Evolution of Cretan Aqueducts and Their Potential for Hydroelectric Exploitation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Physical Settings
2.1. Climate of the Island of Crete
2.2. The Karst Hydrogeology of the Island of Crete
2.3. Water Resource Status
3. Minoan Civilization (ca. 3200–1100 BC)
4. Historical Times
4.1. Classical and Hellenistic Period (ca. 490–67 BC)
4.2. Roman Period (ca. 67 BC–330 AD)
5. Byzantine Period and Venetian Rule (ca. 330–1669 AD)
6. Modern Times
6.1. The Ottoman and the Egyptian Periods (ca. 1669–1898 AD)
6.2. Present Times (1898–Today)
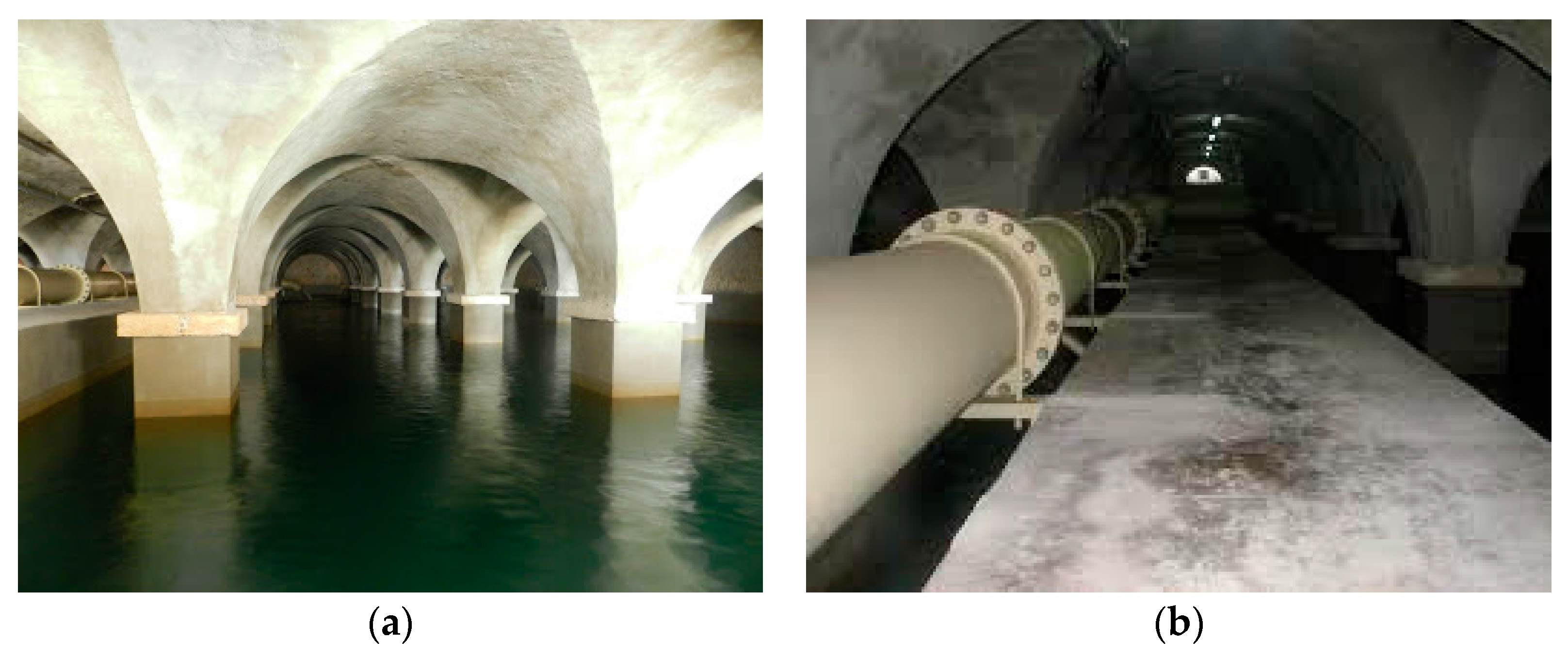
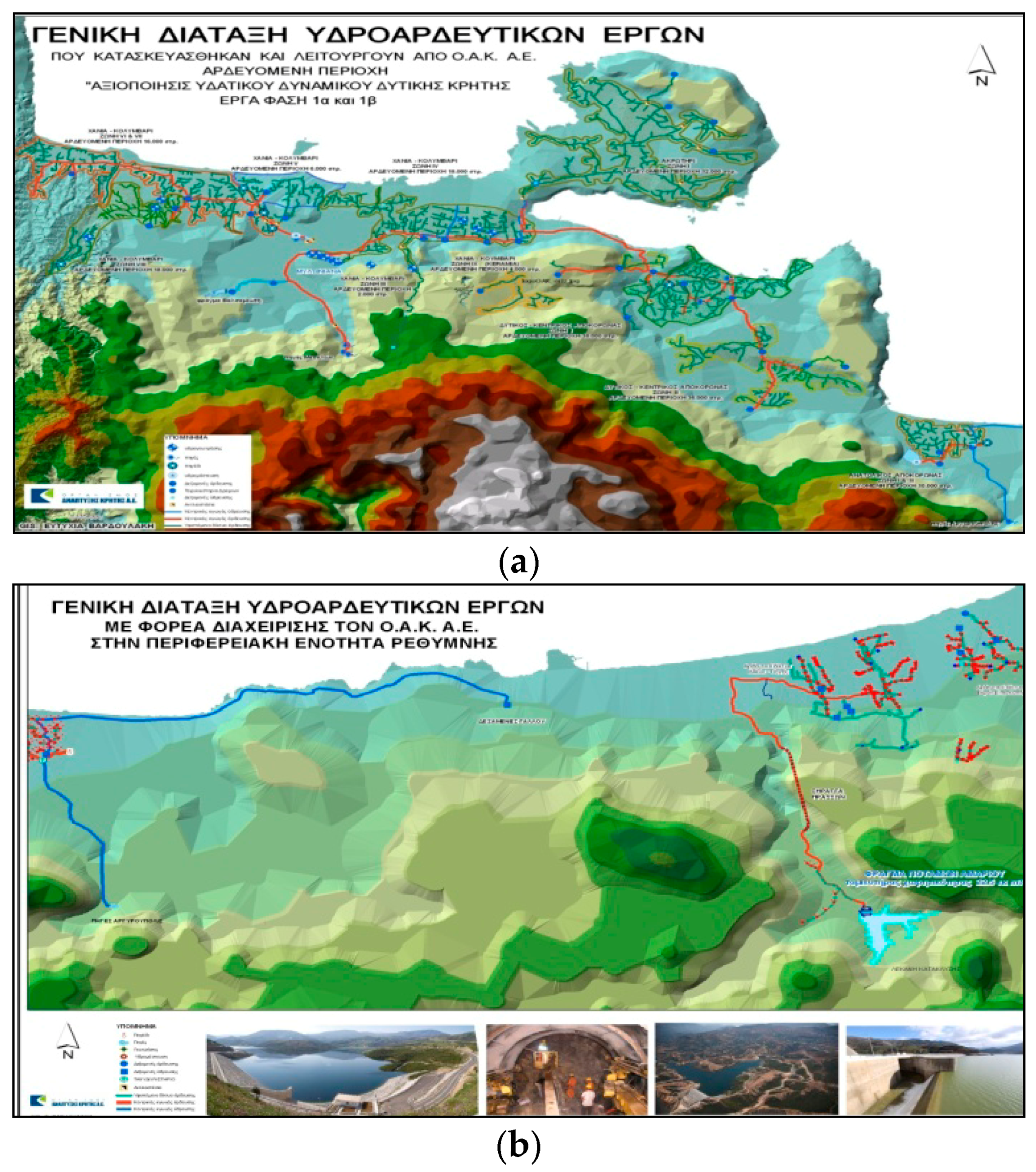
6.2.1. Organization for the Development of Crete, sa (OAK, sa) Water Network at Western Crete
6.2.2. The Municipal Aqueduct of St. Ioannis (Water Supply for City of Chania)
6.2.3. Potamon Aqueduct
6.2.4. Valsamioti Aqueduct
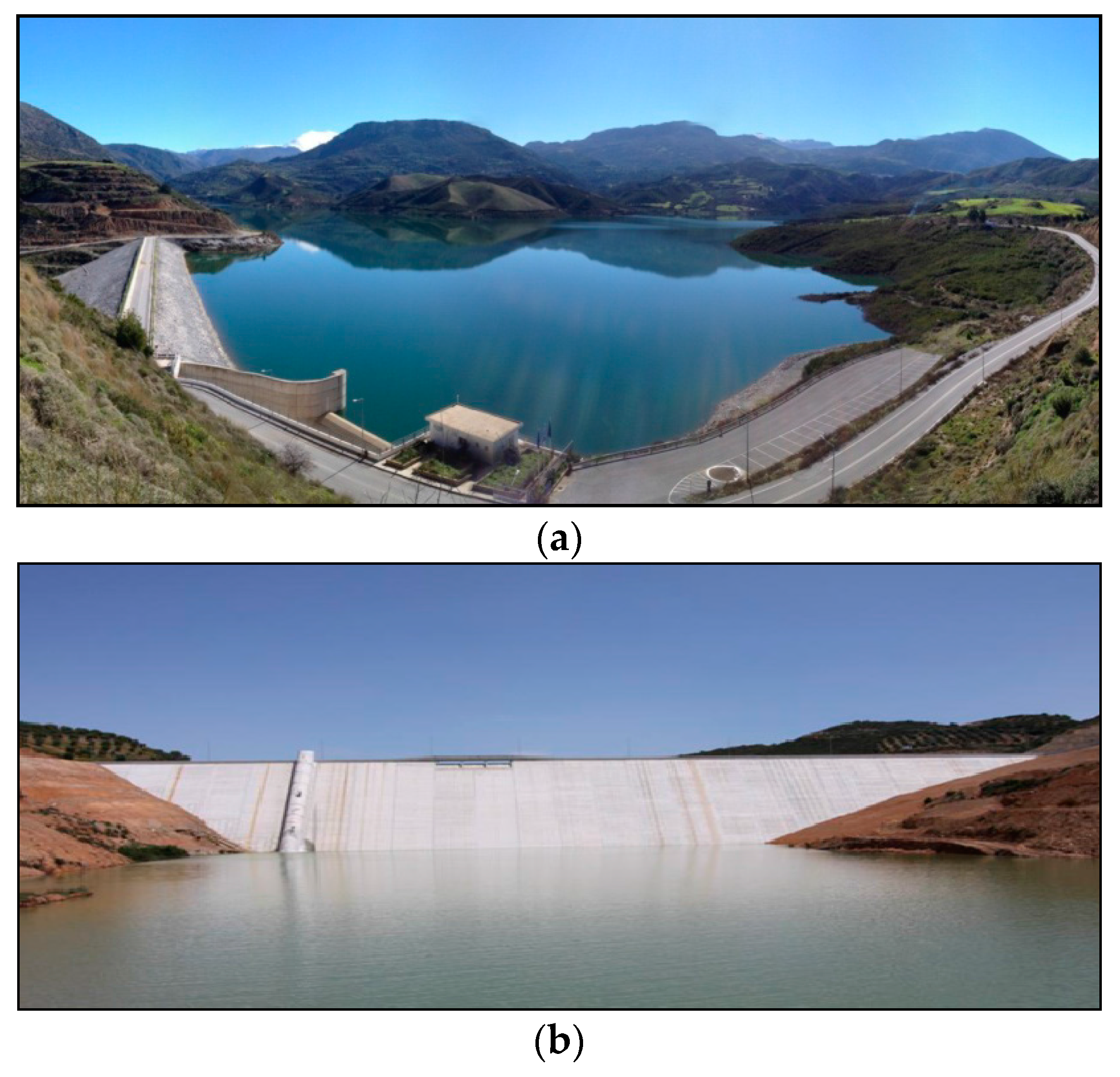
6.2.5. Aposelemis Aqueduct
7. Energy Exploitation of Water Infrastructures and Networks
7.1. Energy Exploitation of the Potamon Dam Hybrid Power Station (HPS) 50 MW
7.2. Small Hydro Turbine in the Pipe Connecting the Aposelemis Dam with Lassithi Plateau
- (a)
- Projects for the water diversion form Lassithi Plateau (to isolate the water sinks of Chonos area and leading the flood water to the tunnel to enhance the reservoir dam Aposelemis).
