Effect of Dust Deposition on Stomatal Conductance and Leaf Temperature of Cotton in Northwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
| Soil Depth | CEC | BD | PH | ECe | Corganic | Ntotal | CaCO3 | CO32− | HCO3− | Cl− | SO42− | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Na+ | K+ | Soil Texture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (cm) | (cmol/kg) | (g/cm3) | (mS/cm) | (g/kg) | ||||||||||||
| 27 | 2.9 | 1.57 | 7.8 | 23.8 | 4.8 | 1.1 | 116.1 | 0.00 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 2.1 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | Sandy loam |
| 52 | 2.0 | 1.55 | 8.1 | 21.0 | 1.7 | 0.9 | 123.5 | 0.00 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | Sandy loam |
| 63 | 1.5 | 1.50 | 8.2 | 21.0 | 1.6 | 0.9 | 120.7 | 0.00 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | loamy sand |
| 85 | 2.9 | 1.56 | 8.2 | 25.2 | 2.4 | 0.9 | 115.9 | 0.01 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.1 | Sandy loam |
| 120 | 1.2 | 1.50 | 8.5 | 16.8 | 1.5 | 0.9 | 111.1 | 0.01 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | Loamy sand |
| 140 | 1.9 | 1.57 | 8.4 | 18.2 | 2.1 | 0.9 | 116.5 | 0.01 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | Sandy loam |
| Month | Tmax (°C) | Tmin (°C) | Tavg (°C) | RH (%) | U2 (m/s) | Rs (W·m−2) | P (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| May | 30 | 16 | 23 | 35 | 1.4 | 203 | 1 |
| June | 31 | 20 | 26 | 45 | 1.3 | 242 | 16 |
| July | 32 | 19 | 26 | 52 | 1.1 | 270 | 21 |
| August | 32 | 18 | 25 | 52 | 1.0 | 228 | 4 |
| September | 29 | 14 | 22. | 48 | 0.7 | 185 | 0 |
2.2. Experiment Design
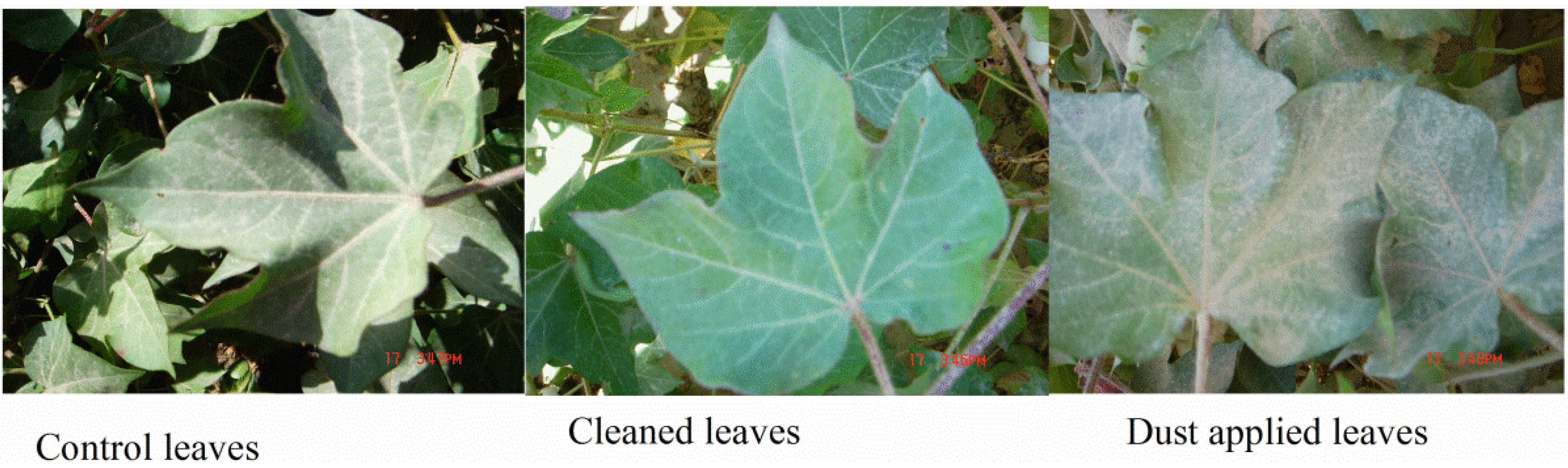



2.3. Measurement of Canopy Temperature and Stomatal Conductance

2.4. Soil Moisture Content, Plant Dry Matter and Yield
2.5. Data Analyses and Statistics
3. Results
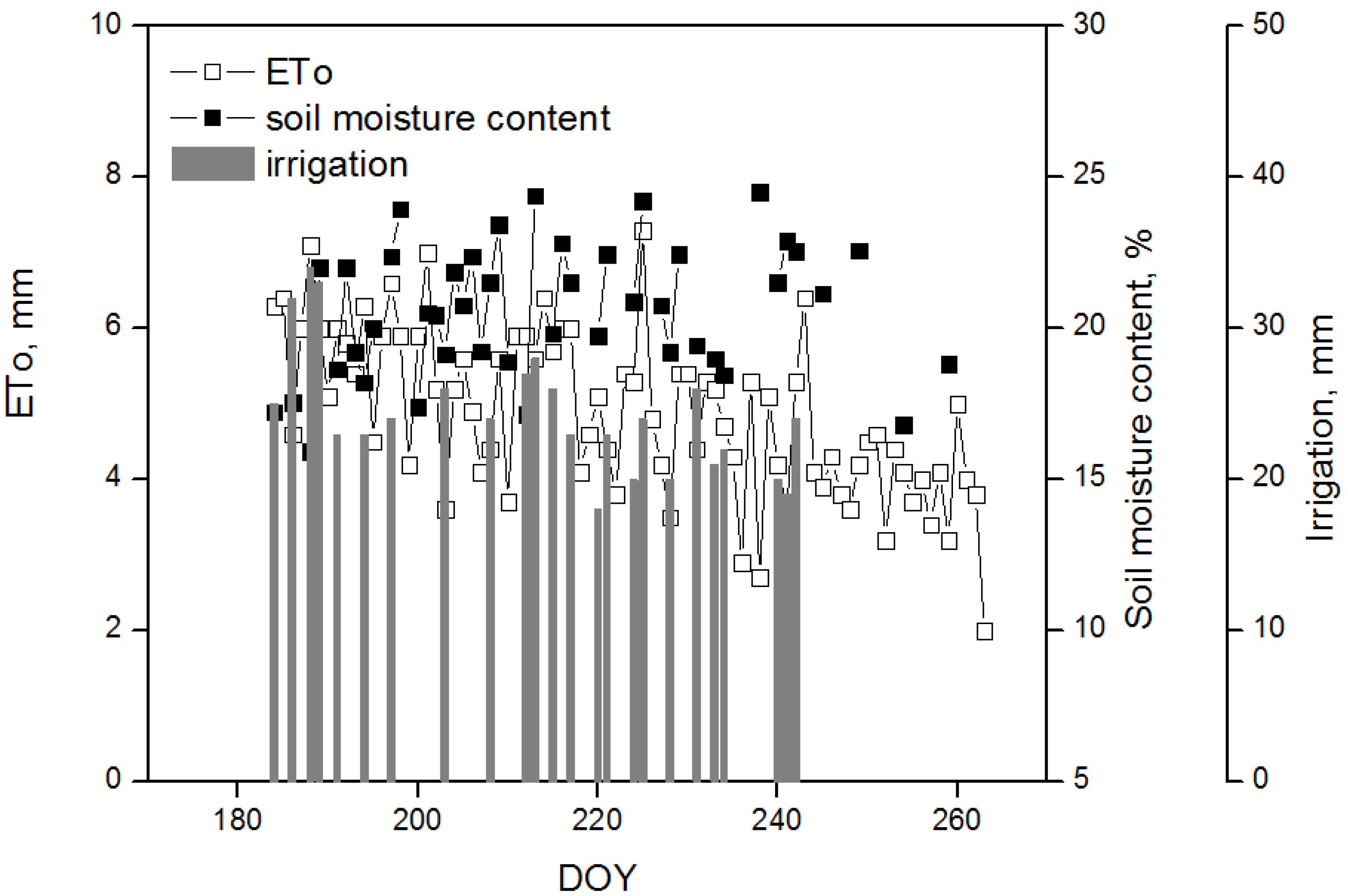
3.1. Irrigation and Soil Moisture Content
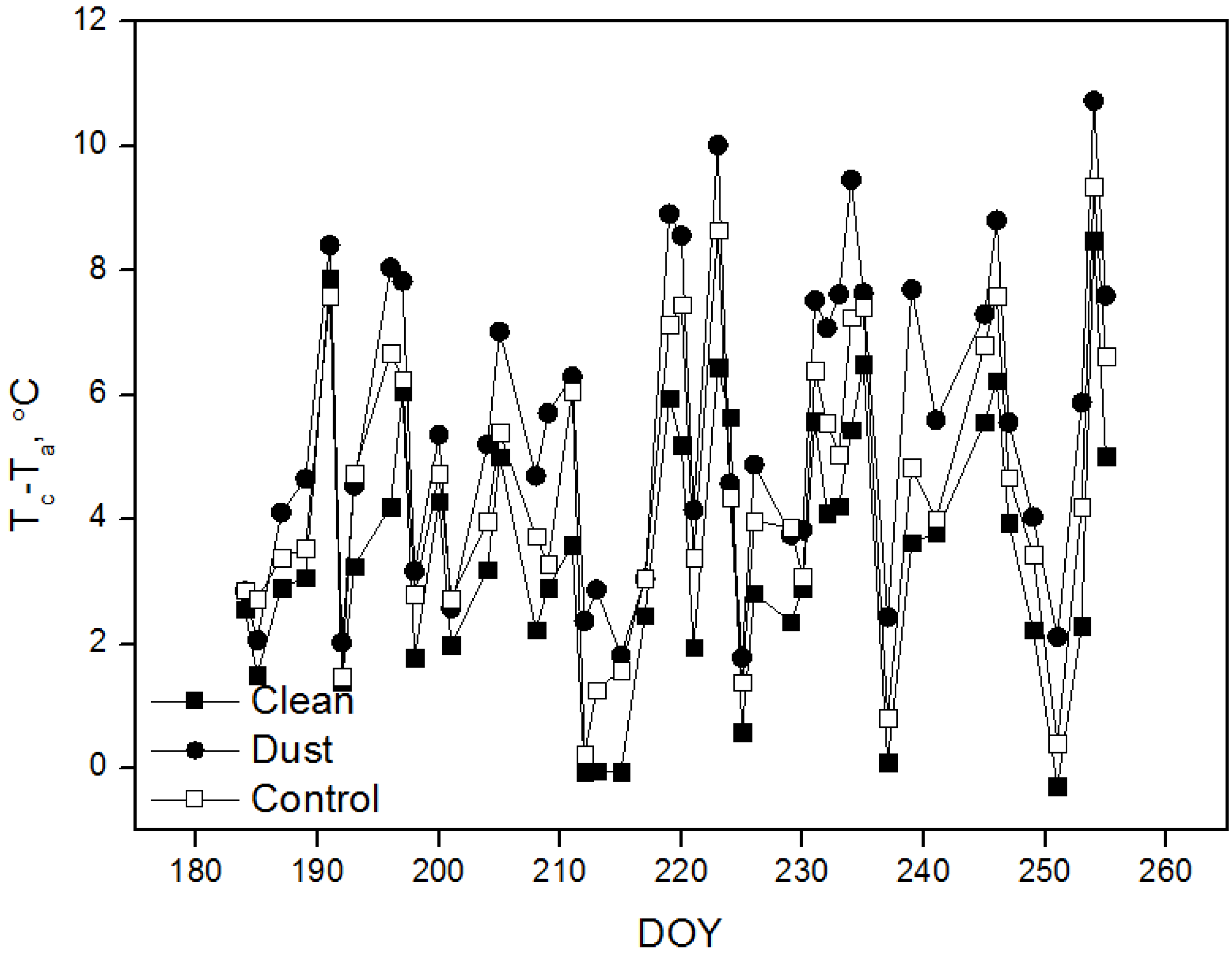
3.2. Canopy Temperature and Stomatal Conductance




3.3. Biomass and Yield

4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Abbreviation
| DSS | Dust and sand storms |
| Tc | Canopy temperature (°C) |
| Ta | Air temperature (°C) |
| gs | Stomatal conductance (mmole.m−2·s−1) |
| FC | Field capacity (m3·m−3) |
