Abstract
The San Francisco Bay (CA, USA) and the Tagus Estuary (Lisbon, Portugal) share striking similarities in terms of morphology and urban development. A finer analysis of development patterns reveals crucial differences in the extent of shoreline alteration and types of land use that now encroach upon natural estuarine habitat. Through historical map analysis and prior stratigraphic and historical research, we reconstruct in GIS environment the evolution of both estuaries over the last millennia and the relative distribution of different classes of land cover. We also discuss the legal frameworks that accompanied this evolution, and how they have influenced the process of wetland reclamation and landfilling. We compared the legal history and synchronous patterns of development by compiling historical mapping information and resorting to GIS analysis to explore spatial patterns over time. This method was useful in isolating events and decisions that were unique to each of the case studies. The Tagus Estuary has experienced disruption of natural environments for over two millennia. Yet, the State has been able to keep estuarine lowlands under public control, even if vast areas have been transformed into farmland. Public control could allow wetland migration with rising seas and restoration efforts. The San Francisco Bay was affected by several decades of elevated sediment loads in the 19th century, which induced rapid wetland expansion, but virtual cutoff of sediment supply by dams in the 20th century now impairs their ability to accrete. Meanwhile, tidal wetlands were subject to extremely fast and poorly regulated development. Artificially filled and/or drained wetlands were transferred to local governments and private landowners, in violation of the Public Trust Doctrine. The transformation of wetlands into salt ponds, industrial zones and even residential neighborhoods created extensive developed areas at or below sea level, which are vulnerable to even modest rises in sea level. Remaining wetlands are now heavily encroached on their landward side by urban development, which prevents their landward migration. Different legal interpretations of comparable definitions of public trusts and jurisdictions over shorelines may have significant implications for the ability to adapt to sea-level rise.
1. Introduction
The estuaries of the Sacramento River, California (San Francisco Bay) and of the Tagus River in Lisbon, Portugal share many commonalities in topography, hydrology, and climate. Both face threats from accelerated sea-level rise, but the exposure of urban areas to rising waters is significantly greater in San Francisco Bay than in the Tagus Estuary [1].
In this paper, we explore differences in the historical evolution of these two estuaries, and key divergences in the legal and institutional histories, such as the degree to which tidelands have historically been treated as public lands, how the “high-water” limits of public trust are defined, and how the public trust zone migrates as the coast erodes and the shoreline shifts landward. We argue that these differences can largely explain the contrasting situations in which the two estuaries find themselves as they confront sea level rise.
The San Francisco Bay, California (henceforth, SF Bay), is the largest estuary along the west coast of North America. The Tagus Estuary, Portugal (henceforth, the Tagus Estuary), is the largest estuary on the Atlantic coast of Europe. With an area of ~1260 km2, SF Bay is significantly larger than the Tagus Estuary, ~320 km2 [2,3]. Both provide critical wetlands habitat along major flyways and are crucial as nurseries replenishing fish stocks offshore [4,5,6,7]. Both SF Bay and the Tagus Estuary are surrounded by large metropolitan areas, with the San Francisco Bay Area being, with a population of about 7 million, the second largest metropolitan area on the Pacific coast of North America, and the Lisbon Metropolitan Area, with about 3 million inhabitants, being the largest urban center located directly on the Atlantic Coast of Europe (Figure 1, Table 1).
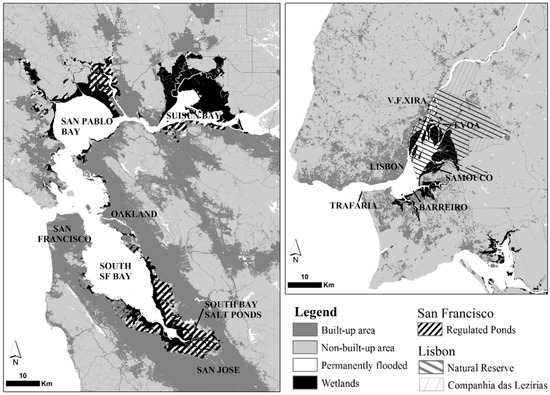
Figure 1.
Side-by-side context maps showing both estuaries at the same scale and locations mentioned in the text. Situation circa 2015.

Table 1.
Statistics for the SF Bay and Tagus Estuary.
Geomorphologically, both estuaries are “drowned valleys”, marked by alternating episodes of active incision during ice ages and marine transgression during warm periods [8]. Thanks to rock type and active tectonics, both estuaries have “bottlenecks” at their mouths, with wide inner basins and inland deltas. The Mediterranean-type climates of both estuaries result in large seasonal and inter-annual variability in precipitation and fresh water inputs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reconstruction and Mapping of Environmental Histories
We reconstructed the environmental histories of both estuaries, drawing upon primary sources such as historical maps and documents, and modern paleogeographic reconstructions (Table 2). We scanned, georeferenced, and processed map sources on GIS software (Esri ArcGIS 9.3, licensed through UC Berkeley) to delineate shorelines and identify (when possible) wetlands, urban areas and infrastructure. It is important to note that older map references (e.g., [9,10]) did not adhere to current standards in terms of their accuracy and projection. These sources provide important information (regarding the existence of more than one branch on the Tagus delta, for instance) but the delineation of the features therein should be regarded as an approximation. Therefore, the maps for 12,000 Y.B.P., 4000 Y.B.P. and 1000 Y.B.P. should be interpreted as well-informed approximations, rather than accurate depictions. As an example, the local processes of subsidence, tectonic activity and simultaneous SLR introduce an added level of complexity to the progressive flooding of the southern edge of the South San Francisco Bay that makes the reconstruction of the earliest time periods especially difficult. We have interpolated the best studies from both estuaries in an attempt to “fill the gaps” in the available information. The degree of certainty for more recent reconstructions is much higher, in keeping with more reliable and accurate maps and additional historiographical references.

Table 2.
Sources used for the reconstruction of environmental histories. Main sources for each reconstruction highlighted in bold, corresponding maps indicated in italics.
For San Francisco Bay, we analyzed historical maps [10,11,12,13,14,15], as well as landscape reconstructions [14,15], which provide valuable information on the status of the estuary before and at the onset of European settlement. We also drew upon reconstructions of past geography and bathymetry [6,16,17,18,19,20,21,22], which provided information on the patterns of post-glacial flooding of the estuary, and the emergence and expansion of wetlands. For the Tagus estuary, we analyzed prior studies of historical change and paleostratigraphy, especially the exceptional work of Vis [23] and others [24,25,26,27,28,29], and complemented them with the abundant information provided by historical maps [9,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39] and historical documentation of land-use [40,41,42,43]. We also consulted historical data [41,42,43] and studies of historical and modern distribution of wetlands [44,45,46,47]. Additionally, we combined map data [18,48,49,50] with the information on wetland distribution from the previous sources in mapping the current situation.
We assembled each reconstruction as a project in GIS software and retrieved the area of each of the following categories: “permanently flooded” (open waters of the estuary); “wetlands” (mudflats, shellfish beds, and saltmarsh); “drained for farmland” (the conjectural extent of former wetlands and permanently flooded areas converted into farmland); “diked ponds” (former wetlands and open waters that were diked for the creation of salt ponds); and “landfilled for urban development” (areas of landfill which were developed as industrial, commercial or residential areas or for large infrastructure—such as ports, airports, highways and rail corridors, refuse disposal). From these values, we created chronograms tracing the relative percentage of each category in relation to the maximum extent of estuarine lands before disturbance (corresponding roughly to the extent of permanently submerged areas and wetlands for the ~4000 Y.B.P. scenario). All values and percentages presented in Section 3.1 are in reference to this historical maximum.
2.2. Analysis of Planning Literature and Legal Documents
We reviewed past and current legal standards, contained in laws and planning documents, and compared them with historical land-use changes. This allowed for a critical analysis of the historical adherence to planning standards and the actual outcomes in terms of land-use changes, especially regarding reclamation, expansion of landfills and shoreline development. For historical law doctrines and standards, our main sources for the Tagus Estuary were Beirante [41], which lists a number of precedent-setting court decisions predating the mid-1800s Portuguese Civil Code (including [60]), and Cândido de Pinho [61] which makes an overview of the legal standards associated with the protection of the Public Domain. For more recent standards for the definition of the Public Domain and delimitation of the high water line used in its definition, we referred to Rilo [62] and the recent Water Law [63]. The latter also provides indication of the current doctrine regarding erosion and avulsion. The new Tagus Estuary Management Plan’s regulation and objectives were consulted [3,64], and the analysis was complemented by recent news regarding environmental standards and enforcement of Public Domain law [65,66]. For the SF Bay, we consulted references on the Public Trust Doctrine [67,68,69,70,71,72,73] and complementary information on the doctrine regarding erosion and avulsion [74,75,76,77]. We also analyzed documents regarding the specific institutional and legal arrangements around the San Francisco Bay [78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85].
We use a novel approach, combining historical/stratigraphic reconstructions with the analysis of the legal and planning frameworks over which the alteration of both estuaries took place. Equally, the compilation of the best-available map resources for each of the systems provides a continuous sequence that allows for a clear interpretation of historic evolution patterns.
Both estuaries, sharing similar geomorphological determinants, experienced comparable natural processes before human disturbance, and would likely have continued to evolve along parallel tracks without human alterations to the catchments and estuarine shorelines. Recognizing this, it was further possible to interpret the evolution of one system by using the other as a reference, and therefore better isolate natural and artificial processes affecting each system at each timeframe. This allowed us to “fill in the blanks” regarding processes which were not sufficiently studied in one system with conscientiously selected information from another.
