A Review of Small Farmer Land Use and Deforestation in Tropical Forest Frontiers: Implications for Conservation and Sustainable Livelihoods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
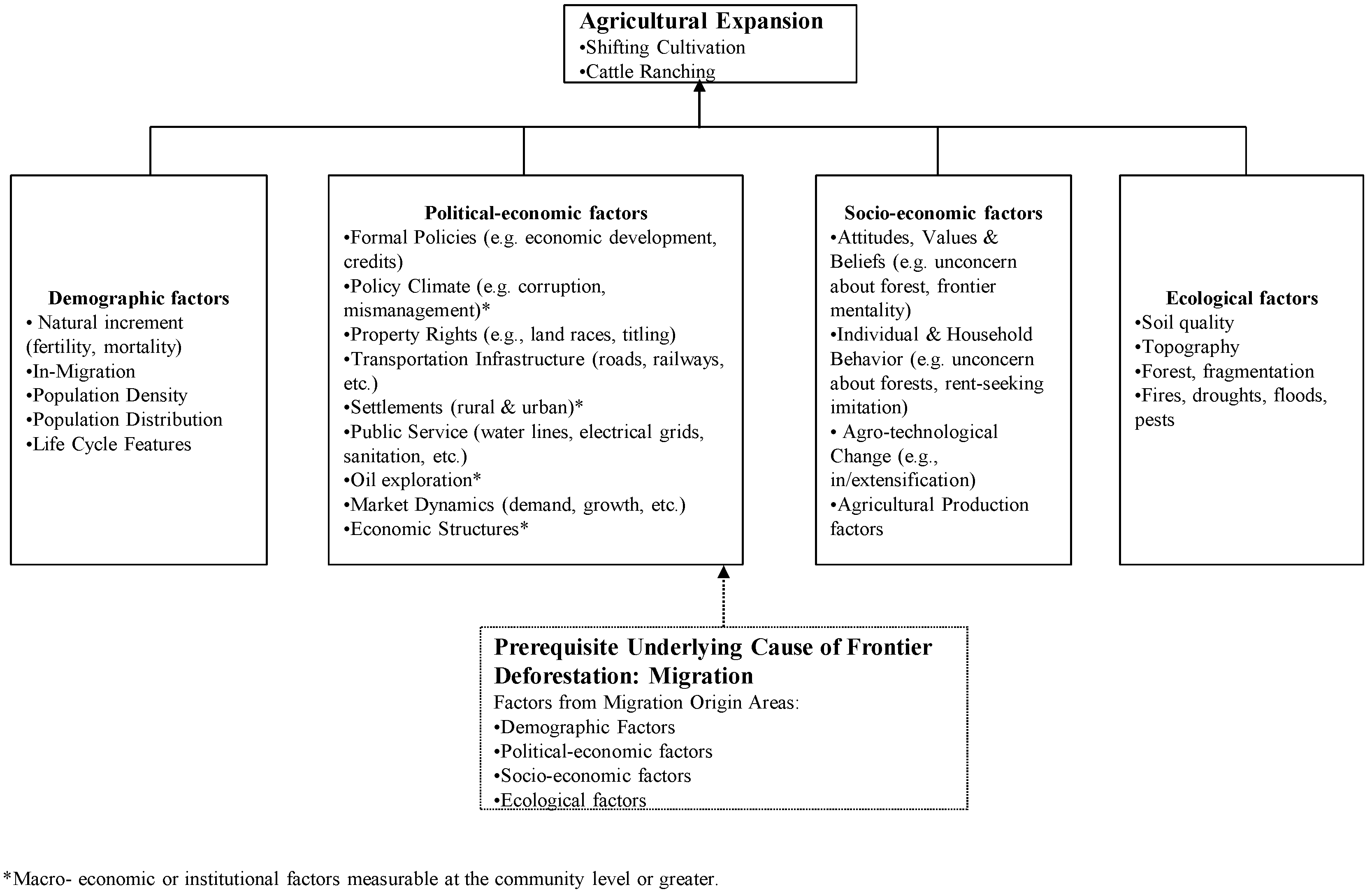
2. Proximate Determinants of Small Farmer Land Use in Tropical Agricultural Frontiers
2.1. Demographic Factors
2.1.1. Frontier In-Migration
2.1.2. Household Size
2.1.3. Household Demographic Life Cycle
2.1.4. Population Density
2.2. Political–Economic Factors
2.2.1. Neoclassical Economics
2.2.2. Macroeconomic Factors
2.2.3. Policy Incentives
2.3. Socioeconomic Factors
2.3.1. Small Farmer Livelihoods
2.3.2. Farm Space, Time Dimensions, and Frontier LUCC
2.3.3. Education, Origin Characteristics, Perception, Ethnicity
2.4. Ecological Factors
3. Discussion: Implications for Protection and Restoration
3.1. Demographic Processes
3.2. Socioeconomic Livelihood and Political Processes
3.3. Ecological, Geographic and Temporal Dimensions
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krogh, A. State of the Tropical Rainforest; Rainforest Foundation: Oslo, Norway, 2020; 32p. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, W.B.; Turner, B.L. Land-use/land-cover change: Challenges for geographers. GeoJournal 1996, 39, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geist, H.J.; Lambin, E.F. What Drives Tropical Deforestation? A Meta-Analysis of Proximate and Underlying Causes of Deforestation Based on Sub-National Case Study Evidence; LUCC International Project Office: Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 2001; 116p. [Google Scholar]
- Pricope, N.; Husak, G.; Lopez-Carr, D.; Funk, C.; Michaelsen, J. The climate-population nexus in the East African Horn: Emerging degradation trends in rangeland and pastoral livelihood zones. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 1525–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.; Meyfroidt, P.; Kuemmerle, T.; Müller, D.; Chowdhury, R.R. Framing the search for a theory of land use. J. Land Use Sci. 2020, 15, 489–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaimowitz, D.; Angelsen, A. Economic Models of Tropical Deforestation: A Review; Centre for International Forestry Research: Jakarta, Indonesia, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, D. Population and deforestation: Why rural migration matters. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2008, 33, 355–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, P. Agricultural expansion and deforestation in lowland Bolivia: The import substitution versus the structural adjustment model. Land Use Policy 2006, 23, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aide, T.M.; Clark, M.L.; Grau, H.R.; López-Carr, D.; Levy, M.A.; Redo, D.; Bonilla-Moheno, M.; Riner, G.; Andrade-Núñez, M.J.; Muñiz, M. Deforestation and Reforestation of Latin America and the Caribbean (2001–2010). Biotropica 2013, 45, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, T.; Meyer, W.B.; Turner, B. Changes in Land Use and Land Cover: A Global Perspective. Geogr. J. 1996, 162, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Carr, D.; Burgdorfer, J. Deforestation Drivers: Population, Migration, and Tropical Land Use. Environ. Sci. Policy Sustain. Dev. 2013, 55, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, C.L.; Prescott, G.W.; De Alban, J.D.T.; Ziegler, A.D.; Webb, E.L. Untangling the proximate causes and underlying drivers of deforestation and forest degradation in Myanmar. Conserv. Biol. 2017, 31, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rueda, X.; Velez, M.A.; Moros, L.; Rodriguez, L.A. Beyond proximate and distal causes of land-use change: Linking Individual motivations to deforestation in rural contexts. Ecol. Soc. 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Achard, F.; Gallego, J.; Richards, T.; Malingreau, J.P.; Eva, H.D.; Stibig, H.J.; Mayaux, P. Determination of deforestation rates of the world’s humid tropical forests. Science 2002, 297, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Carr, D.; Ryan, S.J.; Clark, M. Global economic and diet transitions drove Latin American and Caribbean forest change during the first decade of the century. EcoEvoRxiv. 2021. Available online: https://ecoevorxiv.org/62zpc/ (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Bilsborrow, R.E.; Geores, M. Population Change and Agricultural Intenisification in Developing Countries. Population and Environment: Rethinking the Debatel; Arizpe, L., Major, D.C., Stone, P., Eds.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- López-Carr, D. Agro-ecological determinants of rural out-migration to the Maya biosphere reserve, Guatemala. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 045603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, K. The theory of change and response in modern demographic history. Popul. Index 1963, 29, 345–366. [Google Scholar]
