Morphodynamics of Gully Development on the Platform–Slope System of Spoil Dumps under Platform Concentrated Flow
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
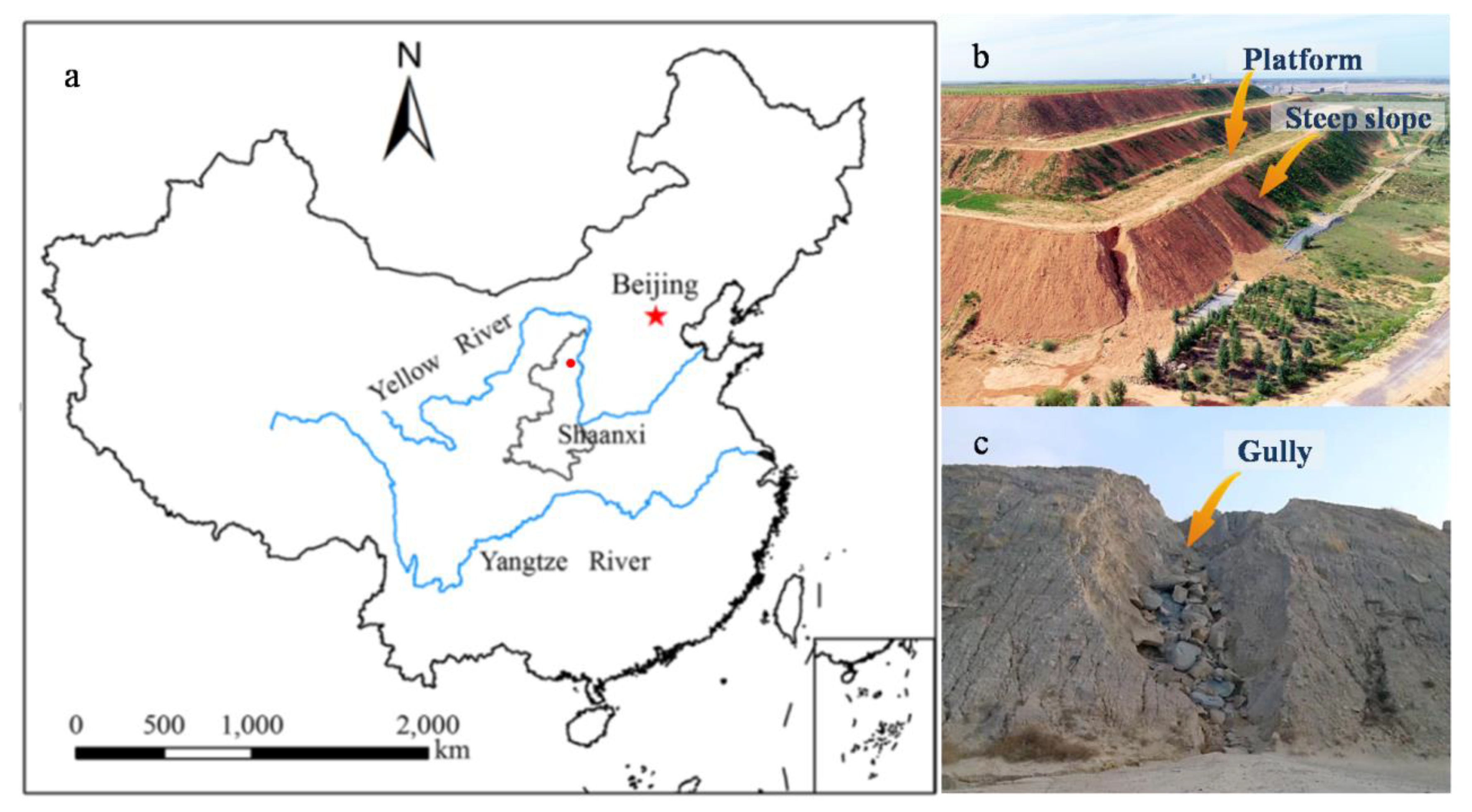
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design and Procedures
2.2.1. Inflow Discharge
2.2.2. Plot Set-Up
2.2.3. Experimental Devices
2.2.4. Experimental Procedure
2.3. Data Calculation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Gully Morphological Development
3.1.1. Gully Dimension
3.1.2. Gully Development
3.2. Flow Hydraulics
3.2.1. Variations in Flow Velocity
3.2.2. Hydraulic Regime
3.2.3. Hydraulic Friction
3.2.4. Interrelation of Hydraulic Parameters
3.3. Hydrodynamic Processes of Gully Development
4. Discussion
4.1. Gully Morphological Development on Spoil Dump
4.2. Morphodynamics of Gully Development on Spoil Dump
4.3. Gully Control on Spoil Dump
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Rimmer, D.L. Soil physical conditions on reclaimed colliery spoil heaps. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 33, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristina, M.M.; José, F.M.D.; José, M.N.I.; Néstor, H.R.; Sanz Santos, M.Á.; Lázaro, S.C. Effects of Topography and Surface Soil Cover on Erosion for Mining Reclamation: The Experimental Spoil Heap at El Machorro Mine (Central Spain). Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, M.M.; Wang, W.L.; Li, J.M.; Bai, Y.; Kang, H.L.; Yang, B. Runoff characteristics and soil erosion dynamic processes on four typical engineered landforms of coalfields: An in-situ simulated rainfall experimental study. Geomorphology 2020, 349, 106896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Wang, W.L.; Kang, H.L.; Bai, Y.; Guo, M.M.; Chen, Z.X. Erosion morphology and runoff and sediment yielding characteristics of platform-slope system in opencast coal mine. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 3194–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilley, J. Water Erosion; Academic Press: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sidorchuk, A. Dynamic and static models of gully erosion. Catena 1999, 37, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zheng, F.; Wilson, G.V.; Zhang, X.J.; He, X. Quantification of upslope and lateral inflow impacts on runoff discharge and soil loss in ephemeral gully systems under laboratory conditions. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingner, R.L.; Wells, R.R.; Momm, H.G.; Rigby, J.R.; Theurer, F.D. Ephemeral gully channel width and erosion simulation technology. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 1949–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.M.; Zheng, F.L.; Wilson, G.V.; Wu, M. Upslope inflow, hillslope gradient and rainfall intensity impacts on ephemeral gully erosion. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 2623–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Pan, C.; Li, C.; Luo, M.; Wang, X. A field investigation on ephemeral gully erosion processes under different upslope inflow and sediment conditions. J. Hydrol. 