By generating maps that represent the same types of land-use at the same scale and over each of the time intervals, it is finally possible to compare and infer similarities and disparities over the way each estuary evolved, allowing us to isolate possible triggers, in both natural and anthropic processes.
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Histories of the Estuaries
3.1.1. The Tagus Estuary
The Tagus Estuary was created after the end of the last glacial period, when the rising sea level drowned the lower Tagus River valley [23,24]. After being drowned by the rapid post-glacial sea level rise, the inland delta of the Tagus grew through sediment deposition, and sediment further accreted along the margins of the estuary, allowing the establishment of tidal wetlands.
The evolution of wetlands and settlement around the Tagus estuary was one marked by repeated cycles of reclamation of the coastal prairie that formed behind the advancing (“prograding”) pro-delta, situated at the upstream section of the estuary; as the frontline of mudflats and saltmarsh accreted and moved downstream, it created behind it a large floodplain of fertile soils, which were seized and used for agriculture by all the successive civilizations that controlled it, from the Romans to the Visigoths, on to the Moors and, eventually, the Portuguese. This special kind of low-land, reclaimed farmland, traditionally protected by low walls or stakes, along the lower Tagus valley, is called the “lezíria”. The term derives from the Arabic “al-jazīrah”, meaning island, and originally referred to depositional islands, point bars, and tidal flats along the river channel. Later, it came to be synonymous with the alluvial plain as a whole.
Although accurate descriptions of the estuary are lacking before formation of the Kingdom of Portugal in the mid-12th century, some documents hint that there was already a practice of draining the “lezírias” for farmlands before then [27,41]. The modification of the watershed and virtual extirpation of primeval forests was completed before the end of the Middle Ages [25,26], resulting in greater influx of sediment into the estuary, which likely accelerated the rate of wetland expansion and extent of potential “lezírias” farmland (Figure 2c).
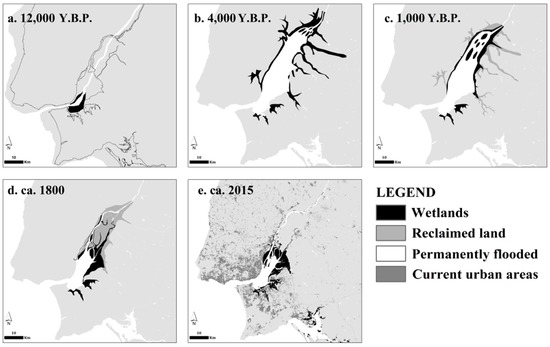
Figure 2.
Environmental history of the Tagus Estuary: (a) situation of the narrow estuary ~12,000 Years Before Present (Y.B.P.), following the Last Glacial Maximum; after the rate of SLR stabilized, the estuary began to fill and wetlands were finally able to establish more permanently on sheltered portions of the estuary. By (b) ~4000 Y.B.P., after a few centuries of expansion, wetlands rimmed narrowly the upstream sections and an expanding delta; (c) ~1000 Y.B.P., after at least one millennium of settlement around the estuary and along the basin, increased sediment inflow fed the prograding delta, with reclamation already occurring along tributaries and margins on the upper delta; (d) ca. 1800 most of the reclamation of the delta and consolidation of the “lezírias” was complete, but the river still displayed remnants of its former anastomosing delta; (e) Current situation. Wetlands are now mostly confined to the widened middle section of the estuary, and the remnant river branches have been transformed into regulated irrigation channels. Urbanization and infrastructure has taken over most of the right bank along Lisbon, Oeiras, and some south bank municipalities. Along the eastern edge of the estuary, the largest expanse of mudflats and marshes is set against farmland, with very limited urban development. The South Bank hosts small but important marshes, heavily encroached by urban development.
The Tagus went through periods of avulsion of the main channel (natural process through which the river abandons a channel and switches to another) and, by the late middle ages, there were at least three channels running parallel, with two of those preserved as navigation canals running parallel to the main course. Historic names for branches, or arms, in the lower Tagus—“Tejo Novo” (New Tagus), “Tejo Velho” (Old Tagus), “Tejinho” (Little Tagus)—indicate that its anastomosing nature lasted until relatively recently [28,41] and this is reproduced in some historic maps. No defined main arm is indicated on the map of Seco [9], and the “Old Tagus” is identified in maps as late as the 18th century [31,32,35], which still display natural arms of the river running into what is now the Lezíria Grande island, and showing that there was at least partial retention of some wetland habitat along the margins of those channels (Figure 2d).
Historical records [41,42] indicate that expansion of farmland through land reclamation was done through cycles of great commitment, usually encouraged by more enterprising kings (more land reclaimed, and greater yields from farming them, equaled more taxes). These periods of intense reclamation followed others of relatively lax central power and/or lack of workers and funds (periods of war, “bad” kings…), during which flood defenses fell into disrepair. Changes to the estuary’s hydrology due to deforestation, avulsion of the river’s channels during floods, or fluctuations in sea level and storminess during the Medieval Warm Period and the Little Ice Age, also contributed decisively to fluctuations on the rates of wetland expansion and reclamation. Protecting farmland against floods and high tides required the construction and constant maintenance of protective walls, and insuring the navigability of the river, was a constant struggle [28].
The most extensive efforts of landfilling for infrastructure, rather than farming, were related to the expansion of the Port along Lisbon municipality’s waterfront, between the last couple of decades of the 19th century and the first three decades of the 20th century [64,86,87]. In total, some 397 hectares (ha) of fill were created along the already urbanized waterfront, mostly within the Lisbon municipality. In the mid-20th century, some areas in the south bank of the estuary were landfilled for the expansion of large industrial units and port areas (notably the Quimiparque grounds, in Barreiro, the Lisnave shipyards and Alfeite naval base, in Almada, and the Siderurgia Nacional complex, in Seixal) but together these areas amounted to only about 236 ha. A further 36.8 ha of localized expansions to pre-existent port areas were added in the first decade of the 21st century. In total, landfilling for purposes other than farming was less than 670 ha. Industrial areas and large infrastructure occupy virtually all these areas, with only negligible residential and commercial development.
A 1950s plan to create a large dyke and bridge between Lisbon and Montijo would have presupposed the reclamation of as much as 8000 ha of marsh and mudflats for the expansion of the irrigation project (as discussed in more detail below). Fortunately, the project was postponed and definitively abandoned for environmental reasons in the 1970s [5].
Since the mid-20th century, dams along the mainstem Tagus and on tributaries (in Spain and Portugal) have extirpated anadromous fish runs of more sensitive species [88], significantly reduced the inflow of fresh water into the lower estuary, and have dramatically affected the sediment loads to as little as 1/3 of its prior level [89]. Nevertheless, the Estuary still appears to have a positive sediment balance, with progradation rates of around 1.1 cm/year [5]. Studies conducted on the Estuary’s marshes estimate that the current sedimentation rates (4–27 mm/year, depending on the location) will allow wetland accretion to keep pace with the rates of sea-level rise predicted for the end of the 21st century [58,90,91].
The estuary’s water quality was severely compromised by untreated industrial and sewage effluent, with severe impacts on the estuarine ecosystem [5,92]. At the turn of the 21st century, the situation improved substantially: the closing down of major industries and a major program to introduce primary and secondary sewage treatment along the Tagus river basin, spurred after Portugal and Spain’s accession to the EU in 1986, resulted in a steady improvement in water quality, increased fish stocks, and the return of some sensitive species [5,43,58].
3.1.2. The San Francisco Bay
During Pleistocene time, what is now San Francisco Bay was an alluvial plain, across which flowed the lower Sacramento River, joined by its many tributaries. The rapid rise in sea level after glacial melting led to the flooding of SF Bay, reaching approximately its current extent ~5000 Years Before Present (Y.B.P.) [16], and slowing to a rate of about 20 cm/century. The estuary began slowly filling with sediment (from tributaries and the mainstem Sacramento), resulting in the fixation and slow expansion of wetlands from around 4700 Y.B.P. [51,53] (Figure 3b,c) with a slightly accelerated expansion during the Little Ice Age (ca. 1550 to ca. 1850) [54] (Figure 3d) due to land cover changes in the watershed [14,15].
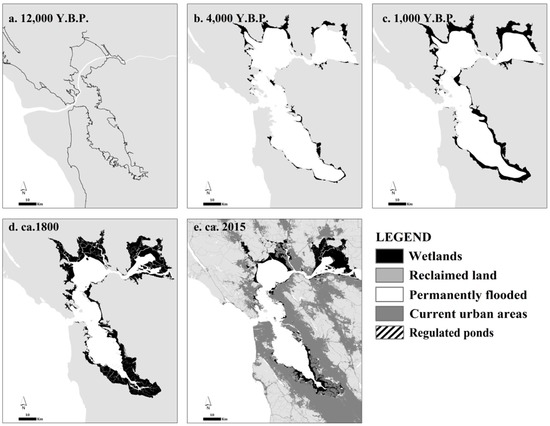
Figure 3.
Environmental history of the San Francisco Bay: (a) Around 12,000 Years before Present (Y.B.P.), with sea-level much lower than present, the narrow river channel emptied into the ocean near the Farallones Islands; In the following millennia, the Bay was flooded with rates of SLR of about 2 cm/year. Around 5000–4700 Y.B.P., following a ten-fold drop in the rate of SLR, wetlands were able to establish more permanently on sheltered sections of the estuary and, by (b) ~4000 Y.B.P., wetlands occupied sheltered and sediment-rich edges; (c) ~1000 Y.B.P., early human activity around the Bay and the Central Valley have influenced sediment input, but the pattern of slow accretion and expansion of wetlands persists; (d) ca. 1800, grazing and changes to land cover upstream accelerate sediment deposition and wetlands expand rapidly; (e) Current situation. After one century marked by much-accelerated deposition due to hydraulic mining, wetlands expand in the mid-1800s, only to be transformed along their edges into farmland, salt ponds, and urban areas. Especially along the South Bay and on the north edge of San Pablo Bay, vast areas remain diked to this day, but recent restoration efforts are converting most of the former salt ponds into restored wetlands. Just upland from these ponds and remaining marshes, most of the farmland has been developed into commerce, industry, housing and infrastructure, encroaching upon most wetlands.