- Aide, T.M.; Grau, H.R. Ecology. Globalization, migration, and Latin American ecosystems. Science 2004, 305, 1915–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ervin, D.; Lopéz-Carr, D.; Riosmena, F.; Ryan, S.J. Examining the relationship between migration and forest cover change in Mexico from 2001 to 2010. Land Use Policy 2020, 91, 104334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bologna, M.; Aquino, G. Deforestation and world population sustainability: A quantitative analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B. Agricultural Expansion, Resource Booms and Growth in Latin America: Implications for Long-run Economic Development. World Dev. 2004, 32, 137–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, D.L.; Bilsborrow, R.E. Population and Land Use/Cover Change: A Regional Comparison between Central America and South America. J. Geogr. Educ. 2001, 43, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Meyfroidt, P.; Lambin, E.F. Forest transition in Vietnam and displacement of deforestation abroad. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16139–16144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caviglia-Harris, J.L.; Sills, E.O.; Mullan, K. Migration and mobility on the Amazon frontier. Popul. Environ. 2013, 34, 338–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, S.; Cockburn, A. The Fate of the Forest; Harper Collins: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, C.H.; Porro, R. (Eds.) Deforestation and Land Use in the Amazon; University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ewers, R.M.; Laurance, W.F. Scale-dependent patterns of deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon. Environ. Conserv. 2006, 33, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, L.L.; Marquette, C.; Pichón, F.J.; Bilsborrow, R. Land use, household composition, and economic status of settlers in Ecuador’s Amazon: A review and synthesis of research findings, 1990–1999. In Proceedings of the University of Florida, Center for Latin American Studies 48th Annual Conference: “Patterns and Processes of Land Use and Forest Change in the Amazon, Gainesville, FL, USA, 23–26 March 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sierra, R. Traditional resource-use systems and tropical deforestation in a multi-ethnic region in North-West Ecuador. Environ. Conserv. 1999, 26, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoghegan, J.; Villar, S.C.; Klepeis, P.; Mendoza, P.M.; Ogneva-Himmelberger, Y.; Chowdhury, R.R.; Turner, B.; Vance, C. Modeling tropical deforestation in the southern Yucatán peninsular region: Comparing survey and satellite data. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 85, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepeis, P.; Turner, B.L. Integrated land history and global change science: The example of the Southern Yucatan Peninsular Region project. Land Use Policy 2001, 18, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L., II; Geoghegan, J.; Foster, D. Integrated Land-Change Science and Tropical Deforestation in the Southern Yucatán: Final Frontiers; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2004; 320p. [Google Scholar]
- Sader, S.A.; Reining, C.; Sever, T.; Soza, C. Human Migration and agricultural expansion: An impending threat to the Maya Biosphere Reserve. J. For. 1997, 95, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- VanWey, L.K. The Power of Home: Remittances to Families and Communities. Immigr. Int. Money Flows 2007, 123, 123–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makunga, J.; Misana, S.B. The Extent and Drivers of Deforestation and Forest Degradation in Masito-Ugalla Ecosystem, Kigoma Region, Tanzania. Open J. For. 2017, 07, 285–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sellers, S. Family planning and deforestation: Evidence from the Ecuadorian Amazon. Popul. Environ. 2017, 38, 424–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, D.L.; Pan, W.; Bilsborrow, R.E. Declining fertility on the frontier: The Ecuadorian Amazon. Popul. Environ. 2007, 28, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, W.K.; Walsh, S.J.; Bilsborrow, R.E.; Frizzelle, B.; Erlien, C.M.; Baquero, F. Farm-level models of spatial patterns of land use and land cover dynamics in the Ecuadorian Amazon. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 101, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosero-Bixby, L.; Palloni, A. Population and deforestation in Costa Rica. Popul. Environ. 1998, 20, 149–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, D.L. Forest Clearing Among Farm Households in the Maya Biosphere Reserve. Prof. Geogr. 2005, 57, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munthali, M.G.; Davis, N.; Adeola, A.M.; Botai, J.O.; Kamwi, J.M.; Chisale, H.L.W.; Orimoogunje, O.O.I. Local Perception of Drivers of Land-Use and Land-Cover Change Dynamics across Dedza District, Central Malawi Region. Sustainability 2019, 11, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carr, D.L. Proximate Population Factors and Deforestation in Tropical Agricultural Frontiers. Popul. Environ. 2003, 25, 585–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chayanov, A.V. The Theory of Peasant Economy; University of Wisconsin Press: Madison, WI, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, R.; Perz, S.; Caldas, M.; Silva, L.G.T. Land use and land cover change in forest frontiers: The role of household life cycles. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2002, 25, 169–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pichón, F.J. Settler households and land-use patterns in the Amazon frontier: Farm-level evidence from Ecuador. World Dev. 1997, 25, 67–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perz, S.G. Household demographic factors as life cycle determinants of land use in the Amazon. Popul. Res. Policy Rev. 2001, 20, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boserup, E. Population and Technological Change: A Study of Long-Term Trends; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Brush, S.B.; Turner, B., II. The Nature of Farming Systems and Views of Their Change. Comparative Farming Systems; Turner, B., II, Brush, S.B., Eds.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Fearnside, P. Deforestation in Brazilian Amzonia: The Effect of Population and Land Tenure. Ambio 1993, 22, 537–545. [Google Scholar]
