Abstract
The information on transpiration is vital for sustaining fragile ecosystem in arid/semiarid environment, including the Horqin Sandy Land (HSL) located in northeast China. However, such information is scarce in existing literature. The objectives of this study were to: (1) measure sap flow of selected individual stems of two sand-fixing plants, namely Salix gordejevii and Caragana microphylla, in HSL; and (2) upscale the measured stem-level sap flow for estimating the community-level transpiration. The measurements were done from 1 May to 30 September 2015 (i.e., during the growing season). The upscaling function was developed to have one dependent variable, namely sap flow rate, and two independent variables, namely stem cross-sectional area of Salix gordejevii and leaf area of Caragana microphylla. The results indicated that during the growing season, the total actual transpiration of the Salix gordejevii and Caragana microphylla communities was found to be 287 ± 31 and 197 ± 24 mm, respectively, implying that the Salix gordejevii community might consume 1.5 times more water than the Caragana microphylla community. For this same growing season, based on the Penman–Monteith equation, the total actual evapotranspiration for these two communities was estimated to be 323 and 229 mm, respectively. The daily transpiration from the upscaling function was well correlated with the daily evapotranspiration by the Penman–Monteith equation (coefficient of determination R2 ≥ 0.67), indicating the applicability of this upscaling function, a useful tool for managing and restoring sand-fixing vegetations.
1. Introduction
Like other arid/semiarid regions across the world, northeast China is incurring various levels of desertification, which can impact about 2.62 × 106 km2 land (i.e., 27.3% of the territory of China) [1]. The sparse vegetation coverage in the degraded areas, especially for the desert sandy lands, is dominated by short shrubs [2] with a highly developed root system, an excellent tolerance to cold and hot temperatures, and a remarkable resistance to wind erosion. The shrubs play important roles in sustaining the fragile ecosystem by providing a habitant shelter from strong wind, stabilizing sand dunes, conserving soil water, and maintaining the regional ecological balance [3]. For such desert lands, because the hydrological processes are dominated by vertical soil moisture movement, it is needed to accurately determine the evapotranspiration [4]. However, given that the sparsely-distributed shrubs have fascicular branches without an obvious trunk and with a small leaf area, it is hard to quantify transpiration of the community by using the conventional mathematical and/or experimental techniques [5]. The traditional experimental methods, such as isotopic tracers [6], potting and weighing [7], lysimeters [8], photosynthesis systems [9], and porometers [10], usually malfunction in directly measuring the transpiration of sparse vegetation in arid/semiarid environment, while the existing mathematical formulas were not developed for such situations and thus have very poor estimation accuracy [11]. Recent developments in thermal technology have made it possible to measure transpiration in stems of branchlets [12,13,14] using a variety of approaches, including thermal pulse, thermal balance, thermal diffusion, and laser thermal pulse. Currently, commercial probes are available that are specifically designed to measure sap flow based on the thermal balance method, and they have been shown to be appropriate for brush branches with a small diameter [15,16,17].
In practice, the measurements of sap flow from individual stems need to be upscaled to derive the transpiration of the entire shrub community. Previous studies on upscaling of transpiration mainly focused on tall trees or vegetation types with a high canopy density, with independent variables (i.e., upscaling factors) of woodland area [18,19], canopy overlap [20], sapwood area [21], and/or diameter at breast height [22]. The accuracy of the upscaling results largely depended on the scalar multipliers of these independent variables between the shrub community and its individual members. In contrast, few studies have been conducted for upscaling the transpiration of sparsely distributed short shrubs in areas prone to deserts, though such studies are crucial for ecotone conservation as well as water and land resource management.
It is therefore of both scientific and practical importance to develop an accurate upscaling method for extrapolating measured stem-level transpiration to the entire shrub community. The objectives of this study were to: (1) measure sap flow of selected individual stems of two sand-fixing plants, namely Salix gordejevii and Caragana microphylla; and (2) upscale the measured stem-level sap flow for estimating the community-level transpiration. The study was conducted in the Horqin Sandy Land (HSL) located in northeast China.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
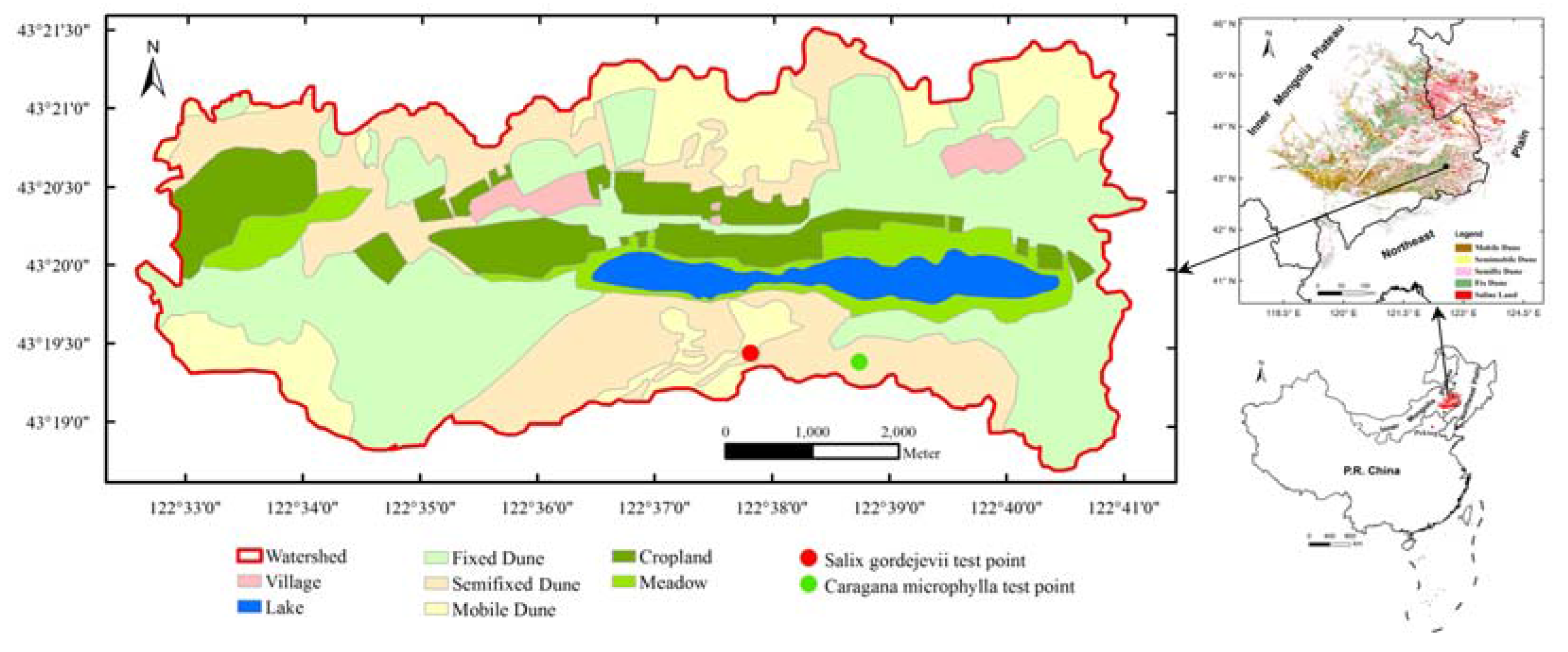
This study was conducted in the 55 km2 Agula Ecohydrologic Laboratory Field (122°33′00″–122°41′00″ E, 43°18′48″–43°21′24″ N), which is operated by the Inner Mongolia Agricultural University of China and part of HSL at its southeastern edge. The field has an altitude of 186 to 232 m above mean sea level. Its geomorphic features consist of sand dunes, meadows, farmlands, forests and lakes (Figure 1). The region has a temperate semiarid continental monsoon climate, with a dry and windy spring, hot summer, short autumn, and long cold winter. The average annual precipitation is about 380 mm, 69.3% of which falls from June to September. The average annual potential evapotranspiration is about 1400 mm, and the average annual temperature is about 6.6 °C.