Around the time the first European settled around the San Francisco Bay, after 1769, the Bay was still a largely undisturbed natural environment. The few thousands of Ohlone Native Americans that had long lived around the Bay introduced changes to land cover, from controlled burnings and selective clearing, but likely had minimal impacts over the environmental performance of the larger estuarine ecosystems [6]. For the most part, the natural assemblage of mudflats/low marsh/high marsh/coastal prairie was still present by the time of the first surveys [18] and features prominently in some early maps of the Bay [10,11,13]. The coastal prairie extending just above the highest tides offered fertile alluvial soils just high enough above the saltwater to allow cultivation, and was the first victim of large-scale settlement. This fringe of the ecotone, rare as it is around SF Bay, has likely been absent from the Tagus Estuary throughout historical times.
Encouraged by policies promoting the draining and filling of wetlands for agriculture, vast areas of tidal wetland were dyked and drained for farmland, from the 1850s onwards. From the late 1800s through the 1930s, vast areas of salt ponds were created at the expense of tidal marshes, with the largest salt-producing company, Leslie Salt, still owning over 21,000 ha of Baylands as late as the mid-70s [6,79]. This was followed by extensive landfilling for large infrastructure, ports, industrial areas, and even residential neighborhoods, such that over 90% of the Bay’s pristine tidal saltmarshes had been lost to dredging and landfilling by 1965 [18,93,94]. The process of reclamation was made easier by parallel changes set off by the introduction of hydraulic mining in the Sierra Nevada (~1852–1884). This practice increased sediment loads of the Sacramento River ten-fold [19,21,51], causing rapid accretion of the shorelines and shallowing of the estuary, making it easier to dredge and landfill vast areas of the Bay’s shorelines. Taking advantage of the deposition of the hydraulic mining sediment and resultant shallowing, the rates of artificial landfill were ~414 hectares/year between 1850 and 1900, ~622 ha/year between 1900 and 1925, ~751 ha/year between 1925 and 1940, reaching a high of 914 ha/year from 1940 to 1965 (as estimated by Swanson [56]), before reclamation was effectively halted in 1965.
Well upstream from SF Bay, extensive construction of dams and water diversions in the Sacramento River basin from the 1920s through the 1970s resulted in reductions in fresh water inflows to SF Bay, blocked migration of anadromous fish, and trapped most of the natural sediment load before reaching SF Bay [6]. From an estimated peak of about 10 million tons/year (Mt/year) in the 19th Century, sediment loads reaching the estuary have dropped to as little 1–1.2 Mt/year today, and sediment yields may have fallen below pre-disturbance levels. Now that most of the hydraulic mining debris has likely been flushed from the system, local catchments draining directly to SF Bay may currently deliver more sediment to the SF Bay than the entire Sacramento-San Joaquin system [51]. If we consider the accelerated rates of SLR expected for the next centuries, the survivability of marshes could be in jeopardy [54,95], as their ability to keep pace with SLR through accretion is largely dependent on the suspended sediment load [96,97].
In the late 19th and 20th centuries, the Bay became heavily polluted by discharge of untreated industrial and municipal sewage until the closure of many bayside industries and extensive construction of wastewater treatment plants following passage of the state’s Porter Cologne Act of 1969 and the federal Clean Water Act of 1972 [6]. After the enactment of the McAteer-Petris Act of 1965 (see next section), landfilling was halted. Wetland restoration efforts have ensued and, especially since the implementation of Bay-wide ecosystem restoration targets [18], the purchase and restoration of several salt ponds has allowed for a steady increase in the provision of habitat [18,57,93,94,98] that culminated in the ongoing South Bay Salt Ponds Restoration Project [99].
3.1.3. Comparison
To compare the relative percentage of estuarine lowlands taken up by each class of land-use, we use as a baseline benchmark the conjectural maximum extent of estuarine lowlands. This corresponds roughly to the situation of each estuary at ~4000 Y.B.P., considering the total extent of open waters and wetlands. Therefore, all values presented ahead are given as a percentage of this maximum extent for each of the estuaries.
Setting side-by-side the chronograms tracking the evolution of both estuaries, in terms of the relative percentage of each main category of land cover (Figure 4), it is apparent that the Tagus Estuary has experienced a much longer process of anthropogenic disruption, and its smaller size lent itself to faster infilling. Therefore, the net loss in open water surface was much greater in the Tagus than in SF Bay, which remained largely undisturbed until a couple of centuries ago. Compared to its reconstructed maximum, open waters in the Tagus Estuary have shrunk to about 27.8% of its mid-Holocene maximum, with most of the loss being attributable to millennia of progradation and consolidation of farmlands before the 1800s. SF Bay experienced an equally slow process of natural progradation, which led to the creation of extensive wetlands around its edges. Yet, about half of SF Bay’s maximum extent is still permanently flooded.
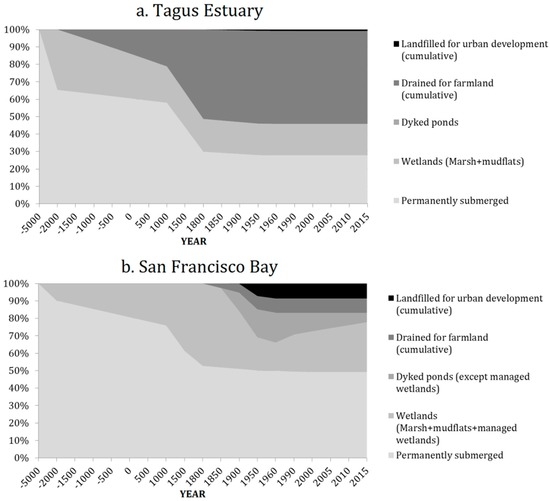
Figure 4.
Chronograms tracing the evolution of land cover in estuarine low lands of (a) the Tagus Estuary; and (b) the San Francisco Bay (relative % of total estuarine lowland).
The San Francisco Bay experienced a mostly undisturbed natural process of progradation from around 4700 BP. with a slow expansion of wetlands and parallel reduction of permanently submerged area. This natural trend accelerated or slowed down through a series of loops and feed-backs between regional trends in rainfall and smaller fluctuations in global sea-level [54]. With the arrival of European settlers, in the mid-1800s, the expansion of wetlands is believed to have accelerated with the increased sediment deposition, first from increased erosion and sediment yield caused by land clearance in the catchment from the 18th century onwards, then especially during the period of hydraulic mining in the late 1800s [21]. After a steady increase in total area of tidal wetlands, reaching a maximum of around 994 km2 (about 47% of the total estuarine area), the subsequent landfilling and draining led to a very rapid decrease to ~700 km2 (~33%) around the turn of 20th century and as little as ~340 km2 (~16%) by the mid-1960s. After early experiments in wetland restoration, large efforts in restoration, focusing especially in the reversion of salt ponds into managed wetlands, have increased significantly the total provision of tidal or managed wetland provision around the Bay, from the 1960s low-point to about ~475 km2 (22.6%) in 1998 and nearly 600 km2 today if ongoing restoration efforts are included, close to the Goals Project target of about 615 km2 [18].
One aspect of the type of transformation experienced by both estuaries is that the level of landfilling for what could be considered as “permanent” uses, that is, urban development, has been at least an order of magnitude greater in SF Bay than in the Tagus Estuary. While the Tagus lowlands have been extensively altered, former estuarine lowlands lost specifically to urban development stand now at just about 0.8% of the total, whereas up to 8.6% of the former San Francisco Bay lowlands have been transformed into urban areas. As we will discuss ahead, this aspect will undoubtedly bear over the selection of alternative land use policy and planning options.
3.2. Legal Context
Besides the obvious disparities in the timelines of human alteration, the differences in tidal wetland conversion and lowland urbanization patterns between Lisbon and San Francisco estuaries can be also attributed to their diverse legal traditions and contexts, as we analyze ahead.
3.2.1. Lisbon and Portuguese Law
Grounded on a legal tradition that can be traced back to at least the 6th century with the Justinian Code, navigable waterways (and, to a lesser extent, their margins) have enjoyed legal protection under the assumption that they should be preserved for the common good. Although not always explicitly stated, for most of history this was used as a mechanism to ensure the Crown or the State’s ability to control, and tax, waterborne commerce and fishing.
The doctrine regarding erosion and avulsion may be equally old. Once the river experienced avulsion, typically during larger flood events, abandoned channels or islands suddenly connected to the margins. In times when the centralized power was weakened, local municipalities, religious orders, or even neighboring landlords would often seize the newly-created land. There is ample documental evidence of the efforts made by several kings in asserting their ownership over those lands, the “lezírias”, and Beirante [41] argues that this struggle marked a defining moment in the affirmation of centralized power in the early centuries of the Kingdom of Portugal.
The long-standing tradition of preserving a fringe of wetland is consistent with the practice of reserving all land below “the January High Waters” for the Crown (that is, in Public Domain), a measure grounded on the old Roman tradition of a public trust protecting all navigable waters and floodplains [61], up to the highest “winter flood”.