- Kaimowitz, D. Land Tenure, Land Markets, and Natural Resource Management by Large Landowners in the Petén and the Northern Transversal of Guatemala. In Proceedings of the Latin American Studies Association (LASA) Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, September 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Armenteras, D.; Rudas, G.; Rodriguez, N.; Sua, S.; Romero, M. Patterns and causes of deforestation in the Colombian Amazon. Ecol. Indic. 2006, 6, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, E.C.; Ramankutty, N. Putting people in the map: Anthropogenic biomes of the world. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nzunda, E.F.; Midtgaard, F. Spatial relationship between deforestation and protected areas, accessibility, population density, GDP and other factors in mainland Tanzania. For. Trees Livelihoods 2017, 26, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelsen, A.; Kaimowitz, D. Intoduction: The role of agricultural technologies in tropical deforestation. In Agricultural Technologies and Tropical Deforestation; Angelsen, A., Kaimowitz, D., Eds.; CABI/CIFOR: 1-18; CAB International: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hecht, S. Logics of Livestock and Deforestation: The Case of Amazonia; Routledge: London, UK, 2019; pp. 7–25. [Google Scholar]
- Perz, S.G. Social Determinants and Land Use Correlates of Agricultural Technology Adoption in a Forest Frontier: A Case Study in the Brazilian Amazon. Hum. Ecol. 2003, 31, 133–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosti, S.; Carpentier, C.; Witcover, J.; Valentim, J. Intensified small-scale livestock systems in the western Brazilian Amazon. In Agricultural Technologies and Tropical Deforestation; Angelsen, A., Kaimowitz, D., Eds.; CABI/CIFOR: 113-134; CAB International: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Abizaid, C.; Coomes, O.T. Land use and forest fallowing dynamics in seasonally dry tropical forests of the southern Yucatán Peninsula, Mexico. Land Use Policy 2004, 21, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.R. Household Land Management and Biodiversity: Secondary Succession in a Forest-Agriculture Mosaic in Southern Mexico. Ecol. Soc. 2007, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, J.C. Responding to deforestation: Productive conservation, the World Bank, and beekeeping in Rondonia, Brazil. Prof. Geogr. 2001, 53, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, D.L. The Role of Population Change in Land Use and Land Cover Change in Rural Latin America: Uncovering Local Processes Concealed by Macro-level Data. In Land Use Changes in Comparative Perspective; Himiyama, M.H.Y., Ichinose, T., Eds.; Science Publishers: Enfield, UK; Plymouth, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, D.L.; Suter, L.; Barbieri, A. Population Dynamics and Tropical Deforestation: State of the Debate and Conceptual Challenges. Popul. Environ. 2005, 27, 89–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jolly, C.L. Four theories of population change and the environment. Popul. Environ. 1994, 16, 61–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christman, Z.; Pearsall, H.; Schmook, B.; Mardero, S. Diversification and adaptive capacity across scales in an emerging post-frontier landscape of the Usumacinta Valley, Chiapas, Mexico. Int. For. Rev. 2015, 17, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J. What are the Real Population and Resource Problems? In The Ultimate Resource; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Grainger, A.; Francisco, H.A.; Tiraswat, P. The impact of changes in agricultural technology on long-term trends in deforestation. Land Use Policy 2003, 20, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nietschmann, B. Ecological Change, Inflation, and Migration in the Far Western Caribbean. Geogr. Rev. 1979, 69, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.A.; Sherman, P.B. Economics of Protected Areas. Ambio 1991, 20, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Rozon, C.; Lucotte, M.; Davidson, R.; Paquet, S.; Oestreicher, J.S.; Mertens, F.; Passos, C.J.S.; Romana, C. Spatial and temporal evolution of family-farming land use in the Tapajós region of the Brazilian Amazon. Acta Amaz. 2015, 45, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbier, E.B.; Burgess, J.C. Economic analysis of deforestation in Mexico. Environ. Dev. Econ. 1996, 1, 203–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dyer, G.A.; Taylor, J.E. The Corn Price Surge: Impacts on Rural Mexico. World Dev. 2011, 39, 1878–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudel, T.; Horowitz, B. Tropical Deforestation: Small Farmers and Land Clearing in Ecuadorian Amazon; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Meyfroidt, P. Trade-offs between environment and livelihoods: Bridging the global land use and food security discussions. Glob. Food Secur. 2018, 16, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, J.R.; McDonald, J.A. Third-world debt and tropical deforestation. Ecol. Econ. 1995, 12, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shandra, J.M.; Shircliff, E.; London, B. World Bank lending and deforestation: A cross-national analysis. Int. Sociol. 2011, 26, 292–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, D.H.; Byron, R.N. Deforestation mechanisms: A survey. Int. J. Soc. Econ. 1999, 26, 455–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moran, E. Private and Public Colonisation Schemes in Amazonia. In The Future of Amazônia: Destruction or Sustainable Development; Goodman, D., Hall, A., Eds.; St. Martin’s Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 70–89. [Google Scholar]