- (b)
- Projects of the Tunnel (drilling and construction of a tunnel with total length in horizontal projection 3425.50 m). A tunnel boring machine (TBM) was used and a steel pipe of 1.8 m diameter was placed in this (Figure 12).
- (c)
- The longitudinal gradient is about 15%, the height difference between the plateau and the Aposelemis dam reservoir is 515 m and the internal diameter of pipe is 4.35 m.
- (d)
- Projects for the destruction of penstock energy, electromechanical facilities.
- (e)
- Water pipe to lead the water from the energy destruction point to the Aposelemis reservoir.
7.3. Hydropower Installation in Water Pipelines
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsagarakis, K.P.; Tsoumanis, P.; Chartzoulakis, K.; Angelakis, A.N. Water resources status including wastewater treatment and reuse in Hellas: Related problems and prospectives. Water Int. 2001, 26, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagarakis, K.P.; Dialynas, G.E.; Angelakis, A.N. Water resources management in Crete, Hellas, including water recycling and reuse, and proposed quality criteria for use of recycled water in the Mediterranean region. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 66, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartzoulakis, K.S.; Paranychianakis, N.V.; Angelakis, A.N. Water resources management in the island of Crete, Hellas: With emphasis the agricultural use. Water Policy 2001, 3, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mays, L.W.; Koutsoyiannis, D.; Angelakis, A.N. A brief history of water in antiquity. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2007, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A. The Palace of Minos at Knossos: A Comparative Account of the Successive Stages of the Early Cretan civilization as Illustrated by the Discoveries, (Volume I–IV); Macmillan Co.: London, UK, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Dialynas, M.G.; Despotakis, V. Evolution of water supply technologies in Crete, Hellas through the Centuries. In Evolution of Water Supply throughout Millennia; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2012; pp. 227–258. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Savvakis, Y.M.; Charalampakis, G. Aqueducts during the minoan era. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2007, 7, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudouris, K.; Christodoulakos, Y.; Stiakakis, M.; Angelakis, A.N. Hydrogeological characteristics of Hellenic aqueducts like qanats. Water 2013, 5, 1326–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudouris, K.; Tsatsanifos, C.; Yannopoulos, S.; Angelakis, A.N. Evolution of underground aqueducts in the Hellenic World. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 16, 1159–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Feo, G.; Angelakis, A.N.; Antoniou, G.P.; El-Gohary, F.; Haut, B.; Passchier, C.W.; Zheng, X.Y. Historical and technical notes on aqueducts from prehistoric to medieval times. Water 2013, 5, 1996–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellenic Central Water Agency. Preliminary Plan of Water Resources Management of the Water Region of Crete; Ministry of Environment, Energy and Climate Change: Athens, Greece, 2013. (In Hellenic) [Google Scholar]
- Decentralized Region of Crete. Management Plan for the River Basin Districts of Crete, Greece according to the Water Framework Directive 2000/60/EC (Ministerial Decision No 163/Official Government Gazette 570/8.4.2015, Volume B); Decentralized Region of Crete: Crete, Greece, 2015. (In Hellenic) [Google Scholar]
- Zografakis, N.; Regional Energy Agency of Crete. The Development of RES in Crete: Comparative Advantage Development. In Proceedings of the International Meeting on Green Development in Crete, Sitia Crete, Greece, 21–22 September 2010.