Major reclamation efforts would traditionally follow either major flood events or periods of abandonment. Faced with the Crown’s inability to single-handedly restore all productive land, the king would often stimulate the rebuilding of flood defenses and retaining walls by granting temporary deeds to those willing to drain, defend, and farm the land. From the omnipresence of references to “swamps”, “beaches”, and “wastelands” throughout historic documentation, it is clear that, even during the periodic spurts of reclamation, a fringe of lower marsh was present. As elsewhere in Europe, the navigable waters and shorelines constituted public trust owned by the Crown, and unwarranted alteration or appropriation by private citizens was often the subject of legal action and generally forbidden.
One particular document, from the early 15th century, is most enlightening in this respect and indeed produced jurisprudence that carried into present-day Portuguese law. King John I (1385–1433) had been, in the first decades of his reign, particularly active in asserting his right to all swamps and “lezírias”. At first, he resorted to the traditional Visigoth concept through which “terras ermas” (wastelands or abandoned lands) belonged to the Crown. In 1410, however, the King successfully argued in the Crown’s Court that a landlord had illegally occupied land (a beach located on the banks of the Estuary) that was his by right resorting to a novel legal mechanism: the river and its banks were both “public in nature” and that the property (the beach) was once “lezíria” and all “lezírias” were his by right [41,60]. The doctrine invoked by the Court to rule for the King explicitly stated that since the property was fully covered with water in January (that is, during the largest floods), and only dry during the summer, it indeed belonged to the Crown’s Estate. That Court’s decision established precedent on two crucial aspects: (1) river banks subject to flooding were to be included in the Crown’s Estate as part of the “Jus Publicum”; (2) for that purpose, the highest elevation of floods was to be considered—the “January high waters”. This decision restored into common doctrine the old Roman tradition of “Public Right” (“Jus Publicum”) to flood-prone beds and banks.
Through different legal ordinations, these standards were preserved and, according to the fluctuations in the effectiveness and power of the central administration, more or less upheld. Eventually, these “Jus Publicum” (corresponding roughly to the American concept of Public Trust) determinations were codified into the modern civil code (Código Civil), through the Royal Decree of 31 December 1864, which clarified that the trust extended over all shores subject to inundation at spring-high tide. The “Domínio Público”, or Public Domain, as this doctrine came to be known in Portugal, was equally expanded so as to include a 50 m buffer inland from this high-water mark in coastal waters. Only deeds predating the creation of the Law would be permitted and all new construction or land use transformation would be severely conditioned.
The expanded jurisdiction over margins was quite innovative at the time (1864) and remains one of the most generous in Europe [89]. In the subsequent 150 years, the Public Domain has remained a staple of Portuguese land law and is to this day one of the country’s strongest mechanisms for the protection of coastal resources, the preservation of wetlands, and maintaining public access to the country’s shorelines.
Some 30 years before the 1864 Decree, the “Companhia das Lezírias”, then a private society, had been created to manage the farmlands belonging to the Crown Prince. The model of public-led management of the bulk of farmland located on the alluvial plain persists to this day and, coupled with the preservation of the Public Domain, has largely prevented extensive urbanization of these productive agricultural lands.
In the last three decades, environmental law has been refined and expanded to increase the level of protection granted to natural systems. Wetlands and all floodplains have been explicitly protected under the National Ecological Reserve since 1983 [100], but coastal wetlands were, by definition, already included in the Public Domain. Further expansion of the protective buffer inland from the domanial waters came with the Water Law of 2005 [63] which matured from earlier legislation the concept of “adjacent zones” in flood-prone or sensitive areas, extending a limited planning mandate over all land considered as vulnerable to flooding from river or sea waters. In the specific instance of waters under tidal influence, as is the case with the Tagus Estuary, the effects of wave run-up are also to be considered as forcing factors when defining the “highest astronomical tide line” (HAT) that serves as the upper limit for the “bed” (Figure 5). In the case of the Tagus Estuary, the Governmental Decree authorizing the Environmental Agency to produce the new Estuary Management Plan [3], also established (according to the concept of “adjacent zones”) a planning mandate for a 500 m transition zone inland from the upper limit of the Public Domain, in addition to the 50 m-wide “margin”. Furthermore, the national law [63] establishes that “land lost to the sea” through erosion is to be automatically incorporated into the Public Domain, and the adjoining buffers realigned according to the new shoreline.
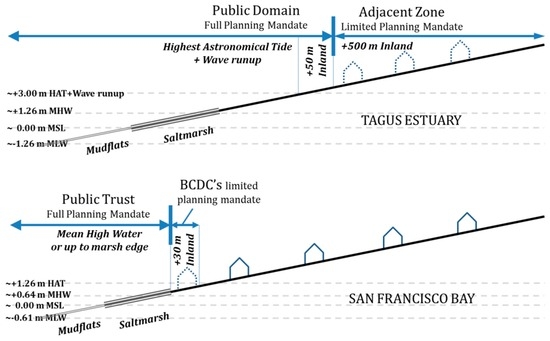
Figure 5.
Definition of Public Trust/Public Domain and additional planning mandates in the Tagus Estuary and the San Francisco Bay.
3.2.2. San Francisco and United States Law
The United States inherited several fundamental doctrines dating back to Medieval English Common Law. Among these is the doctrine that preserves the “Jus Publicum” (the “Public Right”) over navigable waters and flood-prone banks and shorelines. They are “held in trust” by the State, hence its modern denomination as the Public Trust Doctrine. It corresponds to the British concept of Foreshore, trusted to the Crown’s Estate [73].
The Common Law dispositions are themselves distant derivatives of much older doctrines, and in particular the same Roman Justinian Laws, themselves derived from yet older legal codes [71,101]. The aim of this doctrine, as in Portugal, was to preserve natural resources for the common good (albeit through the upholding of the monarch’s right to control and tax all uses and foreshore concessions). The letter of the law includes, for most countries with a Common Law tradition, a variation of the notion that all navigable waters and lands that are subject to regular flooding (that is, those located below the high water line) are to be preserved for the public [67,68,69,101,102]. So, in essence, this is a similar concept to that of the tradition of most European countries, of which the Portuguese Law is an example.
The peculiarities of its practical application, however, derive from the early decision of the American legislature to grant this Trust onto the States, which in turn led to significant differences between different States’ interpretation and jurisprudence. The Federal Arkansas Swamp Lands Grant Act (1850) made appropriations of “swamp and overflowed” lands a prerogative of the individual states. California promoted draining and filling of wetlands for agriculture, as a way of attracting settlers to the newly-created State. Importantly, it granted full property titles, rather than temporary concessions, over reclaimed land. This interpretation would later be determined to be in violation of the prerogatives of the Public Trust, over a century later, as will be discussed further ahead. Between 1855 and 1909, “land” (more often than not, marshes subject to twice-daily flooding) was sold at auctions for as cheap as $1 per acre [79]. The extent of this state support for wetland draining and landfilling is reflected in the Reclamation Map of 1874, showing all wetlands and most shallow flats as subject to reclamation [13,103], and even in a 1959 US Army Corps map that showed all shallow waters as potential landfill [59] (Figure 6).
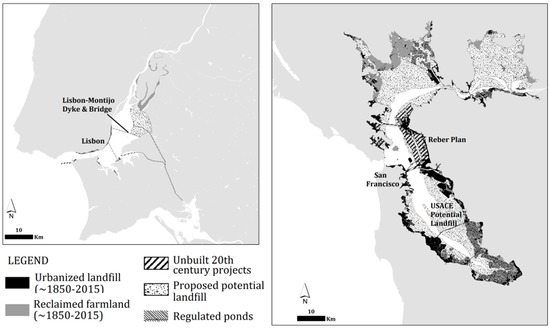
Figure 6.
Urbanized landfill, reclaimed farmland, and cancelled projects (between ~1850 and ~2000) in the Tagus Estuary and San Francisco Bay.
Another state prerogative was the definition of the landward limit of the Trust. In shorelines subject to tidal action, the definition of the “high water”, which is crucial in bounding the upper limits of the Trust, is defined by most US States (including California) by the high water mark [101]. For most purposes, the Mean High Water (MHW) is considered. It corresponds to the average of all high tides of each tidal day during an 18.6-year Astronomical Cycle. This is much lower than the high water mark considered for the Portuguese Public Domain, which extends up to a higher elevation and thus further inland (Figure 5).
The American legal context is more favorable towards the upholding of individual property rights over common good interests than is the case in most of Europe, so the expansion of planning mandates and the upgrading of environmental law and planning standards has proved more difficult in the US. This is especially true whenever these new provisions would entail restrictions to the use of private property. In the absence of a consistent evolution of planning and environmental law to adjust to changing social paradigms and expectations, as was mostly the case in countries belonging to the European Union [104], the Public Trust Doctrine has been used as a proxy for strong environmental legislation. Especially since the 1970s, it has served as a legal loophole of sorts in natural resources preservation [67]. This has led to some criticism over the unnatural expansion of its scope well beyond the common resources it initially aimed to protect. The Public Trust Doctrine has been invoked in cases involving cemeteries, air resources, or in implementing a State’s hazardous waste control legislation [68] to the point where it became almost a moniker for public interest in the protection of natural resources.