- St-Laurent, G.P.; Gélinas, N.; Potvin, C. REDD+ and the agriculture frontier: Understanding colonists’ utilization of the land. Land Use Policy 2013, 31, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, D. After the Trees: Living on the Transamazonian Highway; University of Texas Press: Austin, TX, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Angelsen, A.; Culas, R. Debt and Deforestation: A Tenuous Link; Working Paper No. 10; Christian Michelsen Institute: Bergen, Norway, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Shafik, N. (Ed.) Macroeconomic Causes of Deforestation Barking up the Wrong Tree? The Causes of Tropical Deforestation the Economic and Statistical Analysis of Factors Giving Rise to the Loss of the Tropical Forests; University College London Press Ltd.: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Assa, B.S.K. The deforestation-income relationship: Evidence of deforestation convergence across developing countries. Environ. Dev. Econ. 2021, 26, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, D.B. Forest Cover Dynamics and Forest Transitions in Mexico and Central America: Towards a “Great Restoration”? In Reforesting Landscapes; Landscape Series; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 10, pp. 85–120. [Google Scholar]
- Mather, A.S.; Needle, C.L. The relationships of population and forest trends. Geogr. J. 2000, 166, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, A.; Walker, R. Regional interdependence and forest “transitions”: Substitute deforestation limits the relevance of local reversals. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koop, G.; Tole, L. Measuring differential forest outcomes: A tale of two countries. World Dev. 1997, 25, 2043–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commoner, B. Making Peace with the Planet; Pantheon Books: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, E.A.; de Araújo, A.C.; Artaxo, P.; Balch, J.K.; Brown, I.F.; Bustamante, M.M.; Coe, M.T.; DeFries, R.S.; Keller, M.; Longo, M.; et al. The Amazon Basin in Transition. Nature 2012, 481, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudel, T.K. Shrinking Tropical Forests, Human Agents of Change, and Conservation Policy. Conserv. Biol. 2006, 20, 1604–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, D.S. Space-time dynamics of deforestation in Brazilian Amazônia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 2903–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, E.F.; Brondizio, E.; Mausel, P.; Wu, Y. Integrating Amazonian Vegetation, Land-Use, and Satellite Data. Biosci. 1994, 44, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, A.S. What Drives Deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon?: Evidence from Satellite and Socioeconomic Data. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 1999, 37, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudorff, B.F.T.; Adami, M.; Aguiar, D.A.; Moreira, M.A.; Mello, M.P.; Fabiani, L.; Amaral, D.F.; Pires, B.M. The Soy Moratorium in the Amazon Biome Monitored by Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skole, D.; Tucker, C. Tropical Deforestation and Habitat Fragmentation in the Amazon: Satellite Data from 1978 to 1988. Sci. 1993, 260, 1905–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sader, S.A.; Joyce, A.T. Deforestation Rates and Trends in Costa Rica, 1940 to 1983. Biotropica 1988, 20, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, R. Dynamics and patterns of deforestation in the western Amazon: The Napo deforestation front, 1986–1996. Appl. Geogr. 2000, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, G.C.; Hellerstein, D. Do roads cause deforestation? Using satellite images in econometric analyses of land use. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 1997, 79, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaimowitz, D. Factors determining low deforestation: The Bolivian Amazon. Ambio 1997, 26, 537–540. [Google Scholar]
- Steininger, M.K.; Tucker, C.J.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Killeen, T.J.; Desch, A.; Bell, V.; Ersts, P. Tropical deforestation in the Bolivian Amazon. Environ. Conserv. 2001, 28, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marsik, M.; Stevens, F.; Southworth, J. Amazon deforestation: Rates and patterns of land cover change and fragmentation in Pando, northern Bolivia, 1986 to 2005. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2011, 35, 353–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, P.F.P.R.; Ruivo, M.D.L.P.; Júnior, O.M.D.S.; Maciel, M.D.N.M.; Braga, T.; De Andrade, M.M.N.; Junior, P.C.D.S.; Da Rocha, E.S.; De Freitas, T.P.M.; Leite, T.V.D.S.; et al. Deforestation in protect areas in the Amazon: A threat to biodiversity. Biodivers. Conserv. 2019, 29, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milien, E.J.; Rocha, K.D.S.; Brown, I.F.; Perz, S.G. Roads, deforestation and the mitigating effect of the Chico Mendes extractive reserve in the southwestern Amazon. Trees For. People 2021, 3, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deininger, K.W.; Minten, B. Poverty, Policies, and Deforestation: The Case of Mexico. Econ. Dev. Cult. Chang. 