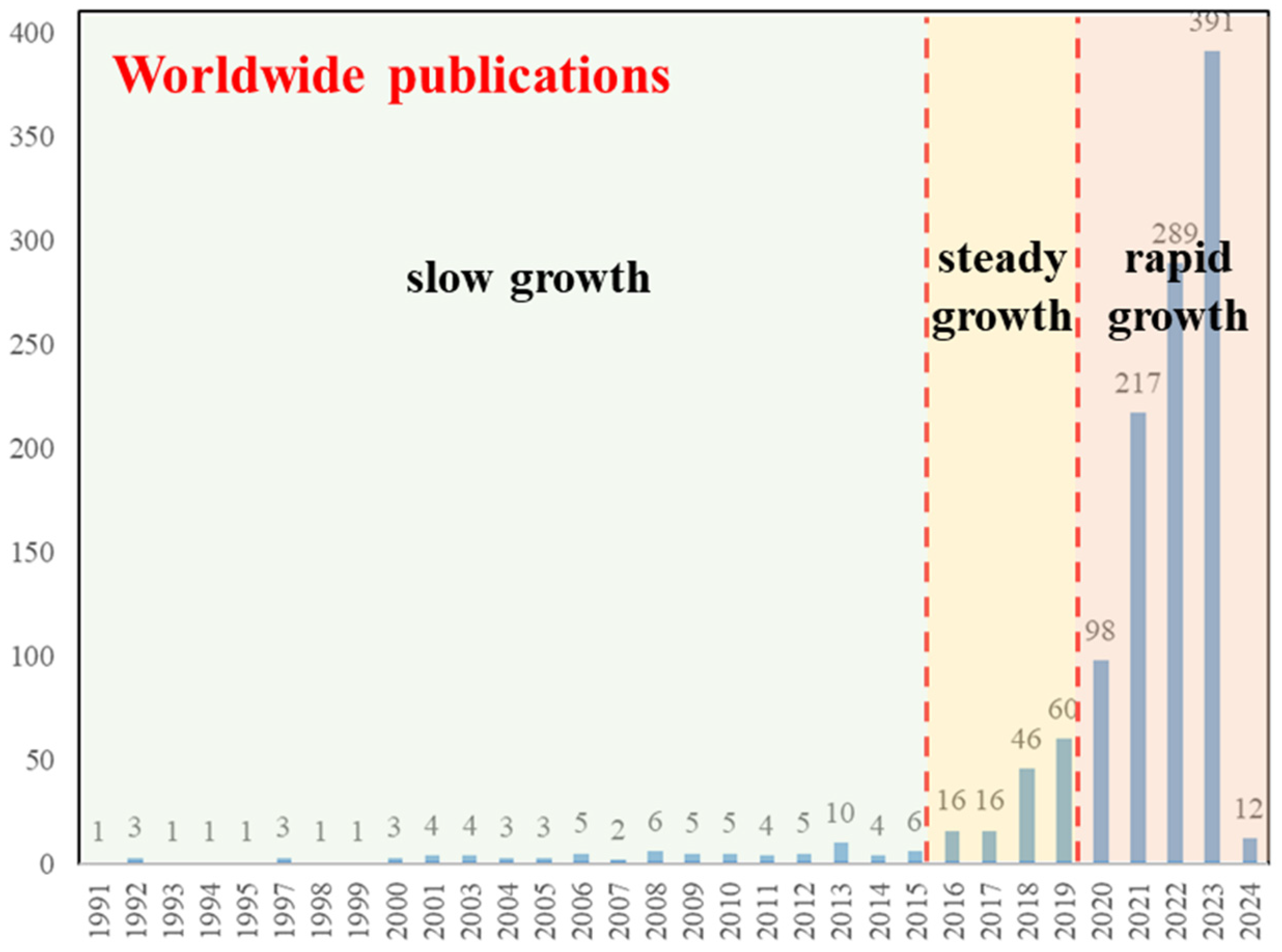
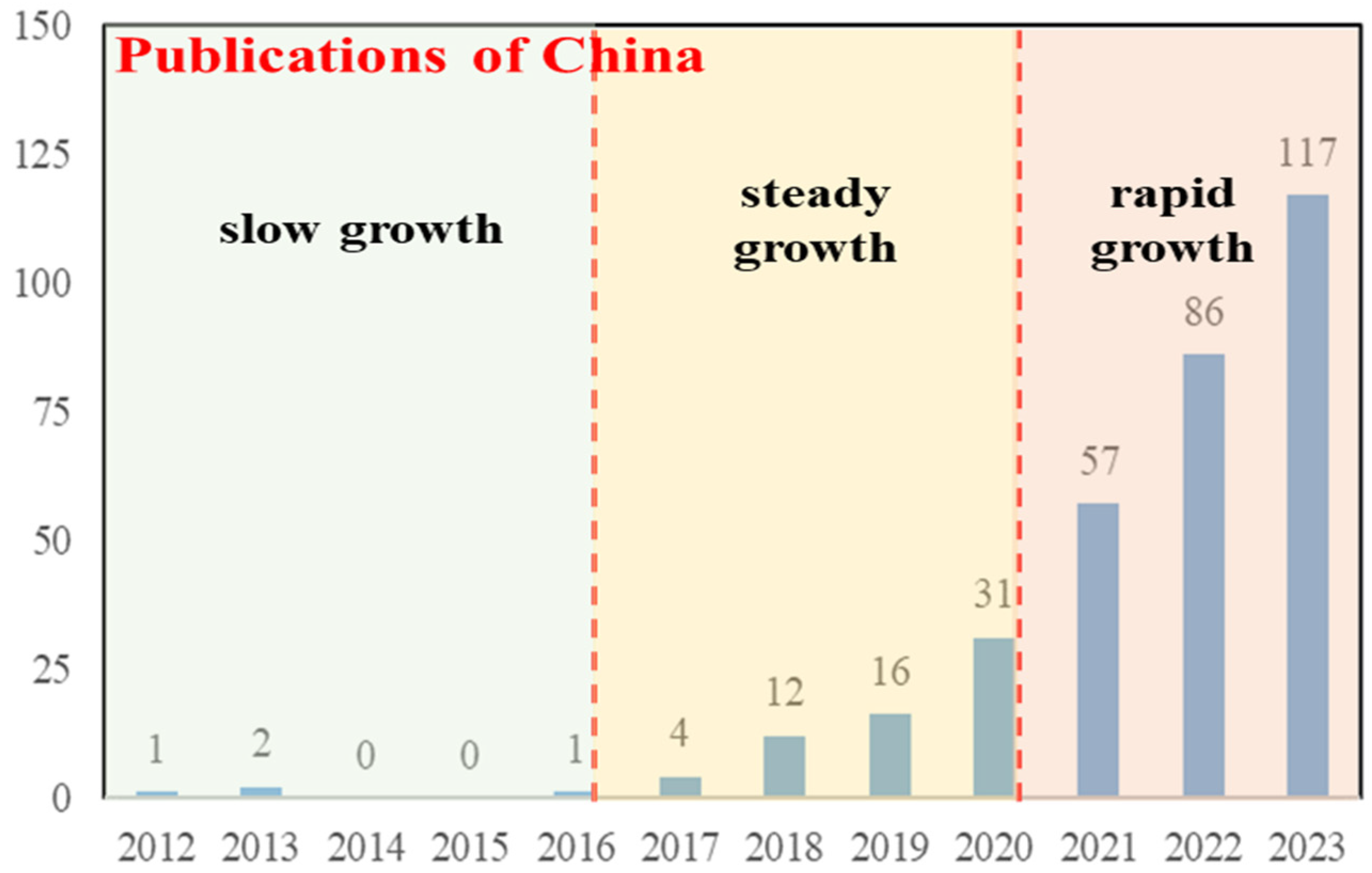
3.1. Publication Characteristics
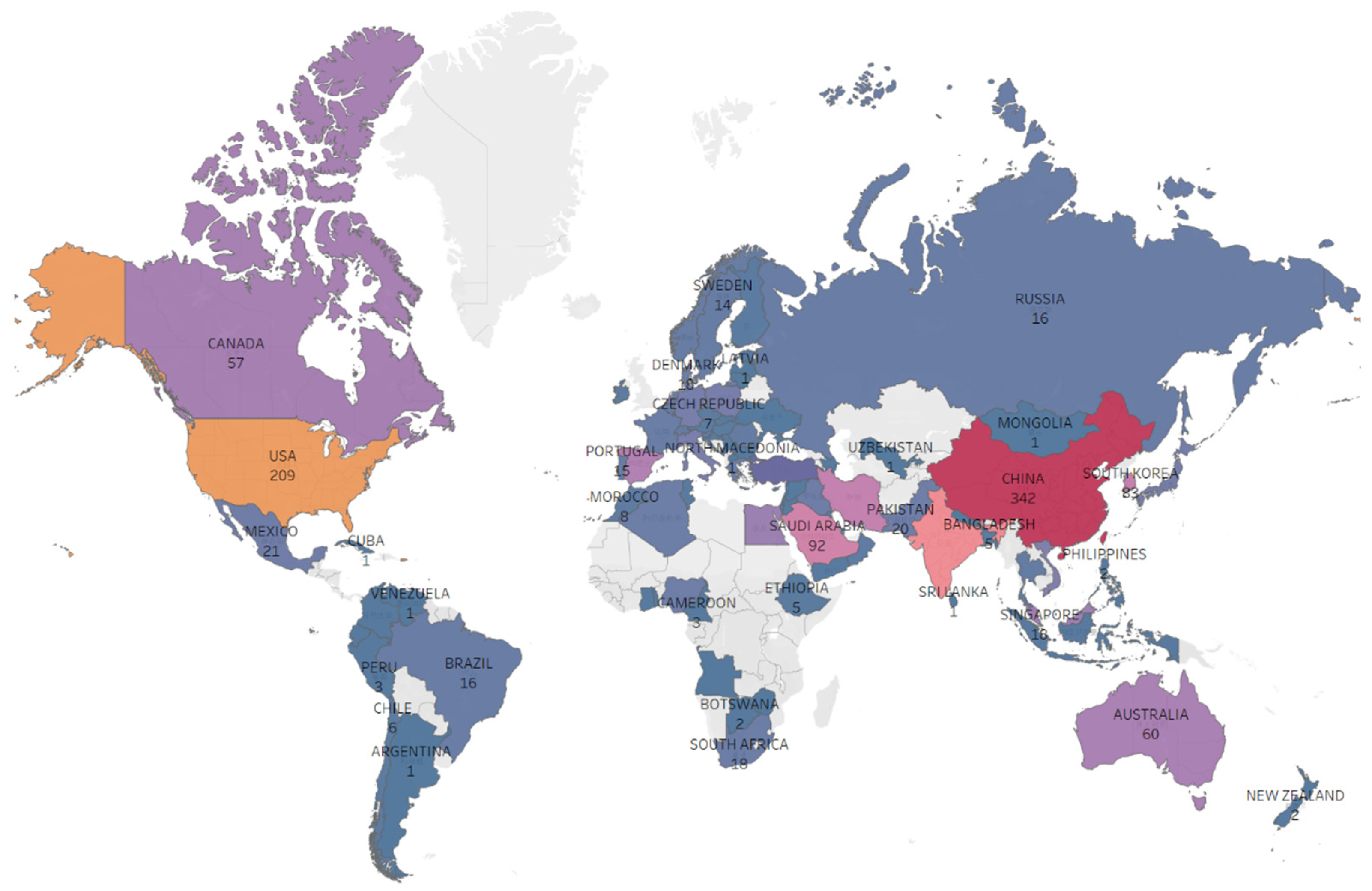
3.2. Country Contributions
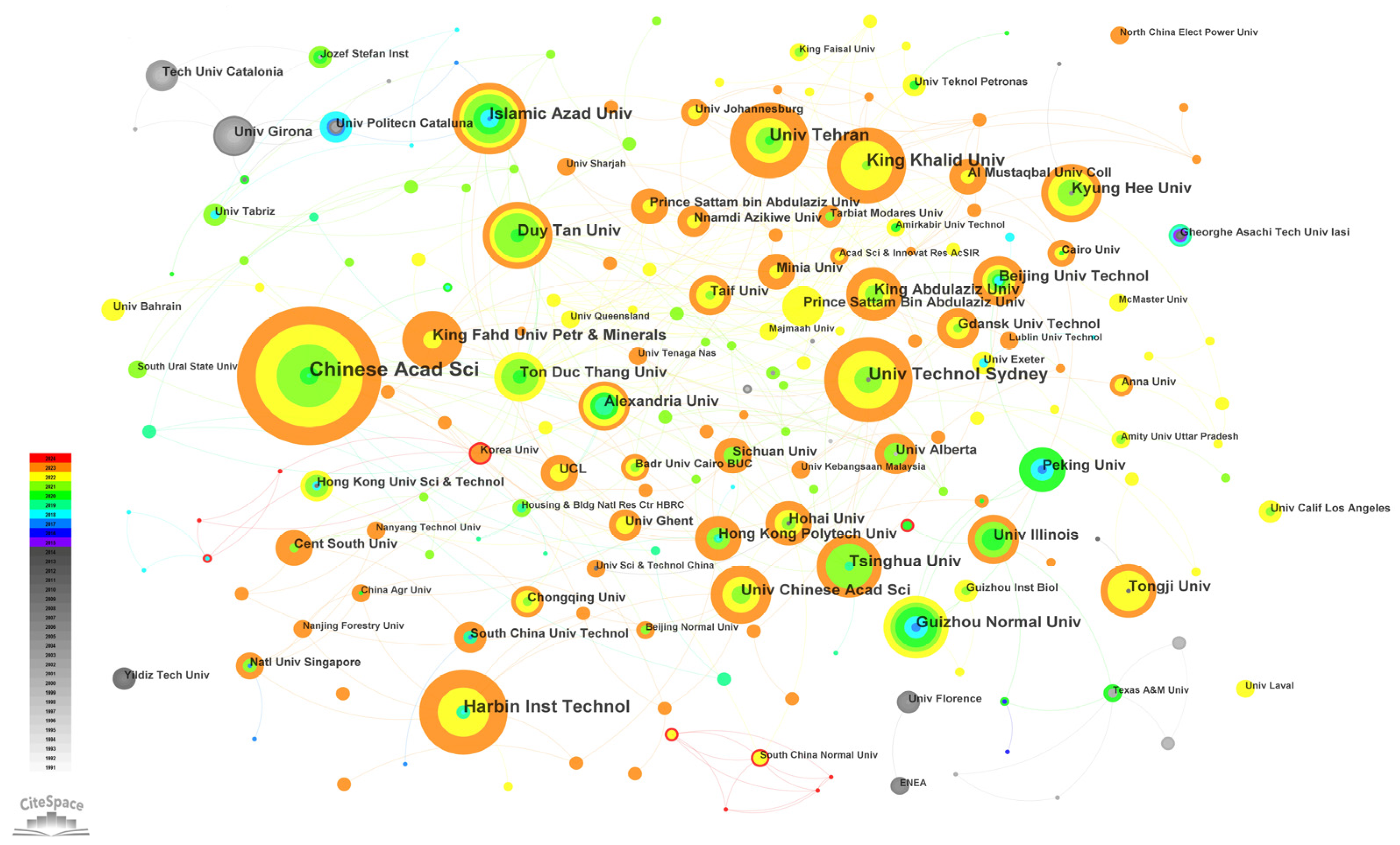
3.3. Institution Contributions
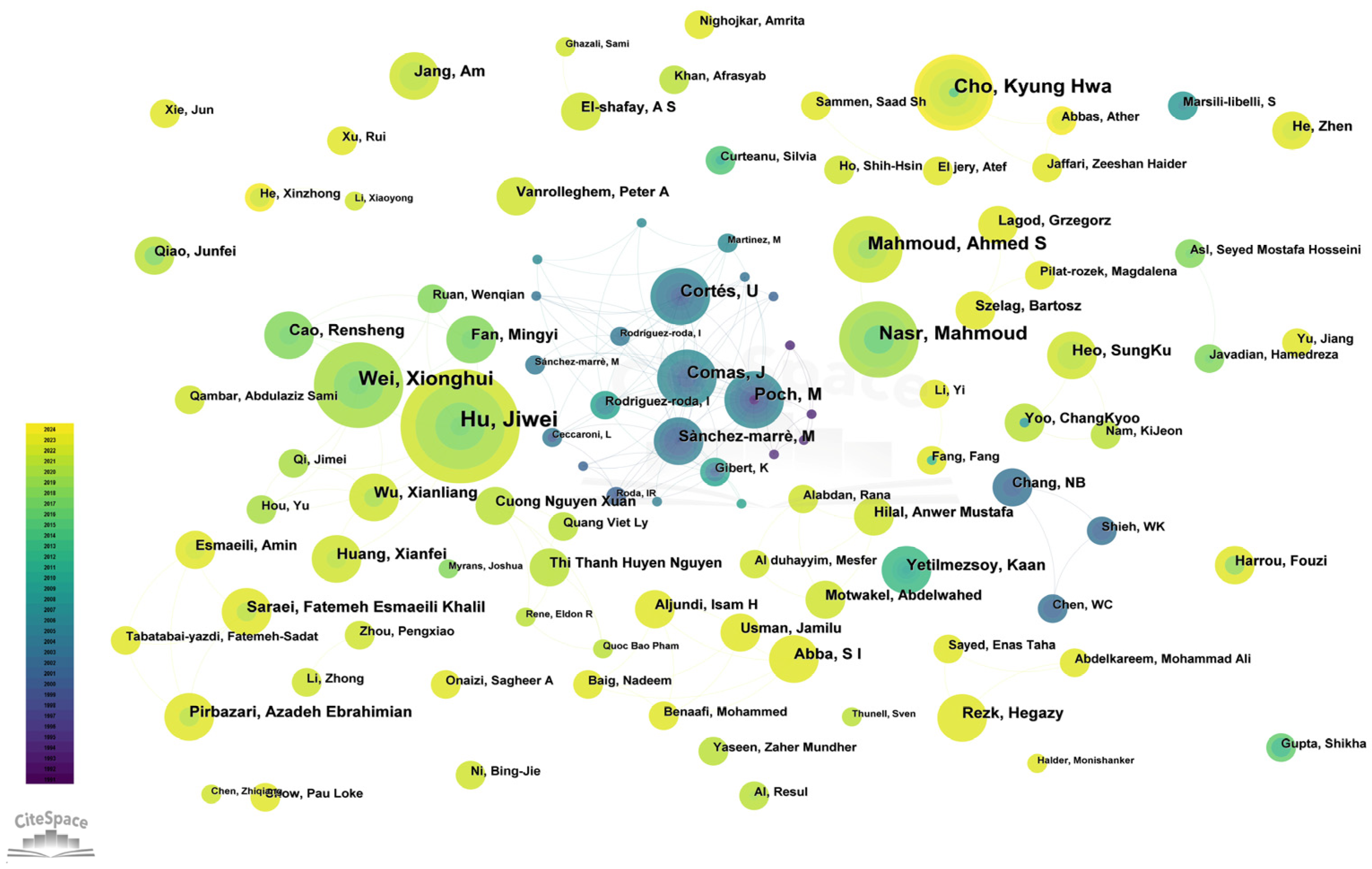
3.4. Author Contributions
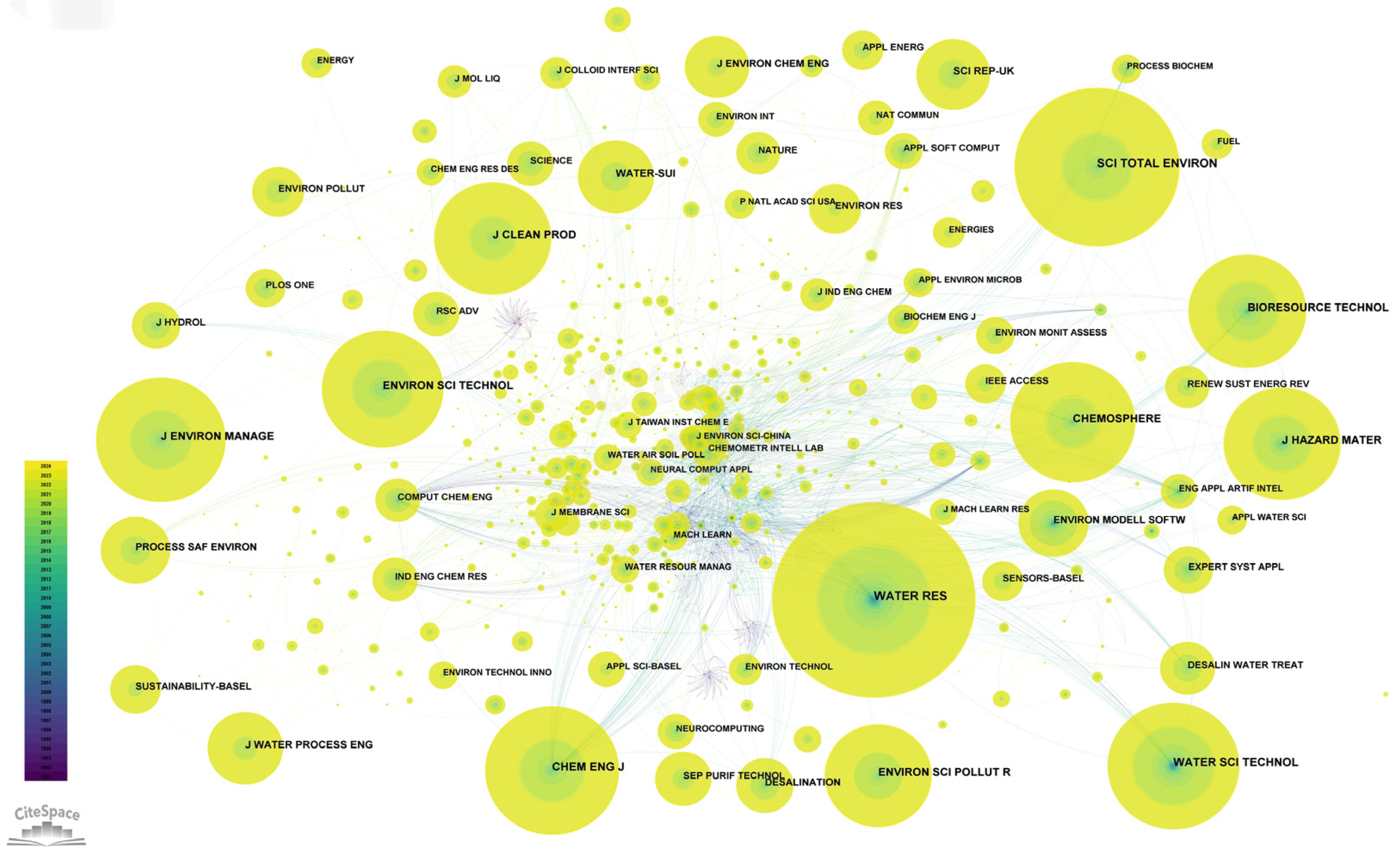
3.5. Journal and Cited Journal Contributions
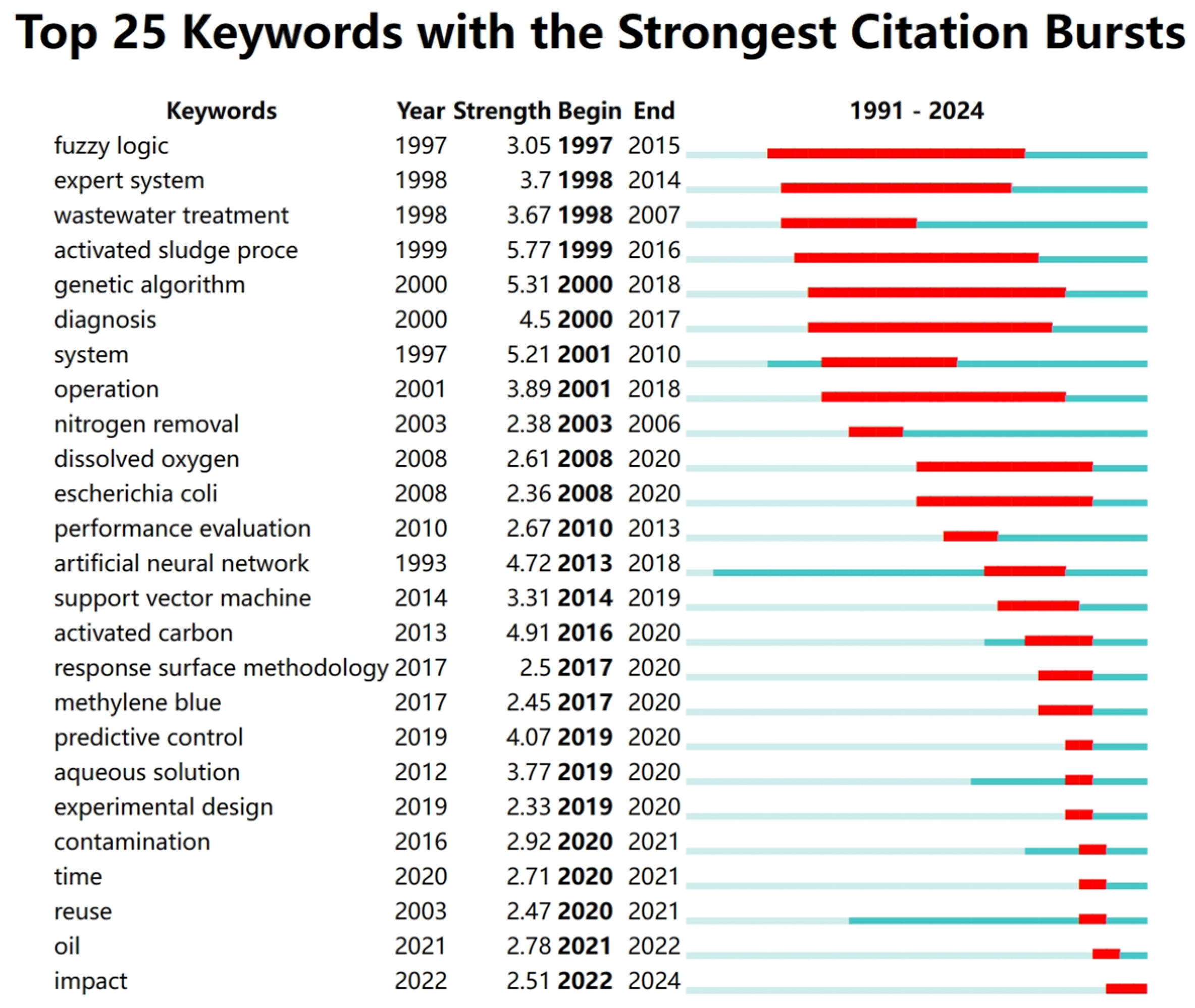
3.6. Keywords Characteristics
4. Discussion
4.1. Future Research Prospects and Challenges—Pollutants Prediction
4.2. Future Research Prospects and Challenges—Process Control
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Z.; Xu, J.; Yin, H.; Jin, W.; Li, H.; He, Z. Urban river pollution control in developing countries. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 158–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.B.; Greene, K.; Vasquez-Arroyo, E.; Awais, M.; Gomez-Sanabria, A.; Kyle, P.; Palatnik, R.R.; Schaeffer, R.; Zhou, P.; Aissaoui, B. Toward Enhancing Wastewater Treatment with Resource Recovery in Integrated Assessment and Computable General Equilibrium Models. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2024, 11, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Ren, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, K.; Yu, G.; Ke, B.; Yu, H.-Q.; Zheng, X.; Li, J. Concept wastewater treatment plants in China. In Pathways to Water Sector Decarbonization, Carbon Capture and Utilization; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2022; p. 265. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, M.J.; Bronstein, K.E. Estimating national sludge generation and disposal from US drinking water and wastewater treatment plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 453, 142121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Chai, X.; Lu, B.; Lu, W.; Han, H.; Mu, Y.; Gu, Q.; Wu, B. Integrated control strategy for dual sludge ages in the high-concentration powder carrier bio-fluidized bed (HPB) technology: Enhancing municipal wastewater treatment efficiency. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murshid, S.; Antonysamy, A.; Dhakshinamoorthy, G.; Jayaseelan, A.; Pugazhendhi, A. A review on biofilm-based reactors for wastewater treatment: Recent advancements in biofilm carriers, kinetics, reactors, economics, and future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, G.; Jiao, Y.; Quan, B.; Lu, W.; Su, P.; Tang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, M.; Xiao, N. Critical analysis on the transformation and upgrading strategy of Chinese municipal wastewater treatment plants: Towards sustainable water remediation and zero carbon emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 165201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigger, G.T.; Kuo, J.; Derlon, N.; Houweling, D.; Jimenez, J.A.; Johnson, B.R.; McQuarrie, J.P.; Murthy, S.; Regmi, P.; Roche, C.; et al. Biological and physical selectors for mobile biofilms, aerobic granules, and densified-biological flocs in continuously flowing wastewater treatment processes: A state-of-the-art review. Water Res. 2023, 242, 120245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayan, G.Ö.; Kayan, A. Polycaprolactone composites/blends and their applications especially in water treatment. ChemEngineering 2023, 7, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaman, H.; Baig, M.T.; Kayan, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Tetrasubstituted Porphyrin Tin (IV) Complexes and Their Adsorption Properties over Tetracycline Antibiotics. Reactions 2025, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidoye, L.K.; Mahdi, F.M.; Idris, M.O.; Alabi, O.O.; Wahab, A.A. ANN-derived equation and ITS application in the prediction of dielectric properties of pure and impure CO2. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 175, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, M.A.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, J.C.P.; Jiang, F.; Wan, Z. A Temporal-Spatial Interpolation and Extrapolation Method Based on Geographic Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network for PM2.5. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117729. [Google Scholar]