The dramatic alteration from natural shorelines to landfilled and dredged urbanized waterfronts, culminating with the threat to completely fill SF Bay as envisioned in the Reber Plan [105], had a deep impact on the public and institutions in the SF Bay region. The multi-decade pet-project of John Reber, the Plan proposed to fill-in SF Bay, except for a narrow ship canal. After garnering widespread attention in the early 1940s, the project was subject to more scrutiny. Ensuing “potential landfill” studies by the US Army Corps [56,59], conducted during the late 1950s and early 1960s, revealed the extent of its environmental impacts and shocked many into realizing that such a large and iconic ecosystem could come under real risk as a result of reckless development decisions (Figure 6). Grassroots movements garnered support for the McAteer-Petris Act, passed by the California legislature in 1965 [106]. It led to the creation of the San Francisco Bay Conservation and Development Commission (BCDC), the first coastal zone management agency in the United States [56]. BCDC was tasked with the elaboration of the Bay Plan, and gave it full planning powers over areas subject to tidal action (mean high water or, in tidal marshlands, the inland edge of marsh vegetation up to five feet above Mean Sea Level). In practice, it was extremely effective in curtailing all major efforts of wetland “reclamation” [78], and it reasserted the State’s right to protect all lands included in its Public Trust. An additional 100 feet (~30 m) buffer extending landward from the high water line was included in BCDC’s jurisdiction (Figure 5), but with no planning mandate other than the ability to impose public access to the shores. Therefore, the Commission has a very limited capacity to prevent new development proposed just above the high water [70].
Paradoxically, the aforementioned extension of litigation over the Public Trust Doctrine well beyond its original scope has led to a legal backlash (already foreseen by Lazarus [68]): while recently amending the Bay Plan (2009), the BCDC was confronted with resistance from developers and local governments in asserting its right to manage tidal lands [85]. BCDC had to assert that their mandate extended over Bay shorelines up to the limit of the Public Trust, the MHW, and therefore encompassed all tidal lands [69,107]. This added difficulty in expanding mandates and jurisdictions of public agencies is by no means new, and has been a recurring problem for SF Bay Area planners [70,82]. Given the difficulty in ensuring their current mandate is respected and acknowledged, an expansion of its planning mandates to incorporate meaningful buffers upland from this limit is unlikely, and would be prone to intense litigation.
Nevertheless, being that the Doctrine is tied to a concept of “high water line”, rather than an actual demarcation, it is now perceived as a plausible mechanism of SLR adaptation. Once coupled with another ancient doctrine regarding erosion and avulsion [76,77,102], it would theoretically permit a migration of the upper limits of the Public Trust (and associated jurisdictions) with rising sea levels. This is sometimes called a “rolling easement” [102,108] and provides a solid legal basis for BCDC to invoke the “ambulatory nature” of its jurisdiction [69].
4. Discussion
4.1. Property and Land Use in Estuarine Lowlands
The King’s Lands were, in the specific case of the Tagus Estuary, granted to the Crown Prince’s Estate, and remained so throughout the Middle Ages, and up until 1836. The unified “Herdade do Infantado” (Prince’s Estate) was then sold off to a single corporation, the “Companhia das Lezírias”. Albeit promoting new irrigation projects and completing the draining of the Lezíria Grande (the large island that was created through the consolidation and unification of several former delta islands), the “Companhia das Lezírias” kept is focus on agriculture and grazing. Nationalized again in the 1970s, this public company manages to this day the farming on the delta, and several species have adapted to forage or shelter in the farmlands. Most of the land remains in public ownership and transmission of full property rights was limited. It remained so until the introduction of modern legislation specifically protecting the best soils and floodplains. The result was that most of the lowlands around the estuary remained construction-free, first through the Crown’s preference to promote profitable farmlands—aided by the frequent reminders, through major flood events, of the active nature of the floodplain—then through legislation specifically protecting the wetlands and farmland.
Around SF Bay, the Arkansas Act of 1850 was used by the State as a means to promote extensive draining and landfilling. Until the early 20th century, the titles to the “lands” were sold in auction, and the buyers were granted full ownership of the land. This was justified based on the need to create new farmland and attract settlers. Later, through the transmission to local city governments, the situation went from bad to worse. While initially this transference was destined to promote infrastructure improvements, most cities were unable to resist the profitability inherent to the transformation of wetland to “fastland”, resulting in as much as a 75-fold increase in land value [79]. Vast areas of former tidal lands were therefore transferred to private landowners, a practice that is clearly at odds with the principles of the Public Trust Doctrine [80,81] and, as a consequence, the first half of the 20th century saw large expanses of former wetlands transformed into salt ponds, industrial land, large infrastructure and, eventually, even residential areas.
4.2. Environmental Protection Standards and the Concept of “High Water Line”
Around the Tagus, a Roman doctrine regarding the protection of public waters has been enforced, with varying degrees of effectiveness, since the first half of the first millennium. It was upheld through a sequence of legal disputes, in the first centuries of Portuguese nationality (12th–15th century) and was clarified during the reign of King John I, with the 1410 Crown Court’s ruling [60] that reasserted the Crown’s right to all lands subject to regular flooding by the “January High Waters”, which in essence were interpreted as the “highest floods of the year”. This standard would later be adapted so as to translate into today’s Portuguese standard for coastal waters, which is the “Highest Astronomical Tide Line” (HAT) [62]. This corresponds to the exceptional elevation of waters during the Equinoctial Spring Tides, that is, the largest tides of the year.
In contrast, the same Roman legal code, when transferred into English Common Law and later into US law, did so with several important distinctions. The most relevant of which would be the interpretation of the “High Water Line”, which delimits the Public Trust. Already present in British legal standards (with the exception of Scotland, which upholds the higher Mean High Water Spring standard), the High Water is considered in most US states, including California, to correspond to the Mean High Water (MHW) in coastal regions. MHW corresponds to an averaging over an 18.6-year lunar cycle of all the high tides of each day.
The subtle distinction between adopting an “average” high tide or an “exceptional” high tide has important implications over the level of protection granted to coastal wetlands and the ability to prevent development in very low-lying land. As an example, the Mean High Water in Lisbon is ~0.86 m below the Highest Astronomical Tide (HAT) standard [109]. Such a difference in elevation can extend dozens of meters across flat shorelines, and could represent the difference between including all beaches, wetlands, and adjacent shorelines or excluding a significant portion of these. Elsewhere [1], we have estimated that as much as ~77,000 ha of land around the San Francisco Bay would be rendered below MSL elevation with a +1 m SLR, and an additional ~41,000 ha with +2 m.
Additionally, the Californian Public Trust was complemented, specifically in the SF Bay, by a very limited planning mandate (addressing mostly provisions for public access) over a buffer strip 100 feet (~30 m) wide granted to the BCDC. Therefore, any development proposed immediately above the MHW may theoretically receive the go-ahead from city planning commissions. In contrast, the already generous Portuguese definition of the high water line is further reinforced with a full public planning mandate over a 50 m buffer inland from the HAT. Together, they form the core of the Portuguese Public Domain, which is complemented by a limited planning mandate for an adjacent zone extending another 500 m inland. In practice, outside existing urban perimeters, no further development is likely to receive approval according to the new Tagus Estuary Management Plan [3].
Both legal codes include provisions regarding erosion and avulsion (again, derived from very old doctrines, which may be traced back to at least the Justinian Code). The Portuguese Water Law of 2005 [63] specifically mentions that all land lost to natural processes of erosion or flooding, including those potentiated by rising sea levels, is to be automatically considered to integrate the “bed” of rivers and sea shorelines, and the Public Domain provisions accordingly realigned. In the US, similar provisions deriving from the Common Law presuppose the inclusion in the Public Trust of land lost to erosion [70]. In both estuaries, the end of landfilling, the steady creation of natural reserves, parks and refuges, as well as the recent introduction of more environmentally-friendly dredging practices [3,84,110] have contributed greatly towards the protection of existing wetlands and permanently submerged habitats.
The water quality in the Bay has been steadily improving since the application of state (1969) and federal (1972) laws regarding waste water treatment [6]. The Tagus Estuary followed suit, albeit with a couple of decades’ delay: waste water treatment was mandated across the whole Tagus river basin as Portugal and Spain complied with the European Urban Waste-Water Directive of 1991 [111] and subsequent provisions. At the estuarine level, the conclusion of the related integrated waste water management system, accompanied by the relocation of heavy industries, led to water quality improvements over the last two decades.
Despite the long sequence of anthropic impacts, both estuaries remain very important natural habitats, and both are recognized as Ramsar sites of international importance along major flyways [5,8]. With water quality becoming less of a problem, the medium- to long-term strategies of dam removal, or at least the integration into existing dams of functional fish passages [71] and other measures, may in time allow the return or stabilization of anadromous fish stocks, and allow for a more sustainable sediment management [112,113]. This later aspect would likely be of crucial importance in enhancing wetland resilience in face of the increased rates of SLR, expected towards the end of the century, as the sustainability of wetlands appears to be strongly connected with the maintenance of a good sediment supply [54,58,90,91,95,96,97].
5. Conclusions
Both estuaries share similar physical settings, have been affected by synchronous fluctuations in eustatic sea levels, and are located in Mediterranean climate zones. The Tagus estuary has experienced continuous human settlement and progressive transformation of natural systems throughout over 2 millennia. The process of transformation of wetlands into farmland was gradual, albeit characterized by periods of accelerated reclamation. The legal framework and actual reclamation practices can be traced back to the Roman tradition, and have been applied to the slowly-evolving landscape ever since. The pushes for transformation can be related to the Crown/State’s desire to expand profitable farmland, but provisions to ensure that it remained within the Public Trust prevented the full appropriation of land by private landowners and, consequently, contributed to limit the more recent transformation of lowlands into residential or industrial uses. In contrast, the San Francisco Bay’s estuarine ecosystem went largely undisturbed until the second half of the 19th century. Since then, it experienced the impacts of human activity at an accelerated rate, with the input of sediment from the Central Valley increasing by a full order of magnitude, and then decreasing to less than original rates, within little more than a century. Direct shoreline alteration was equally extensive and, unlike in the Tagus Estuary, the Public Trust over the bed was not fully upheld until the 1960s. Thus, besides transformation into farmland, landfills around the Bay are now abundantly built-over, with uses ranging from salt ponds, industrial zones, and even residential neighborhoods.