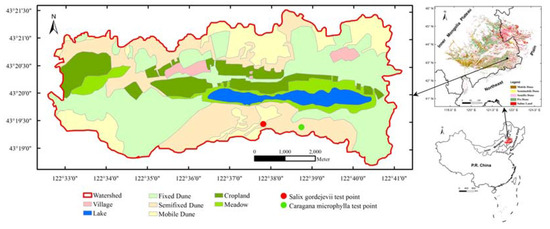
Figure 1.
Map showing the location, boundary, and geomorphic features of the Agula Ecohydrologic Laboratory Field. The dots signify the locations where the stem-level transpiration was measured in this study.
The natural (i.e., sand-fixing) vegetation in the field includes Salix gordejevii, Caragana microphylla, Artemisia halodendron, Agriophyllum squarrosum, Leymus chinensis and Phragmites australis. Maize, paddy, beans, and other secondary crops (e.g., sunflower) are cultivated. The sand-fixing vegetation survives on rainfall. The depth to shallow groundwater table is 2.3 to 26.5 m. The soil texture is mainly composed of sandy, sandy loam, and loamy sand, with more than 80% sand particles (diameter of 0.05 to 2.0 mm). The soils have a very low (<1%) content of organic matter and fertile compounds.
2.2. Survey Plots of Shrub Communities
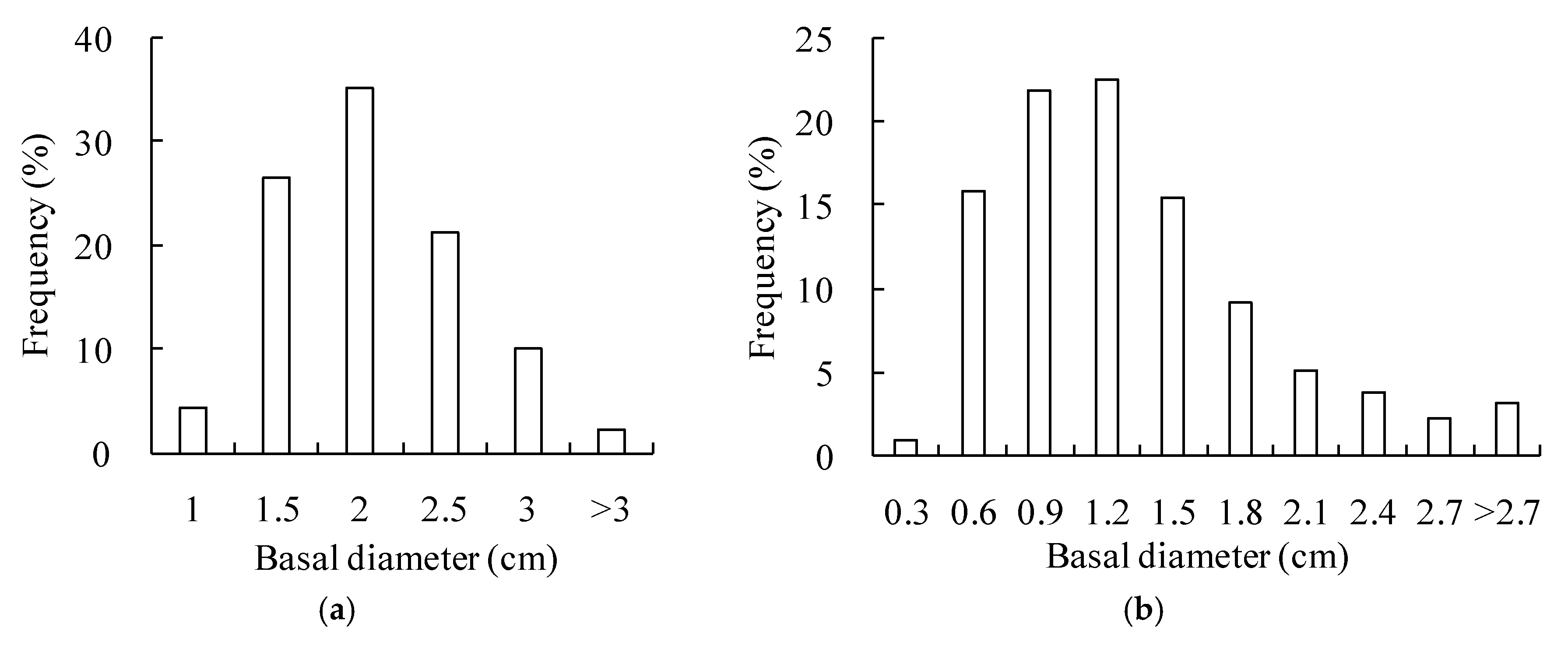
This study selected two plots of shrub communities as test beds. The first plot is a 225 m2 (15 m by 15 m) Salix gordejevii community uniformly distributed across the upper part of the shady slope of a mobile dune, while the second plot is a 625 m2 (25 m by 25 m) Caragana microphylla community growing in a low-lying area of semifixed dunes. For each of the two plots, in addition to the responding shrub, it had very sparse (2–3%) herbs, including Chenopodium glaucum, Corispermum hyssopifolium L., and Artemisia sieversiana. The density of the Salix gordejevii community was 35,882 stems ha−1, the average brush height was 2.7 m, and the average basal diameter was 1.8 cm. On the other hand, the naturally thinning density of the Caragana microphylla community was 1043 plants ha−1, the average brush height was 2.2 m, and the average patch canopy area was 3.4 m2. The basal diameter frequency distribution (Figure 2) was derived by recording the basal diameters of the Salix gordejevii or Caragana microphylla individual stems. The basal diameters of the Salix gordejevii were mostly in the range 1.5 to 3.0 cm (Figure 2a), accounting for 93% of the entire samples, whereas the basal diameters of the Caragana microphylla were primarily in the range 0.6 to 2.4 cm (Figure 2b), accounting for 92% of the entire samples.
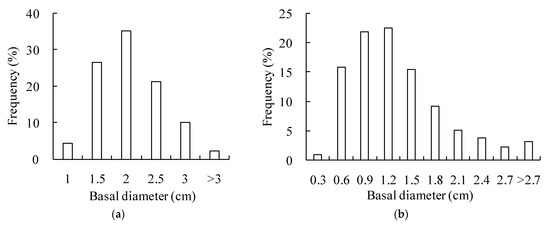
Figure 2.
Plots showing the basal diameter frequency distribution of the: (a) Salix gordejevii community; and (b) Caragana microphylla community.
2.3. Measurement of Sap Flow Rate and Environmental Factors
In terms of the frequency distributions of basal diameters (Figure 2), 5 representative stems were selected from the survey plot of Salix gordejevii, whereas, 8 representative stems were selected from the survey plot of Caragana microphylla. Herein, the representative branches are those that grew well with straight and plump stems and had a diameter with a relatively large frequency. A FLOW32-1K sap flow meter, manufactured by Dynagage, Dynamax Inc., Houston, TX, USA (http://dynamax.com) was attached to each of the representative stems to continuously record water flux through the stem cross-sectional area. Before installation, the stem was cleaned with a knife with care to avoid damaging the phloem, and its surface was polished with abrasive paper. Subsequently, the stem diameter was accurately measured using a vernier caliper. The stem was painted with a G4 oil mixture to strengthen the wrapping and the package firmly bound to ensure that the probe’s thermoelectric couplers maintained good contact with the stem. Finally, three layers of aluminum foil were wrapped around the stem to reduce influences of ambient environment conditions, such as solar radiation, temperature variation and humidity fluctuation. The sap flow was recorded at a time step of 30 min from 1 May to 30 September 2015. Moreover, the ambient environment parameters were measured at a time step of 30 min for the same period by a nearby sensor-based weather station, manufactured by Campbell Scientific Inc., Logan, UT, USA (http://www.campbellsci.com.cn/).
2.4. Leaf Area Measurement and Processing
A LAI-2200, manufactured by Li-Cor, Lincoln, NE, USA (https://www.licor.com), was used to measure leaf area index (LAI). The measurements were done for three relatively uniform subplots (3 m by 3 m each) in the Salix gordejevii survey plot, and for six typical plants in the Caragana microphylla survey plot. The six typical plants include two large ones with a patch canopy area of larger than 4.0 m2, two medium ones with a patch canopy area between 4.0 and 2.5 m2, and two small ones with a patch canopy area of less than 2.5 m2. To ensure the measurement accuracy, the LAI-2200 and its sensors were placed around the center of a subplot or patch area, making sure that the sensors were not shadowed by herbs, branches and leaves that were not parts of the shrub of interest.