- Baarimah, A.O.; Bazel, M.A.; Alaloul, W.S.; Alazaiza, M.Y.; Al-Zghoul, T.M.; Almuhaya, B.; Khan, A.; Mushtaha, A.W. Artificial intelligence in wastewater treatment: Research trends and future perspectives through bibliometric analysis. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 10, 100926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Su, J.; Wang, H.; Boczkaj, G.; Mahlknecht, J.; Singh, S.V.; Wang, C. Bibliometric analysis of artificial intelligence in wastewater treatment: Current status, research progress, and future prospects. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Sun, X.; Ren, H.; Huang, H. Biological filtration for wastewater treatment in the 21st century: A data-driven analysis of hotspots, challenges and prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jin, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Ren, H. Artificial intelligence in wastewater treatment: A data-driven analysis of status and trends. Chemosphere 2023, 336, 139163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hua, Y.; Zhao, S.; Yang, D.; Chen, S.; Song, Q.; Gao, J.; Dai, X. Worldwide research progress and trend in sludge treatment and disposal: A bibliometric analysis. ACS EST Eng. 2023, 3, 1083–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zheng, L.; Yu, F. Current status and future prospects of biochar application in electrochemical energy storage devices: A bibliometric review. Desalination 2024, 581, 117597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plan, S. The National Artificial Intelligence Research and Development Strategic Plan; National Science and Technology Council, Networking and Information Technology Research and Development Subcommittee: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, M.; Hu, J.; Cao, R.; Ruan, W.; Wei, X. A review on experimental design for pollutants removal in water treatment with the aid of artificial intelligence. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, M.; Batstone, D.; Mbamba, C.K.; Keymer, P.; French, T.; Ward, A.; Dwyer, J.; Cardell-Oliver, R. Deep learning in wastewater treatment: A critical review. Water Res. 2023, 245, 120518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croll, H.C.; Ikuma, K.; Ong, S.K.; Sarkar, S. Reinforcement learning applied to wastewater treatment process control optimization: Approaches, challenges, and path forward. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 53, 1775–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Du, B.