While both legal frameworks share a common ancestry which may be traced back to the Roman Law, we have established that they were upheld more rigorously, or at least consistently, in the Tagus Estuary and, as a result, most lowlands around the Estuary remained under public control and free from permanent building. Although most wetlands have been reclaimed, farmland occupies almost all drained areas. Around the SF Bay, estuarine beds and wetlands were, during a period of accelerated urban expansion, sold to private developers and were converted to a much greater extent to industrial, infrastructure, and urban uses. This is in contradiction to the original provisions of the Public Trust Doctrine, and could be characterized as a relaxation of its enforcement during a period when environmental standards were not a priority as compared to the urge to encourage settlement and grow the regional economy.
The standard for the delimitation of the upper limit of the Public Trust/Public Domain is more generous in Portugal than in California. Portugal has, through historic tradition, adopted the Highest Astronomical Tide as a reference, against the Mean High Water standard for California. Portuguese laws also grant the public agencies with a full planning mandate over a 50 m strip inland from the HAT line, and an additional 500 m buffer with limited planning mandate. In contrast, the BCDC only has a limited planning mandate over a 30 m buffer, mostly related to the assurance of public access in new development.
Wetlands around the Tagus Estuary could more easily be allowed to migrate upland as the more sensitive habitat is adjacent to farmland, whereas around the SF Bay most wetlands are severely encroached upon by urban infrastructure. Also, a steady improvement in the Portuguese legal framework, including the expansion of environmental planning mandates of public agencies, now lends the estuary a strong level of protection. On the other hand, SF Bay has experimented with over four decades of wetland restoration and tidal reconnection of formerly diked ponds, and the metropolitan area is now a global leader in green adaptation, with a greater level of involvement of the private sector and civil society in climate adaptation efforts. Diverse legal interpretations of comparable definitions of public trusts and jurisdictions over shorelines may have significant implications for the ability to adapt to sea-level rise.
We resorted to the compilation of environmental histories for two case studies by compiling and making comparable historical mapping information. GIS analysis allowed us to explore spatial patterns and how they evolved through time. By comparing this with the legal history and synchronous patterns of development, we were able to isolate events and decisions that were unique to each of the case studies. This method could prove useful in studies elsewhere that focus on planning legislation and its impact over development patterns, or in comparing case studies across different legal settings.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded through a Ph.D. Grant from the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT), with grant number SFRH/BD/76317/2011. We are deeply thankful for all the helpful comments provided by colleagues from the Water Management in Mediterranean Climates Workgroup at Institute of International Studies, UC Berkeley. The manuscript was significantly improved by constructive comments from two anonymous reviewers.
Author Contributions
Pedro J. Pinto did most of the research and writing for this article, as part of the research leading to the completion of his Ph.D. Dissertation. G. Mathias Kondolf, first as Head Adviser, then as co-author, revised the material at every stage of the research, refocused the scope of the article, provided additional references and edited the drafts and final version.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Pinto, P. Metropolitan Estuaries and Sea-Level Rise: Adaptive Environmental Planning Solutions at the Regional Scale. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA, 2015. Available online: http://escholarship.org/uc/item/77t8p10g (accessed on 11 November 2016). [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. San Francisco Bay Delta Estuary Large Aquatic Ecosystem Factsheet; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Office of Wetlands, Oceans, and Watersheds: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. Available online: http://water.epa.gov/type/oceb/upload/San-Francisco-Bay-LAE-fact-sheet.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2016).
- Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente. Plano de Ordenamento do Estuário do Tejo—Fase 4; Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente—Administração de Região Hidrográfica do Tejo: Lisbon, Portugal, 2013. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.J.; Bruxelas, A. The Structure of Fish Communities in the Tagus Estuary, Portugal, and Its Role as a Nursery for Commercial Fish Species. Sci. Mar. 1989, 53, 561–566. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.J.; Salgado, P. O Estuário Do Tejo; Cotovia: Lisbon, Portugal, 1999. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, A.R.; Wong, K. Natural History of San Francisco Bay; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Catry, T.; Alves, J.A.; Andrade, J.; Costa, H.; Dias, M.P.; Fernandes, P.; Leal, A.; Lourenço, P.M.; Martins, R.C.; Moniz, F.; et al. Long-Term Declines of Wader Populations at the Tagus Estuary, Portugal: A Response to Global or Local Factors? Bird Conserv. Int. 2011, 21, 438–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLusky, D.S.; Elliott, M. The Estuarine Ecosystem: Ecology, Threats and Management; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Seco, F.A. (Map of Portugal); Michaelis Tramezini: Rome, Italy, 1561. [Google Scholar]
- Cañizares, J. Untitled Map of San Francisco Bay; Stored at The Bancroft Library, University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1776. [Google Scholar]
- De Mofras, E.D. Port de San Francisco Dans La Haute Californie; Arthus Bertrand, Librairie de la Societe de Geographie: Paris, France, 1844. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Ringgold, C. Chart of the Farallones and Entrance to the Bay of San Francisco, California; U.S. Navy: Washington, DC, USA, 1850. [Google Scholar]
- Britton & Rey. Map Exhibiting the Salt Marshes, Tide and Lands in and Adjacent to the Bays of San Francisco and San Pablo and Now Subject to Reclamation, Prepared from Maps of the U.S. Coastal Survey and Official Records by Order of the Board of State Harbor Commissioners and the United States Commissioners on San Francisco Harbor; Britton & Rey: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1874. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.S.; Stillick, R.D. 800 Years of Vegetation Change, Fire and Human Settlement in the Sierra Nevada of California, USA. Holocene 2013, 23, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.S.; Ejarque, A.; Brown, P.M.; Hallett, D.J. Holocene and Historical Vegetation Change and Fire History on the North-Central Coast of California, USA. Holocene 2013, 23, 1797–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwater, B.; Hedel, C.W.; Helley, E.J. Late Quaternary Depositional History, Holocene Sea-Level Changes, and Vertical Crust Movement, Southern San Francisco Bay, California; U.S. Government Publishing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1977; Volume 1014.
- Atwater, B.F.; Conard, S.G.; Dowden, J.D.; Hedel, C.W.; MacDonald, R.L.; Savage, W. History, Landforms, and Vegetation of the Estuary’s Tidal Marshes. In San Francisco Bay: The Urbanized Estuary; Conomos, T.J., Ed.; American Association for the Advancement of Science, Pacific Division: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1979; pp. 347–385. Available online: http://downloads.ice.ucdavis.edu/sfestuary/conomos_1979/archive1031.PDF (accessed on 11 November 2016).
- Goals Project. Baylands Ecosystem Habitat Goals. A Report of Habitat Recommendations Prepared by the San Francisco Bay Area Wetlands Ecosystem Goals Project; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: San Francisco, CA, USA; SF Bay Regional Water Quality Control Board: Oakland, CA, USA, 1999.
- Wright, S.A.; Schoellhamer, D.H. Trends in the Sediment Yield of the Sacramento River, California, 1957–2001. San Franc. Estuary Watershed Sci. 2004, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kirwan, M.L.; Murray, A.B.; Donnelly, J.P.; Corbett, D.R. Rapid Wetland Expansion during European Settlement and Its Implication for Marsh Survival under Modern Sediment Delivery Rates. Geology 2011, 39, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoellhamer, D.H.; Wright, S.A.; Drexler, J.Z. Adjustment of the San Francisco Estuary and Watershed to Decreasing Sediment Supply in the 20th Century. Mar. Geol. 2013, 345, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, S. The Story of Cullinan Ranch, Save the Bay Blog, 26 June 2014. Available online: http://blog.savesfbay.org/2014/06/the-story-of-cullinan-ranch/ (accessed on 11 November 2016).