For a given measurement, the DISTS value (Path Length of the Shrub) in the LAI-2200 was set to be the length of the longest branch Li (m) of the shrub. The LAI was determined as the shrub leaf area density LADi (m2·m−3) in a hemisphere volume of radius Li. Thus, the total leaf area Ai (m2) was computed as [23]:
The total leaf area for the Salix gordejevii survey plot was computed as 25 (=225 m2 ÷ 9 m2) times the arithmetic average of the measurements for the three subplots. According to the survey, the Caragana microphylla survey plot had 8 large, 36 medium, and 32 small plants. The total leaf area for this survey plot was determined as the plant number-weighted average of the arithmetic averages of the measurements for the selected two large, medium, and small individual plants.
2.5. Upscaling Transpiration Estimates
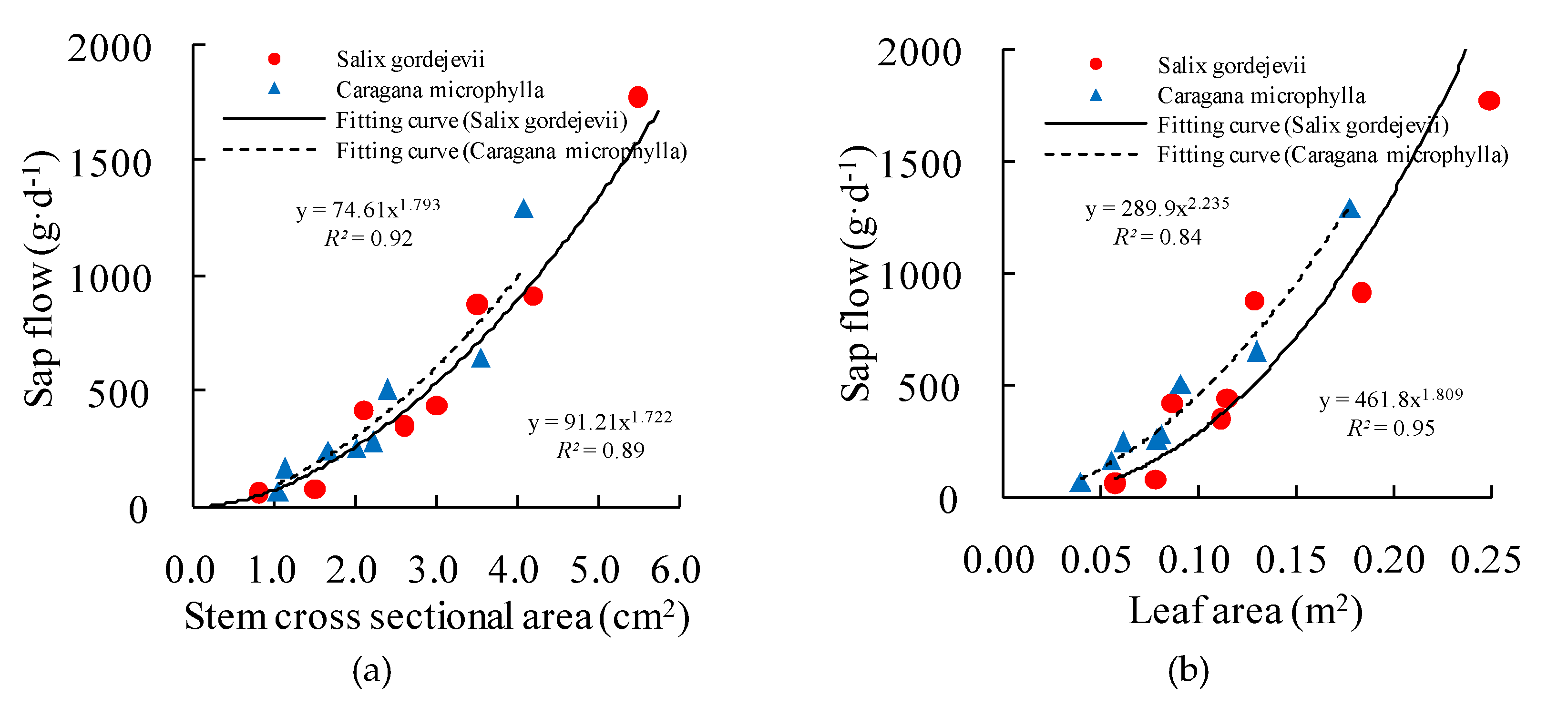
The measured sap flow was the transpiration rate of an individual stem (i.e., stem-level transpiration). However, practices in water management require that the stem-level transpiration be upscaled to derive the community-level transpiration [24]. Previous studies (e.g., [5,25]) revealed that in the sparse/open shrub lands in arid/semiarid environment, stem-level transpiration is proportional to stem cross-sectional area or leaf area. This was true for the study plots as shown in Figure 3. In this regard, this study used the measured and surveyed data to establish functional relationships between stem-level transpiration and stem cross-sectional area and leaf area, and then used the functions to estimate the community-level transpiration for the Salix gordejevii and Caragana microphylla survey plots.
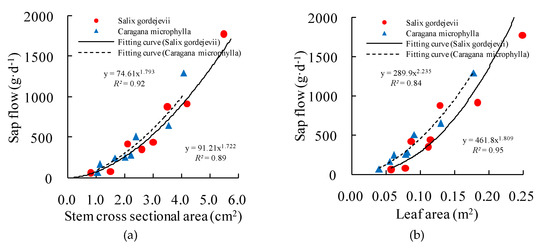
Figure 3.
Relationships (a) betweensap flow and the stem cross-sectional area and (b) betweensap flow and the leaf area of gauged stems for both shrubs.
Figure 3 shows the strong power function relationships between daily average sap flow and stem cross-sectional area, with high values of R2 0.92 and 0.89 for Salix gordejevii and Caragana microphylla, respectively. Further, good relationships also existed between daily average sap flow and leaf area, with high values of R2 0.84 and 0.95 for Salix gordejevii and Caragana microphylla, respectively. Hence, stem cross-sectional area and leaf area both can be chosen as potential upscaling factors according to the strong relationships.
In spite of this, stem cross-sectional area for Salix gordejevii and leaf area for Caragana microphylla were finally selected as the reason of high values of R2. In addition, field test difficulty and accuracy are also important factors. For Salix gordejevii, which has straight and rounded stems, they were easily determined with digital calipers. In contrast, the stems of Caragana microphylla are flexible with irregular shape, rough and growing messily, resulting in difficulty to measure the stem diameter. Besides, it is convenient to use the LAI-2200 instrument to measure LAI of Caragana microphylla due to the obviously single plant morphology. In contrast, it is relatively difficult to measure the LAI of Salix gordejevii due to the contiguous crown.
The community-level actual transpiration rate Tc, in mm·d−1, was estimated as:
where for Salix gordejevii, Ac (m2) is the total basal stem cross-sectional area of the shrubs in the sampling plot; Ai (m2) is the basal stem cross-sectional area of a representative branch i. For Caragana microphylla, Ac (m2) is the total leaf area of the shrubs in the sampling plot; Ai (m2) is the leaf area of a representative branch i. Fi (g·d−1) is the daily average sap flow of a representative branch i, n is the number of representative branch, ρ (kg·m−3) is the density of water, and A (m2) is the land surface area of the sampling plot for both plant species.
2.6. Validation of Upscaling Functions
To validate the upscaling functions, the upscaled community-level actual transpiration was compared with the responding actual evapotranspiration estimated by the Penman–Monteith equation expressed as [26]:
where ET0 and ETc (mm·d−1) are the potential and actual evapotranspiration rates, respectively; Kc is the single crop coefficient; Ks is the water stress coefficient; Rn is the net radiation (MJ·m−2·d−1); G is soil heat flux (MJ·m−2·d−1); T (°C) and (m·s−1) are the air temperature and wind speed at 2 m height above ground surface; es and ea (kPa) are the saturated and actual vapor pressures, respectively; Δ (kPa·°C−1) is the slope of the relation curve between saturated vapor pressure and temperature; γ (kPa·°C−1) is the hygrometer constant of 0.066.