- Nikolaou, T.; Mamagakis, E. Technical Presentation of the Project: Energy Exploitation of the Potamon Dam of Rethymno, Crete, Greece—Hybrid Power Station 50 MW. In Proceedings of the 2nd National Conference of Dams and Reservoirs, Athens, Greece, 7–8 November 2013. (In Hellenic)
- Nikolaou, T.; Piperidis, P.; Kopasis, L.; Vardoulaki, E.; Bazdanis, G. Systems and methods of best management and saving energy in hydro projects in Crete, Greece. In Proceedings of the Jointed Conference of HHA, HWA, and HCoMWR, Athens, Greece, 10–12 December 2015.
- Angelakis, A.N. Evolution of rainwater harvesting and use in Crete, Hellas through the Millennia. Water Sci. Technol Water Supply 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markonis, Y.; Angelakis, A.N.; Christy, J.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Climatic variability and the evolution of water technologies in Crete, Hellas. Water Hist. 2016, 8, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markonis, Y. Stochastic Investigation of Large-Scale Hydroclimatic Correlations over the Mediterranean. Ph.D. Thesis, National Technical University of Athens, Athens, Greece, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tsonis, A.A.; Swanson, K.L.; Sugihara, G.; Tsonis, P.A. Climate change and the demise of Minoan civilization. Clim. Past 2010, 6, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finné, M.; Holmgren, K.; Sundqvist, H.S.; Weiberg, E.; Lindblom, M. Climate in the eastern Mediterranean, and adjacent regions, during the past 6000 years—A review. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 3153–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Spyridakis, S.V. The status of water resources in Minoan times: A preliminary study. In Diachronic Climatic Impacts on Water Resources with Emphasis on Mediterranean Region; Angelakis, A.N., Issar, A.S., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Floods, J. Water Management in Neopalatial Crete and the Development of the Mediterranean Climate. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of The Graduate School at The University of North Carolina at Greensboro, Greensboro, NC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Koutsoyiannis, D.; Tchobanoglous, G. Water resources technologies in the ancient Greece. Water Res. 2005, 39, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büntgen, U.; Tegel, W.; Nicolussi, K.; Mc Cormick, M.; Frank, D.; Trouet, V.; Kaplan, J.O.; Herzig, F.; Heussner, K.; Wanner, H.; et al. 2500 years of European climate variability and human susceptibility. Science 2011, 331, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltas, E.; Tzoraki, O. Water resources management on the island of Crete: Lessons learnt. In Free Flow—Reaching Water Security through Cooperation, Tudor Rose; United Nations International Year of Water Cooperation, Ed.; UNESCO-Publishing: Paris, France, 2013; pp. 285–289. [Google Scholar]
- Malagò, A.; Efstathiou, D.; Bouraoui, F.; Nikolaidis, N.P.; Franchini, M.; Bidoglio, G.; Kritsotakis, M. Regional scale hydrologic modeling of a karst-dominant geomorphology: The case study of the Island of Crete. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise, M.; Sammarco, M. The historical use of water resources in karst. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, D.C.; Williams, P. Karst Hydrogeology and Geomorphology; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Laureano, P. The Water Atlas: Traditional Knowledge to Combat Desertification; Bollati Boringhieri: Torino, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Stevanovic, Z. (Ed.) Karst aquifers—Characterization and engineering. In Professional Practice in Earth Sciences; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015.
- White, W.B. Karst hydrology: Recent developments and open questions. Eng. Geol. 2002, 65, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, F.; Parise, M.; De Waele, J.; Jourde, H. A review on natural and human-induced geohazards and impacts in karst. Earth Sci. Rev. 2014, 138, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Spyridakis, S.V. Major urban water and wastewater systems in Minoan Crete, Hellas. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2013, 13, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, A.N.; De Feo, G.; Laureano, P.; Zourou, A. Minoan and Etruscan hydro-technologies. Water 2013, 5, 972–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Archaeological Site of Ancient Eleftherna. Available online: http://www.crete-kreta.com/eleftherna (accessed on 2 January 2017).