| PWP | Permanent wilting point (m3·m−3) |
| TAW | Total available water content (mm) |
| RAW | Readily available water content (mm) |
| Dp | Plant density |
| Cc | Capsule with cotton |
| Cwc | Capsule without cotton |
| Nsc | Capsules smaller than 2 cm |
| mc | Weight per capsule (g) |
| Nc | Average capsule number per cotton plant |
| Ycs | Cotton seed yield (t·ha−1) |
| ET0 | Potential evapotranspiration (mm) |
| DOY | Days of the year (days) |
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qian, W.; Tang, X.; Quan, L. Regional characteristics of dust storms in China. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4895–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Mamtimin, A.; He, Q.; Liu, X.; Huo, W. Observation of saltation activity at Tazhong area in Taklimakan Desert, China. J. Arid Land 2013, 5, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Tao, Z. Analysis on the climate characteristics of sandstorms in North Xinjiang. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2002, 38, 681–687. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, W.; Quan, L.; Shi, S. Variations of the dust storm in china and its climatic control. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2002, 15, 1216–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Abuduwaili, J.; Liu, D.W.; Wu, G.Y. Saline dust storms and their ecological impacts in arid regions. J. Arid Land 2010, 2, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Paul, C.; Li, S.; Pi, H. Ambient TSP concentration and dustfall variation in Urumqi, China. J. Arid Land 2014, 6, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Qu, J.; Zu, R.; Fang, H. Environmental characteristics of sandstrom of Minqin Oasis in china for recent 50 years. J. Environ. Sci. 2005, 17, 857–860. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, R.; Li, J. Decadal change of the spring dust storm in northwest China and the associated atmospheric circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A.; Lelieveld, J. Modeled global effects of airborne desert dust on air quality and premature mortality. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Oenema, O.; Hoogmoed, W.B.; Perdok, U.D.; Cai, D. Dust storm erosion and its impact on soil carbon and nitrogen losses in northern China. Catena 2006, 66, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleugh, H.A.; Miller, J.M.; Böhm, M. Direct mechanical effects of wind on crops. Agrofor. Syst. 1998, 41, 85–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbrust, D.V.; Retta, A. Wind and sandblast damage to growing vegetation. Ann. Arid Zone 2000, 39, 273–284. [Google Scholar]
- Prajapati, S.K. Ecological effect of airborne particulate matter on plants. Environ. Skept. Crit. 2002, 1, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Prajapati, S.K.; Tripathi, B.D. Seasonal variation of leaf dust accumulation and pigment content in plant species exposed to urban particulates pollution. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish, K.; Radin, J.W.; Turcotte, E.L.; Lu, Z.-M.; Zeiger, E. Enhanced photosynthesis and stomatal conductance of Pima cotton (Gossvpium harbadense L.) bred for increased yield. Plant Physiol. 1991, 97, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitron, O.; Zur, B. Differences in stomatal response within cotton canopy. Biotronic 1990, 19, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wijayratne, U.C.; Scoles-Scilla, S.J.; Defalco, L.A. Dust deposition effects on growth and physiology of the endangered Astragalus Jaegerianus (Fabaceae). Madroño 2009, 56, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, A.M. The effects of dust on vegetation—A review. Environ. Pollut. 1993, 79, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, R.K.; Prasad, S.; Rana, S.; Obaidullah, S.M.; Pandey, V.; Singh, H. Effect of dust load on the leaf attributes of the tree species growing along the roadside. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.N.; Rao, D.N. Certain responses of wheat plants to cement dust pollution. Environ. Pollut. Ser. A 1981, 24, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raajasubramanian, D.; Sundaramoorthy, P.; Baskaran, L.; Ganesh, S.K.; Chidambaram, A.L.A.; Jeganathan, M. Effect of cement dust pollution on germination and growth of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Int. Multidiscip. Res. J. 2011, 1, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Darley, E.F. Studies on the effect of cement-kiln dust on vegetation. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1966, 16, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, R.J.; Barron, J.C.; Papendick, R.; Williams, G.J. Impact on agriculture of the Mount St. Helens Eruptions. Science 1981, 211, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanos, G.D.; Ilias, F.I. Effects of inert dust on olive (Olea europaea L.) leaf physiological parameters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2007, 14, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, J.; Pandey, V.; Singh, S.N.; Yunus, M.; Singh, N.; Ahmad, K.J. Effect of cement dust on the growth and yield of Brassica campestris L. Environ. Pollut. 1990, 66, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.R.; Mueller, P.W.; Fliickigert, W.; Rutter, A.J. The effect of dust on photosynthesis and its significance for roadside plants. Environ. Pollut. Ser. A 1984, 34, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements—FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO—Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nation: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. The Notification of Cotton Yield Calculation. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China. (in Chinese). 2010. Available online: http://www.moa.gov.cn/govpublic/ZZYGLS/201008/t20100816_1619412.htm (accessed on 13 August 2014). [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, M.S.V.; Inamdar, J.A. Effect of cement kiln dust pollution on black gram (Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper). Proc. Plant Sci. 1990, 100, 435–443. [Google Scholar]
- Armbrust, D.V. Effect of particulates (dust) on cotton growth, photosynthesis, and respiration. Agron. J. 1986, 78, 1078–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasia, S.; Karwaria, A.; Gupta, D.A. Cement dust pollution and morphological attributes of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea), Kodinar, Gujrat, India. J. Environ. Sci. Toxicol. Food Technol. 2013, 4, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Quinones, M.A.; Zeiger, E. Abaxial and adaxial stomata from Pima cotton (Gossypium barbadense L.) differ in their pigment content and sensitivity to light quality. Plant Cell Environ. 1993, 16, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallas, J.E., Jr. An apparent anomaly in peanut leaf conductance. Plant Physiol. 