The data for calculating ET0 were measured by the nearby weather station. The Kc and Ks values were from the FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization) irrigation and drainage paper 56 [27]. In this study, the values for Kc at the initial, mid, and end growing stages were determined as Kcini = 0.35, Kcmid = 1.15, and Kcend = 0.20, respectively. In terms of the 30 min data on soil moisture measured by the sensors at various depths of root zones within the survey plots, the values for Ks were determined to be between 0.95 and 0.75.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. The Measured Stem-Level Transpiration
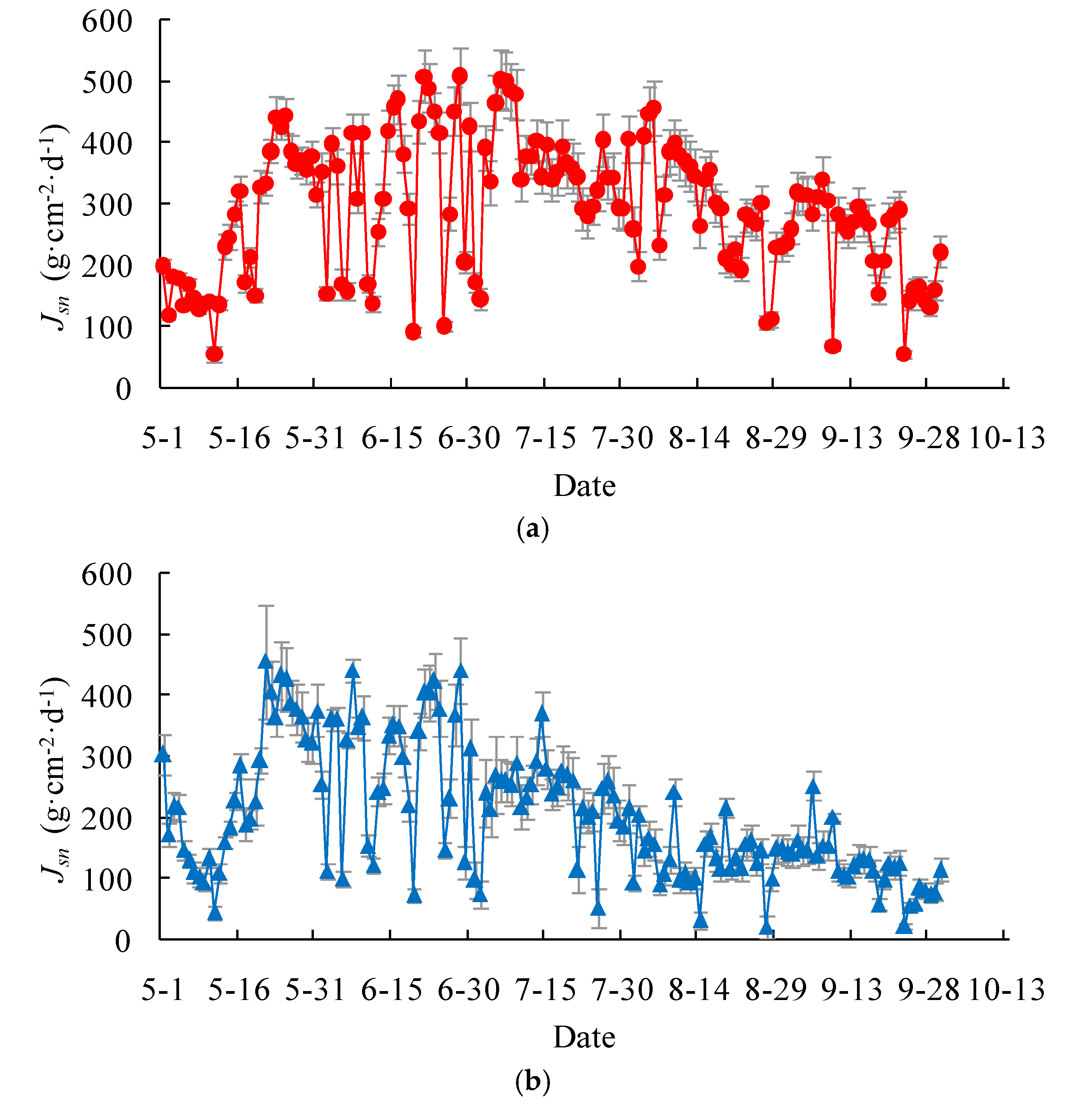
On the daily basis, the measured stem-level transpiration rate, expressed as the mass flux per unit stem cross-sectional area, varied from 54 ± 6 to 508 ± 48 g·cm−2·d−1, with a mean of 293 ± 27 g·cm−2·d−1, for the Salix gordejevii (Figure 4a). On the other hand, the measured stem-level transpiration rate varied from 22 ± 4 to 455 ± 43 g·cm−2·d−1, with a mean of 212 ± 22 g·cm−2·d−1, for the Caragana microphylla (Figure 4b). The Salix gordejevii had a stem-level transpiration rate about 1.38 times larger than the Caragana microphylla. Overall, for either plant, the stem-level transpiration rate increased from May to June, reached a peak around mid-June, and then started to decrease. However, the transpiration rate fluctuated from one day to another, as well as within a day.
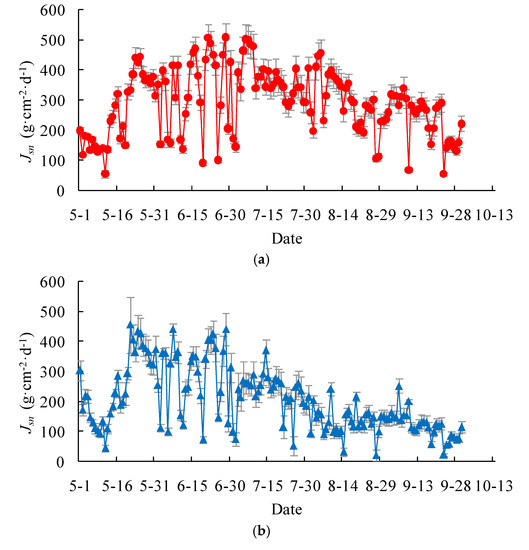
Figure 4.
Plots showing daily stem-level transpiration rate, Jsn, for the: (a) Salix gordejevii; and (b) Caragana microphylla. For a given day, the point represents the mean of the measurements for the measured stems, while the vertical bar represents one standard deviation.