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y.; Li, Q.; Feng, D.; Gao, X.; Wang, H. Data-driven prediction and control of wastewater treatment process through the combination of convolutional neural network and recurrent neural network. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 13410–13419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henze, M.; Gujer, W.; Mino, T.; Van Loosedrecht, M. Activated Sludge Models ASM1, ASM2, ASM2d and ASM3; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Iacopozzi, I.; Innocenti, V.; Marsili-Libelli, S.; Giusti, E. A modified Activated Sludge Model No. 3 (ASM3) with two-step nitrification–denitrification. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 847–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenu, A.; Guglielmi, G.; Jimenez, J.; Spèrandio, M.; Saroj, D.; Lesjean, B.; Brepols, C.; Thoeye, C.; Nopens, I. Activated sludge model (ASM) based modelling of membrane bioreactor (MBR) processes: A critical review with special regard to MBR specificities. Water Res. 2010, 44, 4272–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwangbo, S.; Al, R.; Chen, X.; Sin, G.r. Integrated model for understanding N2O emissions from wastewater treatment plants: A deep learning approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.A.; Dickenson, E.R. Using machine learning classification to detect simulated increases of de facto reuse and urban stormwater surges in surface water. Water Res. 2021, 204, 117556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevkar, S.V.; Khemani, B.; Patil, S.; Kotecha, K.; Vora, D.R.; Abraham, A.; Gabralla, L.A. A review on machine learning styles in computer vision—Techniques and future directions. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 107293–107329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ureel, Y.; Dobbelaere, M.R.; Ouyang, Y.; De Ras, K.; Sabbe, M.K.; Marin, G.B.; Van Geem, K.M. Active machine learning for chemical engineers: A bright future lies ahead! Engineering 2023, 27, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamandipoor, B.; Majd, M.; Sheikhalishahi, S.; Modena, C.; Osmani, V. Monitoring and detecting faults in wastewater treatment plants using deep learning. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaraj, A.; Deka, P.C. Spatial and temporal variations in river water quality of the Middle Ganga Basin using unsupervised machine learning techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, M.; Mojiri, A.; Kindaichi, T.; Cagnetta, G.; Yuan, J.; Wang, B.; Giwa, A.S. Cross-linked chitosan/zeolite as a fixed-bed column for organic micropollutants removal from aqueous solution, optimization with RSM and artificial neural network. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-H.; Song, J.; Yoo, S.S.; Lee, B.-J.; Ji, H.W. Prediction of odor concentration emitted from wastewater treatment plant using an artificial neural network (ANN). Atmosphere 2020, 11, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqub, M.; Asif, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, W. Modeling of a full-scale sewage treatment plant to predict the nutrient removal efficiency using a long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisa, I.; Santin, I.; Morell, A.; Vicario, J.L.; Vilanova, R. LSTM-based wastewater treatment plants operation strategies for effluent quality improvement. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 159773–159786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Harrou, F.; Kadri, F.; Sun, Y.; Leiknes, T. Forecasting of wastewater treatment plant key features using deep learning-based models: A case study. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 184475–184485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Huang, X.; Han, H. Recurrent neural network-based control for wastewater treatment process. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Networks–ISNN 2012: 9th International Symposium on Neural Networks, Shenyang, China, 11–14 July 2012. Proceedings, Part II 9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Man, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Hong, M.; Cui, P. A deep learning based dynamic COD prediction model for urban sewage. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 2210–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghloul, M.S.; Achari, G. Application of machine learning techniques to model a full-scale wastewater treatment plant with biological nutrient removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, B.; Nguyen, H.; Bui, X.