2019, 572, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.M.; Zheng, F.L.; Wilson, G.V. Flow hydraulics in an ephemeral gully system under different slope gradients, rainfall intensities and inflow conditions. Catena 2021, 203, 105359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zheng, F.; Wilson, G.V.; Xu, X.; Liu, C. Three decades of ephemeral gully erosion studies. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 212, 105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, W.; Guo, M.; Chen, Z.; Feng, L.; Zhao, M.; Xiao, H. The impact of flow discharge on the hydraulic characteristics of headcut erosion processes in the gully region of the Loess Plateau. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.G.; Jia, Y.W.; Zhou, Z.H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.L.; Peng, H. An experimental study on dynamic processes of ephemeral gully erosion in loess landscapes. Geomorphology 2011, 125, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionita, I. Gully development in the Moldavian Plateau of Romania. Catena 2006, 68, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani, A.N.; Ahmadi, H.; Mohammadi, A.; Ghoddousi, J.; Salajegheh, A.; Boggs, G.; Pishyar, R. Factors Controlling Gully Advancement and Models Evaluation (Hableh Rood Basin, Iran). Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 1531–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtergaele, J.; Poesen, J.; Wijdenes, D.O.; Vandekerckhove, L. Medium-term evolution of a gully developed in a loess-derived soil. Geomorphology 2002, 46, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.L.; Guo, M.M.; Wang, W.L. Ephemeral gully erosion in concentrated flow channels induced by rainfall and upslope inflow on steep loessial slopes. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 5037–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capra, A.; Mazzara, L.M.; Scicolone, B. Application of the EGEM model to predict ephemeral gully erosion in Sicily, Italy. Catena 2005, 59, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, M.T.; Yang, M.; Deng, J.Y. Estimation of initiation thresholds and soil loss from gully erosion on unpaved roads on China’s Loess Plateau. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2021, 46, 1713–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garosi, Y.; Sheklabadi, M.; Conoscenti, C.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Van, O.K. Assessing the performance of GIS- based machine learning models with different accuracy measures for determining susceptibility to gully erosion. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 1117–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkimäki, M.; González-Olabarria, J.R. Assessing Gully Erosion Occurrence in Forest Lands in Catalonia (Spain). Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, R.R.; Bennett, S.J.; Alonso, C.V. Effect of soil texture, tailwater height, and pore-water pressure on the morphodynamics of migrating headcuts in upland concentrated flows. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 34, 1867–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.H. Advances and prospects for gully erosion researches. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 34, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.M.; Bai, Z.K.; Lv, C.J. Effects of vegetation on runoff and soil erosion on reclaimed land in an opencast coal-mine dump in a loess area. Catena 2015, 128, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.G.; Lei, S.G.; Bian, Z.F.; Liu, Y.R.S. Analysis of the Development of an Erosion Gully in an Open-Pit Coal Mine Dump During a Winter Freeze-Thaw Cycle by Using Low-Cost UAVs. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowry, B.C.J.; Narayan, M.; Hancock, G.R.; Evans, K.G. Understanding post-mining landforms: Utilising pre-mine geomorphology to improve rehabilitation outcomes. Geomorphology 2019, 328, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, G.; Li, Y.X.; Ning, B.K.; Wei, Z.P.; Wang, D.H. Soil erosion process of platform-slope system of dump under heavy rain. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 1463–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, G.R.; Crawter, D.S.; Fityus, S.G.; Chandler, J.A.; Wells, T. The measurement and modelling of rill erosion at angle of repose slopes in mine spoil. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2010, 33, 1006–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.B.; Gao, Z.L.; Li, Y.H.; Lou, Y.C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.T.; Du, J.; Zhang, X.; Luo, K. Characteristics of rill erosion in spoil heaps under simulated inflow: A field runoff plot experiment. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 202, 104655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyssen, J.; Vermeersch, D. Slope aspect affects geomorphic dynamics of coal mining spoil heaps in Belgium. Geomorphology 2010, 123, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ran, H.; Deng, Q.C.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Luo, M.L.; Qin, F.C. Morphology and influencing factors of rills in the steep slope in Yuanmou Dry-Hot Valley (SW China). Catena 2018, 165, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Wang, Z.L. The influence of Shenfu-Dongsheng coal mining on river bed siltation and sediment load of Wulanmulun river. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 1994, 1, 60–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.X. The characteristics of hard rain and its distribution over the Loess Plateau. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1983, 38, 416–425. [Google Scholar]
- Luk, S.H.; Merz, W. Use of the salt tracing technique to determine the velocity of overland flow. Soil Technol. 1992, 5, 289–301. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, M.D.; Watson, C.C.; Schumm, S.A. GullyErosion; USDI Bureauof Reclamation: FortCollins, CO, USA, 1985; p. 181.