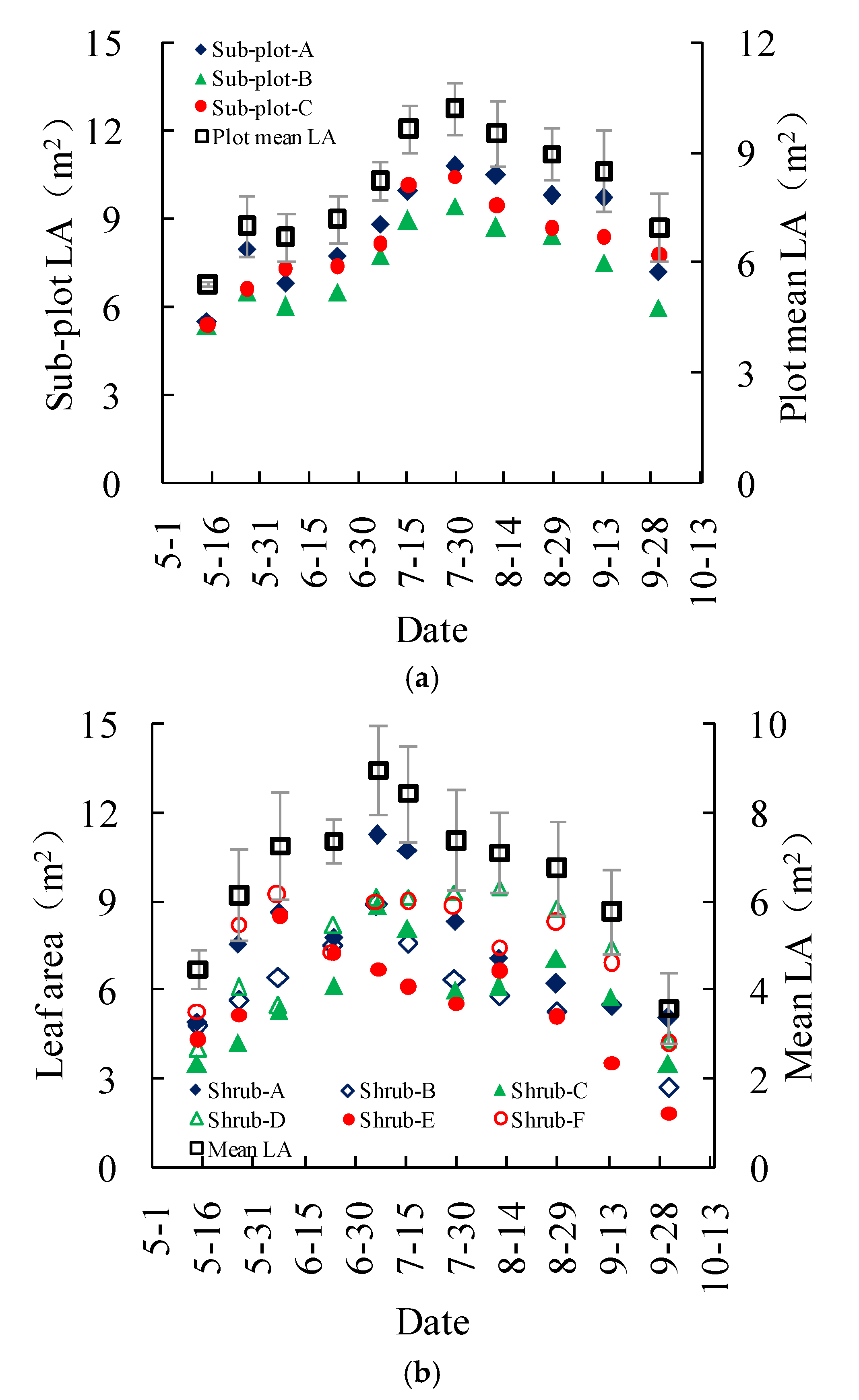
3.2. The Measured Leaf Area
The measured leaf areas of the three subplots in the Salix gordejevii survey plot showed a consistent increasing-peaking-decreasing trend throughout the growing season (Figure 5a). The leaf areas varied from 5.4 ± 0.1 to 10.2 ± 0.7 m2, with a mean of 8.0 ± 0.7 m2. In contrast, the measured leaf areas of the six shrubs in the Caragana microphylla survey plot did not exhibit a positive relationship with the shrub sizes (Figure 5b). The leaf areas for the two large shrubs were not consistently greater than those of the two medium or small shrubs. Also, the maximum leaf areas for the shrubs with different sizes might occur on different dates. The leaf areas varied from 3.6 ± 0.8 to 8.9 ± 1.0 m2, with a mean of 6.7 ± 0.9 m2. On average, the leaf area of the Salix gordejevii might be about 1.2 times larger than that of the Caragana microphylla.
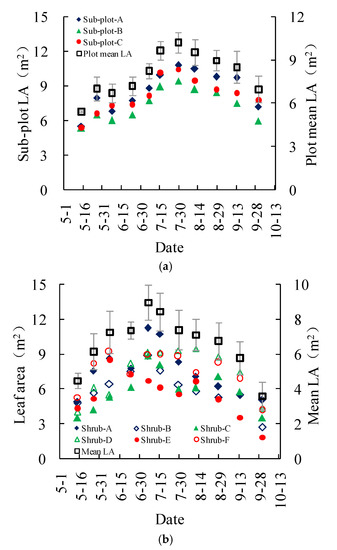
Figure 5.
Plots showing the measured leaf area (LA) of the: (a) Salix gordejevii; and (b) Caragana microphylla. The vertical bar signifies one standard deviation. Shrub-A and Shrub-B are large shrubs with a patch canopy area of larger than 4.0 m2, Shrub-C and Shrub-D are medium shrubs with a patch canopy area between 4.0 and 2.5 m2, and Shrub-E and Shrub-F are small shrubs with a patch canopy area of less than 2.5 m2.
3.3. The Upscaled Community-Level Transpiration
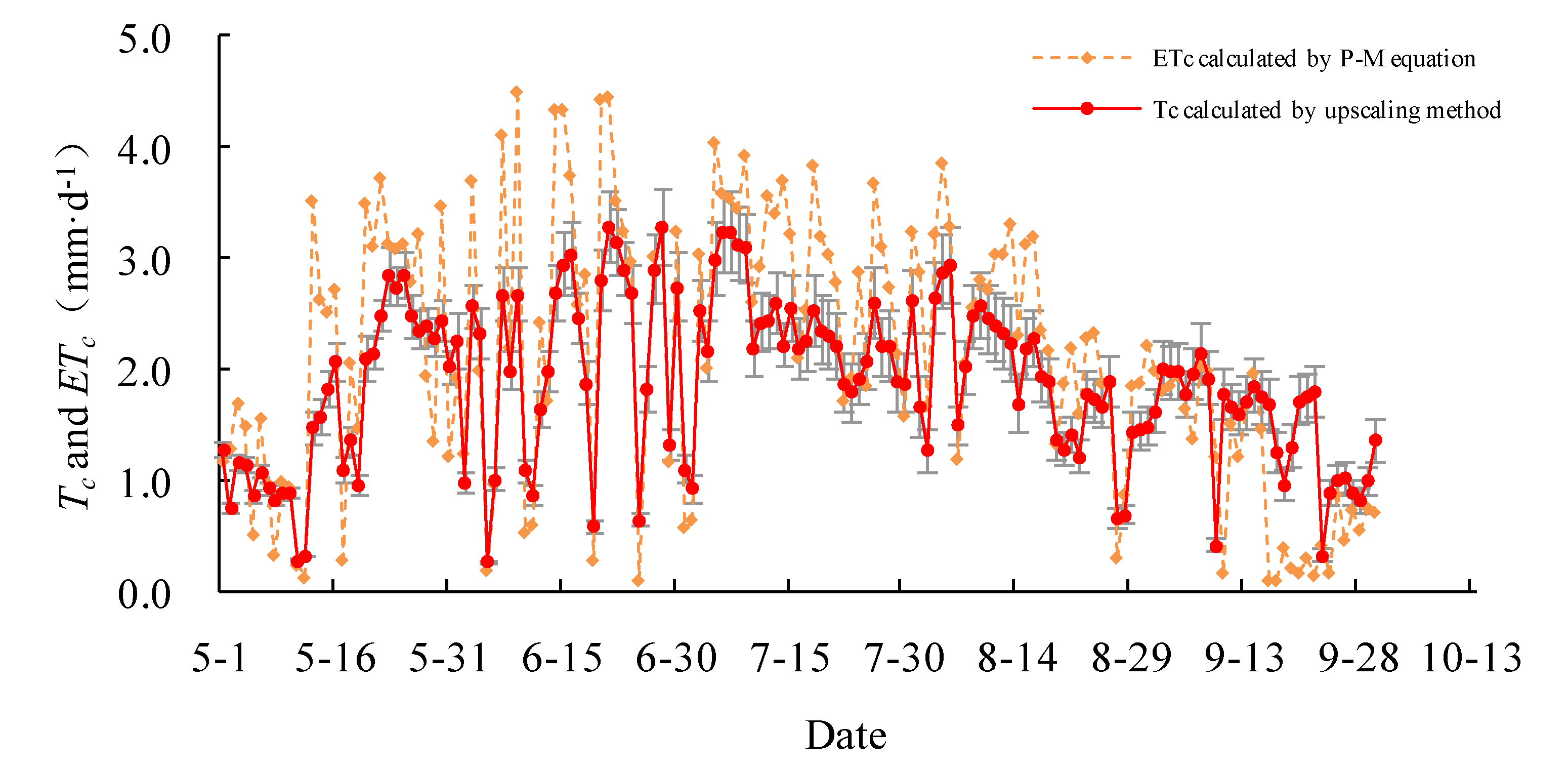
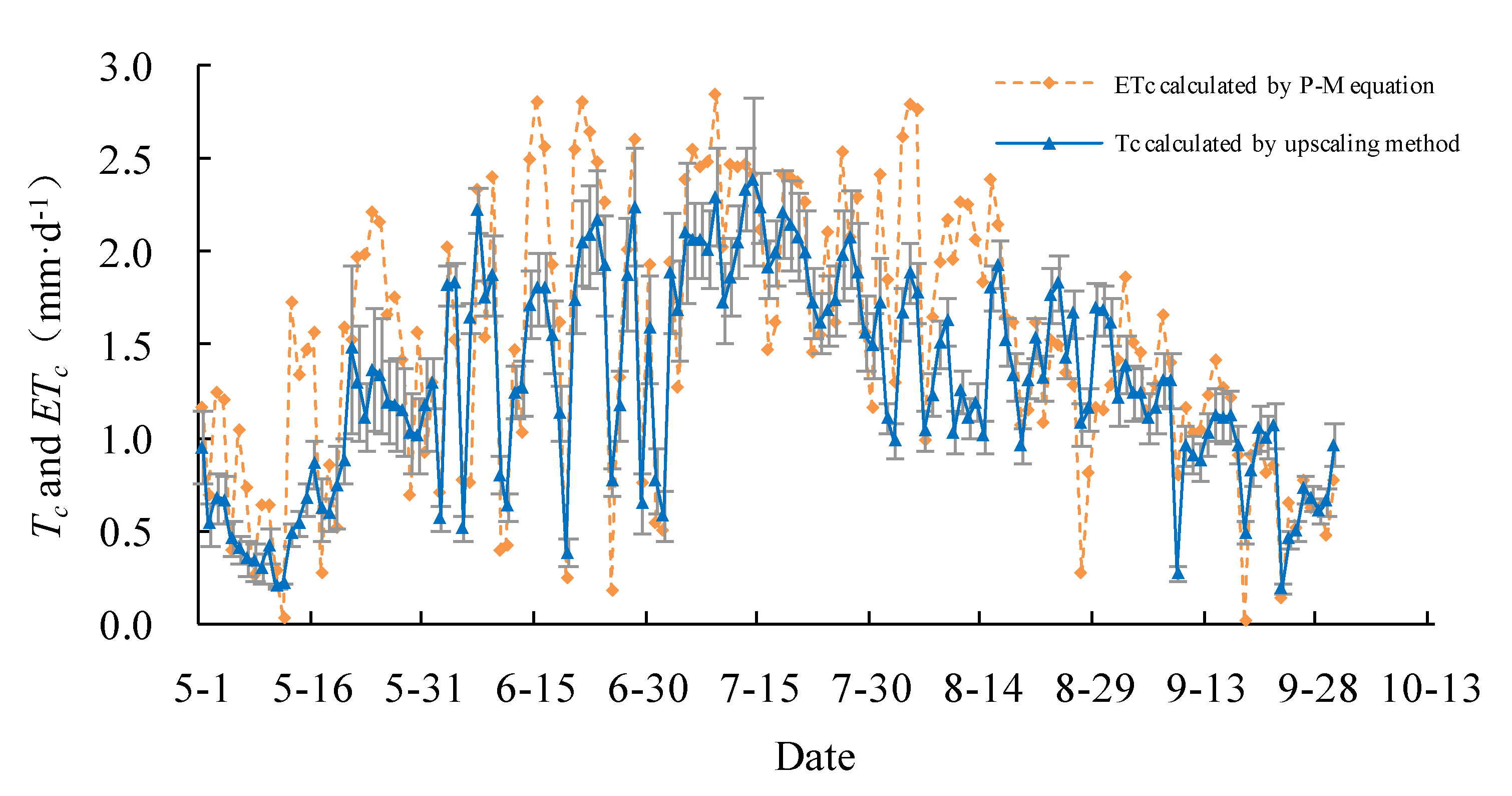