- Vis, G.J.; Kasse, C.; Vandenberghe, J. Late Pleistocene and Holocene Palaeogeography of the Lower Tagus Valley (Portugal): Effects of Relative Sea Level, Valley Morphology and Sediment Supply. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2008, 27, 1682–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.M.A.; Rodrigues, A.; Magalhães, F. Evolução Da Linha de Costa, Em Portugal, Desde O Último Máximo Glaciário Até À Actualidade: Síntese Dos Conhecimentos. Estud. Quat./Quat. Stud. 1997, 1, 53–66. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Uribelarrea, D.; Pérez-González, A.; Benito, G. Channel Changes in the Jarama and Tagus Rivers (Central Spain) over the Past 500 Years. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2003, 22, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, W.J.; Boski, T.; Moura, D. Palynological Evidence for Environmental and Climatic Change in the Lower Guadiana Valley, Portugal, during the Last 13,000 Years. Holocene 2007, 17, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schriek, T.; Passmore, D.G.; Stevenson, A.C.; Rolão, J. The Palaeogeography of Mesolithic Settlement-Subsistence and Shell Midden Formation in the Muge Valley, Lower Tagus Basin, Portugal. Holocene 2007, 17, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.; Vis, G.J.; Cunha, P. Field Guide: Late Quaternary Fluvial Archives of the Tejo River Field Trip from the Upstream Incised to the Aggrading Fluvial-Tidal Domain; Fluvial Archive Groups/Department of Earth Sciences, University of Coimbra: Coimbra, Portugal, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Leorri, E.; Fatela, F.; Drago, T.; Bradley, S.L.; Moreno, J.; Cearreta, A. Lateglacial and Holocene Coastal Evolution in the Minho Estuary (N Portugal): Implications for Understanding Sea-Level Changes in Atlantic Iberia. Holocene 2013, 23, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendron, P. Planta Do Porto de Lisboa E Das Costas Visinhas, 1757. Available online: http://purl.pt/3644/3/ (accessed on 11 November 2016). (In Portuguese)
- Eça, L. Carta Militar Das Principaes Estradas de Portugal; Romão Eloy Almeida: Lisbon, Portugal, 1767–1833; Available online: http://purl.pt/6302/3/ (accessed on 11 November 2016). (In Portuguese)
- Cabral, E.D. Memória Sobre Os Dannos Causados Pelo Téjo Nas Suas Ribanceiras. In Memórias Económicas, Tomo II; Memórias Económicas Da Academia Real Das Ciências de Lisboa—Typographia da Academia Real das Ciências: Lisbon, Portugal, 1790; pp. 155–197. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Costa, J.M.N. Esboço Da Carta Itinerária Militar Que Contém a Topografia Do Terreno a Norte de Lisboa, 1809. Available online: http://cvc.instituto-camoes.pt/ciencia/lisboanevescostam.jpg (accessed on 11 November 2016). (In Portuguese)
- Costa, J.M.N. Carta Da Península de Setúbal. 1813. Available online: http://cvc.instituto-camoes.pt/ciencia/nevescostasetubal01m.jpg (accessed on 11 November 2016). (In Portuguese)
- Lamotte, G. Carte Chorographique Des Environs de Lisbonne; Richard Wahl: Paris, France, 1821; Available online: http://purl.pt/16986 (accessed on 11 November 2016). (In French)
- Silva, F.M.P. Plano Hydrographico Do Porto de Lisboa; Instituto Hidrográfico: Lisbon, Portugal, 1847–1878; Available online: http://purl.pt/16766/2/ (accessed on 11 November 2016). (In Portuguese)
- Lopes, A.F.; Thomaz, R. Plano Hidrográfico Do Porto de Lisboa; Instituto Hidrográfico: Lisbon, Portugal, 1930; Available online: http://ln.hidrografico.pt/pt/detalhe_cartas-historicas_37/portugal-continental_46/carta-de-1930-porto-de-lisboa_o_314.aspx (accessed on 11 November 2016). (In Portuguese)
- Lopes, A.F.; Thomaz, R. Plano Hidrográfico Do Porto de Lisboa; Instituto Hidrográfico: Lisbon, Portugal, 1945; Available online: http://ln.hidrografico.pt/pt/detalhe_cartas-historicas_37/portugal-continental_46/carta-de-1945-porto-de-lisboa_o_316.aspx (accessed on 11 November 2016). (In Portuguese)
- Instituto Hidrográfico. Carta Náutica Do Porto de Lisboa (in Three Sheets); Instituto Hidrográfico: Lisbon, Portugal, 2012; Available online: http://ln.hidrografico.pt/pt/detalhe_cartas-nauticas_14/serie-portuaria_39/porto-de-lisboa-de-alcantara-ao-canal-do-montijo-26305_o_153.aspx (accessed on 11 November 2016). (In Portuguese)
- Companhia das Lezírias. Companhia das Lezirias do Tejo e Sado: Relatorio e Contas Apresentadas na Asamblea Geral Dos Accionistas em 12 de Janeiro de 1839; Typografia Patriotica: Lisbon, Portugal, 1839. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Beirante, M.A. O Tejo Na Construção Do Poder Real Na Idade Média Portuguesa, de D. Afonso I a D. João I. Revista Da Faculdade de Letras-História—Universidade Do Porto, 1998. Série II, XV. pp. 773–782. Available online: http://ler.letras.up.pt/uploads/ficheiros/4034.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2016). (In Portuguese)
- Madaleno, I.M. Companhia Das Lezírias. O Passado E O Presente. Hisp. Nova Rev. Hist. Contemp. 2006, 6, 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, M.; Garcia, R. Esgotos, Porcos, Amêijoas Ilegais E O Sonho Das Ostras. PÚBLICO. 13 March 2011. Available online: http://www.publico.pt/local/noticia/esgotos-porcos-ameijoas-ilegais-e-o-sonho-das-ostras-1484582 (accessed on 11 November 2016). (In Portuguese)
- Vale, C.; Sundby, B. Suspended Sediment Fluctuations in the Tagus Estuary on Semi-Diurnal and Fortnightly Time Scales. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1987, 25, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gameiro, C.P.; Cartaxana, P.; Brotas, V. Environmental Drivers of Phytoplankton Distribution and Composition in Tagus Estuary, Portugal. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 75, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, L.; Brotas, V.; Mascarell, G.; Couté, A. Taxonomic Survey of the Microphytobenthic Communities of Two Tagus Estuary Mudflats. Acta Oecol. 2003, 24 (Suppl. S1), S117–S123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taborda, R.; Freire, P.; Silva, A.; Andrade, C.; Freitas, M.C. Origin and Evolution of Tagus Estuarine Beaches. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 1, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) V2.1 Void Filled; National Aeronautics and Space Administration—earthexplorer.usgs.gov; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. Available online: http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/srtm/ (accessed on 11 November 2016).
- United States Geological Survey. National Elevation Dataset; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2006–2010.
- Instituto Geográfico Português. Carta de Uso e da Ocupação de Solo de Portugal Para 2007; IGP: Lisbon, Portugal, 2007; Available online: http://www.dgterritorio.pt/cartografia_e_geodesia/cartografia/cartografia_tematica/carta_de_ocupacao_do_solo__cos_/cos__2007/ (accessed on 11 November 2016). (In Portuguese)
- Barnard, P.L.; Schoellhamer, D.H.; Jaffe, B.E.; McKee, L.J. Sediment Transport in the San Francisco Bay Coastal System: An Overview. Mar. Geol. 2013, 345, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.E.; Harrison, S.; Firth, C.R.; Jordan, J.T. The Early Holocene Sea Level Rise. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2011, 15–16, 1846–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goman, M.; Malamud-Roam, F.; Ingram, B.L. Holocene Environmental History and Evolution of a Tidal Salt Marsh in San Francisco Bay, California. J. Coast. Res. 2008, 24, 1126–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, E.B.; Byrne, R. Late Holocene Marsh Expansion in Southern San Francisco Bay, California. Estuaries Coasts 2013, 36, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, J.P. Lisboa 2100, Projectar a Frente Ribeirinha em Cenários de Alterações Climáticas: Linha do Século XIX como Projecção do Futuro. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of Architecture, University of Lisbon, Portugal, 2012. Available online: http://www.repository.utl.pt/bitstream/10400.5/5686/1/RELATORIO.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2016). [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, G.C. Coastal Zone Management from an Administrative Perspective: A Case Study of the San Francisco Bay Conservation and Development Commission. Coast. Zone Manag. J. 1975, 2, 81–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Angermeier, P.L.; Cummins, K.; Dunne, T.; Healey, M.; Kimmerer, W.; Moyle, P.B.; Murphy, D.; Patten, D.; Railsback, S.; et al. Projecting Cumulative Benefits of Multiple River Restoration Projects: An Example from the Sacramento-San Joaquin River System in California. Environ. Manag. 2008, 42, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, B.; Caçador, I.; Marques, J.C.; Croudace, I.W. Tagus Estuary Salt Marshes Feedback to Sea Level Rise over a 40-Year Period: Insights from the Application of Geochemical Indices. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Francisco Bay Conservation and Development Commission. San Francisco Bay Conservation and Development Commission Strategic Plan; San Francisco Bay Conservation and Development Commission: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1998. Available online: http://bayplanningcoalition.org/downloads/library/BCDC_1998_Strategic_Plan.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2016).
- King John I v. Rui Velho. Chancelaria de D. João I, Gaveta XI, M.3, Doc 14; Stored at the Arquivo Nacional—Casa da Moeda: Lisbon, Portugal, 1410. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- De Pinho, J.C. As Águas No Código Civil; Almedina: Coimbra, Portugal, 1985. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Rilo, A.; Freire, P.; Mendes, R.N.; Ceia, R.; Catalão, J.; Taborda, R.; Melo, R.; Caçador, M.I.; Freitas, M.D.C.; Fortunato, A.B; et al. Methodological Framework for the Definition and Demarcation of the Highest Astronomical Tide Line in Estuaries: The Case of Tagus Estuary (Portugal). J. Integr. Coast. Zone Manag. 2014, 14, 95–107. [Google Scholar]
- Assembleia da República. Lei da Água. Lei n°45/2005, 2005. Available online: https://dre.pt/application/file/245220 (accessed on 14 November 2016). (In Portuguese)
- Moniz, G. Plano de Ordenamento do Estuário do Tejo. In Presented at the “(re)Viver o Tejo” Workshop of the Fórum Empresarial da Economia do Mar, Lisbon, Portugal, 30 March 2011; Available online: http://www.fem.pt/ReviverTejo/Apresentacoes/ARHTejo.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2016). (In Portuguese)
- Garcia, R. Parlamento Vai Suavizar Lei Polémica Sobre Propriedades Junto À Água. PÚBLICO. 24 April 2014. Available online: http://www.publico.pt/portugal/noticia/parlamento-vai-suavizar-lei-polemica-sobre-propriedades-junto-a-agua-1633522 (accessed on 11 November 2016). (In Portuguese)
- Soares, M. Donos de Empreendimento em Alvor vão Mesmo ter de Repor Habitats Destruídos. PÚBLICO. 13 March 2014. Available online: http://www.publico.pt/local/noticia/tribunal-confirma-condenacao-de-donos-de-quinta-em-alvor-a-repor-habitats-destruidos-1628215 (accessed on 11 November 2016). (In Portuguese)
- Sax, J.L. The Public Trust Doctrine in Natural Resource Law: Effective Judicial Intervention. Mich. Law Rev. 1970, 68, 471–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, R.J. Changing Conceptions of Property and Sovereignty in Natural Resources: Questioning the Public Trust Doctrine. Iowa Law Rev. 1985, 71, 631–716. [Google Scholar]
- Eichenberg, T.; Bothwell, S.; Vaughn, D. Climate Change and the Public Trust Doctrine: Using an Ancient Doctrine to Adapt to Rising Sea Levels in San Francisco Bay. Gold. Gate Univ. Environ. Law J. 2009, 3, 243–282. [Google Scholar]
- Eichenberg, T. The Challenges of Adapting to Climate Change in San Francisco Bay. Hastings West-Northwest J. Environ. Law Policy 2013, 19, 393. [Google Scholar]
- Cech, T.V. Principles of Water Resources: History, Development, Management, and Policy; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- McGinley, P.C. Climate Change and the Public Trust Doctrine. Plan. Environ. Law 2013, 65, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Crown Estate. Shoreline Management Briefing Note; The Crown Estate: London, UK; Available online: https://www.thecrownestate.co.uk/media/5588/shoreline_management_briefing_note.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2016).