1999, 47, 313–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, D.J. Government Policies and Deforestation in Brazil’s Amazon Region; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, E.F. Deforestation and land use in the Brazilian Amazon. Hum. Ecol. 1993, 21, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunker, S.G. Underdeveloping the Amazon: Extraction, Unequal Exchange, and the Failure of the Modern State; University of Illinois Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Southgate, D.; Whitaker, M. Promoting Resource Degradation in Latin America: Tropical Deforestation, Soil Erosion, and Coastal Ecosystem Disturbance in Ecuador. Econ. Dev. Cult. Chang. 1992, 40, 787–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichón, F.J. Agricultural Settlement and Ecological Crisis in the Ecuadorian Amazon Frontier. A Discussion of the Policy Environment. Policy Stud. J. 1992, 20, 662–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.R. Colonization and Environment: Land Settlement Projects in Central America; United Nations University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Angelsen, A. Policies for reduced deforestation and their impact on agricultural production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19639–19644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bray, D.B.; Ellis, E.A.; Armijo-Canto, N.; Beck, C.T. The institutional drivers of sustainable landscapes: A case study of the ‘Mayan Zone’ in Quintana Roo, Mexico. Land Use Policy 2004, 21, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipscomb, M.; Prabakaran, N. Property rights and deforestation: Evidence from the Terra Legal land reform in the Brazilian Amazon. World Dev. 2020, 129, 104854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reydon, B.P.; Fernandes, V.B.; Telles, T.S. Land governance as a precondition for decreasing deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon. Land Use Policy 2020, 94, 104313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roebeling, P.C.; Hendrix, E.M. Land speculation and interest rate subsidies as a cause of deforestation: The role of cattle ranching in Costa Rica. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, B.E.; Holland, M.B.; Naughton-Treves, L. Does Secure Land Tenure Save Forests? A Review of the Relationship between Land Tenure and Tropical Deforestation; CCAFS Working Paper; 2011; Volume 7, Available online: https://cgspace.cgiar.org/bitstream/handle/10568/10720/ccafs-wp-07-does-secure-land-tenure-save-forests.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Wannasai, N.; Shrestha, R.P. Role of land tenure security and farm household characteristics on land use change in the Prasae Watershed, Thailand. Land Use Policy 2008, 25, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frischmann, B.M.; Marciano, A.; Ramello, G.B. Retrospectives: Tragedy of the Commons after 50 Years. J. Econ. Perspect. 2019, 33, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hardin, G. The tragedy of the commons. Science 1968, 162, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostrom, E. Governing the Commons: The Evolution of Institutions for Collective Action; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, M. Security, the Environment and Emancipation: Contestation over Environmental Change; Routledge: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mahar, D.; Schneider, R. Incentives for tropical deforestation: Some examples from Latin America. In The Causes of Tropical Deforestation; Brown, K., Pearce, D.W., Eds.; University College London Press: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Barbier, E.B. The economic determinants of land degradation in developing countries. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 1997, 352, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Southgate, D.; Sanders, J.; Ehui, S. Resource Degradation in Africa and Latin America: Population Pressure, Policies, and Property Arrangements. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 1990, 72, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stonich, M. The dynamics of social processes and environmental destruction: A Central American case study. Popul. Dev. Rev. 1989, 15, 269–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southgate, D. The Causes of Land Degradation along “Spontaneously” Expanding Agricultural Frontiers in the Third World. Land Econ. 1990, 66, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmink, M. The Socioeconomic Matrix of Deforestation. In Population and the Environment: Rethinking the Debate; Arizpe, L., Ed.; Westview: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 253–271. [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn, R.; Balick, M. Private property and rainforest conservation. Conserv. Biol. 1995, 9, 1322–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, C. Seeking Legitimacy: The Story of Land Tenure in the Petén, Guatemala; Fulbright Foundation: Flores, Petén, Guatemala, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Deacon, R.T. Deforestation and Ownership: Evidence from Historical Accounts and Contemporary Data. Land Econ. 1999, 75, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, C.; Bonjean, C.A.; Combes, J.-L.; Motel, P.C.; Reis, E.J. Property rights and deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 2461–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pohle, P.; Gerique, A.; Park, M.; Sandoval, M.F.L. Human ecological dimensions in sustainable utilization and conservation of tropical mountain rain forests under global change in southern Ecuador. In Environmental Science and Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2010; pp. 477–509. [Google Scholar]