The daily actual transpiration Tc of the Salix gordejevii survey plot varied from 0.3 ± 0.1 to 3.3 ± 0.4 mm·d−1 (Figure 6), with a mean of 1.9 ± 0.2 mm·d−1, whereas, the daily actual transpiration Tc of the Caragana microphylla survey plot varied from 0.2 ± 0.1 to 2.4 ± 0.3 mm·d−1 (Figure 7), with a mean of 1.3 ± 0.2 mm·d−1. From 1 May to 30 September 2015, the total transpiration of the Salix gordejevii survey plot was 287 ± 31 mm, whereas, the total transpiration of the Caragana microphylla survey plot was 197 ± 24 mm. The transpiration from the Salix gordejevii survey plot was about 1.5 times larger than that from the Caragana microphylla survey plot.
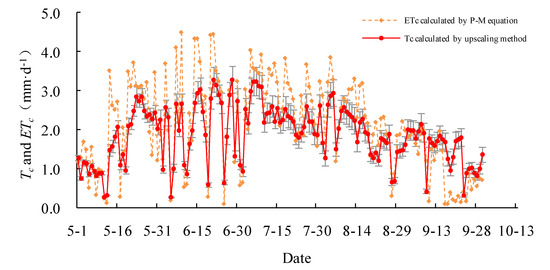
Figure 6.
The upscaled community-level transpiration rate (Tc) and the actual evapotranspiration rate (ETc) estimated by the Penman–Monteith equation for the Salix gordejevii survey plot. The vertical bar signifies one standard deviation.
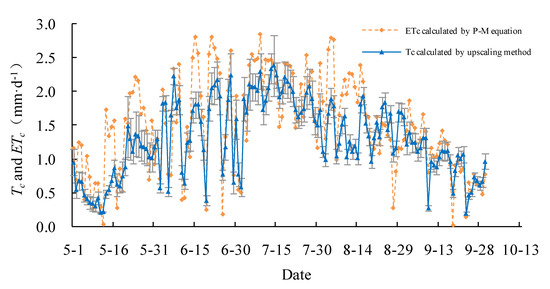
Figure 7.
The upscaled community-level transpiration rate (Tc) and the actual evapotranspiration rate (ETc) estimated by the Penman–Monteith equation for the Caragana microphylla survey plot. The vertical bar signifies one standard deviation.
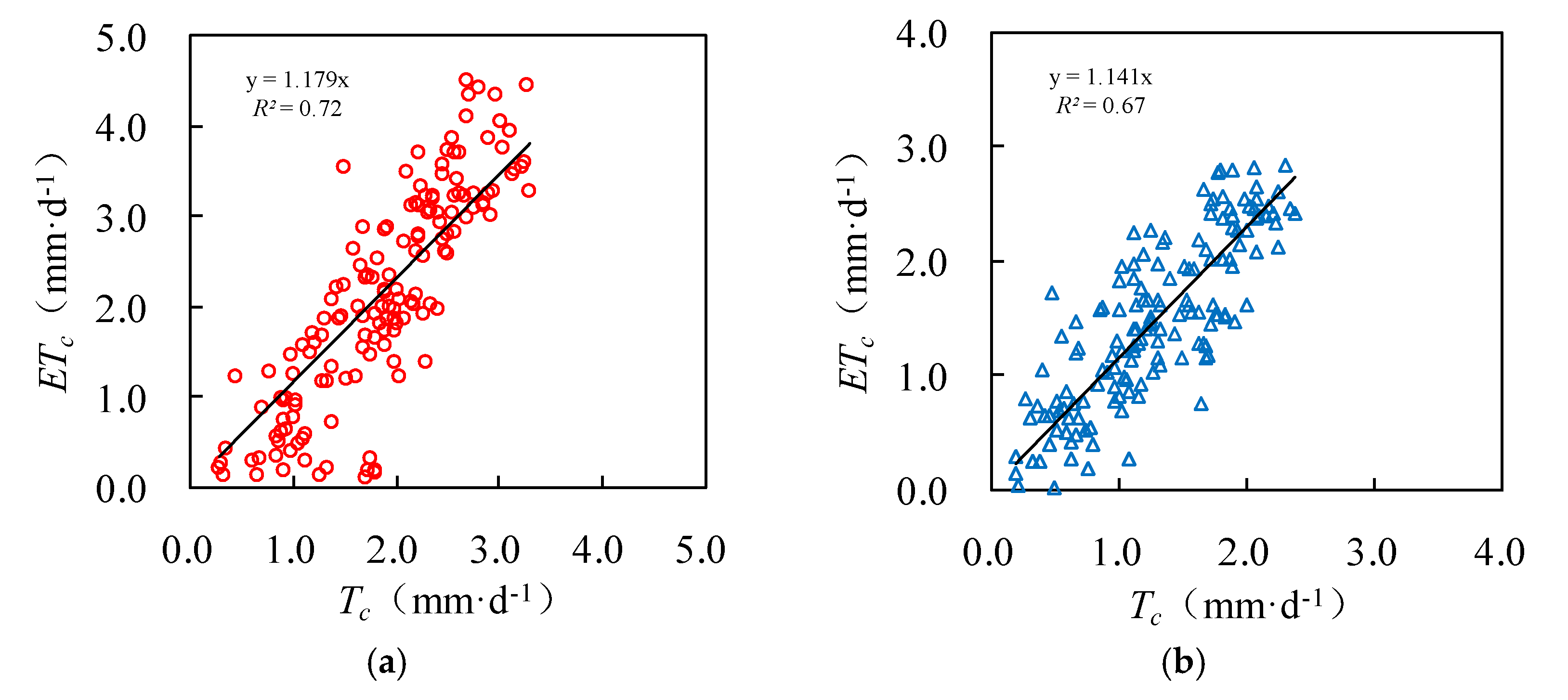
The daily actual evapotranspiration rate ETc estimated by the Penman–Monteith equation is also shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7. For both survey plots, the Tc well matched with ETc. Figure 8 further shows that the Tc and ETc were well correlated (R2 ≥ 0.67), indicating a good accuracy of the upscaling functions. The total transpiration of the Salix gordejevii and Caragana microphylla survey plots was 287 ± 31 and 197 ± 24 mm, respectively, which were slightly lower than the responding ETc of 323 and 229 mm, respectively.