- Stefanovic, J.R.; Bryan, R.B. Experimental study of rill bank collapse. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2007, 32, 180–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, R.S.; Kavvas, M.L. Characterization of the rill geometry over straight hillslopes through spatial scales. J. Hydrol 1992, 130, 339–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brayan, R.B.; Poesen, J. Laboratory experiments on the influence of slope length on runoff, percolation and rill development. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1989, 14, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, M.C.; Bryan, R.B. Hydraulic conditions for rill incision under simulated rainfall: A laboratory experiment. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1992, 17, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xiong, D.; Su, Z.; Yang, D.; Dong, Y.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, S.; Shi, L. Effects of initial step height on the headcut erosion of bank gullies: A case study using a 3D photo-reconstruction method in the dry-hot valley region of southwest China. Phys. Geogr. 2016, 37, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, O.R.; Julien, P.Y.; Alonso, C.V. Mechanics of jet scour downstream of a headcut. J. Hydraul. Res. 1993, 31, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.M.; Feng, S.Y.; Wang, J.G.; Cai, C.F. Relationship between rill erosion morphology and hydraulic characteristics and sediment yield on artificial soils slope with different textures. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.M.; Wang, W.L.; Shi, Q.H.; Chen, T.D.; Li, J.M. An experimental study on the effects of grass root density on gully headcut erosion in the gully region of China’s Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 2107–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larionov, G.A.; Bushueva, O.G.; Dobrovol’Skaya, N.G.; Kiryukhina, Z.P.; Krasnov, S.F.; Litvin, L.F. Effect of gravity on the erosion of model samples. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2015, 48, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, M.; Mengoni, B.; Luppi, L.; Darby, S.E.; Mosselman, E. Numerical simulation of hydrodynamics and bank erosion in a river bend. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robert, R.W.; Henrique, G.M.; James, R.R.; Sean, J.B.; Ronald, L.B.; Seth, M.D. An empirical investigation of gully widening rates in upland concentrated flows. Catena 2013, 101, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.R.; Meyer, L.D. Transport of soil particles by shallow flow. ASAE 1972, 15, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, L.; Bennett, S.; Bingner, R.; Theurer, F.; Alonso, C. REGEM: The revised ephemeral gully erosion model. In Proceedings of the 8th Federal Interagency Sedimentation Conf (FISC), Reno, NV, USA, 2–6 April 2006; pp. 313–319. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, Z.L.; Niu, Y.B.; Li, Y.H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Z.; Su, Y. A comparative study on relationship between rill morphology and sediment yield on slopes of two types of engineering mounds. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2020, 58, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Soil Type | Soil Particle Composition (%) | Soil Bulk Density (g cm−3) | Antecedent Soil Moisture (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand (0.02–2 mm) | Silt (0.002–0.02) | Clay (<0.002) | Platform | Steep Slope | Platform | Steep Slope | |
| Sandy Loess | 67.815 | 17.545 | 14.640 | 1.42 ± 0.02 | 1.23 ± 0.02 | 13.75 ± 3.02 | 11.63 ± 2.63 |
| Clay loam | 42.721 | 33.089 | 24.190 | 1.55 ± 0.03 | 1.43 ± 0.02 | 18.57 ± 2.02 | 17.95 ± 2.34 |
| Parameters | Fitted Equation of Platform | Fitted Equation of Steep Slope |
|---|---|---|
| Fr with ƒ | Fr = 0.492 ƒ−0.510, R2 = 0.996 ** | Fr = 2.195 ƒ−0.530, R2 = 0.900 ** |
| Fr with τ | Fr = 3.601 e−0.240τ, R2 = 0.549 ** | Fr = 36.59 τ−0.720, R2 = 0.500 ** |
| ƒ with τ | ƒ = 0.022 e0.453τ, R2 = 0.493 ** | ƒ = 0.006 τ1.293, R2 = 0.491 ** |
| Re with ω | Re = 3325 ω − 31.29, R2 = 0.998 ** | Re = 308.9 ω0.835, R2 = 0.826 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, Y.; Guo, M.; Kang, H.; Wang, W.; Su, H.; Guo, W.; Ma, C. Morphodynamics of Gully Development on the Platform–Slope System of Spoil Dumps under Platform Concentrated Flow. Land 2021, 10, 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10111270
Bai Y, Guo M, Kang H, Wang W, Su H, Guo W, Ma C. Morphodynamics of Gully Development on the Platform–Slope System of Spoil Dumps under Platform Concentrated Flow. Land. 2021; 10(11):1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10111270
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Yun, Mingming Guo, Hongliang Kang, Wenlong Wang, Huan Su, Wenzhao Guo, and Chunyan Ma. 2021. "Morphodynamics of Gully Development on the Platform–Slope System of Spoil Dumps under Platform Concentrated Flow" Land 10, no. 11: 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10111270
APA StyleBai, Y., Guo, M., Kang, H., Wang, W., Su, H., Guo, W., & Ma, C. (2021). Morphodynamics of Gully Development on the Platform–Slope System of Spoil Dumps under Platform Concentrated Flow. Land, 10(11), 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10111270