- Humphries, S. Milk Cows, Migrants, and Land Markets: Unraveling the Complexities of Forest-to-Pasture Conversion in Northern Honduras. Econ. Dev. Cult. Chang. 1998, 47, 95–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, K.A. Land regularization on agricultural frontiers: The case of Northwestern Petén, Guatemala. Land Use Policy 2006, 23, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, D.L. A comparison of Ladino and Q’eqchi Maya land use and land clearing in the Sierra de Lacandón National Park, Petén, Guatemala. Agric. Hum. Values 2004, 21, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A. The Colonization of the Amazon; University of Texas Press: Austin, TX, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri, A.F.; Pan, W. People, Land, and Context: Multilevel Determinants of Off-farm Employment in the Ecuadorian Amazon. Popul. Space Place 2013, 19, 558–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P. Delivering food security without increasing pressure on land. Glob. Food Secur. 2013, 2, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Azofeifa, A.; Busch, C.; Daily, G.C.; Pfaff, A.S.P. Integrity and isolation of Costa Rica’s national parks and biological reserves: Examining the dynamics of land-cover change. Biol. Conserv. 2003, 109, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuenca, P.; Robalino, J.; Arriagada, R.; Echeverría, C. Are government incentives effective for avoided deforestation in the tropical Andean forest? PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanner, A.M.; Johnston, A.L. The Impact of Rural Electric Access on Deforestation Rates. World Dev. 2017, 94, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.; van Kooten, G.C.; Wang, S. Institutional, social and economic roots of deforestation: A cross-country comparison. Int. For. Rev. 2003, 5, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, B.; Cummins, I.; Ashton, M.S. Large and Intact Forests: Drivers and Inhibitors of Deforestation and Forest Degradation. In Managing Forest Carbon in a Changing Climate; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 285–304. [Google Scholar]
- Schielein, J.; Börner, J. Recent transformations of land-use and land-cover dynamics across different deforestation frontiers in the Brazilian Amazon. Land Use Policy 2018, 76, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.M.; da Silva, C.F.A.; de Almeida Junior, P.M.; Rudke, A.P.; de Melo, S.N. Deforestation drivers in the Brazilian Amazon: Assessing new spatial predictors. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 113020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, C.H.L.S.; Pessôa, A.C.M.; Carvalho, N.S.; Reis, J.B.C.; Anderson, L.O.; Aragão, L.E.O.C. The Brazilian Amazon deforestation rate in 2020 is the greatest of the decade. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pailler, S. Re-election incentives and deforestation cycles in the Brazilian Amazon. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2018, 88, 345–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, L.; Herbohn, J.; Gregorio, N.; Harrison, S. Reforestation and smallholder livelihoods in the humid tropics. Land Use Policy 2020, 92, 104455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, M. The Theory of the Optimizing Peasant. J. Dev. Stud. 1968, 4, 327–351. [Google Scholar]
- Roumasset, J. Rice and Risk; North Holland Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz, S. Uncertainties in Peasant Farming; Atholone Press: London, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, D.P. Crop diversity and fallow management in a tropical decidous forest shifting cultivation system. Hum. Ecol. 1996, 24, 427–455. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg, M.K. Political Ecology and Cultural Change: Impacts on Swidden-fallow Agroforestry Practices among the Mopan Maya in Southern Belize. Prof. Geogr. 1998, 50, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R. Farming Systems and Economic Performance in the Brazilian Amazon. In Congresso Brasileiro Sobre Sistemas Agroforestais, Porto Velho, Anais. Colombo: EMBRAPA-CNPF; (EMBRAPA.CNPF Documentos, 27); 1994; Available online: https://www.alice.cnptia.embrapa.br/handle/doc/394898 (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Chakravarty, S.; Ghosh, S.K.; Suresh, C.P.; Dey, A.N.; Shukla, G. Deforestation: Causes, Effects and Control Strategies; 2012; Available online: https://www.academia.edu/download/47962277/Deforestation_Causes_Effects_and_Control20160810-4916-1ytgyis.pdf#page=17 (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Merry, F.; Hildebrand, P.; Pattie, P.; Carter, D. An analysis of land conversion from sustainable forestry to pasture: A case study in the Bolivian Lowlands. Land Use Policy 2002, 19, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.; Müller, D.; Schierhorn, F.; Gerold, G.; Pacheco, P. Proximate causes of deforestation in the Bolivian lowlands: An analysis of spatial dynamics. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2012, 12, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Thünen, J.H. Isolated State; An English Edition of Der Isolierte Staat; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Peet, R.J. The Spatial Expansion of Commercial Agriculture in the 19th Century: A von Thunen Interpretation. Econ. Geogr. 1969, 45, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, M.M.; Sanderson, M.R.; Mather, M.; Daniels, M.D.; Bergtold, J.S.; Aistrup, J.; Stamm, J.L.H.; Haukos, D.; Douglas-Mankin, K.; Sheshukov, A.Y.; et al. Opinion: Endogenizing culture in sustainability science research and policy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8157–8159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waroux, Y.L.P.D.; Garrett, R.D.; Chapman, M.; Friis, C.; Hoelle, J.; Hodel, L.; Hopping, K.; Zaehringer, J.G. The role of culture in land system science. J. Land Use Sci. 2021, 1–17. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/1747423X.2021.1950229 (accessed on 15 October 2021). [CrossRef]