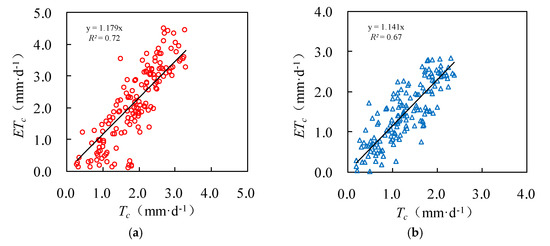
Figure 8.
Plots showing the upscaled (Tc) versus Penman–Monteith estimated (ETc) for the: (a) Salix gordejevii; and (b) Caragana microphylla survey plots.
4. Discussion
For a given date, the leaf area varies from subplot to subplot or from one shrub to another (Figure 5). This is because the location-specific physiographic characteristics (e.g., terrain and soils) could influence the growth of desert plants [28]. The water consumption of the Salix gordejevii is about 1.5 times higher than the Caragana microphylla, which is consistent with the previous studies (e.g., [29,30]).
Practices require that the measured stem-level transpiration be upscaled to derive the community-level transpiration [31,32]. The upscaling functions usually have two independent variables, namely stem cross-sectional area and leaf area, while additional independent variables, such as shrub density, shrub size, leaf weight, basal diameter, and sapwood area can also be included [33,34]. This study selected the two commonly-used independent variables [35] because they: (1) are weakly dependent on topography, slope aspect and soils; (2) vary slightly with age and environment (e.g., precipitation); (3) have little differences among the individual stems; and (4) are well correlated with transpiration (Figure 3).
During the study period (1 May to 30 September 2015), the daily transpiration rate for the Salix gordejevii and Caragana microphylla survey plots was 1.9 and 1.3 mm·d−1, respectively. This is consistent with Allen and Grime [25], who reported the daily transpiration rate of a Guiera senegalensis community in the West African savannah to be 1.5 to 2.0 mm·d−1. Similarly, Niu et al. [23] found that the transpiration rate of the Caragana microphylla community in the HSL varied from 0.5 to 2.3 mm·d−1. These indicate that the upscaling functions developed in this study are accurate for the Salix gordejevii and Caragana microphylla survey plots.
During the study period, the total rainfall was 336 mm, whereas the total transpiration of the Salix gordejevii and Caragana microphylla communities were 287 ± 31 and 197 ± 24 mm, respectively. They are underestimating by about 36 ± 31 mm and 32 ± 24 mm, respectively. This is because the results of Tc are Salix gordejevii and Caragana microphylla communities’ actual transpiration. However, the result of ETc computed by P–M equation is actual evapotranspiration, which includes vegetation transpiration and total evaporation (intercept and bare soil). Hence, ETc is higher than Tc that is logically destined. This result indirectly reflected that the total evaporation, for the period 1 May to 30 September, were 36 ± 31 mm and 32 ± 24 mm of Salix gordejevii and Caragana microphylla community, respectively, that is, accounting for up to 21% and 24% of the ETc, respectively.
The rainfall was thus sufficient enough to meet the transpiration demands of these two plants. Bai [36] examined the evapotranspiration during the growing season of the Salix gordejevii in the Hunshadake Sandy Land for an eight-year period (2006–2013) using the Shuttleworth–Wallace Model, and found that the soil evaporation accounted for 18% and 39% of the total evapotranspiration. Yue et al. [5] reported that soil evaporation of the Caragana microphylla in the HSL in June 2006 accounted for 14% of the total evapotranspiration. The proportion of soil evaporation reported by those studies are consistent with that of this study, which are estimated to be 21% and 24% of the total evapotranspiration for the Salix gordejevii and Caragana microphylla communities, respectively.
This study estimated the community-level transpiration based on the measurements of sap flow from a few of the selected individual stems. The small sample sizes may introduce some degree of uncertainties. In addition, errors may be introduced through the sap flow monitoring methods [24,37] and scaling functions [19,38,39]. The extrapolation of stem-level sap flow to the community-level transpiration rate assumes a constant proportionality between sap flow rate and stem cross-sectional area or leaf area. This assumption may be invalid, as studies have shown universal intra-species variability in sap flow density among individual stems across a wide range of species [19,24,38]. Further, the inadequate stem samples might affect the accuracy of experimental results. Moreover, such uncertainties could somewhat bias the conclusions of this study, which can be further investigated in future studies.
Future studies should focus on measuring more stems to quantify stem-to-stem variability in sap flow and to minimize the potential uncertainty resulting from scaling. Additionally, a more comprehensive approach for future investigation would be to conduct simultaneous measurements using some independent methods at different scales [40,41,42], such as the individual leaf gases exchange and water potential, roots sap flow, and stand scale micrometeorological methods, eddy covariance, among others. These complementary and analytical tools would be useful in improving the accuracy of community transpiration and understanding physiological and environment regulation of transpiration at the stand level, especially with regard to determining water sources used by desert shrubs.
5. Conclusions
This study developed upscaling functions with two independent variables, namely stem cross-sectional area of Salix gordejevii and leaf area of Caragana microphylla, because these variables had a strong correlation with sap flow of the representative stems. Subsequently, these functions were used to estimate the community-level transpiration of these two plants. The total transpiration in the 2015 growing season for the Salix gordejevii community was about 1.5 times larger than that of the Caragana microphylla community, indicating that the water consumption of the Salix gordejevii was relatively higher. The Caragana microphylla community was less susceptible to restricted soil water in the study area, where the plant community can play an important ecological role in stabilizing fixed and semi-fixed sandy dunes. However, the Salix gordejevii community should not be replaced because of its significant role in stabilizing movable sandy dunes. It is suggested that sand fixing plants should be selected in terms of site conditions. The upscaling functions may be improved by measuring more stems and can have broad applications for better managing the fragile ecosystem of desert environments, including the HSL.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51369016, 51620105003 and 51139002), the Excellent Young Scientist Foundation of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University of China (Grant No. 2014XYQ-11), the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia (Grant No. 2015MS0566), the Ministry of Education Innovative Research Team (Grant No. IRT13069), and the Innovation Team in Priority Areas Accredited by the Ministry of Science and Technology (Grant No. 2015RA4013). We thank all members of our Hydrology and Water Resources Research Group. We are very grateful to the editors and anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments, which greatly improved the quality of the paper.