-N.; Bui, H.-B.; Choi, Y.; Zhou, J.; Moayedi, H.; Costache, R.; Nguyen-Trang, T. Predicting the sorption efficiency of heavy metal based on the biochar characteristics, metal sources, and environmental conditions using various novel hybrid machine learning models. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, S.K.; Tung, T.M.; Yaseen, Z.M. Development of artificial intelligence for modeling wastewater heavy metal removal: State of the art, application assessment and possible future research. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Dai, T.; Qiao, Z.; Sun, P.; Hao, J.; Yang, Y. Application of artificial intelligence to wastewater treatment: A bibliometric analysis and systematic review of technology, economy, management, and wastewater reuse. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 133, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Q.; Yin, H. A hybrid deep learning approach to improve real-time effluent quality prediction in wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 2024, 250, 121092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipe, J.; Bessa, R.J.; Reis, M.; Alves, R.; Póvoa, P. Data-driven predictive energy optimization in a wastewater pumping station. Appl. Energy 2019, 252, 113423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-C.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Wang, X.; Yin, W.-X.; Yu, T.-C.; Xue, C.-H.; Wang, A.-J. Multimodal machine learning guides low carbon aeration strategies in urban wastewater treatment. Engineering 2024, 36, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Q.; Wang, H.-C.; Song, Y.-P.; Zhou, S.-Q.; Li, Q.-N.; Liang, B.; Liu, W.-Z.; Zhao, Y.-W.; Wang, A.-J. Machine learning framework for intelligent aeration control in wastewater treatment plants: Automatic feature engineering based on variation sliding layer. Water Res. 2023, 246, 120676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icke, O.; Van Es, D.; de Koning, M.; Wuister, J.; Ng, J.; Phua, K.; Koh, Y.; Chan, W.; Tao, G. Performance improvement of wastewater treatment processes by application of machine learning. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 2671–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazadi Mbamba, C.; Batstone, D. Optimization of deep learning models with genetic algorithms for forecasting performance in water industry. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2023, 175, 108276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Duan, H.; Liu, L.; Qiu, R.; van den Akker, B.; Ni, B.-J.; Chen, T.; Yin, H.; Yuan, Z.; Ye, L. An integrated first principal and deep learning approach for modeling nitrous oxide emissions from wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2816–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ranking | Countries | Count | Centrality |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 342 (highest) | 0.08 |
| 2 | USA | 209 | 0.22 (highest) |
| 3 | India | 128 | 0.13 |
| 4 | Saudi Arabia | 92 | 0.14 |
| 5 | South Korea | 83 | 0.09 |
| 6 | Iran | 79 | 0.13 |
| 8 | Spain | 66 | 0.14 |
| 8 | England | 66 | 0.13 |
| 9 | Australia | 60 | 0.03 |
| 10 | Canada | 57 | 0.08 |
| Ranking | Institutions | Countries | Count | Centrality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chinese Acad Sci | China | 31 (highest) | 0.06 |
| 2 | Harbin Inst Technol | China | 19 | 0.01 |
| 2 | Univ Technol Sydney | Australia | 19 | 0.06 |
| 4 | King Khalid Univ | Saudi Arabia | 17 | 0.04 |
| 4 | Univ Tehran | Iran | 17 | 0.02 |
| 6 | Islamic Azad Univ | Iran | 16 | 0.06 |
| 7 | Duy Tan Univ | Vietnam | 15 | 0.08 (highest) |
| 8 | Guizhou Normal Univ | China | 14 | 0.01 |
| 8 | Tsinghua Univ | China | 14 | 0.06 |
| 10 | King Fahd Univ Petr & Minerals | Saudi Arabia | 13 | 0.02 |
| Ranking | Authors | Countries | Count | Centrality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hu, Jiwei | China | 12 (highest) | 0.00 |
| 2 | Wei, Xionghui | China | 9 | 0.00 |
| 3 | Nasr, Mahmoud | Egypt | 8 | 0.00 |
| 3 | Cho, Kyung Hwa | South Korea | 8 | 0.00 |
| 5 | Mahmoud, Ahmed S | Egypt | 7 | 0.00 |
| 8 | Poch, M | Spain | 6 | 0.00 |
| 8 | Comas, J | Spain | 6 | 0.00 |
| 8 | Cortés, U | Spain | 6 | 0.00 |
| 8 | Rezk, Hegazy | Saudi Arabia | 5 | 0.00 |
| 10 | Huang, Xianfei | China | 5 | 0.00 |
| Ranking | Journals | Count | Journal Impact Factor (2023) | Category Quartile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Water Research | 41 (highest) | 11.4 | Q1 |
| 2 | Science of The Total Environment | 40 | 8.2 | Q1 |