- Twongyirwe, R.; Bithell, M.; Richards, K.S. Revisiting the drivers of deforestation in the tropics: Insights from local and key informant perceptions in western Uganda. J. Rural. Stud. 2018, 63, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durand, L.; Lazos, E. The Local Perception of Tropical Deforestation and its Relation to Conservation Policies in Los Tuxtlas Biosphere Reserve, Mexico. Hum. Ecol. 2008, 36, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelle, J. Quantifying cultural values associated with deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon. J. Land Use Sci. 2018, 13, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepstad, D.; Schwartzman, S.; Bamberger, B.; Santilli, M.; Ray, D.; Schlesinger, P.; Lefebvre, P.; Alencar, A.; Prinz, E.; Fiske, G.; et al. Inhibition of Amazon Deforestation and Fire by Parks and Indigenous Lands. Conserv. Biol. 2006, 20, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, N.M.; Coolsaet, B.; Sterling, E.J.; Loveridge, R.; Nicole, D.; Wongbusarakum, S.; Sangha, K.K.; Scherl, L.M.; Phan, H.P.; Zafra-Calvo, N.; et al. The role of Indigenous peoples and local communities in effective and equitable conservation. Ecol. Soc. 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, E. Colonization in Transamazonia and Rondonia. In Frontier Expansion in Amazonia; Schmink, M., Woods, C.H., Eds.; University of Florida Press: Gainesville, FL, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Godoy, R.; Groff, S.; O’Neill, K. The Role of Education in Neotropical Deforestation: Household Evidence from Amerindians in Honduras. Hum. Ecol. 1998, 26, 649–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vliet, N.; Mertz, O.; Heinimann, A.; Langanke, T.; Pascual, U.; Schmook, B.; Adams, C.; Schmidt-Vogt, D.; Messerli, P.; Leisz, S.; et al. Trends, drivers and impacts of changes in swidden cultivation in tropical forest-agriculture frontiers: A global assessment. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2012, 22, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, L.; Bilsborrow, R.; Pichón, F. Poverty and prosperity among migrant settlers in the Amazon rainforest frontier of Ecuador. J. Dev. Stud. 1997, 34, 35–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sain, G.E.; Barreto, H.J. The adoption of soil conservation technology in El Salvador: Linking productivity and conservation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 313–321. [Google Scholar]
- Garzón, N.V.; León, C.H.R.; Ceccon, E.; Pérez, D.R. Ecological restoration-based education in the Colombian Amazon: Toward a new society–nature relationship. Restor. Ecol. 2020, 28, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimah, B.G.; Bodo, T. Creation of awareness through environmental adult education as a solution to the problem of habitat loss in Ogoni, Rivers State, Nigeria. Int. J. Adv. Res. Publ. 2019, 3, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lambin, E.F.; Meyfroidt, P. Global land use change, economic globalization, and the looming land scarcity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3465–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Posey, D.A. A Preliminary report on diversified management of tropical forest by the Kayapó Indians of the Brazilian Amazon. In Ethnobotany in the Neotropics; Prance, G.T., Kallunki, J.A., Eds.; New York Botanical Garden: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 112–126. [Google Scholar]
- Works, M.A.; Denevan, W.M.; Padoch, C. Swidden-Fallow Agroforestry in the Peruvian Amazon. Geogr. Rev. 1989, 79, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, E. Government-Directed Settlement in the 1970s: An Assessment of Transamazon Highway Colonization. In The Dilemma of Amazonian Development; Moran, E., Ed.; Westview Press: Boulder, CO, USA, 1983; pp. 297–317. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, T. Indigenous responses to an expanding frontier: Jungle Quichua economic conversion to cattle ranching. In Cultural Transformations and Ethnicity in Modern Ecuador; Whitten, N., Ed.; University of Illinois Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Atran, S.; Medin, D.; Ross, N.; Lynch, E.; Coley, J.; Ek’, E.U.; Vapnarsky, V. Folkecology and commons management in the Maya Lowlands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7598–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abman, R.; Carney, C. Agricultural productivity and deforestation: Evidence from input subsidies and ethnic favoritism in Malawi. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2020, 103, 102342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertazzi, S.; Bini, V.; Lindon, A.; Trivellini, G. Relations of power driving tropical deforestation: A case study from the Mau Forest (Kenya). Belgeo. Rev. Belg. De Géographie 2018, 2. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/64d8/4f9b7db1780612eb1f906b4ae92eeb28bd2c.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2021). [CrossRef]
- Turner, B., II; Hanham, R.; Portoraro, A. Population Pressure and Agricultural Intensity. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 1977, 37, 384–396. [Google Scholar]