Author Contributions
Limin Duan developed the initial and final versions of this manuscript and analyzed the data. Yang Lv, Xue Yan, Tingxi Liu and Xixi Wang contributed their expertise and insights, overseeing all of the analysis and supporting the writing of the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cheng, L.L.; Yin, C.B.; Lu, Q.; Wu, B.; Que, X.E. Economic analysis of desertification cause and irrational human activities. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2016, 37, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.L. Vegetation Adaptation Strategy and Sustainable Mechanism under Desertification; China Ocean University Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Hasi, E.; Yang, Y.; Wu, X. Responses of nebkhas morphology to the mode and richness of sand supply. J. Desert Res. 2015, 35, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, G.F.; Zhang, P.; Luo, Y. Some questions on modeling the desert plants transpiration process in China. J. Desert Res. 2012, 32, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, G.Y.; Zhao, H.L.; Zhang, T.H.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhao, W.; Niu, L.; Liu, X.P. Estimation of transpiration in communities dominated by shrub Caragana microphylla. Chin. J. Plant. Ecol. 2009, 33, 508–515. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Sun, H.Y.; Shen, Y.J.; Qi, Y.Q. Application of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes technique in the water depletion of ecosystems. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2012, 32, 289–293. [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura, H.; Sakamoto, D.; Sugiura, T.; Asakura, T.; Moriguchi, T. Evaluation of the use of the Granier sap flow method in Japanese pear by comparison with transpiration by the weighing method. Acta Hortic. 2009, 846, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.H.; Wierenga, P.J.; Mancino, C.F. Monitoring near-surface soil water storage in turfgrass using time domain reflectometry and weighing lysimetry. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, R.L.; Geng, S.; Orang, M.; Sarreshteh, S. Calculation and simulation of evapotranspiration of applied water. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanusa, I.A.M.; Nuberg, I.K.; Fuentes, S.; Lu, P.; Eamus, D. A simple field validation of daily transpiration derived from sapflow using a porometer and minimal meteorological data. Plant Soil 2008, 305, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.L.; Yin, Y.H.; Wu, S.H. Advancements of the metrics of evapotranspiration. Adv. Earth Sci. 2012, 31, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.X.; Liu, Z.J.; Wang, J.H.; Xu, X.Y.; Tang, J.N.; Zhang, D.M. Measurement of shrub’s water consumption with stemheat balance (SHB) in the desert and arid area. Prot. For. Sci. Technol. 2004, 6, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.P.; Wang, Z.N.; Berndtsson, R.; Zhang, Y.F.; Pan, Y.X. Desert shrub stemflow and its significance in soil moisture replenishment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.P.; Alonso, B.N.; Alegre, J. Water storage capacity, stemflow and water funneling in Mediterranean shrubs. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.J.; Cha, T.S.; Qin, S.G.; Qian, D.; Jia, X. Temporal patterns and environmental controls of sap flow in Artemisia ordosica. Chin. J. Ecol. 2014, 33, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Razzaghi, F.; Ahmadi, S.H.; Adolf, V.I.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Andersen, M.N. Water relations and transpiration of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) under salinity and soil drying. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2011, 197, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.G.; Xia, J.B.; Wang, R.R.; Li, T.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Liu, J.T. Effects of soil moisture on characteristics of sap flow of Securinega suffruticosa. J. Desert Res. 2013, 33, 1385–1389. [Google Scholar]
- Ham, J.M.; Heilmann, J.L.; Lascano, R.J. Determination of soil water evaporation and transpiration from energy balance and flow measurements. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1990, 52, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatton, T.J.; Wu, H.I. A scaling theory to extrapolate individual tree water use to stand water use. Hydrol. Process. 1995, 9, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Wang, Y.H.; Yu, P.T.; Liu, H.L.; Xu, L.H.; Shi, Z.J.; Mo, F. Variation of sap flow among individual trees and scaling up for estimation of transpiration of Larix principis rupprechtii stand. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2008, 44, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Jaskierniak, D.; Benyon, R.; Kuczera, G.; Robinson, A. A new method for measuring stand sapwood area in forests. Ecohydrology 2015, 8, 504–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Liang, F.C.; Chang, S.L.; Shi, Q.D.; Li, X.; Lu, J.J. Scaling up for transpiration of Pinaceae schrenkiana stands based on 8 hm2 permanent plots in Tianshan Mountains. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 3330–3339. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, L.; Yue, G.Y.; Zhao, H.L.; Zhang, T.H.; Zhao, X.Y.; Liu, X.P.; Zhao, W. Evaluating transpiration from Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica and Caragana microphylla using sap flow method. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2008, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Köstner, B.; Granier, B.; Cermák, J. Sapflow measurements in forest stands: Methods and uncertainties. Ann. For. Sci. 1998, 55, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.J.; Grime, V.L. Measurements of transpiration from savannah shrubs using sap flow gauges. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 75, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H.; Kisi, O.; Ezani, A.; Talaee, P.H. SVM, ANFIS, regression and climate based models for reference evapotranspiration modeling using limited climatic data in a semi-arid highland environment. J. Hydrol. 2012, 444, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements: FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; FAO of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, H.M.; Lu, R.; Liu, Y.; Fang, N.F.; Wu, G.L.; Shi, G.L. Effects of shrub patch size succession on plant diversity and soil water content in the water-wind erosion crisscross region on the Loess Plateau. Catena 2016, 144, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, G.Y.; Zhang, T.H.; Zhao, H.L.; Niu, L.; Liu, X.P.; Huang, G. Characteristics of sap flow and transpiration of Salix gordejevii and Caragana microphylla in Horqin Sandy Land, northeast China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 3205–3213. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, C.; Gong, J.Z.; Marrs, R.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.Q. Pattern of transpiration of four shrub species and water consumption from shrub stands in an eco-reclamation catchment in northwest China. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2008, 22, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomo’omi, K.; Hisami, N.; Tetsuya, M.; Shigeru, O.; Katsuyoshi, K.; Kimio, K.; Yasuhiro, U.; Shinya, K.; Kyoichi, O. Sources of error in estimating stand transpiration using allometric relationships between stem diameter and sapwood area for Cryptomeria japonica and Chamaecyparis obtusa. For. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 206, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X. The extrapolation of the leaf area-based transpiration of two xerophytic shrubs in a revegetated desert area in the Tengger Desert, China. Hydrol. Res. 2015, 46, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermak, J.; Kucera, J.; Nadezhdina, N. Sap flow measurements with some thermodynamic methods, flow integration with trees and scaling up from sample trees to entire forest stands. Trees 2004, 18, 529–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, J.E.; Khan, A.A.H.; Black, C.R.; Ong, C.K. Water use in a Grevillea robusta-maize overstorey agroforestry system in semi-arid Kenya. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 180, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, Y.D.; Fu, B.J.; Lv, Y.H. Landscape pattern and eco-hydrological process. Adv. Earth Sci. 2009, 24, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L. Research and Analysis of Water Requirement in Growth Period of the Wild Salix gordejevii in the Hunshandake Desert Based on Dual Source Model. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Glenn, E.P.; Morino, K.; Didan, K.; Jordan, F.; Carroll, K.C.; Nagler, P.L.; Hultine, K.; Sheader, L.; Waugh, J. Scaling sap flux measurements of grazed and ungrazed shrub communities with fine and coarse-resolution remote sensing. Ecohydrology 2008, 1, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, C.R.; McGuire, M.A.; Mitchell, R.J.; Teskey, R.O. Assessing variation in the radial profile of the sap flow density in Pinus species and its effects on daily water use. Tree Physiol. 2004, 24, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenn, E.P.; Nagler, P.L.; Morino, K.; Hultine, K.R. Phreatophytes under stress: Transpiration and stomatal conductance of saltcedar (Tamarix spp.) in a high-salinity environment. Plant Soil 2013, 371, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.L.; Huxman, T.E.; Cable, W.L.; Emmerich, W.E. Partitioning of evapotranspiration and its relation to carbon dioxide exchange in a Chihuahua desert shrubland. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 3227–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeppel, M. Convergence of tree water use and hydraulic architecture in water water-limited regions: A review and synthesis. Ecohydrology 2013, 6, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doody, T.M.; Colloff, M.J.; Davies, M.; Koul, V.; Benyon, R.G.; Nagler, P.L. Quantifying water requirements of riparian river red gum (Eucalyptus camaldulensis) in the Murray–Darling Basin, Australia—Implications for the management of environmental flows. Ecohydrology 2015, 8, 1471–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).