| 3 | Water | 35 | 3.0 | Q2 |
| 3 | Journal of Cleaner Production | 31 | 9.7 | Q1 |
| 5 | Environmental Science & Technology | 29 | 10.8 | Q1 |
| 8 | Journal of Water Process Engineering | 29 | 6.3 | Q1 |
| 8 | Water Science & Technology | 28 | 2.5 | Q3 |
| 8 | Journal of Environmental Management | 27 | 8.0 | Q1 |
| 8 | Environmental Science and Pollution Research | 23 | no data | no data |
| 10 | Chemosphere | 22 | 8.1 | Q1 |
| Ranking | Journals | Count | Centrality | Journal Impact Factor (2023) | Category Quartile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Water Research | 574 (highest) | 0.07 | 11.4 | Q1 |
| 2 | Science of The Total Environment | 461 | 0.00 | 8.2 | Q1 |
| 3 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 386 | 0.13 | 13.3 | Q1 |
| 4 | Water Science & Technology | 375 | 0.03 | 2.5 | Q3 |
| 5 | Journal of Environmental Management | 364 | 0.03 | 2.7 | Q3 |
| 6 | Chemosphere | 355 | 0.10 | 8.1 | Q1 |
| 7 | Environmental Science & Technology | 342 | 0.13 | 10.8 | Q1 |
| 8 | Bioresource Technology | 334 | 0.08 | 9.7 | Q1 |
| 9 | Journal of Hazardous Materials | 329 | 0.01 | 12.2 | Q1 |
| 10 | Journal of Cleaner Production | 326 | 0.01 | 9.7 | Q1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, K.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X. Worldwide Research Progress and Trends in Application of Machine Learning to Wastewater Treatment: A Bibliometric Analysis. Water 2025, 17, 1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091314
Zhou K, Wu B, Zhang X. Worldwide Research Progress and Trends in Application of Machine Learning to Wastewater Treatment: A Bibliometric Analysis. Water. 2025; 17(9):1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091314
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Kun, Boran Wu, and Xin Zhang. 2025. "Worldwide Research Progress and Trends in Application of Machine Learning to Wastewater Treatment: A Bibliometric Analysis" Water 17, no. 9: 1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091314
APA StyleZhou, K., Wu, B., & Zhang, X. (2025). Worldwide Research Progress and Trends in Application of Machine Learning to Wastewater Treatment: A Bibliometric Analysis. Water, 17(9), 1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091314