- Blaikie, P.; Brookfield, H. Land Degradation and Society; Methuen: London, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Denevan, W.M.; Fearnside, P.M. Human Carrying Capacity of the Brazilian Rainforest. Geogr. Rev. 1987, 77, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, A.J.; Mordecai, E.A. Amazon deforestation drives malaria transmission, and malaria burden reduces forest clearing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22212–22218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, S. Deforestation in the Amazon Basin: Magnitude, Dynamics, and Soil Resource Effects. Stud. Third World Soc. 1985, 13, 61–100. [Google Scholar]
- Cerri, C.E.P.; Maia, S.M.F.; Cherubin, M.R.; Feigl, B.J.; Lal, R. Reducing Amazon Deforestation through Agricultural Intensification in the Cerrado for Advancing Food Security and Mitigating Climate Change. Sustainability 2018, 10, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spera, S. Agricultural Intensification Can Preserve the Brazilian Cerrado: Applying Lessons from Mato Grosso and Goiás to Brazil’s Last Agricultural Frontier. Trop. Conserv. Sci. 2017, 10, 1940082917720662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrero, G.C.; Fearnside, P.M.; Valle, D.R.D.; Alves, C.D.S. Deforestation Trajectories on a Development Frontier in the Brazilian Amazon: 35 Years of Settlement Colonization, Policy and Economic Shifts, and Land Accumulation. Environ. Manag. 2020, 66, 966–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, R. Deforestation and Economic Development. Can. J. Reg. Sci./Rev. Can. Des Sci. Reg. 1993, 16, 481–497. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.; Lombardi, I.; Sabogal, C.; Diaz, A.; van de Kop, P.; Reategui, K. Dynamics of secondary forests in slash-and-burn farming: Interactions among land use types in the Peruvian Amazon. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1999, 76, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, S. Cattle Ranching in the Eastern Amazon: Environmental and Social Implications. In The Dilemma of Amazonian Development; Moran, E.F., Ed.; Westview Press: Boulder, CO, USA, 1983; pp. 155–188. [Google Scholar]
- Fearnside, P.M. Are climate change impacts already affecting tropical forest biomass? Glob. Environ. Chang. 2004, 14, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armengot, L.; Ferrari, L.; Milz, J.; Velásquez, F.; Hohmann, P.; Schneider, M. Cacao agroforestry systems do not increase pest and disease incidence compared with monocultures under good cultural management practices. Crop. Prot. 2020, 130, 105047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, S.P.; Gunaratne, L.H.P.; Sivanathewer, T.; Ginigaddara, G.A.S. Comparative Analysis of Sustainability in Paddy Monoculture and Paddy-Maize Rotation Farming Systems in Sri Lanka. Trop. Agric. Res. 2021, 32, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, M. The Colonization Experience in Brazil. Land Settlement Policies and Population Redistribution in Developing Countries: Achievements, Problems, and Prospects; Oberai, A., Ed.; Praeger: New York, NY, USA; Westport, CT, USA; London, UK, 1988; pp. 317–354. [Google Scholar]
- Loker, W.M. The Human Ecology of Cattle Raising in the Peruvian Amazon: The View from the Farm. Hum. Organ. 1993, 52, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindfuss, R.R.; Entwisle, B.; Walsh, S.J.; Mena, C.F.; Erlien, C.M.; Gray, C.L. Frontier Land Use Change: Synthesis, Challenges, and Next Steps. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2007, 97, 739–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.R.; Turner, B.L. Reconciling Agency and Structure in Empirical Analysis: Smallholder Land Use in the Southern Yucatán, Mexico. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2006, 96, 302–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, C.; Iovanna, R. Analyzing spatial hierarchies in remotely sensed data: Insights from a multilevel model of tropical deforestation. Land Use Policy 2006, 23, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, O.R.; Lambin, E.F.; Alcock, F.; Haberl, H.; I Karlsson-Vinkhuyzen, S.; McConnell, W.J.; Myint, T.; Pahl-Wostl, C.; Polsky, C.; Ramakrishnan, P.S.; et al. A Portfolio Approach to Analyzing Complex Human-Environment Interactions: Institutions and Land Change. Ecol. Soc. 2006, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheong, S.-M.; Brown, D.G.; Kok, K.; Lopez-Carr, D. Mixed methods in land change research: Towards integration. Trans. Inst. Br. Geogr. 2012, 37, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ness, B.; Anderberg, S.; Olsson, L. Structuring problems in sustainability science: The multi-level DPSIR framework. Geoforum 2010, 41, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L.; Lambin, E.F.; Verburg, P.H. From land-use/land-cover to land system science. Ambio 2021, 50, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-Carr, D. A Review of Small Farmer Land Use and Deforestation in Tropical Forest Frontiers: Implications for Conservation and Sustainable Livelihoods. Land 2021, 10, 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10111113
López-Carr D. A Review of Small Farmer Land Use and Deforestation in Tropical Forest Frontiers: Implications for Conservation and Sustainable Livelihoods. Land. 2021; 10(11):1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10111113
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-Carr, David. 2021. "A Review of Small Farmer Land Use and Deforestation in Tropical Forest Frontiers: Implications for Conservation and Sustainable Livelihoods" Land 10, no. 11: 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10111113
APA StyleLópez-Carr, D. (2021). A Review of Small Farmer Land Use and Deforestation in Tropical Forest Frontiers: Implications for Conservation and Sustainable Livelihoods. Land, 10(11), 1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10111113