- Haut, B.; Viviers, D. Water supply in the Middle East during Roman and Byzantine periods. In Evolution of Water Supply through the Millennia; Angelakis, A.N., Mays, L.W., Koutsoyiannis, D., Mamassis, N., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ortloff, C.R.; Crouch, P.D. The urban water supply and distribution system of the Ionian city of Ephesos. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2001, 28, 843–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juuti, P.S.; Katko, T.S.; Vuorinen, H.S. (Eds.) Environmental History of Water—Global View of Community Water Supply and Sanitation; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2007.
- Strataridaki, A.I.; Chalkiadakis, E.G.; Gigourtakis, N.M. The historical development of water supply to Iraklion, Crete, Greece from antiquity to the present. In Evolution of Water Supply throughout Millennia; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chalkiadakis, E. The Water Supply to Heraklion, Crete, Greece from the Ottoman Period (1669) to the Present; the Modern Aqueduct and the Ancient Springs. In Proceedings of the 3rd IWA Specialized Conference on Water & Wastewater, Turkey, Japan, 22–24 March 2012.
- Strataridaki, A.I.; Chalkiadakis, E.G.; Gigourtakis, N.M. The History of the Fundana Spring Aqueduct and Its Significance for the Water Supply of Heraklion City (Crete) Through the Ages. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium Water and Wastewater Technologies in Ancient Civilizations, International Water Association Conference, Bari, Italy, 28–30 May 2009.
- Nikolaou, T.G.; Christodoulakos, I.; Piperidis, P.G.; Angelakis, A.N. Evolution of Cretan, Greece Aqueducts. In Proceedings of the 4th IWA International Symposium on Water and Wastewater Technologies in Ancient Civilizations, Coimbra, Portugal, 17–19 September 2016.
- Aposelemis Dam, Water Treatment and Supply Works in Northern Crete Island. Available online: http://www.hydroex.gr/projects/aposelemis-dam-water-treatment-and-supply-works-northern-crete-island (accessed on 2 January 2017).
- The Municipal Aqueduct of St. Ioannis. Available online: http://www.deyax.org.gr/index.php?option =com_content&task=view&id=260&Itemid=84 (accessed on 2 January 2017).
- Katsaprakakis, D.A.; Christakis, D.G.; Zervos, A.; Papantonis, D.; Voutsinas, S. Pumped storage systems introduction in isolated power production systems. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 467–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, J.S.; Papantonis, D.E. Simulation and size optimization of a pumped-storage power plant for the recovery of wind-farms rejected energy. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protopapas, K.; Papathanassiou, S. Operation of Hybrid Wind—Pumped Storage Systems in Isolated Island Grids. In Proceedings of the IEEE MEDPOWER 2004 Conference, Lemesos, Cyprus, 14–17 November 2004.
- Anagnostopoulos, J.S.; Papantonis, D.E. Pumping station design for a pumped-storage wind-hydro power plant. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 3009–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudouris, K.; Alexopoulos, A.; Antonakos, A.; Kallergis, G. Water Resources in the Wider Area of the Aposelemis Basin, Island of Crete, Greece. Bulleting of the Geological Society of Greece, 2007. In Proceedings of the 11th International Congress, Athens, Greece, 3–7 May 2007.