- Ruggiero, P.; Komar, P.D.; McDougal, W.G.; Marra, J.J.; Beach, R.A. Wave Runup, Extreme Water Levels and the Erosion of Properties Backing Beaches. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 17, 407–419. [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell, M.; Segall, C.H. No Day at the Beach: Sea Level Rise, Ecosystem Loss, and Public Access along the California Coast. Ecol. Law Q. 2007, 34, 533–578. [Google Scholar]
- Sax, J.L. Some Unorthodox Thoughts about Rising Sea Levels, Beach Erosion, and Property Rights. Vt. J. Environ. Law 2009, 11, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasscock, S. Effects of Accretion and Erosion on Coastal Property in the United States. Int. J. Mar. Coast. Law 1993, 8, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolezel, J.M.; Warren, B.N. Saving San Francisco Bay: A Case Study in Environmental Legislation. Stanf. Law Rev. 1971, 23, 349–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luken, R.A. Preservation of Wetlands: The Case of San Francisco Bay. Nat. Resour. J. 1974, 14, 139. [Google Scholar]
- Briscoe, J. Legal Problems of Tidal Marshes. In San Francisco Bay: The Urbanized Estuary; Conomos, T.J., Ed.; American Association for the Advancement of Science, Pacific Division: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1979; p. 493. Available online: http://downloads.ice.ucdavis.edu/sfestuary/conomos_1979/archive1032.PDF (accessed on 11 November 2016).
- City of Berkeley v. Superior Court. S.F. No. 23686, Supreme Court of California Ruling of 22 February 1980. Available online: http://scocal.stanford.edu/opinion/city-berkeley-v-superior-court-30485 (accessed on 11 November 2016).
- Davoren, W.T. Tragedy of the San Francisco Bay Commons. Coast. Zone Manag. J. 1982, 9, 111–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berke, P. San Francisco Bay: A Successful Case of Coastal Zone Planning Legislation and Implementation. Urban Lawyer 1983, 15, 487–501. [Google Scholar]
- San Francisco Bay Conservation and Development Commission. Climate Change Bay Plan Amendment. Bay Plan Amendment No.1-08; San Francisco Bay Conservation and Development Commission: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2011. Available online: http://www.bcdc.ca.gov/proposed_bay_plan/bp_amend_1-08.shtml (accessed on 14 May 2014).
- Johnson, P. SF Bar Assoc. Panel Asks Whether BCDC’s Sea Level Rise Proposal Is a Power Grab; CUEL Center on Urban Environmental Law at Golden Gate University School of Law: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2013; Available online: http://ggucuel.org/sf-bar-assoc-panel-asks-whether-bcdcs-sea-level-rise-proposal-is-a-power-grab (accessed on 20 October 2015).
- Garcia, P.R. Plataforma Tejo—O Regresso ao Rio; Edições e Publicações de Fundação Serra Henriques: Lisbon, Portugal, 2010. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Durão, V.C.M. Reclaimed Land: An Urban Analysis—The Landfills in Lisbon’s Downtown and Riverfront, Portugal. J. Integr. Coast. Zone Manag. 2012, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Batista, C.; Bastos, M.R.; Azeiteiro, U.; Dias, J.A. Approach to diachronic study of river freshwater fishes in the Tagus valley: The cases of Abrantes and Santarém. In Proceedings of the Actas do 7° Simpósio sobre a Margem Ibérica Atlântica—MIA, Lisboa, Portugal, 16–20 December 2012.
- Andrade, C.; Freitas, M.C. Coastal Zones. In Climate Change in Portugal—Scenarios, Impacts and Adaptation Measures—SIAM Project; Santos, F.D., Forbes, K., Moita, R., Eds.; Gradiva: Lisbon, Portugal, 2002; pp. 173–219. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, H.; Dias, J.M.; Caçador, I. Is the Salt Marsh Vegetation a Determining Factor in the Sedimentation Processes? Hydrobiologia 2008, 621, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.A.; Freitas, M.A.; Andrade, C.; Taborda, R.; Freire, P.; Schmidt, S.; Antunes, C. Geomorphological Response of the Salt-Marshes in the Tagus Estuary to Sea Level Rise. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 1, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caçador, I.; Vale, C. Salt Marshes. In Metals in the Environment: Analysis by Biodiversity; Prasad, M.N.V., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.; Faber, P. Salt Marsh Restoration Experience in San Francisco Bay. J. Coast. Res. 2001, 27, 203–211. [Google Scholar]
- Madsen, F.A.; Honore, A.; Knight, F. Greening the Bay: Financing Wetland Restoration in San Francisco Bay; Save the Bay: Oakland, CA, USA, 2007; Available online: http://www.savesfbay.org/greening-bay (accessed on 30 January 2015).
- Orr, M.; Crooks, S.; Williams, P.B. Will Restored Tidal Marshes Be Sustainable? San Franc. Estuary Watershed Sci. 2003, 1, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Stralberg, D.; Brennan, M.; Callaway, J.C.; Wood, J.K.; Schile, L.M.; Jongsomjit, D.; Kelly, M.; Parker, V.T.; Crooks, S. Evaluating tidal marsh sustainability in the face of sea-level rise: A hybrid modeling approach applied to San Francisco Bay. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, K.M.; Drexler, J.Z.; Fuller, C.C.; Schoellhamer, D.H. Modeling Tidal Freshwater Marsh Sustainability in the Sacramento–San Joaquin Delta Under a Broad Suite of Potential Future Scenarios. San Franc. Estuary Watershed Sci. 2015, 13, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Klatt, M.; Cayce, K. Restoration Progress toward Regional Goals in the San Francisco Baylands; San Francisco Estuary Institute: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2013; Available online: http://www.sfei.org/sites/default/files/SOE%20poster%20M_Klatt%20FINAL%20for%20web-web.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2016).
- South Bay Salt Ponds Restoration Project. Frequently Asked Questions—Restoration Process, 2014. Available online: http://www.southbayrestoration.org/FAQ.html (accessed on 22 October 2014).
- Assembleia da República. Decreto-Lei n°321/83, 1983. Available online: https://dre.pt/application/file/453113 (accessed on 11 November 2016). (In Portuguese)
- Slade, D.C.; Kehoe, R.K.; Stahl, J.K. Putting the Public Trust Doctrine to Work, 2nd ed.; Coastal States Organization: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Titus, J.G. Rising Seas, Coastal Erosion, and the Takings Clause: How to Save Wetlands and Beaches without Hurting Property Owners. Md. Law Rev. 1998, 57, 1279–1399. [Google Scholar]
- Woodbridge, S.B. San Francisco in Maps & Views; Rizzoli International Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, D. The Politics of Precaution: Regulating Health, Safety and Environmental Risks in Europe and the United States; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gleick, P.H.; Heberger, M.; Donnelly, K. Zombie Water Projects. In The World’s Water, Volume 8; Gleick, P.H., Ed.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 123–146. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, R. The Country in the City: The Greening of the San Francisco Bay Area; Weyerhaeuser Environmental Books—University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Travis, W.; Eichenberg, T. Using the Public Trust Doctrine to Adapt to Climate Change in San Francisco Bay (for Commission Consideration on March 5, 2009); Staff Report; San Francisco Bay Conservation and Development Commission (BCDC): San Francisco, CA, USA, 2009.
- Titus, J.G. Rolling Easements Primer; Climate Ready Estuaries—U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/documents/rollingeasementsprimer.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2016).
- Antunes, C. Previsão de Marés dos Portos Principais de Portugal. Faculdade de Ciências da Universidade de Lisboa, 2011. Available online: http://webpages.fc.ul.pt/~cmantunes/hidrografia/hidro_tabelas.html (accessed on 4 February 2015). (In Portuguese)
- LMTS Executive Committee. Long-Term Management Strategy for the Placement of Dredged Material in the San Francisco Bay Region—Management Plan 2001; U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, SF Bay Conservation and Development Commission and SF Bay Regional Water Quality Control Board: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2001; Available online: http://www.spn.usace.army.mil/Portals/68/docs/Dredging/LMTS/entire%20LMTF.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2016).
- European Council. Council Directive 91/271/EEC of 21 May 1991 Concerning Urban Waste-Water Treatment; European Council: Brussels, Belgium, 1991; Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CONSLEG:1991L0271:20081211:EN:PDF (accessed on 11 November 2016).
- Kondolf, G.M. Some Suggested Guidelines for Geomorphic Aspects of Anadromous Salmonid Habitat Restoration Proposals. Restor. Ecol. 2000, 8, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondolf, G.M.; Gao, Y.; Annandale, G.W.; Morris, G.L.; Jiang, E.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Carling, P.; Fu, K.; Guo, Q.; et al. Sustainable Sediment Management in Reservoirs and Regulated Rivers: Experiences from Five Continents. Earth Future 2014, 2, 256–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).