1980, 65, 848–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T.; Kiyota, M.; Aiga, I. Physical effects of dust on leaf physiology of cucumber and kidney beans plants. Environ. Pollut. 1995, 89, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zia, S.; Du, W.; Spreer, W.; Spohrer, K.; He, X.; Müller, J. Assessing crop water stress of winter wheat by thermography under different irrigation regimes in North China Plain. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2012, 5, 24–34. [Google Scholar]
- Eller, B.M. Road dust induced increase of leaf temperature. Environ. Pollut. 1977, 13, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, S.; Romano, G.; Spreer, W.; Sanchez, C.; Cairns, J.; Araus, J.L.; Müller, J. Infrared thermal imaging as a rapid tool for identifying water-stress tolerant maize genotypes of different phenology. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2013, 199, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, R.M.; Gibson, A.C.; Rundel, P.W. Dust impacts on gas exchange in Mojave desert shrubs. J. Appl. Ecol. 1997, 34, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zia-Khan, S.; Spreer, W.; Pengnian, Y.; Zhao, X.; Othmanli, H.; He, X.; Müller, J. Effect of Dust Deposition on Stomatal Conductance and Leaf Temperature of Cotton in Northwest China. Water 2015, 7, 116-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7010116
Zia-Khan S, Spreer W, Pengnian Y, Zhao X, Othmanli H, He X, Müller J. Effect of Dust Deposition on Stomatal Conductance and Leaf Temperature of Cotton in Northwest China. Water. 2015; 7(1):116-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7010116
Chicago/Turabian StyleZia-Khan, Shamaila, Wolfram Spreer, Yang Pengnian, Xiaoning Zhao, Hussein Othmanli, Xiongkui He, and Joachim Müller. 2015. "Effect of Dust Deposition on Stomatal Conductance and Leaf Temperature of Cotton in Northwest China" Water 7, no. 1: 116-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7010116
APA StyleZia-Khan, S., Spreer, W., Pengnian, Y., Zhao, X., Othmanli, H., He, X., & Müller, J. (2015). Effect of Dust Deposition on Stomatal Conductance and Leaf Temperature of Cotton in Northwest China. Water, 7(1), 116-131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7010116