| Area (km2) | Precipitation | ET in Volume (Mm3) | Water Potential (Mm3/Year) | Water Use in 2010 (Mm3/Year) | Cons. Index (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height (mm/Year) | Volume (Mm3/Year) | Surface | Ground | Total | Agricult. | Domestic | Industr. | Total | |||
| 8335 | 927 | 7740 | 4799 | 774 | 2167 | 2941 | 340 | 77 | 4 | 421 | 14.31 |
| Aqueduct Name | Location | Construction | Reconstruction | Length (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gournia | Faneromeni, Asari | Minoan | - | 7 |
| Karphi | Karphi, Lassithi | Minoan | - | not available |
| Knossos (Mavrokolympos) | Knossos | Minoan | Roman | 0.7 |
| Malia | Profitis Ilias, Malia | Minoan | Hellenistic, Roman | 0.85 or 1.15 |
| Mochlos | Mochlos, Lassithi | Minoan | - | 3 |
| Tylissos | Tylissos | Minoan | - | 1.4 |
| Aqueduct Name | Location | Period | Age of Construction | Length (km) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyrrhenia 1 a | Polyrrhenia, Chania | Classical | 4th century BC | ≈0.09 |
| Polyrrhenia 2 a | Polyrrhenia, Chania | Classical | 4th century BC | ≈0.07 |
| Eleuthera b | Eleuthera, Rethymnon | Hellenistic | - | 3.00 |
| Kissamos | Kissamos, Chania | Hellenistic | - | 4.50 |
| Aqueduct Name | Location | Period | Age of Construction | Length (km) | Flow Rate (m3∙Day−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axos | Axos, Rethymnon | - | - | - | - |
| Arkadia | Ini, Iraklion | - | - | - | - |
| Chersonisos | Hellas | Roman | First half of the 2nd century AD | 13 | - |
| Elyros a | Rodovani, Chania | Roman | 2nd century AD | 2 | - |
| Fountana | Skalani, Iraklion | Roman, Egyptian | - | 1.15 | 682.56 |
| Ierapytna | Ierapetra | Roman | - | - | - |
| Syia b | Souyia, Chania | Roman | 2nd century AD | 8.10 | - |
| Falassarna c | Falasarna, Chania | - | 2nd century AD | 1.40 | - |
| Lefki (Koufonissi) | Island Lefki Island | Roman | - | - | - |
| Lebena (Lentas) | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gavdos Island d | Gavdos Island | Roman | 2nd century AD | 1.10 | - |
| Gortys | Crete, Hellas | Roman | Late Roman | 15 | - |
| Lyttos | Hellas | Roman | 33 BC–14 AD | 22 | - |
| Minoa (Chania) e | Crete, Hellas | Roman | 2nd century AD | 1.77 | - |
| Name | Location | Period | Length (km) | Flow Rate (m3∙Day−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potamon Dam | Amari, Rethymnon | 2005–2008 | Main water network: 15.8 Secondary water networks: 3.9 | 48,000 | OAK, sa. Study with title: “Exploitation of Potamon dam” |
| Aposelemis dam | Iraklion | 2012–2015 | 30.00 | 85,000 | [44] |
| Aposelemis dam | Agios Nikolaos | 2012–2015 | 37.00 | 25,000 | [44] |
| Aposelemis dam | TBM tunnel canyon Rosa | 2012–today | 3.50 | 1.728 × 106 For 10 days of flooding per year | OAK, sa. Hydrological Study of the Project, 2010. |
| Valsamiotis dam | Vatolakos, Chania | 2005–2015 | 3.52 | 40,000 | OAK, sa. Study with title: “Valsamioti dam” |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikolaou, T.G.; Christodoulakos, I.; Piperidis, P.G.; Angelakis, A.N. Evolution of Cretan Aqueducts and Their Potential for Hydroelectric Exploitation. Water 2017, 9, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010031
Nikolaou TG, Christodoulakos I, Piperidis PG, Angelakis AN. Evolution of Cretan Aqueducts and Their Potential for Hydroelectric Exploitation. Water. 2017; 9(1):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010031
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikolaou, Triantafyllia G., Ioannis Christodoulakos, Panagiotis G. Piperidis, and Andreas N. Angelakis. 2017. "Evolution of Cretan Aqueducts and Their Potential for Hydroelectric Exploitation" Water 9, no. 1: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010031
APA StyleNikolaou, T. G., Christodoulakos, I., Piperidis, P. G., & Angelakis, A. N. (2017). Evolution of Cretan Aqueducts and Their Potential for Hydroelectric Exploitation. Water, 9(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010031






